User login
ANSWER
The correct answer is pityriasis rosea (PR; choice “d”), which is commonly seen in patients ages 10 to 35 and is about twice as likely to occur in women as in men.
Lichen planus (LP; choice “a”) can mimic PR but lacks the peculiar centripetal scale and oval shape. Furthermore, it does not present with a herald patch.
Guttate psoriasis (choice “b”) could easily be confused for PR. However, it displays heavier white uniform scales with a salmon-pink base, tends to have a distinctly round configuration, and does not involve the appearance of a herald patch.
Secondary syphilis (choice “c”) can usually be ruled out by the sexual history, but also by the lack of a herald patch and the absence of centripetal scaling. Highly variable in appearance, the lesions of secondary syphilis are often seen on the palms.
DISCUSSION
PR was first described in 1860 by Camille Gibert, who used the term pityriasis to describe the fine scale seen with this condition, and chose the term rosea to denote the rosy or pink color.
For a variety of reasons, PR is assumed to be a viral exanthema since, as with many such eruptions, its incidence clusters in the fall and spring, it occurs in close contacts and families, and it is commonly seen in immunocompromised patients. In addition, acquiring the condition appears to confer lifelong immunity.
However, the jury is still out with regard to the exact virus responsible for the disease. Human herpesviruses 6 and 7 are the strongest candidates in terms of antibody production, but no herpesviral particles have been detected in tissue samples.
The so-called herald patch appears initially, in a majority of cases, as a salmon-pink patch that can become as large as 5 to 10 cm, on the trunk or arms. The smaller oval lesions begin to appear within a week or two, averaging 1 to 2 cm in diameter; most display the characteristic “centripetal” scaling, clearly sparing the lesions’ periphery and serving as an essentially pathognomic finding.
On darker-skinned patients, the lesions (including the herald patch) will tend to be brown to black. The examiner must then look for the other characteristic aspects of PR, including the oval (as opposed to round) shape, the long axes of which will often parallel the skin tension lines on the back to produce what is termed the “Christmas tree pattern.” In the author’s experience, the most consistent diagnostic finding is the centripetal scaling seen in at least a few lesions.
Since secondary syphilis is a major item in the differential, obtaining a careful sexual history is essential. If this is uncertain, or if the lesions are not a good fit for PR, obtaining a punch biopsy and serum rapid plasma reagin is necessary. The biopsy in secondary syphilis will show an infiltrate largely composed of plasma cells.
TREATMENT
Once the diagnosis of PR is made, patient education is essential. Affected patients should be reassured about the benign and self-limiting nature of the problem, but also about the likelihood that the condition will persist for up to nine weeks. Darker-skinned patients need to understand that the hyperpigmentation will last for months after the condition has resolved.
Relief of the itching experienced by 75% of PR patients can be achieved with topical steroids (eg, triamcinolone 0.1% cream) and oral antihistamines at bedtime (eg, hydroxyzine 25 to 50 mg) and/or during the daytime (cetirizine 10 mg/d), plus the liberal use of soothing OTC lotions (eg, those containing camphor and menthol). Systemic steroids appear to prolong the condition and are not terribly helpful in controlling the symptoms. In severe cases, phototherapy (narrow-band UVB) can be useful in controlling the itching.
ANSWER
The correct answer is pityriasis rosea (PR; choice “d”), which is commonly seen in patients ages 10 to 35 and is about twice as likely to occur in women as in men.
Lichen planus (LP; choice “a”) can mimic PR but lacks the peculiar centripetal scale and oval shape. Furthermore, it does not present with a herald patch.
Guttate psoriasis (choice “b”) could easily be confused for PR. However, it displays heavier white uniform scales with a salmon-pink base, tends to have a distinctly round configuration, and does not involve the appearance of a herald patch.
Secondary syphilis (choice “c”) can usually be ruled out by the sexual history, but also by the lack of a herald patch and the absence of centripetal scaling. Highly variable in appearance, the lesions of secondary syphilis are often seen on the palms.
DISCUSSION
PR was first described in 1860 by Camille Gibert, who used the term pityriasis to describe the fine scale seen with this condition, and chose the term rosea to denote the rosy or pink color.
For a variety of reasons, PR is assumed to be a viral exanthema since, as with many such eruptions, its incidence clusters in the fall and spring, it occurs in close contacts and families, and it is commonly seen in immunocompromised patients. In addition, acquiring the condition appears to confer lifelong immunity.
However, the jury is still out with regard to the exact virus responsible for the disease. Human herpesviruses 6 and 7 are the strongest candidates in terms of antibody production, but no herpesviral particles have been detected in tissue samples.
The so-called herald patch appears initially, in a majority of cases, as a salmon-pink patch that can become as large as 5 to 10 cm, on the trunk or arms. The smaller oval lesions begin to appear within a week or two, averaging 1 to 2 cm in diameter; most display the characteristic “centripetal” scaling, clearly sparing the lesions’ periphery and serving as an essentially pathognomic finding.
On darker-skinned patients, the lesions (including the herald patch) will tend to be brown to black. The examiner must then look for the other characteristic aspects of PR, including the oval (as opposed to round) shape, the long axes of which will often parallel the skin tension lines on the back to produce what is termed the “Christmas tree pattern.” In the author’s experience, the most consistent diagnostic finding is the centripetal scaling seen in at least a few lesions.
Since secondary syphilis is a major item in the differential, obtaining a careful sexual history is essential. If this is uncertain, or if the lesions are not a good fit for PR, obtaining a punch biopsy and serum rapid plasma reagin is necessary. The biopsy in secondary syphilis will show an infiltrate largely composed of plasma cells.
TREATMENT
Once the diagnosis of PR is made, patient education is essential. Affected patients should be reassured about the benign and self-limiting nature of the problem, but also about the likelihood that the condition will persist for up to nine weeks. Darker-skinned patients need to understand that the hyperpigmentation will last for months after the condition has resolved.
Relief of the itching experienced by 75% of PR patients can be achieved with topical steroids (eg, triamcinolone 0.1% cream) and oral antihistamines at bedtime (eg, hydroxyzine 25 to 50 mg) and/or during the daytime (cetirizine 10 mg/d), plus the liberal use of soothing OTC lotions (eg, those containing camphor and menthol). Systemic steroids appear to prolong the condition and are not terribly helpful in controlling the symptoms. In severe cases, phototherapy (narrow-band UVB) can be useful in controlling the itching.
ANSWER
The correct answer is pityriasis rosea (PR; choice “d”), which is commonly seen in patients ages 10 to 35 and is about twice as likely to occur in women as in men.
Lichen planus (LP; choice “a”) can mimic PR but lacks the peculiar centripetal scale and oval shape. Furthermore, it does not present with a herald patch.
Guttate psoriasis (choice “b”) could easily be confused for PR. However, it displays heavier white uniform scales with a salmon-pink base, tends to have a distinctly round configuration, and does not involve the appearance of a herald patch.
Secondary syphilis (choice “c”) can usually be ruled out by the sexual history, but also by the lack of a herald patch and the absence of centripetal scaling. Highly variable in appearance, the lesions of secondary syphilis are often seen on the palms.
DISCUSSION
PR was first described in 1860 by Camille Gibert, who used the term pityriasis to describe the fine scale seen with this condition, and chose the term rosea to denote the rosy or pink color.
For a variety of reasons, PR is assumed to be a viral exanthema since, as with many such eruptions, its incidence clusters in the fall and spring, it occurs in close contacts and families, and it is commonly seen in immunocompromised patients. In addition, acquiring the condition appears to confer lifelong immunity.
However, the jury is still out with regard to the exact virus responsible for the disease. Human herpesviruses 6 and 7 are the strongest candidates in terms of antibody production, but no herpesviral particles have been detected in tissue samples.
The so-called herald patch appears initially, in a majority of cases, as a salmon-pink patch that can become as large as 5 to 10 cm, on the trunk or arms. The smaller oval lesions begin to appear within a week or two, averaging 1 to 2 cm in diameter; most display the characteristic “centripetal” scaling, clearly sparing the lesions’ periphery and serving as an essentially pathognomic finding.
On darker-skinned patients, the lesions (including the herald patch) will tend to be brown to black. The examiner must then look for the other characteristic aspects of PR, including the oval (as opposed to round) shape, the long axes of which will often parallel the skin tension lines on the back to produce what is termed the “Christmas tree pattern.” In the author’s experience, the most consistent diagnostic finding is the centripetal scaling seen in at least a few lesions.
Since secondary syphilis is a major item in the differential, obtaining a careful sexual history is essential. If this is uncertain, or if the lesions are not a good fit for PR, obtaining a punch biopsy and serum rapid plasma reagin is necessary. The biopsy in secondary syphilis will show an infiltrate largely composed of plasma cells.
TREATMENT
Once the diagnosis of PR is made, patient education is essential. Affected patients should be reassured about the benign and self-limiting nature of the problem, but also about the likelihood that the condition will persist for up to nine weeks. Darker-skinned patients need to understand that the hyperpigmentation will last for months after the condition has resolved.
Relief of the itching experienced by 75% of PR patients can be achieved with topical steroids (eg, triamcinolone 0.1% cream) and oral antihistamines at bedtime (eg, hydroxyzine 25 to 50 mg) and/or during the daytime (cetirizine 10 mg/d), plus the liberal use of soothing OTC lotions (eg, those containing camphor and menthol). Systemic steroids appear to prolong the condition and are not terribly helpful in controlling the symptoms. In severe cases, phototherapy (narrow-band UVB) can be useful in controlling the itching.
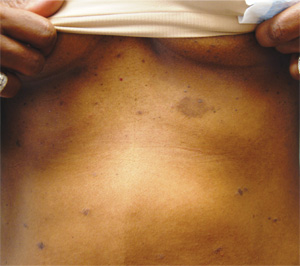
Three weeks ago, a 25-year-old woman noticed an asymp¬tomatic lesion of unknown origin on her chest. Since then, smaller versions have appeared in “crops” on her trunk, arms, and lower neck. Friends were unanimous in their opinion that she had “ringworm,” so she consulted her pharmacist, who recommended clotrimazole cream. Despite her use of it, however, the lesions continue to increase in number. Her original lesion has become less red and scaly, though. The patient has felt fine from the outset and maintains that she is “quite healthy” in other respects. Employed as an IT technician, she denies any exposure to children, pets, or sexually transmitted diseases. The patient, who is African-American, has type V skin. Her original lesion—located on her left inframammary chest—is dark brown, macular, oval to round, and measures about 3.8 cm. On her trunk, arms, and lower neck, 15 to 20 oval, papulosquamous lesions are seen; these are widely scattered, all hyperpigmented (brown), and average 1.5 cm in diameter. Several of these smaller lesions have scaly centers that spare the peripheral margins. The long axes of her oval back lesions are parallel with natural lines of cleavage in the skin.
