User login
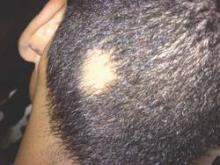
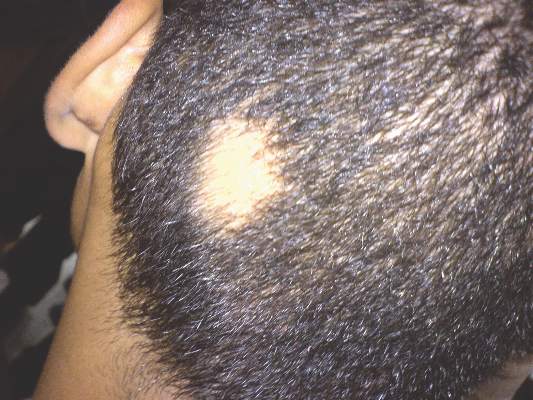
Alopecia areata sends “hundreds of thousands” of patients to the doctor every year in the United States, and six in ten of those visits end with a corticosteroid prescription, investigators reported in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
In contrast, “minoxidil appears either underreported or underutilized in this population of patients, which suggests the need to educate both dermatologists and patients on the potential usefulness of this medication in alopecia areata,” wrote Michael Farhangian and his associates at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, N.C.
About 2% of individuals develop alopecia areata during their lives, but there are no consensus guidelines for disease in the United States. To better understand treatment patterns here, the investigators analyzed data on about 2.6 outpatient visits for alopecia areata between 2001 and 2010. The data came from two national ambulatory health care surveys (J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14[9]:1012-14).
Patients with alopecia areata most often sought care from dermatologists (85%), the researchers reported. Providers prescribed topical and injected corticosteroids far more often (61%) than other drugs, such as minoxidil (5.9%), topical tacrolimus (5.7%), topical retinoid (3.3%), oral steroids (1.8%), or anthralin (1.8%).
The British Association of Dermatologists recommends corticosteroids for localized alopecia areata, but long-term use can lead to skin atrophy, hypopigmentation, and telangiectasia, the researchers warned. “This risk may be increased in patients who are prescribed both topical and injected corticosteroids, as was observed in 9.9% of patients,” they added.
Frequencies of minoxidil and tacrolimus use were nearly identical even though tacrolimus has been found ineffectivein alopecia areata, according to the researchers.
“Patients may be hesitant to use minoxidil since it is only FDA-approved for androgenetic alopecia and not for alopecia areata,” they wrote. Minoxidil also is available over-the-counter, which could explain its scarcity in the dataset, they added.
Galderma Laboratories helped fund the work through an unrestricted educational grant. Mr. Farhangian declared no competing interests. Senior author Dr. Steven Feldman reported relationships with Galderma, Janssen, Taro, Abbott Labs, and a number of other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Feldman also reported holding stock in Causa Research and Medical Quality Enhancement Corporation. Another coauthor reported relationships with several pharmaceutical companies.
Alopecia areata sends “hundreds of thousands” of patients to the doctor every year in the United States, and six in ten of those visits end with a corticosteroid prescription, investigators reported in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
In contrast, “minoxidil appears either underreported or underutilized in this population of patients, which suggests the need to educate both dermatologists and patients on the potential usefulness of this medication in alopecia areata,” wrote Michael Farhangian and his associates at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, N.C.
About 2% of individuals develop alopecia areata during their lives, but there are no consensus guidelines for disease in the United States. To better understand treatment patterns here, the investigators analyzed data on about 2.6 outpatient visits for alopecia areata between 2001 and 2010. The data came from two national ambulatory health care surveys (J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14[9]:1012-14).
Patients with alopecia areata most often sought care from dermatologists (85%), the researchers reported. Providers prescribed topical and injected corticosteroids far more often (61%) than other drugs, such as minoxidil (5.9%), topical tacrolimus (5.7%), topical retinoid (3.3%), oral steroids (1.8%), or anthralin (1.8%).
The British Association of Dermatologists recommends corticosteroids for localized alopecia areata, but long-term use can lead to skin atrophy, hypopigmentation, and telangiectasia, the researchers warned. “This risk may be increased in patients who are prescribed both topical and injected corticosteroids, as was observed in 9.9% of patients,” they added.
Frequencies of minoxidil and tacrolimus use were nearly identical even though tacrolimus has been found ineffectivein alopecia areata, according to the researchers.
“Patients may be hesitant to use minoxidil since it is only FDA-approved for androgenetic alopecia and not for alopecia areata,” they wrote. Minoxidil also is available over-the-counter, which could explain its scarcity in the dataset, they added.
Galderma Laboratories helped fund the work through an unrestricted educational grant. Mr. Farhangian declared no competing interests. Senior author Dr. Steven Feldman reported relationships with Galderma, Janssen, Taro, Abbott Labs, and a number of other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Feldman also reported holding stock in Causa Research and Medical Quality Enhancement Corporation. Another coauthor reported relationships with several pharmaceutical companies.
Alopecia areata sends “hundreds of thousands” of patients to the doctor every year in the United States, and six in ten of those visits end with a corticosteroid prescription, investigators reported in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
In contrast, “minoxidil appears either underreported or underutilized in this population of patients, which suggests the need to educate both dermatologists and patients on the potential usefulness of this medication in alopecia areata,” wrote Michael Farhangian and his associates at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, N.C.
About 2% of individuals develop alopecia areata during their lives, but there are no consensus guidelines for disease in the United States. To better understand treatment patterns here, the investigators analyzed data on about 2.6 outpatient visits for alopecia areata between 2001 and 2010. The data came from two national ambulatory health care surveys (J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14[9]:1012-14).
Patients with alopecia areata most often sought care from dermatologists (85%), the researchers reported. Providers prescribed topical and injected corticosteroids far more often (61%) than other drugs, such as minoxidil (5.9%), topical tacrolimus (5.7%), topical retinoid (3.3%), oral steroids (1.8%), or anthralin (1.8%).
The British Association of Dermatologists recommends corticosteroids for localized alopecia areata, but long-term use can lead to skin atrophy, hypopigmentation, and telangiectasia, the researchers warned. “This risk may be increased in patients who are prescribed both topical and injected corticosteroids, as was observed in 9.9% of patients,” they added.
Frequencies of minoxidil and tacrolimus use were nearly identical even though tacrolimus has been found ineffectivein alopecia areata, according to the researchers.
“Patients may be hesitant to use minoxidil since it is only FDA-approved for androgenetic alopecia and not for alopecia areata,” they wrote. Minoxidil also is available over-the-counter, which could explain its scarcity in the dataset, they added.
Galderma Laboratories helped fund the work through an unrestricted educational grant. Mr. Farhangian declared no competing interests. Senior author Dr. Steven Feldman reported relationships with Galderma, Janssen, Taro, Abbott Labs, and a number of other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Feldman also reported holding stock in Causa Research and Medical Quality Enhancement Corporation. Another coauthor reported relationships with several pharmaceutical companies.
FROM JOURNAL OF DRUGS IN DERMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Topical and injected corticosteroids were by far the most commonly recorded treatment for alopecia areata in the United States.
Major finding: Providers prescribed topical or injected corticosteroids during 61% of visits – far more often than minoxidil (5.9%), topical tacrolimus (5.7%), or other drugs.
Data source: Retrospective analysis of about 2.6 million visits for alopecia areata in the United States between 2001 and 2010.
Disclosures: Galderma Laboratories helped fund the work through an unrestricted educational grant. Mr. Farhangian declared no competing interests. Senior author Dr. Steven Feldman reported relationships with Galderma, Janssen, Taro, Abbott Labs, and a number of other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Feldman also reported holding stock in Causa Research and Medical Quality Enhancement Corporation. Another coauthor reported relationships with several pharmaceutical companies.