User login
A) Mirena or Liletta (52 mg LNG-IUD) CORRECT
Mirena (Bayer) and Liletta (Allergan) are progestin-releasing intrauterine devices (IUDs) of similar size and shape. On ultrasonography, both the arms and the distal tip are echogenic. The progestin-containing plastic sleeve surrounding the stem in the middle demonstrates a laminated acoustic shadowing with distinctive parallel lines.1–4
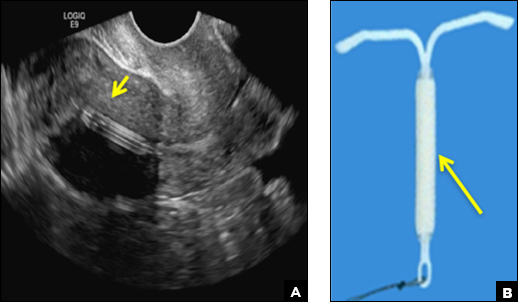
B) Small-framed LNG-IUDs: Skyla (13.5 mg) or Kyleena (19.5 mg) INCORRECT
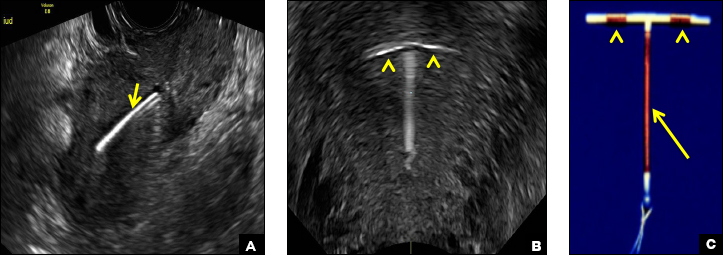
Skyla (Bayer) and Kyleena (Bayer) are small-framed LNG-IUDs. The ultrasound appearance of Skyla (LNG 13.5 mg) is similar to that of Mirena but has a markedly echogenic silver ring superiorly just below the crossbar, best seen with 2D (sagittal) views but also imaged with 3D ultrasound.1,2,5
The Kyleena device (LNG 19.5 mg) uses the same smaller T-shaped frame and metal ring, but the plastic sleeve is longer to accommodate the greater quantity of progestin.6

C) Paragard (intrauterine copper contraceptive) INCORRECT
Paragard (Teva Women’s Health) is a nonhormonal IUD containing copper wire wrapped around its stem and solid copper bands on each crossbar. On ultrasonography, the stem is uniformly and markedly echogenic due to the copper wire.1,2,7
- Stalnaker ML, Kaunitz AM. How to identify and localize IUDs on ultrasound. OBG Manag. 2014;26(8):38,40–41,44.
- Boortz HE, Margolis DJ, Ragavendra N, Patel MK, Kadell BM. Migration of intrauterine devices: Radiologic findings and implications for patient care. Radiographics. 2012;32(2):335–352.
- Mirena [package insert]. Whippany, NJ: Bayer; 2000.
- Liletta [package insert]. Parsippany, NJ: Allergan; 2015.
- Skyla [package insert]. Whippany, NJ: Bayer; 2000.
- Kyleena [package insert]. Whippany, NJ: Bayer; 2000.
- Paragard [package insert]. North Wales, PA: Teva Women’s Health, Inc; 2014.
A) Mirena or Liletta (52 mg LNG-IUD) CORRECT
Mirena (Bayer) and Liletta (Allergan) are progestin-releasing intrauterine devices (IUDs) of similar size and shape. On ultrasonography, both the arms and the distal tip are echogenic. The progestin-containing plastic sleeve surrounding the stem in the middle demonstrates a laminated acoustic shadowing with distinctive parallel lines.1–4

B) Small-framed LNG-IUDs: Skyla (13.5 mg) or Kyleena (19.5 mg) INCORRECT
Skyla (Bayer) and Kyleena (Bayer) are small-framed LNG-IUDs. The ultrasound appearance of Skyla (LNG 13.5 mg) is similar to that of Mirena but has a markedly echogenic silver ring superiorly just below the crossbar, best seen with 2D (sagittal) views but also imaged with 3D ultrasound.1,2,5
The Kyleena device (LNG 19.5 mg) uses the same smaller T-shaped frame and metal ring, but the plastic sleeve is longer to accommodate the greater quantity of progestin.6

C) Paragard (intrauterine copper contraceptive) INCORRECT
Paragard (Teva Women’s Health) is a nonhormonal IUD containing copper wire wrapped around its stem and solid copper bands on each crossbar. On ultrasonography, the stem is uniformly and markedly echogenic due to the copper wire.1,2,7

A) Mirena or Liletta (52 mg LNG-IUD) CORRECT
Mirena (Bayer) and Liletta (Allergan) are progestin-releasing intrauterine devices (IUDs) of similar size and shape. On ultrasonography, both the arms and the distal tip are echogenic. The progestin-containing plastic sleeve surrounding the stem in the middle demonstrates a laminated acoustic shadowing with distinctive parallel lines.1–4

B) Small-framed LNG-IUDs: Skyla (13.5 mg) or Kyleena (19.5 mg) INCORRECT
Skyla (Bayer) and Kyleena (Bayer) are small-framed LNG-IUDs. The ultrasound appearance of Skyla (LNG 13.5 mg) is similar to that of Mirena but has a markedly echogenic silver ring superiorly just below the crossbar, best seen with 2D (sagittal) views but also imaged with 3D ultrasound.1,2,5
The Kyleena device (LNG 19.5 mg) uses the same smaller T-shaped frame and metal ring, but the plastic sleeve is longer to accommodate the greater quantity of progestin.6

C) Paragard (intrauterine copper contraceptive) INCORRECT
Paragard (Teva Women’s Health) is a nonhormonal IUD containing copper wire wrapped around its stem and solid copper bands on each crossbar. On ultrasonography, the stem is uniformly and markedly echogenic due to the copper wire.1,2,7

- Stalnaker ML, Kaunitz AM. How to identify and localize IUDs on ultrasound. OBG Manag. 2014;26(8):38,40–41,44.
- Boortz HE, Margolis DJ, Ragavendra N, Patel MK, Kadell BM. Migration of intrauterine devices: Radiologic findings and implications for patient care. Radiographics. 2012;32(2):335–352.
- Mirena [package insert]. Whippany, NJ: Bayer; 2000.
- Liletta [package insert]. Parsippany, NJ: Allergan; 2015.
- Skyla [package insert]. Whippany, NJ: Bayer; 2000.
- Kyleena [package insert]. Whippany, NJ: Bayer; 2000.
- Paragard [package insert]. North Wales, PA: Teva Women’s Health, Inc; 2014.
- Stalnaker ML, Kaunitz AM. How to identify and localize IUDs on ultrasound. OBG Manag. 2014;26(8):38,40–41,44.
- Boortz HE, Margolis DJ, Ragavendra N, Patel MK, Kadell BM. Migration of intrauterine devices: Radiologic findings and implications for patient care. Radiographics. 2012;32(2):335–352.
- Mirena [package insert]. Whippany, NJ: Bayer; 2000.
- Liletta [package insert]. Parsippany, NJ: Allergan; 2015.
- Skyla [package insert]. Whippany, NJ: Bayer; 2000.
- Kyleena [package insert]. Whippany, NJ: Bayer; 2000.
- Paragard [package insert]. North Wales, PA: Teva Women’s Health, Inc; 2014.
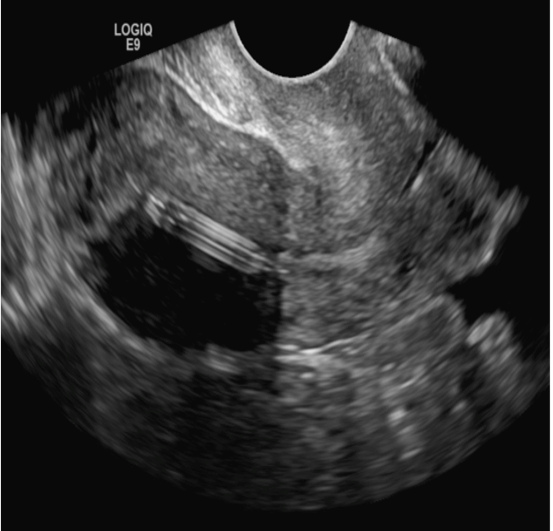
A 25-year-old woman using an IUD presented to her ObGyn’s office for follow-up care of a 4- to 5-cm left simple ovarian cyst. A pelvic ultrasound was performed. The ovarian cyst had resolved and a fundally-positioned IUD was imaged.

