User login
Transrectal ultrasonography–guided needle biopsy of the prostate confirms a diagnosis of metastatic prostate cancer.
With the exception of nonmelanoma skin cancer, prostate cancer is the most commonly occurring cancer and the second most common cause of cancer-associated mortality in men in the United States. Most patients have localized stage at diagnosis; however, the incidence of distant-stage prostate cancer at diagnosis is steadily increasing. Five-year survival for distant-stage prostate cancer is approximately 32%.
High serum levels of PSA have been associated with bone metastases in men with prostate cancer, and the presence of metastatic disease increases with rising PSA levels. Over the past several decades, PSA levels > 100 ng/mL have been used as a marker for metastatic prostate cancer. However, not all men with metastatic prostate cancer will have elevated PSA levels, and bone imaging is necessary for correct staging and treatment stratification.
Bone metastases occur in approximately 70% of men with advanced prostate cancer, most often in the spine, and are a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. Bone metastases can cause severe pain, particularly in the evening; decreased mobility; pathologic fractures; spinal cord compression; bone marrow aplasia; and hypercalcemia.
The bone marrow represents a fertile soil into which prostate tumors can colonize and proliferate. Such colonization by prostate tumor cells is commonly associated with tumor-induced bone lesions, which typically arise from an imbalance between bone-forming osteoblasts and bone-absorbing osteoclasts generated by prostate cancer cells. Whereas most solid tumors, such as breast cancer and melanoma, have a propensity for causing osteolytic lesions with excessive bone resorption, bone lesions resulting from prostate cancer are largely osteoblastic and are associated with uncontrolled low-quality bone formation. The resultant metastases have a unique bone formation that can be detected by plain radiography, bone scan, bone biopsy, and increased serum alkaline phosphatase levels.
CT; skeletal scintigraphy and PET; and single-photon emission CT (SPECT)/CT, PET/CT, and PET/MRI are recommended diagnostics for men at risk for prostate cancer metastasis. Radiotracer-based PET, which mainly uses altered metabolic activity or explicitly overexpressed receptors, is a promising diagnostic modality. However, the choice of a respective radiotracer must be carefully considered because a single radiotracer is typically insufficient to visualize all clinical stages of prostate cancer. In addition, its use is reliant on the extent of malignant tissue, tumor heterogeneity, and previous treatments.
Systemic androgen-deprivation therapy, with or without docetaxel-based chemotherapy, is the standard of care for metastatic prostate cancer. Treatment is largely directed at preventing skeletal-related events and providing pain management.
Radium-223 is the only available therapy for castrate-resistant prostate cancer that specifically targets bone metastases, delays development of skeletal-related events, and improves survival. Based on the results of the ALSYMPCA study, radium-223 in combination with systemic therapies is now considered an effective, efficient, and well-tolerated therapy for castrate-resistant prostate cancer with bone lesions.
The effects of local radiation therapy for men with metastatic prostate cancer and the optimal combination of systemic therapies in the metastatic setting are still under investigation.
Kyle A. Richards, MD, Assistant Professor, Department of Urology, University of Wisconsin-Madison; Chief of Urology, William S. Middleton Memorial VA Hospital, Madison, Wisconsin.
Kyle A. Richards, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Transrectal ultrasonography–guided needle biopsy of the prostate confirms a diagnosis of metastatic prostate cancer.
With the exception of nonmelanoma skin cancer, prostate cancer is the most commonly occurring cancer and the second most common cause of cancer-associated mortality in men in the United States. Most patients have localized stage at diagnosis; however, the incidence of distant-stage prostate cancer at diagnosis is steadily increasing. Five-year survival for distant-stage prostate cancer is approximately 32%.
High serum levels of PSA have been associated with bone metastases in men with prostate cancer, and the presence of metastatic disease increases with rising PSA levels. Over the past several decades, PSA levels > 100 ng/mL have been used as a marker for metastatic prostate cancer. However, not all men with metastatic prostate cancer will have elevated PSA levels, and bone imaging is necessary for correct staging and treatment stratification.
Bone metastases occur in approximately 70% of men with advanced prostate cancer, most often in the spine, and are a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. Bone metastases can cause severe pain, particularly in the evening; decreased mobility; pathologic fractures; spinal cord compression; bone marrow aplasia; and hypercalcemia.
The bone marrow represents a fertile soil into which prostate tumors can colonize and proliferate. Such colonization by prostate tumor cells is commonly associated with tumor-induced bone lesions, which typically arise from an imbalance between bone-forming osteoblasts and bone-absorbing osteoclasts generated by prostate cancer cells. Whereas most solid tumors, such as breast cancer and melanoma, have a propensity for causing osteolytic lesions with excessive bone resorption, bone lesions resulting from prostate cancer are largely osteoblastic and are associated with uncontrolled low-quality bone formation. The resultant metastases have a unique bone formation that can be detected by plain radiography, bone scan, bone biopsy, and increased serum alkaline phosphatase levels.
CT; skeletal scintigraphy and PET; and single-photon emission CT (SPECT)/CT, PET/CT, and PET/MRI are recommended diagnostics for men at risk for prostate cancer metastasis. Radiotracer-based PET, which mainly uses altered metabolic activity or explicitly overexpressed receptors, is a promising diagnostic modality. However, the choice of a respective radiotracer must be carefully considered because a single radiotracer is typically insufficient to visualize all clinical stages of prostate cancer. In addition, its use is reliant on the extent of malignant tissue, tumor heterogeneity, and previous treatments.
Systemic androgen-deprivation therapy, with or without docetaxel-based chemotherapy, is the standard of care for metastatic prostate cancer. Treatment is largely directed at preventing skeletal-related events and providing pain management.
Radium-223 is the only available therapy for castrate-resistant prostate cancer that specifically targets bone metastases, delays development of skeletal-related events, and improves survival. Based on the results of the ALSYMPCA study, radium-223 in combination with systemic therapies is now considered an effective, efficient, and well-tolerated therapy for castrate-resistant prostate cancer with bone lesions.
The effects of local radiation therapy for men with metastatic prostate cancer and the optimal combination of systemic therapies in the metastatic setting are still under investigation.
Kyle A. Richards, MD, Assistant Professor, Department of Urology, University of Wisconsin-Madison; Chief of Urology, William S. Middleton Memorial VA Hospital, Madison, Wisconsin.
Kyle A. Richards, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Transrectal ultrasonography–guided needle biopsy of the prostate confirms a diagnosis of metastatic prostate cancer.
With the exception of nonmelanoma skin cancer, prostate cancer is the most commonly occurring cancer and the second most common cause of cancer-associated mortality in men in the United States. Most patients have localized stage at diagnosis; however, the incidence of distant-stage prostate cancer at diagnosis is steadily increasing. Five-year survival for distant-stage prostate cancer is approximately 32%.
High serum levels of PSA have been associated with bone metastases in men with prostate cancer, and the presence of metastatic disease increases with rising PSA levels. Over the past several decades, PSA levels > 100 ng/mL have been used as a marker for metastatic prostate cancer. However, not all men with metastatic prostate cancer will have elevated PSA levels, and bone imaging is necessary for correct staging and treatment stratification.
Bone metastases occur in approximately 70% of men with advanced prostate cancer, most often in the spine, and are a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. Bone metastases can cause severe pain, particularly in the evening; decreased mobility; pathologic fractures; spinal cord compression; bone marrow aplasia; and hypercalcemia.
The bone marrow represents a fertile soil into which prostate tumors can colonize and proliferate. Such colonization by prostate tumor cells is commonly associated with tumor-induced bone lesions, which typically arise from an imbalance between bone-forming osteoblasts and bone-absorbing osteoclasts generated by prostate cancer cells. Whereas most solid tumors, such as breast cancer and melanoma, have a propensity for causing osteolytic lesions with excessive bone resorption, bone lesions resulting from prostate cancer are largely osteoblastic and are associated with uncontrolled low-quality bone formation. The resultant metastases have a unique bone formation that can be detected by plain radiography, bone scan, bone biopsy, and increased serum alkaline phosphatase levels.
CT; skeletal scintigraphy and PET; and single-photon emission CT (SPECT)/CT, PET/CT, and PET/MRI are recommended diagnostics for men at risk for prostate cancer metastasis. Radiotracer-based PET, which mainly uses altered metabolic activity or explicitly overexpressed receptors, is a promising diagnostic modality. However, the choice of a respective radiotracer must be carefully considered because a single radiotracer is typically insufficient to visualize all clinical stages of prostate cancer. In addition, its use is reliant on the extent of malignant tissue, tumor heterogeneity, and previous treatments.
Systemic androgen-deprivation therapy, with or without docetaxel-based chemotherapy, is the standard of care for metastatic prostate cancer. Treatment is largely directed at preventing skeletal-related events and providing pain management.
Radium-223 is the only available therapy for castrate-resistant prostate cancer that specifically targets bone metastases, delays development of skeletal-related events, and improves survival. Based on the results of the ALSYMPCA study, radium-223 in combination with systemic therapies is now considered an effective, efficient, and well-tolerated therapy for castrate-resistant prostate cancer with bone lesions.
The effects of local radiation therapy for men with metastatic prostate cancer and the optimal combination of systemic therapies in the metastatic setting are still under investigation.
Kyle A. Richards, MD, Assistant Professor, Department of Urology, University of Wisconsin-Madison; Chief of Urology, William S. Middleton Memorial VA Hospital, Madison, Wisconsin.
Kyle A. Richards, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
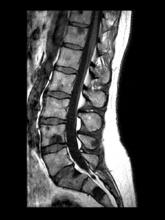
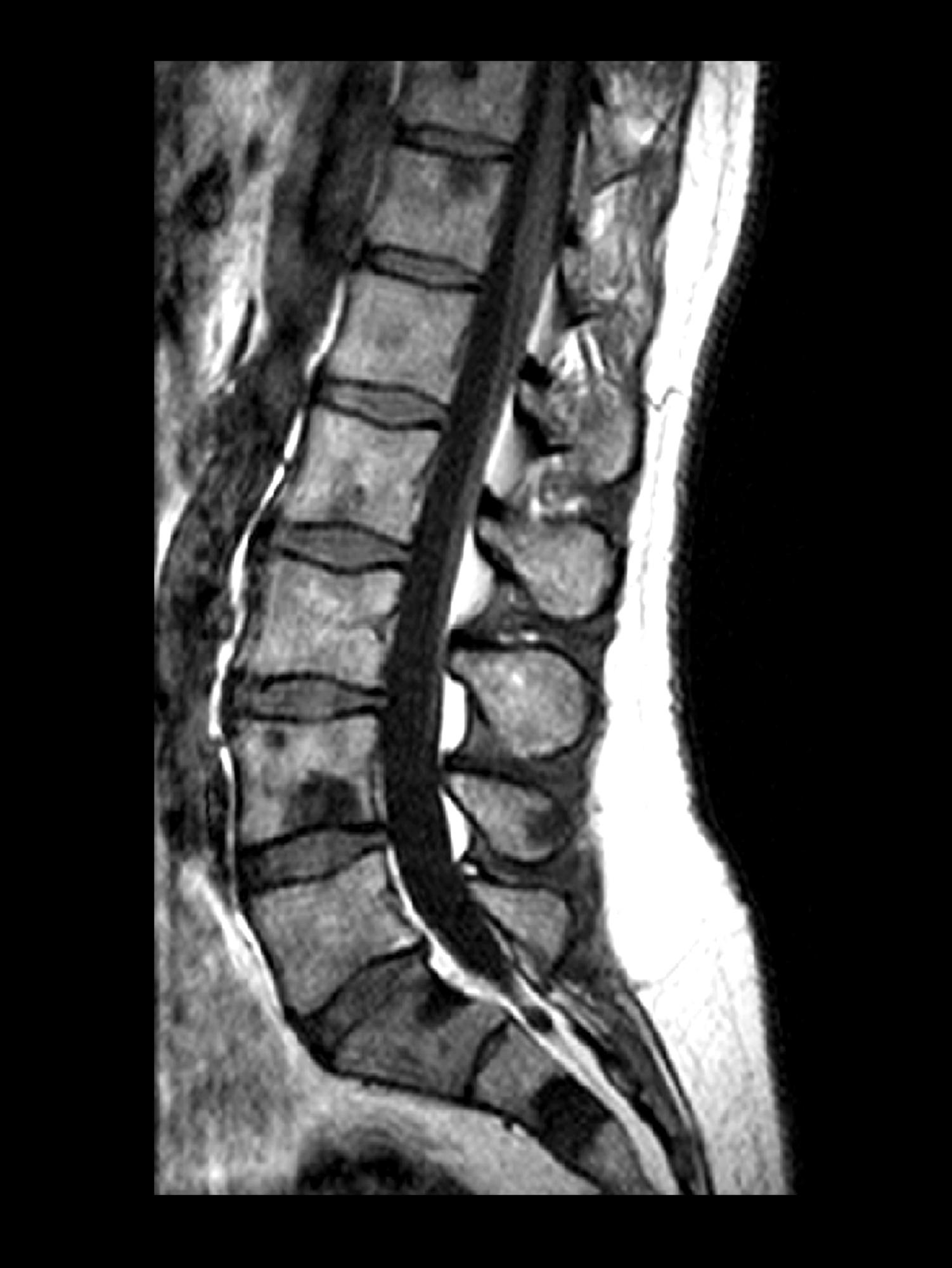
A 71-year-old homeless man presents to the emergency department (ED) with intermittent fever, gradually progressive low back pain restricting physical activities and movement, fatigue, exertional dyspnea, and poor appetite. The patient has been seen in the same ED sporadically over the years for various problems, and his medical history is notable for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, tobacco use, alcoholism, and foot infections. Physical examination findings include tenderness to percussion over the thoracic and lumbar spine and a mildly enlarged prostate that appears to be smooth, normal in texture, and lacking nodules on digital rectal exam. Complete blood cell count and chemistry panel are normal. Both alkaline phosphatase and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels are elevated, at 240 U/L and 115 ng/mL, respectively. Urinalysis shows hematuria. CT shows osteolytic lesions in the patient's lumbar spine and femur.