User login
in a new randomized trial.
In the Bypass Versus Angioplasty in Severe Ischaemia of the Leg (BASIL-2) trial, patients who received vein bypass as the first approach were more likely to require a major amputation or to die during follow-up than patients who were randomly assigned to the endovascular approach as first strategy.
“Our findings suggest that a best endovascular treatment first revascularization strategy is associated with a better amputation-free survival. This is mainly because the best endovascular treatment first revascularization strategy resulted in fewer deaths. Limb-related outcomes were similar between groups,” the authors stated.
“The BASIL-2 trial has produced a statistically robust and clinically meaningful result that is likely to have an influence on the management of chronic limb-threatening ischemia worldwide,” added the study’s chief investigator, Andrew Bradbury, MD, professor of vascular surgery at the University of Birmingham (England).
However, the results of the BASIL-2 trial conflict with those from two previous studies – BASIL-1 and BEST-CLI, which both suggested that a surgical approach for chronic limb-threatening ischemia may be most appropriate.
The BASIL-2 study was published online in The Lancet.
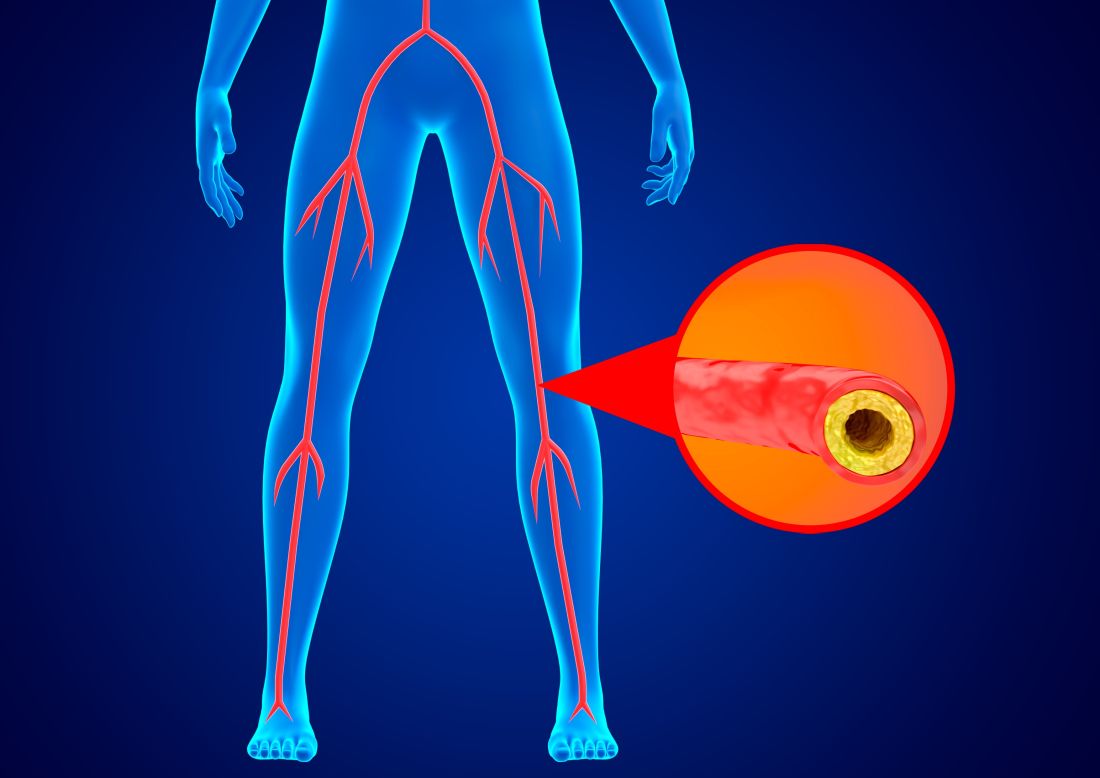
The authors explained that chronic limb-threatening ischemia, previously known as critical limb ischemia and severe ischemia of the leg, is the most severe form of peripheral arterial disease caused by atherosclerosis. Patients present with ischemic rest pain and tissue loss (ulceration, gangrene, or both) that usually affects the foot.
Mainly because of tobacco smoking and the growing prevalence of type 2 diabetes, chronic limb-threatening ischemia represents a growing burden on health care and social care services around the world.
Unless the blood supply to the affected limb is restored, patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia are at high risk for amputation or death. Although it is universally agreed that – in addition to best medical therapy – virtually all patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia should at least be considered for revascularization, there is continuing debate as to whether conducting vein bypass surgery, preferably using a vein taken from the patient’s own leg, or endovascular treatment (balloon angioplasty with or without stents) is preferable.
“BASIL-2 is the only randomized trial to specifically compare a vein bypass first with best endovascular treatment first revascularisation strategy in patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who required an infrapopliteal (with or without an additional more proximal infrainguinal) revascularization procedure to restore limb perfusion,” the authors noted.
For the trial, which was conducted at 41 vascular surgery units in the United Kingdom, Sweden, and Denmark, 345 patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who required an infrapopliteal revascularization procedure to restore limb perfusion were randomly assigned to receive either vein bypass or best endovascular treatment as their first revascularization procedure.
Most vein bypasses used the great saphenous vein and originated from the common or superficial femoral arteries. Most endovascular interventions comprised plain balloon angioplasty with selective use of plain or drug-eluting stents. Participants were followed up for a minimum of 2 years.
The primary outcome was amputation-free survival, defined as time to first major (above the ankle) amputation or death from any cause measured in the intention-to-treat population.
Results showed that major amputation or death occurred in 63% of patients in the vein bypass group and in 53% of those in the best endovascular treatment group (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.35; P = .037).
The results were driven by a higher death rate in the vein bypass group (53% vs. 45%; aHR, 1.37).
In both groups, the most common causes of morbidity and death, including death occurring within 30 days of first revascularization, were cardiovascular and respiratory events.
The authors noted that outcomes for the patients in the BASIL-2 trial were poor (median amputation-free survival was 3.8 years, and half the patients died within 5 years).
They pointed out that severe, multilevel atherosclerotic disease that causes chronic limb-threatening ischemia develops over many years, but at baseline in this study, around 20% of patients said they were still smoking, and around 70% of patients had diabetes, of whom around 50% required insulin. In addition, around 90% of the participants often had quite extensive tissue loss.
“These baseline data suggest that there might still be missed opportunities in public health and primary care to prevent chronic limb-threatening ischemia through medical therapy and lifestyle interventions and missed opportunities to refer patients to secondary care earlier once chronic limb-threatening ischemia begins to develop,” they suggested.
“Better prevention and timely referral are important: the BASIL-2 trial shows that, by the time patients present to vascular and endovascular surgeons and interventional radiologists with established chronic limb-threatening ischemia, their prognosis is often poor regardless of what form of revascularization they are offered,” they added.
Conflicting results
In an accompanying comment, Ankur Kalra, MD, Franciscan Health, Lafayette, Ind., and Ashish Kumar, MD, Cleveland Clinic Akron (Ohio) General, noted that atherosclerotic lower-extremity peripheral artery disease affects more than 230 million people worldwide, and prevalence is increasing. Chronic limb-threatening ischemia is a severe form of peripheral artery disease that affects 11% of patients with peripheral artery disease and is associated with significant cardiovascular morbidity and death.
Furthermore, amputation rates of 10%-40% during a 6-month follow-up of patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who were unable to undergo revascularization have been reported, highlighting the severity of atherosclerotic burden and the need for improved treatment strategies.
Dr. Kalra and Dr. Kumar pointed out that two previous randomized clinical trials compared surgical vein graft bypass with endovascular treatment for patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia – the BASIL-1 trial, and the BEST-CLI trial.
In the BASIL-1 trial, vein bypass was associated with improved overall survival and amputation-free survival for patients who survived at least 2 years. The BEST-CLI trial also reported a lower risk of a composite of major adverse limb events or death among patients undergoing a surgery-first strategy, compared with endovascular therapy, mostly in patients with suitable single segment of great saphenous vein.
Dr. Kalra and Dr. Kumar said the findings of the BASIL-2 trial should be put in context with these previous studies, which report a positive or equivocal effect of surgery. The results of the BEST-CLI trial were driven by fewer major reinterventions and above-ankle amputations in the surgical group, whereas the results of the BASIL-2 trial were driven by fewer deaths in the best endovascular treatment group, “which potentially points towards a difference in the characteristics of the patients randomly assigned in the two trials.”
They concluded: “Considering the results of the BASIL-2 trial and the BEST-CLI trial, choice of intervention should be based on shared decision making between interventional cardiology, vascular surgery, and the patient, until more evidence is accrued.”
The BASIL-2 trial was funded by the U.K. National Institute of Health Research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in a new randomized trial.
In the Bypass Versus Angioplasty in Severe Ischaemia of the Leg (BASIL-2) trial, patients who received vein bypass as the first approach were more likely to require a major amputation or to die during follow-up than patients who were randomly assigned to the endovascular approach as first strategy.
“Our findings suggest that a best endovascular treatment first revascularization strategy is associated with a better amputation-free survival. This is mainly because the best endovascular treatment first revascularization strategy resulted in fewer deaths. Limb-related outcomes were similar between groups,” the authors stated.
“The BASIL-2 trial has produced a statistically robust and clinically meaningful result that is likely to have an influence on the management of chronic limb-threatening ischemia worldwide,” added the study’s chief investigator, Andrew Bradbury, MD, professor of vascular surgery at the University of Birmingham (England).
However, the results of the BASIL-2 trial conflict with those from two previous studies – BASIL-1 and BEST-CLI, which both suggested that a surgical approach for chronic limb-threatening ischemia may be most appropriate.
The BASIL-2 study was published online in The Lancet.
The authors explained that chronic limb-threatening ischemia, previously known as critical limb ischemia and severe ischemia of the leg, is the most severe form of peripheral arterial disease caused by atherosclerosis. Patients present with ischemic rest pain and tissue loss (ulceration, gangrene, or both) that usually affects the foot.
Mainly because of tobacco smoking and the growing prevalence of type 2 diabetes, chronic limb-threatening ischemia represents a growing burden on health care and social care services around the world.
Unless the blood supply to the affected limb is restored, patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia are at high risk for amputation or death. Although it is universally agreed that – in addition to best medical therapy – virtually all patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia should at least be considered for revascularization, there is continuing debate as to whether conducting vein bypass surgery, preferably using a vein taken from the patient’s own leg, or endovascular treatment (balloon angioplasty with or without stents) is preferable.
“BASIL-2 is the only randomized trial to specifically compare a vein bypass first with best endovascular treatment first revascularisation strategy in patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who required an infrapopliteal (with or without an additional more proximal infrainguinal) revascularization procedure to restore limb perfusion,” the authors noted.
For the trial, which was conducted at 41 vascular surgery units in the United Kingdom, Sweden, and Denmark, 345 patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who required an infrapopliteal revascularization procedure to restore limb perfusion were randomly assigned to receive either vein bypass or best endovascular treatment as their first revascularization procedure.
Most vein bypasses used the great saphenous vein and originated from the common or superficial femoral arteries. Most endovascular interventions comprised plain balloon angioplasty with selective use of plain or drug-eluting stents. Participants were followed up for a minimum of 2 years.
The primary outcome was amputation-free survival, defined as time to first major (above the ankle) amputation or death from any cause measured in the intention-to-treat population.
Results showed that major amputation or death occurred in 63% of patients in the vein bypass group and in 53% of those in the best endovascular treatment group (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.35; P = .037).
The results were driven by a higher death rate in the vein bypass group (53% vs. 45%; aHR, 1.37).
In both groups, the most common causes of morbidity and death, including death occurring within 30 days of first revascularization, were cardiovascular and respiratory events.
The authors noted that outcomes for the patients in the BASIL-2 trial were poor (median amputation-free survival was 3.8 years, and half the patients died within 5 years).
They pointed out that severe, multilevel atherosclerotic disease that causes chronic limb-threatening ischemia develops over many years, but at baseline in this study, around 20% of patients said they were still smoking, and around 70% of patients had diabetes, of whom around 50% required insulin. In addition, around 90% of the participants often had quite extensive tissue loss.
“These baseline data suggest that there might still be missed opportunities in public health and primary care to prevent chronic limb-threatening ischemia through medical therapy and lifestyle interventions and missed opportunities to refer patients to secondary care earlier once chronic limb-threatening ischemia begins to develop,” they suggested.
“Better prevention and timely referral are important: the BASIL-2 trial shows that, by the time patients present to vascular and endovascular surgeons and interventional radiologists with established chronic limb-threatening ischemia, their prognosis is often poor regardless of what form of revascularization they are offered,” they added.
Conflicting results
In an accompanying comment, Ankur Kalra, MD, Franciscan Health, Lafayette, Ind., and Ashish Kumar, MD, Cleveland Clinic Akron (Ohio) General, noted that atherosclerotic lower-extremity peripheral artery disease affects more than 230 million people worldwide, and prevalence is increasing. Chronic limb-threatening ischemia is a severe form of peripheral artery disease that affects 11% of patients with peripheral artery disease and is associated with significant cardiovascular morbidity and death.
Furthermore, amputation rates of 10%-40% during a 6-month follow-up of patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who were unable to undergo revascularization have been reported, highlighting the severity of atherosclerotic burden and the need for improved treatment strategies.
Dr. Kalra and Dr. Kumar pointed out that two previous randomized clinical trials compared surgical vein graft bypass with endovascular treatment for patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia – the BASIL-1 trial, and the BEST-CLI trial.
In the BASIL-1 trial, vein bypass was associated with improved overall survival and amputation-free survival for patients who survived at least 2 years. The BEST-CLI trial also reported a lower risk of a composite of major adverse limb events or death among patients undergoing a surgery-first strategy, compared with endovascular therapy, mostly in patients with suitable single segment of great saphenous vein.
Dr. Kalra and Dr. Kumar said the findings of the BASIL-2 trial should be put in context with these previous studies, which report a positive or equivocal effect of surgery. The results of the BEST-CLI trial were driven by fewer major reinterventions and above-ankle amputations in the surgical group, whereas the results of the BASIL-2 trial were driven by fewer deaths in the best endovascular treatment group, “which potentially points towards a difference in the characteristics of the patients randomly assigned in the two trials.”
They concluded: “Considering the results of the BASIL-2 trial and the BEST-CLI trial, choice of intervention should be based on shared decision making between interventional cardiology, vascular surgery, and the patient, until more evidence is accrued.”
The BASIL-2 trial was funded by the U.K. National Institute of Health Research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in a new randomized trial.
In the Bypass Versus Angioplasty in Severe Ischaemia of the Leg (BASIL-2) trial, patients who received vein bypass as the first approach were more likely to require a major amputation or to die during follow-up than patients who were randomly assigned to the endovascular approach as first strategy.
“Our findings suggest that a best endovascular treatment first revascularization strategy is associated with a better amputation-free survival. This is mainly because the best endovascular treatment first revascularization strategy resulted in fewer deaths. Limb-related outcomes were similar between groups,” the authors stated.
“The BASIL-2 trial has produced a statistically robust and clinically meaningful result that is likely to have an influence on the management of chronic limb-threatening ischemia worldwide,” added the study’s chief investigator, Andrew Bradbury, MD, professor of vascular surgery at the University of Birmingham (England).
However, the results of the BASIL-2 trial conflict with those from two previous studies – BASIL-1 and BEST-CLI, which both suggested that a surgical approach for chronic limb-threatening ischemia may be most appropriate.
The BASIL-2 study was published online in The Lancet.
The authors explained that chronic limb-threatening ischemia, previously known as critical limb ischemia and severe ischemia of the leg, is the most severe form of peripheral arterial disease caused by atherosclerosis. Patients present with ischemic rest pain and tissue loss (ulceration, gangrene, or both) that usually affects the foot.
Mainly because of tobacco smoking and the growing prevalence of type 2 diabetes, chronic limb-threatening ischemia represents a growing burden on health care and social care services around the world.
Unless the blood supply to the affected limb is restored, patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia are at high risk for amputation or death. Although it is universally agreed that – in addition to best medical therapy – virtually all patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia should at least be considered for revascularization, there is continuing debate as to whether conducting vein bypass surgery, preferably using a vein taken from the patient’s own leg, or endovascular treatment (balloon angioplasty with or without stents) is preferable.
“BASIL-2 is the only randomized trial to specifically compare a vein bypass first with best endovascular treatment first revascularisation strategy in patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who required an infrapopliteal (with or without an additional more proximal infrainguinal) revascularization procedure to restore limb perfusion,” the authors noted.
For the trial, which was conducted at 41 vascular surgery units in the United Kingdom, Sweden, and Denmark, 345 patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who required an infrapopliteal revascularization procedure to restore limb perfusion were randomly assigned to receive either vein bypass or best endovascular treatment as their first revascularization procedure.
Most vein bypasses used the great saphenous vein and originated from the common or superficial femoral arteries. Most endovascular interventions comprised plain balloon angioplasty with selective use of plain or drug-eluting stents. Participants were followed up for a minimum of 2 years.
The primary outcome was amputation-free survival, defined as time to first major (above the ankle) amputation or death from any cause measured in the intention-to-treat population.
Results showed that major amputation or death occurred in 63% of patients in the vein bypass group and in 53% of those in the best endovascular treatment group (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.35; P = .037).
The results were driven by a higher death rate in the vein bypass group (53% vs. 45%; aHR, 1.37).
In both groups, the most common causes of morbidity and death, including death occurring within 30 days of first revascularization, were cardiovascular and respiratory events.
The authors noted that outcomes for the patients in the BASIL-2 trial were poor (median amputation-free survival was 3.8 years, and half the patients died within 5 years).
They pointed out that severe, multilevel atherosclerotic disease that causes chronic limb-threatening ischemia develops over many years, but at baseline in this study, around 20% of patients said they were still smoking, and around 70% of patients had diabetes, of whom around 50% required insulin. In addition, around 90% of the participants often had quite extensive tissue loss.
“These baseline data suggest that there might still be missed opportunities in public health and primary care to prevent chronic limb-threatening ischemia through medical therapy and lifestyle interventions and missed opportunities to refer patients to secondary care earlier once chronic limb-threatening ischemia begins to develop,” they suggested.
“Better prevention and timely referral are important: the BASIL-2 trial shows that, by the time patients present to vascular and endovascular surgeons and interventional radiologists with established chronic limb-threatening ischemia, their prognosis is often poor regardless of what form of revascularization they are offered,” they added.
Conflicting results
In an accompanying comment, Ankur Kalra, MD, Franciscan Health, Lafayette, Ind., and Ashish Kumar, MD, Cleveland Clinic Akron (Ohio) General, noted that atherosclerotic lower-extremity peripheral artery disease affects more than 230 million people worldwide, and prevalence is increasing. Chronic limb-threatening ischemia is a severe form of peripheral artery disease that affects 11% of patients with peripheral artery disease and is associated with significant cardiovascular morbidity and death.
Furthermore, amputation rates of 10%-40% during a 6-month follow-up of patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia who were unable to undergo revascularization have been reported, highlighting the severity of atherosclerotic burden and the need for improved treatment strategies.
Dr. Kalra and Dr. Kumar pointed out that two previous randomized clinical trials compared surgical vein graft bypass with endovascular treatment for patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia – the BASIL-1 trial, and the BEST-CLI trial.
In the BASIL-1 trial, vein bypass was associated with improved overall survival and amputation-free survival for patients who survived at least 2 years. The BEST-CLI trial also reported a lower risk of a composite of major adverse limb events or death among patients undergoing a surgery-first strategy, compared with endovascular therapy, mostly in patients with suitable single segment of great saphenous vein.
Dr. Kalra and Dr. Kumar said the findings of the BASIL-2 trial should be put in context with these previous studies, which report a positive or equivocal effect of surgery. The results of the BEST-CLI trial were driven by fewer major reinterventions and above-ankle amputations in the surgical group, whereas the results of the BASIL-2 trial were driven by fewer deaths in the best endovascular treatment group, “which potentially points towards a difference in the characteristics of the patients randomly assigned in the two trials.”
They concluded: “Considering the results of the BASIL-2 trial and the BEST-CLI trial, choice of intervention should be based on shared decision making between interventional cardiology, vascular surgery, and the patient, until more evidence is accrued.”
The BASIL-2 trial was funded by the U.K. National Institute of Health Research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET