User login
Dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) appears to have limited utility for differentiating between gout and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD), according to a German prospective cohort study. Findings were reported at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year because of COVID-19.
“Differentiation of gout and pseudogout, or CPPD, is sometimes difficult,” said presenting investigator Valentin S. Schäfer, MD, associate professor of internal medicine and head of the department of rheumatology and clinical immunology at University Hospital Bonn (Germany).
“Arthrocentesis and subsequent polarization microscopy remains the gold standard,” he noted. “Novel diagnostic approaches, such as DECT, have recently been validated for gout, but limited data [are] available on the use of DECT in patients with CPPD.”
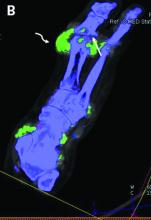
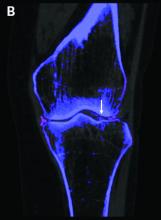
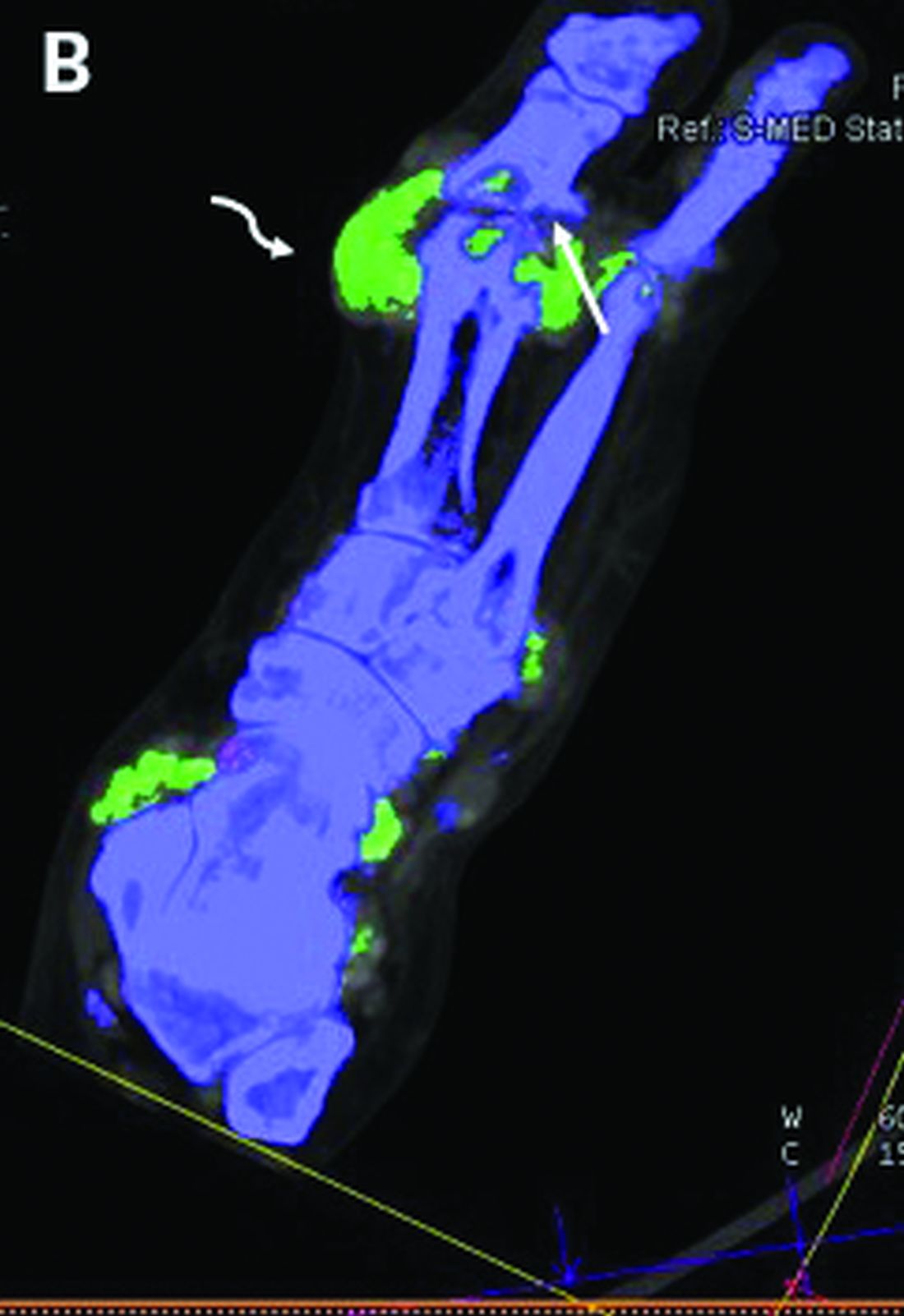
The investigators studied 30 patients: 22 with suspected gout and 8 with suspected CPPD. All underwent arthrocentesis with subsequent polarization microscopy for definitive diagnosis, plus clinical examination, ultrasound examination, conventional radiography, DECT, and assessment of 12 laboratory parameters.
For diagnosis of gout, DECT had a sensitivity and specificity of 59.1% and 100%, respectively, Dr. Schäfer reported, noting that this sensitivity falls considerably short of the 90% previously reported for gout.
Corresponding sensitivity and specificity were 90.9% and 75% for ultrasound, 58.8% and 100% for conventional radiography, and 81.8% and 87.5% for the rheumatologists’ suspected clinical diagnosis.
For diagnosis of CPPD, DECT had sensitivity of 37.5% and specificity of 81.8%. Corresponding values were 87.5% and 91% for ultrasound, 0% and 94.1% for conventional radiography, and 75.0% and 100% for suspected clinical diagnosis.
None of the 12 laboratory parameters studied – uric acid, C-reactive protein, organic phosphate, and leukocytes, among others – significantly differentiated between conditions.
“Both ultrasound and suspected clinical diagnosis had higher sensitivities than DECT for gout and CPPD,” Dr. Schäfer concluded. “Further studies with larger patient cohorts and perhaps modified scan protocols are needed in order to determine the diagnostic utility of DECT in CPPD.”
Findings in context
“Noninvasive, accurate methods for distinguishing between gout and CPPD will improve clinical care,” Sara K. Tedeschi, MD, MPH, predicted in an interview.
“Arthrocentesis is painful in an acutely inflamed joint, can be difficult to perform on small joints, and is underutilized in clinical practice,” she elaborated. And ultrasound is operator dependent and does not quantify crystal volume in and around the joint.
The question addressed by the study is therefore clinically relevant, according to Dr. Tedeschi, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
However, among the patients with CPPD, the study did not report specific phenotypes (acute inflammatory arthritis, chronic inflammatory arthritis, and osteoarthritis with calcium pyrophosphate deposits), she noted. “It is difficult to draw conclusions about the sensitivity or specificity of DECT for CPPD without this information, especially among just 8 CPPD patients.”
In addition, among the patients with gout, the proportion having new-onset disease with flare duration less than 6 weeks and the proportion with tophi were unknown, both of which affected DECT sensitivity in the previous study that reported 90% sensitivity. “Based on the 95% confidence interval in the present study, it is possible that with a larger sample size, DECT sensitivity for gout would have been higher,” she pointed out. “We also do not know the DECT software settings, which impact DECT interpretation as positive or negative for the crystal of interest.”
Finally, “it would be relevant to know what joints were aspirated and imaged in each group,” Dr. Tedeschi said. “For example, if the first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint was aspirated and imaged for half of the gout patients but for none of the CPPD patients, that may affect the study interpretation.”
The study did not receive any specific funding. Dr. Schäfer disclosed a variety of financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Tedeschi disclosed receiving grant support from the National Institutes of Health to study imaging modalities for CPPD, and being first author on a study comparing the sensitivity of DECT, ultrasound, and x-ray for acute CPP crystal arthritis.
SOURCE: Kravchenko D et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jun;79[suppl 1]:196.
Dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) appears to have limited utility for differentiating between gout and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD), according to a German prospective cohort study. Findings were reported at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year because of COVID-19.
“Differentiation of gout and pseudogout, or CPPD, is sometimes difficult,” said presenting investigator Valentin S. Schäfer, MD, associate professor of internal medicine and head of the department of rheumatology and clinical immunology at University Hospital Bonn (Germany).
“Arthrocentesis and subsequent polarization microscopy remains the gold standard,” he noted. “Novel diagnostic approaches, such as DECT, have recently been validated for gout, but limited data [are] available on the use of DECT in patients with CPPD.”
The investigators studied 30 patients: 22 with suspected gout and 8 with suspected CPPD. All underwent arthrocentesis with subsequent polarization microscopy for definitive diagnosis, plus clinical examination, ultrasound examination, conventional radiography, DECT, and assessment of 12 laboratory parameters.
For diagnosis of gout, DECT had a sensitivity and specificity of 59.1% and 100%, respectively, Dr. Schäfer reported, noting that this sensitivity falls considerably short of the 90% previously reported for gout.
Corresponding sensitivity and specificity were 90.9% and 75% for ultrasound, 58.8% and 100% for conventional radiography, and 81.8% and 87.5% for the rheumatologists’ suspected clinical diagnosis.
For diagnosis of CPPD, DECT had sensitivity of 37.5% and specificity of 81.8%. Corresponding values were 87.5% and 91% for ultrasound, 0% and 94.1% for conventional radiography, and 75.0% and 100% for suspected clinical diagnosis.
None of the 12 laboratory parameters studied – uric acid, C-reactive protein, organic phosphate, and leukocytes, among others – significantly differentiated between conditions.
“Both ultrasound and suspected clinical diagnosis had higher sensitivities than DECT for gout and CPPD,” Dr. Schäfer concluded. “Further studies with larger patient cohorts and perhaps modified scan protocols are needed in order to determine the diagnostic utility of DECT in CPPD.”
Findings in context
“Noninvasive, accurate methods for distinguishing between gout and CPPD will improve clinical care,” Sara K. Tedeschi, MD, MPH, predicted in an interview.
“Arthrocentesis is painful in an acutely inflamed joint, can be difficult to perform on small joints, and is underutilized in clinical practice,” she elaborated. And ultrasound is operator dependent and does not quantify crystal volume in and around the joint.
The question addressed by the study is therefore clinically relevant, according to Dr. Tedeschi, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
However, among the patients with CPPD, the study did not report specific phenotypes (acute inflammatory arthritis, chronic inflammatory arthritis, and osteoarthritis with calcium pyrophosphate deposits), she noted. “It is difficult to draw conclusions about the sensitivity or specificity of DECT for CPPD without this information, especially among just 8 CPPD patients.”
In addition, among the patients with gout, the proportion having new-onset disease with flare duration less than 6 weeks and the proportion with tophi were unknown, both of which affected DECT sensitivity in the previous study that reported 90% sensitivity. “Based on the 95% confidence interval in the present study, it is possible that with a larger sample size, DECT sensitivity for gout would have been higher,” she pointed out. “We also do not know the DECT software settings, which impact DECT interpretation as positive or negative for the crystal of interest.”
Finally, “it would be relevant to know what joints were aspirated and imaged in each group,” Dr. Tedeschi said. “For example, if the first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint was aspirated and imaged for half of the gout patients but for none of the CPPD patients, that may affect the study interpretation.”
The study did not receive any specific funding. Dr. Schäfer disclosed a variety of financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Tedeschi disclosed receiving grant support from the National Institutes of Health to study imaging modalities for CPPD, and being first author on a study comparing the sensitivity of DECT, ultrasound, and x-ray for acute CPP crystal arthritis.
SOURCE: Kravchenko D et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jun;79[suppl 1]:196.
Dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) appears to have limited utility for differentiating between gout and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD), according to a German prospective cohort study. Findings were reported at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year because of COVID-19.
“Differentiation of gout and pseudogout, or CPPD, is sometimes difficult,” said presenting investigator Valentin S. Schäfer, MD, associate professor of internal medicine and head of the department of rheumatology and clinical immunology at University Hospital Bonn (Germany).
“Arthrocentesis and subsequent polarization microscopy remains the gold standard,” he noted. “Novel diagnostic approaches, such as DECT, have recently been validated for gout, but limited data [are] available on the use of DECT in patients with CPPD.”
The investigators studied 30 patients: 22 with suspected gout and 8 with suspected CPPD. All underwent arthrocentesis with subsequent polarization microscopy for definitive diagnosis, plus clinical examination, ultrasound examination, conventional radiography, DECT, and assessment of 12 laboratory parameters.
For diagnosis of gout, DECT had a sensitivity and specificity of 59.1% and 100%, respectively, Dr. Schäfer reported, noting that this sensitivity falls considerably short of the 90% previously reported for gout.
Corresponding sensitivity and specificity were 90.9% and 75% for ultrasound, 58.8% and 100% for conventional radiography, and 81.8% and 87.5% for the rheumatologists’ suspected clinical diagnosis.
For diagnosis of CPPD, DECT had sensitivity of 37.5% and specificity of 81.8%. Corresponding values were 87.5% and 91% for ultrasound, 0% and 94.1% for conventional radiography, and 75.0% and 100% for suspected clinical diagnosis.
None of the 12 laboratory parameters studied – uric acid, C-reactive protein, organic phosphate, and leukocytes, among others – significantly differentiated between conditions.
“Both ultrasound and suspected clinical diagnosis had higher sensitivities than DECT for gout and CPPD,” Dr. Schäfer concluded. “Further studies with larger patient cohorts and perhaps modified scan protocols are needed in order to determine the diagnostic utility of DECT in CPPD.”
Findings in context
“Noninvasive, accurate methods for distinguishing between gout and CPPD will improve clinical care,” Sara K. Tedeschi, MD, MPH, predicted in an interview.
“Arthrocentesis is painful in an acutely inflamed joint, can be difficult to perform on small joints, and is underutilized in clinical practice,” she elaborated. And ultrasound is operator dependent and does not quantify crystal volume in and around the joint.
The question addressed by the study is therefore clinically relevant, according to Dr. Tedeschi, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
However, among the patients with CPPD, the study did not report specific phenotypes (acute inflammatory arthritis, chronic inflammatory arthritis, and osteoarthritis with calcium pyrophosphate deposits), she noted. “It is difficult to draw conclusions about the sensitivity or specificity of DECT for CPPD without this information, especially among just 8 CPPD patients.”
In addition, among the patients with gout, the proportion having new-onset disease with flare duration less than 6 weeks and the proportion with tophi were unknown, both of which affected DECT sensitivity in the previous study that reported 90% sensitivity. “Based on the 95% confidence interval in the present study, it is possible that with a larger sample size, DECT sensitivity for gout would have been higher,” she pointed out. “We also do not know the DECT software settings, which impact DECT interpretation as positive or negative for the crystal of interest.”
Finally, “it would be relevant to know what joints were aspirated and imaged in each group,” Dr. Tedeschi said. “For example, if the first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint was aspirated and imaged for half of the gout patients but for none of the CPPD patients, that may affect the study interpretation.”
The study did not receive any specific funding. Dr. Schäfer disclosed a variety of financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Tedeschi disclosed receiving grant support from the National Institutes of Health to study imaging modalities for CPPD, and being first author on a study comparing the sensitivity of DECT, ultrasound, and x-ray for acute CPP crystal arthritis.
SOURCE: Kravchenko D et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jun;79[suppl 1]:196.
FROM THE EULAR 2020 E-CONGRESS