User login
Intravenous albumin is a human-derived blood product studied widely in a variety of patient populations. Despite its frequent use in critical care, few high-quality studies have demonstrated improvements in patient-important outcomes. Compared with crystalloids, albumin increases the risk of fluid overload and bleeding and infections in patients undergoing cardiac surgery.1,2 In addition, albumin is costly, and its production is fraught with donor supply chain ethical concerns (the majority of albumin is derived from paid plasma donors).
Albumin use is highly variable between countries, hospitals, and even clinicians within the same specialty due to several factors, including the perception of minimal risk with albumin, concerns regarding insufficient short-term hemodynamic response to crystalloid, and lack of high-quality evidence to inform clinical practice. We will discuss when intensivists should consider albumin use (with prescription personalized to patient context) and when it should be avoided due to the concerns for patient harm.
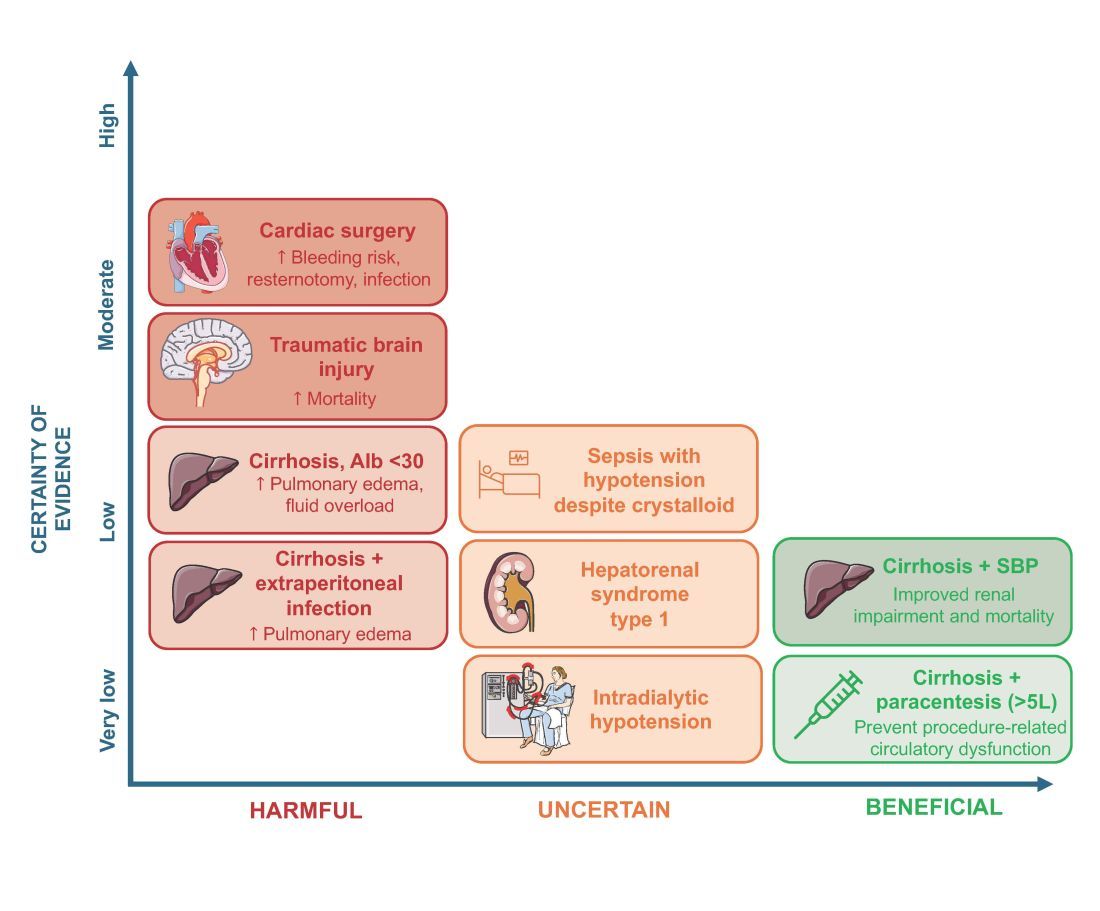
An intensivist might consider albumin as a reasonable treatment option in patients with cirrhosis undergoing large volume paracentesis to prevent paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction, and in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP), as data suggests use in this setting leads to a reduction in mortality.3 Clinicians should be aware that even for these widely accepted albumin indications, which are supported by published guidelines, the certainty of evidence is low, recommendations are weak (conditional), and, therefore, albumin should always be personalized to the patient based on volume of paracentesis fluid removed, prior history of hypotension after procedures, and degree of renal dysfunction.4
There are also several conditions for which an intensivist might consider albumin and for which albumin is commonly administered but lacks high-quality studies to support its use either as a frontline or rescue fluid therapy. One such condition is type 1 hepatorenal syndrome (HRS), for which albumin is widely used; however, there are no randomized controlled trials that have compared albumin with placebo.
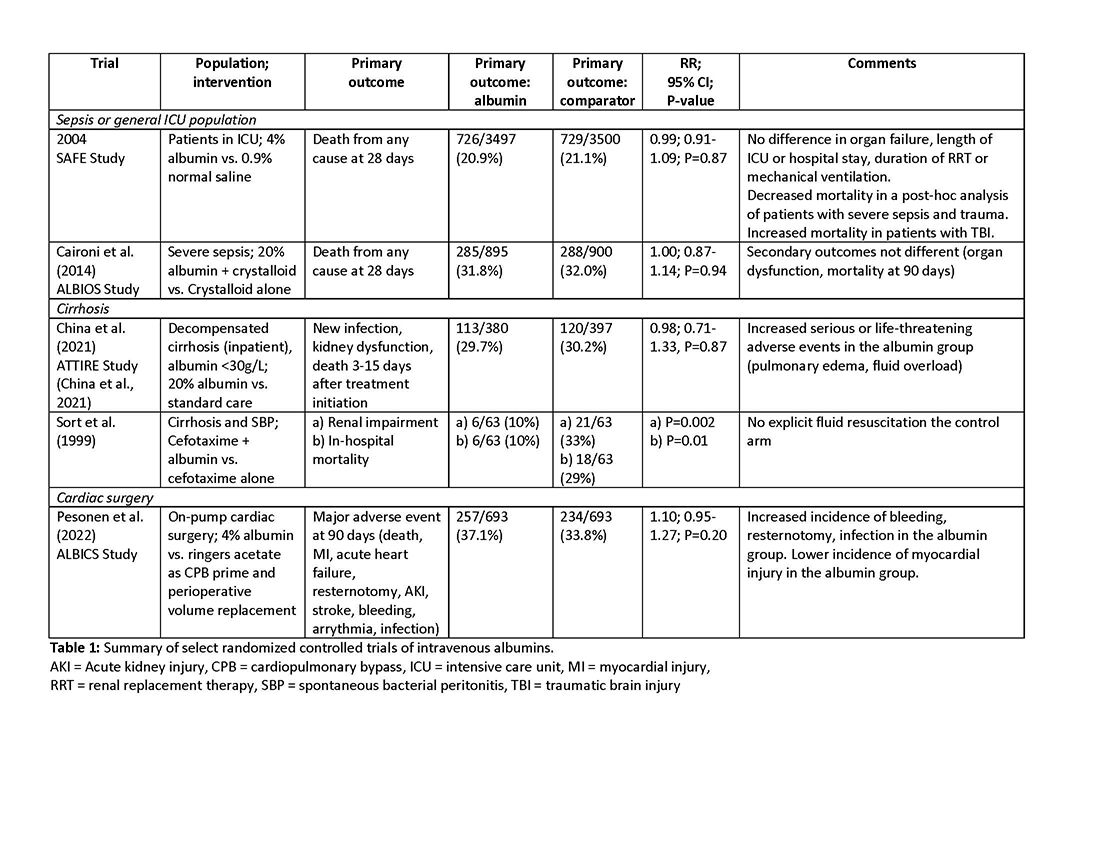
As with any intervention, the use of albumin is associated with risks. In patients undergoing on-pump cardiac surgery, the ALBICS study showed that albumin did not reduce the risk of major adverse events and, instead, increased risk of bleeding, resternotomy, and infection.2 The ATTIRE trial showed that in patients hospitalized with decompensated cirrhosis and serum albumin <30 g/L, albumin failed to reduce infection, renal impairment, or mortality while increasing life-threatening adverse events, including pulmonary edema and fluid overload.1 Similarly, in patients with cirrhosis and extraperitoneal infections, albumin showed no benefit in reducing renal impairment or mortality, and its use was associated with higher rates of pulmonary edema.6 Lastly, critically ill patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) who received fluid resuscitation with albumin have been shown to experience higher mortality compared with saline.7 Thus, based on current evidence, intravenous albumin is not recommended for patients undergoing cardiac surgery (priming of the bypass circuit or volume replacement), patients hospitalized with decompensated cirrhosis and hypoalbuminemia, patients hospitalized with cirrhosis and extraperitoneal infections, and critically ill patients with TBI.4
Overall, intravenous albumin prescription in critical care patients requires a personalized approach informed by current best evidence and is not without potential harm.
High-quality evidence is currently lacking in many clinical settings, and large randomized controlled trials are underway to provide further insights into the utility of albumin. These trials will address albumin use in the following: acute kidney injury requiring renal replacement therapy (ALTER-AKI, NCT04705896), inpatients with community-acquired pneumonia (NCT04071041), high-risk cardiac surgery (ACTRN1261900135516703), and septic shock (NCT03869385).
Financial/nonfinancial disclosures
Nicole Relke: None. Mark Hewitt: None. Bram Rochwerg: None. Jeannie Callum: Research support from Canadian Blood Services and Octapharma.
References
1. China L, Freemantle N, Forrest E, et al. A randomized trial of albumin infusions in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(9):808-817. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2022166
2. Pesonen E, Vlasov H, Suojaranta R, et al. Effect of 4% albumin solution vs ringer acetate on major adverse events in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2022;328(3):251-258. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.10461
3. Sort P, Navasa M, Arroyo V, et al. Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. NEJM. 1999;341:403-409.
4. Callum J, Skubas NJ, Bathla A, et al. Use of intravenous albumin: a guideline from the international collaboration for transfusion medicine guidelines. Chest. 2024:S0012-3692(24)00285-X. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2024.02.049
5. Torp N. High doses of albumin increases mortality and complications in terlipressin treated patients with cirrhosis: insights from the ATTIRE trial. Paper presented at the AASLD; 2023; San Diego, CA. https://www.aasld.org/the-liver-meeting/high-doses-albumin-increases-mortality-and-complications-terlipressin-treated
6. Wong YJ, Qiu TY, Tam YC, Mohan BP, Gallegos-Orozco JF, Adler DG. Efficacy and safety of IV albumin for non-spontaneous bacterial peritonitis infection among patients with cirrhosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Liver Dis. 2020;52(10):1137-1142. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2020.05.047
7. Myburgh J, Cooper JD, Finfer S, et al. Saline or albumin for fluid resuscitation in patients with traumatic brain injury. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(9):874-884.
Intravenous albumin is a human-derived blood product studied widely in a variety of patient populations. Despite its frequent use in critical care, few high-quality studies have demonstrated improvements in patient-important outcomes. Compared with crystalloids, albumin increases the risk of fluid overload and bleeding and infections in patients undergoing cardiac surgery.1,2 In addition, albumin is costly, and its production is fraught with donor supply chain ethical concerns (the majority of albumin is derived from paid plasma donors).
Albumin use is highly variable between countries, hospitals, and even clinicians within the same specialty due to several factors, including the perception of minimal risk with albumin, concerns regarding insufficient short-term hemodynamic response to crystalloid, and lack of high-quality evidence to inform clinical practice. We will discuss when intensivists should consider albumin use (with prescription personalized to patient context) and when it should be avoided due to the concerns for patient harm.
An intensivist might consider albumin as a reasonable treatment option in patients with cirrhosis undergoing large volume paracentesis to prevent paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction, and in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP), as data suggests use in this setting leads to a reduction in mortality.3 Clinicians should be aware that even for these widely accepted albumin indications, which are supported by published guidelines, the certainty of evidence is low, recommendations are weak (conditional), and, therefore, albumin should always be personalized to the patient based on volume of paracentesis fluid removed, prior history of hypotension after procedures, and degree of renal dysfunction.4
There are also several conditions for which an intensivist might consider albumin and for which albumin is commonly administered but lacks high-quality studies to support its use either as a frontline or rescue fluid therapy. One such condition is type 1 hepatorenal syndrome (HRS), for which albumin is widely used; however, there are no randomized controlled trials that have compared albumin with placebo.

As with any intervention, the use of albumin is associated with risks. In patients undergoing on-pump cardiac surgery, the ALBICS study showed that albumin did not reduce the risk of major adverse events and, instead, increased risk of bleeding, resternotomy, and infection.2 The ATTIRE trial showed that in patients hospitalized with decompensated cirrhosis and serum albumin <30 g/L, albumin failed to reduce infection, renal impairment, or mortality while increasing life-threatening adverse events, including pulmonary edema and fluid overload.1 Similarly, in patients with cirrhosis and extraperitoneal infections, albumin showed no benefit in reducing renal impairment or mortality, and its use was associated with higher rates of pulmonary edema.6 Lastly, critically ill patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) who received fluid resuscitation with albumin have been shown to experience higher mortality compared with saline.7 Thus, based on current evidence, intravenous albumin is not recommended for patients undergoing cardiac surgery (priming of the bypass circuit or volume replacement), patients hospitalized with decompensated cirrhosis and hypoalbuminemia, patients hospitalized with cirrhosis and extraperitoneal infections, and critically ill patients with TBI.4
Overall, intravenous albumin prescription in critical care patients requires a personalized approach informed by current best evidence and is not without potential harm.

High-quality evidence is currently lacking in many clinical settings, and large randomized controlled trials are underway to provide further insights into the utility of albumin. These trials will address albumin use in the following: acute kidney injury requiring renal replacement therapy (ALTER-AKI, NCT04705896), inpatients with community-acquired pneumonia (NCT04071041), high-risk cardiac surgery (ACTRN1261900135516703), and septic shock (NCT03869385).
Financial/nonfinancial disclosures
Nicole Relke: None. Mark Hewitt: None. Bram Rochwerg: None. Jeannie Callum: Research support from Canadian Blood Services and Octapharma.
References
1. China L, Freemantle N, Forrest E, et al. A randomized trial of albumin infusions in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(9):808-817. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2022166
2. Pesonen E, Vlasov H, Suojaranta R, et al. Effect of 4% albumin solution vs ringer acetate on major adverse events in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2022;328(3):251-258. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.10461
3. Sort P, Navasa M, Arroyo V, et al. Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. NEJM. 1999;341:403-409.
4. Callum J, Skubas NJ, Bathla A, et al. Use of intravenous albumin: a guideline from the international collaboration for transfusion medicine guidelines. Chest. 2024:S0012-3692(24)00285-X. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2024.02.049
5. Torp N. High doses of albumin increases mortality and complications in terlipressin treated patients with cirrhosis: insights from the ATTIRE trial. Paper presented at the AASLD; 2023; San Diego, CA. https://www.aasld.org/the-liver-meeting/high-doses-albumin-increases-mortality-and-complications-terlipressin-treated
6. Wong YJ, Qiu TY, Tam YC, Mohan BP, Gallegos-Orozco JF, Adler DG. Efficacy and safety of IV albumin for non-spontaneous bacterial peritonitis infection among patients with cirrhosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Liver Dis. 2020;52(10):1137-1142. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2020.05.047
7. Myburgh J, Cooper JD, Finfer S, et al. Saline or albumin for fluid resuscitation in patients with traumatic brain injury. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(9):874-884.
Intravenous albumin is a human-derived blood product studied widely in a variety of patient populations. Despite its frequent use in critical care, few high-quality studies have demonstrated improvements in patient-important outcomes. Compared with crystalloids, albumin increases the risk of fluid overload and bleeding and infections in patients undergoing cardiac surgery.1,2 In addition, albumin is costly, and its production is fraught with donor supply chain ethical concerns (the majority of albumin is derived from paid plasma donors).
Albumin use is highly variable between countries, hospitals, and even clinicians within the same specialty due to several factors, including the perception of minimal risk with albumin, concerns regarding insufficient short-term hemodynamic response to crystalloid, and lack of high-quality evidence to inform clinical practice. We will discuss when intensivists should consider albumin use (with prescription personalized to patient context) and when it should be avoided due to the concerns for patient harm.
An intensivist might consider albumin as a reasonable treatment option in patients with cirrhosis undergoing large volume paracentesis to prevent paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction, and in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP), as data suggests use in this setting leads to a reduction in mortality.3 Clinicians should be aware that even for these widely accepted albumin indications, which are supported by published guidelines, the certainty of evidence is low, recommendations are weak (conditional), and, therefore, albumin should always be personalized to the patient based on volume of paracentesis fluid removed, prior history of hypotension after procedures, and degree of renal dysfunction.4
There are also several conditions for which an intensivist might consider albumin and for which albumin is commonly administered but lacks high-quality studies to support its use either as a frontline or rescue fluid therapy. One such condition is type 1 hepatorenal syndrome (HRS), for which albumin is widely used; however, there are no randomized controlled trials that have compared albumin with placebo.

As with any intervention, the use of albumin is associated with risks. In patients undergoing on-pump cardiac surgery, the ALBICS study showed that albumin did not reduce the risk of major adverse events and, instead, increased risk of bleeding, resternotomy, and infection.2 The ATTIRE trial showed that in patients hospitalized with decompensated cirrhosis and serum albumin <30 g/L, albumin failed to reduce infection, renal impairment, or mortality while increasing life-threatening adverse events, including pulmonary edema and fluid overload.1 Similarly, in patients with cirrhosis and extraperitoneal infections, albumin showed no benefit in reducing renal impairment or mortality, and its use was associated with higher rates of pulmonary edema.6 Lastly, critically ill patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) who received fluid resuscitation with albumin have been shown to experience higher mortality compared with saline.7 Thus, based on current evidence, intravenous albumin is not recommended for patients undergoing cardiac surgery (priming of the bypass circuit or volume replacement), patients hospitalized with decompensated cirrhosis and hypoalbuminemia, patients hospitalized with cirrhosis and extraperitoneal infections, and critically ill patients with TBI.4
Overall, intravenous albumin prescription in critical care patients requires a personalized approach informed by current best evidence and is not without potential harm.

High-quality evidence is currently lacking in many clinical settings, and large randomized controlled trials are underway to provide further insights into the utility of albumin. These trials will address albumin use in the following: acute kidney injury requiring renal replacement therapy (ALTER-AKI, NCT04705896), inpatients with community-acquired pneumonia (NCT04071041), high-risk cardiac surgery (ACTRN1261900135516703), and septic shock (NCT03869385).
Financial/nonfinancial disclosures
Nicole Relke: None. Mark Hewitt: None. Bram Rochwerg: None. Jeannie Callum: Research support from Canadian Blood Services and Octapharma.
References
1. China L, Freemantle N, Forrest E, et al. A randomized trial of albumin infusions in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(9):808-817. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2022166
2. Pesonen E, Vlasov H, Suojaranta R, et al. Effect of 4% albumin solution vs ringer acetate on major adverse events in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2022;328(3):251-258. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.10461
3. Sort P, Navasa M, Arroyo V, et al. Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. NEJM. 1999;341:403-409.
4. Callum J, Skubas NJ, Bathla A, et al. Use of intravenous albumin: a guideline from the international collaboration for transfusion medicine guidelines. Chest. 2024:S0012-3692(24)00285-X. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2024.02.049
5. Torp N. High doses of albumin increases mortality and complications in terlipressin treated patients with cirrhosis: insights from the ATTIRE trial. Paper presented at the AASLD; 2023; San Diego, CA. https://www.aasld.org/the-liver-meeting/high-doses-albumin-increases-mortality-and-complications-terlipressin-treated
6. Wong YJ, Qiu TY, Tam YC, Mohan BP, Gallegos-Orozco JF, Adler DG. Efficacy and safety of IV albumin for non-spontaneous bacterial peritonitis infection among patients with cirrhosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Liver Dis. 2020;52(10):1137-1142. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2020.05.047
7. Myburgh J, Cooper JD, Finfer S, et al. Saline or albumin for fluid resuscitation in patients with traumatic brain injury. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(9):874-884.




