User login
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has recommended orphan designation for Actimab-A, a product intended to treat patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who are over the age of 60 and are ineligible for standard induction therapy.
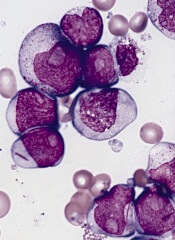
Actimab-A targets CD33, a protein expressed on the surface of AML cells, via the monoclonal antibody, HuM195, which carries the cytotoxic radioisotope actinium-225 to the AML cells.
Actinium Pharmaceuticals, Inc., the company developing Actimab-A, is testing the drug in a phase 2 trial.
Results from a phase 1 trial of the drug were presented at the 2016 ASH Annual Meeting.
At that time, researchers reported results in 18 patients who had been newly diagnosed with AML and were age 60 and older. Their median age was 77 (range, 68-87).
The patients received Actimab-A in combination with low-dose cytarabine. Actimab-A was given at 0.5 μCi/kg/fraction (n=3), 1 μCi/kg/fraction (n=6), 1.5 μCi/kg/fraction (n=3), or 2 μCi/kg/fraction (n=6).
Two patients experienced dose-limiting toxicities. Both had grade 4 thrombocytopenia with marrow aplasia for more than 6 weeks after therapy. One patient was in the 1 µCi/kg/fraction cohort, and the other was in the 2 µCi/kg/fraction cohort.
The maximum-tolerated dose was not reached, but 2 µCi/kg/fraction was chosen as the phase 2 dose.
Grade 3/4 toxicities included neutropenia (n=5), thrombocytopenia (n=9), febrile neutropenia (n=6), pneumonia (n=5), other infections (n=3), atrial fibrillation/syncope (n=1), transient creatinine increase (n=1), generalized fatigue (n=1), hypokalemia (n=1), mucositis (n=1), and rectal hemorrhage (n=1).
Twenty-eight percent of patients (5/18) had objective responses to treatment. Two patients achieved a complete response (CR), 1 had a CR with incomplete platelet recovery, and 2 had a CR with incomplete marrow recovery.
The median duration of response was 9.1 months (range, 4.1-16.9).
About orphan designation
Orphan designation provides regulatory and financial incentives for companies to develop and market therapies that treat life-threatening or chronically debilitating conditions affecting no more than 5 in 10,000 people in the European Union, and where no satisfactory treatment is available.
Orphan designation provides a 10-year period of marketing exclusivity if the drug receives regulatory approval. The designation also provides incentives for companies seeking protocol assistance from the EMA during the product development phase and direct access to the centralized authorization procedure.
The EMA adopts an opinion on the granting of orphan drug designation, and that opinion is submitted to the European Commission for a final decision. The European Commission typically makes a decision within 30 days. ![]()
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has recommended orphan designation for Actimab-A, a product intended to treat patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who are over the age of 60 and are ineligible for standard induction therapy.
Actimab-A targets CD33, a protein expressed on the surface of AML cells, via the monoclonal antibody, HuM195, which carries the cytotoxic radioisotope actinium-225 to the AML cells.
Actinium Pharmaceuticals, Inc., the company developing Actimab-A, is testing the drug in a phase 2 trial.
Results from a phase 1 trial of the drug were presented at the 2016 ASH Annual Meeting.
At that time, researchers reported results in 18 patients who had been newly diagnosed with AML and were age 60 and older. Their median age was 77 (range, 68-87).
The patients received Actimab-A in combination with low-dose cytarabine. Actimab-A was given at 0.5 μCi/kg/fraction (n=3), 1 μCi/kg/fraction (n=6), 1.5 μCi/kg/fraction (n=3), or 2 μCi/kg/fraction (n=6).
Two patients experienced dose-limiting toxicities. Both had grade 4 thrombocytopenia with marrow aplasia for more than 6 weeks after therapy. One patient was in the 1 µCi/kg/fraction cohort, and the other was in the 2 µCi/kg/fraction cohort.
The maximum-tolerated dose was not reached, but 2 µCi/kg/fraction was chosen as the phase 2 dose.
Grade 3/4 toxicities included neutropenia (n=5), thrombocytopenia (n=9), febrile neutropenia (n=6), pneumonia (n=5), other infections (n=3), atrial fibrillation/syncope (n=1), transient creatinine increase (n=1), generalized fatigue (n=1), hypokalemia (n=1), mucositis (n=1), and rectal hemorrhage (n=1).
Twenty-eight percent of patients (5/18) had objective responses to treatment. Two patients achieved a complete response (CR), 1 had a CR with incomplete platelet recovery, and 2 had a CR with incomplete marrow recovery.
The median duration of response was 9.1 months (range, 4.1-16.9).
About orphan designation
Orphan designation provides regulatory and financial incentives for companies to develop and market therapies that treat life-threatening or chronically debilitating conditions affecting no more than 5 in 10,000 people in the European Union, and where no satisfactory treatment is available.
Orphan designation provides a 10-year period of marketing exclusivity if the drug receives regulatory approval. The designation also provides incentives for companies seeking protocol assistance from the EMA during the product development phase and direct access to the centralized authorization procedure.
The EMA adopts an opinion on the granting of orphan drug designation, and that opinion is submitted to the European Commission for a final decision. The European Commission typically makes a decision within 30 days. ![]()
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has recommended orphan designation for Actimab-A, a product intended to treat patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who are over the age of 60 and are ineligible for standard induction therapy.
Actimab-A targets CD33, a protein expressed on the surface of AML cells, via the monoclonal antibody, HuM195, which carries the cytotoxic radioisotope actinium-225 to the AML cells.
Actinium Pharmaceuticals, Inc., the company developing Actimab-A, is testing the drug in a phase 2 trial.
Results from a phase 1 trial of the drug were presented at the 2016 ASH Annual Meeting.
At that time, researchers reported results in 18 patients who had been newly diagnosed with AML and were age 60 and older. Their median age was 77 (range, 68-87).
The patients received Actimab-A in combination with low-dose cytarabine. Actimab-A was given at 0.5 μCi/kg/fraction (n=3), 1 μCi/kg/fraction (n=6), 1.5 μCi/kg/fraction (n=3), or 2 μCi/kg/fraction (n=6).
Two patients experienced dose-limiting toxicities. Both had grade 4 thrombocytopenia with marrow aplasia for more than 6 weeks after therapy. One patient was in the 1 µCi/kg/fraction cohort, and the other was in the 2 µCi/kg/fraction cohort.
The maximum-tolerated dose was not reached, but 2 µCi/kg/fraction was chosen as the phase 2 dose.
Grade 3/4 toxicities included neutropenia (n=5), thrombocytopenia (n=9), febrile neutropenia (n=6), pneumonia (n=5), other infections (n=3), atrial fibrillation/syncope (n=1), transient creatinine increase (n=1), generalized fatigue (n=1), hypokalemia (n=1), mucositis (n=1), and rectal hemorrhage (n=1).
Twenty-eight percent of patients (5/18) had objective responses to treatment. Two patients achieved a complete response (CR), 1 had a CR with incomplete platelet recovery, and 2 had a CR with incomplete marrow recovery.
The median duration of response was 9.1 months (range, 4.1-16.9).
About orphan designation
Orphan designation provides regulatory and financial incentives for companies to develop and market therapies that treat life-threatening or chronically debilitating conditions affecting no more than 5 in 10,000 people in the European Union, and where no satisfactory treatment is available.
Orphan designation provides a 10-year period of marketing exclusivity if the drug receives regulatory approval. The designation also provides incentives for companies seeking protocol assistance from the EMA during the product development phase and direct access to the centralized authorization procedure.
The EMA adopts an opinion on the granting of orphan drug designation, and that opinion is submitted to the European Commission for a final decision. The European Commission typically makes a decision within 30 days. ![]()