User login
DENVER –
At the annual meeting of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, Christopher Zachary, MD, and colleagues described a novel, noninvasive standardized controlled hyperthermia and mapping protocol (CHAMP) designed to help clinicians with margin assessment and treatment of superficial and nodular basal cell cancers (BCCs). “There’s considerable interest on the part of the public in having CHAMP treatment for their BCCs,” Dr. Zachary, professor and chair emeritus, University of California, Irvine, told this news organization in advance of the meeting.
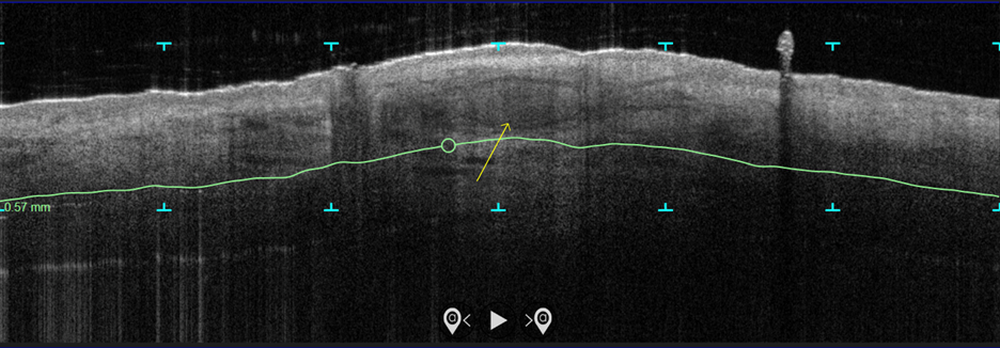
In the study, which is being conducted at three centers and plans to enroll 100 patients, more than 70 patients with biopsy-proven superficial and nodular BCCs have been scanned with the VivoSight Dx optical coherence tomography (OCT) device to map BCC tumor margins. Next, they were treated with the Sciton 1,064-nm Er:YAG laser equipped with a 4-mm beam diameter scan pattern with no overlap and an 8-millisecond pulse duration, randomized to either 120 J/cm2 pulses, until tissue graying and contraction was observed, or a novel controlled hyperthermia technique known as “Low and Slow” using repeated 25 J/cm2 pulses under thermal camera imaging to maintain a consistent temperature of 55º C for 60 seconds.
The researchers reassessed the tissue response both clinically and by OCT at 3 months and the patients were retreated with the same method if residual BCC was demonstrated. At 3-12 months post treatment, the lesion sites were saucerized and examined histologically by step sections to confirm clearance.
“In contrast to the more commonly performed ‘standard’ long-pulse 1,064-nm laser tumor coagulation, where the end point is graying and contraction of tissue, the new controlled ‘Low and Slow’ technique heats the tissue to 55º C for 60 seconds, avoids ulceration, and induces apoptotic tumor disappearance by a caspase-3 and -7 mechanism,” Dr. Zachary explained in an interview. “It’s a gentler process that allows patients an alternative to second intention wounds that occur after electrodessication and curettage or Mohs,” he added, noting that CHAMP is not intended for the treatment of more complex, large, recurrent, or infiltrative BCCs.
In both study arms, the majority of patients enrolled to date have been found to be free of tumor at 3 months by clinical and OCT examination. “The study is ongoing, but the current numbers indicate that 9 out of 10 superficial and nodular BCCs are free of tumor at 3-12 months after the last treatment,” Dr. Zachary said. The standard-treatment arm, where tissue was treated to a gray color with tissue contraction, generally resulted in more blistering and tissue necrosis with prolonged healing, compared with the Low and Slow–controlled hyperthermia arm. BCC lesions treated in the controlled hyperthermia arm had a lilac gray color with “a surprising increase” in the Doppler blood flow rate, compared with those in the standard-treatment arm, he noted.
“Blood flow following the standard technique is dramatically reduced immediately post treatment, which accounts in part for the frequent ulceration and slow healing in that group,” Dr. Zachary said.
He acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its relatively small sample size and the fact that the optimal treatment parameters of the Low and Slow technique have yet to be realized. “It could be that we will achieve better results at 50º C for 70 seconds or similar,” he said. “While this technique will not in any way reduce the great benefits of Mohs surgery for complex BCCs, it will benefit those with simpler superficial and nodular BCCs, particularly in those who are not good surgical candidates.”
As an aside, Dr. Zachary supports the increased use of OCT scanners to improve the ability to diagnose and assess the lateral and deep margins of skin cancers. “I think that all dermatology residents should understand how to use these devices,” he said. “I’m convinced they are going to be useful in their clinical practice in the future.”
Keith L. Duffy, MD, who was asked to comment on the work, said that the study demonstrates novel ways to use existing and developing technologies in dermatology and highlights the intersection of aesthetic, surgical, and medical dermatology. “CHAMP is promising as shown by the data in the abstract and I am eager to see the final results of the study with an eye toward final cure rate and cosmesis,” said Dr. Duffy, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
“In my estimation, this technology will need to prove to be superior in one or both of these parameters in order to be considered a first- or second-line therapy,” he added. “My practice for these types of basal cell carcinomas is a simple one pass of curettage with aluminum chloride or pressure for hemostasis. The healing is fast, the cosmesis is excellent, and the cure rate is more than 90% for this simple in-office destruction. However, for those with access to this technology and proficiency with its use, CHAMP may become a viable alternative to our existing destructive methods. I look forward to seeing the published results of this multicenter trial.”
This study is being funded by Michelson Diagnostics. Sciton provided the long-pulsed 1,064-nm lasers devices being used in the trial. Neither Dr. Zachary nor Dr. Duffy reported having relevant disclosures.
DENVER –
At the annual meeting of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, Christopher Zachary, MD, and colleagues described a novel, noninvasive standardized controlled hyperthermia and mapping protocol (CHAMP) designed to help clinicians with margin assessment and treatment of superficial and nodular basal cell cancers (BCCs). “There’s considerable interest on the part of the public in having CHAMP treatment for their BCCs,” Dr. Zachary, professor and chair emeritus, University of California, Irvine, told this news organization in advance of the meeting.

In the study, which is being conducted at three centers and plans to enroll 100 patients, more than 70 patients with biopsy-proven superficial and nodular BCCs have been scanned with the VivoSight Dx optical coherence tomography (OCT) device to map BCC tumor margins. Next, they were treated with the Sciton 1,064-nm Er:YAG laser equipped with a 4-mm beam diameter scan pattern with no overlap and an 8-millisecond pulse duration, randomized to either 120 J/cm2 pulses, until tissue graying and contraction was observed, or a novel controlled hyperthermia technique known as “Low and Slow” using repeated 25 J/cm2 pulses under thermal camera imaging to maintain a consistent temperature of 55º C for 60 seconds.
The researchers reassessed the tissue response both clinically and by OCT at 3 months and the patients were retreated with the same method if residual BCC was demonstrated. At 3-12 months post treatment, the lesion sites were saucerized and examined histologically by step sections to confirm clearance.
“In contrast to the more commonly performed ‘standard’ long-pulse 1,064-nm laser tumor coagulation, where the end point is graying and contraction of tissue, the new controlled ‘Low and Slow’ technique heats the tissue to 55º C for 60 seconds, avoids ulceration, and induces apoptotic tumor disappearance by a caspase-3 and -7 mechanism,” Dr. Zachary explained in an interview. “It’s a gentler process that allows patients an alternative to second intention wounds that occur after electrodessication and curettage or Mohs,” he added, noting that CHAMP is not intended for the treatment of more complex, large, recurrent, or infiltrative BCCs.
In both study arms, the majority of patients enrolled to date have been found to be free of tumor at 3 months by clinical and OCT examination. “The study is ongoing, but the current numbers indicate that 9 out of 10 superficial and nodular BCCs are free of tumor at 3-12 months after the last treatment,” Dr. Zachary said. The standard-treatment arm, where tissue was treated to a gray color with tissue contraction, generally resulted in more blistering and tissue necrosis with prolonged healing, compared with the Low and Slow–controlled hyperthermia arm. BCC lesions treated in the controlled hyperthermia arm had a lilac gray color with “a surprising increase” in the Doppler blood flow rate, compared with those in the standard-treatment arm, he noted.
“Blood flow following the standard technique is dramatically reduced immediately post treatment, which accounts in part for the frequent ulceration and slow healing in that group,” Dr. Zachary said.
He acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its relatively small sample size and the fact that the optimal treatment parameters of the Low and Slow technique have yet to be realized. “It could be that we will achieve better results at 50º C for 70 seconds or similar,” he said. “While this technique will not in any way reduce the great benefits of Mohs surgery for complex BCCs, it will benefit those with simpler superficial and nodular BCCs, particularly in those who are not good surgical candidates.”
As an aside, Dr. Zachary supports the increased use of OCT scanners to improve the ability to diagnose and assess the lateral and deep margins of skin cancers. “I think that all dermatology residents should understand how to use these devices,” he said. “I’m convinced they are going to be useful in their clinical practice in the future.”
Keith L. Duffy, MD, who was asked to comment on the work, said that the study demonstrates novel ways to use existing and developing technologies in dermatology and highlights the intersection of aesthetic, surgical, and medical dermatology. “CHAMP is promising as shown by the data in the abstract and I am eager to see the final results of the study with an eye toward final cure rate and cosmesis,” said Dr. Duffy, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
“In my estimation, this technology will need to prove to be superior in one or both of these parameters in order to be considered a first- or second-line therapy,” he added. “My practice for these types of basal cell carcinomas is a simple one pass of curettage with aluminum chloride or pressure for hemostasis. The healing is fast, the cosmesis is excellent, and the cure rate is more than 90% for this simple in-office destruction. However, for those with access to this technology and proficiency with its use, CHAMP may become a viable alternative to our existing destructive methods. I look forward to seeing the published results of this multicenter trial.”
This study is being funded by Michelson Diagnostics. Sciton provided the long-pulsed 1,064-nm lasers devices being used in the trial. Neither Dr. Zachary nor Dr. Duffy reported having relevant disclosures.
DENVER –
At the annual meeting of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, Christopher Zachary, MD, and colleagues described a novel, noninvasive standardized controlled hyperthermia and mapping protocol (CHAMP) designed to help clinicians with margin assessment and treatment of superficial and nodular basal cell cancers (BCCs). “There’s considerable interest on the part of the public in having CHAMP treatment for their BCCs,” Dr. Zachary, professor and chair emeritus, University of California, Irvine, told this news organization in advance of the meeting.

In the study, which is being conducted at three centers and plans to enroll 100 patients, more than 70 patients with biopsy-proven superficial and nodular BCCs have been scanned with the VivoSight Dx optical coherence tomography (OCT) device to map BCC tumor margins. Next, they were treated with the Sciton 1,064-nm Er:YAG laser equipped with a 4-mm beam diameter scan pattern with no overlap and an 8-millisecond pulse duration, randomized to either 120 J/cm2 pulses, until tissue graying and contraction was observed, or a novel controlled hyperthermia technique known as “Low and Slow” using repeated 25 J/cm2 pulses under thermal camera imaging to maintain a consistent temperature of 55º C for 60 seconds.
The researchers reassessed the tissue response both clinically and by OCT at 3 months and the patients were retreated with the same method if residual BCC was demonstrated. At 3-12 months post treatment, the lesion sites were saucerized and examined histologically by step sections to confirm clearance.
“In contrast to the more commonly performed ‘standard’ long-pulse 1,064-nm laser tumor coagulation, where the end point is graying and contraction of tissue, the new controlled ‘Low and Slow’ technique heats the tissue to 55º C for 60 seconds, avoids ulceration, and induces apoptotic tumor disappearance by a caspase-3 and -7 mechanism,” Dr. Zachary explained in an interview. “It’s a gentler process that allows patients an alternative to second intention wounds that occur after electrodessication and curettage or Mohs,” he added, noting that CHAMP is not intended for the treatment of more complex, large, recurrent, or infiltrative BCCs.
In both study arms, the majority of patients enrolled to date have been found to be free of tumor at 3 months by clinical and OCT examination. “The study is ongoing, but the current numbers indicate that 9 out of 10 superficial and nodular BCCs are free of tumor at 3-12 months after the last treatment,” Dr. Zachary said. The standard-treatment arm, where tissue was treated to a gray color with tissue contraction, generally resulted in more blistering and tissue necrosis with prolonged healing, compared with the Low and Slow–controlled hyperthermia arm. BCC lesions treated in the controlled hyperthermia arm had a lilac gray color with “a surprising increase” in the Doppler blood flow rate, compared with those in the standard-treatment arm, he noted.
“Blood flow following the standard technique is dramatically reduced immediately post treatment, which accounts in part for the frequent ulceration and slow healing in that group,” Dr. Zachary said.
He acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its relatively small sample size and the fact that the optimal treatment parameters of the Low and Slow technique have yet to be realized. “It could be that we will achieve better results at 50º C for 70 seconds or similar,” he said. “While this technique will not in any way reduce the great benefits of Mohs surgery for complex BCCs, it will benefit those with simpler superficial and nodular BCCs, particularly in those who are not good surgical candidates.”
As an aside, Dr. Zachary supports the increased use of OCT scanners to improve the ability to diagnose and assess the lateral and deep margins of skin cancers. “I think that all dermatology residents should understand how to use these devices,” he said. “I’m convinced they are going to be useful in their clinical practice in the future.”
Keith L. Duffy, MD, who was asked to comment on the work, said that the study demonstrates novel ways to use existing and developing technologies in dermatology and highlights the intersection of aesthetic, surgical, and medical dermatology. “CHAMP is promising as shown by the data in the abstract and I am eager to see the final results of the study with an eye toward final cure rate and cosmesis,” said Dr. Duffy, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
“In my estimation, this technology will need to prove to be superior in one or both of these parameters in order to be considered a first- or second-line therapy,” he added. “My practice for these types of basal cell carcinomas is a simple one pass of curettage with aluminum chloride or pressure for hemostasis. The healing is fast, the cosmesis is excellent, and the cure rate is more than 90% for this simple in-office destruction. However, for those with access to this technology and proficiency with its use, CHAMP may become a viable alternative to our existing destructive methods. I look forward to seeing the published results of this multicenter trial.”
This study is being funded by Michelson Diagnostics. Sciton provided the long-pulsed 1,064-nm lasers devices being used in the trial. Neither Dr. Zachary nor Dr. Duffy reported having relevant disclosures.
AT ASDS 2022