User login
DOACs for treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism
Bleeding risk may determine best option
Case
A 52-year-old female with past medical history of diabetes, hypertension, and stage 4 lung cancer on palliative chemotherapy presents with acute-onset dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, and cough. Her exam is notable for tachycardia, hypoxemia, and diminished breath sounds. A CT pulmonary embolism study shows new left segmental thrombus. What is her preferred method of anticoagulation?
Brief overview of the issue
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), is a significant concern in the context of malignancy and is associated with higher rates of mortality at 1 year.
The standard of care in the recent past has relied on low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) after several trials showed decreased VTE recurrence in cancer patients, compared with vitamin K antagonist (VKA) treatment.1,2 LMWH has been recommended as a first-line treatment by clinical guidelines for cancer-related VTE given lower drug-drug interactions between LMWH and chemotherapy regimens, as compared with traditional VKAs, and it does not rely on intestinal absorption.3
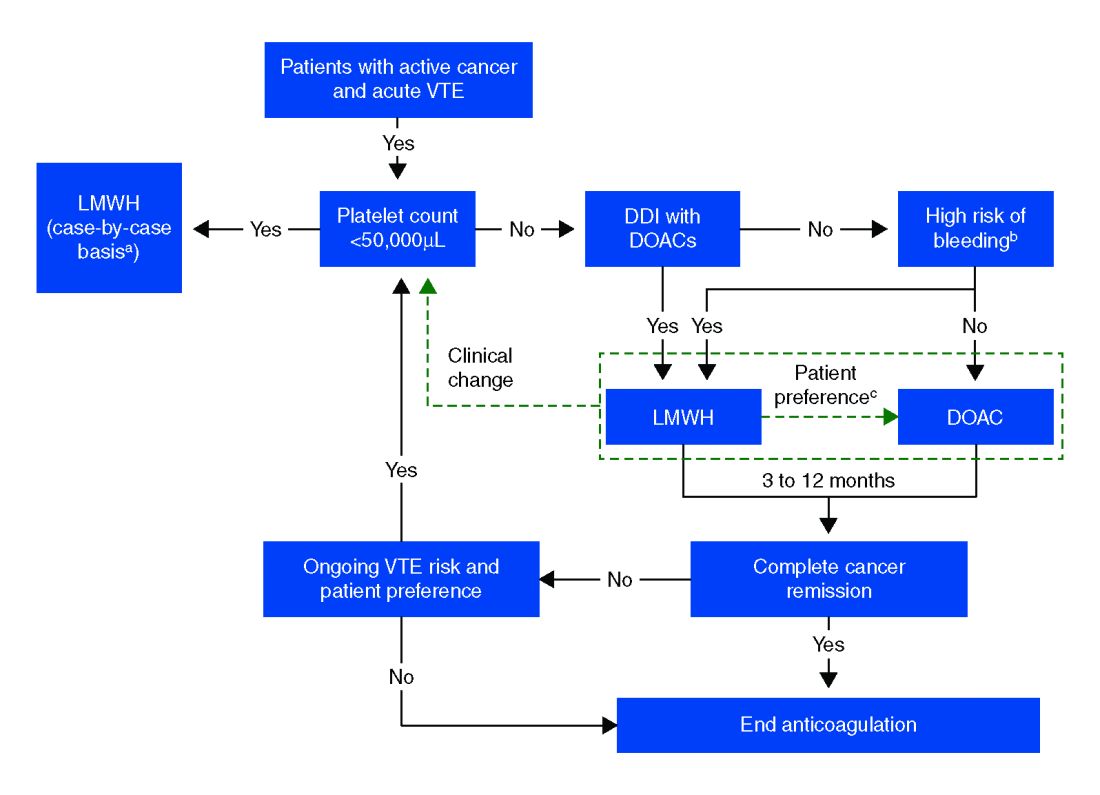
In more recent years, the focus has shifted to direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) as potential treatment options for cancer-related VTE given their ease of administration, low side-effect profile, and decreased cost. Until recently, studies have mainly been small and largely retrospective, however, several larger randomized control studies have recently been published.
Overview of the data
Several retrospective trials have investigated the use of DOACs in cancer-associated VTE. One study looking at VTE recurrence rates showed a trend towards lower rates with rivaroxaban, compared with LMWH at 6 months (13% vs. 17%) that was significantly lower at 12 months (16.5 % vs. 22%). Similar results were found when comparing rivaroxaban to warfarin. Major bleeding rates were similar among cohorts.4
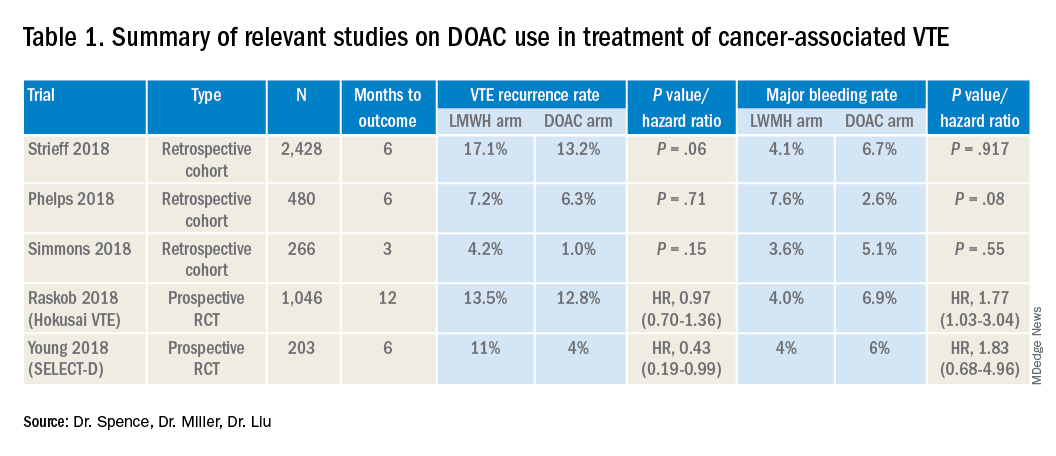
Several other retrospective cohort studies looking at treatment of cancer-associated VTE treated with LMWH vs. DOACs found that overall patients treated with DOACs had cancers with lower risk for VTE and had lower burden of metastatic disease. When this was adjusted for, there was no significant difference in the rate of recurrent cancer-associated thrombosis or major bleeding.5,6
Recently several prospective studies have corroborated the noninferiority or slight superiority of DOACs when compared with LMWH in treatment of cancer-associated VTE, while showing similar rates of bleeding. These are summarized as follows: a prospective, open-label, randomized controlled (RCT), noninferiority trial of 1,046 patients with malignancy-related VTE assigned to either LMWH for at least 5 days, followed by oral edoxaban vs. subcutaneous dalteparin for at least 6 months and up to 12 months. Investigators found no significant difference in the rate of recurrent VTE in the edoxaban group (12.8%), as compared to the dalteparin group (13.5%, P = .006 for noninferiority). Risk of major bleeding was not significantly different between the groups.7
A small RCT of 203 patients comparing recurrent VTE rates with rivaroxaban vs. dalteparin found significantly fewer recurrent clots in the rivaroxaban group compared to the dalteparin group (11% vs 4%) with no significant difference in the 6-month cumulative rate of major bleeding, 4% in the dalteparin group and 6% for the rivaroxaban group.8 Preliminary results from the ADAM VTE trial comparing apixaban to dalteparin found significantly fewer recurrent VTE in the apixaban group (3.4% vs. 14.1%) with no significant difference in major bleeding events (0% vs 2.1%).9 The Caravaggio study is a large multinational randomized, controlled, open-label, noninferiority trial looking at apixaban vs. dalteparin with endpoints being 6-month recurrent VTE and bleeding risk that will likely report results soon.
Risk of bleeding is also a major consideration in VTE treatment as studies suggest that patients with metastatic cancer are at sixfold higher risk for anticoagulant-associated bleeding.3 Subgroup analysis of Hokusai VTE cancer study found that major bleeding occurred in 32 of 522 patients given edoxaban and 16 of 524 patients treated with dalteparin. Excess of major bleeding with edoxaban was confined to patients with GI cancer. However, rates of severe major bleeding at presentation were similar.10
Overall, the existing data suggests that DOACs may be a viable option in the treatment of malignancy-associated VTE given its similar efficacy in preventing recurrent VTE without significant increased risk of major bleeding. The 2018 International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis VTE in cancer guidelines have been updated to include rivaroxaban and edoxaban for use in patients at low risk of bleeding, but recommend an informed discussion between patients and clinicians in deciding between DOAC and LMWH.11 The Chest VTE guidelines have not been updated since 2016, prior to when the above mentioned DOAC studies were published.
Application of data to our patient
Compared with patients without cancer, anticoagulation in cancer patients with acute VTE is challenging because of higher rates of VTE recurrence and bleeding, as well as the potential for drug interactions with anticancer agents. Our patient is not at increased risk for gastrointestinal bleeding and no drug interactions exist between her current chemotherapy regimen and the available DOACs, therefore she is a candidate for treatment with a DOAC.
After an informed discussion, she chose to start rivaroxaban for treatment of her pulmonary embolism. While more studies are needed to definitively determine the best treatment for cancer-associated VTE, DOACs appear to be an attractive alternative to LMWH. Patient preferences of taking oral medications over injections as well as the significant cost savings of DOACs over LMWH will likely play into many patients’ and providers’ anticoagulant choices.
Bottom line
Direct oral anticoagulants are a treatment option for cancer-associated VTE in patients at low risk of bleeding complications. Patients at increased risk of bleeding (especially patients with GI malignancies) should continue to be treated with LMWH.
Dr. Spence is a hospitalist and palliative care physician at Denver Health, and an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Dr. Miller and Dr. Liu are hospitalists at Denver Health, and assistant professors of medicine at the University of Colorado at Denver.
References
1. Hull RD et al. Long term low-molecular-weight heparin versus usual care in proximal-vein thrombosis patient with cancer. Am J Med. 2006;19(12):1062-72.
2. Lee AY et al. Low-molecular-weight heparin versus Coumadin for the prevention of recurrent venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(2):146-53.
3. Ay C et al. Treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism in the age of direct oral anticoagulants. Ann Oncol. 2019 Mar 27 [epub].
4. Streiff MB et al. Effectiveness and safety of anticoagulants for the treatment of venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. Am J Hematol. 2018 May;93(5):664-71.
5. Phelps MK et al. A single center retrospective cohort study comparing low-molecular-weight heparins to direct oral anticoagulants for the treatment of venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer – A real-world experience. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2019 Jun;25(4):793-800.
6. Simmons B et al. Efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban compared to enoxaparin in treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism. Eur J Haematol. 2018 Apr 4. (Epub).
7. Raskob GE et al.; Hokusai VTE Cancer Investigators. Edoxaban for the treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med. 2018 Feb 15;378(7):615-24.
8. Young AM et al. Comparison of an oral factor Xa inhibitor with low molecular weight heparin in patients with cancer with venous thromboembolism: Results of a randomized trial (SELECT-D). J Clin Oncol. 2018 Jul 10;36(20):2017-23.
9. McBane, RD et al. Apixaban, dalteparin, in active cancer associated venous thromboembolism, the ADAM VTE trial. Blood. 2018 Nov 29;132(suppl 1):421.
10. Kraaijpoel N et al. Clinical impact of bleeding in cancer-associated venous thromboembolism: Results from the Hokusai VTE cancer study. Thromb Haemost. 2018 Aug;118(8):1439-49.
11. Khorana AA et al. Role of direct oral anticoagulants in the treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism: Guidance from the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost. 2018 Sep;16(9):1891-94.
Key points
- DOACs are a reasonable treatment option for malignancy-associated VTE in patients without GI tract malignancies and at low risk for bleeding complications.
- In patients with gastrointestinal malignancies or increased risk of bleeding, DOACs may have an increased bleeding risk and therefore LMWH is recommended.
- An informed discussion should occur between providers and patients to determine the best treatment option for cancer patients with VTE.
Additional reading
Dong Y et al. Efficacy and safety of direct oral anticoagulants versus low-molecular-weight heparin in patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2019 May 6.
Khorana AA et al. Role of direct oral anticoagulants in the treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism: guidance from the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost. 2018 Sep;16(9):1891-94.
Tritschler T et al. Venous thromboembolism advances in diagnosis and treatment. JAMA. 2018 Oct;320(15):1583-94.
Quiz
Which of the following is the recommended treatment of VTE in a patient with brain metastases?
A. Unfractionated heparin
B. Low molecular weight heparin
C. Direct oral anticoagulant
D. Vitamin K antagonist
The answer is B. Although there are very few data, LMWH is the recommended agent in patients with VTE and brain metastases.
A. LMWH has been shown to decrease mortality in patients with VTE and cancer, compared with unfractionated heparin (risk ratio, 0.66).
C. The safety of DOACs is not yet well established in patients with brain tumors. Antidotes and/or specific reversal agents for some DOACs are not available.
D. Vitamin K antagonists such as warfarin are not recommended in cancer patients because LMWH has a reduced risk of recurrent VTE without increased risk of bleeding.
Bleeding risk may determine best option
Bleeding risk may determine best option
Case
A 52-year-old female with past medical history of diabetes, hypertension, and stage 4 lung cancer on palliative chemotherapy presents with acute-onset dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, and cough. Her exam is notable for tachycardia, hypoxemia, and diminished breath sounds. A CT pulmonary embolism study shows new left segmental thrombus. What is her preferred method of anticoagulation?
Brief overview of the issue
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), is a significant concern in the context of malignancy and is associated with higher rates of mortality at 1 year.
The standard of care in the recent past has relied on low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) after several trials showed decreased VTE recurrence in cancer patients, compared with vitamin K antagonist (VKA) treatment.1,2 LMWH has been recommended as a first-line treatment by clinical guidelines for cancer-related VTE given lower drug-drug interactions between LMWH and chemotherapy regimens, as compared with traditional VKAs, and it does not rely on intestinal absorption.3

In more recent years, the focus has shifted to direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) as potential treatment options for cancer-related VTE given their ease of administration, low side-effect profile, and decreased cost. Until recently, studies have mainly been small and largely retrospective, however, several larger randomized control studies have recently been published.
Overview of the data
Several retrospective trials have investigated the use of DOACs in cancer-associated VTE. One study looking at VTE recurrence rates showed a trend towards lower rates with rivaroxaban, compared with LMWH at 6 months (13% vs. 17%) that was significantly lower at 12 months (16.5 % vs. 22%). Similar results were found when comparing rivaroxaban to warfarin. Major bleeding rates were similar among cohorts.4

Several other retrospective cohort studies looking at treatment of cancer-associated VTE treated with LMWH vs. DOACs found that overall patients treated with DOACs had cancers with lower risk for VTE and had lower burden of metastatic disease. When this was adjusted for, there was no significant difference in the rate of recurrent cancer-associated thrombosis or major bleeding.5,6
Recently several prospective studies have corroborated the noninferiority or slight superiority of DOACs when compared with LMWH in treatment of cancer-associated VTE, while showing similar rates of bleeding. These are summarized as follows: a prospective, open-label, randomized controlled (RCT), noninferiority trial of 1,046 patients with malignancy-related VTE assigned to either LMWH for at least 5 days, followed by oral edoxaban vs. subcutaneous dalteparin for at least 6 months and up to 12 months. Investigators found no significant difference in the rate of recurrent VTE in the edoxaban group (12.8%), as compared to the dalteparin group (13.5%, P = .006 for noninferiority). Risk of major bleeding was not significantly different between the groups.7
A small RCT of 203 patients comparing recurrent VTE rates with rivaroxaban vs. dalteparin found significantly fewer recurrent clots in the rivaroxaban group compared to the dalteparin group (11% vs 4%) with no significant difference in the 6-month cumulative rate of major bleeding, 4% in the dalteparin group and 6% for the rivaroxaban group.8 Preliminary results from the ADAM VTE trial comparing apixaban to dalteparin found significantly fewer recurrent VTE in the apixaban group (3.4% vs. 14.1%) with no significant difference in major bleeding events (0% vs 2.1%).9 The Caravaggio study is a large multinational randomized, controlled, open-label, noninferiority trial looking at apixaban vs. dalteparin with endpoints being 6-month recurrent VTE and bleeding risk that will likely report results soon.
Risk of bleeding is also a major consideration in VTE treatment as studies suggest that patients with metastatic cancer are at sixfold higher risk for anticoagulant-associated bleeding.3 Subgroup analysis of Hokusai VTE cancer study found that major bleeding occurred in 32 of 522 patients given edoxaban and 16 of 524 patients treated with dalteparin. Excess of major bleeding with edoxaban was confined to patients with GI cancer. However, rates of severe major bleeding at presentation were similar.10
Overall, the existing data suggests that DOACs may be a viable option in the treatment of malignancy-associated VTE given its similar efficacy in preventing recurrent VTE without significant increased risk of major bleeding. The 2018 International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis VTE in cancer guidelines have been updated to include rivaroxaban and edoxaban for use in patients at low risk of bleeding, but recommend an informed discussion between patients and clinicians in deciding between DOAC and LMWH.11 The Chest VTE guidelines have not been updated since 2016, prior to when the above mentioned DOAC studies were published.
Application of data to our patient
Compared with patients without cancer, anticoagulation in cancer patients with acute VTE is challenging because of higher rates of VTE recurrence and bleeding, as well as the potential for drug interactions with anticancer agents. Our patient is not at increased risk for gastrointestinal bleeding and no drug interactions exist between her current chemotherapy regimen and the available DOACs, therefore she is a candidate for treatment with a DOAC.
After an informed discussion, she chose to start rivaroxaban for treatment of her pulmonary embolism. While more studies are needed to definitively determine the best treatment for cancer-associated VTE, DOACs appear to be an attractive alternative to LMWH. Patient preferences of taking oral medications over injections as well as the significant cost savings of DOACs over LMWH will likely play into many patients’ and providers’ anticoagulant choices.
Bottom line
Direct oral anticoagulants are a treatment option for cancer-associated VTE in patients at low risk of bleeding complications. Patients at increased risk of bleeding (especially patients with GI malignancies) should continue to be treated with LMWH.
Dr. Spence is a hospitalist and palliative care physician at Denver Health, and an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Dr. Miller and Dr. Liu are hospitalists at Denver Health, and assistant professors of medicine at the University of Colorado at Denver.
References
1. Hull RD et al. Long term low-molecular-weight heparin versus usual care in proximal-vein thrombosis patient with cancer. Am J Med. 2006;19(12):1062-72.
2. Lee AY et al. Low-molecular-weight heparin versus Coumadin for the prevention of recurrent venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(2):146-53.
3. Ay C et al. Treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism in the age of direct oral anticoagulants. Ann Oncol. 2019 Mar 27 [epub].
4. Streiff MB et al. Effectiveness and safety of anticoagulants for the treatment of venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. Am J Hematol. 2018 May;93(5):664-71.
5. Phelps MK et al. A single center retrospective cohort study comparing low-molecular-weight heparins to direct oral anticoagulants for the treatment of venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer – A real-world experience. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2019 Jun;25(4):793-800.
6. Simmons B et al. Efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban compared to enoxaparin in treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism. Eur J Haematol. 2018 Apr 4. (Epub).
7. Raskob GE et al.; Hokusai VTE Cancer Investigators. Edoxaban for the treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med. 2018 Feb 15;378(7):615-24.
8. Young AM et al. Comparison of an oral factor Xa inhibitor with low molecular weight heparin in patients with cancer with venous thromboembolism: Results of a randomized trial (SELECT-D). J Clin Oncol. 2018 Jul 10;36(20):2017-23.
9. McBane, RD et al. Apixaban, dalteparin, in active cancer associated venous thromboembolism, the ADAM VTE trial. Blood. 2018 Nov 29;132(suppl 1):421.
10. Kraaijpoel N et al. Clinical impact of bleeding in cancer-associated venous thromboembolism: Results from the Hokusai VTE cancer study. Thromb Haemost. 2018 Aug;118(8):1439-49.
11. Khorana AA et al. Role of direct oral anticoagulants in the treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism: Guidance from the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost. 2018 Sep;16(9):1891-94.
Key points
- DOACs are a reasonable treatment option for malignancy-associated VTE in patients without GI tract malignancies and at low risk for bleeding complications.
- In patients with gastrointestinal malignancies or increased risk of bleeding, DOACs may have an increased bleeding risk and therefore LMWH is recommended.
- An informed discussion should occur between providers and patients to determine the best treatment option for cancer patients with VTE.
Additional reading
Dong Y et al. Efficacy and safety of direct oral anticoagulants versus low-molecular-weight heparin in patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2019 May 6.
Khorana AA et al. Role of direct oral anticoagulants in the treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism: guidance from the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost. 2018 Sep;16(9):1891-94.
Tritschler T et al. Venous thromboembolism advances in diagnosis and treatment. JAMA. 2018 Oct;320(15):1583-94.
Quiz
Which of the following is the recommended treatment of VTE in a patient with brain metastases?
A. Unfractionated heparin
B. Low molecular weight heparin
C. Direct oral anticoagulant
D. Vitamin K antagonist
The answer is B. Although there are very few data, LMWH is the recommended agent in patients with VTE and brain metastases.
A. LMWH has been shown to decrease mortality in patients with VTE and cancer, compared with unfractionated heparin (risk ratio, 0.66).
C. The safety of DOACs is not yet well established in patients with brain tumors. Antidotes and/or specific reversal agents for some DOACs are not available.
D. Vitamin K antagonists such as warfarin are not recommended in cancer patients because LMWH has a reduced risk of recurrent VTE without increased risk of bleeding.
Case
A 52-year-old female with past medical history of diabetes, hypertension, and stage 4 lung cancer on palliative chemotherapy presents with acute-onset dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, and cough. Her exam is notable for tachycardia, hypoxemia, and diminished breath sounds. A CT pulmonary embolism study shows new left segmental thrombus. What is her preferred method of anticoagulation?
Brief overview of the issue
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), is a significant concern in the context of malignancy and is associated with higher rates of mortality at 1 year.
The standard of care in the recent past has relied on low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) after several trials showed decreased VTE recurrence in cancer patients, compared with vitamin K antagonist (VKA) treatment.1,2 LMWH has been recommended as a first-line treatment by clinical guidelines for cancer-related VTE given lower drug-drug interactions between LMWH and chemotherapy regimens, as compared with traditional VKAs, and it does not rely on intestinal absorption.3

In more recent years, the focus has shifted to direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) as potential treatment options for cancer-related VTE given their ease of administration, low side-effect profile, and decreased cost. Until recently, studies have mainly been small and largely retrospective, however, several larger randomized control studies have recently been published.
Overview of the data
Several retrospective trials have investigated the use of DOACs in cancer-associated VTE. One study looking at VTE recurrence rates showed a trend towards lower rates with rivaroxaban, compared with LMWH at 6 months (13% vs. 17%) that was significantly lower at 12 months (16.5 % vs. 22%). Similar results were found when comparing rivaroxaban to warfarin. Major bleeding rates were similar among cohorts.4

Several other retrospective cohort studies looking at treatment of cancer-associated VTE treated with LMWH vs. DOACs found that overall patients treated with DOACs had cancers with lower risk for VTE and had lower burden of metastatic disease. When this was adjusted for, there was no significant difference in the rate of recurrent cancer-associated thrombosis or major bleeding.5,6
Recently several prospective studies have corroborated the noninferiority or slight superiority of DOACs when compared with LMWH in treatment of cancer-associated VTE, while showing similar rates of bleeding. These are summarized as follows: a prospective, open-label, randomized controlled (RCT), noninferiority trial of 1,046 patients with malignancy-related VTE assigned to either LMWH for at least 5 days, followed by oral edoxaban vs. subcutaneous dalteparin for at least 6 months and up to 12 months. Investigators found no significant difference in the rate of recurrent VTE in the edoxaban group (12.8%), as compared to the dalteparin group (13.5%, P = .006 for noninferiority). Risk of major bleeding was not significantly different between the groups.7
A small RCT of 203 patients comparing recurrent VTE rates with rivaroxaban vs. dalteparin found significantly fewer recurrent clots in the rivaroxaban group compared to the dalteparin group (11% vs 4%) with no significant difference in the 6-month cumulative rate of major bleeding, 4% in the dalteparin group and 6% for the rivaroxaban group.8 Preliminary results from the ADAM VTE trial comparing apixaban to dalteparin found significantly fewer recurrent VTE in the apixaban group (3.4% vs. 14.1%) with no significant difference in major bleeding events (0% vs 2.1%).9 The Caravaggio study is a large multinational randomized, controlled, open-label, noninferiority trial looking at apixaban vs. dalteparin with endpoints being 6-month recurrent VTE and bleeding risk that will likely report results soon.
Risk of bleeding is also a major consideration in VTE treatment as studies suggest that patients with metastatic cancer are at sixfold higher risk for anticoagulant-associated bleeding.3 Subgroup analysis of Hokusai VTE cancer study found that major bleeding occurred in 32 of 522 patients given edoxaban and 16 of 524 patients treated with dalteparin. Excess of major bleeding with edoxaban was confined to patients with GI cancer. However, rates of severe major bleeding at presentation were similar.10
Overall, the existing data suggests that DOACs may be a viable option in the treatment of malignancy-associated VTE given its similar efficacy in preventing recurrent VTE without significant increased risk of major bleeding. The 2018 International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis VTE in cancer guidelines have been updated to include rivaroxaban and edoxaban for use in patients at low risk of bleeding, but recommend an informed discussion between patients and clinicians in deciding between DOAC and LMWH.11 The Chest VTE guidelines have not been updated since 2016, prior to when the above mentioned DOAC studies were published.
Application of data to our patient
Compared with patients without cancer, anticoagulation in cancer patients with acute VTE is challenging because of higher rates of VTE recurrence and bleeding, as well as the potential for drug interactions with anticancer agents. Our patient is not at increased risk for gastrointestinal bleeding and no drug interactions exist between her current chemotherapy regimen and the available DOACs, therefore she is a candidate for treatment with a DOAC.
After an informed discussion, she chose to start rivaroxaban for treatment of her pulmonary embolism. While more studies are needed to definitively determine the best treatment for cancer-associated VTE, DOACs appear to be an attractive alternative to LMWH. Patient preferences of taking oral medications over injections as well as the significant cost savings of DOACs over LMWH will likely play into many patients’ and providers’ anticoagulant choices.
Bottom line
Direct oral anticoagulants are a treatment option for cancer-associated VTE in patients at low risk of bleeding complications. Patients at increased risk of bleeding (especially patients with GI malignancies) should continue to be treated with LMWH.
Dr. Spence is a hospitalist and palliative care physician at Denver Health, and an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Dr. Miller and Dr. Liu are hospitalists at Denver Health, and assistant professors of medicine at the University of Colorado at Denver.
References
1. Hull RD et al. Long term low-molecular-weight heparin versus usual care in proximal-vein thrombosis patient with cancer. Am J Med. 2006;19(12):1062-72.
2. Lee AY et al. Low-molecular-weight heparin versus Coumadin for the prevention of recurrent venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(2):146-53.
3. Ay C et al. Treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism in the age of direct oral anticoagulants. Ann Oncol. 2019 Mar 27 [epub].
4. Streiff MB et al. Effectiveness and safety of anticoagulants for the treatment of venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. Am J Hematol. 2018 May;93(5):664-71.
5. Phelps MK et al. A single center retrospective cohort study comparing low-molecular-weight heparins to direct oral anticoagulants for the treatment of venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer – A real-world experience. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2019 Jun;25(4):793-800.
6. Simmons B et al. Efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban compared to enoxaparin in treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism. Eur J Haematol. 2018 Apr 4. (Epub).
7. Raskob GE et al.; Hokusai VTE Cancer Investigators. Edoxaban for the treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med. 2018 Feb 15;378(7):615-24.
8. Young AM et al. Comparison of an oral factor Xa inhibitor with low molecular weight heparin in patients with cancer with venous thromboembolism: Results of a randomized trial (SELECT-D). J Clin Oncol. 2018 Jul 10;36(20):2017-23.
9. McBane, RD et al. Apixaban, dalteparin, in active cancer associated venous thromboembolism, the ADAM VTE trial. Blood. 2018 Nov 29;132(suppl 1):421.
10. Kraaijpoel N et al. Clinical impact of bleeding in cancer-associated venous thromboembolism: Results from the Hokusai VTE cancer study. Thromb Haemost. 2018 Aug;118(8):1439-49.
11. Khorana AA et al. Role of direct oral anticoagulants in the treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism: Guidance from the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost. 2018 Sep;16(9):1891-94.
Key points
- DOACs are a reasonable treatment option for malignancy-associated VTE in patients without GI tract malignancies and at low risk for bleeding complications.
- In patients with gastrointestinal malignancies or increased risk of bleeding, DOACs may have an increased bleeding risk and therefore LMWH is recommended.
- An informed discussion should occur between providers and patients to determine the best treatment option for cancer patients with VTE.
Additional reading
Dong Y et al. Efficacy and safety of direct oral anticoagulants versus low-molecular-weight heparin in patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2019 May 6.
Khorana AA et al. Role of direct oral anticoagulants in the treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism: guidance from the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost. 2018 Sep;16(9):1891-94.
Tritschler T et al. Venous thromboembolism advances in diagnosis and treatment. JAMA. 2018 Oct;320(15):1583-94.
Quiz
Which of the following is the recommended treatment of VTE in a patient with brain metastases?
A. Unfractionated heparin
B. Low molecular weight heparin
C. Direct oral anticoagulant
D. Vitamin K antagonist
The answer is B. Although there are very few data, LMWH is the recommended agent in patients with VTE and brain metastases.
A. LMWH has been shown to decrease mortality in patients with VTE and cancer, compared with unfractionated heparin (risk ratio, 0.66).
C. The safety of DOACs is not yet well established in patients with brain tumors. Antidotes and/or specific reversal agents for some DOACs are not available.
D. Vitamin K antagonists such as warfarin are not recommended in cancer patients because LMWH has a reduced risk of recurrent VTE without increased risk of bleeding.



