User login
However, at least one expert believes the study has “significant flaws.”
Investigators randomly assigned 20 individuals with sporadic ALS to receive either ropinirole or placebo for 24 weeks. During the double-blind period, there was no difference between the groups in terms of decline in functional status.
However, during a further open-label extension period, the ropinirole group showed significant suppression of functional decline and an average of an additional 7 months of progression-free survival.
The researchers were able to predict clinical responsiveness to ropinirole in vitro by analyzing motor neurons derived from participants’ stem cells.
“We found that ropinirole is safe and tolerable for ALS patients and shows therapeutic promise at helping them sustain daily activity and muscle strength,” first author Satoru Morimoto, MD, of the department of physiology, Keio University School of Medicine, Tokyo, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Cell Stem Cell.
Feasibility study
“ALS is totally incurable and it’s a very difficult disease to treat,” senior author Hideyuki Okano, MD, PhD, professor, department of physiology, Keio University, said in the news release.
Preclinical animal models have “limited translational potential” for identifying drug candidates, but induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)–derived motor neurons (MNs) from ALS patients can “overcome these limitations for drug screening,” the authors write.
“We previously identified ropinirole [a dopamine D2 receptor agonist] as a potential anti-ALS drug in vitro by iPSC drug discovery,” Dr. Okano said.
The current trial was a randomized, placebo-controlled phase 1/2a feasibility trial that evaluated the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of ropinirole in patients with ALS, using several parameters:
- The revised ALS functional rating scale (ALSFRS-R) score.
- Composite functional endpoints.
- Event-free survival.
- Time to ≤ 50% forced vital capacity (FVC).
The trial consisted of a 12-week run-in period, a 24-week double-blind period, an open-label extension period that lasted from 4 to 24 weeks, and a 4-week follow-up period after administration.
Thirteen patients were assigned to receive ropinirole (23.1% women; mean age, 65.2 ± 12.6 years; 7.7% with clinically definite and 76.9% with clinically probable ALS); seven were assigned to receive placebo (57.1% women; mean age, 66.3 ± 7.5 years; 14.3% with clinically definite and 85.7% with clinically probable ALS).
Of the treatment group, 30.8% had a bulbar onset lesion vs. 57.1% in the placebo group. At baseline, the mean FVC was 94.4% ± 14.9 and 81.5% ± 23.2 in the ropinirole and placebo groups, respectively. The mean body mass index (BMI) was 22.91 ± 3.82 and 19.69 ± 2.63, respectively.
Of the participants,12 in the ropinirole and six in the control group completed the full 24-week treatment protocol; 12 in the ropinirole and five in the placebo group completed the open-label extension (participants who had received placebo were switched to the active drug).
However only seven participants in the ropinirole group and one participant in the placebo group completed the full 1-year trial.
‘Striking correlation’
“During the double-blind period, muscle strength and daily activity were maintained, but a decline in the ALSFRS-R … was not different from that in the placebo group,” the researchers write.
In the open-label extension period, the ropinirole group showed “significant suppression of ALSFRS-R decline,” with an ALSFRS-R score change of only 7.75 (95% confidence interval, 10.66-4.63) for the treatment group vs. 17.51 (95% CI, 22.46-12.56) for the placebo group.
The researchers used the assessment of function and survival (CAFS) score, which adjusts the ALSFRS-R score against mortality, to see whether functional benefits translated into improved survival.
The score “favored ropinirole” in the open-extension period and the entire treatment period but not in the double-blind period.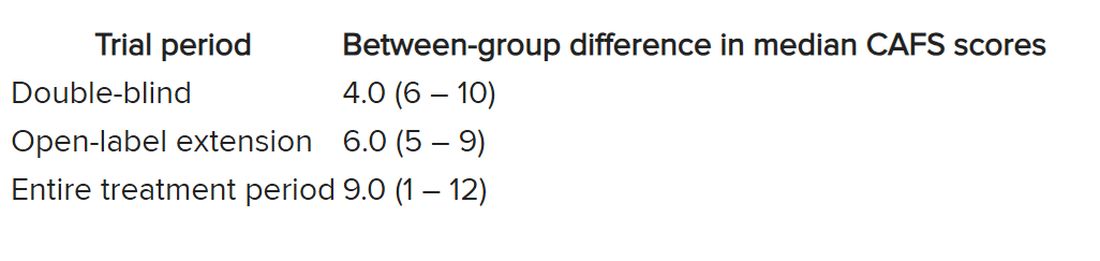
Disease progression events occurred in 7 of 7 (100%) participants in the placebo group and 7 of 13 (54%) in the ropinirole group, “suggesting a twofold decrease in disease progression” in the treatment group.
The ropinirole group experienced an additional 27.9 weeks of disease progression–free survival, compared with the placebo group.
“No participant discontinued treatment because of adverse experiences in either treatment group,” the authors report.
The analysis of iPSC-derived motor neurons from participants showed dopamine D2 receptor expression, as well as the potential involvement of the cholesterol pathway SREBP2 in the therapeutic effects of ropinirole. Lipid peroxide was also identified as a good “surrogate clinical marker to assess disease progression and drug efficacy.”
“We found a very striking correlation between a patient’s clinical response and the response of their motor neurons in vitro,” said Dr. Morimoto. “Patients whose motor neurons responded robustly to ropinirole in vitro had a much slower clinical disease progression with ropinirole treatment, while suboptimal responders showed much more rapid disease progression, despite taking ropinirole.”
Limitations include “small sample sizes and high attrition rates in the open-label extension period,” so “further validation” is required, the authors state.
Significant flaws
Commenting for this article, Carmel Armon, MD, MHS, professor of neurology, Loma Linda (Calif.) University, said the study “falls short of being a credible 1/2a clinical trial.”
Although the “intentions were good and the design not unusual,” the two groups were not “balanced on risk factors for faster progressing disease.” Rather, the placebo group was “tilted towards faster progressing disease” because there were more clinically definite and probable ALS patients in the placebo group than the treatment group, and there were more patients with bulbar onset.
Participants in the placebo group also had shorter median disease duration, lower BMI, and lower FVC, noted Dr. Armon, who was not involved with the study.
And only 1 in 7 control patients completed the open-label extension, compared with 7 of 13 patients in the intervention group.
“With these limitations, I would be disinclined to rely on the findings to justify a larger clinical trial,” Dr. Armon concluded.
The trial was sponsored by K Pharma. The study drug, active drugs, and placebo were supplied free of charge by GlaxoSmithKline K.K. Dr. Okano received grants from JSPS and AMED and grants and personal fees from K Pharma during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Sanbio, outside the submitted work. Dr. Okano has a patent on a therapeutic agent for ALS and composition for treatment licensed to K Pharma. The other authors’ disclosures and additional information are available in the original article. Dr. Armon reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
However, at least one expert believes the study has “significant flaws.”
Investigators randomly assigned 20 individuals with sporadic ALS to receive either ropinirole or placebo for 24 weeks. During the double-blind period, there was no difference between the groups in terms of decline in functional status.
However, during a further open-label extension period, the ropinirole group showed significant suppression of functional decline and an average of an additional 7 months of progression-free survival.
The researchers were able to predict clinical responsiveness to ropinirole in vitro by analyzing motor neurons derived from participants’ stem cells.
“We found that ropinirole is safe and tolerable for ALS patients and shows therapeutic promise at helping them sustain daily activity and muscle strength,” first author Satoru Morimoto, MD, of the department of physiology, Keio University School of Medicine, Tokyo, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Cell Stem Cell.
Feasibility study
“ALS is totally incurable and it’s a very difficult disease to treat,” senior author Hideyuki Okano, MD, PhD, professor, department of physiology, Keio University, said in the news release.
Preclinical animal models have “limited translational potential” for identifying drug candidates, but induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)–derived motor neurons (MNs) from ALS patients can “overcome these limitations for drug screening,” the authors write.
“We previously identified ropinirole [a dopamine D2 receptor agonist] as a potential anti-ALS drug in vitro by iPSC drug discovery,” Dr. Okano said.
The current trial was a randomized, placebo-controlled phase 1/2a feasibility trial that evaluated the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of ropinirole in patients with ALS, using several parameters:
- The revised ALS functional rating scale (ALSFRS-R) score.
- Composite functional endpoints.
- Event-free survival.
- Time to ≤ 50% forced vital capacity (FVC).
The trial consisted of a 12-week run-in period, a 24-week double-blind period, an open-label extension period that lasted from 4 to 24 weeks, and a 4-week follow-up period after administration.
Thirteen patients were assigned to receive ropinirole (23.1% women; mean age, 65.2 ± 12.6 years; 7.7% with clinically definite and 76.9% with clinically probable ALS); seven were assigned to receive placebo (57.1% women; mean age, 66.3 ± 7.5 years; 14.3% with clinically definite and 85.7% with clinically probable ALS).
Of the treatment group, 30.8% had a bulbar onset lesion vs. 57.1% in the placebo group. At baseline, the mean FVC was 94.4% ± 14.9 and 81.5% ± 23.2 in the ropinirole and placebo groups, respectively. The mean body mass index (BMI) was 22.91 ± 3.82 and 19.69 ± 2.63, respectively.
Of the participants,12 in the ropinirole and six in the control group completed the full 24-week treatment protocol; 12 in the ropinirole and five in the placebo group completed the open-label extension (participants who had received placebo were switched to the active drug).
However only seven participants in the ropinirole group and one participant in the placebo group completed the full 1-year trial.
‘Striking correlation’
“During the double-blind period, muscle strength and daily activity were maintained, but a decline in the ALSFRS-R … was not different from that in the placebo group,” the researchers write.
In the open-label extension period, the ropinirole group showed “significant suppression of ALSFRS-R decline,” with an ALSFRS-R score change of only 7.75 (95% confidence interval, 10.66-4.63) for the treatment group vs. 17.51 (95% CI, 22.46-12.56) for the placebo group.
The researchers used the assessment of function and survival (CAFS) score, which adjusts the ALSFRS-R score against mortality, to see whether functional benefits translated into improved survival.
The score “favored ropinirole” in the open-extension period and the entire treatment period but not in the double-blind period.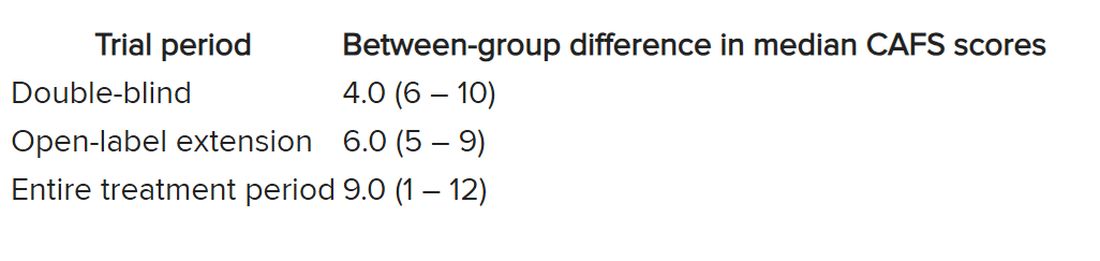
Disease progression events occurred in 7 of 7 (100%) participants in the placebo group and 7 of 13 (54%) in the ropinirole group, “suggesting a twofold decrease in disease progression” in the treatment group.
The ropinirole group experienced an additional 27.9 weeks of disease progression–free survival, compared with the placebo group.
“No participant discontinued treatment because of adverse experiences in either treatment group,” the authors report.
The analysis of iPSC-derived motor neurons from participants showed dopamine D2 receptor expression, as well as the potential involvement of the cholesterol pathway SREBP2 in the therapeutic effects of ropinirole. Lipid peroxide was also identified as a good “surrogate clinical marker to assess disease progression and drug efficacy.”
“We found a very striking correlation between a patient’s clinical response and the response of their motor neurons in vitro,” said Dr. Morimoto. “Patients whose motor neurons responded robustly to ropinirole in vitro had a much slower clinical disease progression with ropinirole treatment, while suboptimal responders showed much more rapid disease progression, despite taking ropinirole.”
Limitations include “small sample sizes and high attrition rates in the open-label extension period,” so “further validation” is required, the authors state.
Significant flaws
Commenting for this article, Carmel Armon, MD, MHS, professor of neurology, Loma Linda (Calif.) University, said the study “falls short of being a credible 1/2a clinical trial.”
Although the “intentions were good and the design not unusual,” the two groups were not “balanced on risk factors for faster progressing disease.” Rather, the placebo group was “tilted towards faster progressing disease” because there were more clinically definite and probable ALS patients in the placebo group than the treatment group, and there were more patients with bulbar onset.
Participants in the placebo group also had shorter median disease duration, lower BMI, and lower FVC, noted Dr. Armon, who was not involved with the study.
And only 1 in 7 control patients completed the open-label extension, compared with 7 of 13 patients in the intervention group.
“With these limitations, I would be disinclined to rely on the findings to justify a larger clinical trial,” Dr. Armon concluded.
The trial was sponsored by K Pharma. The study drug, active drugs, and placebo were supplied free of charge by GlaxoSmithKline K.K. Dr. Okano received grants from JSPS and AMED and grants and personal fees from K Pharma during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Sanbio, outside the submitted work. Dr. Okano has a patent on a therapeutic agent for ALS and composition for treatment licensed to K Pharma. The other authors’ disclosures and additional information are available in the original article. Dr. Armon reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
However, at least one expert believes the study has “significant flaws.”
Investigators randomly assigned 20 individuals with sporadic ALS to receive either ropinirole or placebo for 24 weeks. During the double-blind period, there was no difference between the groups in terms of decline in functional status.
However, during a further open-label extension period, the ropinirole group showed significant suppression of functional decline and an average of an additional 7 months of progression-free survival.
The researchers were able to predict clinical responsiveness to ropinirole in vitro by analyzing motor neurons derived from participants’ stem cells.
“We found that ropinirole is safe and tolerable for ALS patients and shows therapeutic promise at helping them sustain daily activity and muscle strength,” first author Satoru Morimoto, MD, of the department of physiology, Keio University School of Medicine, Tokyo, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Cell Stem Cell.
Feasibility study
“ALS is totally incurable and it’s a very difficult disease to treat,” senior author Hideyuki Okano, MD, PhD, professor, department of physiology, Keio University, said in the news release.
Preclinical animal models have “limited translational potential” for identifying drug candidates, but induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)–derived motor neurons (MNs) from ALS patients can “overcome these limitations for drug screening,” the authors write.
“We previously identified ropinirole [a dopamine D2 receptor agonist] as a potential anti-ALS drug in vitro by iPSC drug discovery,” Dr. Okano said.
The current trial was a randomized, placebo-controlled phase 1/2a feasibility trial that evaluated the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of ropinirole in patients with ALS, using several parameters:
- The revised ALS functional rating scale (ALSFRS-R) score.
- Composite functional endpoints.
- Event-free survival.
- Time to ≤ 50% forced vital capacity (FVC).
The trial consisted of a 12-week run-in period, a 24-week double-blind period, an open-label extension period that lasted from 4 to 24 weeks, and a 4-week follow-up period after administration.
Thirteen patients were assigned to receive ropinirole (23.1% women; mean age, 65.2 ± 12.6 years; 7.7% with clinically definite and 76.9% with clinically probable ALS); seven were assigned to receive placebo (57.1% women; mean age, 66.3 ± 7.5 years; 14.3% with clinically definite and 85.7% with clinically probable ALS).
Of the treatment group, 30.8% had a bulbar onset lesion vs. 57.1% in the placebo group. At baseline, the mean FVC was 94.4% ± 14.9 and 81.5% ± 23.2 in the ropinirole and placebo groups, respectively. The mean body mass index (BMI) was 22.91 ± 3.82 and 19.69 ± 2.63, respectively.
Of the participants,12 in the ropinirole and six in the control group completed the full 24-week treatment protocol; 12 in the ropinirole and five in the placebo group completed the open-label extension (participants who had received placebo were switched to the active drug).
However only seven participants in the ropinirole group and one participant in the placebo group completed the full 1-year trial.
‘Striking correlation’
“During the double-blind period, muscle strength and daily activity were maintained, but a decline in the ALSFRS-R … was not different from that in the placebo group,” the researchers write.
In the open-label extension period, the ropinirole group showed “significant suppression of ALSFRS-R decline,” with an ALSFRS-R score change of only 7.75 (95% confidence interval, 10.66-4.63) for the treatment group vs. 17.51 (95% CI, 22.46-12.56) for the placebo group.
The researchers used the assessment of function and survival (CAFS) score, which adjusts the ALSFRS-R score against mortality, to see whether functional benefits translated into improved survival.
The score “favored ropinirole” in the open-extension period and the entire treatment period but not in the double-blind period.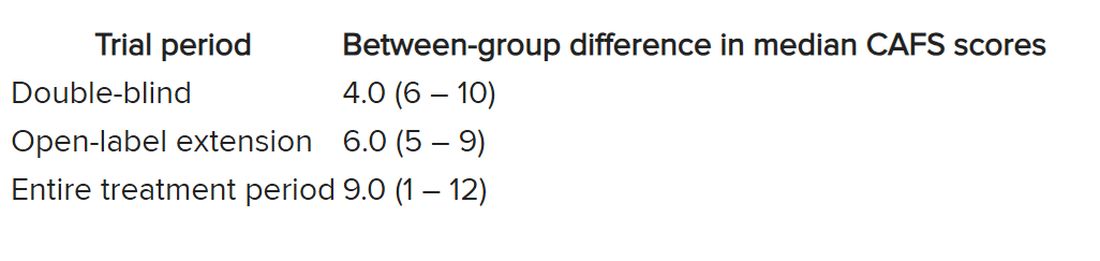
Disease progression events occurred in 7 of 7 (100%) participants in the placebo group and 7 of 13 (54%) in the ropinirole group, “suggesting a twofold decrease in disease progression” in the treatment group.
The ropinirole group experienced an additional 27.9 weeks of disease progression–free survival, compared with the placebo group.
“No participant discontinued treatment because of adverse experiences in either treatment group,” the authors report.
The analysis of iPSC-derived motor neurons from participants showed dopamine D2 receptor expression, as well as the potential involvement of the cholesterol pathway SREBP2 in the therapeutic effects of ropinirole. Lipid peroxide was also identified as a good “surrogate clinical marker to assess disease progression and drug efficacy.”
“We found a very striking correlation between a patient’s clinical response and the response of their motor neurons in vitro,” said Dr. Morimoto. “Patients whose motor neurons responded robustly to ropinirole in vitro had a much slower clinical disease progression with ropinirole treatment, while suboptimal responders showed much more rapid disease progression, despite taking ropinirole.”
Limitations include “small sample sizes and high attrition rates in the open-label extension period,” so “further validation” is required, the authors state.
Significant flaws
Commenting for this article, Carmel Armon, MD, MHS, professor of neurology, Loma Linda (Calif.) University, said the study “falls short of being a credible 1/2a clinical trial.”
Although the “intentions were good and the design not unusual,” the two groups were not “balanced on risk factors for faster progressing disease.” Rather, the placebo group was “tilted towards faster progressing disease” because there were more clinically definite and probable ALS patients in the placebo group than the treatment group, and there were more patients with bulbar onset.
Participants in the placebo group also had shorter median disease duration, lower BMI, and lower FVC, noted Dr. Armon, who was not involved with the study.
And only 1 in 7 control patients completed the open-label extension, compared with 7 of 13 patients in the intervention group.
“With these limitations, I would be disinclined to rely on the findings to justify a larger clinical trial,” Dr. Armon concluded.
The trial was sponsored by K Pharma. The study drug, active drugs, and placebo were supplied free of charge by GlaxoSmithKline K.K. Dr. Okano received grants from JSPS and AMED and grants and personal fees from K Pharma during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Sanbio, outside the submitted work. Dr. Okano has a patent on a therapeutic agent for ALS and composition for treatment licensed to K Pharma. The other authors’ disclosures and additional information are available in the original article. Dr. Armon reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CELL STEM CELL