User login
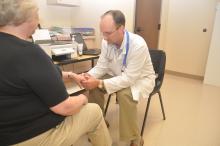
Why More Doctors Are Joining Unions
With huge shifts over the past decade in the way doctors are employed — half of all doctors now work for a health system or large medical group — the idea of unionizing is not only being explored but gaining traction within the profession. In fact, 8% of the physician workforce (or 70,000 physicians) belong to a union, according to statistics gathered in 2022.
Exact numbers are hard to come by, and, interestingly, although the American Medical Association (AMA) “ supports the right of physicians to engage in collective bargaining,” the organization doesn’t track union membership among physicians, according to an AMA spokesperson.
Forming a Union
One challenge is that forming a union is not only time-consuming but also difficult, owing to several barriers. For starters, the laws dictating unionization differ by state, and the rules governing unionization vary if a hospital is public or private. If there’s enough momentum from doctors leading unionization efforts, approval from hospital leaders is required before an official election can be requested from the National Labor Relations Board.
That said, for doctors who are in a union — the two most popular are the Union of American Physicians and Dentists and the Doctors Council branch of the Service Employees International Union (SEIU)—the benefits are immense, especially because union members can focus on what matters, such as providing the best patient care possible.
, reported WBUR in Boston.
Belonging Matters
“When you build a relationship with your patients, it’s special, and that connection isn’t replaceable,” said Nicholas VenOsdel, MD, a pediatrician at Allina Health Primary Care in Hastings, Minnesota, and a union member of the Doctors Council. “However, a lot of us have felt like that hasn’t been respected as the climate of healthcare has changed so fast.”
In fact, autonomy over how much time doctors spend with patients is driving a lot of interest in unionization.
“We don’t necessarily have that autonomy now,” said Amber Higgins, MD, an emergency physician and an obstetrician at ChristianaCare, a hospital network in Newark, Delaware, and a member of the Doctors Council. “There are so many other demands, whether it’s billing, patient documentation, or other demands from the employer, and all of that takes time away from patient care.”
Another primary driver of physician unionization is the physician burnout epidemic. Physicians collectively complain that they spend more time on electronic health record documentation and bureaucratic administration. Yet if unions can improve these working conditions, the benefit to physicians and their patients would be a welcome change.
Union members are bullish and believe that having a cohesive voice will make a difference.
“We need to use our collective voices to get back to focusing on patient care instead of staring at a computer screen for 80% of the day,” Dr. Higgins told this news organization. “So much of medicine involves getting to the correct diagnosis, listening to patients, observing them, and building a relationship with them. We need time to build that.”
With corporate consolidation and a profit-driven mandate by healthcare systems, doctors are increasingly frustrated and feel that their voices haven’t been heard enough when it comes to issues like workplace safety, working hours, and benefits, said Stuart Bussey, MD, JD, a family practice physician and president of the Union of American Physicians and Dentists in Sacramento, California.
However, he adds that urging doctors to join together to fight for a better working environment hasn’t been easy.
“Doctors are individualists, and they don’t know how to work in packs like hospital administrators do,” said Dr. Bussey. “They’re hard to organize, but I want them to understand that unless they join hands, sign petitions, and speak as one voice, they’re going to lose out on an amazing opportunity.”
Overcoming Misperceptions About Unions
One barrier to doctors getting involved is the sentiment that unions might do the opposite of what’s intended — that is, they might further reduce a doctor’s autonomy and work flexibility. Or there may be a perception that the drive to join a union is predicated on making more money.
Though he’s now in a union, Dr. VenOsdel, who has been in a hospital-based practice for 7 years, admits that he initially felt very differently about unions than he does today.
“Even though I have family members in healthcare unions, I had a neutral to even slightly negative view of unions,” said Dr. VenOsdel. “It took me working directly with the Minnesota Nurses Association and the Doctors Council to learn the other side of the story.”
Armed with more information, he began lobbying for stricter rules about how his state’s large healthcare systems were closing hospitals and ending much-needed community services.
“I remember standing at the Capitol in Minnesota and telling one of the members that I once felt negatively about unions,” he added. “I realized then that I only knew what employers were telling me via such things as emails about strikes — that information was all being shared from the employers’ perspective.”
The other misperception is that unions only exist to argue against management, including against colleagues who are also part of the management structure, said Dr. Higgins.
“Some doctors perceive being in a union as ‘how can those same leaders also be in a union,’” she said. She feels that they currently don’t have leadership representing them that can help with such things as restructuring their support teams or getting them help with certain tasks. “That’s another way unions can help.”
Social Justice Plays a Role
For Dr. VenOsdel, being part of a union has helped him return to what he calls the “art” of medicine.
“Philosophically, the union gave me an option for change in what felt like a hopeless situation,” he said. “It wasn’t just that I was tossing the keys to someone else and saying, ‘I can’t fix this.’ Instead, we’re taking the reins back and fixing things ourselves.”
Bussey argues that as the uneven balance between administrators and providers in many healthcare organizations grows, the time to consider forming a union is now.
“We’re in a $4 trillion medical industrial revolution,” he said. “Administrators and bureaucrats are multiplying 30-fold times vs providers, and most of that $4 trillion supports things that don’t contribute to the doctor-patient relationship.”
Furthermore, union proponents say that where a one-on-one relationship between doctor and patient once existed, that has now been “triangulated” to include administrators.
“We’ve lost power in every way,” Dr. Bussey said. “We have the degrees, the liability, and the knowledge — we should have more power to make our workplaces safer and better.”
Ultimately, for some unionized doctors, the very holding of a union card is rooted in supporting social justice issues.
“When doctors realize how powerful a tool a union can be for social justice and change, this will alter perceptions of unions within our profession,” Dr. VenOsdel said. “Our union helps give us a voice to stand up for other staff who aren’t unionized and, most importantly, to stand up for the patients who need us.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With huge shifts over the past decade in the way doctors are employed — half of all doctors now work for a health system or large medical group — the idea of unionizing is not only being explored but gaining traction within the profession. In fact, 8% of the physician workforce (or 70,000 physicians) belong to a union, according to statistics gathered in 2022.
Exact numbers are hard to come by, and, interestingly, although the American Medical Association (AMA) “ supports the right of physicians to engage in collective bargaining,” the organization doesn’t track union membership among physicians, according to an AMA spokesperson.
Forming a Union
One challenge is that forming a union is not only time-consuming but also difficult, owing to several barriers. For starters, the laws dictating unionization differ by state, and the rules governing unionization vary if a hospital is public or private. If there’s enough momentum from doctors leading unionization efforts, approval from hospital leaders is required before an official election can be requested from the National Labor Relations Board.
That said, for doctors who are in a union — the two most popular are the Union of American Physicians and Dentists and the Doctors Council branch of the Service Employees International Union (SEIU)—the benefits are immense, especially because union members can focus on what matters, such as providing the best patient care possible.
, reported WBUR in Boston.
Belonging Matters
“When you build a relationship with your patients, it’s special, and that connection isn’t replaceable,” said Nicholas VenOsdel, MD, a pediatrician at Allina Health Primary Care in Hastings, Minnesota, and a union member of the Doctors Council. “However, a lot of us have felt like that hasn’t been respected as the climate of healthcare has changed so fast.”
In fact, autonomy over how much time doctors spend with patients is driving a lot of interest in unionization.
“We don’t necessarily have that autonomy now,” said Amber Higgins, MD, an emergency physician and an obstetrician at ChristianaCare, a hospital network in Newark, Delaware, and a member of the Doctors Council. “There are so many other demands, whether it’s billing, patient documentation, or other demands from the employer, and all of that takes time away from patient care.”
Another primary driver of physician unionization is the physician burnout epidemic. Physicians collectively complain that they spend more time on electronic health record documentation and bureaucratic administration. Yet if unions can improve these working conditions, the benefit to physicians and their patients would be a welcome change.
Union members are bullish and believe that having a cohesive voice will make a difference.
“We need to use our collective voices to get back to focusing on patient care instead of staring at a computer screen for 80% of the day,” Dr. Higgins told this news organization. “So much of medicine involves getting to the correct diagnosis, listening to patients, observing them, and building a relationship with them. We need time to build that.”
With corporate consolidation and a profit-driven mandate by healthcare systems, doctors are increasingly frustrated and feel that their voices haven’t been heard enough when it comes to issues like workplace safety, working hours, and benefits, said Stuart Bussey, MD, JD, a family practice physician and president of the Union of American Physicians and Dentists in Sacramento, California.
However, he adds that urging doctors to join together to fight for a better working environment hasn’t been easy.
“Doctors are individualists, and they don’t know how to work in packs like hospital administrators do,” said Dr. Bussey. “They’re hard to organize, but I want them to understand that unless they join hands, sign petitions, and speak as one voice, they’re going to lose out on an amazing opportunity.”
Overcoming Misperceptions About Unions
One barrier to doctors getting involved is the sentiment that unions might do the opposite of what’s intended — that is, they might further reduce a doctor’s autonomy and work flexibility. Or there may be a perception that the drive to join a union is predicated on making more money.
Though he’s now in a union, Dr. VenOsdel, who has been in a hospital-based practice for 7 years, admits that he initially felt very differently about unions than he does today.
“Even though I have family members in healthcare unions, I had a neutral to even slightly negative view of unions,” said Dr. VenOsdel. “It took me working directly with the Minnesota Nurses Association and the Doctors Council to learn the other side of the story.”
Armed with more information, he began lobbying for stricter rules about how his state’s large healthcare systems were closing hospitals and ending much-needed community services.
“I remember standing at the Capitol in Minnesota and telling one of the members that I once felt negatively about unions,” he added. “I realized then that I only knew what employers were telling me via such things as emails about strikes — that information was all being shared from the employers’ perspective.”
The other misperception is that unions only exist to argue against management, including against colleagues who are also part of the management structure, said Dr. Higgins.
“Some doctors perceive being in a union as ‘how can those same leaders also be in a union,’” she said. She feels that they currently don’t have leadership representing them that can help with such things as restructuring their support teams or getting them help with certain tasks. “That’s another way unions can help.”
Social Justice Plays a Role
For Dr. VenOsdel, being part of a union has helped him return to what he calls the “art” of medicine.
“Philosophically, the union gave me an option for change in what felt like a hopeless situation,” he said. “It wasn’t just that I was tossing the keys to someone else and saying, ‘I can’t fix this.’ Instead, we’re taking the reins back and fixing things ourselves.”
Bussey argues that as the uneven balance between administrators and providers in many healthcare organizations grows, the time to consider forming a union is now.
“We’re in a $4 trillion medical industrial revolution,” he said. “Administrators and bureaucrats are multiplying 30-fold times vs providers, and most of that $4 trillion supports things that don’t contribute to the doctor-patient relationship.”
Furthermore, union proponents say that where a one-on-one relationship between doctor and patient once existed, that has now been “triangulated” to include administrators.
“We’ve lost power in every way,” Dr. Bussey said. “We have the degrees, the liability, and the knowledge — we should have more power to make our workplaces safer and better.”
Ultimately, for some unionized doctors, the very holding of a union card is rooted in supporting social justice issues.
“When doctors realize how powerful a tool a union can be for social justice and change, this will alter perceptions of unions within our profession,” Dr. VenOsdel said. “Our union helps give us a voice to stand up for other staff who aren’t unionized and, most importantly, to stand up for the patients who need us.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With huge shifts over the past decade in the way doctors are employed — half of all doctors now work for a health system or large medical group — the idea of unionizing is not only being explored but gaining traction within the profession. In fact, 8% of the physician workforce (or 70,000 physicians) belong to a union, according to statistics gathered in 2022.
Exact numbers are hard to come by, and, interestingly, although the American Medical Association (AMA) “ supports the right of physicians to engage in collective bargaining,” the organization doesn’t track union membership among physicians, according to an AMA spokesperson.
Forming a Union
One challenge is that forming a union is not only time-consuming but also difficult, owing to several barriers. For starters, the laws dictating unionization differ by state, and the rules governing unionization vary if a hospital is public or private. If there’s enough momentum from doctors leading unionization efforts, approval from hospital leaders is required before an official election can be requested from the National Labor Relations Board.
That said, for doctors who are in a union — the two most popular are the Union of American Physicians and Dentists and the Doctors Council branch of the Service Employees International Union (SEIU)—the benefits are immense, especially because union members can focus on what matters, such as providing the best patient care possible.
, reported WBUR in Boston.
Belonging Matters
“When you build a relationship with your patients, it’s special, and that connection isn’t replaceable,” said Nicholas VenOsdel, MD, a pediatrician at Allina Health Primary Care in Hastings, Minnesota, and a union member of the Doctors Council. “However, a lot of us have felt like that hasn’t been respected as the climate of healthcare has changed so fast.”
In fact, autonomy over how much time doctors spend with patients is driving a lot of interest in unionization.
“We don’t necessarily have that autonomy now,” said Amber Higgins, MD, an emergency physician and an obstetrician at ChristianaCare, a hospital network in Newark, Delaware, and a member of the Doctors Council. “There are so many other demands, whether it’s billing, patient documentation, or other demands from the employer, and all of that takes time away from patient care.”
Another primary driver of physician unionization is the physician burnout epidemic. Physicians collectively complain that they spend more time on electronic health record documentation and bureaucratic administration. Yet if unions can improve these working conditions, the benefit to physicians and their patients would be a welcome change.
Union members are bullish and believe that having a cohesive voice will make a difference.
“We need to use our collective voices to get back to focusing on patient care instead of staring at a computer screen for 80% of the day,” Dr. Higgins told this news organization. “So much of medicine involves getting to the correct diagnosis, listening to patients, observing them, and building a relationship with them. We need time to build that.”
With corporate consolidation and a profit-driven mandate by healthcare systems, doctors are increasingly frustrated and feel that their voices haven’t been heard enough when it comes to issues like workplace safety, working hours, and benefits, said Stuart Bussey, MD, JD, a family practice physician and president of the Union of American Physicians and Dentists in Sacramento, California.
However, he adds that urging doctors to join together to fight for a better working environment hasn’t been easy.
“Doctors are individualists, and they don’t know how to work in packs like hospital administrators do,” said Dr. Bussey. “They’re hard to organize, but I want them to understand that unless they join hands, sign petitions, and speak as one voice, they’re going to lose out on an amazing opportunity.”
Overcoming Misperceptions About Unions
One barrier to doctors getting involved is the sentiment that unions might do the opposite of what’s intended — that is, they might further reduce a doctor’s autonomy and work flexibility. Or there may be a perception that the drive to join a union is predicated on making more money.
Though he’s now in a union, Dr. VenOsdel, who has been in a hospital-based practice for 7 years, admits that he initially felt very differently about unions than he does today.
“Even though I have family members in healthcare unions, I had a neutral to even slightly negative view of unions,” said Dr. VenOsdel. “It took me working directly with the Minnesota Nurses Association and the Doctors Council to learn the other side of the story.”
Armed with more information, he began lobbying for stricter rules about how his state’s large healthcare systems were closing hospitals and ending much-needed community services.
“I remember standing at the Capitol in Minnesota and telling one of the members that I once felt negatively about unions,” he added. “I realized then that I only knew what employers were telling me via such things as emails about strikes — that information was all being shared from the employers’ perspective.”
The other misperception is that unions only exist to argue against management, including against colleagues who are also part of the management structure, said Dr. Higgins.
“Some doctors perceive being in a union as ‘how can those same leaders also be in a union,’” she said. She feels that they currently don’t have leadership representing them that can help with such things as restructuring their support teams or getting them help with certain tasks. “That’s another way unions can help.”
Social Justice Plays a Role
For Dr. VenOsdel, being part of a union has helped him return to what he calls the “art” of medicine.
“Philosophically, the union gave me an option for change in what felt like a hopeless situation,” he said. “It wasn’t just that I was tossing the keys to someone else and saying, ‘I can’t fix this.’ Instead, we’re taking the reins back and fixing things ourselves.”
Bussey argues that as the uneven balance between administrators and providers in many healthcare organizations grows, the time to consider forming a union is now.
“We’re in a $4 trillion medical industrial revolution,” he said. “Administrators and bureaucrats are multiplying 30-fold times vs providers, and most of that $4 trillion supports things that don’t contribute to the doctor-patient relationship.”
Furthermore, union proponents say that where a one-on-one relationship between doctor and patient once existed, that has now been “triangulated” to include administrators.
“We’ve lost power in every way,” Dr. Bussey said. “We have the degrees, the liability, and the knowledge — we should have more power to make our workplaces safer and better.”
Ultimately, for some unionized doctors, the very holding of a union card is rooted in supporting social justice issues.
“When doctors realize how powerful a tool a union can be for social justice and change, this will alter perceptions of unions within our profession,” Dr. VenOsdel said. “Our union helps give us a voice to stand up for other staff who aren’t unionized and, most importantly, to stand up for the patients who need us.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Small Business of Medicine
Black Friday is coming up. Although it seems (fortunately) to have lost some of its insanity since the pandemic, it’s still a huge shopping day for those who want to spend their day off in hand-to-hand combat at a Walmart. For me it’s a good day not to leave my house at all.
Following Black Friday we have Cyber Monday, where people go online to start buying stuff, presumably using business WiFi when they’re back at work. In spite of the apparent contradiction of having an online shopping day when people are at their jobs, it’s shamelessly promoted by the online retail giants.
Sandwiched between them is the quieter Small Business Saturday, started in 2010 by American Express and since gradually taking hold here and across the pond. The idea is to support the smaller local, perhaps family-owned, stores of varying kinds. Politicians love to talk about small businesses, calling them the backbone of the economy, promising to support them, etc.
I have no issue with that. I agree with it. I try to support my smaller, local places whenever I can. I’m glad AMEX started it, and that it’s taken off.
So why don’t we have a campaign to support small medical practices? Aren’t we small businesses, too? I’m the only doctor at my place, that’s about as small as you can get.
Like other small businesses, I don’t have the resources to advertise, aside from a simple website. At the same time I can’t drive too far without seeing a billboard, or hearing a radio ad, for one of the large local healthcare systems promising better convenience and care than that of their competitors.
I’m certainly not in a position to offer extended or weekend hours — I mean, I could, but I also have my own sanity to keep. But at the same time small practices may know their patients better than Huge Medicine Inc. We don’t have as many patients, and the staff turnover at small places is usually lower.
No one, though, is going to stand up for us, AMEX included (outside of cosmetic services, doctor visit charges are probably a tiny fraction of credit card company charges). Even our own organizations, like the AMA and others, won’t (at least not too much). They might pay lip service to us, but the reality is that most of their members work for large healthcare systems. Those groups probably make some big donations to them, too. So the last thing they want to do is tick them off.
I’m not against large groups. They have capabilities I don’t, like the ability to run research trials and have subspecialists. Even the best of us in solo practice needs someone better to refer to, such as an epileptologist, Parkinsonologist, neuromuscular disease-ologist, When I can’t help a patient any further those are the doctors I turn to, and, believe me, I appreciate them.
But
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Black Friday is coming up. Although it seems (fortunately) to have lost some of its insanity since the pandemic, it’s still a huge shopping day for those who want to spend their day off in hand-to-hand combat at a Walmart. For me it’s a good day not to leave my house at all.
Following Black Friday we have Cyber Monday, where people go online to start buying stuff, presumably using business WiFi when they’re back at work. In spite of the apparent contradiction of having an online shopping day when people are at their jobs, it’s shamelessly promoted by the online retail giants.
Sandwiched between them is the quieter Small Business Saturday, started in 2010 by American Express and since gradually taking hold here and across the pond. The idea is to support the smaller local, perhaps family-owned, stores of varying kinds. Politicians love to talk about small businesses, calling them the backbone of the economy, promising to support them, etc.
I have no issue with that. I agree with it. I try to support my smaller, local places whenever I can. I’m glad AMEX started it, and that it’s taken off.
So why don’t we have a campaign to support small medical practices? Aren’t we small businesses, too? I’m the only doctor at my place, that’s about as small as you can get.
Like other small businesses, I don’t have the resources to advertise, aside from a simple website. At the same time I can’t drive too far without seeing a billboard, or hearing a radio ad, for one of the large local healthcare systems promising better convenience and care than that of their competitors.
I’m certainly not in a position to offer extended or weekend hours — I mean, I could, but I also have my own sanity to keep. But at the same time small practices may know their patients better than Huge Medicine Inc. We don’t have as many patients, and the staff turnover at small places is usually lower.
No one, though, is going to stand up for us, AMEX included (outside of cosmetic services, doctor visit charges are probably a tiny fraction of credit card company charges). Even our own organizations, like the AMA and others, won’t (at least not too much). They might pay lip service to us, but the reality is that most of their members work for large healthcare systems. Those groups probably make some big donations to them, too. So the last thing they want to do is tick them off.
I’m not against large groups. They have capabilities I don’t, like the ability to run research trials and have subspecialists. Even the best of us in solo practice needs someone better to refer to, such as an epileptologist, Parkinsonologist, neuromuscular disease-ologist, When I can’t help a patient any further those are the doctors I turn to, and, believe me, I appreciate them.
But
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Black Friday is coming up. Although it seems (fortunately) to have lost some of its insanity since the pandemic, it’s still a huge shopping day for those who want to spend their day off in hand-to-hand combat at a Walmart. For me it’s a good day not to leave my house at all.
Following Black Friday we have Cyber Monday, where people go online to start buying stuff, presumably using business WiFi when they’re back at work. In spite of the apparent contradiction of having an online shopping day when people are at their jobs, it’s shamelessly promoted by the online retail giants.
Sandwiched between them is the quieter Small Business Saturday, started in 2010 by American Express and since gradually taking hold here and across the pond. The idea is to support the smaller local, perhaps family-owned, stores of varying kinds. Politicians love to talk about small businesses, calling them the backbone of the economy, promising to support them, etc.
I have no issue with that. I agree with it. I try to support my smaller, local places whenever I can. I’m glad AMEX started it, and that it’s taken off.
So why don’t we have a campaign to support small medical practices? Aren’t we small businesses, too? I’m the only doctor at my place, that’s about as small as you can get.
Like other small businesses, I don’t have the resources to advertise, aside from a simple website. At the same time I can’t drive too far without seeing a billboard, or hearing a radio ad, for one of the large local healthcare systems promising better convenience and care than that of their competitors.
I’m certainly not in a position to offer extended or weekend hours — I mean, I could, but I also have my own sanity to keep. But at the same time small practices may know their patients better than Huge Medicine Inc. We don’t have as many patients, and the staff turnover at small places is usually lower.
No one, though, is going to stand up for us, AMEX included (outside of cosmetic services, doctor visit charges are probably a tiny fraction of credit card company charges). Even our own organizations, like the AMA and others, won’t (at least not too much). They might pay lip service to us, but the reality is that most of their members work for large healthcare systems. Those groups probably make some big donations to them, too. So the last thing they want to do is tick them off.
I’m not against large groups. They have capabilities I don’t, like the ability to run research trials and have subspecialists. Even the best of us in solo practice needs someone better to refer to, such as an epileptologist, Parkinsonologist, neuromuscular disease-ologist, When I can’t help a patient any further those are the doctors I turn to, and, believe me, I appreciate them.
But
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Focusing on Value in Social Media Posts
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — Posting on social media may not be your cup of tea, but in the opinion of Jessica G. Labadie, MD,
“Over the past 2 decades, there has been a surge in social media use,” Dr. Labadie, a dermatologist who practices in Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts, said at the Controversies & Conversations in Laser & Cosmetic Surgery symposium. “Most of our patients use social media to find their doctors, and it plays a role in how our patients form their decision about whether to have a cosmetic procedure or not. Doctors, especially dermatologists, continue to actively participate in this ‘skinfluencer’ trend.”
According to a review of social media’s impact on aesthetic medicine, use of social media by American adults increased from 5% in 2005 to 72% in 2020, and 77% of patients search for a physician online. The review’s authors cited YouTube as the most popular platform among adults and noted that social media ranks as the sixth top factor for a patient deciding whether to have a laser procedure.
Dr. Labadie, who is also an assistant professor of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, said several factors should be considered when establishing and maintaining a social media presence, starting with personal ones. “Your followers are not your patients yet, and just because you may have thousands of followers does not necessarily mean that you’re busier in the clinic,” she said. “Be careful if you combine professional and personal accounts; be careful of those parasocial relationships that can form. Your followers tend to learn a lot about you. Posting can take a lot of time; it can take away from your clinical duties. Do you want to make your account private or public? There are pros and cons to both.”
Ethics also play a role. “Be transparent in your disclosure forms, especially if you’re posting ‘before’ and ‘after’ images of patients,” advised Dr. Labadie, who described herself as a social media minimalist. “Stay true to yourself in your posts, and always prioritize safety over posting.”
Don’t forget legal obligations. “Social media can facilitate a passive income, but make sure this isn’t impacting any conflicts of interest, and make sure that you meticulously follow any Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act regulations,” she said. She also cautioned against violating intellectual property rights and making false claims about a product or procedure.
Deciding which platforms to use and what voice or tone to adopt requires some soul-searching. “What is your brand?” Dr. Labadie asked. “How do you want to portray yourself? Does your social media brand match your office brand? Does it match who you are as a provider and the type of patient you wish to attract? Would you prefer to have one collective social media presence as an office or multiple provider accounts?”
Being mindful of how your patients perceive and use social media in relation to their dermatologic concerns is also important. “What are your patients viewing on social media, and how is it affecting their decisions?” Dr. Labadie asked. “Are they coming in asking for something that is not right for what they need? At the end of the day, you are their doctor, and it’s your duty to treat the patients and not the trend.”
She encouraged dermatologists to “aim for high value and accurate posts coupled with high popularity and reach.” She added that “this is really the future of getting our research out there to the public. Academic notoriety is not enough. Our professional societies and skinfluencer colleagues need to get involved to help promote our expert research.”
Dr. Labadie reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — Posting on social media may not be your cup of tea, but in the opinion of Jessica G. Labadie, MD,
“Over the past 2 decades, there has been a surge in social media use,” Dr. Labadie, a dermatologist who practices in Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts, said at the Controversies & Conversations in Laser & Cosmetic Surgery symposium. “Most of our patients use social media to find their doctors, and it plays a role in how our patients form their decision about whether to have a cosmetic procedure or not. Doctors, especially dermatologists, continue to actively participate in this ‘skinfluencer’ trend.”
According to a review of social media’s impact on aesthetic medicine, use of social media by American adults increased from 5% in 2005 to 72% in 2020, and 77% of patients search for a physician online. The review’s authors cited YouTube as the most popular platform among adults and noted that social media ranks as the sixth top factor for a patient deciding whether to have a laser procedure.
Dr. Labadie, who is also an assistant professor of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, said several factors should be considered when establishing and maintaining a social media presence, starting with personal ones. “Your followers are not your patients yet, and just because you may have thousands of followers does not necessarily mean that you’re busier in the clinic,” she said. “Be careful if you combine professional and personal accounts; be careful of those parasocial relationships that can form. Your followers tend to learn a lot about you. Posting can take a lot of time; it can take away from your clinical duties. Do you want to make your account private or public? There are pros and cons to both.”
Ethics also play a role. “Be transparent in your disclosure forms, especially if you’re posting ‘before’ and ‘after’ images of patients,” advised Dr. Labadie, who described herself as a social media minimalist. “Stay true to yourself in your posts, and always prioritize safety over posting.”
Don’t forget legal obligations. “Social media can facilitate a passive income, but make sure this isn’t impacting any conflicts of interest, and make sure that you meticulously follow any Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act regulations,” she said. She also cautioned against violating intellectual property rights and making false claims about a product or procedure.
Deciding which platforms to use and what voice or tone to adopt requires some soul-searching. “What is your brand?” Dr. Labadie asked. “How do you want to portray yourself? Does your social media brand match your office brand? Does it match who you are as a provider and the type of patient you wish to attract? Would you prefer to have one collective social media presence as an office or multiple provider accounts?”
Being mindful of how your patients perceive and use social media in relation to their dermatologic concerns is also important. “What are your patients viewing on social media, and how is it affecting their decisions?” Dr. Labadie asked. “Are they coming in asking for something that is not right for what they need? At the end of the day, you are their doctor, and it’s your duty to treat the patients and not the trend.”
She encouraged dermatologists to “aim for high value and accurate posts coupled with high popularity and reach.” She added that “this is really the future of getting our research out there to the public. Academic notoriety is not enough. Our professional societies and skinfluencer colleagues need to get involved to help promote our expert research.”
Dr. Labadie reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — Posting on social media may not be your cup of tea, but in the opinion of Jessica G. Labadie, MD,
“Over the past 2 decades, there has been a surge in social media use,” Dr. Labadie, a dermatologist who practices in Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts, said at the Controversies & Conversations in Laser & Cosmetic Surgery symposium. “Most of our patients use social media to find their doctors, and it plays a role in how our patients form their decision about whether to have a cosmetic procedure or not. Doctors, especially dermatologists, continue to actively participate in this ‘skinfluencer’ trend.”
According to a review of social media’s impact on aesthetic medicine, use of social media by American adults increased from 5% in 2005 to 72% in 2020, and 77% of patients search for a physician online. The review’s authors cited YouTube as the most popular platform among adults and noted that social media ranks as the sixth top factor for a patient deciding whether to have a laser procedure.
Dr. Labadie, who is also an assistant professor of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, said several factors should be considered when establishing and maintaining a social media presence, starting with personal ones. “Your followers are not your patients yet, and just because you may have thousands of followers does not necessarily mean that you’re busier in the clinic,” she said. “Be careful if you combine professional and personal accounts; be careful of those parasocial relationships that can form. Your followers tend to learn a lot about you. Posting can take a lot of time; it can take away from your clinical duties. Do you want to make your account private or public? There are pros and cons to both.”
Ethics also play a role. “Be transparent in your disclosure forms, especially if you’re posting ‘before’ and ‘after’ images of patients,” advised Dr. Labadie, who described herself as a social media minimalist. “Stay true to yourself in your posts, and always prioritize safety over posting.”
Don’t forget legal obligations. “Social media can facilitate a passive income, but make sure this isn’t impacting any conflicts of interest, and make sure that you meticulously follow any Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act regulations,” she said. She also cautioned against violating intellectual property rights and making false claims about a product or procedure.
Deciding which platforms to use and what voice or tone to adopt requires some soul-searching. “What is your brand?” Dr. Labadie asked. “How do you want to portray yourself? Does your social media brand match your office brand? Does it match who you are as a provider and the type of patient you wish to attract? Would you prefer to have one collective social media presence as an office or multiple provider accounts?”
Being mindful of how your patients perceive and use social media in relation to their dermatologic concerns is also important. “What are your patients viewing on social media, and how is it affecting their decisions?” Dr. Labadie asked. “Are they coming in asking for something that is not right for what they need? At the end of the day, you are their doctor, and it’s your duty to treat the patients and not the trend.”
She encouraged dermatologists to “aim for high value and accurate posts coupled with high popularity and reach.” She added that “this is really the future of getting our research out there to the public. Academic notoriety is not enough. Our professional societies and skinfluencer colleagues need to get involved to help promote our expert research.”
Dr. Labadie reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Wait, a Health Worker Surplus? Workforce Report Projects Big Surprises
A surprising new report by the Mercer consulting firm projects that the American healthcare workforce will face a small shortfall in 2028 — a shortage of less than 1% of all employees.
Mercer’s projections are rosier than federal workforce projections, which paint a grimmer picture of impending shortages.
“The labor market is a little more stabilized right now, and most healthcare systems are seeing less turnover,” Dan Lezotte, PhD, a partner with Mercer, said in an interview. But he noted “critical shortages” are still expected in some areas.
Mercer last projected workforce numbers in a 2020-2021 report released during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. Now, “the labor market is drastically different,” Dr. Lezotte said. Health workforce shortages and surpluses have long varied significantly by region across the country.
The report forecasts a small surplus of physicians in 2028 but not in states such as California, New York, and Texas. The upper Midwest states will largely see doctor surpluses while Southern states face shortages. Some states with general physician surpluses may still experience shortages of specialists.
A surplus of nearly 30,000 registered nurses is expected, but New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut are projected to have a combined shortage of 16,000 nurses.
Overall, the report projects a shortage of more than 100,000 healthcare workers nationally by 2028. That’s less than 1% of the entire healthcare workforce of 18.6 million expected by then.
The report also predicts a shortage of nurse practitioners, especially in California and New York, and a shortage of 73,000 nursing assistants, especially in California, New York, and Texas.
“Healthcare systems are having the most difficulty hiring and hanging on to those workers who are supposed to take up the load off physicians and nurses,” Dr. Lezotte said. “They’re competing not only with other healthcare systems but with other industries like Amazon warehouses or McDonald’s in California paying $20 an hour. Healthcare was a little slow to keep up with that. In a lot of healthcare systems, that’s their biggest headache right now.”
On the other hand, the report projects a national surplus of 48,000 home health/personal care aides.
That surprised Bianca K. Frogner, PhD, director of the Center for Health Workforce Studies at the University of Washington, Seattle.
“We are seeing increasing movement of investments toward moving patients out of skilled nursing facilities and keeping them in the home and community, which requires many more home health aides,” Dr. Frogner said. “Given such high turnover in this occupation, it’s hard to know if the surplus is really a surplus or if they will quickly be employed.”
Dr. Frogner receives grants and contracts from not-for-profit entities to investigate issues related to the health workforce.
Dr. Lezotte said the report’s findings are based on data from sources such as public and private databases and job postings. According to the report, “projections were made up to 2028 based on historical data up to 2023,” and “supply projections were derived using a linear autoregressive model based on historical supply within each occupation and geography.”
It’s not clear why some states like New York are expected to have huge shortages, but migration might be a factor, along with a lack of nearby nursing schools, Dr. Lezotte said.
As for shortages, Dr. Lezotte said healthcare systems will have to understand their local workforce situation and adapt. “They’ll need to be more proactive about their employee value proposition” via competitive pay and benefits Flexibility regarding scheduling is also important.
“They’re going to have to figure out how to up their game,” he said.
What about states with surpluses? They might be target-rich environments for states facing shortages, he said.
Positive Outlook Not Shared by Other Researchers
Other workforce projections conflict with Mercer’s, according to Jean Moore, DrPH, and Gaetano Forte, MS, director and assistant director of the Center for Health Workforce Studies, School of Public Health, University at Albany, New York.
The National Center for Health Workforce Analysis projects a 10% shortage of registered nurses and a 13% shortage of physicians in 2031. The agency didn’t make projections for home health aides because that workforce is in flux.
Why are Mercer’s projections so different? Dr. Lezotte said other projections assume that equity efforts will bring healthcare to everyone who needs it. The report assumes this won’t happen, he said. As a result, it expects there will be fewer patients who need to be served by workers.
Other projections expect a shortage of 300,000 registered nurses by 2035, Mr. Forte said. But the number of nurse practitioners in New York is growing quickly, Dr. Moore said.
Dr. Moore said it’s difficult to interpret Mercer’s findings because the company doesn’t provide enough information about its methodology.
“At some level, it’s not particularly useful regarding what the next steps are,” she said. “Projections should make you think about what you should do to change and improve, to create more of what you need.”
The Center for Health Workforce Studies at the University of Albany has provided consulting services to multiple companies that provide healthcare workforce projections. It has no relationship with Mercer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A surprising new report by the Mercer consulting firm projects that the American healthcare workforce will face a small shortfall in 2028 — a shortage of less than 1% of all employees.
Mercer’s projections are rosier than federal workforce projections, which paint a grimmer picture of impending shortages.
“The labor market is a little more stabilized right now, and most healthcare systems are seeing less turnover,” Dan Lezotte, PhD, a partner with Mercer, said in an interview. But he noted “critical shortages” are still expected in some areas.
Mercer last projected workforce numbers in a 2020-2021 report released during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. Now, “the labor market is drastically different,” Dr. Lezotte said. Health workforce shortages and surpluses have long varied significantly by region across the country.
The report forecasts a small surplus of physicians in 2028 but not in states such as California, New York, and Texas. The upper Midwest states will largely see doctor surpluses while Southern states face shortages. Some states with general physician surpluses may still experience shortages of specialists.
A surplus of nearly 30,000 registered nurses is expected, but New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut are projected to have a combined shortage of 16,000 nurses.
Overall, the report projects a shortage of more than 100,000 healthcare workers nationally by 2028. That’s less than 1% of the entire healthcare workforce of 18.6 million expected by then.
The report also predicts a shortage of nurse practitioners, especially in California and New York, and a shortage of 73,000 nursing assistants, especially in California, New York, and Texas.
“Healthcare systems are having the most difficulty hiring and hanging on to those workers who are supposed to take up the load off physicians and nurses,” Dr. Lezotte said. “They’re competing not only with other healthcare systems but with other industries like Amazon warehouses or McDonald’s in California paying $20 an hour. Healthcare was a little slow to keep up with that. In a lot of healthcare systems, that’s their biggest headache right now.”
On the other hand, the report projects a national surplus of 48,000 home health/personal care aides.
That surprised Bianca K. Frogner, PhD, director of the Center for Health Workforce Studies at the University of Washington, Seattle.
“We are seeing increasing movement of investments toward moving patients out of skilled nursing facilities and keeping them in the home and community, which requires many more home health aides,” Dr. Frogner said. “Given such high turnover in this occupation, it’s hard to know if the surplus is really a surplus or if they will quickly be employed.”
Dr. Frogner receives grants and contracts from not-for-profit entities to investigate issues related to the health workforce.
Dr. Lezotte said the report’s findings are based on data from sources such as public and private databases and job postings. According to the report, “projections were made up to 2028 based on historical data up to 2023,” and “supply projections were derived using a linear autoregressive model based on historical supply within each occupation and geography.”
It’s not clear why some states like New York are expected to have huge shortages, but migration might be a factor, along with a lack of nearby nursing schools, Dr. Lezotte said.
As for shortages, Dr. Lezotte said healthcare systems will have to understand their local workforce situation and adapt. “They’ll need to be more proactive about their employee value proposition” via competitive pay and benefits Flexibility regarding scheduling is also important.
“They’re going to have to figure out how to up their game,” he said.
What about states with surpluses? They might be target-rich environments for states facing shortages, he said.
Positive Outlook Not Shared by Other Researchers
Other workforce projections conflict with Mercer’s, according to Jean Moore, DrPH, and Gaetano Forte, MS, director and assistant director of the Center for Health Workforce Studies, School of Public Health, University at Albany, New York.
The National Center for Health Workforce Analysis projects a 10% shortage of registered nurses and a 13% shortage of physicians in 2031. The agency didn’t make projections for home health aides because that workforce is in flux.
Why are Mercer’s projections so different? Dr. Lezotte said other projections assume that equity efforts will bring healthcare to everyone who needs it. The report assumes this won’t happen, he said. As a result, it expects there will be fewer patients who need to be served by workers.
Other projections expect a shortage of 300,000 registered nurses by 2035, Mr. Forte said. But the number of nurse practitioners in New York is growing quickly, Dr. Moore said.
Dr. Moore said it’s difficult to interpret Mercer’s findings because the company doesn’t provide enough information about its methodology.
“At some level, it’s not particularly useful regarding what the next steps are,” she said. “Projections should make you think about what you should do to change and improve, to create more of what you need.”
The Center for Health Workforce Studies at the University of Albany has provided consulting services to multiple companies that provide healthcare workforce projections. It has no relationship with Mercer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A surprising new report by the Mercer consulting firm projects that the American healthcare workforce will face a small shortfall in 2028 — a shortage of less than 1% of all employees.
Mercer’s projections are rosier than federal workforce projections, which paint a grimmer picture of impending shortages.
“The labor market is a little more stabilized right now, and most healthcare systems are seeing less turnover,” Dan Lezotte, PhD, a partner with Mercer, said in an interview. But he noted “critical shortages” are still expected in some areas.
Mercer last projected workforce numbers in a 2020-2021 report released during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. Now, “the labor market is drastically different,” Dr. Lezotte said. Health workforce shortages and surpluses have long varied significantly by region across the country.
The report forecasts a small surplus of physicians in 2028 but not in states such as California, New York, and Texas. The upper Midwest states will largely see doctor surpluses while Southern states face shortages. Some states with general physician surpluses may still experience shortages of specialists.
A surplus of nearly 30,000 registered nurses is expected, but New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut are projected to have a combined shortage of 16,000 nurses.
Overall, the report projects a shortage of more than 100,000 healthcare workers nationally by 2028. That’s less than 1% of the entire healthcare workforce of 18.6 million expected by then.
The report also predicts a shortage of nurse practitioners, especially in California and New York, and a shortage of 73,000 nursing assistants, especially in California, New York, and Texas.
“Healthcare systems are having the most difficulty hiring and hanging on to those workers who are supposed to take up the load off physicians and nurses,” Dr. Lezotte said. “They’re competing not only with other healthcare systems but with other industries like Amazon warehouses or McDonald’s in California paying $20 an hour. Healthcare was a little slow to keep up with that. In a lot of healthcare systems, that’s their biggest headache right now.”
On the other hand, the report projects a national surplus of 48,000 home health/personal care aides.
That surprised Bianca K. Frogner, PhD, director of the Center for Health Workforce Studies at the University of Washington, Seattle.
“We are seeing increasing movement of investments toward moving patients out of skilled nursing facilities and keeping them in the home and community, which requires many more home health aides,” Dr. Frogner said. “Given such high turnover in this occupation, it’s hard to know if the surplus is really a surplus or if they will quickly be employed.”
Dr. Frogner receives grants and contracts from not-for-profit entities to investigate issues related to the health workforce.
Dr. Lezotte said the report’s findings are based on data from sources such as public and private databases and job postings. According to the report, “projections were made up to 2028 based on historical data up to 2023,” and “supply projections were derived using a linear autoregressive model based on historical supply within each occupation and geography.”
It’s not clear why some states like New York are expected to have huge shortages, but migration might be a factor, along with a lack of nearby nursing schools, Dr. Lezotte said.
As for shortages, Dr. Lezotte said healthcare systems will have to understand their local workforce situation and adapt. “They’ll need to be more proactive about their employee value proposition” via competitive pay and benefits Flexibility regarding scheduling is also important.
“They’re going to have to figure out how to up their game,” he said.
What about states with surpluses? They might be target-rich environments for states facing shortages, he said.
Positive Outlook Not Shared by Other Researchers
Other workforce projections conflict with Mercer’s, according to Jean Moore, DrPH, and Gaetano Forte, MS, director and assistant director of the Center for Health Workforce Studies, School of Public Health, University at Albany, New York.
The National Center for Health Workforce Analysis projects a 10% shortage of registered nurses and a 13% shortage of physicians in 2031. The agency didn’t make projections for home health aides because that workforce is in flux.
Why are Mercer’s projections so different? Dr. Lezotte said other projections assume that equity efforts will bring healthcare to everyone who needs it. The report assumes this won’t happen, he said. As a result, it expects there will be fewer patients who need to be served by workers.
Other projections expect a shortage of 300,000 registered nurses by 2035, Mr. Forte said. But the number of nurse practitioners in New York is growing quickly, Dr. Moore said.
Dr. Moore said it’s difficult to interpret Mercer’s findings because the company doesn’t provide enough information about its methodology.
“At some level, it’s not particularly useful regarding what the next steps are,” she said. “Projections should make you think about what you should do to change and improve, to create more of what you need.”
The Center for Health Workforce Studies at the University of Albany has provided consulting services to multiple companies that provide healthcare workforce projections. It has no relationship with Mercer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To Choose the Best First-line Drug for CML, Consider Efficacy and Cost
When it comes to selecting a cost-effective, first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), consider the treatment goal.
For survival, generic imatinib remains the gold standard, Elias Jabbour, MD, said during a session at the annual meeting of the Society of Hematologic Oncology in Houston.
For treatment-free remission, generic dasatinib or another generic second-generation TKI is needed, but not yet available in the United States, so generic imatinib is the best current choice, said Dr. Jabbour, a professor of medicine in the Department of Leukemia at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Prior to the availability of generic imatinib, that wasn’t the case, he noted, explaining that second-generation TKIs met the cost-efficacy criteria, but now — at about $35 per month or about $400 per year — imatinib is far less expensive than the approximately $250,000 per year that brand-name second- and third-generation TKIs can currently cost.
To have treatment value, any new TKI should cost $40,000-$50,000 per quality-adjusted life-year, which is defined as the quality and duration of life after a novel TKI vs with the existing standard of care, Dr. Jabbour said.
And to qualify as a frontline therapy for CML, any new TKI should show efficacy superior to second-generation TKIs, in addition to meeting the cost-effectiveness criteria.
“It is hard to show survival benefit anymore, but we need to improve on the rate of durable deep molecular remission,” he said.
An equivalent or better long-term safety profile over at least 7-8 years is also needed.
Based on the current literature, none of the TKIs currently being evaluated has met that standard, although some trials are ongoing.
In a recent editorial, Dr. Jabbour and colleagues outlined treatment recommendations based on the currently available data. They suggested using lower-than-approved doses of TKIs in both frontline and later therapies to reduce toxicity, improve treatment compliance, and reduce costs.
They also suggested that the absence of an early molecular response might not warrant changing the TKI, especially when a second-generation TKI was used first line.
When treatment-free remission is not a therapeutic goal or is unlikely, changing the TKI to improve the depth of molecular response, which has been shown to improve the likelihood of treatment-free remission, could do more harm than good, they argued.
Instead, consider reducing the dose to manage reversible side effects, they suggested, noting that generic imatinib, and eventually generic dasatinib and possibly other generic second-generation TKIs, will likely offer 90% of patients with CML an effective, safe, and affordable treatment that normalizes life expectancy and leads to treatment-free remission in 30%-50% of patients over time.
Dr. Jabbour disclosed ties with AbbVie, Almoosa Specialist Hospital, Amgen, Ascentage Pharma, Biologix FZ, Hikma Pharmaceuticals, Kite, Takeda, and Terns.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When it comes to selecting a cost-effective, first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), consider the treatment goal.
For survival, generic imatinib remains the gold standard, Elias Jabbour, MD, said during a session at the annual meeting of the Society of Hematologic Oncology in Houston.
For treatment-free remission, generic dasatinib or another generic second-generation TKI is needed, but not yet available in the United States, so generic imatinib is the best current choice, said Dr. Jabbour, a professor of medicine in the Department of Leukemia at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Prior to the availability of generic imatinib, that wasn’t the case, he noted, explaining that second-generation TKIs met the cost-efficacy criteria, but now — at about $35 per month or about $400 per year — imatinib is far less expensive than the approximately $250,000 per year that brand-name second- and third-generation TKIs can currently cost.
To have treatment value, any new TKI should cost $40,000-$50,000 per quality-adjusted life-year, which is defined as the quality and duration of life after a novel TKI vs with the existing standard of care, Dr. Jabbour said.
And to qualify as a frontline therapy for CML, any new TKI should show efficacy superior to second-generation TKIs, in addition to meeting the cost-effectiveness criteria.
“It is hard to show survival benefit anymore, but we need to improve on the rate of durable deep molecular remission,” he said.
An equivalent or better long-term safety profile over at least 7-8 years is also needed.
Based on the current literature, none of the TKIs currently being evaluated has met that standard, although some trials are ongoing.
In a recent editorial, Dr. Jabbour and colleagues outlined treatment recommendations based on the currently available data. They suggested using lower-than-approved doses of TKIs in both frontline and later therapies to reduce toxicity, improve treatment compliance, and reduce costs.
They also suggested that the absence of an early molecular response might not warrant changing the TKI, especially when a second-generation TKI was used first line.
When treatment-free remission is not a therapeutic goal or is unlikely, changing the TKI to improve the depth of molecular response, which has been shown to improve the likelihood of treatment-free remission, could do more harm than good, they argued.
Instead, consider reducing the dose to manage reversible side effects, they suggested, noting that generic imatinib, and eventually generic dasatinib and possibly other generic second-generation TKIs, will likely offer 90% of patients with CML an effective, safe, and affordable treatment that normalizes life expectancy and leads to treatment-free remission in 30%-50% of patients over time.
Dr. Jabbour disclosed ties with AbbVie, Almoosa Specialist Hospital, Amgen, Ascentage Pharma, Biologix FZ, Hikma Pharmaceuticals, Kite, Takeda, and Terns.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When it comes to selecting a cost-effective, first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), consider the treatment goal.
For survival, generic imatinib remains the gold standard, Elias Jabbour, MD, said during a session at the annual meeting of the Society of Hematologic Oncology in Houston.
For treatment-free remission, generic dasatinib or another generic second-generation TKI is needed, but not yet available in the United States, so generic imatinib is the best current choice, said Dr. Jabbour, a professor of medicine in the Department of Leukemia at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Prior to the availability of generic imatinib, that wasn’t the case, he noted, explaining that second-generation TKIs met the cost-efficacy criteria, but now — at about $35 per month or about $400 per year — imatinib is far less expensive than the approximately $250,000 per year that brand-name second- and third-generation TKIs can currently cost.
To have treatment value, any new TKI should cost $40,000-$50,000 per quality-adjusted life-year, which is defined as the quality and duration of life after a novel TKI vs with the existing standard of care, Dr. Jabbour said.
And to qualify as a frontline therapy for CML, any new TKI should show efficacy superior to second-generation TKIs, in addition to meeting the cost-effectiveness criteria.
“It is hard to show survival benefit anymore, but we need to improve on the rate of durable deep molecular remission,” he said.
An equivalent or better long-term safety profile over at least 7-8 years is also needed.
Based on the current literature, none of the TKIs currently being evaluated has met that standard, although some trials are ongoing.
In a recent editorial, Dr. Jabbour and colleagues outlined treatment recommendations based on the currently available data. They suggested using lower-than-approved doses of TKIs in both frontline and later therapies to reduce toxicity, improve treatment compliance, and reduce costs.
They also suggested that the absence of an early molecular response might not warrant changing the TKI, especially when a second-generation TKI was used first line.
When treatment-free remission is not a therapeutic goal or is unlikely, changing the TKI to improve the depth of molecular response, which has been shown to improve the likelihood of treatment-free remission, could do more harm than good, they argued.
Instead, consider reducing the dose to manage reversible side effects, they suggested, noting that generic imatinib, and eventually generic dasatinib and possibly other generic second-generation TKIs, will likely offer 90% of patients with CML an effective, safe, and affordable treatment that normalizes life expectancy and leads to treatment-free remission in 30%-50% of patients over time.
Dr. Jabbour disclosed ties with AbbVie, Almoosa Specialist Hospital, Amgen, Ascentage Pharma, Biologix FZ, Hikma Pharmaceuticals, Kite, Takeda, and Terns.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SOHO 2024
Creative Strategies Hospitals Use to Attract Nursing Talent
In a fiercely competitive healthcare landscape, hospitals are pulling out all the stops to lure top nursing talent through their doors.
As the nursing shortage intensifies, the creative recruitment approach isn’t just about the perks — it’s becoming an essential tool in the race to build a skilled nursing workforce.
Nursing vacancies are as high as 17% — more than double prepandemic levels — and hospitals scrambling to fill them need to do more than raise salaries and bolster benefits packages to entice nurses.
“I am very thankful when I hear of creative ideas that nurse administrators come up with to try to get their ultimate goal, which is enough qualified nurses to take care of patients,” said Linda Plank, dean of the Louise Herrington School of Nursing at Baylor University in Dallas, Texas.
Signing Bonuses, Tuition Reimbursement, and Self-Scheduling, Please
Signing bonuses were among the top perks offered to healthcare workers, with almost 18% of job openings advertising the incentive for new nurse hires; the average signing bonus for registered nurses (RNs) topped $11,000. In 2023, California-based Palomar Health made headlines when it offered eligible RNs a $100,000 signing bonus paid over a 3-year period.
“We are seeing a variety of incentives, like sign-on bonuses, that can be effective at getting the attention of potential new hires,” said Deborah Trautman, PhD, RN, FAAN, president, and CEO of the American Association of Colleges of Nursing. “With the growing competition for registered nurses, especially those prepared in baccalaureate programs, employers should consider what’s most important to nurses entering the field.”
Hospitals have also invested in benefits ranging from tuition reimbursement, student loan forgiveness, and professional development opportunities to expanded parental leave and onsite childcare. Flexible scheduling is a sought-after perk that benefits both new and experienced RNs and could also help with recruitment.
“In the past, [hospitals said], ‘our shift starts at 7 and ends at 7,’ ” Ms. Plank said. “Now, hospitals are a little bit more flexible ... and being open to flexible shifts has merit. If we’re willing to look at things differently, it could get more people involved in patient care.”
An American Nurses Foundation report found that nurses preferred variable and flexible shift lengths, flexible start times, and self-scheduling options over set schedules. In fact, 45% of nurses who left clinical practice would consider returning to work if hospitals switched to a self-scheduling model.
The Cleveland Clinic in Ohio introduced staggered shifts that start at nontraditional times, including 11 AM to 11 PM, flexible shift lengths, and split RN positions that allow clinical care nurses to divide their time between different departments. Last year, Hackensack Meridian Health in New Jersey also piloted a self-scheduling program for its nursing staff.
Hiring Outside the United States
Despite the prevalence of signing bonuses and premium perks, some hospitals still struggled to fill open positions with nurses recruited from outside the United States. Data from The Kaiser Family Foundation show that 32% of hospitals hired foreign-educated RNs in 2022 — more than double the number hired in 2010.
Jennifer Mensik Kennedy, PhD, MBA, RN, NEA-BC, FAAN, president of the American Nurses Association (ANA), is concerned about that trend. The ANA supports the International Council of Nurses and their call for “stronger codes for ethical recruitment of nurses” because international nurse recruitment practices can negatively affect the quality of healthcare in countries that are depleted of nurses.
“Recruiting international nurses as a key strategy for building core staffing is not sustainable in the long term,” Ms. Kennedy said in an interview. “We need to redirect our focus on how to retain staff through fostering healthy work environments and addressing antiquated payment models.”
Reinforcing Retention
Recruiting nurses is just one element of addressing the nursing shortage. Prioritizing job satisfaction is essential to retaining nursing staff. Currently, 33% of nurses who enter the profession quit within the first 2 years.
A growing number of hospitals have implemented programs focused on increasing retention. Lifepoint Health, a national network of 60-plus acute care hospitals, launched a Nurse Residency Program in 2023. The 12-month program, which offers training and mentorship to help recent nursing school graduates, has recruited 750 new nurses and helped them transition to clinical practice.
The Nurse Residency Program has been so successful that the hospital system plans to introduce a 2-year fellowship program in the fall of 2024 that supports the professional development of nurses who want to specialize in areas like acute care, obstetrics, or the intensive care unit.
“We are more focused than ever on increasing partnerships and alignment with our local nursing programs, expanding clinical education opportunities for nursing students, owning and driving a nursing culture, and creating an environment where employees want to work,” said Michelle Watson, MSN, RN, CENP, chief nurse executive and senior vice president of clinical operations at Lifepoint Health.
Ms. Watson also credits their facilities’ chief nursing officers as being “highly engaged and visible leaders” who spend time with RNs to learn about their career aspirations and help them understand how the organization can support their desires for ongoing professional development.
The 2022 Nurse Staffing Task Force, a collaborative initiative by the ANA and other prominent national nursing and healthcare organizations, has developed and widely disseminated a set of recommendations for hospitals focusing on investing in nurse staffing, safe and supportive work environments, and competitive wages.
In addition, the Reimagining Nursing Initiative, started by the American Nurses Foundation, is striving to help nurses feel valued and compensated by creating pilot programs that can help modernize nurses’ reimbursement structure so that they can direct bill.
In the end, attracting and retaining top nursing talent is about more than filling positions — it’s about building a healthcare system where nurses thrive. “In the United States and abroad, we owe it to nurses and the communities they serve to have sustainable and appropriate solutions to staffing and work environment challenges,” said Ms. Kennedy.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In a fiercely competitive healthcare landscape, hospitals are pulling out all the stops to lure top nursing talent through their doors.
As the nursing shortage intensifies, the creative recruitment approach isn’t just about the perks — it’s becoming an essential tool in the race to build a skilled nursing workforce.
Nursing vacancies are as high as 17% — more than double prepandemic levels — and hospitals scrambling to fill them need to do more than raise salaries and bolster benefits packages to entice nurses.
“I am very thankful when I hear of creative ideas that nurse administrators come up with to try to get their ultimate goal, which is enough qualified nurses to take care of patients,” said Linda Plank, dean of the Louise Herrington School of Nursing at Baylor University in Dallas, Texas.
Signing Bonuses, Tuition Reimbursement, and Self-Scheduling, Please
Signing bonuses were among the top perks offered to healthcare workers, with almost 18% of job openings advertising the incentive for new nurse hires; the average signing bonus for registered nurses (RNs) topped $11,000. In 2023, California-based Palomar Health made headlines when it offered eligible RNs a $100,000 signing bonus paid over a 3-year period.
“We are seeing a variety of incentives, like sign-on bonuses, that can be effective at getting the attention of potential new hires,” said Deborah Trautman, PhD, RN, FAAN, president, and CEO of the American Association of Colleges of Nursing. “With the growing competition for registered nurses, especially those prepared in baccalaureate programs, employers should consider what’s most important to nurses entering the field.”
Hospitals have also invested in benefits ranging from tuition reimbursement, student loan forgiveness, and professional development opportunities to expanded parental leave and onsite childcare. Flexible scheduling is a sought-after perk that benefits both new and experienced RNs and could also help with recruitment.
“In the past, [hospitals said], ‘our shift starts at 7 and ends at 7,’ ” Ms. Plank said. “Now, hospitals are a little bit more flexible ... and being open to flexible shifts has merit. If we’re willing to look at things differently, it could get more people involved in patient care.”
An American Nurses Foundation report found that nurses preferred variable and flexible shift lengths, flexible start times, and self-scheduling options over set schedules. In fact, 45% of nurses who left clinical practice would consider returning to work if hospitals switched to a self-scheduling model.
The Cleveland Clinic in Ohio introduced staggered shifts that start at nontraditional times, including 11 AM to 11 PM, flexible shift lengths, and split RN positions that allow clinical care nurses to divide their time between different departments. Last year, Hackensack Meridian Health in New Jersey also piloted a self-scheduling program for its nursing staff.
Hiring Outside the United States
Despite the prevalence of signing bonuses and premium perks, some hospitals still struggled to fill open positions with nurses recruited from outside the United States. Data from The Kaiser Family Foundation show that 32% of hospitals hired foreign-educated RNs in 2022 — more than double the number hired in 2010.
Jennifer Mensik Kennedy, PhD, MBA, RN, NEA-BC, FAAN, president of the American Nurses Association (ANA), is concerned about that trend. The ANA supports the International Council of Nurses and their call for “stronger codes for ethical recruitment of nurses” because international nurse recruitment practices can negatively affect the quality of healthcare in countries that are depleted of nurses.
“Recruiting international nurses as a key strategy for building core staffing is not sustainable in the long term,” Ms. Kennedy said in an interview. “We need to redirect our focus on how to retain staff through fostering healthy work environments and addressing antiquated payment models.”
Reinforcing Retention
Recruiting nurses is just one element of addressing the nursing shortage. Prioritizing job satisfaction is essential to retaining nursing staff. Currently, 33% of nurses who enter the profession quit within the first 2 years.
A growing number of hospitals have implemented programs focused on increasing retention. Lifepoint Health, a national network of 60-plus acute care hospitals, launched a Nurse Residency Program in 2023. The 12-month program, which offers training and mentorship to help recent nursing school graduates, has recruited 750 new nurses and helped them transition to clinical practice.
The Nurse Residency Program has been so successful that the hospital system plans to introduce a 2-year fellowship program in the fall of 2024 that supports the professional development of nurses who want to specialize in areas like acute care, obstetrics, or the intensive care unit.
“We are more focused than ever on increasing partnerships and alignment with our local nursing programs, expanding clinical education opportunities for nursing students, owning and driving a nursing culture, and creating an environment where employees want to work,” said Michelle Watson, MSN, RN, CENP, chief nurse executive and senior vice president of clinical operations at Lifepoint Health.
Ms. Watson also credits their facilities’ chief nursing officers as being “highly engaged and visible leaders” who spend time with RNs to learn about their career aspirations and help them understand how the organization can support their desires for ongoing professional development.
The 2022 Nurse Staffing Task Force, a collaborative initiative by the ANA and other prominent national nursing and healthcare organizations, has developed and widely disseminated a set of recommendations for hospitals focusing on investing in nurse staffing, safe and supportive work environments, and competitive wages.
In addition, the Reimagining Nursing Initiative, started by the American Nurses Foundation, is striving to help nurses feel valued and compensated by creating pilot programs that can help modernize nurses’ reimbursement structure so that they can direct bill.
In the end, attracting and retaining top nursing talent is about more than filling positions — it’s about building a healthcare system where nurses thrive. “In the United States and abroad, we owe it to nurses and the communities they serve to have sustainable and appropriate solutions to staffing and work environment challenges,” said Ms. Kennedy.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In a fiercely competitive healthcare landscape, hospitals are pulling out all the stops to lure top nursing talent through their doors.
As the nursing shortage intensifies, the creative recruitment approach isn’t just about the perks — it’s becoming an essential tool in the race to build a skilled nursing workforce.
Nursing vacancies are as high as 17% — more than double prepandemic levels — and hospitals scrambling to fill them need to do more than raise salaries and bolster benefits packages to entice nurses.
“I am very thankful when I hear of creative ideas that nurse administrators come up with to try to get their ultimate goal, which is enough qualified nurses to take care of patients,” said Linda Plank, dean of the Louise Herrington School of Nursing at Baylor University in Dallas, Texas.
Signing Bonuses, Tuition Reimbursement, and Self-Scheduling, Please
Signing bonuses were among the top perks offered to healthcare workers, with almost 18% of job openings advertising the incentive for new nurse hires; the average signing bonus for registered nurses (RNs) topped $11,000. In 2023, California-based Palomar Health made headlines when it offered eligible RNs a $100,000 signing bonus paid over a 3-year period.
“We are seeing a variety of incentives, like sign-on bonuses, that can be effective at getting the attention of potential new hires,” said Deborah Trautman, PhD, RN, FAAN, president, and CEO of the American Association of Colleges of Nursing. “With the growing competition for registered nurses, especially those prepared in baccalaureate programs, employers should consider what’s most important to nurses entering the field.”
Hospitals have also invested in benefits ranging from tuition reimbursement, student loan forgiveness, and professional development opportunities to expanded parental leave and onsite childcare. Flexible scheduling is a sought-after perk that benefits both new and experienced RNs and could also help with recruitment.
“In the past, [hospitals said], ‘our shift starts at 7 and ends at 7,’ ” Ms. Plank said. “Now, hospitals are a little bit more flexible ... and being open to flexible shifts has merit. If we’re willing to look at things differently, it could get more people involved in patient care.”
An American Nurses Foundation report found that nurses preferred variable and flexible shift lengths, flexible start times, and self-scheduling options over set schedules. In fact, 45% of nurses who left clinical practice would consider returning to work if hospitals switched to a self-scheduling model.
The Cleveland Clinic in Ohio introduced staggered shifts that start at nontraditional times, including 11 AM to 11 PM, flexible shift lengths, and split RN positions that allow clinical care nurses to divide their time between different departments. Last year, Hackensack Meridian Health in New Jersey also piloted a self-scheduling program for its nursing staff.
Hiring Outside the United States
Despite the prevalence of signing bonuses and premium perks, some hospitals still struggled to fill open positions with nurses recruited from outside the United States. Data from The Kaiser Family Foundation show that 32% of hospitals hired foreign-educated RNs in 2022 — more than double the number hired in 2010.
Jennifer Mensik Kennedy, PhD, MBA, RN, NEA-BC, FAAN, president of the American Nurses Association (ANA), is concerned about that trend. The ANA supports the International Council of Nurses and their call for “stronger codes for ethical recruitment of nurses” because international nurse recruitment practices can negatively affect the quality of healthcare in countries that are depleted of nurses.
“Recruiting international nurses as a key strategy for building core staffing is not sustainable in the long term,” Ms. Kennedy said in an interview. “We need to redirect our focus on how to retain staff through fostering healthy work environments and addressing antiquated payment models.”
Reinforcing Retention
Recruiting nurses is just one element of addressing the nursing shortage. Prioritizing job satisfaction is essential to retaining nursing staff. Currently, 33% of nurses who enter the profession quit within the first 2 years.
A growing number of hospitals have implemented programs focused on increasing retention. Lifepoint Health, a national network of 60-plus acute care hospitals, launched a Nurse Residency Program in 2023. The 12-month program, which offers training and mentorship to help recent nursing school graduates, has recruited 750 new nurses and helped them transition to clinical practice.
The Nurse Residency Program has been so successful that the hospital system plans to introduce a 2-year fellowship program in the fall of 2024 that supports the professional development of nurses who want to specialize in areas like acute care, obstetrics, or the intensive care unit.
“We are more focused than ever on increasing partnerships and alignment with our local nursing programs, expanding clinical education opportunities for nursing students, owning and driving a nursing culture, and creating an environment where employees want to work,” said Michelle Watson, MSN, RN, CENP, chief nurse executive and senior vice president of clinical operations at Lifepoint Health.
Ms. Watson also credits their facilities’ chief nursing officers as being “highly engaged and visible leaders” who spend time with RNs to learn about their career aspirations and help them understand how the organization can support their desires for ongoing professional development.
The 2022 Nurse Staffing Task Force, a collaborative initiative by the ANA and other prominent national nursing and healthcare organizations, has developed and widely disseminated a set of recommendations for hospitals focusing on investing in nurse staffing, safe and supportive work environments, and competitive wages.
In addition, the Reimagining Nursing Initiative, started by the American Nurses Foundation, is striving to help nurses feel valued and compensated by creating pilot programs that can help modernize nurses’ reimbursement structure so that they can direct bill.
In the end, attracting and retaining top nursing talent is about more than filling positions — it’s about building a healthcare system where nurses thrive. “In the United States and abroad, we owe it to nurses and the communities they serve to have sustainable and appropriate solutions to staffing and work environment challenges,” said Ms. Kennedy.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary Care Physicians Track an Average of 57 Quality Measures for Value-Based Care Pay
A new analysis suggests one reason doctors are wary of value-based care arrangements: Overkill.
Researchers found that primary care physicians in one large integrated health system were required to track an average of 57 different quality measures across multiple insurers that linked outcomes to payments under value-based contracts.
Medicare contracts were the most likely to pile quality measures on physicians with an average of 13.42 measures vs 10.07 for commercial insurer contracts and 5.37 for Medicaid contracts, reported Claire Boone, PhD, of the University of Chicago in Illinois and Providence Research Network, Portland, Oregon, and colleagues in JAMA Health Forum. The analysis, which may be the first of its kind, tracked 890 primary care physicians from 2020 to 2022.
The average of 57 quality measures per physician was unexpectedly high, Dr. Boone said in an interview.
“The magnitude of that number surprised us,” Dr. Boone said. “Primary care physicians and their practices have a lot on their plate. Now we know that one of those things is a very large number of different quality metrics to pay attention to, measure, report on, and implement.
Value-based care programs use quality measures to evaluate how well clinicians are doing their jobs and adjust reimbursement accordingly. A payer, for example, may raise reimbursements if a clinician has higher numbers of patients who meet quality measure standards for depression screening or blood pressure.
Dr. Boone said her research group is studying the impact of quality measures and was surprised that data showed individual primary care physicians had to deal with a high number of value-based contracts.
The researchers tracked value-based contracts for 890 physicians (58.3% women, 41.7% men) in an unidentified West Coast Health system. (Several study authors work for the Providence Health System, which serves several Western States and Texas.) The average number of patients per physician was 1309.
The physicians were part of an average of 11.18 value-based contracts (commercial insurers, 49.50%; Medicaid, 21.49%; and Medicare, 29.01%). This number grew from 9.39 in 2020 to 12.26 in 2022. Quality measure data weren’t available for 29% of contracts.
Quality measures were considered unique if they referenced different conditions.
For example, colorectal cancer screening is unique from depression screening. The researchers also considered measures for the same condition unique if the target value differed — for example, blood pressure control defined as < 140/90 vs blood pressure control defined as < 130/80, Dr. Boone said.
Dr. Boone said she expected payers to coordinate quality measures.
“The fact that they largely are not is really the main finding of this paper. Without coordination, the use of value-based contracts and quality measures at scale leads to many unique measures being used. This may reflect the fact that there are so many important tasks to do in primary care, and there’s no consensus on which ones should be included in quality-based contracts.”
Ronald N. Adler, MD, an associate professor in the Department of Family Medicine and Community Health at UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts, who’s familiar with the findings but didn’t take part in the research, said the study offers something new — the quantification of quality measures.
He said in an interview that physicians deal with quality measures in different ways. Some clinicians “don’t really care,” and have an attitude of “this is not why I got into medicine.” But others “are very competitive around this, and it leads to a lot of a lot of stress. Trying to address 50-plus measures is impossible and demoralizing.”
The metrics may measure things like mammogram screening that are out of the physician’s control, Dr. Adler said. “I can recommend a mammogram, and my patient can choose not to do it. Or maybe my patient is homeless; she doesn’t have transportation, and it’s not a priority for her, even though she wants to do it.”
Patients may not take medication as prescribed, or they may be unable to afford it, he said. “Can they afford to eat healthy foods? Or is ramen all they can afford, and their sugars are through the roof? There are a lot of factors at play here that are independent of the quality of care provided by the doctor.”
As for his own approach, Dr. Adler said he worries about some measures more than others. “I’m very proactive about screening my patients for colon cancer and maybe a little less so about mammography.”
For colon cancer screening, “there are a lot of benefits and not that many harms as opposed to mammography, which has harms such as false positives and overdiagnosis of breast cancer.”
Dr. Adler is a member of the Quality Measure Alignment Taskforce in Massachusetts, which is trying to establish consensus on appropriate quality measures. But payer participation is voluntary. “Our health systems are too siloed ... so there is no readily available mechanism for enforcing such recommendations.”
Wayne Altman, MD, chair of Family Medicine at Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts, is also familiar with the study findings but didn’t take part in the research. He said in an interview that clinicians shouldn’t have to deal with more than 5-10 quality measures in total.
He pointed out that many measures don’t make sense in certain populations. Titrating blood pressure to < 140/90 isn’t ideal for elderly patients because aggressive control can send their blood pressure dangerously low. “They’re going to fall down, break a hip, and likely die within a year. You have to have the right population and be aware of unintended consequences.”
Still, Dr. Adler noted, there’s an important role for quality measures in healthcare.
“We need data to inform our quality improvement activities, but they need to be the right measures. People can’t respond reasonably to improve on 50-plus measures,” he said. “They need to be consolidated and prioritized. It would be really helpful if we could have a much lower number of measures that are meaningful, safe, and connect to things that matter.”
No funding has been reported. Dr. Boone disclosed a grant from the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Adler and Dr. Altman had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new analysis suggests one reason doctors are wary of value-based care arrangements: Overkill.
Researchers found that primary care physicians in one large integrated health system were required to track an average of 57 different quality measures across multiple insurers that linked outcomes to payments under value-based contracts.
Medicare contracts were the most likely to pile quality measures on physicians with an average of 13.42 measures vs 10.07 for commercial insurer contracts and 5.37 for Medicaid contracts, reported Claire Boone, PhD, of the University of Chicago in Illinois and Providence Research Network, Portland, Oregon, and colleagues in JAMA Health Forum. The analysis, which may be the first of its kind, tracked 890 primary care physicians from 2020 to 2022.
The average of 57 quality measures per physician was unexpectedly high, Dr. Boone said in an interview.
“The magnitude of that number surprised us,” Dr. Boone said. “Primary care physicians and their practices have a lot on their plate. Now we know that one of those things is a very large number of different quality metrics to pay attention to, measure, report on, and implement.
Value-based care programs use quality measures to evaluate how well clinicians are doing their jobs and adjust reimbursement accordingly. A payer, for example, may raise reimbursements if a clinician has higher numbers of patients who meet quality measure standards for depression screening or blood pressure.
Dr. Boone said her research group is studying the impact of quality measures and was surprised that data showed individual primary care physicians had to deal with a high number of value-based contracts.
The researchers tracked value-based contracts for 890 physicians (58.3% women, 41.7% men) in an unidentified West Coast Health system. (Several study authors work for the Providence Health System, which serves several Western States and Texas.) The average number of patients per physician was 1309.
The physicians were part of an average of 11.18 value-based contracts (commercial insurers, 49.50%; Medicaid, 21.49%; and Medicare, 29.01%). This number grew from 9.39 in 2020 to 12.26 in 2022. Quality measure data weren’t available for 29% of contracts.
Quality measures were considered unique if they referenced different conditions.
For example, colorectal cancer screening is unique from depression screening. The researchers also considered measures for the same condition unique if the target value differed — for example, blood pressure control defined as < 140/90 vs blood pressure control defined as < 130/80, Dr. Boone said.
Dr. Boone said she expected payers to coordinate quality measures.
“The fact that they largely are not is really the main finding of this paper. Without coordination, the use of value-based contracts and quality measures at scale leads to many unique measures being used. This may reflect the fact that there are so many important tasks to do in primary care, and there’s no consensus on which ones should be included in quality-based contracts.”
Ronald N. Adler, MD, an associate professor in the Department of Family Medicine and Community Health at UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts, who’s familiar with the findings but didn’t take part in the research, said the study offers something new — the quantification of quality measures.
He said in an interview that physicians deal with quality measures in different ways. Some clinicians “don’t really care,” and have an attitude of “this is not why I got into medicine.” But others “are very competitive around this, and it leads to a lot of a lot of stress. Trying to address 50-plus measures is impossible and demoralizing.”
The metrics may measure things like mammogram screening that are out of the physician’s control, Dr. Adler said. “I can recommend a mammogram, and my patient can choose not to do it. Or maybe my patient is homeless; she doesn’t have transportation, and it’s not a priority for her, even though she wants to do it.”
Patients may not take medication as prescribed, or they may be unable to afford it, he said. “Can they afford to eat healthy foods? Or is ramen all they can afford, and their sugars are through the roof? There are a lot of factors at play here that are independent of the quality of care provided by the doctor.”
As for his own approach, Dr. Adler said he worries about some measures more than others. “I’m very proactive about screening my patients for colon cancer and maybe a little less so about mammography.”
For colon cancer screening, “there are a lot of benefits and not that many harms as opposed to mammography, which has harms such as false positives and overdiagnosis of breast cancer.”
Dr. Adler is a member of the Quality Measure Alignment Taskforce in Massachusetts, which is trying to establish consensus on appropriate quality measures. But payer participation is voluntary. “Our health systems are too siloed ... so there is no readily available mechanism for enforcing such recommendations.”
Wayne Altman, MD, chair of Family Medicine at Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts, is also familiar with the study findings but didn’t take part in the research. He said in an interview that clinicians shouldn’t have to deal with more than 5-10 quality measures in total.
He pointed out that many measures don’t make sense in certain populations. Titrating blood pressure to < 140/90 isn’t ideal for elderly patients because aggressive control can send their blood pressure dangerously low. “They’re going to fall down, break a hip, and likely die within a year. You have to have the right population and be aware of unintended consequences.”
Still, Dr. Adler noted, there’s an important role for quality measures in healthcare.
“We need data to inform our quality improvement activities, but they need to be the right measures. People can’t respond reasonably to improve on 50-plus measures,” he said. “They need to be consolidated and prioritized. It would be really helpful if we could have a much lower number of measures that are meaningful, safe, and connect to things that matter.”
No funding has been reported. Dr. Boone disclosed a grant from the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Adler and Dr. Altman had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new analysis suggests one reason doctors are wary of value-based care arrangements: Overkill.
Researchers found that primary care physicians in one large integrated health system were required to track an average of 57 different quality measures across multiple insurers that linked outcomes to payments under value-based contracts.
Medicare contracts were the most likely to pile quality measures on physicians with an average of 13.42 measures vs 10.07 for commercial insurer contracts and 5.37 for Medicaid contracts, reported Claire Boone, PhD, of the University of Chicago in Illinois and Providence Research Network, Portland, Oregon, and colleagues in JAMA Health Forum. The analysis, which may be the first of its kind, tracked 890 primary care physicians from 2020 to 2022.
The average of 57 quality measures per physician was unexpectedly high, Dr. Boone said in an interview.
“The magnitude of that number surprised us,” Dr. Boone said. “Primary care physicians and their practices have a lot on their plate. Now we know that one of those things is a very large number of different quality metrics to pay attention to, measure, report on, and implement.
Value-based care programs use quality measures to evaluate how well clinicians are doing their jobs and adjust reimbursement accordingly. A payer, for example, may raise reimbursements if a clinician has higher numbers of patients who meet quality measure standards for depression screening or blood pressure.
Dr. Boone said her research group is studying the impact of quality measures and was surprised that data showed individual primary care physicians had to deal with a high number of value-based contracts.
The researchers tracked value-based contracts for 890 physicians (58.3% women, 41.7% men) in an unidentified West Coast Health system. (Several study authors work for the Providence Health System, which serves several Western States and Texas.) The average number of patients per physician was 1309.
The physicians were part of an average of 11.18 value-based contracts (commercial insurers, 49.50%; Medicaid, 21.49%; and Medicare, 29.01%). This number grew from 9.39 in 2020 to 12.26 in 2022. Quality measure data weren’t available for 29% of contracts.
Quality measures were considered unique if they referenced different conditions.
For example, colorectal cancer screening is unique from depression screening. The researchers also considered measures for the same condition unique if the target value differed — for example, blood pressure control defined as < 140/90 vs blood pressure control defined as < 130/80, Dr. Boone said.
Dr. Boone said she expected payers to coordinate quality measures.
“The fact that they largely are not is really the main finding of this paper. Without coordination, the use of value-based contracts and quality measures at scale leads to many unique measures being used. This may reflect the fact that there are so many important tasks to do in primary care, and there’s no consensus on which ones should be included in quality-based contracts.”
Ronald N. Adler, MD, an associate professor in the Department of Family Medicine and Community Health at UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts, who’s familiar with the findings but didn’t take part in the research, said the study offers something new — the quantification of quality measures.
He said in an interview that physicians deal with quality measures in different ways. Some clinicians “don’t really care,” and have an attitude of “this is not why I got into medicine.” But others “are very competitive around this, and it leads to a lot of a lot of stress. Trying to address 50-plus measures is impossible and demoralizing.”
The metrics may measure things like mammogram screening that are out of the physician’s control, Dr. Adler said. “I can recommend a mammogram, and my patient can choose not to do it. Or maybe my patient is homeless; she doesn’t have transportation, and it’s not a priority for her, even though she wants to do it.”
Patients may not take medication as prescribed, or they may be unable to afford it, he said. “Can they afford to eat healthy foods? Or is ramen all they can afford, and their sugars are through the roof? There are a lot of factors at play here that are independent of the quality of care provided by the doctor.”
As for his own approach, Dr. Adler said he worries about some measures more than others. “I’m very proactive about screening my patients for colon cancer and maybe a little less so about mammography.”
For colon cancer screening, “there are a lot of benefits and not that many harms as opposed to mammography, which has harms such as false positives and overdiagnosis of breast cancer.”
Dr. Adler is a member of the Quality Measure Alignment Taskforce in Massachusetts, which is trying to establish consensus on appropriate quality measures. But payer participation is voluntary. “Our health systems are too siloed ... so there is no readily available mechanism for enforcing such recommendations.”
Wayne Altman, MD, chair of Family Medicine at Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts, is also familiar with the study findings but didn’t take part in the research. He said in an interview that clinicians shouldn’t have to deal with more than 5-10 quality measures in total.
He pointed out that many measures don’t make sense in certain populations. Titrating blood pressure to < 140/90 isn’t ideal for elderly patients because aggressive control can send their blood pressure dangerously low. “They’re going to fall down, break a hip, and likely die within a year. You have to have the right population and be aware of unintended consequences.”
Still, Dr. Adler noted, there’s an important role for quality measures in healthcare.
“We need data to inform our quality improvement activities, but they need to be the right measures. People can’t respond reasonably to improve on 50-plus measures,” he said. “They need to be consolidated and prioritized. It would be really helpful if we could have a much lower number of measures that are meaningful, safe, and connect to things that matter.”
No funding has been reported. Dr. Boone disclosed a grant from the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Adler and Dr. Altman had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA HEALTH FORUM
The Wellness Industry: Financially Toxic, Says Ethicist
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine in New York City.
We have many debates and arguments that are swirling around about the out-of-control costs of Medicare. Many people are arguing we’ve got to trim it and cut back, and many people note that we can’t just go on and on with that kind of expenditure.
People look around for savings. Rightly, we can’t go on with the prices that we’re paying. No system could. We’ll bankrupt ourselves if we don’t drive prices down.
There’s another area that is driving up cost where, despite the fact that Medicare doesn’t pay for it, we could capture resources and hopefully shift them back to things like Medicare coverage or the insurance of other efficacious procedures. That area is the wellness industry.
That’s money coming out of people’s pockets that we could hopefully aim at the payment of things that we know work, not seeing the money drain out to cover bunk, nonsense, and charlatanism.
Does any or most of this stuff work? Do anything? Help anybody? No. We are spending money on charlatans and quacks. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which you might think is the agency that could step in and start to get rid of some of this nonsense, is just too overwhelmed trying to track drugs, devices, and vaccines to give much attention to the wellness industry.
What am I talking about specifically? I’m talking about everything from gut probiotics that are sold in sodas to probiotic facial creams and the Goop industry of Gwyneth Paltrow, where you have people buying things like wellness mats or vaginal eggs that are supposed to maintain gynecologic health.
We’re talking about things like PEMF, or pulse electronic magnetic fields, where you buy a machine and expose yourself to mild magnetic pulses. I went online to look them up, and the machines cost $5000-$50,000. There’s no evidence that it works. By the way, the machines are not only out there as being sold for pain relief and many other things to humans, but also they’re being sold for your pets.
That industry is completely out of control. Wellness interventions, whether it’s transcranial magnetism or all manner of supplements that are sold in health food stores, over and over again, we see a world in which wellness is promoted but no data are introduced to show that any of it helps, works, or does anybody any good.
It may not be all that harmful, but it’s certainly financially toxic to many people who end up spending good amounts of money using these things. I think doctors need to ask patients if they are using any of these things, particularly if they have chronic conditions. They’re likely, many of them, to be seduced by online advertisement to get involved with this stuff because it’s preventive or it’ll help treat some condition that they have.
The industry is out of control. We’re trying to figure out how to spend money on things we know work in medicine, and yet we continue to tolerate bunk, nonsense, quackery, and charlatanism, just letting it grow and grow and grow in terms of cost.
That’s money that could go elsewhere. That is money that is being taken out of the pockets of patients. They’re doing things that may even delay medical treatment, which won’t really help them, and they are doing things that perhaps might even interfere with medical care that really is known to be beneficial.
I think it’s time to push for more money for the FDA to regulate the wellness side. I think it’s time for the Federal Trade Commission to go after ads that promise health benefits. I think it’s time to have some honest conversations with patients: What are you using? What are you doing? Tell me about it, and here’s why I think you could probably spend your money in a better way.
Dr. Caplan, director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York, disclosed ties with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). He serves as a contributing author and adviser for Medscape.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine in New York City.
We have many debates and arguments that are swirling around about the out-of-control costs of Medicare. Many people are arguing we’ve got to trim it and cut back, and many people note that we can’t just go on and on with that kind of expenditure.
People look around for savings. Rightly, we can’t go on with the prices that we’re paying. No system could. We’ll bankrupt ourselves if we don’t drive prices down.
There’s another area that is driving up cost where, despite the fact that Medicare doesn’t pay for it, we could capture resources and hopefully shift them back to things like Medicare coverage or the insurance of other efficacious procedures. That area is the wellness industry.
That’s money coming out of people’s pockets that we could hopefully aim at the payment of things that we know work, not seeing the money drain out to cover bunk, nonsense, and charlatanism.
Does any or most of this stuff work? Do anything? Help anybody? No. We are spending money on charlatans and quacks. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which you might think is the agency that could step in and start to get rid of some of this nonsense, is just too overwhelmed trying to track drugs, devices, and vaccines to give much attention to the wellness industry.
What am I talking about specifically? I’m talking about everything from gut probiotics that are sold in sodas to probiotic facial creams and the Goop industry of Gwyneth Paltrow, where you have people buying things like wellness mats or vaginal eggs that are supposed to maintain gynecologic health.
We’re talking about things like PEMF, or pulse electronic magnetic fields, where you buy a machine and expose yourself to mild magnetic pulses. I went online to look them up, and the machines cost $5000-$50,000. There’s no evidence that it works. By the way, the machines are not only out there as being sold for pain relief and many other things to humans, but also they’re being sold for your pets.
That industry is completely out of control. Wellness interventions, whether it’s transcranial magnetism or all manner of supplements that are sold in health food stores, over and over again, we see a world in which wellness is promoted but no data are introduced to show that any of it helps, works, or does anybody any good.
It may not be all that harmful, but it’s certainly financially toxic to many people who end up spending good amounts of money using these things. I think doctors need to ask patients if they are using any of these things, particularly if they have chronic conditions. They’re likely, many of them, to be seduced by online advertisement to get involved with this stuff because it’s preventive or it’ll help treat some condition that they have.
The industry is out of control. We’re trying to figure out how to spend money on things we know work in medicine, and yet we continue to tolerate bunk, nonsense, quackery, and charlatanism, just letting it grow and grow and grow in terms of cost.
That’s money that could go elsewhere. That is money that is being taken out of the pockets of patients. They’re doing things that may even delay medical treatment, which won’t really help them, and they are doing things that perhaps might even interfere with medical care that really is known to be beneficial.
I think it’s time to push for more money for the FDA to regulate the wellness side. I think it’s time for the Federal Trade Commission to go after ads that promise health benefits. I think it’s time to have some honest conversations with patients: What are you using? What are you doing? Tell me about it, and here’s why I think you could probably spend your money in a better way.
Dr. Caplan, director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York, disclosed ties with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). He serves as a contributing author and adviser for Medscape.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine in New York City.
We have many debates and arguments that are swirling around about the out-of-control costs of Medicare. Many people are arguing we’ve got to trim it and cut back, and many people note that we can’t just go on and on with that kind of expenditure.
People look around for savings. Rightly, we can’t go on with the prices that we’re paying. No system could. We’ll bankrupt ourselves if we don’t drive prices down.
There’s another area that is driving up cost where, despite the fact that Medicare doesn’t pay for it, we could capture resources and hopefully shift them back to things like Medicare coverage or the insurance of other efficacious procedures. That area is the wellness industry.
That’s money coming out of people’s pockets that we could hopefully aim at the payment of things that we know work, not seeing the money drain out to cover bunk, nonsense, and charlatanism.
Does any or most of this stuff work? Do anything? Help anybody? No. We are spending money on charlatans and quacks. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which you might think is the agency that could step in and start to get rid of some of this nonsense, is just too overwhelmed trying to track drugs, devices, and vaccines to give much attention to the wellness industry.
What am I talking about specifically? I’m talking about everything from gut probiotics that are sold in sodas to probiotic facial creams and the Goop industry of Gwyneth Paltrow, where you have people buying things like wellness mats or vaginal eggs that are supposed to maintain gynecologic health.
We’re talking about things like PEMF, or pulse electronic magnetic fields, where you buy a machine and expose yourself to mild magnetic pulses. I went online to look them up, and the machines cost $5000-$50,000. There’s no evidence that it works. By the way, the machines are not only out there as being sold for pain relief and many other things to humans, but also they’re being sold for your pets.
That industry is completely out of control. Wellness interventions, whether it’s transcranial magnetism or all manner of supplements that are sold in health food stores, over and over again, we see a world in which wellness is promoted but no data are introduced to show that any of it helps, works, or does anybody any good.
It may not be all that harmful, but it’s certainly financially toxic to many people who end up spending good amounts of money using these things. I think doctors need to ask patients if they are using any of these things, particularly if they have chronic conditions. They’re likely, many of them, to be seduced by online advertisement to get involved with this stuff because it’s preventive or it’ll help treat some condition that they have.
The industry is out of control. We’re trying to figure out how to spend money on things we know work in medicine, and yet we continue to tolerate bunk, nonsense, quackery, and charlatanism, just letting it grow and grow and grow in terms of cost.
That’s money that could go elsewhere. That is money that is being taken out of the pockets of patients. They’re doing things that may even delay medical treatment, which won’t really help them, and they are doing things that perhaps might even interfere with medical care that really is known to be beneficial.
I think it’s time to push for more money for the FDA to regulate the wellness side. I think it’s time for the Federal Trade Commission to go after ads that promise health benefits. I think it’s time to have some honest conversations with patients: What are you using? What are you doing? Tell me about it, and here’s why I think you could probably spend your money in a better way.
Dr. Caplan, director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York, disclosed ties with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). He serves as a contributing author and adviser for Medscape.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Rheumatologist Volunteers Make a Difference to Those in Need at Home and Overseas
As a resident, rheumatologist Daniel Albert, MD, did his first volunteer mission to Afghanistan. The clinic had one portable chest x-ray machine, and physicians could order a complete blood count but no other laboratory studies.
“We could do sputum stains, but that was about it. You had to use your clinical acumen and make decisions based on examining the patient and taking a history,” said Dr. Albert, a professor of medicine and pediatrics at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, and The Dartmouth Institute in Lebanon, both in New Hampshire. Such tasks can be difficult in a non–English-speaking country.
“There’s a language barrier no matter where you are,” Dr. Albert said.
In Nashville, Tennessee, James Gore, MD, had an epiphany about opening a free rheumatology clinic during a church service. His priest was discussing St. Sampson the Hospitable’s story and closed with “you don’t have to change the world. All you have to do is your little part,” Dr. Gore said. He knew he didn’t need much: a computer, a stethoscope, and a printer for prescriptions.
When his church expanded its building space, Dr. Gore took the opportunity to achieve his goal.
“I didn’t feel responsible for the clinic to succeed, but I did feel responsible to try my best,” he said. That was 14 years ago. To date, the monthly clinic has served 1124 patients representing 55 counties in Tennessee and several other patients from Kentucky.
Volunteer work is a juggling act. Dr. Gore divides his time between the clinic and his work as associate professor of clinical medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC), also in Nashville.
Dr. Albert often gave up his vacation time and had to balance commitments with his own medical practice and family to do his overseas missions. In his view, it’s worth the extra time and effort.
“It makes you a better physician because you make reasonable decisions and conclusions based on the resources available. Various places had various limitations, but none of them had the kind of resources that we routinely avail ourselves of in the US,” he said.
Tennessee Clients Get Access to Care, Medications
In some parts of the United States, good rheumatology care is hard to come by. One in four people in Tennessee have no health insurance. There’s a big need for rheumatology care in the state, Dr. Gore said.
On the second Saturday of each month, he volunteers his services at the St. Sampson Medical Clinic at Holy Trinity Greek Orthodox Church, Nashville, Tennessee, from 9 AM to 4 PM, providing care for uninsured adult rheumatology patients.
Patients come by referral from a charity clinic or health department and appointment only. The clinic asks for a $10 payment for their visits. “If they can’t pay, we still see them. But we only take care of patients who don’t have insurance,” Dr. Gore said. Allowing patients to pay gives them an opportunity to show they are vested in their own care. Often, patients will donate extra in gratitude.
Dr. Gore, along with VUMC colleague and rheumatologist Narender Annapureddy, MD, and nurse practitioner Julie Barnes, treats a variety of rheumatic diseases. For Ms. Barnes, volunteering has many rewarding aspects, “as the patients would be unable to have the treatments they need without insurance,” she said.
“We have had patients waiting for many months or sometimes years and have not had a diagnosis, and in a short time, we have been able to diagnose and get them on specific treatment,” Dr. Annapureddy said.
Most people come in for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and lupus and also positive antinuclear antibody tests. They also see patients with psoriatic arthritis, Sjögren’s disease, gout, scleroderma, Behçet disease, and leukocytoclastic vasculitis. On a typical clinic day, the team can treat up to 30-plus patients. The clinic recently expanded its services to include cardiology care, seeing about 10 patients each month.
Prior to St. Sampson, there were no volunteer clinics in Tennessee specifically dedicated to helping patients with rheumatologic disease. Untreated, these diseases may cause chronic, severe pain, lead to irreversible joint damage, and increase the risk for death.
Many patients have received medications such as adalimumab, etanercept, or tofacitinib for free. The drug companies will provide free medications, provided that they’re prescribed by a board-certified rheumatologist and the patient is uninsured and qualifies for the medication, Dr. Gore said.
Drugs like these can cost about $50,000 a year. “We have pharmacists that donate their time to help these patients get approved for those medicines,” Dr. Gore said. To date, more than 100 patients have received a biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug through the clinic.
The clinic has received more than $100,000 in donated professional fees, including $48,706 for consultations. Dr. Gore and colleagues relied on other volunteers to bring the clinic to life. He worked with his sister to develop an electronic medical record system that the clinic still uses today. “We did not buy expensive laptops or printers. I had a very generous volunteer, Damon Miltner, our IT guy, who set everything up to make our intranet secure,” he said.
The volunteer nurses, IT, and front desk all work together to make the clinic run efficiently, said Ms. Barnes, who also works as a nurse practitioner with Vanderbilt Rheumatology Cool Springs in Franklin, Tennessee. “We share a lunch together, all in a beautiful and holy church. I do not think of this as work, but as spending time with people who are appreciative and kind,” she said.
“It is amazing to see patients who are able to walk in by themselves after having used a cane for years,” Dr. Annapureddy said. “While doing this on weekends with young kids is challenging, having a supportive spouse who shares the same value makes it much easier to be able to do volunteer work.”
Working Outside Your Comfort Zone
Dr. Albert has traveled to all parts of the world to volunteer his services as a rheumatologist and general practitioner. This includes missions to Uganda, Rwanda, Ecuador, Peru, Nepal, and Borneo. He’s participated with several volunteer organizations, among them the International Student & Scholar Services program at the University of Pennsylvania, CARE, Global Volunteers, Project Amazonas, Asha Nepal, Health in Harmony, and several others.
Rheumatologists who volunteer in underdeveloped countries should be prepared to work outside of their specialty — and their comfort zone. In some instances, Dr. Albert took care of AIDS-related infectious diseases. “It’s not something I am particularly knowledgeable about, and I actually spent a fair amount of time reading about it before I went on the plane in order to get some comfort level.”
Dr. Albert often found himself doing more primary care and general pediatrics than rheumatology care. “I would see rheumatic conditions. But there’s not a lot of RA in developing countries, which is something that people have noted before. And the same goes for other autoimmune conditions. They’re just not that common.”
He did see a lot of septic arthritis and tuberculosis in Uganda. “We had a rheum clinic and saw a mixture of the consequences of septic arthritis and also a few RA and lupus patients.”
Limited resources are another thing to prepare for.
Whenever he traveled to a place that didn’t have a lot of resources, Dr. Albert would collect as many supplies as he could from the nearest hospital, pack them away, and try to get the supplies to the mission location.
Sometimes it worked out, and sometimes it didn’t, he said. “I probably had $10,000 worth of medical supplies when I went to Armenia, and American Airlines lost it. It ended up back in my apartment 3 months later. That was unfortunate because there was lot of good stuff there.”
He thought about FedEx-ing some supplies to a mission in Uganda, but it was astronomically expensive, so that didn’t work.
Luggage weight restrictions are another obstacle that sometimes requires a waiver. Dr. Albert once had to get the Red Cross to work with an airline to get a luggage waiver. “Other airlines were very good and didn’t have those kinds of restrictions. But most of the time I got some supplies to go with me, and sometimes that was a very helpful addition,” especially if the mission site was lacking in resources, he said.
When Charity Work Produces Success Stories
During one of his missions in Uganda with the University of Pennsylvania, Dr. Albert helped the Makerere University Medical School, Kampala, to establish a rheumatology clinic, which was affiliated with Mulago National Specialised Hospital. The clinic operated once a week for half a day, mostly treating patients with RA and lupus.
The mission also established an AIDS clinic. Many of the patients with musculoskeletal complaints also had HIV and were able to get antiretroviral drugs through the clinic, he said.
For Dr. Gore, seeing patients from more than half the counties in Tennessee was one of the clinic’s biggest accomplishments. “That was all through word of mouth,” he said.
In rheumatology, many patients may feel their condition is hopeless, Ms. Barnes noted. “There have been many patients that, through months of proper treatment, have normal lives. A high percentage would be disabled without the needed medical therapies.”
Dr. Gore has seen patients who literally couldn’t walk or had severe, painful psoriasis all over their body. The clinic would put them on medicine that would give them new life. The psoriasis would clear up, or their joints would heal, and they could walk again.
One of Dr. Gore’s patients, a woman in her mid-50s, got on an expensive medication that brought her arthritis into remission. She’s now able to care for her grandchildren.
The fact that the clinic, with the help of volunteer pharmacologists, can provide medications to enable patients to have a less destructive disease and improved quality of life “is a major reward,” Ms. Barnes said.
Balancing Your Priorities
Overseas missions can last for a few weeks to several months, depending on the mission, the organization, and the type of care involved.
Rheumatologists who want to volunteer need to do so in a way that doesn’t generate a lot of angst with supervisors or colleagues. Dr. Albert balanced this by keeping his missions reasonably short. “I would have someone cover my service. And since there’s reciprocity in the places I worked for, if they covered me for a month, I would cover them for a month, so it wasn’t a burden on anybody.”
“By and large, I used my vacation time to do it, and it does cost some money, but it’s a lot less than the cost of a typical vacation,” Dr. Albert said.
Volunteer work can also compete with family time. Dr. Albert ended up taking his family along on several of his missions to Ecuador and Uganda. He would tell the organization: “My family wants to come. Is there anything they can do while I’m working in the program? And they usually found an occupation.”
At St. Sampson, volunteering is also a family affair. “My wife acts as the administrator, so she’s the one that helps schedule patients and deals with a lot of the faxes.” It’s a big commitment for Dr. Gore’s family and for the church, which gives up a significant chunk of the building one Saturday a month.
“However, for us, I think that it’s a real manifestation of giving back and trying to help those in need and doing what we can do,” he said.
Volunteer Work Involves Prep Work
Establishing the St. Sampson clinic took some planning. Dr. Gore and colleagues had to fill out a 501(c)(3) application; establish a charter, bylaws, articles of incorporation, policies, and procedures; and obtain medical malpractice and general liability insurance.
The clinic was able to get financing from the Mid-South Chapter of the Lupus Foundation of America as well as in-kind donations from the church. “We’ve had a lot of different companies who were very generous in donating money and excited to help the clinic continue,” Dr. Gore said.
All volunteers sign a Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act consent form.
Although the clinic operates for about 7 hours a month, it’s still important to have malpractice insurance, Dr. Gore said. He and his colleagues also have tail insurance that covers medical malpractice insurance for up to 7 years if the clinic closes.
“If somebody were to slip and fall and then try to sue the church, we have a separate policy for the clinic for that. We also have a director’s and officer’s insurance policy,” he said.
Anyone who volunteers abroad should get a travel medicine clinic consultation. “Most of the time, it’s of very little consequence. You might have to get [a] yellow fever vaccine” when traveling to certain parts of the world, Dr. Albert said.
“If you’re going into an area that is all volatile politically or in some way a threat to your personal security, I think you have to think very carefully about that,” he said, suggesting that doctors consult with the US Department of State about potential dangers.
Talk to other physicians who have gone on missions and your sponsoring institution. “By and large, you want to go with a large organization that’s been doing ongoing work,” Dr. Albert said.
Volunteer work teaches you about the breadth of humanist endeavors across the world, he noted. “The people that you deal with are very grateful for your help. Whether you’re successful or not, they’re still very appreciative of the efforts that you’re making to help.”
Dr. Albert and Dr. Gore had no disclosures. Dr. Annapureddy has done consulting for GlaxoSmithKline. Ms. Barnes had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As a resident, rheumatologist Daniel Albert, MD, did his first volunteer mission to Afghanistan. The clinic had one portable chest x-ray machine, and physicians could order a complete blood count but no other laboratory studies.
“We could do sputum stains, but that was about it. You had to use your clinical acumen and make decisions based on examining the patient and taking a history,” said Dr. Albert, a professor of medicine and pediatrics at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, and The Dartmouth Institute in Lebanon, both in New Hampshire. Such tasks can be difficult in a non–English-speaking country.
“There’s a language barrier no matter where you are,” Dr. Albert said.
In Nashville, Tennessee, James Gore, MD, had an epiphany about opening a free rheumatology clinic during a church service. His priest was discussing St. Sampson the Hospitable’s story and closed with “you don’t have to change the world. All you have to do is your little part,” Dr. Gore said. He knew he didn’t need much: a computer, a stethoscope, and a printer for prescriptions.
When his church expanded its building space, Dr. Gore took the opportunity to achieve his goal.
“I didn’t feel responsible for the clinic to succeed, but I did feel responsible to try my best,” he said. That was 14 years ago. To date, the monthly clinic has served 1124 patients representing 55 counties in Tennessee and several other patients from Kentucky.
Volunteer work is a juggling act. Dr. Gore divides his time between the clinic and his work as associate professor of clinical medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC), also in Nashville.
Dr. Albert often gave up his vacation time and had to balance commitments with his own medical practice and family to do his overseas missions. In his view, it’s worth the extra time and effort.
“It makes you a better physician because you make reasonable decisions and conclusions based on the resources available. Various places had various limitations, but none of them had the kind of resources that we routinely avail ourselves of in the US,” he said.
Tennessee Clients Get Access to Care, Medications
In some parts of the United States, good rheumatology care is hard to come by. One in four people in Tennessee have no health insurance. There’s a big need for rheumatology care in the state, Dr. Gore said.
On the second Saturday of each month, he volunteers his services at the St. Sampson Medical Clinic at Holy Trinity Greek Orthodox Church, Nashville, Tennessee, from 9 AM to 4 PM, providing care for uninsured adult rheumatology patients.
Patients come by referral from a charity clinic or health department and appointment only. The clinic asks for a $10 payment for their visits. “If they can’t pay, we still see them. But we only take care of patients who don’t have insurance,” Dr. Gore said. Allowing patients to pay gives them an opportunity to show they are vested in their own care. Often, patients will donate extra in gratitude.
Dr. Gore, along with VUMC colleague and rheumatologist Narender Annapureddy, MD, and nurse practitioner Julie Barnes, treats a variety of rheumatic diseases. For Ms. Barnes, volunteering has many rewarding aspects, “as the patients would be unable to have the treatments they need without insurance,” she said.
“We have had patients waiting for many months or sometimes years and have not had a diagnosis, and in a short time, we have been able to diagnose and get them on specific treatment,” Dr. Annapureddy said.
Most people come in for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and lupus and also positive antinuclear antibody tests. They also see patients with psoriatic arthritis, Sjögren’s disease, gout, scleroderma, Behçet disease, and leukocytoclastic vasculitis. On a typical clinic day, the team can treat up to 30-plus patients. The clinic recently expanded its services to include cardiology care, seeing about 10 patients each month.
Prior to St. Sampson, there were no volunteer clinics in Tennessee specifically dedicated to helping patients with rheumatologic disease. Untreated, these diseases may cause chronic, severe pain, lead to irreversible joint damage, and increase the risk for death.
Many patients have received medications such as adalimumab, etanercept, or tofacitinib for free. The drug companies will provide free medications, provided that they’re prescribed by a board-certified rheumatologist and the patient is uninsured and qualifies for the medication, Dr. Gore said.
Drugs like these can cost about $50,000 a year. “We have pharmacists that donate their time to help these patients get approved for those medicines,” Dr. Gore said. To date, more than 100 patients have received a biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug through the clinic.
The clinic has received more than $100,000 in donated professional fees, including $48,706 for consultations. Dr. Gore and colleagues relied on other volunteers to bring the clinic to life. He worked with his sister to develop an electronic medical record system that the clinic still uses today. “We did not buy expensive laptops or printers. I had a very generous volunteer, Damon Miltner, our IT guy, who set everything up to make our intranet secure,” he said.
The volunteer nurses, IT, and front desk all work together to make the clinic run efficiently, said Ms. Barnes, who also works as a nurse practitioner with Vanderbilt Rheumatology Cool Springs in Franklin, Tennessee. “We share a lunch together, all in a beautiful and holy church. I do not think of this as work, but as spending time with people who are appreciative and kind,” she said.
“It is amazing to see patients who are able to walk in by themselves after having used a cane for years,” Dr. Annapureddy said. “While doing this on weekends with young kids is challenging, having a supportive spouse who shares the same value makes it much easier to be able to do volunteer work.”
Working Outside Your Comfort Zone
Dr. Albert has traveled to all parts of the world to volunteer his services as a rheumatologist and general practitioner. This includes missions to Uganda, Rwanda, Ecuador, Peru, Nepal, and Borneo. He’s participated with several volunteer organizations, among them the International Student & Scholar Services program at the University of Pennsylvania, CARE, Global Volunteers, Project Amazonas, Asha Nepal, Health in Harmony, and several others.
Rheumatologists who volunteer in underdeveloped countries should be prepared to work outside of their specialty — and their comfort zone. In some instances, Dr. Albert took care of AIDS-related infectious diseases. “It’s not something I am particularly knowledgeable about, and I actually spent a fair amount of time reading about it before I went on the plane in order to get some comfort level.”
Dr. Albert often found himself doing more primary care and general pediatrics than rheumatology care. “I would see rheumatic conditions. But there’s not a lot of RA in developing countries, which is something that people have noted before. And the same goes for other autoimmune conditions. They’re just not that common.”
He did see a lot of septic arthritis and tuberculosis in Uganda. “We had a rheum clinic and saw a mixture of the consequences of septic arthritis and also a few RA and lupus patients.”
Limited resources are another thing to prepare for.
Whenever he traveled to a place that didn’t have a lot of resources, Dr. Albert would collect as many supplies as he could from the nearest hospital, pack them away, and try to get the supplies to the mission location.
Sometimes it worked out, and sometimes it didn’t, he said. “I probably had $10,000 worth of medical supplies when I went to Armenia, and American Airlines lost it. It ended up back in my apartment 3 months later. That was unfortunate because there was lot of good stuff there.”
He thought about FedEx-ing some supplies to a mission in Uganda, but it was astronomically expensive, so that didn’t work.
Luggage weight restrictions are another obstacle that sometimes requires a waiver. Dr. Albert once had to get the Red Cross to work with an airline to get a luggage waiver. “Other airlines were very good and didn’t have those kinds of restrictions. But most of the time I got some supplies to go with me, and sometimes that was a very helpful addition,” especially if the mission site was lacking in resources, he said.
When Charity Work Produces Success Stories
During one of his missions in Uganda with the University of Pennsylvania, Dr. Albert helped the Makerere University Medical School, Kampala, to establish a rheumatology clinic, which was affiliated with Mulago National Specialised Hospital. The clinic operated once a week for half a day, mostly treating patients with RA and lupus.
The mission also established an AIDS clinic. Many of the patients with musculoskeletal complaints also had HIV and were able to get antiretroviral drugs through the clinic, he said.
For Dr. Gore, seeing patients from more than half the counties in Tennessee was one of the clinic’s biggest accomplishments. “That was all through word of mouth,” he said.
In rheumatology, many patients may feel their condition is hopeless, Ms. Barnes noted. “There have been many patients that, through months of proper treatment, have normal lives. A high percentage would be disabled without the needed medical therapies.”
Dr. Gore has seen patients who literally couldn’t walk or had severe, painful psoriasis all over their body. The clinic would put them on medicine that would give them new life. The psoriasis would clear up, or their joints would heal, and they could walk again.
One of Dr. Gore’s patients, a woman in her mid-50s, got on an expensive medication that brought her arthritis into remission. She’s now able to care for her grandchildren.
The fact that the clinic, with the help of volunteer pharmacologists, can provide medications to enable patients to have a less destructive disease and improved quality of life “is a major reward,” Ms. Barnes said.
Balancing Your Priorities
Overseas missions can last for a few weeks to several months, depending on the mission, the organization, and the type of care involved.
Rheumatologists who want to volunteer need to do so in a way that doesn’t generate a lot of angst with supervisors or colleagues. Dr. Albert balanced this by keeping his missions reasonably short. “I would have someone cover my service. And since there’s reciprocity in the places I worked for, if they covered me for a month, I would cover them for a month, so it wasn’t a burden on anybody.”
“By and large, I used my vacation time to do it, and it does cost some money, but it’s a lot less than the cost of a typical vacation,” Dr. Albert said.
Volunteer work can also compete with family time. Dr. Albert ended up taking his family along on several of his missions to Ecuador and Uganda. He would tell the organization: “My family wants to come. Is there anything they can do while I’m working in the program? And they usually found an occupation.”
At St. Sampson, volunteering is also a family affair. “My wife acts as the administrator, so she’s the one that helps schedule patients and deals with a lot of the faxes.” It’s a big commitment for Dr. Gore’s family and for the church, which gives up a significant chunk of the building one Saturday a month.
“However, for us, I think that it’s a real manifestation of giving back and trying to help those in need and doing what we can do,” he said.
Volunteer Work Involves Prep Work
Establishing the St. Sampson clinic took some planning. Dr. Gore and colleagues had to fill out a 501(c)(3) application; establish a charter, bylaws, articles of incorporation, policies, and procedures; and obtain medical malpractice and general liability insurance.
The clinic was able to get financing from the Mid-South Chapter of the Lupus Foundation of America as well as in-kind donations from the church. “We’ve had a lot of different companies who were very generous in donating money and excited to help the clinic continue,” Dr. Gore said.
All volunteers sign a Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act consent form.
Although the clinic operates for about 7 hours a month, it’s still important to have malpractice insurance, Dr. Gore said. He and his colleagues also have tail insurance that covers medical malpractice insurance for up to 7 years if the clinic closes.
“If somebody were to slip and fall and then try to sue the church, we have a separate policy for the clinic for that. We also have a director’s and officer’s insurance policy,” he said.
Anyone who volunteers abroad should get a travel medicine clinic consultation. “Most of the time, it’s of very little consequence. You might have to get [a] yellow fever vaccine” when traveling to certain parts of the world, Dr. Albert said.
“If you’re going into an area that is all volatile politically or in some way a threat to your personal security, I think you have to think very carefully about that,” he said, suggesting that doctors consult with the US Department of State about potential dangers.
Talk to other physicians who have gone on missions and your sponsoring institution. “By and large, you want to go with a large organization that’s been doing ongoing work,” Dr. Albert said.
Volunteer work teaches you about the breadth of humanist endeavors across the world, he noted. “The people that you deal with are very grateful for your help. Whether you’re successful or not, they’re still very appreciative of the efforts that you’re making to help.”
Dr. Albert and Dr. Gore had no disclosures. Dr. Annapureddy has done consulting for GlaxoSmithKline. Ms. Barnes had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As a resident, rheumatologist Daniel Albert, MD, did his first volunteer mission to Afghanistan. The clinic had one portable chest x-ray machine, and physicians could order a complete blood count but no other laboratory studies.
“We could do sputum stains, but that was about it. You had to use your clinical acumen and make decisions based on examining the patient and taking a history,” said Dr. Albert, a professor of medicine and pediatrics at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, and The Dartmouth Institute in Lebanon, both in New Hampshire. Such tasks can be difficult in a non–English-speaking country.
“There’s a language barrier no matter where you are,” Dr. Albert said.
In Nashville, Tennessee, James Gore, MD, had an epiphany about opening a free rheumatology clinic during a church service. His priest was discussing St. Sampson the Hospitable’s story and closed with “you don’t have to change the world. All you have to do is your little part,” Dr. Gore said. He knew he didn’t need much: a computer, a stethoscope, and a printer for prescriptions.
When his church expanded its building space, Dr. Gore took the opportunity to achieve his goal.
“I didn’t feel responsible for the clinic to succeed, but I did feel responsible to try my best,” he said. That was 14 years ago. To date, the monthly clinic has served 1124 patients representing 55 counties in Tennessee and several other patients from Kentucky.
Volunteer work is a juggling act. Dr. Gore divides his time between the clinic and his work as associate professor of clinical medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC), also in Nashville.
Dr. Albert often gave up his vacation time and had to balance commitments with his own medical practice and family to do his overseas missions. In his view, it’s worth the extra time and effort.
“It makes you a better physician because you make reasonable decisions and conclusions based on the resources available. Various places had various limitations, but none of them had the kind of resources that we routinely avail ourselves of in the US,” he said.
Tennessee Clients Get Access to Care, Medications
In some parts of the United States, good rheumatology care is hard to come by. One in four people in Tennessee have no health insurance. There’s a big need for rheumatology care in the state, Dr. Gore said.
On the second Saturday of each month, he volunteers his services at the St. Sampson Medical Clinic at Holy Trinity Greek Orthodox Church, Nashville, Tennessee, from 9 AM to 4 PM, providing care for uninsured adult rheumatology patients.
Patients come by referral from a charity clinic or health department and appointment only. The clinic asks for a $10 payment for their visits. “If they can’t pay, we still see them. But we only take care of patients who don’t have insurance,” Dr. Gore said. Allowing patients to pay gives them an opportunity to show they are vested in their own care. Often, patients will donate extra in gratitude.
Dr. Gore, along with VUMC colleague and rheumatologist Narender Annapureddy, MD, and nurse practitioner Julie Barnes, treats a variety of rheumatic diseases. For Ms. Barnes, volunteering has many rewarding aspects, “as the patients would be unable to have the treatments they need without insurance,” she said.
“We have had patients waiting for many months or sometimes years and have not had a diagnosis, and in a short time, we have been able to diagnose and get them on specific treatment,” Dr. Annapureddy said.
Most people come in for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and lupus and also positive antinuclear antibody tests. They also see patients with psoriatic arthritis, Sjögren’s disease, gout, scleroderma, Behçet disease, and leukocytoclastic vasculitis. On a typical clinic day, the team can treat up to 30-plus patients. The clinic recently expanded its services to include cardiology care, seeing about 10 patients each month.
Prior to St. Sampson, there were no volunteer clinics in Tennessee specifically dedicated to helping patients with rheumatologic disease. Untreated, these diseases may cause chronic, severe pain, lead to irreversible joint damage, and increase the risk for death.
Many patients have received medications such as adalimumab, etanercept, or tofacitinib for free. The drug companies will provide free medications, provided that they’re prescribed by a board-certified rheumatologist and the patient is uninsured and qualifies for the medication, Dr. Gore said.
Drugs like these can cost about $50,000 a year. “We have pharmacists that donate their time to help these patients get approved for those medicines,” Dr. Gore said. To date, more than 100 patients have received a biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug through the clinic.
The clinic has received more than $100,000 in donated professional fees, including $48,706 for consultations. Dr. Gore and colleagues relied on other volunteers to bring the clinic to life. He worked with his sister to develop an electronic medical record system that the clinic still uses today. “We did not buy expensive laptops or printers. I had a very generous volunteer, Damon Miltner, our IT guy, who set everything up to make our intranet secure,” he said.
The volunteer nurses, IT, and front desk all work together to make the clinic run efficiently, said Ms. Barnes, who also works as a nurse practitioner with Vanderbilt Rheumatology Cool Springs in Franklin, Tennessee. “We share a lunch together, all in a beautiful and holy church. I do not think of this as work, but as spending time with people who are appreciative and kind,” she said.
“It is amazing to see patients who are able to walk in by themselves after having used a cane for years,” Dr. Annapureddy said. “While doing this on weekends with young kids is challenging, having a supportive spouse who shares the same value makes it much easier to be able to do volunteer work.”
Working Outside Your Comfort Zone
Dr. Albert has traveled to all parts of the world to volunteer his services as a rheumatologist and general practitioner. This includes missions to Uganda, Rwanda, Ecuador, Peru, Nepal, and Borneo. He’s participated with several volunteer organizations, among them the International Student & Scholar Services program at the University of Pennsylvania, CARE, Global Volunteers, Project Amazonas, Asha Nepal, Health in Harmony, and several others.
Rheumatologists who volunteer in underdeveloped countries should be prepared to work outside of their specialty — and their comfort zone. In some instances, Dr. Albert took care of AIDS-related infectious diseases. “It’s not something I am particularly knowledgeable about, and I actually spent a fair amount of time reading about it before I went on the plane in order to get some comfort level.”
Dr. Albert often found himself doing more primary care and general pediatrics than rheumatology care. “I would see rheumatic conditions. But there’s not a lot of RA in developing countries, which is something that people have noted before. And the same goes for other autoimmune conditions. They’re just not that common.”
He did see a lot of septic arthritis and tuberculosis in Uganda. “We had a rheum clinic and saw a mixture of the consequences of septic arthritis and also a few RA and lupus patients.”
Limited resources are another thing to prepare for.
Whenever he traveled to a place that didn’t have a lot of resources, Dr. Albert would collect as many supplies as he could from the nearest hospital, pack them away, and try to get the supplies to the mission location.
Sometimes it worked out, and sometimes it didn’t, he said. “I probably had $10,000 worth of medical supplies when I went to Armenia, and American Airlines lost it. It ended up back in my apartment 3 months later. That was unfortunate because there was lot of good stuff there.”
He thought about FedEx-ing some supplies to a mission in Uganda, but it was astronomically expensive, so that didn’t work.
Luggage weight restrictions are another obstacle that sometimes requires a waiver. Dr. Albert once had to get the Red Cross to work with an airline to get a luggage waiver. “Other airlines were very good and didn’t have those kinds of restrictions. But most of the time I got some supplies to go with me, and sometimes that was a very helpful addition,” especially if the mission site was lacking in resources, he said.
When Charity Work Produces Success Stories
During one of his missions in Uganda with the University of Pennsylvania, Dr. Albert helped the Makerere University Medical School, Kampala, to establish a rheumatology clinic, which was affiliated with Mulago National Specialised Hospital. The clinic operated once a week for half a day, mostly treating patients with RA and lupus.
The mission also established an AIDS clinic. Many of the patients with musculoskeletal complaints also had HIV and were able to get antiretroviral drugs through the clinic, he said.
For Dr. Gore, seeing patients from more than half the counties in Tennessee was one of the clinic’s biggest accomplishments. “That was all through word of mouth,” he said.
In rheumatology, many patients may feel their condition is hopeless, Ms. Barnes noted. “There have been many patients that, through months of proper treatment, have normal lives. A high percentage would be disabled without the needed medical therapies.”
Dr. Gore has seen patients who literally couldn’t walk or had severe, painful psoriasis all over their body. The clinic would put them on medicine that would give them new life. The psoriasis would clear up, or their joints would heal, and they could walk again.
One of Dr. Gore’s patients, a woman in her mid-50s, got on an expensive medication that brought her arthritis into remission. She’s now able to care for her grandchildren.
The fact that the clinic, with the help of volunteer pharmacologists, can provide medications to enable patients to have a less destructive disease and improved quality of life “is a major reward,” Ms. Barnes said.
Balancing Your Priorities
Overseas missions can last for a few weeks to several months, depending on the mission, the organization, and the type of care involved.
Rheumatologists who want to volunteer need to do so in a way that doesn’t generate a lot of angst with supervisors or colleagues. Dr. Albert balanced this by keeping his missions reasonably short. “I would have someone cover my service. And since there’s reciprocity in the places I worked for, if they covered me for a month, I would cover them for a month, so it wasn’t a burden on anybody.”
“By and large, I used my vacation time to do it, and it does cost some money, but it’s a lot less than the cost of a typical vacation,” Dr. Albert said.
Volunteer work can also compete with family time. Dr. Albert ended up taking his family along on several of his missions to Ecuador and Uganda. He would tell the organization: “My family wants to come. Is there anything they can do while I’m working in the program? And they usually found an occupation.”
At St. Sampson, volunteering is also a family affair. “My wife acts as the administrator, so she’s the one that helps schedule patients and deals with a lot of the faxes.” It’s a big commitment for Dr. Gore’s family and for the church, which gives up a significant chunk of the building one Saturday a month.
“However, for us, I think that it’s a real manifestation of giving back and trying to help those in need and doing what we can do,” he said.
Volunteer Work Involves Prep Work
Establishing the St. Sampson clinic took some planning. Dr. Gore and colleagues had to fill out a 501(c)(3) application; establish a charter, bylaws, articles of incorporation, policies, and procedures; and obtain medical malpractice and general liability insurance.
The clinic was able to get financing from the Mid-South Chapter of the Lupus Foundation of America as well as in-kind donations from the church. “We’ve had a lot of different companies who were very generous in donating money and excited to help the clinic continue,” Dr. Gore said.
All volunteers sign a Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act consent form.
Although the clinic operates for about 7 hours a month, it’s still important to have malpractice insurance, Dr. Gore said. He and his colleagues also have tail insurance that covers medical malpractice insurance for up to 7 years if the clinic closes.
“If somebody were to slip and fall and then try to sue the church, we have a separate policy for the clinic for that. We also have a director’s and officer’s insurance policy,” he said.
Anyone who volunteers abroad should get a travel medicine clinic consultation. “Most of the time, it’s of very little consequence. You might have to get [a] yellow fever vaccine” when traveling to certain parts of the world, Dr. Albert said.
“If you’re going into an area that is all volatile politically or in some way a threat to your personal security, I think you have to think very carefully about that,” he said, suggesting that doctors consult with the US Department of State about potential dangers.
Talk to other physicians who have gone on missions and your sponsoring institution. “By and large, you want to go with a large organization that’s been doing ongoing work,” Dr. Albert said.
Volunteer work teaches you about the breadth of humanist endeavors across the world, he noted. “The people that you deal with are very grateful for your help. Whether you’re successful or not, they’re still very appreciative of the efforts that you’re making to help.”
Dr. Albert and Dr. Gore had no disclosures. Dr. Annapureddy has done consulting for GlaxoSmithKline. Ms. Barnes had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ustekinumab’s ‘Egregious’ Medicare Part B and D Pricing Differences Led to Federal Intervention
A US government report showed how a Medicare policy change made the drug ustekinumab (Stelara) for autoimmune diseases much more expensive, a finding that experts say illustrates the need for reforms created by the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (IRA).
The topline findings of an August report from the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) about ustekinumab may seem somewhat surprising and a bit counterintuitive.
Ustekinumab costs spiked as Medicare pushed patients to get their supply through the Part D pharmacy program. The aim of Part D is to make medicines more affordable and accessible for patients. It runs on a model of insurers to negotiate deals for pharmaceuticals.
Earlier, many patients who needed ustekinumab had the drug covered by Medicare Part B. For many years, Medicare Part B has been largely a passive purchaser of medicines. Part B covers drugs administered by physicians. Its longtime model has been to add a premium of 6% to the reported average sales price to reimburse physicians who buy and administer the drug for patients.
But it was Part D, the Medicare program based on insurers’ negotiating clout, that saw a spike in ustekinumab costs after patients were shifted out of Part B coverage, where the cost of the medicine fell.
The average reported Part B cost for an ustekinumab injection slipped from $14,450 in 2016 to $12,912 by 2023, according to the report from HHS’ Office of Inspector General (OIG).
The Part D cost jumped in the same period. It rose by 84% from $17,717 in 2016 to $32,559 by 2023.
The IRA is intended to curb these kinds of increases in the future for drugs covered by Medicare, said Stacie B. Dusetzina, PhD, professor of health policy at Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tennessee. The law demands companies pay rebates to Medicare if they increase drug prices faster than consumer inflation.
“That should at least help with some of this price growth that over time has seemed quite egregious,” Dr. Dusetzina told this news organization.
The IRA contains several provisions intended to curb rising drug costs for people enrolled in Medicare, including allowing the federal government to directly negotiate on some medicines.
Ustekinumab is one of the first 10 medicines that are subject to negotiations. Medicare will select as many as 15 additional drugs covered under Part D for negotiation in 2025, another 15 Part B and D drugs in 2026, and up to 20 drugs every year after that.
Earlier in August, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) announced the results of its first drug negotiations, with prices set to take effect in 2026. The Part D price for a 30-day supply of ustekinumab will be $4695 in 2026, a 66% reduction from the list price last year of $13,836.
Even at the negotiated price, ustekinumab’s cost will be high enough to trigger a new cap on out-of-pocket Part D spending, Dr. Dusetzina said.
Starting in 2025, Part D will have a cap of $2000 on individuals’ out-of-pocket costs, with annual adjustments in future years.
“It may not be better for someone who was filling this on Part B, who had a supplement [that covered their share of the ustekinumab cost], but it will be better for a lot of people that it’s covered under Part D,” Dr. Dusetzina said. “The good news is that at least from a beneficiary affordability standpoint, they’re going to have some price protection.”
OIG noted that the US Food and Drug Administration has approved three competing biosimilar versions of ustekinumab. These could also potentially work to lower costs.
‘A Complicated and Not Particularly Transparent Process’
OIG said it expects to release a report later this year with more detail about the decision that shifted ustekinumab coverage from Part B to Part D.
First cleared for US sales in 2009, ustekinumab is approved for psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis. It can be given subcutaneously or intravenously.
Part B does not generally cover self-administered drugs. The infused version of ustekinumab has been covered under Medicare Part B since it reached the market.
“However, Part B coverage of the subcutaneous versions has been less straightforward,” OIG said in the report.
In 2020, Medicare administrative contractors — the units or affiliates of insurers that for decades have processed Part B claims for the traditional Medicare programs — determined that subcutaneous ustekinumab did not meet the criteria for coverage under Part B. Implementation of this change was delayed due to the COVID public health emergency but has since taken effect.
The shift in ustekinumab coverage to Part D eroded financial protections of many people on Medicare when Part B covered the drug.
Almost 9 in 10 people enrolled in Medicare Part B have supplemental insurance such as Medigap, employer coverage, or Medicaid to fully or partially cover their cost-sharing requirements, the OIG report said. That means Part B coverage shielded many patients from high ustekinumab costs.
In contrast, patients who self-administered the drug at home under Part D coverage paid an average of almost $6000 out of pocket if they did not receive any type of financial assistance, OIG said.
“From a financial standpoint, as long as you have Part B coinsurance, it would be much cheaper to get the drug in your doctor’s office than getting it through a pharmacy, unless you qualify for the low-income subsidy,” OIG Regional Inspector General David Tawes, who supervised the team that produced the report, told this news organization.
OIG has previously reported that post–point-of-sale rebates paid by manufacturers sometimes lower the costs incurred by Part D plans by a significant margin. But this was not the case with ustekinumab. Instead, OIG said the gap between initial and actual costs of ustekinumab was reduced by less than one third even with rebates. Rebate information is considered confidential.
“The whole negotiation structure is a complicated and not particularly transparent process,” Mr. Tawes said.
Backchannel Discounts, Top-Line Prices
The IRA is bringing some more transparency to the process through negotiations, said Mariana P. Socal, MD, associate professor at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore. Patients who buy medicines that have been through the CMS negotiation process will be able to see if they are being charged correctly.
Dr. Socal noted that there’s something of a disconnect in discussions of Part D between how insurers and consumers view prices.
For Part D plans, the list prices represent the beginning of negotiations. They get rebates from drugmakers’ list prices for medicines, which insurers say work to lower premium costs.
“For plans, those prices are unrealistic. They are simply a sticker price. But for patients, for the Medicare beneficiaries, these prices are very real” because they are used to set copays, Dr. Socal said.
Dr. Dusetzina reported receiving funding from Arnold Ventures and the Commonwealth Fund for research related to drug pricing. Dr. Socal reported receiving funding from Arnold Ventures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A US government report showed how a Medicare policy change made the drug ustekinumab (Stelara) for autoimmune diseases much more expensive, a finding that experts say illustrates the need for reforms created by the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (IRA).
The topline findings of an August report from the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) about ustekinumab may seem somewhat surprising and a bit counterintuitive.
Ustekinumab costs spiked as Medicare pushed patients to get their supply through the Part D pharmacy program. The aim of Part D is to make medicines more affordable and accessible for patients. It runs on a model of insurers to negotiate deals for pharmaceuticals.
Earlier, many patients who needed ustekinumab had the drug covered by Medicare Part B. For many years, Medicare Part B has been largely a passive purchaser of medicines. Part B covers drugs administered by physicians. Its longtime model has been to add a premium of 6% to the reported average sales price to reimburse physicians who buy and administer the drug for patients.
But it was Part D, the Medicare program based on insurers’ negotiating clout, that saw a spike in ustekinumab costs after patients were shifted out of Part B coverage, where the cost of the medicine fell.
The average reported Part B cost for an ustekinumab injection slipped from $14,450 in 2016 to $12,912 by 2023, according to the report from HHS’ Office of Inspector General (OIG).
The Part D cost jumped in the same period. It rose by 84% from $17,717 in 2016 to $32,559 by 2023.
The IRA is intended to curb these kinds of increases in the future for drugs covered by Medicare, said Stacie B. Dusetzina, PhD, professor of health policy at Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tennessee. The law demands companies pay rebates to Medicare if they increase drug prices faster than consumer inflation.
“That should at least help with some of this price growth that over time has seemed quite egregious,” Dr. Dusetzina told this news organization.
The IRA contains several provisions intended to curb rising drug costs for people enrolled in Medicare, including allowing the federal government to directly negotiate on some medicines.
Ustekinumab is one of the first 10 medicines that are subject to negotiations. Medicare will select as many as 15 additional drugs covered under Part D for negotiation in 2025, another 15 Part B and D drugs in 2026, and up to 20 drugs every year after that.
Earlier in August, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) announced the results of its first drug negotiations, with prices set to take effect in 2026. The Part D price for a 30-day supply of ustekinumab will be $4695 in 2026, a 66% reduction from the list price last year of $13,836.
Even at the negotiated price, ustekinumab’s cost will be high enough to trigger a new cap on out-of-pocket Part D spending, Dr. Dusetzina said.
Starting in 2025, Part D will have a cap of $2000 on individuals’ out-of-pocket costs, with annual adjustments in future years.
“It may not be better for someone who was filling this on Part B, who had a supplement [that covered their share of the ustekinumab cost], but it will be better for a lot of people that it’s covered under Part D,” Dr. Dusetzina said. “The good news is that at least from a beneficiary affordability standpoint, they’re going to have some price protection.”
OIG noted that the US Food and Drug Administration has approved three competing biosimilar versions of ustekinumab. These could also potentially work to lower costs.
‘A Complicated and Not Particularly Transparent Process’
OIG said it expects to release a report later this year with more detail about the decision that shifted ustekinumab coverage from Part B to Part D.
First cleared for US sales in 2009, ustekinumab is approved for psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis. It can be given subcutaneously or intravenously.
Part B does not generally cover self-administered drugs. The infused version of ustekinumab has been covered under Medicare Part B since it reached the market.
“However, Part B coverage of the subcutaneous versions has been less straightforward,” OIG said in the report.
In 2020, Medicare administrative contractors — the units or affiliates of insurers that for decades have processed Part B claims for the traditional Medicare programs — determined that subcutaneous ustekinumab did not meet the criteria for coverage under Part B. Implementation of this change was delayed due to the COVID public health emergency but has since taken effect.
The shift in ustekinumab coverage to Part D eroded financial protections of many people on Medicare when Part B covered the drug.
Almost 9 in 10 people enrolled in Medicare Part B have supplemental insurance such as Medigap, employer coverage, or Medicaid to fully or partially cover their cost-sharing requirements, the OIG report said. That means Part B coverage shielded many patients from high ustekinumab costs.
In contrast, patients who self-administered the drug at home under Part D coverage paid an average of almost $6000 out of pocket if they did not receive any type of financial assistance, OIG said.
“From a financial standpoint, as long as you have Part B coinsurance, it would be much cheaper to get the drug in your doctor’s office than getting it through a pharmacy, unless you qualify for the low-income subsidy,” OIG Regional Inspector General David Tawes, who supervised the team that produced the report, told this news organization.
OIG has previously reported that post–point-of-sale rebates paid by manufacturers sometimes lower the costs incurred by Part D plans by a significant margin. But this was not the case with ustekinumab. Instead, OIG said the gap between initial and actual costs of ustekinumab was reduced by less than one third even with rebates. Rebate information is considered confidential.
“The whole negotiation structure is a complicated and not particularly transparent process,” Mr. Tawes said.
Backchannel Discounts, Top-Line Prices
The IRA is bringing some more transparency to the process through negotiations, said Mariana P. Socal, MD, associate professor at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore. Patients who buy medicines that have been through the CMS negotiation process will be able to see if they are being charged correctly.
Dr. Socal noted that there’s something of a disconnect in discussions of Part D between how insurers and consumers view prices.
For Part D plans, the list prices represent the beginning of negotiations. They get rebates from drugmakers’ list prices for medicines, which insurers say work to lower premium costs.
“For plans, those prices are unrealistic. They are simply a sticker price. But for patients, for the Medicare beneficiaries, these prices are very real” because they are used to set copays, Dr. Socal said.
Dr. Dusetzina reported receiving funding from Arnold Ventures and the Commonwealth Fund for research related to drug pricing. Dr. Socal reported receiving funding from Arnold Ventures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A US government report showed how a Medicare policy change made the drug ustekinumab (Stelara) for autoimmune diseases much more expensive, a finding that experts say illustrates the need for reforms created by the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (IRA).
The topline findings of an August report from the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) about ustekinumab may seem somewhat surprising and a bit counterintuitive.
Ustekinumab costs spiked as Medicare pushed patients to get their supply through the Part D pharmacy program. The aim of Part D is to make medicines more affordable and accessible for patients. It runs on a model of insurers to negotiate deals for pharmaceuticals.
Earlier, many patients who needed ustekinumab had the drug covered by Medicare Part B. For many years, Medicare Part B has been largely a passive purchaser of medicines. Part B covers drugs administered by physicians. Its longtime model has been to add a premium of 6% to the reported average sales price to reimburse physicians who buy and administer the drug for patients.
But it was Part D, the Medicare program based on insurers’ negotiating clout, that saw a spike in ustekinumab costs after patients were shifted out of Part B coverage, where the cost of the medicine fell.
The average reported Part B cost for an ustekinumab injection slipped from $14,450 in 2016 to $12,912 by 2023, according to the report from HHS’ Office of Inspector General (OIG).
The Part D cost jumped in the same period. It rose by 84% from $17,717 in 2016 to $32,559 by 2023.
The IRA is intended to curb these kinds of increases in the future for drugs covered by Medicare, said Stacie B. Dusetzina, PhD, professor of health policy at Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tennessee. The law demands companies pay rebates to Medicare if they increase drug prices faster than consumer inflation.
“That should at least help with some of this price growth that over time has seemed quite egregious,” Dr. Dusetzina told this news organization.
The IRA contains several provisions intended to curb rising drug costs for people enrolled in Medicare, including allowing the federal government to directly negotiate on some medicines.
Ustekinumab is one of the first 10 medicines that are subject to negotiations. Medicare will select as many as 15 additional drugs covered under Part D for negotiation in 2025, another 15 Part B and D drugs in 2026, and up to 20 drugs every year after that.
Earlier in August, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) announced the results of its first drug negotiations, with prices set to take effect in 2026. The Part D price for a 30-day supply of ustekinumab will be $4695 in 2026, a 66% reduction from the list price last year of $13,836.
Even at the negotiated price, ustekinumab’s cost will be high enough to trigger a new cap on out-of-pocket Part D spending, Dr. Dusetzina said.
Starting in 2025, Part D will have a cap of $2000 on individuals’ out-of-pocket costs, with annual adjustments in future years.
“It may not be better for someone who was filling this on Part B, who had a supplement [that covered their share of the ustekinumab cost], but it will be better for a lot of people that it’s covered under Part D,” Dr. Dusetzina said. “The good news is that at least from a beneficiary affordability standpoint, they’re going to have some price protection.”
OIG noted that the US Food and Drug Administration has approved three competing biosimilar versions of ustekinumab. These could also potentially work to lower costs.
‘A Complicated and Not Particularly Transparent Process’
OIG said it expects to release a report later this year with more detail about the decision that shifted ustekinumab coverage from Part B to Part D.
First cleared for US sales in 2009, ustekinumab is approved for psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis. It can be given subcutaneously or intravenously.
Part B does not generally cover self-administered drugs. The infused version of ustekinumab has been covered under Medicare Part B since it reached the market.
“However, Part B coverage of the subcutaneous versions has been less straightforward,” OIG said in the report.
In 2020, Medicare administrative contractors — the units or affiliates of insurers that for decades have processed Part B claims for the traditional Medicare programs — determined that subcutaneous ustekinumab did not meet the criteria for coverage under Part B. Implementation of this change was delayed due to the COVID public health emergency but has since taken effect.
The shift in ustekinumab coverage to Part D eroded financial protections of many people on Medicare when Part B covered the drug.
Almost 9 in 10 people enrolled in Medicare Part B have supplemental insurance such as Medigap, employer coverage, or Medicaid to fully or partially cover their cost-sharing requirements, the OIG report said. That means Part B coverage shielded many patients from high ustekinumab costs.
In contrast, patients who self-administered the drug at home under Part D coverage paid an average of almost $6000 out of pocket if they did not receive any type of financial assistance, OIG said.
“From a financial standpoint, as long as you have Part B coinsurance, it would be much cheaper to get the drug in your doctor’s office than getting it through a pharmacy, unless you qualify for the low-income subsidy,” OIG Regional Inspector General David Tawes, who supervised the team that produced the report, told this news organization.
OIG has previously reported that post–point-of-sale rebates paid by manufacturers sometimes lower the costs incurred by Part D plans by a significant margin. But this was not the case with ustekinumab. Instead, OIG said the gap between initial and actual costs of ustekinumab was reduced by less than one third even with rebates. Rebate information is considered confidential.
“The whole negotiation structure is a complicated and not particularly transparent process,” Mr. Tawes said.
Backchannel Discounts, Top-Line Prices
The IRA is bringing some more transparency to the process through negotiations, said Mariana P. Socal, MD, associate professor at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore. Patients who buy medicines that have been through the CMS negotiation process will be able to see if they are being charged correctly.
Dr. Socal noted that there’s something of a disconnect in discussions of Part D between how insurers and consumers view prices.
For Part D plans, the list prices represent the beginning of negotiations. They get rebates from drugmakers’ list prices for medicines, which insurers say work to lower premium costs.
“For plans, those prices are unrealistic. They are simply a sticker price. But for patients, for the Medicare beneficiaries, these prices are very real” because they are used to set copays, Dr. Socal said.
Dr. Dusetzina reported receiving funding from Arnold Ventures and the Commonwealth Fund for research related to drug pricing. Dr. Socal reported receiving funding from Arnold Ventures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.