User login
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted priority review to the new drug application (NDA) for copanlisib, an intravenous PI3K inhibitor.
The NDA is for copanlisib as a treatment for patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL) who have received at least 2 prior therapies.
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that may provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
The agency’s goal is to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it, rather than the standard 10 months.
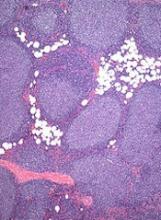
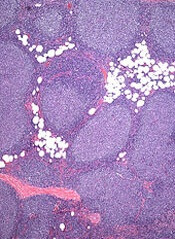
The application for copanlisib is supported by data from the CHRONOS-1 trial. This phase 2 trial enrolled 141 patients with relapsed/refractory, indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Most of these patients had FL (n=104).
In all patients, copanlisib produced an objective response rate of 59.2%, with a complete response rate of 12%. The median duration of response exceeded 98 weeks.
In the FL subset, copanlisib produced an overall response rate of 58.7%, with a complete response rate of 14.4%. The median duration of response exceeded 52 weeks.
In the entire cohort, there were 3 deaths considered related to copanlisib.
The most common treatment-related adverse events were transient hyperglycemia (all grades: 49%/grade 3-4: 40%) and hypertension (all grades: 29%/grade 3: 23%).
“Patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma have a poor prognosis, and new treatment options which are well tolerated and effective are needed to prolong progression-free survival and improve quality of life for these patients,” said Martin Dreyling, MD, a professor at the University of Munich Hospital (Grosshadern) in Germany and lead investigator of the CHRONOS-1 study.
“Based on the CHRONOS-1 results, where copanlisib showed durable efficacy with a manageable and distinct safety profile, the compound may have the potential to address this unmet medical need.”
Data from CHRONOS-1 were presented at the AACR Annual Meeting 2017.
Data from the FL subset of the trial are scheduled to be presented at the 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting in June.
Copanlisib is being developed by Bayer. The compound has fast track and orphan drug designations from the FDA.
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.
The FDA’s fast track program is designed to facilitate the development and expedite the review of products intended to treat or prevent serious or life-threatening conditions and address unmet medical need.
Through the fast track program, a product may be eligible for priority review. In addition, the company developing the product may be allowed to submit sections of the NDA or biologic license application on a rolling basis as data become available.
Fast track designation also provides the company with opportunities for more frequent meetings and written communications with the FDA. ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted priority review to the new drug application (NDA) for copanlisib, an intravenous PI3K inhibitor.
The NDA is for copanlisib as a treatment for patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL) who have received at least 2 prior therapies.
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that may provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
The agency’s goal is to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it, rather than the standard 10 months.
The application for copanlisib is supported by data from the CHRONOS-1 trial. This phase 2 trial enrolled 141 patients with relapsed/refractory, indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Most of these patients had FL (n=104).
In all patients, copanlisib produced an objective response rate of 59.2%, with a complete response rate of 12%. The median duration of response exceeded 98 weeks.
In the FL subset, copanlisib produced an overall response rate of 58.7%, with a complete response rate of 14.4%. The median duration of response exceeded 52 weeks.
In the entire cohort, there were 3 deaths considered related to copanlisib.
The most common treatment-related adverse events were transient hyperglycemia (all grades: 49%/grade 3-4: 40%) and hypertension (all grades: 29%/grade 3: 23%).
“Patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma have a poor prognosis, and new treatment options which are well tolerated and effective are needed to prolong progression-free survival and improve quality of life for these patients,” said Martin Dreyling, MD, a professor at the University of Munich Hospital (Grosshadern) in Germany and lead investigator of the CHRONOS-1 study.
“Based on the CHRONOS-1 results, where copanlisib showed durable efficacy with a manageable and distinct safety profile, the compound may have the potential to address this unmet medical need.”
Data from CHRONOS-1 were presented at the AACR Annual Meeting 2017.
Data from the FL subset of the trial are scheduled to be presented at the 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting in June.
Copanlisib is being developed by Bayer. The compound has fast track and orphan drug designations from the FDA.
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.
The FDA’s fast track program is designed to facilitate the development and expedite the review of products intended to treat or prevent serious or life-threatening conditions and address unmet medical need.
Through the fast track program, a product may be eligible for priority review. In addition, the company developing the product may be allowed to submit sections of the NDA or biologic license application on a rolling basis as data become available.
Fast track designation also provides the company with opportunities for more frequent meetings and written communications with the FDA. ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted priority review to the new drug application (NDA) for copanlisib, an intravenous PI3K inhibitor.
The NDA is for copanlisib as a treatment for patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL) who have received at least 2 prior therapies.
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that may provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
The agency’s goal is to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it, rather than the standard 10 months.
The application for copanlisib is supported by data from the CHRONOS-1 trial. This phase 2 trial enrolled 141 patients with relapsed/refractory, indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Most of these patients had FL (n=104).
In all patients, copanlisib produced an objective response rate of 59.2%, with a complete response rate of 12%. The median duration of response exceeded 98 weeks.
In the FL subset, copanlisib produced an overall response rate of 58.7%, with a complete response rate of 14.4%. The median duration of response exceeded 52 weeks.
In the entire cohort, there were 3 deaths considered related to copanlisib.
The most common treatment-related adverse events were transient hyperglycemia (all grades: 49%/grade 3-4: 40%) and hypertension (all grades: 29%/grade 3: 23%).
“Patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma have a poor prognosis, and new treatment options which are well tolerated and effective are needed to prolong progression-free survival and improve quality of life for these patients,” said Martin Dreyling, MD, a professor at the University of Munich Hospital (Grosshadern) in Germany and lead investigator of the CHRONOS-1 study.
“Based on the CHRONOS-1 results, where copanlisib showed durable efficacy with a manageable and distinct safety profile, the compound may have the potential to address this unmet medical need.”
Data from CHRONOS-1 were presented at the AACR Annual Meeting 2017.
Data from the FL subset of the trial are scheduled to be presented at the 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting in June.
Copanlisib is being developed by Bayer. The compound has fast track and orphan drug designations from the FDA.
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.
The FDA’s fast track program is designed to facilitate the development and expedite the review of products intended to treat or prevent serious or life-threatening conditions and address unmet medical need.
Through the fast track program, a product may be eligible for priority review. In addition, the company developing the product may be allowed to submit sections of the NDA or biologic license application on a rolling basis as data become available.
Fast track designation also provides the company with opportunities for more frequent meetings and written communications with the FDA. ![]()