User login
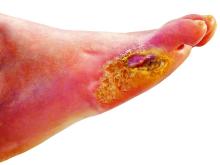
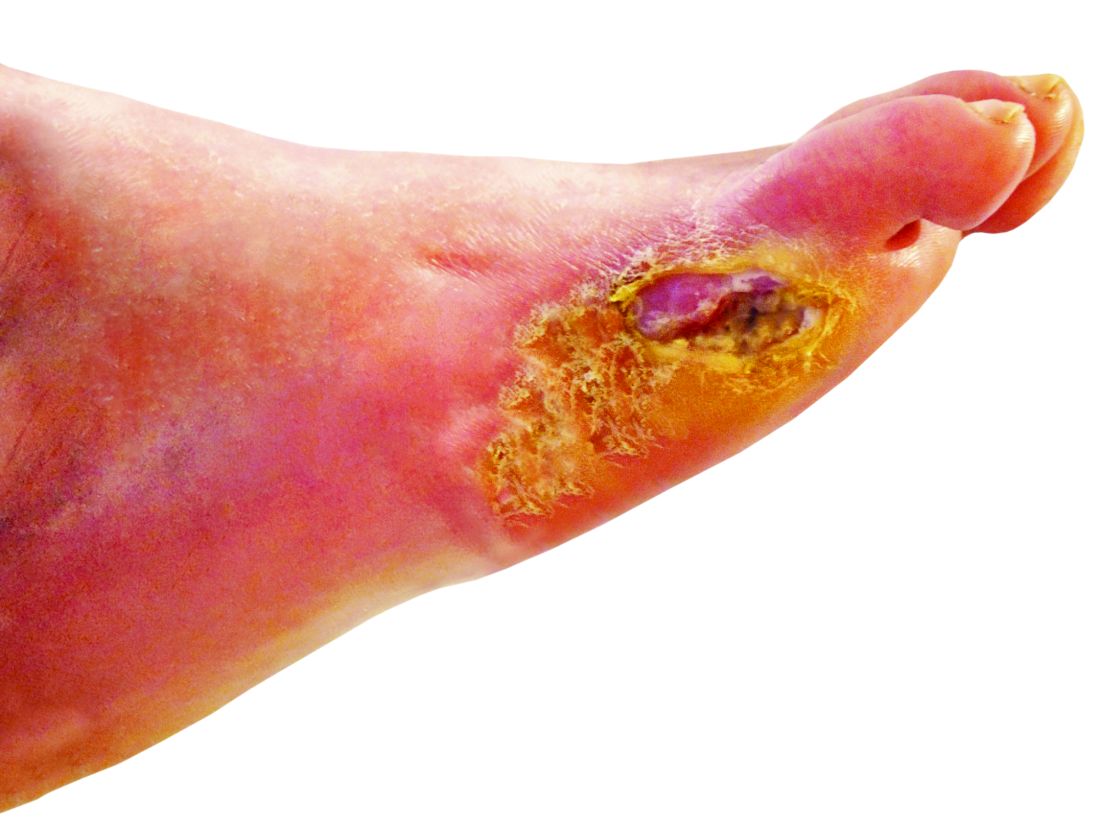
STOCKHOLM – Esmolol hydrochloride gel (Galnobax, NovoLead) appears to be a safe and effective novel topical treatment option for diabetic foot ulcers, according to results from a new trial of the drug, which is widely available as a generic and is inexpensive.
Of note, the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure at 12 weeks with esmolol (plus standard of care) was around 60% compared with just over 40% in patients who received standard of care alone.
Presenting the findings at this year’s annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes was Ashu Rastogi, MD, a professor of endocrinology at the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research in Chandigarh, India.
“Esmolol can be given topically as a 14% gel and is a novel treatment option in diabetic foot ulcer,” said Dr. Rastogi.
Esmolol, a short-acting beta-adrenergic blocker, is currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for cardiac indications only, such as short-term use for controlling supraventricular tachycardia. Beta-blockers are also used to treat hypertension.
However, esmolol has also been repurposed and formulated as a topical gel for the treatment of hard-to-heal diabetic foot ulcers (mainly neuropathic grade 1).
Audience member Ketan Dhatariya, MBBS, MD, PhD, a National Health Service consultant in diabetes, endocrinology, and general medicine and honorary senior lecturer at Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals, England, enthused about the findings.
“This is an amazing study. I’m part of a working group looking at the updating of a guideline for the International Working Group of the Diabetic Foot, reviewing all the studies on wound healing, specifically pharmacological interventions. This is way beyond anything shown to date in terms of medical intervention. [The authors] should be congratulated; this is really astounding,” he told this news organization.
“Right now, there is very little out there in terms of pharmacological interventions that have shown benefit,” he added. “Once this study has been peer-reviewed and is published properly, it is potentially game-changing because it is a generic, worldwide, cheap, and freely available medication.”
Study across 27 sites in India
Prior phase 1/2 data have shown that 60% of ulcers completely closed with esmolol (14% gel) compared with 39% with standard of care. Encouraged by these findings, a phase 3 randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study was conducted across 27 sites in India.
Patients were a mean age of 56 years, and had a body mass index (BMI) of 25-26 kg/m2 and mean hemoglobin A1c of 8.4%-8.7%. Around 70% of participants were men. Mean ulcer area was approximately 460-500 mm2, two-thirds of the ulcers were plantar, and mean ulcer duration was 40-50 weeks.
After screening and discontinuations (39 participants), a 12-week treatment phase began with patients randomized to one of three groups: esmolol (14% gel) along with standard of care administered twice daily (57 completers); standard of care only (63 completers); or vehicle gel (placebo) along with standard of care administered twice daily (17 completers).
Standard of care comprised wound cleaning, debridement, maintenance of moist wound environment, twice-daily fresh bandages, and off-loading footwear as needed, and was provided to all participants irrespective of study group.
The 12-week treatment period was followed by an observation period of 12 weeks up to the 24-week study endpoint.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure (100% re-epithelialization without drainage or dressing requirement) within the 12-week treatment phase.
Secondary endpoints included time to target ulcer closure during the 12-week treatment phase and proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure by 24 weeks (end of study). Investigators were blinded throughout.
Subanalyses were conducted based on ulcer location, size, and age, as well as estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 90 mL/min and ankle-brachial index under 0.9 but greater than 0.7.
50% more patients on esmolol had complete ulcer closure
The proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure at 12 weeks was 60.3% in the esmolol plus standard of care group, compared with 41.7% with standard of care only, a difference of 18.6% (odds ratio, 2.13; P = .0276).
“The 24-week end-of-study data show what happened in the 12 weeks following end of treatment,” said Dr. Rastogi, turning to results showing that by 24 weeks the proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure was 77.2% versus 55.6%, respectively, with a difference of 21.6% (OR, 2.71; P = .013).
Time to ulcer closure (a secondary endpoint) was similar between the esmolol plus standard of care vs. standard of care groups (74.3 vs. 72.5 days).
The impact of ulcer location on complete ulcer closure, a subanalysis, showed a higher proportion of patients experienced complete ulcer closure with esmolol plus standard of care versus standard of care. For example, in plantar-based ulcers, esmolol led to complete closure in 58.7% vs. 43.1%, while for nonplantar ulcers, complete closure was found in 63.6% vs. 38.1%.
In wounds less than 5 cm2, the proportion of complete closures was 66.0% vs. 50.0% for esmolol compared with standard of care alone, while in wounds over 5 cm2, these proportions were 47.6% vs. 26.9%.
Subanalyses also showed that esmolol was substantially better in patients with BMI greater than 25, ulcer duration over 12 weeks, and A1c above 8%.
Also, a subanalysis stratified by “real-life” situations favored esmolol, showing a 50.9% difference in the proportion of patients with diabetic foot ulcer healing in those with a history of hypertension and a 31.8% difference favoring esmolol in those with an abnormal electrocardiogram.
Overall, the proportions of patients who had an adverse event were 13.2%, 18.4%, and 37.5% in the esmolol plus standard of care, standard of care alone, and vehicle plus standard of care groups, respectively, and the vast majority were unrelated to study drug. There were no serious adverse events in the esmolol plus standard of care group.
A class effect of beta blockers?
The proposed mechanism of action of esmolol relates to a sequence of reducing inflammation (via vasodilation, fibroblast migration, and cytokine reduction); proliferation by beta-blockade (improves keratinocyte migration and epithelialization); and remodeling (increases collagen turnover).
Asked by an audience member if the observations were a class effect and systemic effect of beta-blockers, Dr. Rastogi said he could not say for sure that it was a class effect, but they deliberately used a beta-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist.
“It may not be a systemic effect because we have some patients who use beta-blockers systemically and they still have diabetic foot ulcers,” he said.
Dr. Rastogi and Dr. Dhatariya have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – Esmolol hydrochloride gel (Galnobax, NovoLead) appears to be a safe and effective novel topical treatment option for diabetic foot ulcers, according to results from a new trial of the drug, which is widely available as a generic and is inexpensive.
Of note, the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure at 12 weeks with esmolol (plus standard of care) was around 60% compared with just over 40% in patients who received standard of care alone.
Presenting the findings at this year’s annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes was Ashu Rastogi, MD, a professor of endocrinology at the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research in Chandigarh, India.
“Esmolol can be given topically as a 14% gel and is a novel treatment option in diabetic foot ulcer,” said Dr. Rastogi.
Esmolol, a short-acting beta-adrenergic blocker, is currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for cardiac indications only, such as short-term use for controlling supraventricular tachycardia. Beta-blockers are also used to treat hypertension.
However, esmolol has also been repurposed and formulated as a topical gel for the treatment of hard-to-heal diabetic foot ulcers (mainly neuropathic grade 1).
Audience member Ketan Dhatariya, MBBS, MD, PhD, a National Health Service consultant in diabetes, endocrinology, and general medicine and honorary senior lecturer at Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals, England, enthused about the findings.
“This is an amazing study. I’m part of a working group looking at the updating of a guideline for the International Working Group of the Diabetic Foot, reviewing all the studies on wound healing, specifically pharmacological interventions. This is way beyond anything shown to date in terms of medical intervention. [The authors] should be congratulated; this is really astounding,” he told this news organization.
“Right now, there is very little out there in terms of pharmacological interventions that have shown benefit,” he added. “Once this study has been peer-reviewed and is published properly, it is potentially game-changing because it is a generic, worldwide, cheap, and freely available medication.”
Study across 27 sites in India
Prior phase 1/2 data have shown that 60% of ulcers completely closed with esmolol (14% gel) compared with 39% with standard of care. Encouraged by these findings, a phase 3 randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study was conducted across 27 sites in India.
Patients were a mean age of 56 years, and had a body mass index (BMI) of 25-26 kg/m2 and mean hemoglobin A1c of 8.4%-8.7%. Around 70% of participants were men. Mean ulcer area was approximately 460-500 mm2, two-thirds of the ulcers were plantar, and mean ulcer duration was 40-50 weeks.
After screening and discontinuations (39 participants), a 12-week treatment phase began with patients randomized to one of three groups: esmolol (14% gel) along with standard of care administered twice daily (57 completers); standard of care only (63 completers); or vehicle gel (placebo) along with standard of care administered twice daily (17 completers).
Standard of care comprised wound cleaning, debridement, maintenance of moist wound environment, twice-daily fresh bandages, and off-loading footwear as needed, and was provided to all participants irrespective of study group.
The 12-week treatment period was followed by an observation period of 12 weeks up to the 24-week study endpoint.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure (100% re-epithelialization without drainage or dressing requirement) within the 12-week treatment phase.
Secondary endpoints included time to target ulcer closure during the 12-week treatment phase and proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure by 24 weeks (end of study). Investigators were blinded throughout.
Subanalyses were conducted based on ulcer location, size, and age, as well as estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 90 mL/min and ankle-brachial index under 0.9 but greater than 0.7.
50% more patients on esmolol had complete ulcer closure
The proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure at 12 weeks was 60.3% in the esmolol plus standard of care group, compared with 41.7% with standard of care only, a difference of 18.6% (odds ratio, 2.13; P = .0276).
“The 24-week end-of-study data show what happened in the 12 weeks following end of treatment,” said Dr. Rastogi, turning to results showing that by 24 weeks the proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure was 77.2% versus 55.6%, respectively, with a difference of 21.6% (OR, 2.71; P = .013).
Time to ulcer closure (a secondary endpoint) was similar between the esmolol plus standard of care vs. standard of care groups (74.3 vs. 72.5 days).
The impact of ulcer location on complete ulcer closure, a subanalysis, showed a higher proportion of patients experienced complete ulcer closure with esmolol plus standard of care versus standard of care. For example, in plantar-based ulcers, esmolol led to complete closure in 58.7% vs. 43.1%, while for nonplantar ulcers, complete closure was found in 63.6% vs. 38.1%.
In wounds less than 5 cm2, the proportion of complete closures was 66.0% vs. 50.0% for esmolol compared with standard of care alone, while in wounds over 5 cm2, these proportions were 47.6% vs. 26.9%.
Subanalyses also showed that esmolol was substantially better in patients with BMI greater than 25, ulcer duration over 12 weeks, and A1c above 8%.
Also, a subanalysis stratified by “real-life” situations favored esmolol, showing a 50.9% difference in the proportion of patients with diabetic foot ulcer healing in those with a history of hypertension and a 31.8% difference favoring esmolol in those with an abnormal electrocardiogram.
Overall, the proportions of patients who had an adverse event were 13.2%, 18.4%, and 37.5% in the esmolol plus standard of care, standard of care alone, and vehicle plus standard of care groups, respectively, and the vast majority were unrelated to study drug. There were no serious adverse events in the esmolol plus standard of care group.
A class effect of beta blockers?
The proposed mechanism of action of esmolol relates to a sequence of reducing inflammation (via vasodilation, fibroblast migration, and cytokine reduction); proliferation by beta-blockade (improves keratinocyte migration and epithelialization); and remodeling (increases collagen turnover).
Asked by an audience member if the observations were a class effect and systemic effect of beta-blockers, Dr. Rastogi said he could not say for sure that it was a class effect, but they deliberately used a beta-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist.
“It may not be a systemic effect because we have some patients who use beta-blockers systemically and they still have diabetic foot ulcers,” he said.
Dr. Rastogi and Dr. Dhatariya have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – Esmolol hydrochloride gel (Galnobax, NovoLead) appears to be a safe and effective novel topical treatment option for diabetic foot ulcers, according to results from a new trial of the drug, which is widely available as a generic and is inexpensive.
Of note, the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure at 12 weeks with esmolol (plus standard of care) was around 60% compared with just over 40% in patients who received standard of care alone.
Presenting the findings at this year’s annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes was Ashu Rastogi, MD, a professor of endocrinology at the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research in Chandigarh, India.
“Esmolol can be given topically as a 14% gel and is a novel treatment option in diabetic foot ulcer,” said Dr. Rastogi.
Esmolol, a short-acting beta-adrenergic blocker, is currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for cardiac indications only, such as short-term use for controlling supraventricular tachycardia. Beta-blockers are also used to treat hypertension.
However, esmolol has also been repurposed and formulated as a topical gel for the treatment of hard-to-heal diabetic foot ulcers (mainly neuropathic grade 1).
Audience member Ketan Dhatariya, MBBS, MD, PhD, a National Health Service consultant in diabetes, endocrinology, and general medicine and honorary senior lecturer at Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals, England, enthused about the findings.
“This is an amazing study. I’m part of a working group looking at the updating of a guideline for the International Working Group of the Diabetic Foot, reviewing all the studies on wound healing, specifically pharmacological interventions. This is way beyond anything shown to date in terms of medical intervention. [The authors] should be congratulated; this is really astounding,” he told this news organization.
“Right now, there is very little out there in terms of pharmacological interventions that have shown benefit,” he added. “Once this study has been peer-reviewed and is published properly, it is potentially game-changing because it is a generic, worldwide, cheap, and freely available medication.”
Study across 27 sites in India
Prior phase 1/2 data have shown that 60% of ulcers completely closed with esmolol (14% gel) compared with 39% with standard of care. Encouraged by these findings, a phase 3 randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study was conducted across 27 sites in India.
Patients were a mean age of 56 years, and had a body mass index (BMI) of 25-26 kg/m2 and mean hemoglobin A1c of 8.4%-8.7%. Around 70% of participants were men. Mean ulcer area was approximately 460-500 mm2, two-thirds of the ulcers were plantar, and mean ulcer duration was 40-50 weeks.
After screening and discontinuations (39 participants), a 12-week treatment phase began with patients randomized to one of three groups: esmolol (14% gel) along with standard of care administered twice daily (57 completers); standard of care only (63 completers); or vehicle gel (placebo) along with standard of care administered twice daily (17 completers).
Standard of care comprised wound cleaning, debridement, maintenance of moist wound environment, twice-daily fresh bandages, and off-loading footwear as needed, and was provided to all participants irrespective of study group.
The 12-week treatment period was followed by an observation period of 12 weeks up to the 24-week study endpoint.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure (100% re-epithelialization without drainage or dressing requirement) within the 12-week treatment phase.
Secondary endpoints included time to target ulcer closure during the 12-week treatment phase and proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure by 24 weeks (end of study). Investigators were blinded throughout.
Subanalyses were conducted based on ulcer location, size, and age, as well as estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 90 mL/min and ankle-brachial index under 0.9 but greater than 0.7.
50% more patients on esmolol had complete ulcer closure
The proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure at 12 weeks was 60.3% in the esmolol plus standard of care group, compared with 41.7% with standard of care only, a difference of 18.6% (odds ratio, 2.13; P = .0276).
“The 24-week end-of-study data show what happened in the 12 weeks following end of treatment,” said Dr. Rastogi, turning to results showing that by 24 weeks the proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure was 77.2% versus 55.6%, respectively, with a difference of 21.6% (OR, 2.71; P = .013).
Time to ulcer closure (a secondary endpoint) was similar between the esmolol plus standard of care vs. standard of care groups (74.3 vs. 72.5 days).
The impact of ulcer location on complete ulcer closure, a subanalysis, showed a higher proportion of patients experienced complete ulcer closure with esmolol plus standard of care versus standard of care. For example, in plantar-based ulcers, esmolol led to complete closure in 58.7% vs. 43.1%, while for nonplantar ulcers, complete closure was found in 63.6% vs. 38.1%.
In wounds less than 5 cm2, the proportion of complete closures was 66.0% vs. 50.0% for esmolol compared with standard of care alone, while in wounds over 5 cm2, these proportions were 47.6% vs. 26.9%.
Subanalyses also showed that esmolol was substantially better in patients with BMI greater than 25, ulcer duration over 12 weeks, and A1c above 8%.
Also, a subanalysis stratified by “real-life” situations favored esmolol, showing a 50.9% difference in the proportion of patients with diabetic foot ulcer healing in those with a history of hypertension and a 31.8% difference favoring esmolol in those with an abnormal electrocardiogram.
Overall, the proportions of patients who had an adverse event were 13.2%, 18.4%, and 37.5% in the esmolol plus standard of care, standard of care alone, and vehicle plus standard of care groups, respectively, and the vast majority were unrelated to study drug. There were no serious adverse events in the esmolol plus standard of care group.
A class effect of beta blockers?
The proposed mechanism of action of esmolol relates to a sequence of reducing inflammation (via vasodilation, fibroblast migration, and cytokine reduction); proliferation by beta-blockade (improves keratinocyte migration and epithelialization); and remodeling (increases collagen turnover).
Asked by an audience member if the observations were a class effect and systemic effect of beta-blockers, Dr. Rastogi said he could not say for sure that it was a class effect, but they deliberately used a beta-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist.
“It may not be a systemic effect because we have some patients who use beta-blockers systemically and they still have diabetic foot ulcers,” he said.
Dr. Rastogi and Dr. Dhatariya have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EASD 2022