User login
PORTLAND, ORE. – Janus kinase inhibitors are relatively safe and can produce a full head of hair in patients with moderate to severe alopecia areata (AA), although patients tend to shed hair after stopping treatment, Julian Mackay-Wiggan, MD, said at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology.
“At this point, there are 17 publications in the literature, from clinical trials to case reports, looking at JAK [Janus kinase] inhibitors in patients with alopecia areata,” said Dr. Mackay-Wiggan of the department of dermatology, Columbia University, New York, where she specializes in hair disorders. “Pretty much all report very positive findings. It definitely appears that Janus kinase inhibitors can play a very significant role in treatment.”
In an open label, uncontrolled pilot study at Columbia, 9 of 12 (75%) patients with moderate to severe AA improved by at least 50% on the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) after receiving 20 mg ruxolitinib twice daily for 3 to 6 months (JCI Insight. 2016 Sep 22;1[15]:e89790). Responses started with the first month, and all but one responder achieved at least 50% hair regrowth by week 12, said Dr. Mackay-Wiggan, who is also the director of the Dermatology Clinical Research Unit at Columbia.
By the end of treatment, seven of nine responders achieved more than 95% regrowth, one achieved 85% regrowth, and one achieved 55% regrowth. Importantly, none of these relatively healthy patients experienced serious adverse events on ruxolitinib, and none needed to stop treatment, although one patient experienced declining hemoglobin levels that resolved after dose modification.
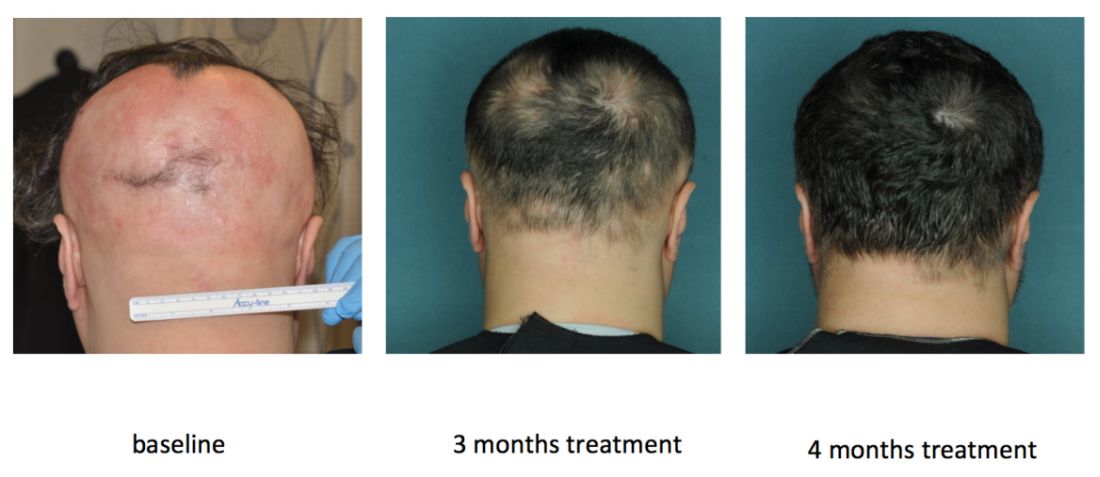
Columbia researchers are also conducting an uncontrolled, open label pilot trial of the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz) in 12 patients, of whom seven have moderate to severe patchy AA and five have alopecia totalis or universalis. Tofacitinib is approved for treating rheumatoid arthritis at a dose of 5 mg twice daily, but patients have needed up to 10 mg twice daily to achieve hair regrowth, Dr. Mackay-Wiggan said. To date, 11 (92%) have achieved at least some hair regrowth, and 8 (67%) have achieved at least 50% regrowth. So far, there have been no serious adverse events over 6 to 16 months of treatment, although one patient stopped treatment after developing hypertension, a known adverse effect of tofacitinib.
In this study, heatmaps of RNA sequencing of CD8+ T cell populations clearly showed pathogenic signatures for AA and a “robust molecular response to treatment,” Dr. Mackay-Wiggan said. “These two signatures also overlapped statistically, producing 114 genes that may be targetable mediators of disease.” But as with ruxolitinib, regrowth started to decline as patients were taken off treatment.
Research indicates that inhibiting the JAK-STAT signaling pathway induces anagen and subsequent hair growth, but activating STAT 5 in the dermal papilla is also important to induce the growth phase of the hair follicle, according to Dr. Mackay-Wiggan. “Bottom line, it’s complicated,” she added. “The mode of delivery – topical versus systemic – may be important, and the timing of delivery may be crucial.”
Other studies point to a role for JAK inhibition in treating AA. In an uncontrolled, retrospective study of 90 adults with alopecia totalis, alopecia universalis, or moderate to severe AA, 58% had SALT scores of 50% or better after receiving 5 mg tofacitinib twice daily for 4 to 18 months. Patients with AA improved more than those with alopecia totalis or universalis. There were no severe adverse effects, although nearly a third of patients developed upper respiratory tract infections. In another uncontrolled study of 13 patients with AA, totalis, or universalis, 9 (70%) patients achieved full regrowth and there were no serious adverse effects, although patients experienced headaches, upper respiratory infections, and mild increases in liver transaminase levels.
JAK inhibition also has a potential role for treating some scarring alopecias, including lichen planopilaris and frontal fibrosing alopecia. These diseases are histologically “identical” and both exhibit perifollicular erythema, papules, and scale, all of which suggest active inflammation, Dr. Mackay-Wiggan said. Hair follicles from affected patients show immune markers such as interferon-inducible chemokines, cytotoxic T cell responses, and expression of major histocompatibility complexes I and II. “The important message here is that JAK/STAT signaling may play a significant role in other types of hair loss other than alopecia areata,” Dr. Mackay-Wiggan said. “These diseases may also be autoimmune diseases, and may also be treatable with JAK inhibitors.”
Studies continue to evaluate JAK inhibitors for treating alopecia and its variants. Investigators at Yale and Stanford are conducting three uncontrolled trials of oral or topical tofacitinib, while Incyte, the manufacturer of ruxolitinib, is sponsoring a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of ruxolitinib phosphate cream for adults with AA, with topline results expected in May 2018. Concert Pharmaceuticals also is recruiting for a trial of a modified, investigational form of ruxolitinib called CTP-543 for treating moderate to severe AA. “Many more trials are in development,” Dr. Mackay-Wiggan noted.
The ruxolitinib pilot study was funded by the Locks of Love Foundation, the Alopecia Areata Initiative, NIH/National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and by an Irving Institute for Clinical and Translational Research/Columbia University Medical Center Clinical and Translational Science Award. The ongoing tofacitinib pilot study is sponsored by Dr. Mackay-Wiggan, Locks of Love, and Columbia University.
Dr. Mackay-Wiggan also acknowledged support from the Alopecia Areata Initiative – the Gates Foundation, the National Alopecia Areata Registry, and the National Alopecia Areata Foundation. She had no other relevant financial disclosures.
PORTLAND, ORE. – Janus kinase inhibitors are relatively safe and can produce a full head of hair in patients with moderate to severe alopecia areata (AA), although patients tend to shed hair after stopping treatment, Julian Mackay-Wiggan, MD, said at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology.
“At this point, there are 17 publications in the literature, from clinical trials to case reports, looking at JAK [Janus kinase] inhibitors in patients with alopecia areata,” said Dr. Mackay-Wiggan of the department of dermatology, Columbia University, New York, where she specializes in hair disorders. “Pretty much all report very positive findings. It definitely appears that Janus kinase inhibitors can play a very significant role in treatment.”
In an open label, uncontrolled pilot study at Columbia, 9 of 12 (75%) patients with moderate to severe AA improved by at least 50% on the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) after receiving 20 mg ruxolitinib twice daily for 3 to 6 months (JCI Insight. 2016 Sep 22;1[15]:e89790). Responses started with the first month, and all but one responder achieved at least 50% hair regrowth by week 12, said Dr. Mackay-Wiggan, who is also the director of the Dermatology Clinical Research Unit at Columbia.
By the end of treatment, seven of nine responders achieved more than 95% regrowth, one achieved 85% regrowth, and one achieved 55% regrowth. Importantly, none of these relatively healthy patients experienced serious adverse events on ruxolitinib, and none needed to stop treatment, although one patient experienced declining hemoglobin levels that resolved after dose modification.

Columbia researchers are also conducting an uncontrolled, open label pilot trial of the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz) in 12 patients, of whom seven have moderate to severe patchy AA and five have alopecia totalis or universalis. Tofacitinib is approved for treating rheumatoid arthritis at a dose of 5 mg twice daily, but patients have needed up to 10 mg twice daily to achieve hair regrowth, Dr. Mackay-Wiggan said. To date, 11 (92%) have achieved at least some hair regrowth, and 8 (67%) have achieved at least 50% regrowth. So far, there have been no serious adverse events over 6 to 16 months of treatment, although one patient stopped treatment after developing hypertension, a known adverse effect of tofacitinib.
In this study, heatmaps of RNA sequencing of CD8+ T cell populations clearly showed pathogenic signatures for AA and a “robust molecular response to treatment,” Dr. Mackay-Wiggan said. “These two signatures also overlapped statistically, producing 114 genes that may be targetable mediators of disease.” But as with ruxolitinib, regrowth started to decline as patients were taken off treatment.
Research indicates that inhibiting the JAK-STAT signaling pathway induces anagen and subsequent hair growth, but activating STAT 5 in the dermal papilla is also important to induce the growth phase of the hair follicle, according to Dr. Mackay-Wiggan. “Bottom line, it’s complicated,” she added. “The mode of delivery – topical versus systemic – may be important, and the timing of delivery may be crucial.”
Other studies point to a role for JAK inhibition in treating AA. In an uncontrolled, retrospective study of 90 adults with alopecia totalis, alopecia universalis, or moderate to severe AA, 58% had SALT scores of 50% or better after receiving 5 mg tofacitinib twice daily for 4 to 18 months. Patients with AA improved more than those with alopecia totalis or universalis. There were no severe adverse effects, although nearly a third of patients developed upper respiratory tract infections. In another uncontrolled study of 13 patients with AA, totalis, or universalis, 9 (70%) patients achieved full regrowth and there were no serious adverse effects, although patients experienced headaches, upper respiratory infections, and mild increases in liver transaminase levels.
JAK inhibition also has a potential role for treating some scarring alopecias, including lichen planopilaris and frontal fibrosing alopecia. These diseases are histologically “identical” and both exhibit perifollicular erythema, papules, and scale, all of which suggest active inflammation, Dr. Mackay-Wiggan said. Hair follicles from affected patients show immune markers such as interferon-inducible chemokines, cytotoxic T cell responses, and expression of major histocompatibility complexes I and II. “The important message here is that JAK/STAT signaling may play a significant role in other types of hair loss other than alopecia areata,” Dr. Mackay-Wiggan said. “These diseases may also be autoimmune diseases, and may also be treatable with JAK inhibitors.”
Studies continue to evaluate JAK inhibitors for treating alopecia and its variants. Investigators at Yale and Stanford are conducting three uncontrolled trials of oral or topical tofacitinib, while Incyte, the manufacturer of ruxolitinib, is sponsoring a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of ruxolitinib phosphate cream for adults with AA, with topline results expected in May 2018. Concert Pharmaceuticals also is recruiting for a trial of a modified, investigational form of ruxolitinib called CTP-543 for treating moderate to severe AA. “Many more trials are in development,” Dr. Mackay-Wiggan noted.
The ruxolitinib pilot study was funded by the Locks of Love Foundation, the Alopecia Areata Initiative, NIH/National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and by an Irving Institute for Clinical and Translational Research/Columbia University Medical Center Clinical and Translational Science Award. The ongoing tofacitinib pilot study is sponsored by Dr. Mackay-Wiggan, Locks of Love, and Columbia University.
Dr. Mackay-Wiggan also acknowledged support from the Alopecia Areata Initiative – the Gates Foundation, the National Alopecia Areata Registry, and the National Alopecia Areata Foundation. She had no other relevant financial disclosures.
PORTLAND, ORE. – Janus kinase inhibitors are relatively safe and can produce a full head of hair in patients with moderate to severe alopecia areata (AA), although patients tend to shed hair after stopping treatment, Julian Mackay-Wiggan, MD, said at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology.
“At this point, there are 17 publications in the literature, from clinical trials to case reports, looking at JAK [Janus kinase] inhibitors in patients with alopecia areata,” said Dr. Mackay-Wiggan of the department of dermatology, Columbia University, New York, where she specializes in hair disorders. “Pretty much all report very positive findings. It definitely appears that Janus kinase inhibitors can play a very significant role in treatment.”
In an open label, uncontrolled pilot study at Columbia, 9 of 12 (75%) patients with moderate to severe AA improved by at least 50% on the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) after receiving 20 mg ruxolitinib twice daily for 3 to 6 months (JCI Insight. 2016 Sep 22;1[15]:e89790). Responses started with the first month, and all but one responder achieved at least 50% hair regrowth by week 12, said Dr. Mackay-Wiggan, who is also the director of the Dermatology Clinical Research Unit at Columbia.
By the end of treatment, seven of nine responders achieved more than 95% regrowth, one achieved 85% regrowth, and one achieved 55% regrowth. Importantly, none of these relatively healthy patients experienced serious adverse events on ruxolitinib, and none needed to stop treatment, although one patient experienced declining hemoglobin levels that resolved after dose modification.

Columbia researchers are also conducting an uncontrolled, open label pilot trial of the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz) in 12 patients, of whom seven have moderate to severe patchy AA and five have alopecia totalis or universalis. Tofacitinib is approved for treating rheumatoid arthritis at a dose of 5 mg twice daily, but patients have needed up to 10 mg twice daily to achieve hair regrowth, Dr. Mackay-Wiggan said. To date, 11 (92%) have achieved at least some hair regrowth, and 8 (67%) have achieved at least 50% regrowth. So far, there have been no serious adverse events over 6 to 16 months of treatment, although one patient stopped treatment after developing hypertension, a known adverse effect of tofacitinib.
In this study, heatmaps of RNA sequencing of CD8+ T cell populations clearly showed pathogenic signatures for AA and a “robust molecular response to treatment,” Dr. Mackay-Wiggan said. “These two signatures also overlapped statistically, producing 114 genes that may be targetable mediators of disease.” But as with ruxolitinib, regrowth started to decline as patients were taken off treatment.
Research indicates that inhibiting the JAK-STAT signaling pathway induces anagen and subsequent hair growth, but activating STAT 5 in the dermal papilla is also important to induce the growth phase of the hair follicle, according to Dr. Mackay-Wiggan. “Bottom line, it’s complicated,” she added. “The mode of delivery – topical versus systemic – may be important, and the timing of delivery may be crucial.”
Other studies point to a role for JAK inhibition in treating AA. In an uncontrolled, retrospective study of 90 adults with alopecia totalis, alopecia universalis, or moderate to severe AA, 58% had SALT scores of 50% or better after receiving 5 mg tofacitinib twice daily for 4 to 18 months. Patients with AA improved more than those with alopecia totalis or universalis. There were no severe adverse effects, although nearly a third of patients developed upper respiratory tract infections. In another uncontrolled study of 13 patients with AA, totalis, or universalis, 9 (70%) patients achieved full regrowth and there were no serious adverse effects, although patients experienced headaches, upper respiratory infections, and mild increases in liver transaminase levels.
JAK inhibition also has a potential role for treating some scarring alopecias, including lichen planopilaris and frontal fibrosing alopecia. These diseases are histologically “identical” and both exhibit perifollicular erythema, papules, and scale, all of which suggest active inflammation, Dr. Mackay-Wiggan said. Hair follicles from affected patients show immune markers such as interferon-inducible chemokines, cytotoxic T cell responses, and expression of major histocompatibility complexes I and II. “The important message here is that JAK/STAT signaling may play a significant role in other types of hair loss other than alopecia areata,” Dr. Mackay-Wiggan said. “These diseases may also be autoimmune diseases, and may also be treatable with JAK inhibitors.”
Studies continue to evaluate JAK inhibitors for treating alopecia and its variants. Investigators at Yale and Stanford are conducting three uncontrolled trials of oral or topical tofacitinib, while Incyte, the manufacturer of ruxolitinib, is sponsoring a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of ruxolitinib phosphate cream for adults with AA, with topline results expected in May 2018. Concert Pharmaceuticals also is recruiting for a trial of a modified, investigational form of ruxolitinib called CTP-543 for treating moderate to severe AA. “Many more trials are in development,” Dr. Mackay-Wiggan noted.
The ruxolitinib pilot study was funded by the Locks of Love Foundation, the Alopecia Areata Initiative, NIH/National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and by an Irving Institute for Clinical and Translational Research/Columbia University Medical Center Clinical and Translational Science Award. The ongoing tofacitinib pilot study is sponsored by Dr. Mackay-Wiggan, Locks of Love, and Columbia University.
Dr. Mackay-Wiggan also acknowledged support from the Alopecia Areata Initiative – the Gates Foundation, the National Alopecia Areata Registry, and the National Alopecia Areata Foundation. She had no other relevant financial disclosures.
AT SID 2017

