User login
Hybrid ablation superior for persistent AFib: CEASE-AF
BARCELONA – Staged hybrid ablation provided superior freedom from atrial arrhythmias compared with endocardial catheter ablation alone, including the need for repeat ablations in patients with advanced atrial fibrillation (AF), new data show.
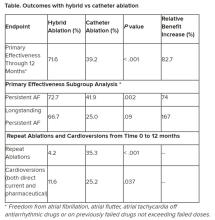
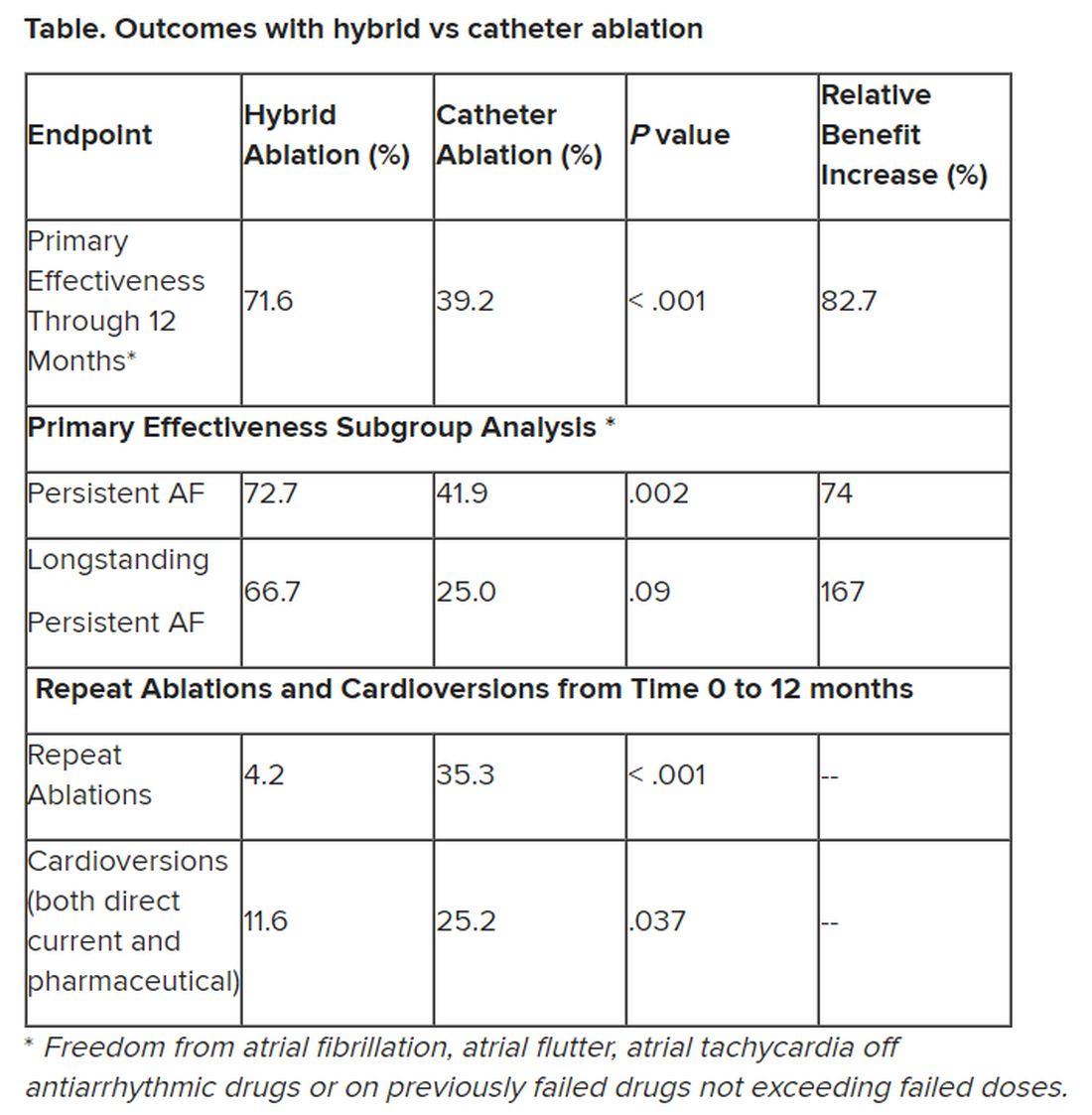
“We have seen that hybrid ablation resulted in 32.4% absolute benefit increase in effectiveness and 83% relative benefit increase, so this is a huge difference,” concluded cardiac surgeon Nicholas Doll, MD, PhD, Schüchtermann Clinic, Bad Rothenfelde, Germany.
Dr. Doll presented the 12-month follow up results of the Combined Endoscopic Epicardial and Percutaneous Endocardial Ablation Versus Repeated Catheter Ablation in Persistent and Longstanding Persistent Atrial Fibrillation (CEASE-AF) trial at the European Heart Rhythm Association 2023 Congress, held recently in Barcelona and virtually.
He said CEASE-AF is the largest multicenter randomized clinical trial comparing these two approaches for control of atrial arrhythmias.
Safety outcomes were numerically higher in the hybrid ablation (HA) group of the trial but not statistically different from the catheter ablation (CA) group.
Unstable wavefront
As background, Dr. Doll explained that in advanced AF, there is a high degree of endocardial-epicardial dissociation with unstable wavefront propagation transitioning between the endocardial and epicardial surfaces. Endocardial mapping and ablation alone may be insufficient to address the mechanism of AF.
“So, the hypothesis of the CEASE-AF study was a minimally invasive hybrid ablation approach which combines endocardial and epicardial ablation to achieve superior effectiveness when compared to endocardial catheter ablation alone,” he said.
This prospective clinical trial randomized patients 2:1 at nine sites in five countries to HA (n = 102) or CA (n = 52). All had left atrial diameter of 4 cm to 6 cm and persistent AF for up to 1 year or longstanding persistent AF for greater than 1 year up to 10 years.
Any patient with a previous ablation procedure, BMI greater than 35 kg/m2, or left ventricular ejection fraction less than 30% was excluded.
For HA, stage 1 consisted of epicardial lesions for pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) plus the posterior wall box plus left atrial appendage exclusion using the AtriClip (AtriCure Inc.) left atrial appendage exclusion device. Stage 2 involved endocardial mapping and catheter ablation to address gaps.
For CA, the index procedure involved catheter-mediated PVI plus repeat endocardial ablation as clinically indicated. For both HA and CA, additional ablation techniques and lesions were allowed for nonparoxysmal AF.
The HA timeline was the first stage, index procedure at time 0 (n = 102), a 90-day blanking period, and then the second stage, endocardial procedure at 90 to 180 days from the index procedure (n = 93).
For the CA arm of the trial, endocardial catheter ablation was performed on a minimal endocardial lesion set at time 0. Then after a 90-day blanking period, repeat catheter ablation was performed if clinically indicated (6/52).
Repeat ablations and electrical or pharmaceutical cardioversions were allowed during the 12-month follow-up period from time 0.
The primary efficacy endpoint was freedom from AF, atrial flutter, or atrial tachycardia of greater than 30 seconds through 12 months in the absence of class I/III antiarrhythmic drugs except ones that previously had failed, at doses not exceeding those previously failed doses. The safety endpoint was a composite rate of major complications over the course of the study.
Even with relatively modest cohort sizes, the HA and CA arms of the trial were well matched at baseline for age (approximately 60 years), gender (75.5% and 73.1% male, respectively), BMI (29.7 and 29.8 kg/m2), and persistent AF (79.4% and 82.7%).
The groups had persistent AF for 2.94 ± 3.29 years and 3.34 ± 3.52 years, respectively. The mean left atrial size was 4.7 ± 0.5 cm for the HA group and 4.7 ± 0.4 cm for the CA group.
Outcomes favored hybrid ablation over catheter ablation, the researchers reported. “We never would have expected these huge differences,” Dr. Doll told the congress. “We have seen that hybrid ablation resulted in 32.4% absolute benefit increase in effectiveness and 83% relative benefit increase.”
Subgroup analyses were consistent with the primary endpoint, but he said they would not be published because the trial was not powered for such comparisons.
Still, he noted that “there are only slightly reduced outcomes in the long-standing [persistent AF subgroup] in a really challenging patient arm, and we still have a success rate of 67%.” And the repeat ablations in about one-third of patients in the CA arm and need for cardioversions in about one quarter of them may have implications for reduced quality of life.
The total procedure duration was higher for the hybrid group at 336.4 ± 97 minutes, taking into account the index procedure plus the second stage procedure, vs. endocardial ablation at 251.9 ± 114 minutes, which includes the index procedure plus any repeat ablations (HA vs AF total duration, P < .001). Overall fluoroscopy time was approximately 8 minutes shorter for the HA arm.
Complications were assessed for 30 days post index procedure and 30 days post second stage procedure for the HA arm and for 30 days post index procedure and any repeat ablation for the CA arm.
The HA arm showed a complication rate of 7.8% vs. 5.8% for the CA arm (P = .751). Two patients in the former and three patients in the latter group had more than one major complication. There was one death in the HA group 93 days after the index procedure, and it was adjudicated as unrelated to the procedure.
“If you look back in the past, other studies showed a ... higher complication rate in the hybrid arm, so we feel very comfortable with these complication rates, which [are] very low and almost comparable,” Dr. Doll said.
Limitations of the study included symptom-driven electrocardiogram monitoring performed at unscheduled visits. Also, ablation beyond PVI in the CA arm and PVI/posterior box in the HA arm was not standardized and was performed according to standard practices in the participating countries.
“Success of epicardial-endocardial approach emphasizes the role of the collaborative heart team approach in the treatment of nonparoxysmal atrial fibrillation, and if I sum it up together, we can do it better” together, Dr. Doll advised.
‘Exceptional’ trial
After Dr. Doll’s presentation, appointed discussant Stylianos Tzeis, MD, PhD, head of the cardiology clinic and electrophysiology and pacing department at Mitera Hospital in Athens, congratulated the investigators and called CEASE-AF “an exceptional trial. It was really challenging to enroll patients in such a randomized controlled clinical trial.”
But Dr. Tzeis questioned whether pitting CA against HA was a fair comparison.
“Were the ablation targets similar between the two groups?” he asked. He noted that for the HA group, in the first stage the patients had PVI, posterior wall isolation, exclusion of the left atrial appendage, and additional lesions at the discretion of the operator. Ninety percent proceeded to the second stage, which was endocardial catheter ablation with verification of posterior wall isolation and PVI and additional lesions made if needed.
In the CA group, repeat catheter ablation could be performed after the 90-day blanking period if clinically indicated. “Please take note that only 10% were offered the second ablation. So at least in my perspective, this was a comparison of a two-stage approach versus a single-stage approach with a much more aggressive ablation protocol in the hybrid ablation group as compared to the endocardial group,” he said.
Seeing the higher success rate of the HA group in achieving the primary efficacy endpoint of freedom from all arrhythmias at 12 months, Dr. Tzeis asked, “Does this reflect the superiority of the epi-endo approach, or does it reflect the suboptimal performance of the catheter ablation approach?”
There was a 40% success rate in the CA patient population, a cohort that he deemed “not the most challenging persistent AF population in the world”: those with left atrial diameter of 47 millimeters and with 80% having an AF duration less than 12 months.
He also noted that “the average duration of the catheter ablation for the PVI in the vast majority of cases was 4 hours, which does not reflect what really happens in the everyday practice.”
All those critiques having been advanced, Dr. Tzeis said, “Definitely do not doubt my first comment that the authors should be congratulated, and I strongly believe that the main objective has been achieved to bring electrophysiologist and cardiac surgeons ... closer.”
The study sponsor was AtriCure Inc. with collaboration of Cardialysis BV. Doll has received consulting fees or royalties and/or has ownership or stockholder interest in AtriCure. Tzeis reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
BARCELONA – Staged hybrid ablation provided superior freedom from atrial arrhythmias compared with endocardial catheter ablation alone, including the need for repeat ablations in patients with advanced atrial fibrillation (AF), new data show.
“We have seen that hybrid ablation resulted in 32.4% absolute benefit increase in effectiveness and 83% relative benefit increase, so this is a huge difference,” concluded cardiac surgeon Nicholas Doll, MD, PhD, Schüchtermann Clinic, Bad Rothenfelde, Germany.
Dr. Doll presented the 12-month follow up results of the Combined Endoscopic Epicardial and Percutaneous Endocardial Ablation Versus Repeated Catheter Ablation in Persistent and Longstanding Persistent Atrial Fibrillation (CEASE-AF) trial at the European Heart Rhythm Association 2023 Congress, held recently in Barcelona and virtually.
He said CEASE-AF is the largest multicenter randomized clinical trial comparing these two approaches for control of atrial arrhythmias.
Safety outcomes were numerically higher in the hybrid ablation (HA) group of the trial but not statistically different from the catheter ablation (CA) group.
Unstable wavefront
As background, Dr. Doll explained that in advanced AF, there is a high degree of endocardial-epicardial dissociation with unstable wavefront propagation transitioning between the endocardial and epicardial surfaces. Endocardial mapping and ablation alone may be insufficient to address the mechanism of AF.
“So, the hypothesis of the CEASE-AF study was a minimally invasive hybrid ablation approach which combines endocardial and epicardial ablation to achieve superior effectiveness when compared to endocardial catheter ablation alone,” he said.
This prospective clinical trial randomized patients 2:1 at nine sites in five countries to HA (n = 102) or CA (n = 52). All had left atrial diameter of 4 cm to 6 cm and persistent AF for up to 1 year or longstanding persistent AF for greater than 1 year up to 10 years.
Any patient with a previous ablation procedure, BMI greater than 35 kg/m2, or left ventricular ejection fraction less than 30% was excluded.
For HA, stage 1 consisted of epicardial lesions for pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) plus the posterior wall box plus left atrial appendage exclusion using the AtriClip (AtriCure Inc.) left atrial appendage exclusion device. Stage 2 involved endocardial mapping and catheter ablation to address gaps.
For CA, the index procedure involved catheter-mediated PVI plus repeat endocardial ablation as clinically indicated. For both HA and CA, additional ablation techniques and lesions were allowed for nonparoxysmal AF.
The HA timeline was the first stage, index procedure at time 0 (n = 102), a 90-day blanking period, and then the second stage, endocardial procedure at 90 to 180 days from the index procedure (n = 93).
For the CA arm of the trial, endocardial catheter ablation was performed on a minimal endocardial lesion set at time 0. Then after a 90-day blanking period, repeat catheter ablation was performed if clinically indicated (6/52).
Repeat ablations and electrical or pharmaceutical cardioversions were allowed during the 12-month follow-up period from time 0.
The primary efficacy endpoint was freedom from AF, atrial flutter, or atrial tachycardia of greater than 30 seconds through 12 months in the absence of class I/III antiarrhythmic drugs except ones that previously had failed, at doses not exceeding those previously failed doses. The safety endpoint was a composite rate of major complications over the course of the study.
Even with relatively modest cohort sizes, the HA and CA arms of the trial were well matched at baseline for age (approximately 60 years), gender (75.5% and 73.1% male, respectively), BMI (29.7 and 29.8 kg/m2), and persistent AF (79.4% and 82.7%).
The groups had persistent AF for 2.94 ± 3.29 years and 3.34 ± 3.52 years, respectively. The mean left atrial size was 4.7 ± 0.5 cm for the HA group and 4.7 ± 0.4 cm for the CA group.
Outcomes favored hybrid ablation over catheter ablation, the researchers reported. “We never would have expected these huge differences,” Dr. Doll told the congress. “We have seen that hybrid ablation resulted in 32.4% absolute benefit increase in effectiveness and 83% relative benefit increase.”
Subgroup analyses were consistent with the primary endpoint, but he said they would not be published because the trial was not powered for such comparisons.
Still, he noted that “there are only slightly reduced outcomes in the long-standing [persistent AF subgroup] in a really challenging patient arm, and we still have a success rate of 67%.” And the repeat ablations in about one-third of patients in the CA arm and need for cardioversions in about one quarter of them may have implications for reduced quality of life.
The total procedure duration was higher for the hybrid group at 336.4 ± 97 minutes, taking into account the index procedure plus the second stage procedure, vs. endocardial ablation at 251.9 ± 114 minutes, which includes the index procedure plus any repeat ablations (HA vs AF total duration, P < .001). Overall fluoroscopy time was approximately 8 minutes shorter for the HA arm.
Complications were assessed for 30 days post index procedure and 30 days post second stage procedure for the HA arm and for 30 days post index procedure and any repeat ablation for the CA arm.
The HA arm showed a complication rate of 7.8% vs. 5.8% for the CA arm (P = .751). Two patients in the former and three patients in the latter group had more than one major complication. There was one death in the HA group 93 days after the index procedure, and it was adjudicated as unrelated to the procedure.
“If you look back in the past, other studies showed a ... higher complication rate in the hybrid arm, so we feel very comfortable with these complication rates, which [are] very low and almost comparable,” Dr. Doll said.
Limitations of the study included symptom-driven electrocardiogram monitoring performed at unscheduled visits. Also, ablation beyond PVI in the CA arm and PVI/posterior box in the HA arm was not standardized and was performed according to standard practices in the participating countries.
“Success of epicardial-endocardial approach emphasizes the role of the collaborative heart team approach in the treatment of nonparoxysmal atrial fibrillation, and if I sum it up together, we can do it better” together, Dr. Doll advised.
‘Exceptional’ trial
After Dr. Doll’s presentation, appointed discussant Stylianos Tzeis, MD, PhD, head of the cardiology clinic and electrophysiology and pacing department at Mitera Hospital in Athens, congratulated the investigators and called CEASE-AF “an exceptional trial. It was really challenging to enroll patients in such a randomized controlled clinical trial.”
But Dr. Tzeis questioned whether pitting CA against HA was a fair comparison.
“Were the ablation targets similar between the two groups?” he asked. He noted that for the HA group, in the first stage the patients had PVI, posterior wall isolation, exclusion of the left atrial appendage, and additional lesions at the discretion of the operator. Ninety percent proceeded to the second stage, which was endocardial catheter ablation with verification of posterior wall isolation and PVI and additional lesions made if needed.
In the CA group, repeat catheter ablation could be performed after the 90-day blanking period if clinically indicated. “Please take note that only 10% were offered the second ablation. So at least in my perspective, this was a comparison of a two-stage approach versus a single-stage approach with a much more aggressive ablation protocol in the hybrid ablation group as compared to the endocardial group,” he said.
Seeing the higher success rate of the HA group in achieving the primary efficacy endpoint of freedom from all arrhythmias at 12 months, Dr. Tzeis asked, “Does this reflect the superiority of the epi-endo approach, or does it reflect the suboptimal performance of the catheter ablation approach?”
There was a 40% success rate in the CA patient population, a cohort that he deemed “not the most challenging persistent AF population in the world”: those with left atrial diameter of 47 millimeters and with 80% having an AF duration less than 12 months.
He also noted that “the average duration of the catheter ablation for the PVI in the vast majority of cases was 4 hours, which does not reflect what really happens in the everyday practice.”
All those critiques having been advanced, Dr. Tzeis said, “Definitely do not doubt my first comment that the authors should be congratulated, and I strongly believe that the main objective has been achieved to bring electrophysiologist and cardiac surgeons ... closer.”
The study sponsor was AtriCure Inc. with collaboration of Cardialysis BV. Doll has received consulting fees or royalties and/or has ownership or stockholder interest in AtriCure. Tzeis reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
BARCELONA – Staged hybrid ablation provided superior freedom from atrial arrhythmias compared with endocardial catheter ablation alone, including the need for repeat ablations in patients with advanced atrial fibrillation (AF), new data show.
“We have seen that hybrid ablation resulted in 32.4% absolute benefit increase in effectiveness and 83% relative benefit increase, so this is a huge difference,” concluded cardiac surgeon Nicholas Doll, MD, PhD, Schüchtermann Clinic, Bad Rothenfelde, Germany.
Dr. Doll presented the 12-month follow up results of the Combined Endoscopic Epicardial and Percutaneous Endocardial Ablation Versus Repeated Catheter Ablation in Persistent and Longstanding Persistent Atrial Fibrillation (CEASE-AF) trial at the European Heart Rhythm Association 2023 Congress, held recently in Barcelona and virtually.
He said CEASE-AF is the largest multicenter randomized clinical trial comparing these two approaches for control of atrial arrhythmias.
Safety outcomes were numerically higher in the hybrid ablation (HA) group of the trial but not statistically different from the catheter ablation (CA) group.
Unstable wavefront
As background, Dr. Doll explained that in advanced AF, there is a high degree of endocardial-epicardial dissociation with unstable wavefront propagation transitioning between the endocardial and epicardial surfaces. Endocardial mapping and ablation alone may be insufficient to address the mechanism of AF.
“So, the hypothesis of the CEASE-AF study was a minimally invasive hybrid ablation approach which combines endocardial and epicardial ablation to achieve superior effectiveness when compared to endocardial catheter ablation alone,” he said.
This prospective clinical trial randomized patients 2:1 at nine sites in five countries to HA (n = 102) or CA (n = 52). All had left atrial diameter of 4 cm to 6 cm and persistent AF for up to 1 year or longstanding persistent AF for greater than 1 year up to 10 years.
Any patient with a previous ablation procedure, BMI greater than 35 kg/m2, or left ventricular ejection fraction less than 30% was excluded.
For HA, stage 1 consisted of epicardial lesions for pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) plus the posterior wall box plus left atrial appendage exclusion using the AtriClip (AtriCure Inc.) left atrial appendage exclusion device. Stage 2 involved endocardial mapping and catheter ablation to address gaps.
For CA, the index procedure involved catheter-mediated PVI plus repeat endocardial ablation as clinically indicated. For both HA and CA, additional ablation techniques and lesions were allowed for nonparoxysmal AF.
The HA timeline was the first stage, index procedure at time 0 (n = 102), a 90-day blanking period, and then the second stage, endocardial procedure at 90 to 180 days from the index procedure (n = 93).
For the CA arm of the trial, endocardial catheter ablation was performed on a minimal endocardial lesion set at time 0. Then after a 90-day blanking period, repeat catheter ablation was performed if clinically indicated (6/52).
Repeat ablations and electrical or pharmaceutical cardioversions were allowed during the 12-month follow-up period from time 0.
The primary efficacy endpoint was freedom from AF, atrial flutter, or atrial tachycardia of greater than 30 seconds through 12 months in the absence of class I/III antiarrhythmic drugs except ones that previously had failed, at doses not exceeding those previously failed doses. The safety endpoint was a composite rate of major complications over the course of the study.
Even with relatively modest cohort sizes, the HA and CA arms of the trial were well matched at baseline for age (approximately 60 years), gender (75.5% and 73.1% male, respectively), BMI (29.7 and 29.8 kg/m2), and persistent AF (79.4% and 82.7%).
The groups had persistent AF for 2.94 ± 3.29 years and 3.34 ± 3.52 years, respectively. The mean left atrial size was 4.7 ± 0.5 cm for the HA group and 4.7 ± 0.4 cm for the CA group.
Outcomes favored hybrid ablation over catheter ablation, the researchers reported. “We never would have expected these huge differences,” Dr. Doll told the congress. “We have seen that hybrid ablation resulted in 32.4% absolute benefit increase in effectiveness and 83% relative benefit increase.”
Subgroup analyses were consistent with the primary endpoint, but he said they would not be published because the trial was not powered for such comparisons.
Still, he noted that “there are only slightly reduced outcomes in the long-standing [persistent AF subgroup] in a really challenging patient arm, and we still have a success rate of 67%.” And the repeat ablations in about one-third of patients in the CA arm and need for cardioversions in about one quarter of them may have implications for reduced quality of life.
The total procedure duration was higher for the hybrid group at 336.4 ± 97 minutes, taking into account the index procedure plus the second stage procedure, vs. endocardial ablation at 251.9 ± 114 minutes, which includes the index procedure plus any repeat ablations (HA vs AF total duration, P < .001). Overall fluoroscopy time was approximately 8 minutes shorter for the HA arm.
Complications were assessed for 30 days post index procedure and 30 days post second stage procedure for the HA arm and for 30 days post index procedure and any repeat ablation for the CA arm.
The HA arm showed a complication rate of 7.8% vs. 5.8% for the CA arm (P = .751). Two patients in the former and three patients in the latter group had more than one major complication. There was one death in the HA group 93 days after the index procedure, and it was adjudicated as unrelated to the procedure.
“If you look back in the past, other studies showed a ... higher complication rate in the hybrid arm, so we feel very comfortable with these complication rates, which [are] very low and almost comparable,” Dr. Doll said.
Limitations of the study included symptom-driven electrocardiogram monitoring performed at unscheduled visits. Also, ablation beyond PVI in the CA arm and PVI/posterior box in the HA arm was not standardized and was performed according to standard practices in the participating countries.
“Success of epicardial-endocardial approach emphasizes the role of the collaborative heart team approach in the treatment of nonparoxysmal atrial fibrillation, and if I sum it up together, we can do it better” together, Dr. Doll advised.
‘Exceptional’ trial
After Dr. Doll’s presentation, appointed discussant Stylianos Tzeis, MD, PhD, head of the cardiology clinic and electrophysiology and pacing department at Mitera Hospital in Athens, congratulated the investigators and called CEASE-AF “an exceptional trial. It was really challenging to enroll patients in such a randomized controlled clinical trial.”
But Dr. Tzeis questioned whether pitting CA against HA was a fair comparison.
“Were the ablation targets similar between the two groups?” he asked. He noted that for the HA group, in the first stage the patients had PVI, posterior wall isolation, exclusion of the left atrial appendage, and additional lesions at the discretion of the operator. Ninety percent proceeded to the second stage, which was endocardial catheter ablation with verification of posterior wall isolation and PVI and additional lesions made if needed.
In the CA group, repeat catheter ablation could be performed after the 90-day blanking period if clinically indicated. “Please take note that only 10% were offered the second ablation. So at least in my perspective, this was a comparison of a two-stage approach versus a single-stage approach with a much more aggressive ablation protocol in the hybrid ablation group as compared to the endocardial group,” he said.
Seeing the higher success rate of the HA group in achieving the primary efficacy endpoint of freedom from all arrhythmias at 12 months, Dr. Tzeis asked, “Does this reflect the superiority of the epi-endo approach, or does it reflect the suboptimal performance of the catheter ablation approach?”
There was a 40% success rate in the CA patient population, a cohort that he deemed “not the most challenging persistent AF population in the world”: those with left atrial diameter of 47 millimeters and with 80% having an AF duration less than 12 months.
He also noted that “the average duration of the catheter ablation for the PVI in the vast majority of cases was 4 hours, which does not reflect what really happens in the everyday practice.”
All those critiques having been advanced, Dr. Tzeis said, “Definitely do not doubt my first comment that the authors should be congratulated, and I strongly believe that the main objective has been achieved to bring electrophysiologist and cardiac surgeons ... closer.”
The study sponsor was AtriCure Inc. with collaboration of Cardialysis BV. Doll has received consulting fees or royalties and/or has ownership or stockholder interest in AtriCure. Tzeis reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT EHRA 2023