User login
according to a new analysis.
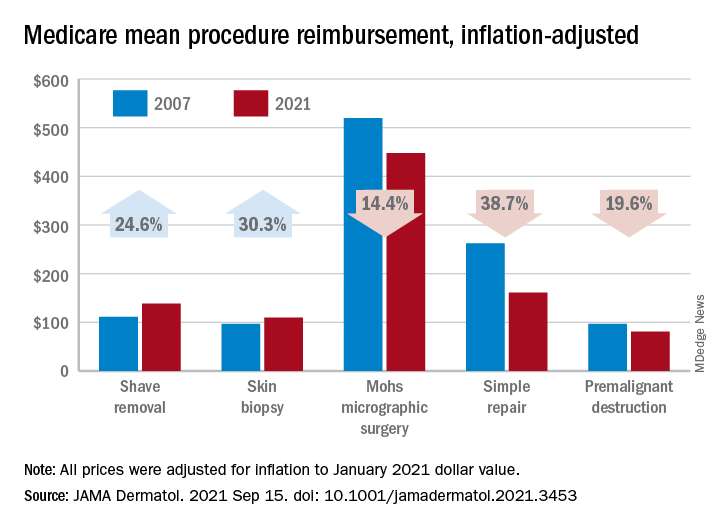
Large increases in mean reimbursement for skin biopsies (+30.3%) and shave removal (+24.6%) were not enough to offset lower rates for procedures such as simple repair (–38.7%), premalignant destruction (–19.6%), Mohs micrographic surgery (–14.4%), and flap repair (–14.1%), Rishabh S. Mazmudar, BS, of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and associates said.
“Given Medicare’s contribution to a large proportion of health care expenditures, changes in Medicare reimbursement rates may result in parallel changes in private insurance reimbursement,” they wrote in JAMA Dermatology.
A recently published study showed that Medicare reimbursement for 20 dermatologic service codes had fallen by 10% between the two comparison years, 2000 and 2020. The current study expanded the number of procedures to 46 (divided into nine categories) and used historical Medicare fee schedules to examine annual trends over a 15-year period, Mr. Mazmudar and associates explained.
Other specialties have seen reimbursement fall by more than 4.8%, including emergency medicine (–21.2% from 2000 to 2020) and general surgery (–24.4% from 2000 to 2018), but “these comparisons are likely skewed by the disproportionate increase in reimbursement rates for biopsies and shave removals during this time period,” the investigators said.
If those two procedure categories were excluded from the analysis, the mean change in overall reimbursement for the remaining dermatologic procedures would be −9.6%, they noted.
Detailed payment information provided for 15 of the 46 procedures shows that only intermediate repair (+4.5%) and benign destruction (+2.3%) joined biopsies and shave excisions with increased reimbursement from 2007 to 2021. The smallest drop among the other procedures was –1.9% for malignant destruction, the research team reported.
The inflation-adjusted, year-by-year analysis showed that reimbursement for the nine procedure categories has gradually declined since peaking in 2011, with the most notable exceptions being biopsies and shave excisions. Both had been following the trend until 2013, when reimbursement for shave removals jumped by almost 30 percentage points, and 2019, when rates for biopsies soared by more than 30 percentage points, according to the investigators.
The increase for skin biopsies followed the split of the original CPT code into three categories, but “the jump in reimbursement for shave removals in 2013 requires further investigation,” Mr. Mazmudar and associates wrote.
The investigators did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
according to a new analysis.

Large increases in mean reimbursement for skin biopsies (+30.3%) and shave removal (+24.6%) were not enough to offset lower rates for procedures such as simple repair (–38.7%), premalignant destruction (–19.6%), Mohs micrographic surgery (–14.4%), and flap repair (–14.1%), Rishabh S. Mazmudar, BS, of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and associates said.
“Given Medicare’s contribution to a large proportion of health care expenditures, changes in Medicare reimbursement rates may result in parallel changes in private insurance reimbursement,” they wrote in JAMA Dermatology.
A recently published study showed that Medicare reimbursement for 20 dermatologic service codes had fallen by 10% between the two comparison years, 2000 and 2020. The current study expanded the number of procedures to 46 (divided into nine categories) and used historical Medicare fee schedules to examine annual trends over a 15-year period, Mr. Mazmudar and associates explained.
Other specialties have seen reimbursement fall by more than 4.8%, including emergency medicine (–21.2% from 2000 to 2020) and general surgery (–24.4% from 2000 to 2018), but “these comparisons are likely skewed by the disproportionate increase in reimbursement rates for biopsies and shave removals during this time period,” the investigators said.
If those two procedure categories were excluded from the analysis, the mean change in overall reimbursement for the remaining dermatologic procedures would be −9.6%, they noted.
Detailed payment information provided for 15 of the 46 procedures shows that only intermediate repair (+4.5%) and benign destruction (+2.3%) joined biopsies and shave excisions with increased reimbursement from 2007 to 2021. The smallest drop among the other procedures was –1.9% for malignant destruction, the research team reported.
The inflation-adjusted, year-by-year analysis showed that reimbursement for the nine procedure categories has gradually declined since peaking in 2011, with the most notable exceptions being biopsies and shave excisions. Both had been following the trend until 2013, when reimbursement for shave removals jumped by almost 30 percentage points, and 2019, when rates for biopsies soared by more than 30 percentage points, according to the investigators.
The increase for skin biopsies followed the split of the original CPT code into three categories, but “the jump in reimbursement for shave removals in 2013 requires further investigation,” Mr. Mazmudar and associates wrote.
The investigators did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
according to a new analysis.

Large increases in mean reimbursement for skin biopsies (+30.3%) and shave removal (+24.6%) were not enough to offset lower rates for procedures such as simple repair (–38.7%), premalignant destruction (–19.6%), Mohs micrographic surgery (–14.4%), and flap repair (–14.1%), Rishabh S. Mazmudar, BS, of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and associates said.
“Given Medicare’s contribution to a large proportion of health care expenditures, changes in Medicare reimbursement rates may result in parallel changes in private insurance reimbursement,” they wrote in JAMA Dermatology.
A recently published study showed that Medicare reimbursement for 20 dermatologic service codes had fallen by 10% between the two comparison years, 2000 and 2020. The current study expanded the number of procedures to 46 (divided into nine categories) and used historical Medicare fee schedules to examine annual trends over a 15-year period, Mr. Mazmudar and associates explained.
Other specialties have seen reimbursement fall by more than 4.8%, including emergency medicine (–21.2% from 2000 to 2020) and general surgery (–24.4% from 2000 to 2018), but “these comparisons are likely skewed by the disproportionate increase in reimbursement rates for biopsies and shave removals during this time period,” the investigators said.
If those two procedure categories were excluded from the analysis, the mean change in overall reimbursement for the remaining dermatologic procedures would be −9.6%, they noted.
Detailed payment information provided for 15 of the 46 procedures shows that only intermediate repair (+4.5%) and benign destruction (+2.3%) joined biopsies and shave excisions with increased reimbursement from 2007 to 2021. The smallest drop among the other procedures was –1.9% for malignant destruction, the research team reported.
The inflation-adjusted, year-by-year analysis showed that reimbursement for the nine procedure categories has gradually declined since peaking in 2011, with the most notable exceptions being biopsies and shave excisions. Both had been following the trend until 2013, when reimbursement for shave removals jumped by almost 30 percentage points, and 2019, when rates for biopsies soared by more than 30 percentage points, according to the investigators.
The increase for skin biopsies followed the split of the original CPT code into three categories, but “the jump in reimbursement for shave removals in 2013 requires further investigation,” Mr. Mazmudar and associates wrote.
The investigators did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY