User login
Editor’s note: “Everything We Say and Do” is an informational series developed by the Society of Hospital Medicine’s Patient Experience Committee to provide readers with thoughtful and actionable communication tactics that have great potential to positively impact patients’ experiences of care. Each article will focus on how the contributor applies one or more of the “key communication” tactics in practice to maintain provider accountability for “everything we say and do that affects our patients’ thoughts, feelings, and well-being.”
What I say and do
I empower all of my patients by giving them the opportunity to consider advance care planning.
Why I do it
Everyone deserves advance care planning, and every health care encounter, including a hospitalization, is an opportunity to better identify and document patients’ wishes for care should they become unable to express them. If we wait for patients to develop serious advanced illness before having advance care planning conversations, we risk depriving them of the care they would want in these situations. Additionally, we place a huge burden on family members who may struggle with excruciatingly difficult decisions in the absence of guidance about their loved one’s wishes.
How I do it
I start by identifying which components of advance care planning each patient needs, using a simple algorithm (see figure). All of my patients are queried about code status, and I give them the opportunity to better understand the value of having a healthcare proxy and advance directives, if they are not already in place.
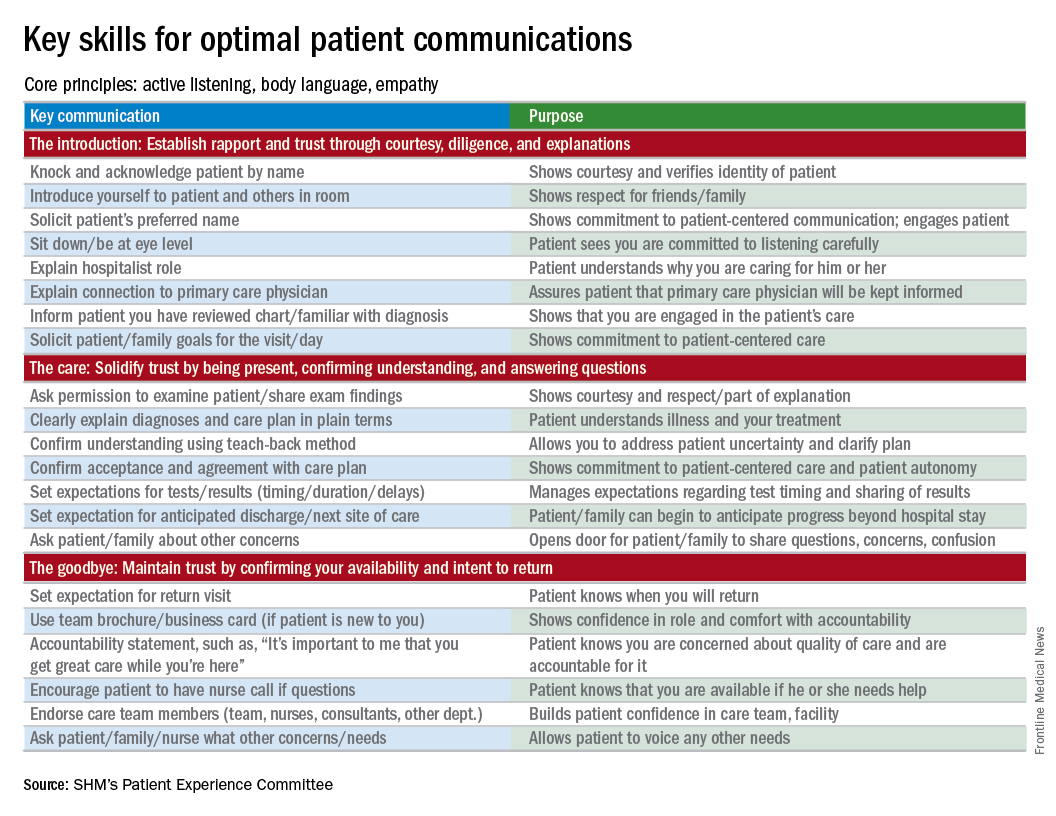
For the remainder of this column, I’m going to focus on patients who have an acute and/or chronic treatable illness – those who require simpler advance-care-planning conversations.
To comfortably initiate the conversation about advance care planning, I always start by asking permission. I commonly say, “There are a couple of important items I discuss with all of my patients to make sure they get the care they want. Would it be okay for us to talk about those now?” This respectfully puts the patient in control. I then initiate a discussion of code status by saying, “It’s important that all of us on your care team know what you would like us to do if you got so sick that we couldn’t communicate with you. I’m not expecting this to happen, but I ask all my patients this question so that we have your instructions.” From there, the conversation evolves depending on whether the patient has any familiarity with this question and its implications.
To introduce the concept of a health care proxy and advance directives, I ask, “Have you ever thought about who you might choose to make medical decisions on your behalf if you became too sick to make those decisions yourself?” Then, finally, I share the following information, usually referring to the blank advance directives document they received in their admission packet: “There is a valuable way to put your wishes about specific care options in writing so others will know your wishes if you’re unable to communicate with them. Would you like to talk about that right now?” Again, this gives the patient control of the situation and an opportunity to decline the conversation if they are not interested or comfortable at that time.
It’s important to document the nature and outcome of these conversations. Keep in mind, advance care planning discussions need not occur at the time of admission. In fact, admission may be the worst time for some patients, further underscoring the importance of documentation so that subsequent providers can see whether advance care planning has been addressed during the hospital stay.
Note: For useful educational resources that address goals-of-care conversations in patients toward the end of life, the Center to Advance Palliative Care (www.capc.org) has a number of educational courses that address these important communication skills.
Dr. Rudolph is vice president of physician development and patient experience for Sound Physicians, Tacoma, Wash. and chair of the SHM Patient Experience Committee .
Reference
1. Moss, A.H., Ganjoo, J, Sharma S, et al. Utility of the “Surprise” Question to Identify Dialysis Patients with High Mortality. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: CJASN. 2008;3(5):1379-84. doi:10.2215/CJN.00940208.
Editor’s note: “Everything We Say and Do” is an informational series developed by the Society of Hospital Medicine’s Patient Experience Committee to provide readers with thoughtful and actionable communication tactics that have great potential to positively impact patients’ experiences of care. Each article will focus on how the contributor applies one or more of the “key communication” tactics in practice to maintain provider accountability for “everything we say and do that affects our patients’ thoughts, feelings, and well-being.”
What I say and do
I empower all of my patients by giving them the opportunity to consider advance care planning.
Why I do it
Everyone deserves advance care planning, and every health care encounter, including a hospitalization, is an opportunity to better identify and document patients’ wishes for care should they become unable to express them. If we wait for patients to develop serious advanced illness before having advance care planning conversations, we risk depriving them of the care they would want in these situations. Additionally, we place a huge burden on family members who may struggle with excruciatingly difficult decisions in the absence of guidance about their loved one’s wishes.
How I do it
I start by identifying which components of advance care planning each patient needs, using a simple algorithm (see figure). All of my patients are queried about code status, and I give them the opportunity to better understand the value of having a healthcare proxy and advance directives, if they are not already in place.

For the remainder of this column, I’m going to focus on patients who have an acute and/or chronic treatable illness – those who require simpler advance-care-planning conversations.
To comfortably initiate the conversation about advance care planning, I always start by asking permission. I commonly say, “There are a couple of important items I discuss with all of my patients to make sure they get the care they want. Would it be okay for us to talk about those now?” This respectfully puts the patient in control. I then initiate a discussion of code status by saying, “It’s important that all of us on your care team know what you would like us to do if you got so sick that we couldn’t communicate with you. I’m not expecting this to happen, but I ask all my patients this question so that we have your instructions.” From there, the conversation evolves depending on whether the patient has any familiarity with this question and its implications.
To introduce the concept of a health care proxy and advance directives, I ask, “Have you ever thought about who you might choose to make medical decisions on your behalf if you became too sick to make those decisions yourself?” Then, finally, I share the following information, usually referring to the blank advance directives document they received in their admission packet: “There is a valuable way to put your wishes about specific care options in writing so others will know your wishes if you’re unable to communicate with them. Would you like to talk about that right now?” Again, this gives the patient control of the situation and an opportunity to decline the conversation if they are not interested or comfortable at that time.
It’s important to document the nature and outcome of these conversations. Keep in mind, advance care planning discussions need not occur at the time of admission. In fact, admission may be the worst time for some patients, further underscoring the importance of documentation so that subsequent providers can see whether advance care planning has been addressed during the hospital stay.
Note: For useful educational resources that address goals-of-care conversations in patients toward the end of life, the Center to Advance Palliative Care (www.capc.org) has a number of educational courses that address these important communication skills.
Dr. Rudolph is vice president of physician development and patient experience for Sound Physicians, Tacoma, Wash. and chair of the SHM Patient Experience Committee .
Reference
1. Moss, A.H., Ganjoo, J, Sharma S, et al. Utility of the “Surprise” Question to Identify Dialysis Patients with High Mortality. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: CJASN. 2008;3(5):1379-84. doi:10.2215/CJN.00940208.
Editor’s note: “Everything We Say and Do” is an informational series developed by the Society of Hospital Medicine’s Patient Experience Committee to provide readers with thoughtful and actionable communication tactics that have great potential to positively impact patients’ experiences of care. Each article will focus on how the contributor applies one or more of the “key communication” tactics in practice to maintain provider accountability for “everything we say and do that affects our patients’ thoughts, feelings, and well-being.”
What I say and do
I empower all of my patients by giving them the opportunity to consider advance care planning.
Why I do it
Everyone deserves advance care planning, and every health care encounter, including a hospitalization, is an opportunity to better identify and document patients’ wishes for care should they become unable to express them. If we wait for patients to develop serious advanced illness before having advance care planning conversations, we risk depriving them of the care they would want in these situations. Additionally, we place a huge burden on family members who may struggle with excruciatingly difficult decisions in the absence of guidance about their loved one’s wishes.
How I do it
I start by identifying which components of advance care planning each patient needs, using a simple algorithm (see figure). All of my patients are queried about code status, and I give them the opportunity to better understand the value of having a healthcare proxy and advance directives, if they are not already in place.

For the remainder of this column, I’m going to focus on patients who have an acute and/or chronic treatable illness – those who require simpler advance-care-planning conversations.
To comfortably initiate the conversation about advance care planning, I always start by asking permission. I commonly say, “There are a couple of important items I discuss with all of my patients to make sure they get the care they want. Would it be okay for us to talk about those now?” This respectfully puts the patient in control. I then initiate a discussion of code status by saying, “It’s important that all of us on your care team know what you would like us to do if you got so sick that we couldn’t communicate with you. I’m not expecting this to happen, but I ask all my patients this question so that we have your instructions.” From there, the conversation evolves depending on whether the patient has any familiarity with this question and its implications.
To introduce the concept of a health care proxy and advance directives, I ask, “Have you ever thought about who you might choose to make medical decisions on your behalf if you became too sick to make those decisions yourself?” Then, finally, I share the following information, usually referring to the blank advance directives document they received in their admission packet: “There is a valuable way to put your wishes about specific care options in writing so others will know your wishes if you’re unable to communicate with them. Would you like to talk about that right now?” Again, this gives the patient control of the situation and an opportunity to decline the conversation if they are not interested or comfortable at that time.
It’s important to document the nature and outcome of these conversations. Keep in mind, advance care planning discussions need not occur at the time of admission. In fact, admission may be the worst time for some patients, further underscoring the importance of documentation so that subsequent providers can see whether advance care planning has been addressed during the hospital stay.
Note: For useful educational resources that address goals-of-care conversations in patients toward the end of life, the Center to Advance Palliative Care (www.capc.org) has a number of educational courses that address these important communication skills.
Dr. Rudolph is vice president of physician development and patient experience for Sound Physicians, Tacoma, Wash. and chair of the SHM Patient Experience Committee .
Reference
1. Moss, A.H., Ganjoo, J, Sharma S, et al. Utility of the “Surprise” Question to Identify Dialysis Patients with High Mortality. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: CJASN. 2008;3(5):1379-84. doi:10.2215/CJN.00940208.

