User login
Without a doubt, immunotherapy has transformed the treatment landscape of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and enhanced survival rates across the different stages of disease. High recurrence rates following complete surgical resection prompted the study of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in earlier, operable stages of disease. This shift toward early application of ICI reflects the larger trend toward merging precision oncology with lung cancer staging. The resulting complexity in treatment and decision making creates systemic and logistical challenges that will require health care systems to adapt and improve.
Adjuvant immunotherapy for NSCLC
Prior to recent approvals for adjuvant immunotherapy, it was standard to give chemotherapy following resection of stage IB-IIIA disease, which offered a statistically nonsignificant survival gain. Recurrence in these patients is believed to be related to postsurgical micrometastasis. The utilization of alternative mechanisms to prevent recurrence is increasingly more common.
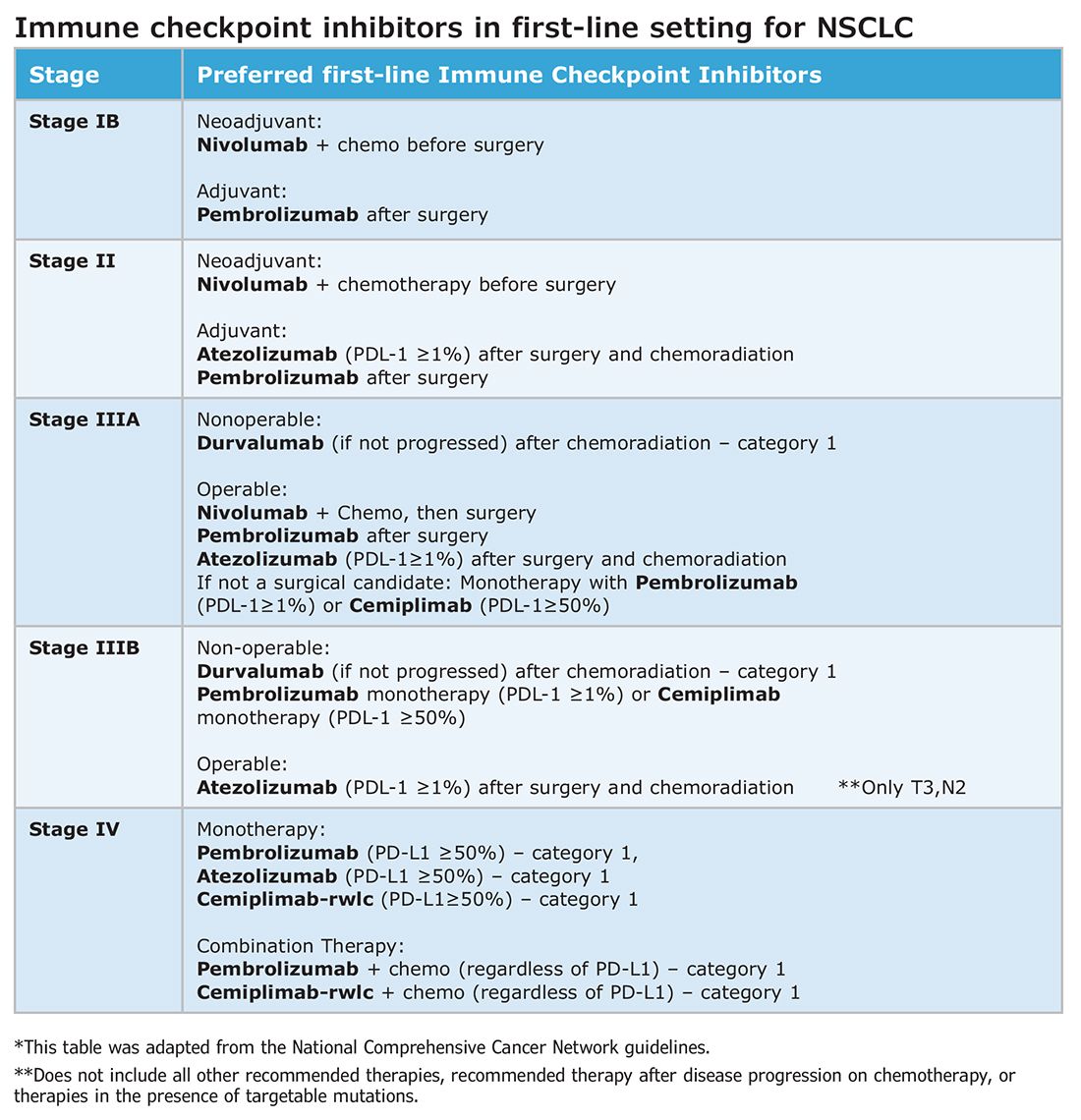
Atezolizumab, a PD-L1 inhibitor, is currently approved as first-line adjuvant treatment following chemotherapy in post-NSCLC resection patients with PD-L1 scores ≥1%. This category one recommendation by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) is based on results from the IMpower010 trial, which randomized patients to Atezolizumab vs best supportive care. All were early-stage NSCLC, stage IB-IIIA, who underwent resection followed by platinum-based chemotherapy. Statistically significant benefits were found in disease-free survival (DFS) with a trend toward overall survival.1
The PEARLS/KEYNOTE-091 trial evaluated another PD-L1 inhibitor, Pembrolizumab, as adjuvant therapy. Its design largely mirrored the IMPower010 study, but it differed in that the ICI was administered with or without chemotherapy following resection in patients with stage IB-IIIA NSCLC. Improvements in DFS were found in the overall population, leading to FDA approval for adjuvant therapy in 2023.2
These approvals require changes to the management of operable NSCLC. Until recently, it was not routine to send surgical specimens for additional testing because adjuvant treatment meant chemotherapy only. However, it is now essential that all surgically resected malignant tissue be sent for genomic sequencing and PD-L1 testing. Selecting the next form of therapy, whether it is an ICI or targeted drug therapy, depends on it.
From a surgical perspective, quality surgery with accurate nodal staging is crucial. The surgical findings can determine and identify those who are candidates for adjuvant immunotherapy. For these same reasons, it is helpful to advise surgeons preoperatively that targeted adjuvant therapy is being considered after resection.
Neoadjuvant immunotherapy for NSCLC
ICIs have also been used as neoadjuvant treatment for operable NSCLC. In 2021, the Checkmate-816 trial evaluated Nivolumab with platinum doublet chemotherapy prior to resection of stage IB-IIIa NSCLC. When compared with chemotherapy alone, there were significant improvements in EFS, MPR, and time to death or distant metastasis (TTDM) out to 3 years. At a median follow-up time of 41.4 months, only 28% in the nivolumab group had recurrence postsurgery compared with 42% in the chemotherapy-alone group.3 As a result, certain patients who are likely to receive adjuvant chemotherapy may additionally receive neoadjuvant immunotherapy with chemotherapy before surgical resection. In 2023, the KEYNOTE-671 study demonstrated that neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab and chemotherapy in patients with resectable stage II-IIIb (N2 stage) NSCLC improved EFS. At a median follow-up of 25.2 months, the EFS was 62.4% in the Pembrolizumab group vs 40.6% in the placebo group (P < .001).4
Such changes in treatment options mean patients should be discussed first and simultaneous referrals to oncology and surgery should occur in early-stage NSCLC. Up-front genomic phenotyping and PD-L1 testing may assist in decision making. High PD-L1 levels correlate better with response.
When an ICI-chemotherapy combination is given up front for newly diagnosed NSCLC, there is the potential for large reductions in tumor size and lymph node burden. Although the NCCN does not recommend ICIs to induce resectability, a patient originally deemed inoperable could theoretically become a surgical candidate with neoadjuvant ICI treatment. There is also the potential for toxicity, which could increase the risk of surgery when it does occur. Such scenarios will require frequent tumor board discussions so plans can be adjusted in real time to optimize outcomes as clinical circumstances change.
Perioperative immunotherapy for NSCLC
It is clear that both neoadjuvant and adjuvant immunotherapy can improve outcomes for patients with resectable NSCLC. The combination of neoadjuvant with adjuvant immunotherapy/chemotherapy is currently being studied. Two recent phase III clinical trials, NEOTORCH and AEGAEN, have found statistical improvements in EFS and MPR with this approach.5,6 These studies have not found their way into the NCCN guidelines yet but are sure to be considered in future iterations. Once adopted, the tumor board at each institution will have more options to choose from but many more decisions to make.
References
1. Felip E, Altorki N, Zhou C, et al. Adjuvant atezolizumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in resected stage IB-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower010): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;398(10308):1344-1357. [Published correction appears in Lancet. 2021 Nov 6;398(10312):1686.]
2. O’Brien M, Paz-Ares L, Marreaud S, et al. Pembrolizumab versus placebo as adjuvant therapy for completely resected stage IB-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (PEARLS/KEYNOTE-091): an interim analysis of a randomised, triple-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022;23(10):1274-1286.
3. Forde PM, Spicer J, Lu S, et al. Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy in resectable lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(21):1973-1985.
4. Wakelee H, Liberman M, Kato T, et al. Perioperative pembrolizumab for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(6):491-503.
5. Lu S, Zhang W, Wu L, et al. Perioperative toripalimab plus chemotherapy for patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer: the neotorch randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2024;331(3):201-211.
6. Heymach JV, Harpole D, Mitsudomi T, et al. Perioperative durvalumab for resectable non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(18):1672-1684.
Without a doubt, immunotherapy has transformed the treatment landscape of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and enhanced survival rates across the different stages of disease. High recurrence rates following complete surgical resection prompted the study of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in earlier, operable stages of disease. This shift toward early application of ICI reflects the larger trend toward merging precision oncology with lung cancer staging. The resulting complexity in treatment and decision making creates systemic and logistical challenges that will require health care systems to adapt and improve.
Adjuvant immunotherapy for NSCLC
Prior to recent approvals for adjuvant immunotherapy, it was standard to give chemotherapy following resection of stage IB-IIIA disease, which offered a statistically nonsignificant survival gain. Recurrence in these patients is believed to be related to postsurgical micrometastasis. The utilization of alternative mechanisms to prevent recurrence is increasingly more common.
Atezolizumab, a PD-L1 inhibitor, is currently approved as first-line adjuvant treatment following chemotherapy in post-NSCLC resection patients with PD-L1 scores ≥1%. This category one recommendation by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) is based on results from the IMpower010 trial, which randomized patients to Atezolizumab vs best supportive care. All were early-stage NSCLC, stage IB-IIIA, who underwent resection followed by platinum-based chemotherapy. Statistically significant benefits were found in disease-free survival (DFS) with a trend toward overall survival.1
The PEARLS/KEYNOTE-091 trial evaluated another PD-L1 inhibitor, Pembrolizumab, as adjuvant therapy. Its design largely mirrored the IMPower010 study, but it differed in that the ICI was administered with or without chemotherapy following resection in patients with stage IB-IIIA NSCLC. Improvements in DFS were found in the overall population, leading to FDA approval for adjuvant therapy in 2023.2
These approvals require changes to the management of operable NSCLC. Until recently, it was not routine to send surgical specimens for additional testing because adjuvant treatment meant chemotherapy only. However, it is now essential that all surgically resected malignant tissue be sent for genomic sequencing and PD-L1 testing. Selecting the next form of therapy, whether it is an ICI or targeted drug therapy, depends on it.
From a surgical perspective, quality surgery with accurate nodal staging is crucial. The surgical findings can determine and identify those who are candidates for adjuvant immunotherapy. For these same reasons, it is helpful to advise surgeons preoperatively that targeted adjuvant therapy is being considered after resection.
Neoadjuvant immunotherapy for NSCLC
ICIs have also been used as neoadjuvant treatment for operable NSCLC. In 2021, the Checkmate-816 trial evaluated Nivolumab with platinum doublet chemotherapy prior to resection of stage IB-IIIa NSCLC. When compared with chemotherapy alone, there were significant improvements in EFS, MPR, and time to death or distant metastasis (TTDM) out to 3 years. At a median follow-up time of 41.4 months, only 28% in the nivolumab group had recurrence postsurgery compared with 42% in the chemotherapy-alone group.3 As a result, certain patients who are likely to receive adjuvant chemotherapy may additionally receive neoadjuvant immunotherapy with chemotherapy before surgical resection. In 2023, the KEYNOTE-671 study demonstrated that neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab and chemotherapy in patients with resectable stage II-IIIb (N2 stage) NSCLC improved EFS. At a median follow-up of 25.2 months, the EFS was 62.4% in the Pembrolizumab group vs 40.6% in the placebo group (P < .001).4

Such changes in treatment options mean patients should be discussed first and simultaneous referrals to oncology and surgery should occur in early-stage NSCLC. Up-front genomic phenotyping and PD-L1 testing may assist in decision making. High PD-L1 levels correlate better with response.
When an ICI-chemotherapy combination is given up front for newly diagnosed NSCLC, there is the potential for large reductions in tumor size and lymph node burden. Although the NCCN does not recommend ICIs to induce resectability, a patient originally deemed inoperable could theoretically become a surgical candidate with neoadjuvant ICI treatment. There is also the potential for toxicity, which could increase the risk of surgery when it does occur. Such scenarios will require frequent tumor board discussions so plans can be adjusted in real time to optimize outcomes as clinical circumstances change.
Perioperative immunotherapy for NSCLC
It is clear that both neoadjuvant and adjuvant immunotherapy can improve outcomes for patients with resectable NSCLC. The combination of neoadjuvant with adjuvant immunotherapy/chemotherapy is currently being studied. Two recent phase III clinical trials, NEOTORCH and AEGAEN, have found statistical improvements in EFS and MPR with this approach.5,6 These studies have not found their way into the NCCN guidelines yet but are sure to be considered in future iterations. Once adopted, the tumor board at each institution will have more options to choose from but many more decisions to make.
References
1. Felip E, Altorki N, Zhou C, et al. Adjuvant atezolizumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in resected stage IB-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower010): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;398(10308):1344-1357. [Published correction appears in Lancet. 2021 Nov 6;398(10312):1686.]
2. O’Brien M, Paz-Ares L, Marreaud S, et al. Pembrolizumab versus placebo as adjuvant therapy for completely resected stage IB-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (PEARLS/KEYNOTE-091): an interim analysis of a randomised, triple-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022;23(10):1274-1286.
3. Forde PM, Spicer J, Lu S, et al. Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy in resectable lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(21):1973-1985.
4. Wakelee H, Liberman M, Kato T, et al. Perioperative pembrolizumab for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(6):491-503.
5. Lu S, Zhang W, Wu L, et al. Perioperative toripalimab plus chemotherapy for patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer: the neotorch randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2024;331(3):201-211.
6. Heymach JV, Harpole D, Mitsudomi T, et al. Perioperative durvalumab for resectable non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(18):1672-1684.
Without a doubt, immunotherapy has transformed the treatment landscape of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and enhanced survival rates across the different stages of disease. High recurrence rates following complete surgical resection prompted the study of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in earlier, operable stages of disease. This shift toward early application of ICI reflects the larger trend toward merging precision oncology with lung cancer staging. The resulting complexity in treatment and decision making creates systemic and logistical challenges that will require health care systems to adapt and improve.
Adjuvant immunotherapy for NSCLC
Prior to recent approvals for adjuvant immunotherapy, it was standard to give chemotherapy following resection of stage IB-IIIA disease, which offered a statistically nonsignificant survival gain. Recurrence in these patients is believed to be related to postsurgical micrometastasis. The utilization of alternative mechanisms to prevent recurrence is increasingly more common.
Atezolizumab, a PD-L1 inhibitor, is currently approved as first-line adjuvant treatment following chemotherapy in post-NSCLC resection patients with PD-L1 scores ≥1%. This category one recommendation by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) is based on results from the IMpower010 trial, which randomized patients to Atezolizumab vs best supportive care. All were early-stage NSCLC, stage IB-IIIA, who underwent resection followed by platinum-based chemotherapy. Statistically significant benefits were found in disease-free survival (DFS) with a trend toward overall survival.1
The PEARLS/KEYNOTE-091 trial evaluated another PD-L1 inhibitor, Pembrolizumab, as adjuvant therapy. Its design largely mirrored the IMPower010 study, but it differed in that the ICI was administered with or without chemotherapy following resection in patients with stage IB-IIIA NSCLC. Improvements in DFS were found in the overall population, leading to FDA approval for adjuvant therapy in 2023.2
These approvals require changes to the management of operable NSCLC. Until recently, it was not routine to send surgical specimens for additional testing because adjuvant treatment meant chemotherapy only. However, it is now essential that all surgically resected malignant tissue be sent for genomic sequencing and PD-L1 testing. Selecting the next form of therapy, whether it is an ICI or targeted drug therapy, depends on it.
From a surgical perspective, quality surgery with accurate nodal staging is crucial. The surgical findings can determine and identify those who are candidates for adjuvant immunotherapy. For these same reasons, it is helpful to advise surgeons preoperatively that targeted adjuvant therapy is being considered after resection.
Neoadjuvant immunotherapy for NSCLC
ICIs have also been used as neoadjuvant treatment for operable NSCLC. In 2021, the Checkmate-816 trial evaluated Nivolumab with platinum doublet chemotherapy prior to resection of stage IB-IIIa NSCLC. When compared with chemotherapy alone, there were significant improvements in EFS, MPR, and time to death or distant metastasis (TTDM) out to 3 years. At a median follow-up time of 41.4 months, only 28% in the nivolumab group had recurrence postsurgery compared with 42% in the chemotherapy-alone group.3 As a result, certain patients who are likely to receive adjuvant chemotherapy may additionally receive neoadjuvant immunotherapy with chemotherapy before surgical resection. In 2023, the KEYNOTE-671 study demonstrated that neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab and chemotherapy in patients with resectable stage II-IIIb (N2 stage) NSCLC improved EFS. At a median follow-up of 25.2 months, the EFS was 62.4% in the Pembrolizumab group vs 40.6% in the placebo group (P < .001).4

Such changes in treatment options mean patients should be discussed first and simultaneous referrals to oncology and surgery should occur in early-stage NSCLC. Up-front genomic phenotyping and PD-L1 testing may assist in decision making. High PD-L1 levels correlate better with response.
When an ICI-chemotherapy combination is given up front for newly diagnosed NSCLC, there is the potential for large reductions in tumor size and lymph node burden. Although the NCCN does not recommend ICIs to induce resectability, a patient originally deemed inoperable could theoretically become a surgical candidate with neoadjuvant ICI treatment. There is also the potential for toxicity, which could increase the risk of surgery when it does occur. Such scenarios will require frequent tumor board discussions so plans can be adjusted in real time to optimize outcomes as clinical circumstances change.
Perioperative immunotherapy for NSCLC
It is clear that both neoadjuvant and adjuvant immunotherapy can improve outcomes for patients with resectable NSCLC. The combination of neoadjuvant with adjuvant immunotherapy/chemotherapy is currently being studied. Two recent phase III clinical trials, NEOTORCH and AEGAEN, have found statistical improvements in EFS and MPR with this approach.5,6 These studies have not found their way into the NCCN guidelines yet but are sure to be considered in future iterations. Once adopted, the tumor board at each institution will have more options to choose from but many more decisions to make.
References
1. Felip E, Altorki N, Zhou C, et al. Adjuvant atezolizumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in resected stage IB-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower010): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;398(10308):1344-1357. [Published correction appears in Lancet. 2021 Nov 6;398(10312):1686.]
2. O’Brien M, Paz-Ares L, Marreaud S, et al. Pembrolizumab versus placebo as adjuvant therapy for completely resected stage IB-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (PEARLS/KEYNOTE-091): an interim analysis of a randomised, triple-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022;23(10):1274-1286.
3. Forde PM, Spicer J, Lu S, et al. Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy in resectable lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(21):1973-1985.
4. Wakelee H, Liberman M, Kato T, et al. Perioperative pembrolizumab for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(6):491-503.
5. Lu S, Zhang W, Wu L, et al. Perioperative toripalimab plus chemotherapy for patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer: the neotorch randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2024;331(3):201-211.
6. Heymach JV, Harpole D, Mitsudomi T, et al. Perioperative durvalumab for resectable non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(18):1672-1684.


