User login
What is the most plausible diagnosis and what would be the next step?
The diagnosis
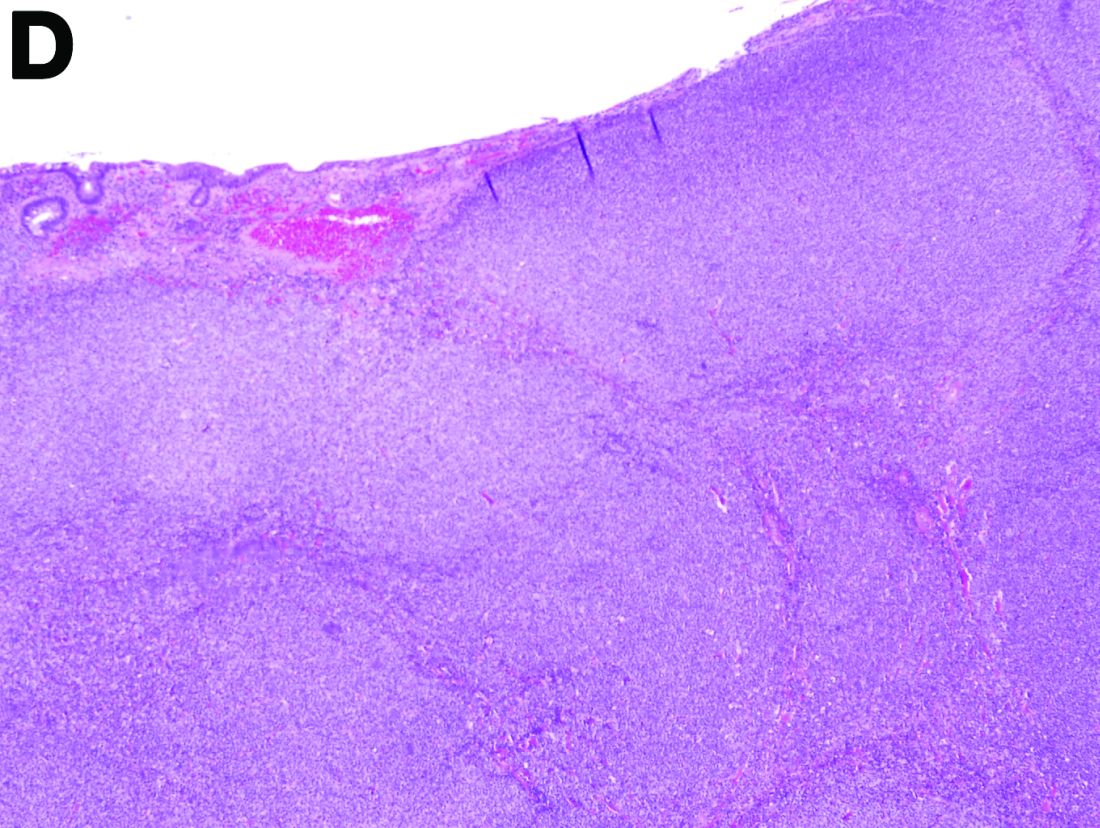
To clarify the diagnosis, endoscopic resection of the smaller lesion was performed and deeper biopsies of the other lesions were taken. Histology revealed lymphoid, centroblast, and centrocyte-like cell proliferation with follicular pattern (Figure D). Immunohistochemically, the follicles stained for bcl-6, CD20, and bcl-2 (Figure E), but not CD3, CD5, CD10, or cyclin D1.
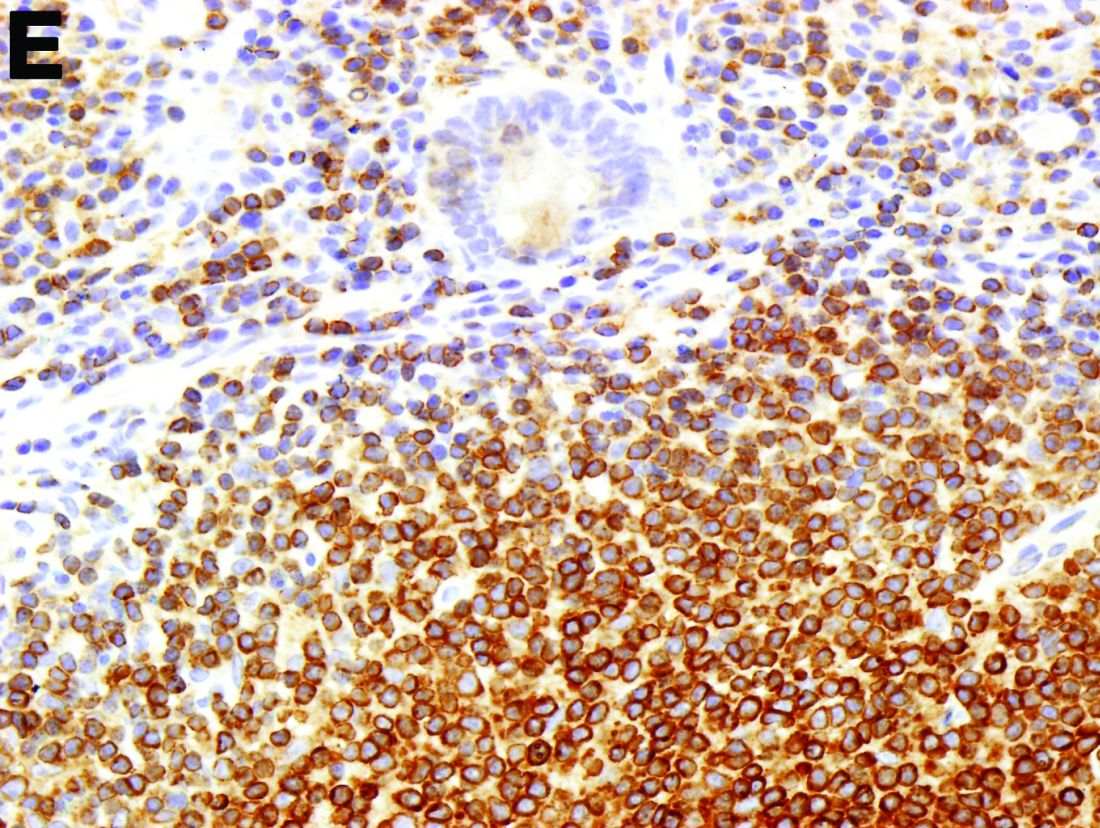
Malignant lymphomas of the colon represent about 0.2% of all colonic neoplasms and most frequently are diffuse large B-cell, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue, and mantle cell lymphomas.2 This phenotypic presentation, as multiple lymphomatous polyposis, has been reported in colon follicular lymphomas but is more typical of mantle cell lymphoma.3 Treatment usually consists of chemotherapy containing rituximab (anti-CD20) and should be decided on a case-by-case basis owing to possible relapse and the often indolent course.1
References
1. Damaj, G., Verkarre, V., Delmer, A. et al. Primary follicular lymphoma of the gastrointestinal tract: A study of 25 cases and a literature review. Ann Oncol. 2003;14:623-9.
2. Muller-Hermelink, H.K., Chott, A., Gascoyne, R.D. et al. B-cell lymphoma of the colon and rectum. In: S.R. Hamilton, L.A. Asltonen, eds. WHO Classification of Tumours. Lyon, France: IARC Press;2001:139-41.
3. Hiraide, T., Shoji, T., Higashi, Y. et al. Extranodal multiple polypoid follicular lymphoma of the sigmoid colon. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73(1):182-4.
The diagnosis
To clarify the diagnosis, endoscopic resection of the smaller lesion was performed and deeper biopsies of the other lesions were taken. Histology revealed lymphoid, centroblast, and centrocyte-like cell proliferation with follicular pattern (Figure D). Immunohistochemically, the follicles stained for bcl-6, CD20, and bcl-2 (Figure E), but not CD3, CD5, CD10, or cyclin D1.


Malignant lymphomas of the colon represent about 0.2% of all colonic neoplasms and most frequently are diffuse large B-cell, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue, and mantle cell lymphomas.2 This phenotypic presentation, as multiple lymphomatous polyposis, has been reported in colon follicular lymphomas but is more typical of mantle cell lymphoma.3 Treatment usually consists of chemotherapy containing rituximab (anti-CD20) and should be decided on a case-by-case basis owing to possible relapse and the often indolent course.1
References
1. Damaj, G., Verkarre, V., Delmer, A. et al. Primary follicular lymphoma of the gastrointestinal tract: A study of 25 cases and a literature review. Ann Oncol. 2003;14:623-9.
2. Muller-Hermelink, H.K., Chott, A., Gascoyne, R.D. et al. B-cell lymphoma of the colon and rectum. In: S.R. Hamilton, L.A. Asltonen, eds. WHO Classification of Tumours. Lyon, France: IARC Press;2001:139-41.
3. Hiraide, T., Shoji, T., Higashi, Y. et al. Extranodal multiple polypoid follicular lymphoma of the sigmoid colon. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73(1):182-4.
The diagnosis
To clarify the diagnosis, endoscopic resection of the smaller lesion was performed and deeper biopsies of the other lesions were taken. Histology revealed lymphoid, centroblast, and centrocyte-like cell proliferation with follicular pattern (Figure D). Immunohistochemically, the follicles stained for bcl-6, CD20, and bcl-2 (Figure E), but not CD3, CD5, CD10, or cyclin D1.


Malignant lymphomas of the colon represent about 0.2% of all colonic neoplasms and most frequently are diffuse large B-cell, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue, and mantle cell lymphomas.2 This phenotypic presentation, as multiple lymphomatous polyposis, has been reported in colon follicular lymphomas but is more typical of mantle cell lymphoma.3 Treatment usually consists of chemotherapy containing rituximab (anti-CD20) and should be decided on a case-by-case basis owing to possible relapse and the often indolent course.1
References
1. Damaj, G., Verkarre, V., Delmer, A. et al. Primary follicular lymphoma of the gastrointestinal tract: A study of 25 cases and a literature review. Ann Oncol. 2003;14:623-9.
2. Muller-Hermelink, H.K., Chott, A., Gascoyne, R.D. et al. B-cell lymphoma of the colon and rectum. In: S.R. Hamilton, L.A. Asltonen, eds. WHO Classification of Tumours. Lyon, France: IARC Press;2001:139-41.
3. Hiraide, T., Shoji, T., Higashi, Y. et al. Extranodal multiple polypoid follicular lymphoma of the sigmoid colon. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73(1):182-4.
What is the most plausible diagnosis and what would be the next step?
What is the most plausible diagnosis and what would be the next step?
What’s your diagnosis?
By Aníbal Ferreira, MD, PhD , Raquel Gonçalves, MD, and Carla Rolanda, MD. Published previously in Gastroenterology (2012 Dec;143[6]:1440, 1693-4).
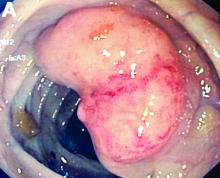
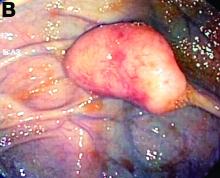
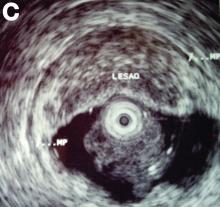
An asymptomatic, 74-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes was referred for endoscopic colorectal cancer screening. Colonoscopy revealed a 30-mm, polypoid, firm lesion in the transverse colon (Figure A), a 20-mm similar lesion in the cecum (Figure B),