User login
In late 2015, Congress passed the Bipartisan Budget Act (BBA) to address numerous wide-ranging budget concerns, including issues related to agriculture, pensions, the strategic petroleum reserve, along with some Medicare issues. Section 603 of BBA is now coming back to haunt pulmonary rehabilitation services.
The intent of Section 603 is reasonable – to address the phenomenon of hospitals purchasing physician practices to take advantage of payment differentials between identical or virtually identical services when comparing the hospital outpatient prospective payment system (HOPPS) and the physician fee schedule (PFS). For example, an orthopedic practice might own its own MRI and related support services. It will bill for those services under the PFS. However, if the practice sells that segment of the revenue stream (the MRI assets, etc) to a hospital, the hospital can bill Medicare for those same services under the hospital outpatient prospective payment system at an amount notably higher than the PFS payment.
To address this payment aberration, Congress instructed the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to craft a system to preclude a hospital from such behavior. If a hospital offers new or expanded outpatient services, it could NOT bill Medicare under the hospital outpatient services methodology and would be required to bill under the PFS payment methodology. Importantly, a few exemptions exist. If the new or expanded service is within 250 yards of the main hospital campus, the outpatient billing methodology is permitted. Likewise, if expansion of a current off-campus service occurs at the same location of the current off-site service, the hospital may continue to bill under the outpatient rules. Several other technical exceptions are permitted, for example construction planned prior to passage of BBA.
The implications for pulmonary rehabilitation are critical to its growth. A hospital that wishes to expand its current program and bill under the hospital outpatient methodology MUST do so by expanding at its current location. An expansion at a new location that is not within 250 yards of the main hospital campus triggers Section 603 provisions, and the hospital will bill at the physician fee schedule rate. Because the PFS payment rate is just over half of the payment rate for HOPPS payment, it is unlikely that a hospital would expand an existing program or establish a new one if it would be forced to bill under the lower rate.
While congressional logic may be relatively understandable, for pulmonary medicine, it is based on the premise that a hospital would purchase a pulmonary practice because that practice had a lucrative pulmonary rehabilitation services cash flow. NAMDRC and other societies were able to document major flaws in the basic premise, resulting in very problematic unintended consequences. A detailed review of Medicare claims data provides strong evidence that pulmonary practices simply do not provide pulmonary rehab services.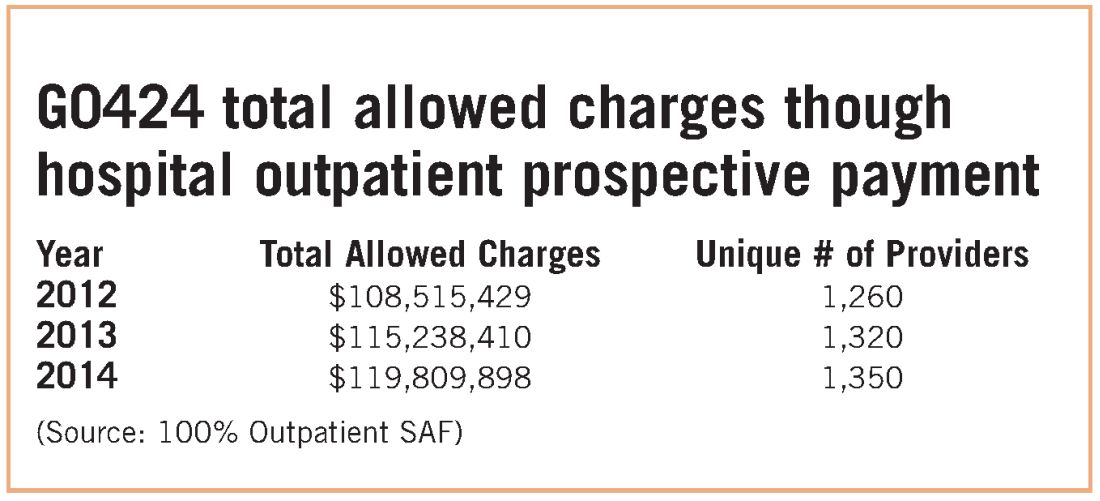
These data strongly indicate that G0424 pulmonary practice physician office billing for the most recent year data are available ($230K), compared with hospital outpatient allowed charges ($119M), is less than two-tenths of 1% of billing through the hospital setting. To argue that hospitals are purchasing pulmonary practices for financial gain tied to pulmonary rehab services defies Medicare data, as well as financial logic. If the CMS premise was valid, one would expect the aggregate physician office billing to be much greater than $535K. In discussions with CMS, the Agency did agree that there are likely to be unintended consequences related to Section 603 implementation. The Agency also emphasizes that it does not have the statutory authority for a “carve out” exemption. CMS stated that even if it agreed with us, it simply lacked the authority to exempt pulmonary rehab services. CMS also agreed that there is growing evidence that pulmonary rehab is a underutilized service that may very well save the program money through reduced hospitalizations and rehospitalizations, but it has little choice to implement the statute as Congress so mandated.
Therefore, the only solution is a legislative one. NAMDRC and other societies are seriously considering approaching Congress for such resolution.
In late 2015, Congress passed the Bipartisan Budget Act (BBA) to address numerous wide-ranging budget concerns, including issues related to agriculture, pensions, the strategic petroleum reserve, along with some Medicare issues. Section 603 of BBA is now coming back to haunt pulmonary rehabilitation services.
The intent of Section 603 is reasonable – to address the phenomenon of hospitals purchasing physician practices to take advantage of payment differentials between identical or virtually identical services when comparing the hospital outpatient prospective payment system (HOPPS) and the physician fee schedule (PFS). For example, an orthopedic practice might own its own MRI and related support services. It will bill for those services under the PFS. However, if the practice sells that segment of the revenue stream (the MRI assets, etc) to a hospital, the hospital can bill Medicare for those same services under the hospital outpatient prospective payment system at an amount notably higher than the PFS payment.
To address this payment aberration, Congress instructed the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to craft a system to preclude a hospital from such behavior. If a hospital offers new or expanded outpatient services, it could NOT bill Medicare under the hospital outpatient services methodology and would be required to bill under the PFS payment methodology. Importantly, a few exemptions exist. If the new or expanded service is within 250 yards of the main hospital campus, the outpatient billing methodology is permitted. Likewise, if expansion of a current off-campus service occurs at the same location of the current off-site service, the hospital may continue to bill under the outpatient rules. Several other technical exceptions are permitted, for example construction planned prior to passage of BBA.
The implications for pulmonary rehabilitation are critical to its growth. A hospital that wishes to expand its current program and bill under the hospital outpatient methodology MUST do so by expanding at its current location. An expansion at a new location that is not within 250 yards of the main hospital campus triggers Section 603 provisions, and the hospital will bill at the physician fee schedule rate. Because the PFS payment rate is just over half of the payment rate for HOPPS payment, it is unlikely that a hospital would expand an existing program or establish a new one if it would be forced to bill under the lower rate.
While congressional logic may be relatively understandable, for pulmonary medicine, it is based on the premise that a hospital would purchase a pulmonary practice because that practice had a lucrative pulmonary rehabilitation services cash flow. NAMDRC and other societies were able to document major flaws in the basic premise, resulting in very problematic unintended consequences. A detailed review of Medicare claims data provides strong evidence that pulmonary practices simply do not provide pulmonary rehab services.
These data strongly indicate that G0424 pulmonary practice physician office billing for the most recent year data are available ($230K), compared with hospital outpatient allowed charges ($119M), is less than two-tenths of 1% of billing through the hospital setting. To argue that hospitals are purchasing pulmonary practices for financial gain tied to pulmonary rehab services defies Medicare data, as well as financial logic. If the CMS premise was valid, one would expect the aggregate physician office billing to be much greater than $535K. In discussions with CMS, the Agency did agree that there are likely to be unintended consequences related to Section 603 implementation. The Agency also emphasizes that it does not have the statutory authority for a “carve out” exemption. CMS stated that even if it agreed with us, it simply lacked the authority to exempt pulmonary rehab services. CMS also agreed that there is growing evidence that pulmonary rehab is a underutilized service that may very well save the program money through reduced hospitalizations and rehospitalizations, but it has little choice to implement the statute as Congress so mandated.
Therefore, the only solution is a legislative one. NAMDRC and other societies are seriously considering approaching Congress for such resolution.
In late 2015, Congress passed the Bipartisan Budget Act (BBA) to address numerous wide-ranging budget concerns, including issues related to agriculture, pensions, the strategic petroleum reserve, along with some Medicare issues. Section 603 of BBA is now coming back to haunt pulmonary rehabilitation services.
The intent of Section 603 is reasonable – to address the phenomenon of hospitals purchasing physician practices to take advantage of payment differentials between identical or virtually identical services when comparing the hospital outpatient prospective payment system (HOPPS) and the physician fee schedule (PFS). For example, an orthopedic practice might own its own MRI and related support services. It will bill for those services under the PFS. However, if the practice sells that segment of the revenue stream (the MRI assets, etc) to a hospital, the hospital can bill Medicare for those same services under the hospital outpatient prospective payment system at an amount notably higher than the PFS payment.
To address this payment aberration, Congress instructed the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to craft a system to preclude a hospital from such behavior. If a hospital offers new or expanded outpatient services, it could NOT bill Medicare under the hospital outpatient services methodology and would be required to bill under the PFS payment methodology. Importantly, a few exemptions exist. If the new or expanded service is within 250 yards of the main hospital campus, the outpatient billing methodology is permitted. Likewise, if expansion of a current off-campus service occurs at the same location of the current off-site service, the hospital may continue to bill under the outpatient rules. Several other technical exceptions are permitted, for example construction planned prior to passage of BBA.
The implications for pulmonary rehabilitation are critical to its growth. A hospital that wishes to expand its current program and bill under the hospital outpatient methodology MUST do so by expanding at its current location. An expansion at a new location that is not within 250 yards of the main hospital campus triggers Section 603 provisions, and the hospital will bill at the physician fee schedule rate. Because the PFS payment rate is just over half of the payment rate for HOPPS payment, it is unlikely that a hospital would expand an existing program or establish a new one if it would be forced to bill under the lower rate.
While congressional logic may be relatively understandable, for pulmonary medicine, it is based on the premise that a hospital would purchase a pulmonary practice because that practice had a lucrative pulmonary rehabilitation services cash flow. NAMDRC and other societies were able to document major flaws in the basic premise, resulting in very problematic unintended consequences. A detailed review of Medicare claims data provides strong evidence that pulmonary practices simply do not provide pulmonary rehab services.
These data strongly indicate that G0424 pulmonary practice physician office billing for the most recent year data are available ($230K), compared with hospital outpatient allowed charges ($119M), is less than two-tenths of 1% of billing through the hospital setting. To argue that hospitals are purchasing pulmonary practices for financial gain tied to pulmonary rehab services defies Medicare data, as well as financial logic. If the CMS premise was valid, one would expect the aggregate physician office billing to be much greater than $535K. In discussions with CMS, the Agency did agree that there are likely to be unintended consequences related to Section 603 implementation. The Agency also emphasizes that it does not have the statutory authority for a “carve out” exemption. CMS stated that even if it agreed with us, it simply lacked the authority to exempt pulmonary rehab services. CMS also agreed that there is growing evidence that pulmonary rehab is a underutilized service that may very well save the program money through reduced hospitalizations and rehospitalizations, but it has little choice to implement the statute as Congress so mandated.
Therefore, the only solution is a legislative one. NAMDRC and other societies are seriously considering approaching Congress for such resolution.
