User login
With hospital reimbursement increasingly being linked to patient satisfaction,1 about half of US hospitals have embraced arts programs as a means of humanizing clinical environments and improving the patient experience.2,3 There is emerging evidence that integrating such programs into clinical settings is associated with less pain, stress, and anxiety4-10 as well as improved mood,11 greater levels of interaction,12 and feeling less institutionalized.13 However, it has been observed that existing studies have been undertaken with variable methodological rigor,14 and few randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have linked specific design features or interventions directly to healthcare outcomes. We designed a RCT to test the hypotheses that (1) placing a painting by a local artist in the line of vision of hospitalized patients would improve psychological and clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction and (2) letting patients choose their own painting would offer even greater benefit in these areas.
METHODS
Outcomes and Measures
The primary outcomes were psychological and included the following: anxiety, mood, depression, and sense of control and/or influence. These were measured using the validated State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI)15 an emotional thermometer instrument (ETI)16, and a self-designed instrument measuring one’s sense of control and influence over the environment. Secondary outcomes were clinical, encompassing pain, quality of life (QOL), length of stay (LOS), and related to perceptions of the hospital environment. These were assessed using data extracted from the electronic medical record (EMR) as well as the Room Assessment (RA) survey, a validated instrument used in prior clinical studies to assess inpatient settings.17 The RA survey uses the Semantic Differential scale, a rating scale designed to measure emotional associations by using paired attributes.18 In our scale, we listed 17 paired and polar opposite attributes, with one descriptor reflecting a more positive impression than the other. Anxiety, emotional state, and control and/or influence were assessed at baseline and prior to discharge; emotional state was assessed every 1 to 2 days; and perceptions of the room and overall patient experience were measured once, prior to discharge, using the RA survey.
Data Analysis
A sample of 180 participants were chosen, with a 2:1 ratio of art group to no-art control group to provide at least 80% power to detect a difference in anxiety score of 4 units, for the comparisons of interest among the groups. The calculations assumed a 2-sided test with α = 0.05.
Comparisons were made between (1) those with paintings versus those without and (2) those with a choice of paintings versus those with no choice. For the primary psychological outcome, the average anxiety score at discharge was compared between groups of interest by using analysis of covariance, with adjustment for baseline score. Items measuring mood, depression, control, and influence that were collected more frequently were compared between groups by using repeated measures analysis of covariance, with adjustment for corresponding score at baseline. For clinical outcomes, median LOS was compared between groups by using the Wilcoxon rank sum test due to the skewed distribution of data, and QOL and pain were compared between groups by using repeated measures analysis of covariance. The model for patient-reported pain included covariates for pain medication received and level of pain tolerance. Outcomes measuring perceptions of hospital environment were collected at a single time point and compared between groups by using the 2-sample t-test. Results were reported in terms of means and 95% confidence intervals or medians and quartiles. Significance was defined by P < .05. All facets of this study were approved by the Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine Institutional Review Board.
RESULTS
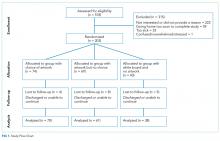
We approached 518 patients to participate in the study, and 203 elected to enroll. Seventeen patients withdrew from the study because they had been discharged from the hospital or were unable to continue. Of the 186 participants who completed the study, 74 chose the painting displayed in their rooms, 69 had paintings randomly selected for them, and 43 had no paintings in their rooms, only white boards in their line of vision. The average age of participants in the trial was 56 years, 49% were male, and 89% were Caucasian. There were no significant differences between participants and decliners in terms of race (P = .13) and mean age (P = .08). However, they did differ by gender, with 49% of participants being male compared with 68% of decliners (P < .001). There were no significant differences among the 3 study groups with respect to these demographic characteristics. No harms were observed for any patients; however, several patients in the group whose artwork was randomly selected expressed distaste for the image and/or color scheme of their painting.
Psychological Outcomes: Anxiety (STAI), Mood and Depression (ETI), and Sense of Control and/or Influence (Self-Designed Instrument)
There were no differences in anxiety for the primary comparison of artwork versus no artwork or the secondary comparison of choice versus no choice. Likewise, there were no differences in mood, depression, or sense of control and/or influence across the 3 groups.
Clinical Outcomes: Self-Reported Pain, LOS, and QOL (from EMR)
There were no differences in self-reported pain, LOS, or QOL across the 3 groups. With regard to LOS, the median (quartile 1 [Q1], quartile 3 [Q3]) stay was 6 days for the choice group (4.0, 12.0), 6 days for the no-choice group (5.0, 9.5), and 9.5 days for the group with no artwork (5.0, 20.0; see supplementary Table).
Perceptions of Hospital Environment (RA Survey)
DISCUSSION
While having paintings in cancer inpatient rooms did not affect the psychological or clinical outcomes we assessed, patients who had paintings in their rooms had more positive impressions of the hospital environment. Given that healthcare administrators are under strong pressures to control costs while increasing care quality and patient satisfaction to maximize reimbursement, integrating local artwork into inpatient rooms may represent a simple and relatively inexpensive way (approximately $90 per room) to humanize clinical environments, systematically improve perceptions of the institution, and perhaps contribute to increased patient satisfaction scores. While more work must be done to establish a positive link between access to artwork and improved standardized patient satisfaction outcomes, our results suggest that there may be potential benefit in giving patients an opportunity to engage artwork as a therapeutic resource during the physical, emotional, and spiritual challenges that arise during inpatient treatment.
These findings also have implications for inpatients with illnesses other than cancer. Though we did not explicitly study noncancer patients, we know that nearly 40 million Americans are admitted annually to institutional care (ie, acute hospitalizations, rehabilitation hospitals, and skilled nursing facilities) and often find themselves in environments that can be stark and medicalized. We would anticipate that providing art in these patients’ rooms would likewise improve perceptions of the institutions where they receive their inpatient medical care.
This study had several limitations that could affect the generalizability of our findings. First, it was difficult to enroll patients, with greater than 50% of persons approached declining to participate. Second, nonparticipants were more likely to be male, and this clearly provides a biased sample. Third, we have incomplete data for some patients who were unavailable or changed rooms during the study. Fourth, while each patient room had standardized features (eg, windows, televisions, etc.), there were logistical challenges with placing paintings in the exact same location (ie, in the patient’s direct line of vision) in every hospital room because the shape, size, and idiosyncratic decorating of hospital rooms varied, so we were not able to fully control for all room décor features. Fifth, the study was conducted at a single site and only among patients with cancer; other populations could respond very differently. It is possible that other confounding factors (such as prior hospital experience, patient predilection for artwork, and usage of digital devices during hospitalization) could have affected outcomes, but these were not measured in this study.
In conclusion, as patient satisfaction continues to influence hospital reimbursement, identifying novel and effective approaches to improving patient perceptions can play a meaningful role in patient care. Future research should focus on different inpatient populations and venues; new strategies to effectively evaluate relevant clinical outcomes; comparisons with other nonpharmacological, arts-based interventions in inpatient settings (eg, music, creation of artwork, etc.); and assessment of aggregate scores on standardized patient satisfaction instruments (eg, Press Ganey, Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems). There may also be an additive benefit in providing “coaching” to healthcare providers on how to engage with patients regarding the artwork they have chosen. Such approaches might also examine the value of giving patients control over multiple opportunities to influence the aesthetics in their room versus a single opportunity during the course of their stay.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the contributions of Lorna Davis, Lori Snyder, and Renee Stewart to this work.
Disclosure
This work was supported by funding from the National Endowment for the Arts (grant 14-3800-7008). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier for Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center Protocol Record STUDY00000378: NCT02357160. The authors report no conflicts of interest.
1. Mehta SJ. Patient Satisfaction Reporting and Its Implications for Patient Care. AMA J Ethics. 2015;17(7):616-621. PubMed
2. Hathorn KN. A Guide to Evidence-based Art. The Center for Health and Design; 2008. https://www.healthdesign.org/sites/default/files/Hathorn_Nanda_Mar08.pdf . Accessed November 5, 2017.
3. Sonke J, Rollins J, Brandman R, Graham-Pole J. The state of the arts in healthcare in the United States. Arts & Health. 2009;1(2):107-135.
4. Ulrich RS, Zimring C, Zhu X, et al. A Review of the Research Literature on Evidence-Based Healthcare Design. HERD. 2008;1(3):61-125. PubMed
5. Beukeboom CJ, Langeveld D, Tanja-Dijkstra K. Stress-reducing effects of real and artificial nature in a hospital waiting room. J Altern Complement Med. 2012;18(4):329-333. PubMed
6. Miller AC, Hickman LC, Lemaster GK. A Distraction Technique for Control of Burn Pain. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1992;13(5):576-580. PubMed
7. Diette GB, Lechtzin N, Haponik E, Devrotes A, Rubin HR. Distraction Therapy with Nature Sights and Sounds Reduces Pain During Flexible Bronchoscopy: A Complementary Approach to Routine Analgesic. Chest. 2003;123(3):941-948. PubMed
8. Tse MM, Ng JK, Chung JW, Wong TK. The effect of visual stimuli on pain threshold and tolerance. J Clin Nursing. 2002;11(4):462-469.
PubMed
9. Vincent E, Battisto D, Grimes L. The Effects of Nature Images on Pain in a Simulated Hospital Patient Room. HERD. 2010;3(3):56-69. PubMed
10. Staricoff RL. Arts in health: the value of evaluation. J R Soc Promot Health. 2006;126(3):116-120. PubMed
11. Karnik M, Printz B, Finkel J. A Hospital’s Contemporary Art Collection: Effects on Patient Mood, Stress, Comfort, and Expectations. HERD. 2014;7(3):60-77. PubMed
12. Suter E, Baylin D. Choosing art as a complement to healing. Appl Nurs Res. 2007;20(1):32-38. PubMed
13. Harris PB, McBride G, Ross C, Curtis L. A Place to Heal: Environmental Sources of Satisfaction among Hospital Patients. J Appl Soc Psychol. 2002;32(6):1276-1299.
14. Moss H, Donnellan C, O’Neill D. A review of qualitative methodologies used to explore patient perceptions of arts and healthcare. Med Humanit. 2012;38(2):106-109. PubMed
15. Corsini RJ, Ozaki BD. Encyclopedia of psychology. Vol. 1. New York: Wiley; 1994. State-Trait Anxiety Inventory.
16. Beck KR, Tan SM, Lum SS, Lim LE, Krishna LK. Validation of the emotion thermometers and hospital anxiety and depression scales in Singapore: Screening cancer patients for distress, anxiety and depression. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2016;12(2):e241-e249. PubMed
17. Lohr VI, Pearson-Mims CH. Physical discomfort may be reduced in the presence of interior plants. HortTechnology. 2000;10(1):53-58.
18. Semantic Differential. http://psc.dss.ucdavis.edu/sommerb/sommerdemo/scaling/semdiff.htm. Accessed November 5, 2017.
With hospital reimbursement increasingly being linked to patient satisfaction,1 about half of US hospitals have embraced arts programs as a means of humanizing clinical environments and improving the patient experience.2,3 There is emerging evidence that integrating such programs into clinical settings is associated with less pain, stress, and anxiety4-10 as well as improved mood,11 greater levels of interaction,12 and feeling less institutionalized.13 However, it has been observed that existing studies have been undertaken with variable methodological rigor,14 and few randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have linked specific design features or interventions directly to healthcare outcomes. We designed a RCT to test the hypotheses that (1) placing a painting by a local artist in the line of vision of hospitalized patients would improve psychological and clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction and (2) letting patients choose their own painting would offer even greater benefit in these areas.
METHODS
Outcomes and Measures
The primary outcomes were psychological and included the following: anxiety, mood, depression, and sense of control and/or influence. These were measured using the validated State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI)15 an emotional thermometer instrument (ETI)16, and a self-designed instrument measuring one’s sense of control and influence over the environment. Secondary outcomes were clinical, encompassing pain, quality of life (QOL), length of stay (LOS), and related to perceptions of the hospital environment. These were assessed using data extracted from the electronic medical record (EMR) as well as the Room Assessment (RA) survey, a validated instrument used in prior clinical studies to assess inpatient settings.17 The RA survey uses the Semantic Differential scale, a rating scale designed to measure emotional associations by using paired attributes.18 In our scale, we listed 17 paired and polar opposite attributes, with one descriptor reflecting a more positive impression than the other. Anxiety, emotional state, and control and/or influence were assessed at baseline and prior to discharge; emotional state was assessed every 1 to 2 days; and perceptions of the room and overall patient experience were measured once, prior to discharge, using the RA survey.
Data Analysis
A sample of 180 participants were chosen, with a 2:1 ratio of art group to no-art control group to provide at least 80% power to detect a difference in anxiety score of 4 units, for the comparisons of interest among the groups. The calculations assumed a 2-sided test with α = 0.05.
Comparisons were made between (1) those with paintings versus those without and (2) those with a choice of paintings versus those with no choice. For the primary psychological outcome, the average anxiety score at discharge was compared between groups of interest by using analysis of covariance, with adjustment for baseline score. Items measuring mood, depression, control, and influence that were collected more frequently were compared between groups by using repeated measures analysis of covariance, with adjustment for corresponding score at baseline. For clinical outcomes, median LOS was compared between groups by using the Wilcoxon rank sum test due to the skewed distribution of data, and QOL and pain were compared between groups by using repeated measures analysis of covariance. The model for patient-reported pain included covariates for pain medication received and level of pain tolerance. Outcomes measuring perceptions of hospital environment were collected at a single time point and compared between groups by using the 2-sample t-test. Results were reported in terms of means and 95% confidence intervals or medians and quartiles. Significance was defined by P < .05. All facets of this study were approved by the Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine Institutional Review Board.
RESULTS
We approached 518 patients to participate in the study, and 203 elected to enroll. Seventeen patients withdrew from the study because they had been discharged from the hospital or were unable to continue. Of the 186 participants who completed the study, 74 chose the painting displayed in their rooms, 69 had paintings randomly selected for them, and 43 had no paintings in their rooms, only white boards in their line of vision. The average age of participants in the trial was 56 years, 49% were male, and 89% were Caucasian. There were no significant differences between participants and decliners in terms of race (P = .13) and mean age (P = .08). However, they did differ by gender, with 49% of participants being male compared with 68% of decliners (P < .001). There were no significant differences among the 3 study groups with respect to these demographic characteristics. No harms were observed for any patients; however, several patients in the group whose artwork was randomly selected expressed distaste for the image and/or color scheme of their painting.
Psychological Outcomes: Anxiety (STAI), Mood and Depression (ETI), and Sense of Control and/or Influence (Self-Designed Instrument)
There were no differences in anxiety for the primary comparison of artwork versus no artwork or the secondary comparison of choice versus no choice. Likewise, there were no differences in mood, depression, or sense of control and/or influence across the 3 groups.
Clinical Outcomes: Self-Reported Pain, LOS, and QOL (from EMR)
There were no differences in self-reported pain, LOS, or QOL across the 3 groups. With regard to LOS, the median (quartile 1 [Q1], quartile 3 [Q3]) stay was 6 days for the choice group (4.0, 12.0), 6 days for the no-choice group (5.0, 9.5), and 9.5 days for the group with no artwork (5.0, 20.0; see supplementary Table).
Perceptions of Hospital Environment (RA Survey)
DISCUSSION
While having paintings in cancer inpatient rooms did not affect the psychological or clinical outcomes we assessed, patients who had paintings in their rooms had more positive impressions of the hospital environment. Given that healthcare administrators are under strong pressures to control costs while increasing care quality and patient satisfaction to maximize reimbursement, integrating local artwork into inpatient rooms may represent a simple and relatively inexpensive way (approximately $90 per room) to humanize clinical environments, systematically improve perceptions of the institution, and perhaps contribute to increased patient satisfaction scores. While more work must be done to establish a positive link between access to artwork and improved standardized patient satisfaction outcomes, our results suggest that there may be potential benefit in giving patients an opportunity to engage artwork as a therapeutic resource during the physical, emotional, and spiritual challenges that arise during inpatient treatment.
These findings also have implications for inpatients with illnesses other than cancer. Though we did not explicitly study noncancer patients, we know that nearly 40 million Americans are admitted annually to institutional care (ie, acute hospitalizations, rehabilitation hospitals, and skilled nursing facilities) and often find themselves in environments that can be stark and medicalized. We would anticipate that providing art in these patients’ rooms would likewise improve perceptions of the institutions where they receive their inpatient medical care.
This study had several limitations that could affect the generalizability of our findings. First, it was difficult to enroll patients, with greater than 50% of persons approached declining to participate. Second, nonparticipants were more likely to be male, and this clearly provides a biased sample. Third, we have incomplete data for some patients who were unavailable or changed rooms during the study. Fourth, while each patient room had standardized features (eg, windows, televisions, etc.), there were logistical challenges with placing paintings in the exact same location (ie, in the patient’s direct line of vision) in every hospital room because the shape, size, and idiosyncratic decorating of hospital rooms varied, so we were not able to fully control for all room décor features. Fifth, the study was conducted at a single site and only among patients with cancer; other populations could respond very differently. It is possible that other confounding factors (such as prior hospital experience, patient predilection for artwork, and usage of digital devices during hospitalization) could have affected outcomes, but these were not measured in this study.
In conclusion, as patient satisfaction continues to influence hospital reimbursement, identifying novel and effective approaches to improving patient perceptions can play a meaningful role in patient care. Future research should focus on different inpatient populations and venues; new strategies to effectively evaluate relevant clinical outcomes; comparisons with other nonpharmacological, arts-based interventions in inpatient settings (eg, music, creation of artwork, etc.); and assessment of aggregate scores on standardized patient satisfaction instruments (eg, Press Ganey, Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems). There may also be an additive benefit in providing “coaching” to healthcare providers on how to engage with patients regarding the artwork they have chosen. Such approaches might also examine the value of giving patients control over multiple opportunities to influence the aesthetics in their room versus a single opportunity during the course of their stay.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the contributions of Lorna Davis, Lori Snyder, and Renee Stewart to this work.
Disclosure
This work was supported by funding from the National Endowment for the Arts (grant 14-3800-7008). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier for Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center Protocol Record STUDY00000378: NCT02357160. The authors report no conflicts of interest.
With hospital reimbursement increasingly being linked to patient satisfaction,1 about half of US hospitals have embraced arts programs as a means of humanizing clinical environments and improving the patient experience.2,3 There is emerging evidence that integrating such programs into clinical settings is associated with less pain, stress, and anxiety4-10 as well as improved mood,11 greater levels of interaction,12 and feeling less institutionalized.13 However, it has been observed that existing studies have been undertaken with variable methodological rigor,14 and few randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have linked specific design features or interventions directly to healthcare outcomes. We designed a RCT to test the hypotheses that (1) placing a painting by a local artist in the line of vision of hospitalized patients would improve psychological and clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction and (2) letting patients choose their own painting would offer even greater benefit in these areas.
METHODS
Outcomes and Measures
The primary outcomes were psychological and included the following: anxiety, mood, depression, and sense of control and/or influence. These were measured using the validated State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI)15 an emotional thermometer instrument (ETI)16, and a self-designed instrument measuring one’s sense of control and influence over the environment. Secondary outcomes were clinical, encompassing pain, quality of life (QOL), length of stay (LOS), and related to perceptions of the hospital environment. These were assessed using data extracted from the electronic medical record (EMR) as well as the Room Assessment (RA) survey, a validated instrument used in prior clinical studies to assess inpatient settings.17 The RA survey uses the Semantic Differential scale, a rating scale designed to measure emotional associations by using paired attributes.18 In our scale, we listed 17 paired and polar opposite attributes, with one descriptor reflecting a more positive impression than the other. Anxiety, emotional state, and control and/or influence were assessed at baseline and prior to discharge; emotional state was assessed every 1 to 2 days; and perceptions of the room and overall patient experience were measured once, prior to discharge, using the RA survey.
Data Analysis
A sample of 180 participants were chosen, with a 2:1 ratio of art group to no-art control group to provide at least 80% power to detect a difference in anxiety score of 4 units, for the comparisons of interest among the groups. The calculations assumed a 2-sided test with α = 0.05.
Comparisons were made between (1) those with paintings versus those without and (2) those with a choice of paintings versus those with no choice. For the primary psychological outcome, the average anxiety score at discharge was compared between groups of interest by using analysis of covariance, with adjustment for baseline score. Items measuring mood, depression, control, and influence that were collected more frequently were compared between groups by using repeated measures analysis of covariance, with adjustment for corresponding score at baseline. For clinical outcomes, median LOS was compared between groups by using the Wilcoxon rank sum test due to the skewed distribution of data, and QOL and pain were compared between groups by using repeated measures analysis of covariance. The model for patient-reported pain included covariates for pain medication received and level of pain tolerance. Outcomes measuring perceptions of hospital environment were collected at a single time point and compared between groups by using the 2-sample t-test. Results were reported in terms of means and 95% confidence intervals or medians and quartiles. Significance was defined by P < .05. All facets of this study were approved by the Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine Institutional Review Board.
RESULTS
We approached 518 patients to participate in the study, and 203 elected to enroll. Seventeen patients withdrew from the study because they had been discharged from the hospital or were unable to continue. Of the 186 participants who completed the study, 74 chose the painting displayed in their rooms, 69 had paintings randomly selected for them, and 43 had no paintings in their rooms, only white boards in their line of vision. The average age of participants in the trial was 56 years, 49% were male, and 89% were Caucasian. There were no significant differences between participants and decliners in terms of race (P = .13) and mean age (P = .08). However, they did differ by gender, with 49% of participants being male compared with 68% of decliners (P < .001). There were no significant differences among the 3 study groups with respect to these demographic characteristics. No harms were observed for any patients; however, several patients in the group whose artwork was randomly selected expressed distaste for the image and/or color scheme of their painting.
Psychological Outcomes: Anxiety (STAI), Mood and Depression (ETI), and Sense of Control and/or Influence (Self-Designed Instrument)
There were no differences in anxiety for the primary comparison of artwork versus no artwork or the secondary comparison of choice versus no choice. Likewise, there were no differences in mood, depression, or sense of control and/or influence across the 3 groups.
Clinical Outcomes: Self-Reported Pain, LOS, and QOL (from EMR)
There were no differences in self-reported pain, LOS, or QOL across the 3 groups. With regard to LOS, the median (quartile 1 [Q1], quartile 3 [Q3]) stay was 6 days for the choice group (4.0, 12.0), 6 days for the no-choice group (5.0, 9.5), and 9.5 days for the group with no artwork (5.0, 20.0; see supplementary Table).
Perceptions of Hospital Environment (RA Survey)
DISCUSSION
While having paintings in cancer inpatient rooms did not affect the psychological or clinical outcomes we assessed, patients who had paintings in their rooms had more positive impressions of the hospital environment. Given that healthcare administrators are under strong pressures to control costs while increasing care quality and patient satisfaction to maximize reimbursement, integrating local artwork into inpatient rooms may represent a simple and relatively inexpensive way (approximately $90 per room) to humanize clinical environments, systematically improve perceptions of the institution, and perhaps contribute to increased patient satisfaction scores. While more work must be done to establish a positive link between access to artwork and improved standardized patient satisfaction outcomes, our results suggest that there may be potential benefit in giving patients an opportunity to engage artwork as a therapeutic resource during the physical, emotional, and spiritual challenges that arise during inpatient treatment.
These findings also have implications for inpatients with illnesses other than cancer. Though we did not explicitly study noncancer patients, we know that nearly 40 million Americans are admitted annually to institutional care (ie, acute hospitalizations, rehabilitation hospitals, and skilled nursing facilities) and often find themselves in environments that can be stark and medicalized. We would anticipate that providing art in these patients’ rooms would likewise improve perceptions of the institutions where they receive their inpatient medical care.
This study had several limitations that could affect the generalizability of our findings. First, it was difficult to enroll patients, with greater than 50% of persons approached declining to participate. Second, nonparticipants were more likely to be male, and this clearly provides a biased sample. Third, we have incomplete data for some patients who were unavailable or changed rooms during the study. Fourth, while each patient room had standardized features (eg, windows, televisions, etc.), there were logistical challenges with placing paintings in the exact same location (ie, in the patient’s direct line of vision) in every hospital room because the shape, size, and idiosyncratic decorating of hospital rooms varied, so we were not able to fully control for all room décor features. Fifth, the study was conducted at a single site and only among patients with cancer; other populations could respond very differently. It is possible that other confounding factors (such as prior hospital experience, patient predilection for artwork, and usage of digital devices during hospitalization) could have affected outcomes, but these were not measured in this study.
In conclusion, as patient satisfaction continues to influence hospital reimbursement, identifying novel and effective approaches to improving patient perceptions can play a meaningful role in patient care. Future research should focus on different inpatient populations and venues; new strategies to effectively evaluate relevant clinical outcomes; comparisons with other nonpharmacological, arts-based interventions in inpatient settings (eg, music, creation of artwork, etc.); and assessment of aggregate scores on standardized patient satisfaction instruments (eg, Press Ganey, Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems). There may also be an additive benefit in providing “coaching” to healthcare providers on how to engage with patients regarding the artwork they have chosen. Such approaches might also examine the value of giving patients control over multiple opportunities to influence the aesthetics in their room versus a single opportunity during the course of their stay.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the contributions of Lorna Davis, Lori Snyder, and Renee Stewart to this work.
Disclosure
This work was supported by funding from the National Endowment for the Arts (grant 14-3800-7008). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier for Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center Protocol Record STUDY00000378: NCT02357160. The authors report no conflicts of interest.
1. Mehta SJ. Patient Satisfaction Reporting and Its Implications for Patient Care. AMA J Ethics. 2015;17(7):616-621. PubMed
2. Hathorn KN. A Guide to Evidence-based Art. The Center for Health and Design; 2008. https://www.healthdesign.org/sites/default/files/Hathorn_Nanda_Mar08.pdf . Accessed November 5, 2017.
3. Sonke J, Rollins J, Brandman R, Graham-Pole J. The state of the arts in healthcare in the United States. Arts & Health. 2009;1(2):107-135.
4. Ulrich RS, Zimring C, Zhu X, et al. A Review of the Research Literature on Evidence-Based Healthcare Design. HERD. 2008;1(3):61-125. PubMed
5. Beukeboom CJ, Langeveld D, Tanja-Dijkstra K. Stress-reducing effects of real and artificial nature in a hospital waiting room. J Altern Complement Med. 2012;18(4):329-333. PubMed
6. Miller AC, Hickman LC, Lemaster GK. A Distraction Technique for Control of Burn Pain. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1992;13(5):576-580. PubMed
7. Diette GB, Lechtzin N, Haponik E, Devrotes A, Rubin HR. Distraction Therapy with Nature Sights and Sounds Reduces Pain During Flexible Bronchoscopy: A Complementary Approach to Routine Analgesic. Chest. 2003;123(3):941-948. PubMed
8. Tse MM, Ng JK, Chung JW, Wong TK. The effect of visual stimuli on pain threshold and tolerance. J Clin Nursing. 2002;11(4):462-469.
PubMed
9. Vincent E, Battisto D, Grimes L. The Effects of Nature Images on Pain in a Simulated Hospital Patient Room. HERD. 2010;3(3):56-69. PubMed
10. Staricoff RL. Arts in health: the value of evaluation. J R Soc Promot Health. 2006;126(3):116-120. PubMed
11. Karnik M, Printz B, Finkel J. A Hospital’s Contemporary Art Collection: Effects on Patient Mood, Stress, Comfort, and Expectations. HERD. 2014;7(3):60-77. PubMed
12. Suter E, Baylin D. Choosing art as a complement to healing. Appl Nurs Res. 2007;20(1):32-38. PubMed
13. Harris PB, McBride G, Ross C, Curtis L. A Place to Heal: Environmental Sources of Satisfaction among Hospital Patients. J Appl Soc Psychol. 2002;32(6):1276-1299.
14. Moss H, Donnellan C, O’Neill D. A review of qualitative methodologies used to explore patient perceptions of arts and healthcare. Med Humanit. 2012;38(2):106-109. PubMed
15. Corsini RJ, Ozaki BD. Encyclopedia of psychology. Vol. 1. New York: Wiley; 1994. State-Trait Anxiety Inventory.
16. Beck KR, Tan SM, Lum SS, Lim LE, Krishna LK. Validation of the emotion thermometers and hospital anxiety and depression scales in Singapore: Screening cancer patients for distress, anxiety and depression. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2016;12(2):e241-e249. PubMed
17. Lohr VI, Pearson-Mims CH. Physical discomfort may be reduced in the presence of interior plants. HortTechnology. 2000;10(1):53-58.
18. Semantic Differential. http://psc.dss.ucdavis.edu/sommerb/sommerdemo/scaling/semdiff.htm. Accessed November 5, 2017.
1. Mehta SJ. Patient Satisfaction Reporting and Its Implications for Patient Care. AMA J Ethics. 2015;17(7):616-621. PubMed
2. Hathorn KN. A Guide to Evidence-based Art. The Center for Health and Design; 2008. https://www.healthdesign.org/sites/default/files/Hathorn_Nanda_Mar08.pdf . Accessed November 5, 2017.
3. Sonke J, Rollins J, Brandman R, Graham-Pole J. The state of the arts in healthcare in the United States. Arts & Health. 2009;1(2):107-135.
4. Ulrich RS, Zimring C, Zhu X, et al. A Review of the Research Literature on Evidence-Based Healthcare Design. HERD. 2008;1(3):61-125. PubMed
5. Beukeboom CJ, Langeveld D, Tanja-Dijkstra K. Stress-reducing effects of real and artificial nature in a hospital waiting room. J Altern Complement Med. 2012;18(4):329-333. PubMed
6. Miller AC, Hickman LC, Lemaster GK. A Distraction Technique for Control of Burn Pain. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1992;13(5):576-580. PubMed
7. Diette GB, Lechtzin N, Haponik E, Devrotes A, Rubin HR. Distraction Therapy with Nature Sights and Sounds Reduces Pain During Flexible Bronchoscopy: A Complementary Approach to Routine Analgesic. Chest. 2003;123(3):941-948. PubMed
8. Tse MM, Ng JK, Chung JW, Wong TK. The effect of visual stimuli on pain threshold and tolerance. J Clin Nursing. 2002;11(4):462-469.
PubMed
9. Vincent E, Battisto D, Grimes L. The Effects of Nature Images on Pain in a Simulated Hospital Patient Room. HERD. 2010;3(3):56-69. PubMed
10. Staricoff RL. Arts in health: the value of evaluation. J R Soc Promot Health. 2006;126(3):116-120. PubMed
11. Karnik M, Printz B, Finkel J. A Hospital’s Contemporary Art Collection: Effects on Patient Mood, Stress, Comfort, and Expectations. HERD. 2014;7(3):60-77. PubMed
12. Suter E, Baylin D. Choosing art as a complement to healing. Appl Nurs Res. 2007;20(1):32-38. PubMed
13. Harris PB, McBride G, Ross C, Curtis L. A Place to Heal: Environmental Sources of Satisfaction among Hospital Patients. J Appl Soc Psychol. 2002;32(6):1276-1299.
14. Moss H, Donnellan C, O’Neill D. A review of qualitative methodologies used to explore patient perceptions of arts and healthcare. Med Humanit. 2012;38(2):106-109. PubMed
15. Corsini RJ, Ozaki BD. Encyclopedia of psychology. Vol. 1. New York: Wiley; 1994. State-Trait Anxiety Inventory.
16. Beck KR, Tan SM, Lum SS, Lim LE, Krishna LK. Validation of the emotion thermometers and hospital anxiety and depression scales in Singapore: Screening cancer patients for distress, anxiety and depression. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2016;12(2):e241-e249. PubMed
17. Lohr VI, Pearson-Mims CH. Physical discomfort may be reduced in the presence of interior plants. HortTechnology. 2000;10(1):53-58.
18. Semantic Differential. http://psc.dss.ucdavis.edu/sommerb/sommerdemo/scaling/semdiff.htm. Accessed November 5, 2017.
© 2018 Society of Hospital Medicine