User login
A device that noninvasively measures intracranial pressure (ICP) had a sensitivity of 75% and a specificity of 89%, compared with standard invasive monitoring, based on the results of an industry-sponsored study of 14 patients with traumatic brain injury or subarachnoid hemorrhage.
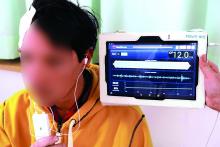
“This study provides the first clinical data on the accuracy of the HS-1000 noninvasive ICP monitor, which uses advanced signal analysis algorithms to evaluate properties of acoustic signals traveling through the brain,” wrote Oliver Ganslandt, MD, of Klinikum Stuttgart (Germany) and his associates. The findings were published online Aug. 8 in the Journal of Neurosurgery.
The noninvasive and invasive measurements produced more than 2,500 parallel ICP data points. Notably, each of the two methods produced the same number of data points. Readings averaged 10 (standard deviation, 6.1) mm Hg with invasive monitoring and 9.5 (SD, 4.7) mm Hg for noninvasive monitoring with the HS-1000. Compared with invasive ICP monitoring, the HS-1000 had a sensitivity of 75% and a specificity of 89% at an arbitrary cutoff of at least 17 mm Hg. Linear regression showed a “strong positive relationship between the [noninvasive and invasive] measurements,” the investigators said. In all, 63% of paired data points fell within 3 mm Hg of each other, and 85% fell within 5 mm Hg of each other. A receiver operating characteristic area under the curve analysis of the two methods generated an area under the curve of almost 90%.
The study did not include children or patients who were pregnant or had ear disease or ear injuries, rhinorrhea or otorrhea, or skull defects, the researchers said. If the HS-1000 holds up in other ongoing studies (NCT02284217, NCT02773901), physicians might be able to use it to decide if patients needs invasive ICP monitoring, they added. Use of the noninvasive method could also help prevent infections and other morbidity associated with invasive ICP monitoring in both neurocritical intensive care units and low-resource settings, they said.
HeadSense Medical sponsored the study. The researchers had no relevant disclosures.
A device that noninvasively measures intracranial pressure (ICP) had a sensitivity of 75% and a specificity of 89%, compared with standard invasive monitoring, based on the results of an industry-sponsored study of 14 patients with traumatic brain injury or subarachnoid hemorrhage.
“This study provides the first clinical data on the accuracy of the HS-1000 noninvasive ICP monitor, which uses advanced signal analysis algorithms to evaluate properties of acoustic signals traveling through the brain,” wrote Oliver Ganslandt, MD, of Klinikum Stuttgart (Germany) and his associates. The findings were published online Aug. 8 in the Journal of Neurosurgery.
The noninvasive and invasive measurements produced more than 2,500 parallel ICP data points. Notably, each of the two methods produced the same number of data points. Readings averaged 10 (standard deviation, 6.1) mm Hg with invasive monitoring and 9.5 (SD, 4.7) mm Hg for noninvasive monitoring with the HS-1000. Compared with invasive ICP monitoring, the HS-1000 had a sensitivity of 75% and a specificity of 89% at an arbitrary cutoff of at least 17 mm Hg. Linear regression showed a “strong positive relationship between the [noninvasive and invasive] measurements,” the investigators said. In all, 63% of paired data points fell within 3 mm Hg of each other, and 85% fell within 5 mm Hg of each other. A receiver operating characteristic area under the curve analysis of the two methods generated an area under the curve of almost 90%.
The study did not include children or patients who were pregnant or had ear disease or ear injuries, rhinorrhea or otorrhea, or skull defects, the researchers said. If the HS-1000 holds up in other ongoing studies (NCT02284217, NCT02773901), physicians might be able to use it to decide if patients needs invasive ICP monitoring, they added. Use of the noninvasive method could also help prevent infections and other morbidity associated with invasive ICP monitoring in both neurocritical intensive care units and low-resource settings, they said.
HeadSense Medical sponsored the study. The researchers had no relevant disclosures.
A device that noninvasively measures intracranial pressure (ICP) had a sensitivity of 75% and a specificity of 89%, compared with standard invasive monitoring, based on the results of an industry-sponsored study of 14 patients with traumatic brain injury or subarachnoid hemorrhage.
“This study provides the first clinical data on the accuracy of the HS-1000 noninvasive ICP monitor, which uses advanced signal analysis algorithms to evaluate properties of acoustic signals traveling through the brain,” wrote Oliver Ganslandt, MD, of Klinikum Stuttgart (Germany) and his associates. The findings were published online Aug. 8 in the Journal of Neurosurgery.
The noninvasive and invasive measurements produced more than 2,500 parallel ICP data points. Notably, each of the two methods produced the same number of data points. Readings averaged 10 (standard deviation, 6.1) mm Hg with invasive monitoring and 9.5 (SD, 4.7) mm Hg for noninvasive monitoring with the HS-1000. Compared with invasive ICP monitoring, the HS-1000 had a sensitivity of 75% and a specificity of 89% at an arbitrary cutoff of at least 17 mm Hg. Linear regression showed a “strong positive relationship between the [noninvasive and invasive] measurements,” the investigators said. In all, 63% of paired data points fell within 3 mm Hg of each other, and 85% fell within 5 mm Hg of each other. A receiver operating characteristic area under the curve analysis of the two methods generated an area under the curve of almost 90%.
The study did not include children or patients who were pregnant or had ear disease or ear injuries, rhinorrhea or otorrhea, or skull defects, the researchers said. If the HS-1000 holds up in other ongoing studies (NCT02284217, NCT02773901), physicians might be able to use it to decide if patients needs invasive ICP monitoring, they added. Use of the noninvasive method could also help prevent infections and other morbidity associated with invasive ICP monitoring in both neurocritical intensive care units and low-resource settings, they said.
HeadSense Medical sponsored the study. The researchers had no relevant disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF NEUROSURGERY
Key clinical point: A noninvasive device that measures intracranial pressure generated data that was comparable with standard invasive methods.
Major finding: Sensitivity was 75%, and specificity was 89%, compared with standard invasive monitoring at an arbitrary cutoff of at least 17 mm Hg.
Data source: Noninvasive and invasive intracranial pressure monitoring of 14 patients with traumatic brain injury or subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Disclosures: HeadSense Medical sponsored the study. The researchers had no relevant disclosures.