User login
Researchers say they’ve developed a technique for single-cell analysis that has revealed a population of treatment-resistant stem cells in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
“It is increasingly recognized that tumors contain a variety of different cell types, including so-called cancer stem cells, that drive the growth and relapse of a patient’s cancer,” said study author Adam Mead, BM BCh, PhD, of University of Oxford in the UK.
“These cells can be very rare and extremely difficult to find after treatment as they become hidden within the normal tissue. We used a new genetic technique to identify and analyze single cancer stem cells in leukemia patients before and after treatment.”
Dr Mead and his colleagues detailed this research in Nature Medicine.
The team’s single-cell analysis technique combines high-sensitivity mutation detection with whole-transcriptome analysis.
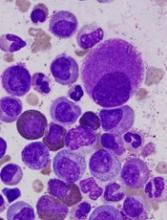
The researchers used the method to analyze stem cells from patients with CML and found the cells to be heterogeneous.
In addition, the team was able to identify a subset of CML stem cells that proved resistant to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
“We found that, even in individual cases of leukemia, there are various types of cancer stem cell that respond differently to the treatment,” Dr Mead said.
“A small number of these cells are highly resistant to the treatment and are likely to be responsible for disease recurrence when the treatment is stopped. Our research allowed us uniquely to analyze these crucial cells that evade treatment so that we might learn how to more effectively eradicate them.”
The researchers said these TKI-resistant CML stem cells were “transcriptionally distinct” from normal hematopoietic stem cells.
The TKI-resistant cells were characterized by dysregulation of specific genes and pathways—TGF-β, TNF-α, JAK–STAT, CTNNB1, and NFKB1A—that could potentially be targeted to improve the treatment of CML.
The researchers also said their single-cell analysis technique can be used beyond CML.
“This technique could be adapted to analyze a range of different cancers to help predict both the likely response to treatment and the risk of the disease returning in the future,” Dr Mead said. “This should eventually enable treatment to be tailored to target each and every type of cancer stem cell that may be present.” ![]()
Researchers say they’ve developed a technique for single-cell analysis that has revealed a population of treatment-resistant stem cells in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
“It is increasingly recognized that tumors contain a variety of different cell types, including so-called cancer stem cells, that drive the growth and relapse of a patient’s cancer,” said study author Adam Mead, BM BCh, PhD, of University of Oxford in the UK.
“These cells can be very rare and extremely difficult to find after treatment as they become hidden within the normal tissue. We used a new genetic technique to identify and analyze single cancer stem cells in leukemia patients before and after treatment.”
Dr Mead and his colleagues detailed this research in Nature Medicine.
The team’s single-cell analysis technique combines high-sensitivity mutation detection with whole-transcriptome analysis.
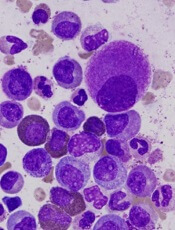
The researchers used the method to analyze stem cells from patients with CML and found the cells to be heterogeneous.
In addition, the team was able to identify a subset of CML stem cells that proved resistant to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
“We found that, even in individual cases of leukemia, there are various types of cancer stem cell that respond differently to the treatment,” Dr Mead said.
“A small number of these cells are highly resistant to the treatment and are likely to be responsible for disease recurrence when the treatment is stopped. Our research allowed us uniquely to analyze these crucial cells that evade treatment so that we might learn how to more effectively eradicate them.”
The researchers said these TKI-resistant CML stem cells were “transcriptionally distinct” from normal hematopoietic stem cells.
The TKI-resistant cells were characterized by dysregulation of specific genes and pathways—TGF-β, TNF-α, JAK–STAT, CTNNB1, and NFKB1A—that could potentially be targeted to improve the treatment of CML.
The researchers also said their single-cell analysis technique can be used beyond CML.
“This technique could be adapted to analyze a range of different cancers to help predict both the likely response to treatment and the risk of the disease returning in the future,” Dr Mead said. “This should eventually enable treatment to be tailored to target each and every type of cancer stem cell that may be present.” ![]()
Researchers say they’ve developed a technique for single-cell analysis that has revealed a population of treatment-resistant stem cells in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
“It is increasingly recognized that tumors contain a variety of different cell types, including so-called cancer stem cells, that drive the growth and relapse of a patient’s cancer,” said study author Adam Mead, BM BCh, PhD, of University of Oxford in the UK.
“These cells can be very rare and extremely difficult to find after treatment as they become hidden within the normal tissue. We used a new genetic technique to identify and analyze single cancer stem cells in leukemia patients before and after treatment.”
Dr Mead and his colleagues detailed this research in Nature Medicine.
The team’s single-cell analysis technique combines high-sensitivity mutation detection with whole-transcriptome analysis.
The researchers used the method to analyze stem cells from patients with CML and found the cells to be heterogeneous.
In addition, the team was able to identify a subset of CML stem cells that proved resistant to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
“We found that, even in individual cases of leukemia, there are various types of cancer stem cell that respond differently to the treatment,” Dr Mead said.
“A small number of these cells are highly resistant to the treatment and are likely to be responsible for disease recurrence when the treatment is stopped. Our research allowed us uniquely to analyze these crucial cells that evade treatment so that we might learn how to more effectively eradicate them.”
The researchers said these TKI-resistant CML stem cells were “transcriptionally distinct” from normal hematopoietic stem cells.
The TKI-resistant cells were characterized by dysregulation of specific genes and pathways—TGF-β, TNF-α, JAK–STAT, CTNNB1, and NFKB1A—that could potentially be targeted to improve the treatment of CML.
The researchers also said their single-cell analysis technique can be used beyond CML.
“This technique could be adapted to analyze a range of different cancers to help predict both the likely response to treatment and the risk of the disease returning in the future,” Dr Mead said. “This should eventually enable treatment to be tailored to target each and every type of cancer stem cell that may be present.” ![]()