User login
Admissions for septicemia nearly tripled from 2005 to 2014, as it became the third most common diagnosis for hospital stays, according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
There were over 1.5 million hospital stays with a principal diagnosis of septicemia in 2014, an increase of 192% over the 518,000 stays in 2005. The only diagnoses with more admissions in 2014 were pregnancy/childbirth with 4.1 million stays and newborns/neonates at almost 4 million, although both were down from 2005. That year, septicemia did not even rank among the top 10 diagnoses, the AHRQ reported.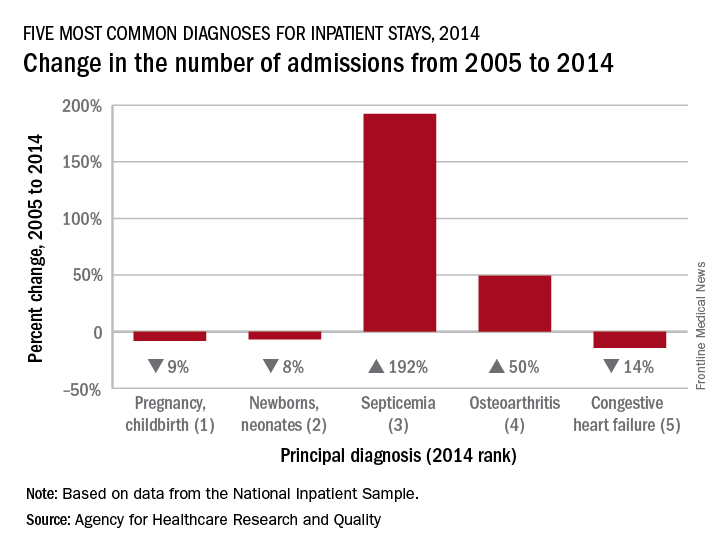
Pneumonia, which was the third most common diagnosis in 2005, dropped by 32% and ended up in sixth place in 2014, while admissions for coronary atherosclerosis, which was fourth in 2005, decreased by 63%, dropping out of the top 10, by 2014, the AHRQ said.
Septicemia was the most common diagnosis for inpatient stays among those aged 75 years and older and the second most common for those aged 65-74 and 45-64. The leading nonmaternal, nonneonatal diagnosis in the two youngest age groups, 0-17 and 18-44 years, was mood disorders, and the most common cause of admissions for those aged 45-64 and 65-74 was osteoarthritis, the AHRQ reported.
Admissions for septicemia nearly tripled from 2005 to 2014, as it became the third most common diagnosis for hospital stays, according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
There were over 1.5 million hospital stays with a principal diagnosis of septicemia in 2014, an increase of 192% over the 518,000 stays in 2005. The only diagnoses with more admissions in 2014 were pregnancy/childbirth with 4.1 million stays and newborns/neonates at almost 4 million, although both were down from 2005. That year, septicemia did not even rank among the top 10 diagnoses, the AHRQ reported.
Pneumonia, which was the third most common diagnosis in 2005, dropped by 32% and ended up in sixth place in 2014, while admissions for coronary atherosclerosis, which was fourth in 2005, decreased by 63%, dropping out of the top 10, by 2014, the AHRQ said.
Septicemia was the most common diagnosis for inpatient stays among those aged 75 years and older and the second most common for those aged 65-74 and 45-64. The leading nonmaternal, nonneonatal diagnosis in the two youngest age groups, 0-17 and 18-44 years, was mood disorders, and the most common cause of admissions for those aged 45-64 and 65-74 was osteoarthritis, the AHRQ reported.
Admissions for septicemia nearly tripled from 2005 to 2014, as it became the third most common diagnosis for hospital stays, according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
There were over 1.5 million hospital stays with a principal diagnosis of septicemia in 2014, an increase of 192% over the 518,000 stays in 2005. The only diagnoses with more admissions in 2014 were pregnancy/childbirth with 4.1 million stays and newborns/neonates at almost 4 million, although both were down from 2005. That year, septicemia did not even rank among the top 10 diagnoses, the AHRQ reported.
Pneumonia, which was the third most common diagnosis in 2005, dropped by 32% and ended up in sixth place in 2014, while admissions for coronary atherosclerosis, which was fourth in 2005, decreased by 63%, dropping out of the top 10, by 2014, the AHRQ said.
Septicemia was the most common diagnosis for inpatient stays among those aged 75 years and older and the second most common for those aged 65-74 and 45-64. The leading nonmaternal, nonneonatal diagnosis in the two youngest age groups, 0-17 and 18-44 years, was mood disorders, and the most common cause of admissions for those aged 45-64 and 65-74 was osteoarthritis, the AHRQ reported.