User login
Mr. J, age 30, a Black man with major depressive disorder (MDD), has been your patient for the past year. At the time of his diagnosis, Mr. J received sertraline, 100 mg/d, but had little to no improvement. During the past year, he received trials of citalopram and paroxetine, but they were not effective for his recurrent depressive symptoms and/or resulted in significant adverse effects.
During a recent visit, Mr. J asks you about “the genetic tests that help determine which medications will work.” He mentions that his brother had this testing done and that it had “worked for him,” but offers no other details. You research the different testing panels to see which test you might use. After a brief online review, you identify at least 4 different products, and are not sure which test—if any—you should consider.
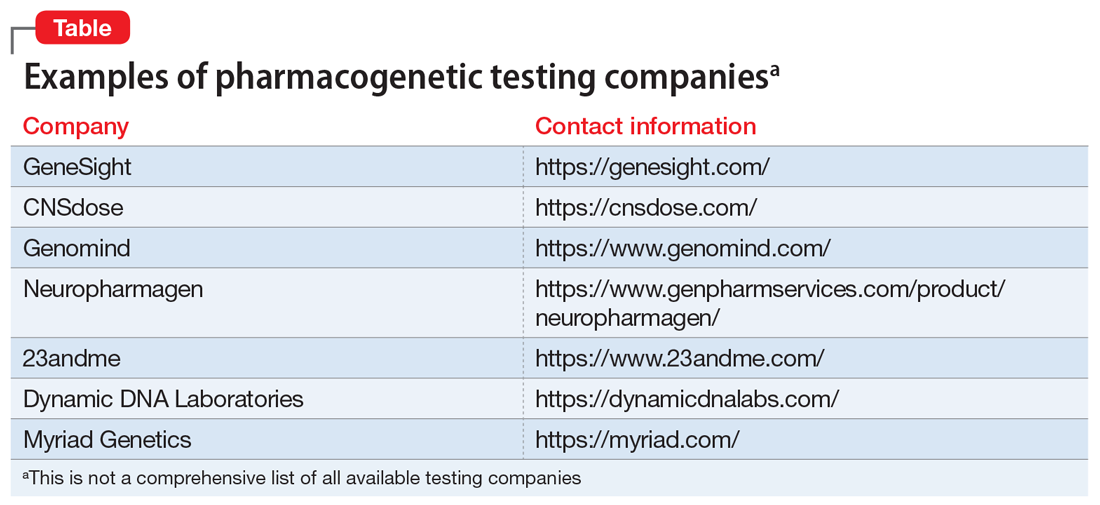
During the last few years, there has been a rise in commercial pharmacogenetic testing options, including tests available to clinicians at academic medical centers as well as direct-to-consumer testing (Table). Clinician and patient interest regarding pharmacogenetic testing in practice is often followed by the question, “Which test is best?” Although this is a logical question, providing an answer is multifactorial.1-3 Because none of the currently available tests have been compared in head-to-head clinical trials, it is nearly impossible to identify the “best” test.
In this article, we focus on the evidence-based principles that clinicians should consider when adopting pharmacogenetic testing in their practice. We discuss which genes are of most interest when prescribing psychotropic medications, the value of decision support tools, cost considerations, and patient education regarding this type of testing.
Which genes and variants should be tested?
The genes relevant to medication treatment outcomes can be broadly classified into those with pharmacokinetic vs pharmacodynamic effects. Pharmacogenes, such as those coding for the drug-metabolizing enzymes cytochrome P450 (CYP) 1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT)2B1, may alter the rate at which medications are metabolized, thus varying the serum drug concentration across patients. Variants that impact the function of these enzymes are considered pharmacokinetic. Up to 40% of the variance in patients’ response to antidepressants may be due to variations in the pharmacokinetic genes.4 Alternatively, pharmacodynamic pharmacogenes impact drug action and therefore may affect the degree of receptor activation at a given drug concentration, overall drug efficacy, and/or the occurrence of medication sensitivity. These pharmacogenes may include:
- brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)
- catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT)
- human leukocyte antigens A (HLA-A)
- serotonin receptor subtype 2 (HTR2)
- serotonin receptor subtype 2C (HTR2C)
- opioid receptor mu 1 (OPRM1)
- solute carrier family 6 member 4 (SLC6A4).
In articles previously published in
Currently, there is no standardization among commercial pharmacogenetic tests on:
- which genes to test
- which variants specific to a gene need to be included
- how the genetic data is translated to phenotype
- how the phenotype is translated to a treatment recommendation.
Continue to: Due to these factors...
Due to these factors, the FDA has advised clinicians to consult the dosing recommendations provided in a medication’s package insert for information regarding how genetic information should be used in making treatment decisions.2
The value of decision support tools
Researchers have assessed how various manufacturers’ decision support tools (DSTs) (ie, the reports the commercial testing companies send to the clinician who orders the test) agree on genotypes, predicted phenotypes, and medication recommendations.4 Overall, this research found varying levels of disagreement in the medication recommendations of the testing panels they studied, which indicates that not all tests are equivalent or interchangeable.4 Of the actionable recommendations for antidepressants, 16% were conflicting; the recommendations for fluoxetine and imipramine were most frequently in disagreement.4 Similarly, 20% of the actionable antipsychotic advice was conflicting, with the recommendations for aripiprazole and clozapine most frequently in disagreement.4 Researchers also reported a situation in which 4 testing panels agreed on the patient’s phenotyping status for CYP2C19, but the dosing recommendations provided for the CYP2C19 substrate, amitriptyline, differed.4 Thus, it is understandable why DSTs can result in confusion, and why clinicians should use testing panels with recommendations that best align with their individual practices, their patient’s needs, and FDA information.
Additionally, while the genes included on these panels vary, these testing panels also may not evaluate the same variants within a specific gene. These differences may impact the patient’s reported phenotypes and medication recommendations across DSTs. For example, the FDA has recommended HLA gene testing prior to prescribing carbamazepine. However, few of the available tests may include the HLA-B*15:02 variant, which has been associated with carbamazepine-induced severe cutaneous reactions in patients of Asian descent, and fewer may include the HLA-A*31:01 variant, for which testing is recommended prior to prescribing carbamazepine in patients of Caucasian descent.4 Additionally, some of the CYP enzymes—such as CYP2D6*17 and CYP2C19*3 variants, which may be more common in certain populations of patients who are members of ethnic or racial minority groups—may not be consistently included in the various panels. Thus, before deciding on a specific test, clinicians should understand which gene variants are relevant to their patients with regard to race and ethnicity, and key variants for specific medications. Clinicians should refer to FDA guidance and the Clinical Pharmacogenomics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines to determine the appropriate interpretations of genetic test results.1,2
Despite the disagreement in recommendations from the various testing companies, DSTs are useful and have been shown to facilitate implementation of relevant psychopharmacology dosing guidelines, assist in identifying optimal medication therapy, and improve patient outcomes. A recently published meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of pharmacogenetic testing found that DSTs improved symptom remission among individuals with MDD by 70%.5 This suggests that pharmacogenetic-guided DSTs may provide superior treatment compared with treatment for DSTs were not used. However, the RCTs in this meta-analysis only included patients who had previously failed an antidepressant trial.5 Therefore, it is currently unknown at what point in care DSTs should be used, and whether they would be more beneficial if they are used when starting a new therapy, or after several trials have failed.
Consider the cost
The cost and availability of pharmacogenetic testing can be an issue when making treatment decisions, and such testing may not be covered by a patient’s insurance plan. Recently, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services announced that Medicare would cover FDA-approved genomic tests that encompass broad gene panels if the evidence supports their use. Similarly, commercial insurers such as UnitedHealthcare have begun to cover some pharmacogenetic tests.6 Medicare or Medicaid plans cover some testing panels’ costs and patients do not incur any out-of-pocket costs; however, some private insurance companies require patients to pay at least a portion of the cost, and many companies offer financial assistance for patients based on income and other factors. Although financial coverage for testing has improved, patients may still face out-of-pocket costs; therefore, clinicians may need to weigh the benefits of pharmacogenetic testing vs its cost.7 Clinicians should also determine what timeline best suits their patient’s financial and clinical needs, and test accordingly.
Continue to: Patient education is critical
Patient education is critical
Although the benefits of using pharmacogenetic testing information when making certain treatment decisions is promising, it is important for both patients and clinicians to understand that test results do not always change therapy. A study on the impact of pharmacogenetic testing on clinical outcomes of patients with MDD found that 79% of patients were already prescribed medications that aligned with recommendations.8 Therefore, switching medications based on the test results of a patient who is doing well clinically is not recommended. However, DSTs may help with clinical decisions for ambiguous cases. For example, if a patient has a genotype and/or phenotype that aligns with medication recommendations, the DST might not be able to identify a better medication to use, but may be able to recommend dosing guidance to improve the tolerability of the patient’s current therapy.6 It is also important to understand that the results of such testing may have a broader use beyond the initial reason for obtaining testing, such as when prescribing a common blood thinner such as warfarin or clopidogrel. However, for many of the pharmacodynamic genes that are included in these panels, their use beyond the treatment of depression may be limited because outcome studies for pharmacodynamic pharmacogenes may vary based on psychiatric diagnosis. Regardless, it may be beneficial to securely save and store patient test results in a standardized place within the medical record for future use.
CASE CONTINUED
You work with Mr. J to help him understand the benefits and limitations associated with pharmacogenetic testing. Assuming Mr. J is comfortable with the costs of obtaining testing, you contact the testing companies you identified to determine the specific pharmacogene variants included on each of these panels, and which would be the most appropriate given his race. If the decision is made to order the testing, provide Mr. J with a copy of his testing report so that he can use this information should he need any additional pharmacotherapy in the future, and also maintain a copy in his patient records using a standardized location for easy future access. If Mr. J is not comfortable with the costs associated with the testing, find out which medication his brother is currently receiving for treatment; this information may help identify a treatment plan for Mr. J.
Impact on practice
As psychiatry continues to gain experience in using pharmacogenetic testing and DSTs to help guide treatments for depression and other disorders, clinicians need to learn about these tools and how to use an evidence-based approach to best implement them in their practice. Many academic medical centers have developed continuing education programs or consult services to help with this.9,10 Just as the choice of which medication to use may be based partly on clinician experience, so too may be which pharmacogenetic test to use.
Bottom Line
Pharmacogenetic tests have not been examined in head-to-head clinical trials, which makes it nearly impossible to identify which test is best to use. Although the testing companies’ decision support tools (DSTs) often disagree in their recommendations, research has shown that using DSTs can facilitate implementation of relevant psychopharmacology dosing guidelines, assist in identifying optimal medication therapy, and improve patient outcomes. Clinicians should use testing panels with recommendations that best align with their individual practices, their patient’s needs, and FDA information.
Related Resources
- PGx Gene-specific information tables. www.pharmgkb.org/page/pgxGeneRef
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium. https://cpicpgx.org/guidelines/
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Carbamazepine • Tegretol
Citalopram • Celexa
Clopidogrel • Plavix
Clozapine • Clozaril
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Imipramine • Tofranil
Paroxetine • Paxil
Sertraline • Zoloft
Warfarin • Coumadin, Jantoven
1. Ellingrod, VL. Using pharmacogenetics guidelines when prescribing: what’s available. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(1):43-46.
2. Ellingrod VL. Pharmacogenomics testing: what the FDA says. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(4):29-33.
3. Ramsey LB. Pharmacogenetic testing in children: what to test and how to use it. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(9):30-36.
4. Bousman CA, Dunlop BW. Genotype, phenotype, and medication recommendation agreement among commercial pharmacogenetic-based decision support tools. The Pharmacogenomics Journal. 2018;18(5):613-622. doi:10.1038/s41397-018-0027-3
5. Bousman CA, Arandjelovic K, Mancuso SG, et al. Pharmacogenetic tests and depressive symptom remission: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacogenomics. 2019;20(1). doi:10.2217/pgs-2018-0142
6. Nicholson WT, Formea CM, Matey ET, et al. Considerations when applying pharmacogenomics to your practice. Mayo Clin Proc. 2021;96(1);218-230. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.03.011
7. Krebs K, Milani L. Translating pharmacogenomics into clinical decisions: do not let the perfect be the enemy of the good. Human Genomics. 2019;13(1). doi:10.1186/s40246-019-0229-z
8. Greden JF, Parikh S, Rothschild AJ, et al. Impact of pharmacogenomics on clinical outcomes in major depressive disorder in the GUIDED trial: a large, patient- and rater-blinded, randomized, controlled study. J Psychiatr Res. 2019;111;59-67. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2019.01.003
9. Haga SB. Integrating pharmacogenetic testing into primary care. Expert Review of Precision Medicine and Drug Development. 2017;2(6):327-336. doi:10.1080/23808993.2017.1398046
10. Ward KM, Taubman DS, Pasternak AL, et al. Teaching psychiatric pharmacogenomics effectively: evaluation of a novel interprofessional online course. J Am Coll Clin Pharm. 2021; 4:176-183.
Mr. J, age 30, a Black man with major depressive disorder (MDD), has been your patient for the past year. At the time of his diagnosis, Mr. J received sertraline, 100 mg/d, but had little to no improvement. During the past year, he received trials of citalopram and paroxetine, but they were not effective for his recurrent depressive symptoms and/or resulted in significant adverse effects.
During a recent visit, Mr. J asks you about “the genetic tests that help determine which medications will work.” He mentions that his brother had this testing done and that it had “worked for him,” but offers no other details. You research the different testing panels to see which test you might use. After a brief online review, you identify at least 4 different products, and are not sure which test—if any—you should consider.
During the last few years, there has been a rise in commercial pharmacogenetic testing options, including tests available to clinicians at academic medical centers as well as direct-to-consumer testing (Table). Clinician and patient interest regarding pharmacogenetic testing in practice is often followed by the question, “Which test is best?” Although this is a logical question, providing an answer is multifactorial.1-3 Because none of the currently available tests have been compared in head-to-head clinical trials, it is nearly impossible to identify the “best” test.

In this article, we focus on the evidence-based principles that clinicians should consider when adopting pharmacogenetic testing in their practice. We discuss which genes are of most interest when prescribing psychotropic medications, the value of decision support tools, cost considerations, and patient education regarding this type of testing.
Which genes and variants should be tested?
The genes relevant to medication treatment outcomes can be broadly classified into those with pharmacokinetic vs pharmacodynamic effects. Pharmacogenes, such as those coding for the drug-metabolizing enzymes cytochrome P450 (CYP) 1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT)2B1, may alter the rate at which medications are metabolized, thus varying the serum drug concentration across patients. Variants that impact the function of these enzymes are considered pharmacokinetic. Up to 40% of the variance in patients’ response to antidepressants may be due to variations in the pharmacokinetic genes.4 Alternatively, pharmacodynamic pharmacogenes impact drug action and therefore may affect the degree of receptor activation at a given drug concentration, overall drug efficacy, and/or the occurrence of medication sensitivity. These pharmacogenes may include:
- brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)
- catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT)
- human leukocyte antigens A (HLA-A)
- serotonin receptor subtype 2 (HTR2)
- serotonin receptor subtype 2C (HTR2C)
- opioid receptor mu 1 (OPRM1)
- solute carrier family 6 member 4 (SLC6A4).
In articles previously published in
Currently, there is no standardization among commercial pharmacogenetic tests on:
- which genes to test
- which variants specific to a gene need to be included
- how the genetic data is translated to phenotype
- how the phenotype is translated to a treatment recommendation.
Continue to: Due to these factors...
Due to these factors, the FDA has advised clinicians to consult the dosing recommendations provided in a medication’s package insert for information regarding how genetic information should be used in making treatment decisions.2
The value of decision support tools
Researchers have assessed how various manufacturers’ decision support tools (DSTs) (ie, the reports the commercial testing companies send to the clinician who orders the test) agree on genotypes, predicted phenotypes, and medication recommendations.4 Overall, this research found varying levels of disagreement in the medication recommendations of the testing panels they studied, which indicates that not all tests are equivalent or interchangeable.4 Of the actionable recommendations for antidepressants, 16% were conflicting; the recommendations for fluoxetine and imipramine were most frequently in disagreement.4 Similarly, 20% of the actionable antipsychotic advice was conflicting, with the recommendations for aripiprazole and clozapine most frequently in disagreement.4 Researchers also reported a situation in which 4 testing panels agreed on the patient’s phenotyping status for CYP2C19, but the dosing recommendations provided for the CYP2C19 substrate, amitriptyline, differed.4 Thus, it is understandable why DSTs can result in confusion, and why clinicians should use testing panels with recommendations that best align with their individual practices, their patient’s needs, and FDA information.
Additionally, while the genes included on these panels vary, these testing panels also may not evaluate the same variants within a specific gene. These differences may impact the patient’s reported phenotypes and medication recommendations across DSTs. For example, the FDA has recommended HLA gene testing prior to prescribing carbamazepine. However, few of the available tests may include the HLA-B*15:02 variant, which has been associated with carbamazepine-induced severe cutaneous reactions in patients of Asian descent, and fewer may include the HLA-A*31:01 variant, for which testing is recommended prior to prescribing carbamazepine in patients of Caucasian descent.4 Additionally, some of the CYP enzymes—such as CYP2D6*17 and CYP2C19*3 variants, which may be more common in certain populations of patients who are members of ethnic or racial minority groups—may not be consistently included in the various panels. Thus, before deciding on a specific test, clinicians should understand which gene variants are relevant to their patients with regard to race and ethnicity, and key variants for specific medications. Clinicians should refer to FDA guidance and the Clinical Pharmacogenomics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines to determine the appropriate interpretations of genetic test results.1,2
Despite the disagreement in recommendations from the various testing companies, DSTs are useful and have been shown to facilitate implementation of relevant psychopharmacology dosing guidelines, assist in identifying optimal medication therapy, and improve patient outcomes. A recently published meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of pharmacogenetic testing found that DSTs improved symptom remission among individuals with MDD by 70%.5 This suggests that pharmacogenetic-guided DSTs may provide superior treatment compared with treatment for DSTs were not used. However, the RCTs in this meta-analysis only included patients who had previously failed an antidepressant trial.5 Therefore, it is currently unknown at what point in care DSTs should be used, and whether they would be more beneficial if they are used when starting a new therapy, or after several trials have failed.
Consider the cost
The cost and availability of pharmacogenetic testing can be an issue when making treatment decisions, and such testing may not be covered by a patient’s insurance plan. Recently, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services announced that Medicare would cover FDA-approved genomic tests that encompass broad gene panels if the evidence supports their use. Similarly, commercial insurers such as UnitedHealthcare have begun to cover some pharmacogenetic tests.6 Medicare or Medicaid plans cover some testing panels’ costs and patients do not incur any out-of-pocket costs; however, some private insurance companies require patients to pay at least a portion of the cost, and many companies offer financial assistance for patients based on income and other factors. Although financial coverage for testing has improved, patients may still face out-of-pocket costs; therefore, clinicians may need to weigh the benefits of pharmacogenetic testing vs its cost.7 Clinicians should also determine what timeline best suits their patient’s financial and clinical needs, and test accordingly.
Continue to: Patient education is critical
Patient education is critical
Although the benefits of using pharmacogenetic testing information when making certain treatment decisions is promising, it is important for both patients and clinicians to understand that test results do not always change therapy. A study on the impact of pharmacogenetic testing on clinical outcomes of patients with MDD found that 79% of patients were already prescribed medications that aligned with recommendations.8 Therefore, switching medications based on the test results of a patient who is doing well clinically is not recommended. However, DSTs may help with clinical decisions for ambiguous cases. For example, if a patient has a genotype and/or phenotype that aligns with medication recommendations, the DST might not be able to identify a better medication to use, but may be able to recommend dosing guidance to improve the tolerability of the patient’s current therapy.6 It is also important to understand that the results of such testing may have a broader use beyond the initial reason for obtaining testing, such as when prescribing a common blood thinner such as warfarin or clopidogrel. However, for many of the pharmacodynamic genes that are included in these panels, their use beyond the treatment of depression may be limited because outcome studies for pharmacodynamic pharmacogenes may vary based on psychiatric diagnosis. Regardless, it may be beneficial to securely save and store patient test results in a standardized place within the medical record for future use.
CASE CONTINUED
You work with Mr. J to help him understand the benefits and limitations associated with pharmacogenetic testing. Assuming Mr. J is comfortable with the costs of obtaining testing, you contact the testing companies you identified to determine the specific pharmacogene variants included on each of these panels, and which would be the most appropriate given his race. If the decision is made to order the testing, provide Mr. J with a copy of his testing report so that he can use this information should he need any additional pharmacotherapy in the future, and also maintain a copy in his patient records using a standardized location for easy future access. If Mr. J is not comfortable with the costs associated with the testing, find out which medication his brother is currently receiving for treatment; this information may help identify a treatment plan for Mr. J.
Impact on practice
As psychiatry continues to gain experience in using pharmacogenetic testing and DSTs to help guide treatments for depression and other disorders, clinicians need to learn about these tools and how to use an evidence-based approach to best implement them in their practice. Many academic medical centers have developed continuing education programs or consult services to help with this.9,10 Just as the choice of which medication to use may be based partly on clinician experience, so too may be which pharmacogenetic test to use.
Bottom Line
Pharmacogenetic tests have not been examined in head-to-head clinical trials, which makes it nearly impossible to identify which test is best to use. Although the testing companies’ decision support tools (DSTs) often disagree in their recommendations, research has shown that using DSTs can facilitate implementation of relevant psychopharmacology dosing guidelines, assist in identifying optimal medication therapy, and improve patient outcomes. Clinicians should use testing panels with recommendations that best align with their individual practices, their patient’s needs, and FDA information.
Related Resources
- PGx Gene-specific information tables. www.pharmgkb.org/page/pgxGeneRef
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium. https://cpicpgx.org/guidelines/
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Carbamazepine • Tegretol
Citalopram • Celexa
Clopidogrel • Plavix
Clozapine • Clozaril
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Imipramine • Tofranil
Paroxetine • Paxil
Sertraline • Zoloft
Warfarin • Coumadin, Jantoven
Mr. J, age 30, a Black man with major depressive disorder (MDD), has been your patient for the past year. At the time of his diagnosis, Mr. J received sertraline, 100 mg/d, but had little to no improvement. During the past year, he received trials of citalopram and paroxetine, but they were not effective for his recurrent depressive symptoms and/or resulted in significant adverse effects.
During a recent visit, Mr. J asks you about “the genetic tests that help determine which medications will work.” He mentions that his brother had this testing done and that it had “worked for him,” but offers no other details. You research the different testing panels to see which test you might use. After a brief online review, you identify at least 4 different products, and are not sure which test—if any—you should consider.
During the last few years, there has been a rise in commercial pharmacogenetic testing options, including tests available to clinicians at academic medical centers as well as direct-to-consumer testing (Table). Clinician and patient interest regarding pharmacogenetic testing in practice is often followed by the question, “Which test is best?” Although this is a logical question, providing an answer is multifactorial.1-3 Because none of the currently available tests have been compared in head-to-head clinical trials, it is nearly impossible to identify the “best” test.

In this article, we focus on the evidence-based principles that clinicians should consider when adopting pharmacogenetic testing in their practice. We discuss which genes are of most interest when prescribing psychotropic medications, the value of decision support tools, cost considerations, and patient education regarding this type of testing.
Which genes and variants should be tested?
The genes relevant to medication treatment outcomes can be broadly classified into those with pharmacokinetic vs pharmacodynamic effects. Pharmacogenes, such as those coding for the drug-metabolizing enzymes cytochrome P450 (CYP) 1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT)2B1, may alter the rate at which medications are metabolized, thus varying the serum drug concentration across patients. Variants that impact the function of these enzymes are considered pharmacokinetic. Up to 40% of the variance in patients’ response to antidepressants may be due to variations in the pharmacokinetic genes.4 Alternatively, pharmacodynamic pharmacogenes impact drug action and therefore may affect the degree of receptor activation at a given drug concentration, overall drug efficacy, and/or the occurrence of medication sensitivity. These pharmacogenes may include:
- brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)
- catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT)
- human leukocyte antigens A (HLA-A)
- serotonin receptor subtype 2 (HTR2)
- serotonin receptor subtype 2C (HTR2C)
- opioid receptor mu 1 (OPRM1)
- solute carrier family 6 member 4 (SLC6A4).
In articles previously published in
Currently, there is no standardization among commercial pharmacogenetic tests on:
- which genes to test
- which variants specific to a gene need to be included
- how the genetic data is translated to phenotype
- how the phenotype is translated to a treatment recommendation.
Continue to: Due to these factors...
Due to these factors, the FDA has advised clinicians to consult the dosing recommendations provided in a medication’s package insert for information regarding how genetic information should be used in making treatment decisions.2
The value of decision support tools
Researchers have assessed how various manufacturers’ decision support tools (DSTs) (ie, the reports the commercial testing companies send to the clinician who orders the test) agree on genotypes, predicted phenotypes, and medication recommendations.4 Overall, this research found varying levels of disagreement in the medication recommendations of the testing panels they studied, which indicates that not all tests are equivalent or interchangeable.4 Of the actionable recommendations for antidepressants, 16% were conflicting; the recommendations for fluoxetine and imipramine were most frequently in disagreement.4 Similarly, 20% of the actionable antipsychotic advice was conflicting, with the recommendations for aripiprazole and clozapine most frequently in disagreement.4 Researchers also reported a situation in which 4 testing panels agreed on the patient’s phenotyping status for CYP2C19, but the dosing recommendations provided for the CYP2C19 substrate, amitriptyline, differed.4 Thus, it is understandable why DSTs can result in confusion, and why clinicians should use testing panels with recommendations that best align with their individual practices, their patient’s needs, and FDA information.
Additionally, while the genes included on these panels vary, these testing panels also may not evaluate the same variants within a specific gene. These differences may impact the patient’s reported phenotypes and medication recommendations across DSTs. For example, the FDA has recommended HLA gene testing prior to prescribing carbamazepine. However, few of the available tests may include the HLA-B*15:02 variant, which has been associated with carbamazepine-induced severe cutaneous reactions in patients of Asian descent, and fewer may include the HLA-A*31:01 variant, for which testing is recommended prior to prescribing carbamazepine in patients of Caucasian descent.4 Additionally, some of the CYP enzymes—such as CYP2D6*17 and CYP2C19*3 variants, which may be more common in certain populations of patients who are members of ethnic or racial minority groups—may not be consistently included in the various panels. Thus, before deciding on a specific test, clinicians should understand which gene variants are relevant to their patients with regard to race and ethnicity, and key variants for specific medications. Clinicians should refer to FDA guidance and the Clinical Pharmacogenomics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines to determine the appropriate interpretations of genetic test results.1,2
Despite the disagreement in recommendations from the various testing companies, DSTs are useful and have been shown to facilitate implementation of relevant psychopharmacology dosing guidelines, assist in identifying optimal medication therapy, and improve patient outcomes. A recently published meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of pharmacogenetic testing found that DSTs improved symptom remission among individuals with MDD by 70%.5 This suggests that pharmacogenetic-guided DSTs may provide superior treatment compared with treatment for DSTs were not used. However, the RCTs in this meta-analysis only included patients who had previously failed an antidepressant trial.5 Therefore, it is currently unknown at what point in care DSTs should be used, and whether they would be more beneficial if they are used when starting a new therapy, or after several trials have failed.
Consider the cost
The cost and availability of pharmacogenetic testing can be an issue when making treatment decisions, and such testing may not be covered by a patient’s insurance plan. Recently, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services announced that Medicare would cover FDA-approved genomic tests that encompass broad gene panels if the evidence supports their use. Similarly, commercial insurers such as UnitedHealthcare have begun to cover some pharmacogenetic tests.6 Medicare or Medicaid plans cover some testing panels’ costs and patients do not incur any out-of-pocket costs; however, some private insurance companies require patients to pay at least a portion of the cost, and many companies offer financial assistance for patients based on income and other factors. Although financial coverage for testing has improved, patients may still face out-of-pocket costs; therefore, clinicians may need to weigh the benefits of pharmacogenetic testing vs its cost.7 Clinicians should also determine what timeline best suits their patient’s financial and clinical needs, and test accordingly.
Continue to: Patient education is critical
Patient education is critical
Although the benefits of using pharmacogenetic testing information when making certain treatment decisions is promising, it is important for both patients and clinicians to understand that test results do not always change therapy. A study on the impact of pharmacogenetic testing on clinical outcomes of patients with MDD found that 79% of patients were already prescribed medications that aligned with recommendations.8 Therefore, switching medications based on the test results of a patient who is doing well clinically is not recommended. However, DSTs may help with clinical decisions for ambiguous cases. For example, if a patient has a genotype and/or phenotype that aligns with medication recommendations, the DST might not be able to identify a better medication to use, but may be able to recommend dosing guidance to improve the tolerability of the patient’s current therapy.6 It is also important to understand that the results of such testing may have a broader use beyond the initial reason for obtaining testing, such as when prescribing a common blood thinner such as warfarin or clopidogrel. However, for many of the pharmacodynamic genes that are included in these panels, their use beyond the treatment of depression may be limited because outcome studies for pharmacodynamic pharmacogenes may vary based on psychiatric diagnosis. Regardless, it may be beneficial to securely save and store patient test results in a standardized place within the medical record for future use.
CASE CONTINUED
You work with Mr. J to help him understand the benefits and limitations associated with pharmacogenetic testing. Assuming Mr. J is comfortable with the costs of obtaining testing, you contact the testing companies you identified to determine the specific pharmacogene variants included on each of these panels, and which would be the most appropriate given his race. If the decision is made to order the testing, provide Mr. J with a copy of his testing report so that he can use this information should he need any additional pharmacotherapy in the future, and also maintain a copy in his patient records using a standardized location for easy future access. If Mr. J is not comfortable with the costs associated with the testing, find out which medication his brother is currently receiving for treatment; this information may help identify a treatment plan for Mr. J.
Impact on practice
As psychiatry continues to gain experience in using pharmacogenetic testing and DSTs to help guide treatments for depression and other disorders, clinicians need to learn about these tools and how to use an evidence-based approach to best implement them in their practice. Many academic medical centers have developed continuing education programs or consult services to help with this.9,10 Just as the choice of which medication to use may be based partly on clinician experience, so too may be which pharmacogenetic test to use.
Bottom Line
Pharmacogenetic tests have not been examined in head-to-head clinical trials, which makes it nearly impossible to identify which test is best to use. Although the testing companies’ decision support tools (DSTs) often disagree in their recommendations, research has shown that using DSTs can facilitate implementation of relevant psychopharmacology dosing guidelines, assist in identifying optimal medication therapy, and improve patient outcomes. Clinicians should use testing panels with recommendations that best align with their individual practices, their patient’s needs, and FDA information.
Related Resources
- PGx Gene-specific information tables. www.pharmgkb.org/page/pgxGeneRef
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium. https://cpicpgx.org/guidelines/
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Carbamazepine • Tegretol
Citalopram • Celexa
Clopidogrel • Plavix
Clozapine • Clozaril
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Imipramine • Tofranil
Paroxetine • Paxil
Sertraline • Zoloft
Warfarin • Coumadin, Jantoven
1. Ellingrod, VL. Using pharmacogenetics guidelines when prescribing: what’s available. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(1):43-46.
2. Ellingrod VL. Pharmacogenomics testing: what the FDA says. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(4):29-33.
3. Ramsey LB. Pharmacogenetic testing in children: what to test and how to use it. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(9):30-36.
4. Bousman CA, Dunlop BW. Genotype, phenotype, and medication recommendation agreement among commercial pharmacogenetic-based decision support tools. The Pharmacogenomics Journal. 2018;18(5):613-622. doi:10.1038/s41397-018-0027-3
5. Bousman CA, Arandjelovic K, Mancuso SG, et al. Pharmacogenetic tests and depressive symptom remission: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacogenomics. 2019;20(1). doi:10.2217/pgs-2018-0142
6. Nicholson WT, Formea CM, Matey ET, et al. Considerations when applying pharmacogenomics to your practice. Mayo Clin Proc. 2021;96(1);218-230. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.03.011
7. Krebs K, Milani L. Translating pharmacogenomics into clinical decisions: do not let the perfect be the enemy of the good. Human Genomics. 2019;13(1). doi:10.1186/s40246-019-0229-z
8. Greden JF, Parikh S, Rothschild AJ, et al. Impact of pharmacogenomics on clinical outcomes in major depressive disorder in the GUIDED trial: a large, patient- and rater-blinded, randomized, controlled study. J Psychiatr Res. 2019;111;59-67. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2019.01.003
9. Haga SB. Integrating pharmacogenetic testing into primary care. Expert Review of Precision Medicine and Drug Development. 2017;2(6):327-336. doi:10.1080/23808993.2017.1398046
10. Ward KM, Taubman DS, Pasternak AL, et al. Teaching psychiatric pharmacogenomics effectively: evaluation of a novel interprofessional online course. J Am Coll Clin Pharm. 2021; 4:176-183.
1. Ellingrod, VL. Using pharmacogenetics guidelines when prescribing: what’s available. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(1):43-46.
2. Ellingrod VL. Pharmacogenomics testing: what the FDA says. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(4):29-33.
3. Ramsey LB. Pharmacogenetic testing in children: what to test and how to use it. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(9):30-36.
4. Bousman CA, Dunlop BW. Genotype, phenotype, and medication recommendation agreement among commercial pharmacogenetic-based decision support tools. The Pharmacogenomics Journal. 2018;18(5):613-622. doi:10.1038/s41397-018-0027-3
5. Bousman CA, Arandjelovic K, Mancuso SG, et al. Pharmacogenetic tests and depressive symptom remission: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacogenomics. 2019;20(1). doi:10.2217/pgs-2018-0142
6. Nicholson WT, Formea CM, Matey ET, et al. Considerations when applying pharmacogenomics to your practice. Mayo Clin Proc. 2021;96(1);218-230. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.03.011
7. Krebs K, Milani L. Translating pharmacogenomics into clinical decisions: do not let the perfect be the enemy of the good. Human Genomics. 2019;13(1). doi:10.1186/s40246-019-0229-z
8. Greden JF, Parikh S, Rothschild AJ, et al. Impact of pharmacogenomics on clinical outcomes in major depressive disorder in the GUIDED trial: a large, patient- and rater-blinded, randomized, controlled study. J Psychiatr Res. 2019;111;59-67. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2019.01.003
9. Haga SB. Integrating pharmacogenetic testing into primary care. Expert Review of Precision Medicine and Drug Development. 2017;2(6):327-336. doi:10.1080/23808993.2017.1398046
10. Ward KM, Taubman DS, Pasternak AL, et al. Teaching psychiatric pharmacogenomics effectively: evaluation of a novel interprofessional online course. J Am Coll Clin Pharm. 2021; 4:176-183.
