User login
The prevalence of hepatitis C virus (HCV) varies considerably by state, and the same can be said for the state laws and policies attempting to decrease that prevalence, according to an assessment by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In 2015, incidence of acute HCV infection exceeded the national average of 0.8 per 100,000 population in 17 states, including seven with rates that at least doubled it, the report noted. New HCV infections have increased in recent years despite curative therapies “and known preventive measures to interrupt transmission.”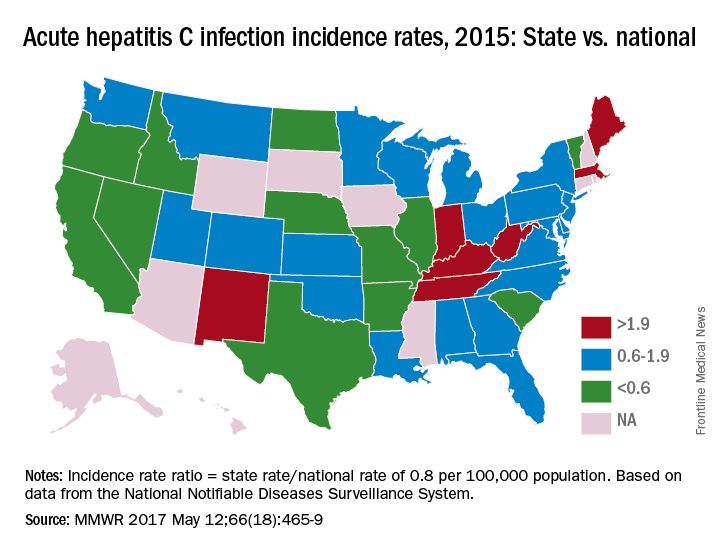
The “most comprehensive” laws on prevention through clean needle access as of 2016 were found in Maine, Nevada, and Utah, with laws in 12 other states categorized as “more comprehensive” and 18 states falling into the “least comprehensive” category. On the Medicaid side of the equation, 16 states had permissive policies that did not require sobriety or required only screening and counseling before treatment, 24 states had restrictive policies that requited sobriety, and 10 states had no policy available, the report showed (MMWR. 2017 May 12:66[18]:465-9).
Only three states – Massachusetts, New Mexico, and Washington – had a comprehensive (all three were considered “more comprehensive”) set of prevention laws and a permissive treatment policy, the investigators said, while also noting that two of the three – Massachusetts and New Mexico – were among the states with acute HCV rates that were at least twice the national average.
“Although the costs of HCV therapies have raised budgetary issues for state Medicaid programs in the past, the costs of HCV treatment have declined in recent years, increasing the cost-effectiveness of treatment, particularly among persons who inject drugs and who might serve as an ongoing source of transmission to others,” the report concluded.
The analysis examined three types of laws on access to clean needles and syringes: authorization of exchange programs, the scope of drug paraphernalia laws, and retail sale of needles and syringes. Each law was assessed for five elements, including authorization of syringe exchange statewide or in selected jurisdictions and exemption of needles or syringes from the definition of drug paraphernalia.
For the accompanying map (see “Acute hepatitis C infection incidence rates, 2015: State vs. national”), each state’s acute HCV incidence rate for 2015 was divided by the national rate to determine the incidence rate ratio, with data unavailable for 10 states.
The prevalence of hepatitis C virus (HCV) varies considerably by state, and the same can be said for the state laws and policies attempting to decrease that prevalence, according to an assessment by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In 2015, incidence of acute HCV infection exceeded the national average of 0.8 per 100,000 population in 17 states, including seven with rates that at least doubled it, the report noted. New HCV infections have increased in recent years despite curative therapies “and known preventive measures to interrupt transmission.”
The “most comprehensive” laws on prevention through clean needle access as of 2016 were found in Maine, Nevada, and Utah, with laws in 12 other states categorized as “more comprehensive” and 18 states falling into the “least comprehensive” category. On the Medicaid side of the equation, 16 states had permissive policies that did not require sobriety or required only screening and counseling before treatment, 24 states had restrictive policies that requited sobriety, and 10 states had no policy available, the report showed (MMWR. 2017 May 12:66[18]:465-9).
Only three states – Massachusetts, New Mexico, and Washington – had a comprehensive (all three were considered “more comprehensive”) set of prevention laws and a permissive treatment policy, the investigators said, while also noting that two of the three – Massachusetts and New Mexico – were among the states with acute HCV rates that were at least twice the national average.
“Although the costs of HCV therapies have raised budgetary issues for state Medicaid programs in the past, the costs of HCV treatment have declined in recent years, increasing the cost-effectiveness of treatment, particularly among persons who inject drugs and who might serve as an ongoing source of transmission to others,” the report concluded.
The analysis examined three types of laws on access to clean needles and syringes: authorization of exchange programs, the scope of drug paraphernalia laws, and retail sale of needles and syringes. Each law was assessed for five elements, including authorization of syringe exchange statewide or in selected jurisdictions and exemption of needles or syringes from the definition of drug paraphernalia.
For the accompanying map (see “Acute hepatitis C infection incidence rates, 2015: State vs. national”), each state’s acute HCV incidence rate for 2015 was divided by the national rate to determine the incidence rate ratio, with data unavailable for 10 states.
The prevalence of hepatitis C virus (HCV) varies considerably by state, and the same can be said for the state laws and policies attempting to decrease that prevalence, according to an assessment by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In 2015, incidence of acute HCV infection exceeded the national average of 0.8 per 100,000 population in 17 states, including seven with rates that at least doubled it, the report noted. New HCV infections have increased in recent years despite curative therapies “and known preventive measures to interrupt transmission.”
The “most comprehensive” laws on prevention through clean needle access as of 2016 were found in Maine, Nevada, and Utah, with laws in 12 other states categorized as “more comprehensive” and 18 states falling into the “least comprehensive” category. On the Medicaid side of the equation, 16 states had permissive policies that did not require sobriety or required only screening and counseling before treatment, 24 states had restrictive policies that requited sobriety, and 10 states had no policy available, the report showed (MMWR. 2017 May 12:66[18]:465-9).
Only three states – Massachusetts, New Mexico, and Washington – had a comprehensive (all three were considered “more comprehensive”) set of prevention laws and a permissive treatment policy, the investigators said, while also noting that two of the three – Massachusetts and New Mexico – were among the states with acute HCV rates that were at least twice the national average.
“Although the costs of HCV therapies have raised budgetary issues for state Medicaid programs in the past, the costs of HCV treatment have declined in recent years, increasing the cost-effectiveness of treatment, particularly among persons who inject drugs and who might serve as an ongoing source of transmission to others,” the report concluded.
The analysis examined three types of laws on access to clean needles and syringes: authorization of exchange programs, the scope of drug paraphernalia laws, and retail sale of needles and syringes. Each law was assessed for five elements, including authorization of syringe exchange statewide or in selected jurisdictions and exemption of needles or syringes from the definition of drug paraphernalia.
For the accompanying map (see “Acute hepatitis C infection incidence rates, 2015: State vs. national”), each state’s acute HCV incidence rate for 2015 was divided by the national rate to determine the incidence rate ratio, with data unavailable for 10 states.
FROM MMWR