User login
On the basis of the patient’s family history, personal history, and presentation, the likely diagnosis is Crohn disease. Although the disease may be diagnosed at any age, onset shows a bimodal distribution, with the first, more predominant wave occurring in adolescence and early adulthood. Peak global onset is between the ages of 15 and 30. Compared with adult-onset disease, pediatric Crohn disease is associated with a more serious disease course. Patients of Ashkenazi Jewish descent are at higher risk of developing this autoimmune disease than any other ethnic group.
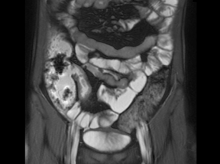
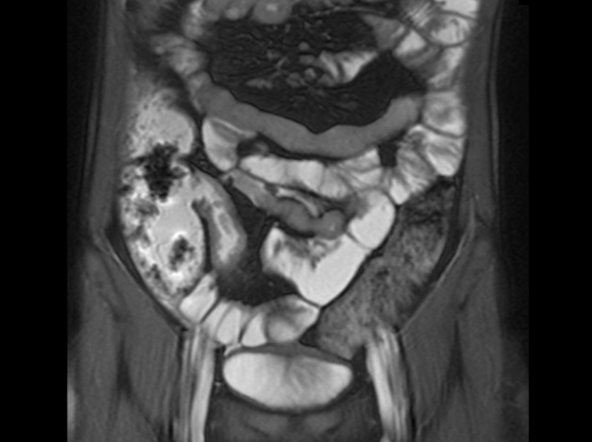
Colonoscopy is the first-line approach for diagnosing and monitoring inflammatory bowel disease. Typical findings in patients with Crohn disease include histologic changes, such as focal crypt irregularity, transmural lymphoid aggregates, fissures and fistulas, and perianal disorders. In the differential diagnosis, ulcerative colitis (UC) must be carefully ruled out. UC involves only the large bowel, rarely causes fistulas, and is frequently seen with bleeding. Crohn disease is characteristically noncontiguous, with linear ulcerations of a cobblestone appearance. In addition, noncaseating granulomas are specific for Crohn disease. Micronutrient and vitamin levels are usually low, as seen in the present case. During workup, fecal calprotectin can help differentiate inflammatory bowel disease from irritable bowel syndrome.
The patient in this case may be a candidate for 5-aminosalicylic acid, together with a nutritional plan, used in mild or moderate cases of pediatric Crohn disease. Clinical improvement plus a decrease of fecal calprotectin would be an indication of positive treatment response. Being newly diagnosed, if the patient does not achieve remission after the induction period, he may be at risk for a more complicated disease course. Treatment for Crohn disease in the pediatric setting, as in the adult setting, should be implemented through a step-up approach. Other treatment options for pediatric disease include antibiotics; immunomodulators; and, in moderate-to severe cases, corticosteroids and biologics.
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
On the basis of the patient’s family history, personal history, and presentation, the likely diagnosis is Crohn disease. Although the disease may be diagnosed at any age, onset shows a bimodal distribution, with the first, more predominant wave occurring in adolescence and early adulthood. Peak global onset is between the ages of 15 and 30. Compared with adult-onset disease, pediatric Crohn disease is associated with a more serious disease course. Patients of Ashkenazi Jewish descent are at higher risk of developing this autoimmune disease than any other ethnic group.
Colonoscopy is the first-line approach for diagnosing and monitoring inflammatory bowel disease. Typical findings in patients with Crohn disease include histologic changes, such as focal crypt irregularity, transmural lymphoid aggregates, fissures and fistulas, and perianal disorders. In the differential diagnosis, ulcerative colitis (UC) must be carefully ruled out. UC involves only the large bowel, rarely causes fistulas, and is frequently seen with bleeding. Crohn disease is characteristically noncontiguous, with linear ulcerations of a cobblestone appearance. In addition, noncaseating granulomas are specific for Crohn disease. Micronutrient and vitamin levels are usually low, as seen in the present case. During workup, fecal calprotectin can help differentiate inflammatory bowel disease from irritable bowel syndrome.
The patient in this case may be a candidate for 5-aminosalicylic acid, together with a nutritional plan, used in mild or moderate cases of pediatric Crohn disease. Clinical improvement plus a decrease of fecal calprotectin would be an indication of positive treatment response. Being newly diagnosed, if the patient does not achieve remission after the induction period, he may be at risk for a more complicated disease course. Treatment for Crohn disease in the pediatric setting, as in the adult setting, should be implemented through a step-up approach. Other treatment options for pediatric disease include antibiotics; immunomodulators; and, in moderate-to severe cases, corticosteroids and biologics.
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
On the basis of the patient’s family history, personal history, and presentation, the likely diagnosis is Crohn disease. Although the disease may be diagnosed at any age, onset shows a bimodal distribution, with the first, more predominant wave occurring in adolescence and early adulthood. Peak global onset is between the ages of 15 and 30. Compared with adult-onset disease, pediatric Crohn disease is associated with a more serious disease course. Patients of Ashkenazi Jewish descent are at higher risk of developing this autoimmune disease than any other ethnic group.
Colonoscopy is the first-line approach for diagnosing and monitoring inflammatory bowel disease. Typical findings in patients with Crohn disease include histologic changes, such as focal crypt irregularity, transmural lymphoid aggregates, fissures and fistulas, and perianal disorders. In the differential diagnosis, ulcerative colitis (UC) must be carefully ruled out. UC involves only the large bowel, rarely causes fistulas, and is frequently seen with bleeding. Crohn disease is characteristically noncontiguous, with linear ulcerations of a cobblestone appearance. In addition, noncaseating granulomas are specific for Crohn disease. Micronutrient and vitamin levels are usually low, as seen in the present case. During workup, fecal calprotectin can help differentiate inflammatory bowel disease from irritable bowel syndrome.
The patient in this case may be a candidate for 5-aminosalicylic acid, together with a nutritional plan, used in mild or moderate cases of pediatric Crohn disease. Clinical improvement plus a decrease of fecal calprotectin would be an indication of positive treatment response. Being newly diagnosed, if the patient does not achieve remission after the induction period, he may be at risk for a more complicated disease course. Treatment for Crohn disease in the pediatric setting, as in the adult setting, should be implemented through a step-up approach. Other treatment options for pediatric disease include antibiotics; immunomodulators; and, in moderate-to severe cases, corticosteroids and biologics.
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 12-year-old boy presents to an urgent care center with severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. His height is 5 ft 3 in and weight is 99 lb (BMI 18.7). The patient has a history of chronic diarrhea and reports intermittent abdominal pain that began about 6 months ago. During this time, he has lost about 12 lb, as many foods exacerbate his symptoms, though his mother notes that even plain foods can bother his stomach. Further questioning reveals that his father has moderate Crohn disease (age of onset, 29 years), his sister has celiac disease, and the patient is of Ashkenazi Jewish descent. His body temperature is 100.2 °F. Vitamin B12, serum iron, total iron binding capacity, calcium, and magnesium are low. Stool cultures are negative. Ileocolonoscopy shows small aphthous erosions in the large intestine and in the terminal ileum.