User login
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
The idea of rationing medical care is anathema to most doctors. Sure, we acknowledge that the realities of health care costs and insurance companies might limit our options, but there is always a sense that when something is truly, truly needed, we can get it done.
Except in one very particular situation, a situation where rationing of care is the norm. That situation? Organ transplantation.
There is no way around this: More patients need organ transplants than there are organs available to transplant. It is cold, hard arithmetic. No amount of negotiating with an insurance company or engaging in prior authorization can change that.
As a kidney doctor, this issue is close to my heart. There are around 100,000 people on the kidney transplant waiting list in the U.S., with 3,000 new patients being added per month. There are only 25,000 kidney transplants per year. And each year, around 5,000 people die while waiting for a transplant.
A world of scarcity, like the world of kidney transplant, is ripe for bias at best and abuse at worst. It is in part for that reason that the Kidney Allocation System exists. It answers the cold, hard arithmetic of transplant scarcity with the cold, hard arithmetic of a computer algorithm, ranking individuals on the waitlist on a variety of factors to ensure that those who will benefit most from a transplant get it first.
This area is a bit complex but I’ll try to break it down into what you need to know. There are 56 organ procurement organizations (OPOs) in the United States. These are nonprofits with the responsibility to recover organs from deceased donors in their area.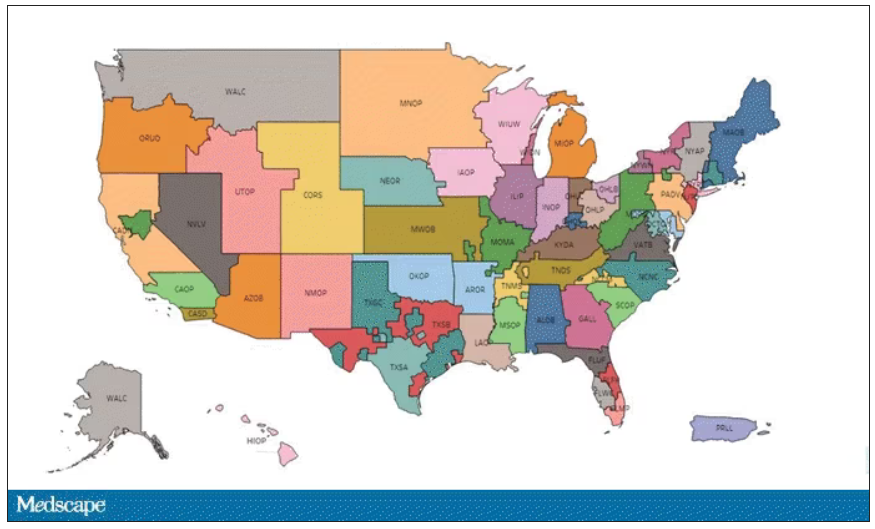
Each of those OPOs maintains a ranked list of those waiting for a kidney transplant. Depending on the OPO, the list may range from a couple hundred people to a couple thousand, but one thing is the same, no matter what: If you are at the top of the list, you should be the next to get a transplant.
Most OPOs have multiple transplant centers in them, and each center is going to prioritize its own patients. If a Yale patient is No. 1 on the list and a kidney offer comes in, it would be a good idea for us to accept, because if we reject the offer, the organ may go to a competing center whose patients is ranked No. 2.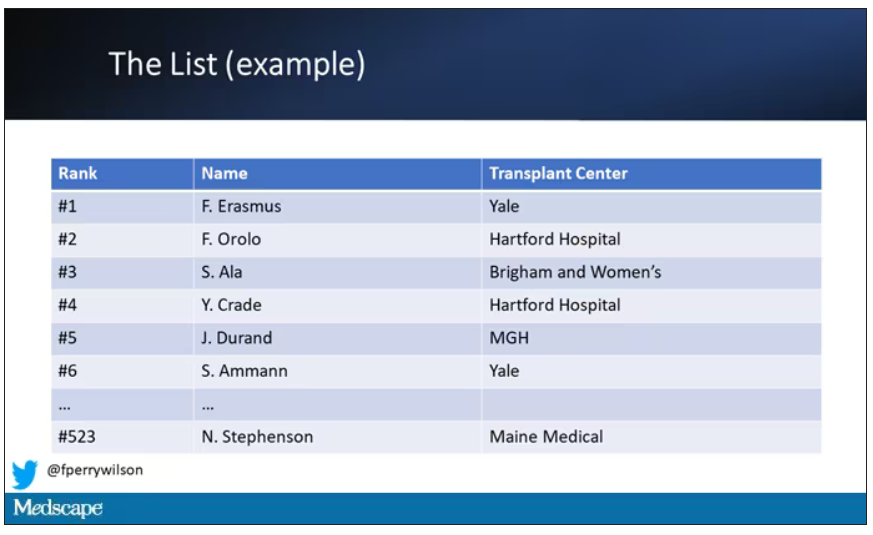
But 11 OPOs around the country are served by only one center. This gives that center huge flexibility to determine who gets what kidney, because if they refuse an offer for whoever is at the top of their list, they can still give the kidney to the second person on their list, or third, or 30th, theoretically.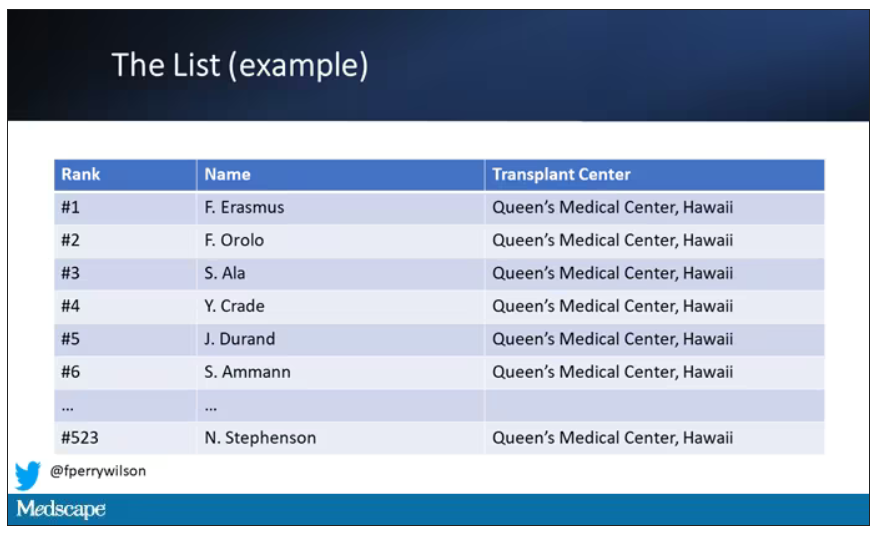
But in practice, does this phenomenon, known colloquially as “list diving,” actually happen? This manuscript from Sumit Mohan and colleagues suggests that it does, and at rates that are, frankly, eye-popping.
The Columbia team used data from the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients to conduct the analysis. The database tracks all aspects of the transplant process, from listing to ranking to, eventually, the transplant itself. With that data, they could determine how often, across these 11 OPOs, the No. 1 person on the list did not get the available kidney.
The answer? Out of 4,668 transplants conducted from 2015 to 2019, the transplant centers skipped their highest-ranked person 3,169 times – 68% of the time.
This graph shows the distribution of where on the list these kidneys went. You can see some centers diving down 100 or 200 places.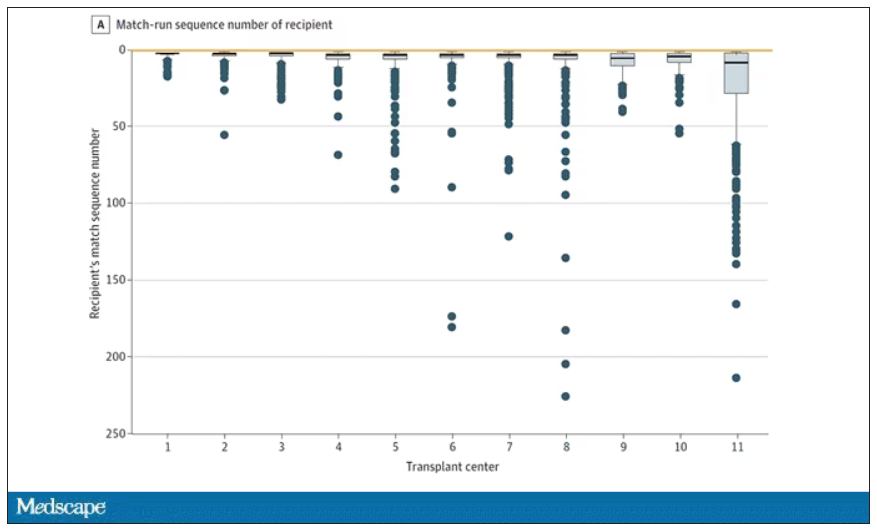
Transplant centers have lists of different lengths, so this graph shows you how far down on the percentage scale the centers dived. You can see centers skipping right to the bottom of their list in some cases.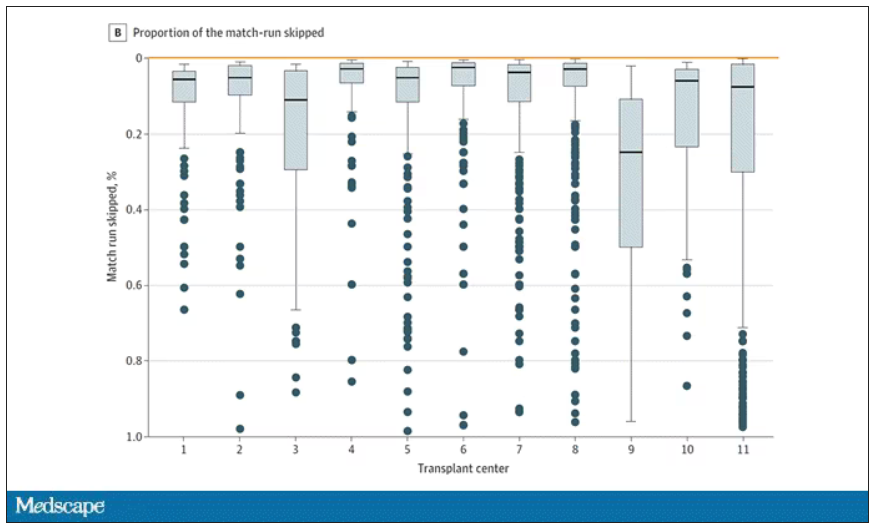
Now, I should make it clear that transplant centers do have legitimate discretion here. Transplant centers may pass up a less-than-perfect kidney for their No. 1 spot, knowing that that individual will get more offers soon, in favor of someone further down the list who will not see an offer for a while. It’s gaming the system a bit, but not, you know, for evil. And the data support this. Top-ranked people who got skipped had received a lower-quality kidney offer than those who did not get skipped. But I will also note that those who were skipped were less likely to be White, less likely to be Hispanic, and more likely to be male. That should raise your eyebrows.
Interestingly, this practice may not be limited to those cases where the OPO has only one transplant center. Conducting the same analysis across all 231 kidney transplant centers in the U.S., the authors found that the top candidate was skipped 76% of the time.
So, what’s going on here? I’m sure that some of this list-skipping is for legitimate medical reasons. And it should be pointed out that recipients have a right to refuse an offer as well – and might be more picky if they know they are at the top of the list. But patient preference was listed as the reason for list diving in only about 14% of cases. The vast majority (65%) of reasons given were based on donor quality. The problem is that donor quality can be quite subjective. And remember, these organs were transplanted eventually so they couldn’t have been that bad.
Putting the data together, though, I can’t shake the sense that centers are using the list more for guidance than as a real mechanism to ensure an equitable allocation system. With all the flexibility that centers have to bypass individuals on the list, the list loses its meaning and its power.
I spoke to one transplant nephrologist who suggested that these data should prompt an investigation by the United Network for Organ Sharing, the body that governs all these OPOs. That may be a necessary step.
I hope there comes a day when this issue is moot, when growing kidneys in the lab – or regenerating one’s own kidneys – is a possibility. But that day is not yet here and we must deal with the scarcity we have. In this world, we need the list to prevent abuse. But the list only works if the list is followed.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, New Haven, Conn. He reported having no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
The idea of rationing medical care is anathema to most doctors. Sure, we acknowledge that the realities of health care costs and insurance companies might limit our options, but there is always a sense that when something is truly, truly needed, we can get it done.
Except in one very particular situation, a situation where rationing of care is the norm. That situation? Organ transplantation.
There is no way around this: More patients need organ transplants than there are organs available to transplant. It is cold, hard arithmetic. No amount of negotiating with an insurance company or engaging in prior authorization can change that.
As a kidney doctor, this issue is close to my heart. There are around 100,000 people on the kidney transplant waiting list in the U.S., with 3,000 new patients being added per month. There are only 25,000 kidney transplants per year. And each year, around 5,000 people die while waiting for a transplant.
A world of scarcity, like the world of kidney transplant, is ripe for bias at best and abuse at worst. It is in part for that reason that the Kidney Allocation System exists. It answers the cold, hard arithmetic of transplant scarcity with the cold, hard arithmetic of a computer algorithm, ranking individuals on the waitlist on a variety of factors to ensure that those who will benefit most from a transplant get it first.
This area is a bit complex but I’ll try to break it down into what you need to know. There are 56 organ procurement organizations (OPOs) in the United States. These are nonprofits with the responsibility to recover organs from deceased donors in their area.
Each of those OPOs maintains a ranked list of those waiting for a kidney transplant. Depending on the OPO, the list may range from a couple hundred people to a couple thousand, but one thing is the same, no matter what: If you are at the top of the list, you should be the next to get a transplant.
Most OPOs have multiple transplant centers in them, and each center is going to prioritize its own patients. If a Yale patient is No. 1 on the list and a kidney offer comes in, it would be a good idea for us to accept, because if we reject the offer, the organ may go to a competing center whose patients is ranked No. 2.
But 11 OPOs around the country are served by only one center. This gives that center huge flexibility to determine who gets what kidney, because if they refuse an offer for whoever is at the top of their list, they can still give the kidney to the second person on their list, or third, or 30th, theoretically.
But in practice, does this phenomenon, known colloquially as “list diving,” actually happen? This manuscript from Sumit Mohan and colleagues suggests that it does, and at rates that are, frankly, eye-popping.
The Columbia team used data from the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients to conduct the analysis. The database tracks all aspects of the transplant process, from listing to ranking to, eventually, the transplant itself. With that data, they could determine how often, across these 11 OPOs, the No. 1 person on the list did not get the available kidney.
The answer? Out of 4,668 transplants conducted from 2015 to 2019, the transplant centers skipped their highest-ranked person 3,169 times – 68% of the time.
This graph shows the distribution of where on the list these kidneys went. You can see some centers diving down 100 or 200 places.
Transplant centers have lists of different lengths, so this graph shows you how far down on the percentage scale the centers dived. You can see centers skipping right to the bottom of their list in some cases.
Now, I should make it clear that transplant centers do have legitimate discretion here. Transplant centers may pass up a less-than-perfect kidney for their No. 1 spot, knowing that that individual will get more offers soon, in favor of someone further down the list who will not see an offer for a while. It’s gaming the system a bit, but not, you know, for evil. And the data support this. Top-ranked people who got skipped had received a lower-quality kidney offer than those who did not get skipped. But I will also note that those who were skipped were less likely to be White, less likely to be Hispanic, and more likely to be male. That should raise your eyebrows.
Interestingly, this practice may not be limited to those cases where the OPO has only one transplant center. Conducting the same analysis across all 231 kidney transplant centers in the U.S., the authors found that the top candidate was skipped 76% of the time.
So, what’s going on here? I’m sure that some of this list-skipping is for legitimate medical reasons. And it should be pointed out that recipients have a right to refuse an offer as well – and might be more picky if they know they are at the top of the list. But patient preference was listed as the reason for list diving in only about 14% of cases. The vast majority (65%) of reasons given were based on donor quality. The problem is that donor quality can be quite subjective. And remember, these organs were transplanted eventually so they couldn’t have been that bad.
Putting the data together, though, I can’t shake the sense that centers are using the list more for guidance than as a real mechanism to ensure an equitable allocation system. With all the flexibility that centers have to bypass individuals on the list, the list loses its meaning and its power.
I spoke to one transplant nephrologist who suggested that these data should prompt an investigation by the United Network for Organ Sharing, the body that governs all these OPOs. That may be a necessary step.
I hope there comes a day when this issue is moot, when growing kidneys in the lab – or regenerating one’s own kidneys – is a possibility. But that day is not yet here and we must deal with the scarcity we have. In this world, we need the list to prevent abuse. But the list only works if the list is followed.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, New Haven, Conn. He reported having no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
The idea of rationing medical care is anathema to most doctors. Sure, we acknowledge that the realities of health care costs and insurance companies might limit our options, but there is always a sense that when something is truly, truly needed, we can get it done.
Except in one very particular situation, a situation where rationing of care is the norm. That situation? Organ transplantation.
There is no way around this: More patients need organ transplants than there are organs available to transplant. It is cold, hard arithmetic. No amount of negotiating with an insurance company or engaging in prior authorization can change that.
As a kidney doctor, this issue is close to my heart. There are around 100,000 people on the kidney transplant waiting list in the U.S., with 3,000 new patients being added per month. There are only 25,000 kidney transplants per year. And each year, around 5,000 people die while waiting for a transplant.
A world of scarcity, like the world of kidney transplant, is ripe for bias at best and abuse at worst. It is in part for that reason that the Kidney Allocation System exists. It answers the cold, hard arithmetic of transplant scarcity with the cold, hard arithmetic of a computer algorithm, ranking individuals on the waitlist on a variety of factors to ensure that those who will benefit most from a transplant get it first.
This area is a bit complex but I’ll try to break it down into what you need to know. There are 56 organ procurement organizations (OPOs) in the United States. These are nonprofits with the responsibility to recover organs from deceased donors in their area.
Each of those OPOs maintains a ranked list of those waiting for a kidney transplant. Depending on the OPO, the list may range from a couple hundred people to a couple thousand, but one thing is the same, no matter what: If you are at the top of the list, you should be the next to get a transplant.
Most OPOs have multiple transplant centers in them, and each center is going to prioritize its own patients. If a Yale patient is No. 1 on the list and a kidney offer comes in, it would be a good idea for us to accept, because if we reject the offer, the organ may go to a competing center whose patients is ranked No. 2.
But 11 OPOs around the country are served by only one center. This gives that center huge flexibility to determine who gets what kidney, because if they refuse an offer for whoever is at the top of their list, they can still give the kidney to the second person on their list, or third, or 30th, theoretically.
But in practice, does this phenomenon, known colloquially as “list diving,” actually happen? This manuscript from Sumit Mohan and colleagues suggests that it does, and at rates that are, frankly, eye-popping.
The Columbia team used data from the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients to conduct the analysis. The database tracks all aspects of the transplant process, from listing to ranking to, eventually, the transplant itself. With that data, they could determine how often, across these 11 OPOs, the No. 1 person on the list did not get the available kidney.
The answer? Out of 4,668 transplants conducted from 2015 to 2019, the transplant centers skipped their highest-ranked person 3,169 times – 68% of the time.
This graph shows the distribution of where on the list these kidneys went. You can see some centers diving down 100 or 200 places.
Transplant centers have lists of different lengths, so this graph shows you how far down on the percentage scale the centers dived. You can see centers skipping right to the bottom of their list in some cases.
Now, I should make it clear that transplant centers do have legitimate discretion here. Transplant centers may pass up a less-than-perfect kidney for their No. 1 spot, knowing that that individual will get more offers soon, in favor of someone further down the list who will not see an offer for a while. It’s gaming the system a bit, but not, you know, for evil. And the data support this. Top-ranked people who got skipped had received a lower-quality kidney offer than those who did not get skipped. But I will also note that those who were skipped were less likely to be White, less likely to be Hispanic, and more likely to be male. That should raise your eyebrows.
Interestingly, this practice may not be limited to those cases where the OPO has only one transplant center. Conducting the same analysis across all 231 kidney transplant centers in the U.S., the authors found that the top candidate was skipped 76% of the time.
So, what’s going on here? I’m sure that some of this list-skipping is for legitimate medical reasons. And it should be pointed out that recipients have a right to refuse an offer as well – and might be more picky if they know they are at the top of the list. But patient preference was listed as the reason for list diving in only about 14% of cases. The vast majority (65%) of reasons given were based on donor quality. The problem is that donor quality can be quite subjective. And remember, these organs were transplanted eventually so they couldn’t have been that bad.
Putting the data together, though, I can’t shake the sense that centers are using the list more for guidance than as a real mechanism to ensure an equitable allocation system. With all the flexibility that centers have to bypass individuals on the list, the list loses its meaning and its power.
I spoke to one transplant nephrologist who suggested that these data should prompt an investigation by the United Network for Organ Sharing, the body that governs all these OPOs. That may be a necessary step.
I hope there comes a day when this issue is moot, when growing kidneys in the lab – or regenerating one’s own kidneys – is a possibility. But that day is not yet here and we must deal with the scarcity we have. In this world, we need the list to prevent abuse. But the list only works if the list is followed.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, New Haven, Conn. He reported having no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.