User login
One of the most difficult challenges in staffing a hospitalist practice is handling the unpredictable daily fluctuations in patient volume. It isn’t difficult to decide how many hospitalists will work each day to handle the average number of daily visits (aka encounters), but the actual number of visits on any given day is almost always significantly different than the average. I think many groups could more effectively handle day-to-day variations in workload by eliminating predetermined lengths of the shifts that the doctors work. It isn’t a perfect strategy, but it is worth some consideration by nearly any practice. Let me explain.
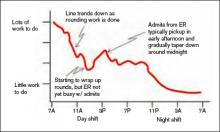
First, think about how the workload for a typical day might be represented. For many or most practices it often looks something like the wavy line in Figure 1. (See Figure 1, p. 52.)
Of course, the line representing a day’s work will be different every day, but I’ve tried to draw it in a way that represents a typical day.
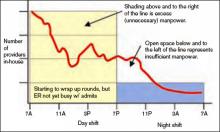
In Figure 2 (see p. 52), I’ve added horizontal bars to represent a common way that groups might schedule four daytime doctors who each work 7 a.m. to 7 p.m., and one night doctor working 7 p.m. to 7 a.m. The four horizontal bars represent the four day doctors, and the one horizontal bar at the bottom right represents the one night doctor. Ideally, the manpower (horizontal bars) should match the workload (wavy line) every hour of the day.
This graph shows that—at least for this particular day—there are many hours in the afternoon when there is excess manpower. The doctors may be sitting around waiting for their shift to end or waiting to see if it will suddenly get busy again. We all know that happens unpredictably. And from about 7 p.m. to about 11:30 p.m., the single night doctor has more work than he/she can reasonably handle.
In fact, there probably isn’t ever a day when the work that needs to be done is just the right amount for all four doctors from 7 a.m. to 7 p.m. with a sudden drop at 7 p.m. that is just right for one doctor for the next 12 hours. Because the doctors have scheduled themselves to work 12-hour shifts, they know in advance that their manpower will quite regularly fail to match the workload for that day.
Groups have devised a number of strategies to try to get manpower to more closely match the unpredictable workload for a given day. These include having a member of the group available on standby (often called “jeopardy”) for that day; this physician comes in only if it is unusually busy. Some groups have a patient volume cap to prevent the practice from becoming too busy. I think a cap is a poor strategy that should be used only as a last resort, and I will discuss this in detail in a future column. Other groups have a swing shift from late in the afternoon until around 11 p.m. or so to help with evening admits and cross cover. And an often overlooked but potentially valuable strategy is to eliminate clearly specified start and stop times for the shifts that the doctors work. For an idea of what that might look like, see Figure 3 (p. 52).
Notice that the right-hand side of each yellow bar in Figures 2 and 3 is indistinct. That is meant to show that the precise time that the doctor leaves varies, depending on the day’s workload. That way the manpower can be adjusted from one day to the next to more closely match the workload than if the doctors work fixed shifts of a specified duration. On some days, all of the doctors may stay 12 hours or more, but on many days at least some of the doctors will end up leaving in less than 12 hours. If all day doctors work a 12-hour shift, they have provided 48 hours—four doctors at 12 hours each—of physician manpower, but if there is some flexibility about when the doctors leave, the same four day doctors could provide between about 34 and 52 hours of manpower, depending on the day’s workload.
If your practice is contracted to keep a doctor in the hospital around the clock, you will probably need the night doctor and at least one day doctor to stay around—even if it is a slow day. But the other doctors might be able to leave when their work is done. And it is also reasonable for some groups to eliminate precise times that the doctors start working in the morning each day, though they might be required to be available by pager by a specified time in the morning.
One common concern about such a system is how to handle issues that arise with the patients cared for by a doctor who has left. I think it is best for the doctor to stay available by pager and handle simple issues by phone. For more complicated issues (e.g., a patient who needs attention at the bedside) the doctor could either come back to the hospital or phone another member of the practice (e.g., the doctor required to stay at least 12 hours that day) and see if he or she can handle the emergency.
All of the specifics of a system that allows doctors to leave when their work is done rather than according to shifts of a predetermined number of hours would be too long for this column. But they aren’t complicated, and given the variability that exists in the number of daily patient visits to any hospitalist practice, the application of this kind of approach is well worth considering. TH
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988 and is a co-founder and past-president of SHM. He is a principal in Nelson/Flores Associates, a national hospitalist practice management consulting firm. This column represents his views and is not intended to reflect an official position of SHM.
One of the most difficult challenges in staffing a hospitalist practice is handling the unpredictable daily fluctuations in patient volume. It isn’t difficult to decide how many hospitalists will work each day to handle the average number of daily visits (aka encounters), but the actual number of visits on any given day is almost always significantly different than the average. I think many groups could more effectively handle day-to-day variations in workload by eliminating predetermined lengths of the shifts that the doctors work. It isn’t a perfect strategy, but it is worth some consideration by nearly any practice. Let me explain.
First, think about how the workload for a typical day might be represented. For many or most practices it often looks something like the wavy line in Figure 1. (See Figure 1, p. 52.)
Of course, the line representing a day’s work will be different every day, but I’ve tried to draw it in a way that represents a typical day.
In Figure 2 (see p. 52), I’ve added horizontal bars to represent a common way that groups might schedule four daytime doctors who each work 7 a.m. to 7 p.m., and one night doctor working 7 p.m. to 7 a.m. The four horizontal bars represent the four day doctors, and the one horizontal bar at the bottom right represents the one night doctor. Ideally, the manpower (horizontal bars) should match the workload (wavy line) every hour of the day.
This graph shows that—at least for this particular day—there are many hours in the afternoon when there is excess manpower. The doctors may be sitting around waiting for their shift to end or waiting to see if it will suddenly get busy again. We all know that happens unpredictably. And from about 7 p.m. to about 11:30 p.m., the single night doctor has more work than he/she can reasonably handle.
In fact, there probably isn’t ever a day when the work that needs to be done is just the right amount for all four doctors from 7 a.m. to 7 p.m. with a sudden drop at 7 p.m. that is just right for one doctor for the next 12 hours. Because the doctors have scheduled themselves to work 12-hour shifts, they know in advance that their manpower will quite regularly fail to match the workload for that day.
Groups have devised a number of strategies to try to get manpower to more closely match the unpredictable workload for a given day. These include having a member of the group available on standby (often called “jeopardy”) for that day; this physician comes in only if it is unusually busy. Some groups have a patient volume cap to prevent the practice from becoming too busy. I think a cap is a poor strategy that should be used only as a last resort, and I will discuss this in detail in a future column. Other groups have a swing shift from late in the afternoon until around 11 p.m. or so to help with evening admits and cross cover. And an often overlooked but potentially valuable strategy is to eliminate clearly specified start and stop times for the shifts that the doctors work. For an idea of what that might look like, see Figure 3 (p. 52).
Notice that the right-hand side of each yellow bar in Figures 2 and 3 is indistinct. That is meant to show that the precise time that the doctor leaves varies, depending on the day’s workload. That way the manpower can be adjusted from one day to the next to more closely match the workload than if the doctors work fixed shifts of a specified duration. On some days, all of the doctors may stay 12 hours or more, but on many days at least some of the doctors will end up leaving in less than 12 hours. If all day doctors work a 12-hour shift, they have provided 48 hours—four doctors at 12 hours each—of physician manpower, but if there is some flexibility about when the doctors leave, the same four day doctors could provide between about 34 and 52 hours of manpower, depending on the day’s workload.
If your practice is contracted to keep a doctor in the hospital around the clock, you will probably need the night doctor and at least one day doctor to stay around—even if it is a slow day. But the other doctors might be able to leave when their work is done. And it is also reasonable for some groups to eliminate precise times that the doctors start working in the morning each day, though they might be required to be available by pager by a specified time in the morning.
One common concern about such a system is how to handle issues that arise with the patients cared for by a doctor who has left. I think it is best for the doctor to stay available by pager and handle simple issues by phone. For more complicated issues (e.g., a patient who needs attention at the bedside) the doctor could either come back to the hospital or phone another member of the practice (e.g., the doctor required to stay at least 12 hours that day) and see if he or she can handle the emergency.
All of the specifics of a system that allows doctors to leave when their work is done rather than according to shifts of a predetermined number of hours would be too long for this column. But they aren’t complicated, and given the variability that exists in the number of daily patient visits to any hospitalist practice, the application of this kind of approach is well worth considering. TH
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988 and is a co-founder and past-president of SHM. He is a principal in Nelson/Flores Associates, a national hospitalist practice management consulting firm. This column represents his views and is not intended to reflect an official position of SHM.
One of the most difficult challenges in staffing a hospitalist practice is handling the unpredictable daily fluctuations in patient volume. It isn’t difficult to decide how many hospitalists will work each day to handle the average number of daily visits (aka encounters), but the actual number of visits on any given day is almost always significantly different than the average. I think many groups could more effectively handle day-to-day variations in workload by eliminating predetermined lengths of the shifts that the doctors work. It isn’t a perfect strategy, but it is worth some consideration by nearly any practice. Let me explain.
First, think about how the workload for a typical day might be represented. For many or most practices it often looks something like the wavy line in Figure 1. (See Figure 1, p. 52.)
Of course, the line representing a day’s work will be different every day, but I’ve tried to draw it in a way that represents a typical day.
In Figure 2 (see p. 52), I’ve added horizontal bars to represent a common way that groups might schedule four daytime doctors who each work 7 a.m. to 7 p.m., and one night doctor working 7 p.m. to 7 a.m. The four horizontal bars represent the four day doctors, and the one horizontal bar at the bottom right represents the one night doctor. Ideally, the manpower (horizontal bars) should match the workload (wavy line) every hour of the day.
This graph shows that—at least for this particular day—there are many hours in the afternoon when there is excess manpower. The doctors may be sitting around waiting for their shift to end or waiting to see if it will suddenly get busy again. We all know that happens unpredictably. And from about 7 p.m. to about 11:30 p.m., the single night doctor has more work than he/she can reasonably handle.
In fact, there probably isn’t ever a day when the work that needs to be done is just the right amount for all four doctors from 7 a.m. to 7 p.m. with a sudden drop at 7 p.m. that is just right for one doctor for the next 12 hours. Because the doctors have scheduled themselves to work 12-hour shifts, they know in advance that their manpower will quite regularly fail to match the workload for that day.
Groups have devised a number of strategies to try to get manpower to more closely match the unpredictable workload for a given day. These include having a member of the group available on standby (often called “jeopardy”) for that day; this physician comes in only if it is unusually busy. Some groups have a patient volume cap to prevent the practice from becoming too busy. I think a cap is a poor strategy that should be used only as a last resort, and I will discuss this in detail in a future column. Other groups have a swing shift from late in the afternoon until around 11 p.m. or so to help with evening admits and cross cover. And an often overlooked but potentially valuable strategy is to eliminate clearly specified start and stop times for the shifts that the doctors work. For an idea of what that might look like, see Figure 3 (p. 52).
Notice that the right-hand side of each yellow bar in Figures 2 and 3 is indistinct. That is meant to show that the precise time that the doctor leaves varies, depending on the day’s workload. That way the manpower can be adjusted from one day to the next to more closely match the workload than if the doctors work fixed shifts of a specified duration. On some days, all of the doctors may stay 12 hours or more, but on many days at least some of the doctors will end up leaving in less than 12 hours. If all day doctors work a 12-hour shift, they have provided 48 hours—four doctors at 12 hours each—of physician manpower, but if there is some flexibility about when the doctors leave, the same four day doctors could provide between about 34 and 52 hours of manpower, depending on the day’s workload.
If your practice is contracted to keep a doctor in the hospital around the clock, you will probably need the night doctor and at least one day doctor to stay around—even if it is a slow day. But the other doctors might be able to leave when their work is done. And it is also reasonable for some groups to eliminate precise times that the doctors start working in the morning each day, though they might be required to be available by pager by a specified time in the morning.
One common concern about such a system is how to handle issues that arise with the patients cared for by a doctor who has left. I think it is best for the doctor to stay available by pager and handle simple issues by phone. For more complicated issues (e.g., a patient who needs attention at the bedside) the doctor could either come back to the hospital or phone another member of the practice (e.g., the doctor required to stay at least 12 hours that day) and see if he or she can handle the emergency.
All of the specifics of a system that allows doctors to leave when their work is done rather than according to shifts of a predetermined number of hours would be too long for this column. But they aren’t complicated, and given the variability that exists in the number of daily patient visits to any hospitalist practice, the application of this kind of approach is well worth considering. TH
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988 and is a co-founder and past-president of SHM. He is a principal in Nelson/Flores Associates, a national hospitalist practice management consulting firm. This column represents his views and is not intended to reflect an official position of SHM.