User login
CHEST recently released a new clinical guideline on central airway obstruction (CAO).
“Central airway obstruction is associated with a poor prognosis, and the management of CAO is highly variable dependent on the provider expertise and local resources. By releasing this guideline, the panel hopes to standardize the definition of CAO and provide guidance for the management of patients to optimize care and improve outcomes,” said Kamran Mahmood, MD, MPH, FCCP, lead author on the guideline. “The guideline recommendations are developed using GRADE methodology and based on thorough evidence review and expert input. But the quality of overall evidence is very low, and the panel calls for well-designed studies and randomized controlled trials for the management of CAO.”
CAO can be caused by a variety of malignant and nonmalignant disorders, and multiple specialists may be involved in the care, including pulmonologists, interventional pulmonologists, radiologists, anesthesiologists, oncologists, radiation oncologists, thoracic surgeons and otolaryngologists, etc. The panel recommends shared decision-making with the patients and a multidisciplinary approach to manage CAO.
Below, you’ll find flowcharts outlining the suggested treatments for patients with a malignant or nonmalignant CAO.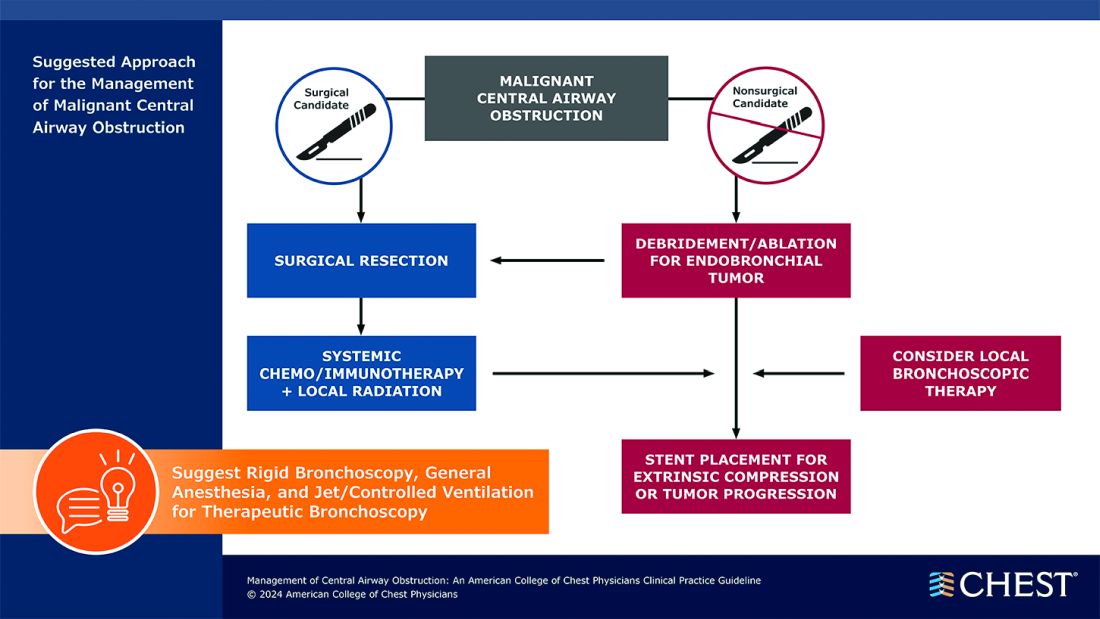
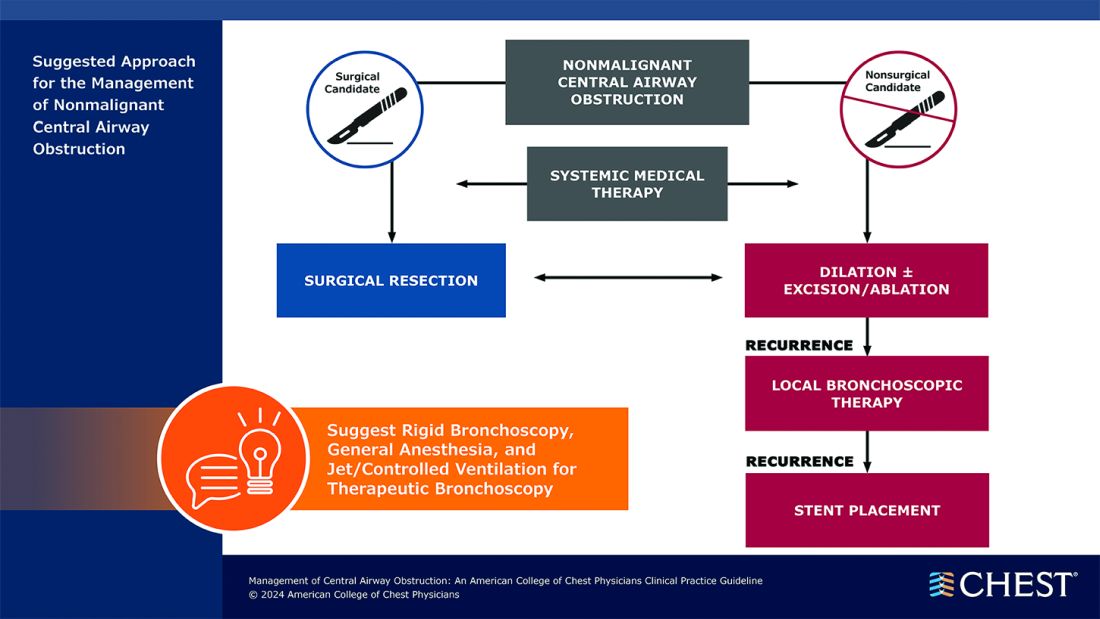
Visit www.chestnet.org/CAO-guideline to download the flowcharts and access the complete guideline.
CHEST recently released a new clinical guideline on central airway obstruction (CAO).
“Central airway obstruction is associated with a poor prognosis, and the management of CAO is highly variable dependent on the provider expertise and local resources. By releasing this guideline, the panel hopes to standardize the definition of CAO and provide guidance for the management of patients to optimize care and improve outcomes,” said Kamran Mahmood, MD, MPH, FCCP, lead author on the guideline. “The guideline recommendations are developed using GRADE methodology and based on thorough evidence review and expert input. But the quality of overall evidence is very low, and the panel calls for well-designed studies and randomized controlled trials for the management of CAO.”
CAO can be caused by a variety of malignant and nonmalignant disorders, and multiple specialists may be involved in the care, including pulmonologists, interventional pulmonologists, radiologists, anesthesiologists, oncologists, radiation oncologists, thoracic surgeons and otolaryngologists, etc. The panel recommends shared decision-making with the patients and a multidisciplinary approach to manage CAO.
Below, you’ll find flowcharts outlining the suggested treatments for patients with a malignant or nonmalignant CAO.

Visit www.chestnet.org/CAO-guideline to download the flowcharts and access the complete guideline.
CHEST recently released a new clinical guideline on central airway obstruction (CAO).
“Central airway obstruction is associated with a poor prognosis, and the management of CAO is highly variable dependent on the provider expertise and local resources. By releasing this guideline, the panel hopes to standardize the definition of CAO and provide guidance for the management of patients to optimize care and improve outcomes,” said Kamran Mahmood, MD, MPH, FCCP, lead author on the guideline. “The guideline recommendations are developed using GRADE methodology and based on thorough evidence review and expert input. But the quality of overall evidence is very low, and the panel calls for well-designed studies and randomized controlled trials for the management of CAO.”
CAO can be caused by a variety of malignant and nonmalignant disorders, and multiple specialists may be involved in the care, including pulmonologists, interventional pulmonologists, radiologists, anesthesiologists, oncologists, radiation oncologists, thoracic surgeons and otolaryngologists, etc. The panel recommends shared decision-making with the patients and a multidisciplinary approach to manage CAO.
Below, you’ll find flowcharts outlining the suggested treatments for patients with a malignant or nonmalignant CAO.

Visit www.chestnet.org/CAO-guideline to download the flowcharts and access the complete guideline.