User login
Hospitalists must consider clinical factors and patient preferences
Case
A 70-year old woman with hypertension, diabetes, nonischemic stroke, moderate renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance [CrCl] 45 mL/min), heart failure, and nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AF) on warfarin is admitted because of a very supratherapeutic INR. She reports labile INR values despite strict adherence to her medication regimen. Her cancer screening tests had previously been unremarkable. She inquires about the risks and benefits of switching to a novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) as advertised on television. Should you consider it while she is still in the hospital?
Brief overview of the issue
Lifelong anticoagulation therapy is common among patients with AF or recurrent venous thromboembolism (VTE). Until the advent of NOACs, a great majority of patients were prescribed warfarin, the oral vitamin K antagonist that requires regular blood tests for monitoring of the INR. In contrast to warfarin, NOACs are direct-acting agents (hence also known as “direct oral anticoagulants” or DOACs) that are selective for one specific coagulation factor, either thrombin (e.g., dabigatran) or factor Xa (e.g., rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban, all with an “X” in their names).
NOACS have been studied and approved by the Food and Drug Administration for nonvalvular AF, i.e., patients without rheumatic mitral stenosis, mechanical or bioprosthetic heart valve, or prior mitral valve repair. Compared to warfarin, NOACS have fewer drug or food interactions, have more predictable pharmacokinetics, and may be associated with reduced risk of major bleeding depending on the agent. The latter is a particularly attractive feature of NOAC therapy, especially when its use is considered among older patients at risk of intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), such as those with previous strokes, ICH, or reduced renal function. Unfortunately, data on the efficacy and safety of the use of NOACs in certain patient populations (e.g., those with severe renal insufficiency, active malignancy, the elderly, patients with suboptimal medication adherence) are generally lacking.
Overview of the data
There are no randomized controlled trials (RCTs) addressing the clinical benefits of switching from warfarin to NOAC therapy. However, based on a number of RCTs comparing warfarin to individual NOACs and their related meta-analyses, the following conclusions may be made about their attributes:
1. Noninferiority to warfarin in reducing the risk of ischemic stroke in AF.
2. Association with a lower rate of major bleeds (statistically significant or trend) and a lower rate of ICH and hemorrhagic strokes compared to warfarin.
3. Association with a higher rate of gastrointestinal bleeding compared to warfarin (except for apixaban, low-dose dabigatran, and edoxaban1).
4. Association with a decreased rate of all stroke and thromboembolism events compared to warfarin.
5. Association with a slightly decreased all-cause mortality in AF compared to warfarin in many studies,2-8 but not all.1,9
6. Noninferiority to warfarin in all-cause mortality in patients with VTE and for its secondary prevention.1,4
NOACS should be used with caution or avoided altogether in patients with severe liver disease or renal insufficiency (see Table 1). 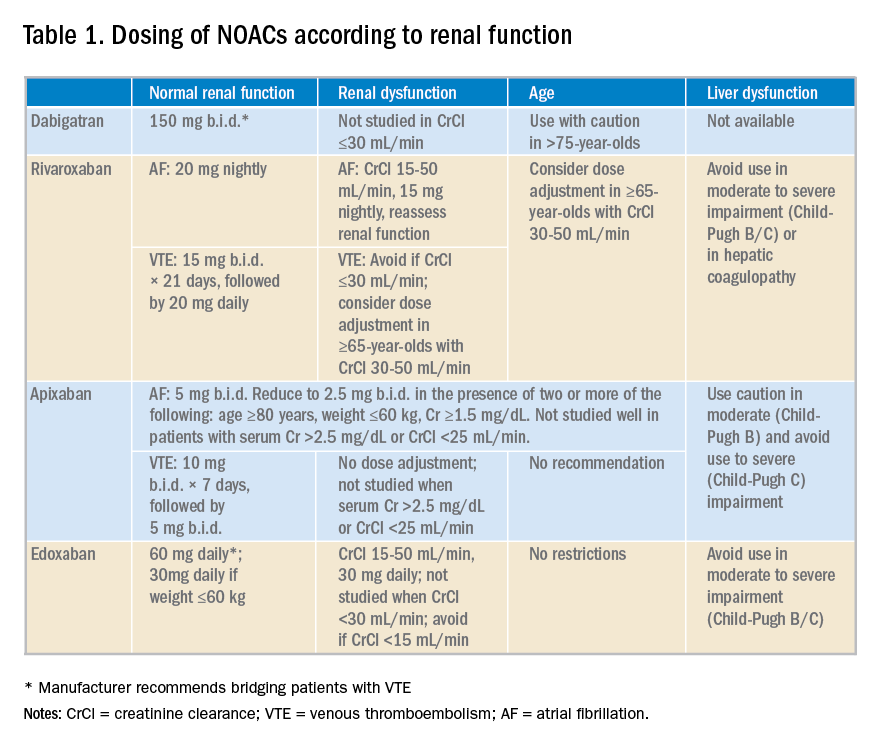
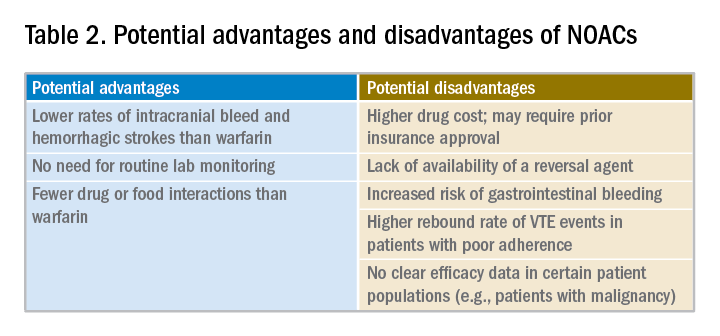
Potential advantages and disadvantages of NOAC therapy are listed in Table 2.
It should be emphasized that in patients with cancer or hypercoagulable state, no clear efficacy or safety data are currently available for the use of NOACs.
The 2016 CHEST guideline on antithrombotic therapy for VTE recommends NOACs over warfarin.10 The 2012 European Society of Cardiology AF guidelines also recommend NOACs over warfarin.11 However, the 2014 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/Heart Rhythm Society guidelines on AF state that it is not necessary to change to a NOAC when patients are “stable, easily controlled, and satisfied with warfarin therapy.”12
Data from a relatively small, short-term study examining the safety of switching patients from warfarin to a NOAC suggest that although bleeding events are relatively common (12%) following such a switch, major bleeding and cardiac or cerebrovascular events are rare.10
Application of the data to our original case
Given a high calculated CHADS2VASC score of 8 in our patient, she has a clear indication for anticoagulation for AF. Her history of labile INRs, ischemic stroke, and moderate renal insufficiency place her at high risk for ICH.
A NOAC may reduce this risk but possibly at the expense of an increased risk for a gastrointestinal bleed. More importantly, however, she may be a good candidate for a switch to a NOAC because of her labile INRs despite good medication adherence. Her warfarin can be held while hospitalized and a NOAC may be initiated when the INR falls below 2.
Prior to discharge, potential cost of the drug to the patient should be explored and discussed. It is also important to involve the primary care physician in the decision-making process. Ultimately, selection of an appropriate NOAC should be based on a careful review of its risks and benefits, clinical factors, patient preference, and shared decision making.
Bottom line
Hospitalists are in a great position to discuss a switch to a NOAC in selected patients with history of good medication adherence and labile INRs or ICH risk factors.
Dr. Geisler, Dr. Liao, and Dr. Manian are hospitalists at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
References
1. Sharma M et al. Efficacy and harms of direct oral anticoagulants in the elderly for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation and secondary prevention of venous thromboembolism: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation. 2015;132(3):194-204.
2. Ruff CT et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet. 2014;383(9921):955-62.
3. Dentali F et al. Efficacy and safety of the novel oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Circulation. 2012;126(20):2381-91.
4. Adam SS et al. Comparative effectiveness of warfarin and new oral anticoagulants for the management of atrial fibrillation and venous thromboembolism: A systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2012;157(11):796-807.
5. Bruins Slot KM and Berge E. Factor Xa inhibitors versus vitamin K antagonists for preventing cerebral or systemic embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013(8):CD008980.
6. Gomez-Outes A et al. Dabigatran, rivaroxaban, or apixaban versus warfarin in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of subgroups. Thrombosis. 2013;2013:640723.
7. Miller CS et al. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants (dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban) versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 2012;110(3):453-60.
8. Baker WL and Phung OJ. Systematic review and adjusted indirect comparison meta-analysis of oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2012;5(5):711-19.
9. Ntaios G et al. Nonvitamin-K-antagonist oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation and previous stroke or transient ischemic attack: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stroke. 2012;43(12):3298-304.
10. Kearon C et al. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest. 2016;149(2):315-52.
11. Camm AJ et al. 2012 focused update of the ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation – developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. Europace. 2012;14(10):1385-413.
12. January CT et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on practice guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2014;130(23):e199-267.
Quiz
When considering a switch from warfarin to a NOAC, all the following factors should be considered a potential advantage, except:
A. No need for routing lab monitoring.
B. Lower risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
C. Fewer drug interactions.
D. Lower rates of intracranial bleed and hemorrhagic stroke.
The correct answer is B. NOACs have been associated with lower risk of intracranial bleed and hemorrhagic stroke but not gastrointestinal bleed. Routine lab monitoring is not necessary during their use and they are associated with fewer drug interactions compared to warfarin.
Key Points
- NOACs represent a clear advancement in our anticoagulation armamentarium.
- Potential advantages of their use include lower rates of intracranial bleed and hemorrhagic strokes, fewer drug or food interactions, and lack of need for routing lab monitoring.
- Potential disadvantages of their use include increased rates of gastrointestinal bleed with some agents, general lack of availability of reversal agents, higher drug cost, unsuitability in patients with poor medication compliance, and lack of efficacy data in certain patient populations.
- Decision to switch from warfarin to a NOAC should thoroughly consider its pros and cons, clinical factors, and patient preferences.
Hospitalists must consider clinical factors and patient preferences
Hospitalists must consider clinical factors and patient preferences
Case
A 70-year old woman with hypertension, diabetes, nonischemic stroke, moderate renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance [CrCl] 45 mL/min), heart failure, and nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AF) on warfarin is admitted because of a very supratherapeutic INR. She reports labile INR values despite strict adherence to her medication regimen. Her cancer screening tests had previously been unremarkable. She inquires about the risks and benefits of switching to a novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) as advertised on television. Should you consider it while she is still in the hospital?
Brief overview of the issue
Lifelong anticoagulation therapy is common among patients with AF or recurrent venous thromboembolism (VTE). Until the advent of NOACs, a great majority of patients were prescribed warfarin, the oral vitamin K antagonist that requires regular blood tests for monitoring of the INR. In contrast to warfarin, NOACs are direct-acting agents (hence also known as “direct oral anticoagulants” or DOACs) that are selective for one specific coagulation factor, either thrombin (e.g., dabigatran) or factor Xa (e.g., rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban, all with an “X” in their names).
NOACS have been studied and approved by the Food and Drug Administration for nonvalvular AF, i.e., patients without rheumatic mitral stenosis, mechanical or bioprosthetic heart valve, or prior mitral valve repair. Compared to warfarin, NOACS have fewer drug or food interactions, have more predictable pharmacokinetics, and may be associated with reduced risk of major bleeding depending on the agent. The latter is a particularly attractive feature of NOAC therapy, especially when its use is considered among older patients at risk of intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), such as those with previous strokes, ICH, or reduced renal function. Unfortunately, data on the efficacy and safety of the use of NOACs in certain patient populations (e.g., those with severe renal insufficiency, active malignancy, the elderly, patients with suboptimal medication adherence) are generally lacking.
Overview of the data
There are no randomized controlled trials (RCTs) addressing the clinical benefits of switching from warfarin to NOAC therapy. However, based on a number of RCTs comparing warfarin to individual NOACs and their related meta-analyses, the following conclusions may be made about their attributes:
1. Noninferiority to warfarin in reducing the risk of ischemic stroke in AF.
2. Association with a lower rate of major bleeds (statistically significant or trend) and a lower rate of ICH and hemorrhagic strokes compared to warfarin.
3. Association with a higher rate of gastrointestinal bleeding compared to warfarin (except for apixaban, low-dose dabigatran, and edoxaban1).
4. Association with a decreased rate of all stroke and thromboembolism events compared to warfarin.
5. Association with a slightly decreased all-cause mortality in AF compared to warfarin in many studies,2-8 but not all.1,9
6. Noninferiority to warfarin in all-cause mortality in patients with VTE and for its secondary prevention.1,4
NOACS should be used with caution or avoided altogether in patients with severe liver disease or renal insufficiency (see Table 1). 
Potential advantages and disadvantages of NOAC therapy are listed in Table 2.

It should be emphasized that in patients with cancer or hypercoagulable state, no clear efficacy or safety data are currently available for the use of NOACs.
The 2016 CHEST guideline on antithrombotic therapy for VTE recommends NOACs over warfarin.10 The 2012 European Society of Cardiology AF guidelines also recommend NOACs over warfarin.11 However, the 2014 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/Heart Rhythm Society guidelines on AF state that it is not necessary to change to a NOAC when patients are “stable, easily controlled, and satisfied with warfarin therapy.”12
Data from a relatively small, short-term study examining the safety of switching patients from warfarin to a NOAC suggest that although bleeding events are relatively common (12%) following such a switch, major bleeding and cardiac or cerebrovascular events are rare.10
Application of the data to our original case
Given a high calculated CHADS2VASC score of 8 in our patient, she has a clear indication for anticoagulation for AF. Her history of labile INRs, ischemic stroke, and moderate renal insufficiency place her at high risk for ICH.
A NOAC may reduce this risk but possibly at the expense of an increased risk for a gastrointestinal bleed. More importantly, however, she may be a good candidate for a switch to a NOAC because of her labile INRs despite good medication adherence. Her warfarin can be held while hospitalized and a NOAC may be initiated when the INR falls below 2.
Prior to discharge, potential cost of the drug to the patient should be explored and discussed. It is also important to involve the primary care physician in the decision-making process. Ultimately, selection of an appropriate NOAC should be based on a careful review of its risks and benefits, clinical factors, patient preference, and shared decision making.
Bottom line
Hospitalists are in a great position to discuss a switch to a NOAC in selected patients with history of good medication adherence and labile INRs or ICH risk factors.
Dr. Geisler, Dr. Liao, and Dr. Manian are hospitalists at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
References
1. Sharma M et al. Efficacy and harms of direct oral anticoagulants in the elderly for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation and secondary prevention of venous thromboembolism: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation. 2015;132(3):194-204.
2. Ruff CT et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet. 2014;383(9921):955-62.
3. Dentali F et al. Efficacy and safety of the novel oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Circulation. 2012;126(20):2381-91.
4. Adam SS et al. Comparative effectiveness of warfarin and new oral anticoagulants for the management of atrial fibrillation and venous thromboembolism: A systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2012;157(11):796-807.
5. Bruins Slot KM and Berge E. Factor Xa inhibitors versus vitamin K antagonists for preventing cerebral or systemic embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013(8):CD008980.
6. Gomez-Outes A et al. Dabigatran, rivaroxaban, or apixaban versus warfarin in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of subgroups. Thrombosis. 2013;2013:640723.
7. Miller CS et al. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants (dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban) versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 2012;110(3):453-60.
8. Baker WL and Phung OJ. Systematic review and adjusted indirect comparison meta-analysis of oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2012;5(5):711-19.
9. Ntaios G et al. Nonvitamin-K-antagonist oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation and previous stroke or transient ischemic attack: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stroke. 2012;43(12):3298-304.
10. Kearon C et al. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest. 2016;149(2):315-52.
11. Camm AJ et al. 2012 focused update of the ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation – developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. Europace. 2012;14(10):1385-413.
12. January CT et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on practice guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2014;130(23):e199-267.
Quiz
When considering a switch from warfarin to a NOAC, all the following factors should be considered a potential advantage, except:
A. No need for routing lab monitoring.
B. Lower risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
C. Fewer drug interactions.
D. Lower rates of intracranial bleed and hemorrhagic stroke.
The correct answer is B. NOACs have been associated with lower risk of intracranial bleed and hemorrhagic stroke but not gastrointestinal bleed. Routine lab monitoring is not necessary during their use and they are associated with fewer drug interactions compared to warfarin.
Key Points
- NOACs represent a clear advancement in our anticoagulation armamentarium.
- Potential advantages of their use include lower rates of intracranial bleed and hemorrhagic strokes, fewer drug or food interactions, and lack of need for routing lab monitoring.
- Potential disadvantages of their use include increased rates of gastrointestinal bleed with some agents, general lack of availability of reversal agents, higher drug cost, unsuitability in patients with poor medication compliance, and lack of efficacy data in certain patient populations.
- Decision to switch from warfarin to a NOAC should thoroughly consider its pros and cons, clinical factors, and patient preferences.
Case
A 70-year old woman with hypertension, diabetes, nonischemic stroke, moderate renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance [CrCl] 45 mL/min), heart failure, and nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AF) on warfarin is admitted because of a very supratherapeutic INR. She reports labile INR values despite strict adherence to her medication regimen. Her cancer screening tests had previously been unremarkable. She inquires about the risks and benefits of switching to a novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) as advertised on television. Should you consider it while she is still in the hospital?
Brief overview of the issue
Lifelong anticoagulation therapy is common among patients with AF or recurrent venous thromboembolism (VTE). Until the advent of NOACs, a great majority of patients were prescribed warfarin, the oral vitamin K antagonist that requires regular blood tests for monitoring of the INR. In contrast to warfarin, NOACs are direct-acting agents (hence also known as “direct oral anticoagulants” or DOACs) that are selective for one specific coagulation factor, either thrombin (e.g., dabigatran) or factor Xa (e.g., rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban, all with an “X” in their names).
NOACS have been studied and approved by the Food and Drug Administration for nonvalvular AF, i.e., patients without rheumatic mitral stenosis, mechanical or bioprosthetic heart valve, or prior mitral valve repair. Compared to warfarin, NOACS have fewer drug or food interactions, have more predictable pharmacokinetics, and may be associated with reduced risk of major bleeding depending on the agent. The latter is a particularly attractive feature of NOAC therapy, especially when its use is considered among older patients at risk of intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), such as those with previous strokes, ICH, or reduced renal function. Unfortunately, data on the efficacy and safety of the use of NOACs in certain patient populations (e.g., those with severe renal insufficiency, active malignancy, the elderly, patients with suboptimal medication adherence) are generally lacking.
Overview of the data
There are no randomized controlled trials (RCTs) addressing the clinical benefits of switching from warfarin to NOAC therapy. However, based on a number of RCTs comparing warfarin to individual NOACs and their related meta-analyses, the following conclusions may be made about their attributes:
1. Noninferiority to warfarin in reducing the risk of ischemic stroke in AF.
2. Association with a lower rate of major bleeds (statistically significant or trend) and a lower rate of ICH and hemorrhagic strokes compared to warfarin.
3. Association with a higher rate of gastrointestinal bleeding compared to warfarin (except for apixaban, low-dose dabigatran, and edoxaban1).
4. Association with a decreased rate of all stroke and thromboembolism events compared to warfarin.
5. Association with a slightly decreased all-cause mortality in AF compared to warfarin in many studies,2-8 but not all.1,9
6. Noninferiority to warfarin in all-cause mortality in patients with VTE and for its secondary prevention.1,4
NOACS should be used with caution or avoided altogether in patients with severe liver disease or renal insufficiency (see Table 1). 
Potential advantages and disadvantages of NOAC therapy are listed in Table 2.

It should be emphasized that in patients with cancer or hypercoagulable state, no clear efficacy or safety data are currently available for the use of NOACs.
The 2016 CHEST guideline on antithrombotic therapy for VTE recommends NOACs over warfarin.10 The 2012 European Society of Cardiology AF guidelines also recommend NOACs over warfarin.11 However, the 2014 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/Heart Rhythm Society guidelines on AF state that it is not necessary to change to a NOAC when patients are “stable, easily controlled, and satisfied with warfarin therapy.”12
Data from a relatively small, short-term study examining the safety of switching patients from warfarin to a NOAC suggest that although bleeding events are relatively common (12%) following such a switch, major bleeding and cardiac or cerebrovascular events are rare.10
Application of the data to our original case
Given a high calculated CHADS2VASC score of 8 in our patient, she has a clear indication for anticoagulation for AF. Her history of labile INRs, ischemic stroke, and moderate renal insufficiency place her at high risk for ICH.
A NOAC may reduce this risk but possibly at the expense of an increased risk for a gastrointestinal bleed. More importantly, however, she may be a good candidate for a switch to a NOAC because of her labile INRs despite good medication adherence. Her warfarin can be held while hospitalized and a NOAC may be initiated when the INR falls below 2.
Prior to discharge, potential cost of the drug to the patient should be explored and discussed. It is also important to involve the primary care physician in the decision-making process. Ultimately, selection of an appropriate NOAC should be based on a careful review of its risks and benefits, clinical factors, patient preference, and shared decision making.
Bottom line
Hospitalists are in a great position to discuss a switch to a NOAC in selected patients with history of good medication adherence and labile INRs or ICH risk factors.
Dr. Geisler, Dr. Liao, and Dr. Manian are hospitalists at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
References
1. Sharma M et al. Efficacy and harms of direct oral anticoagulants in the elderly for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation and secondary prevention of venous thromboembolism: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation. 2015;132(3):194-204.
2. Ruff CT et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet. 2014;383(9921):955-62.
3. Dentali F et al. Efficacy and safety of the novel oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Circulation. 2012;126(20):2381-91.
4. Adam SS et al. Comparative effectiveness of warfarin and new oral anticoagulants for the management of atrial fibrillation and venous thromboembolism: A systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2012;157(11):796-807.
5. Bruins Slot KM and Berge E. Factor Xa inhibitors versus vitamin K antagonists for preventing cerebral or systemic embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013(8):CD008980.
6. Gomez-Outes A et al. Dabigatran, rivaroxaban, or apixaban versus warfarin in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of subgroups. Thrombosis. 2013;2013:640723.
7. Miller CS et al. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants (dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban) versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 2012;110(3):453-60.
8. Baker WL and Phung OJ. Systematic review and adjusted indirect comparison meta-analysis of oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2012;5(5):711-19.
9. Ntaios G et al. Nonvitamin-K-antagonist oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation and previous stroke or transient ischemic attack: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stroke. 2012;43(12):3298-304.
10. Kearon C et al. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest. 2016;149(2):315-52.
11. Camm AJ et al. 2012 focused update of the ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation – developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. Europace. 2012;14(10):1385-413.
12. January CT et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on practice guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2014;130(23):e199-267.
Quiz
When considering a switch from warfarin to a NOAC, all the following factors should be considered a potential advantage, except:
A. No need for routing lab monitoring.
B. Lower risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
C. Fewer drug interactions.
D. Lower rates of intracranial bleed and hemorrhagic stroke.
The correct answer is B. NOACs have been associated with lower risk of intracranial bleed and hemorrhagic stroke but not gastrointestinal bleed. Routine lab monitoring is not necessary during their use and they are associated with fewer drug interactions compared to warfarin.
Key Points
- NOACs represent a clear advancement in our anticoagulation armamentarium.
- Potential advantages of their use include lower rates of intracranial bleed and hemorrhagic strokes, fewer drug or food interactions, and lack of need for routing lab monitoring.
- Potential disadvantages of their use include increased rates of gastrointestinal bleed with some agents, general lack of availability of reversal agents, higher drug cost, unsuitability in patients with poor medication compliance, and lack of efficacy data in certain patient populations.
- Decision to switch from warfarin to a NOAC should thoroughly consider its pros and cons, clinical factors, and patient preferences.


