User login
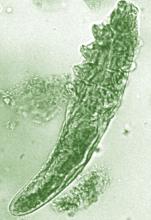
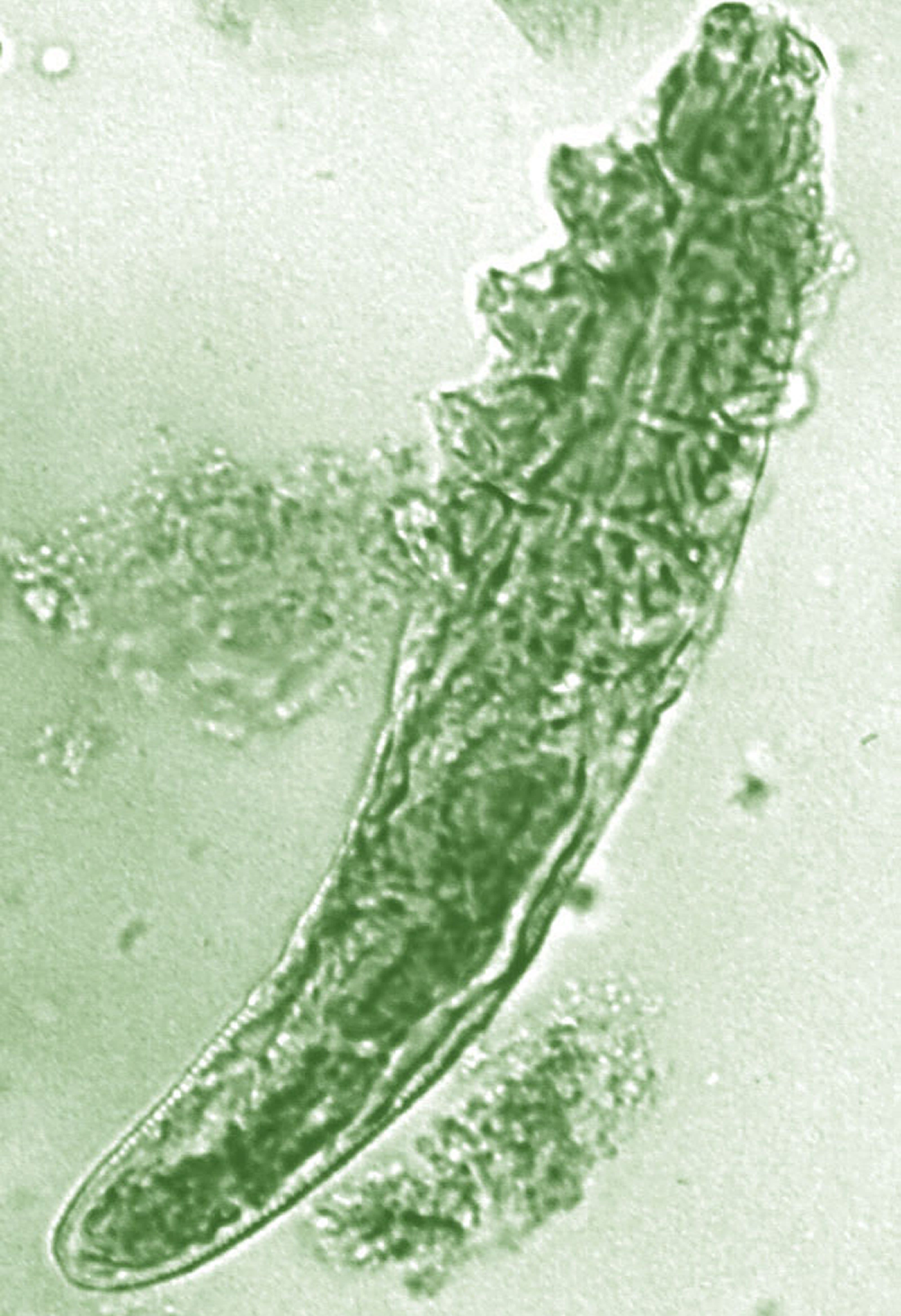
Daily treatment with benzyl benzoate (BB) cream reduced Demodex densities in patients with and without rosacea, and was associated with improvement in clinical signs, according to F.M.N. Forton, MD, of the Dermatology Clinic, Brussels, and his coauthor in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
The retrospective study comprised 394 patients treated between 2002 and 2010; 117 of them had rosacea with papulopustules and the remainder only demodicosis. Their mean age was 49 years; most (278) were women. They had been treated with one of three doses of BB cream with crotamiton 10% cream: crotamiton applied in the morning, and BB 12% plus crotamiton in the evening; BB 12% plus crotamiton applied twice daily; and BB 20%-24% plus crotamiton applied once in the evening. Demodex densities (Dds) were measured with two consecutive standardized skin surface biopsies and deep biopsies at baseline and follow-up. Symptoms were measured with an investigator global assessment (IGA).
The authors said they had previously found that BB had acaricidal effects on Demodex, as did crotamiton “to a lesser extent,” but that the two treatments have not been well studied. They also referred to the increasing evidence that Demodex has a role in papulopustular rosacea, and that ivermectin, which is acaricidal, is recommended for topical treatment of papulopustular rosacea.
In the study, a mean of 2.7 months after starting treatment, mean Dds were significantly lower for the entire cohort, decreasing by 72.4% (plus or minus 2.6%) from baseline. Dds had normalized in 35% of patients, and in 31% of patients, symptoms had cleared.
Treatment was considered effective in 46% of patients and curative in 20%. Men responded slightly better, with clearance in 34% vs. 20% of women. The two regimens using the higher dose of BB were more effective than those using the lower dose and were associated with better compliance. Compliance overall was 77%.
After a mean of nearly 3 months of treatment, “topical application of BB (with crotamiton) was effective at reducing Dds and clearing clinical symptoms, not only in demodicosis but also in rosacea with papulopustules, indirectly supporting a key role of the mite in the pathophysiology of rosacea,” the authors concluded.
Neither of these products are approved in the United States for treating rosacea.
Dr. Forton disclosed that he occasionally works as a consultant for Galderma; the second author had no disclosures. The study had no funding source.
Source: Forton FMN et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Sep 7. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15938.
Daily treatment with benzyl benzoate (BB) cream reduced Demodex densities in patients with and without rosacea, and was associated with improvement in clinical signs, according to F.M.N. Forton, MD, of the Dermatology Clinic, Brussels, and his coauthor in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
The retrospective study comprised 394 patients treated between 2002 and 2010; 117 of them had rosacea with papulopustules and the remainder only demodicosis. Their mean age was 49 years; most (278) were women. They had been treated with one of three doses of BB cream with crotamiton 10% cream: crotamiton applied in the morning, and BB 12% plus crotamiton in the evening; BB 12% plus crotamiton applied twice daily; and BB 20%-24% plus crotamiton applied once in the evening. Demodex densities (Dds) were measured with two consecutive standardized skin surface biopsies and deep biopsies at baseline and follow-up. Symptoms were measured with an investigator global assessment (IGA).
The authors said they had previously found that BB had acaricidal effects on Demodex, as did crotamiton “to a lesser extent,” but that the two treatments have not been well studied. They also referred to the increasing evidence that Demodex has a role in papulopustular rosacea, and that ivermectin, which is acaricidal, is recommended for topical treatment of papulopustular rosacea.
In the study, a mean of 2.7 months after starting treatment, mean Dds were significantly lower for the entire cohort, decreasing by 72.4% (plus or minus 2.6%) from baseline. Dds had normalized in 35% of patients, and in 31% of patients, symptoms had cleared.
Treatment was considered effective in 46% of patients and curative in 20%. Men responded slightly better, with clearance in 34% vs. 20% of women. The two regimens using the higher dose of BB were more effective than those using the lower dose and were associated with better compliance. Compliance overall was 77%.
After a mean of nearly 3 months of treatment, “topical application of BB (with crotamiton) was effective at reducing Dds and clearing clinical symptoms, not only in demodicosis but also in rosacea with papulopustules, indirectly supporting a key role of the mite in the pathophysiology of rosacea,” the authors concluded.
Neither of these products are approved in the United States for treating rosacea.
Dr. Forton disclosed that he occasionally works as a consultant for Galderma; the second author had no disclosures. The study had no funding source.
Source: Forton FMN et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Sep 7. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15938.
Daily treatment with benzyl benzoate (BB) cream reduced Demodex densities in patients with and without rosacea, and was associated with improvement in clinical signs, according to F.M.N. Forton, MD, of the Dermatology Clinic, Brussels, and his coauthor in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
The retrospective study comprised 394 patients treated between 2002 and 2010; 117 of them had rosacea with papulopustules and the remainder only demodicosis. Their mean age was 49 years; most (278) were women. They had been treated with one of three doses of BB cream with crotamiton 10% cream: crotamiton applied in the morning, and BB 12% plus crotamiton in the evening; BB 12% plus crotamiton applied twice daily; and BB 20%-24% plus crotamiton applied once in the evening. Demodex densities (Dds) were measured with two consecutive standardized skin surface biopsies and deep biopsies at baseline and follow-up. Symptoms were measured with an investigator global assessment (IGA).
The authors said they had previously found that BB had acaricidal effects on Demodex, as did crotamiton “to a lesser extent,” but that the two treatments have not been well studied. They also referred to the increasing evidence that Demodex has a role in papulopustular rosacea, and that ivermectin, which is acaricidal, is recommended for topical treatment of papulopustular rosacea.
In the study, a mean of 2.7 months after starting treatment, mean Dds were significantly lower for the entire cohort, decreasing by 72.4% (plus or minus 2.6%) from baseline. Dds had normalized in 35% of patients, and in 31% of patients, symptoms had cleared.
Treatment was considered effective in 46% of patients and curative in 20%. Men responded slightly better, with clearance in 34% vs. 20% of women. The two regimens using the higher dose of BB were more effective than those using the lower dose and were associated with better compliance. Compliance overall was 77%.
After a mean of nearly 3 months of treatment, “topical application of BB (with crotamiton) was effective at reducing Dds and clearing clinical symptoms, not only in demodicosis but also in rosacea with papulopustules, indirectly supporting a key role of the mite in the pathophysiology of rosacea,” the authors concluded.
Neither of these products are approved in the United States for treating rosacea.
Dr. Forton disclosed that he occasionally works as a consultant for Galderma; the second author had no disclosures. The study had no funding source.
Source: Forton FMN et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Sep 7. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15938.
FROM JEADV