User login
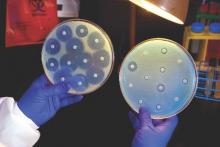
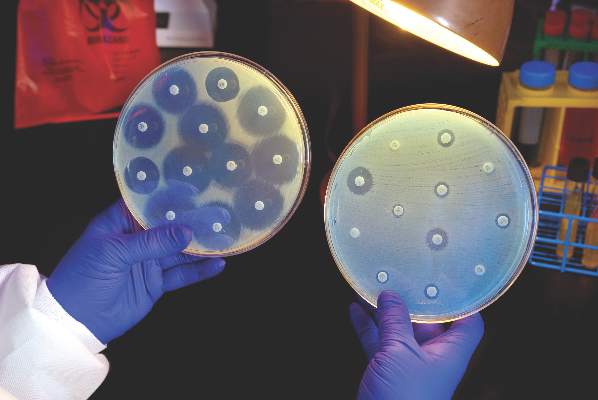
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is providing $67 million to help U.S. health departments address antibiotic resistance and related patient safety concerns.
The new funding was made available through the CDC’s Epidemiology and Laboratory Capacity for Infectious Diseases Cooperative Agreement (ELC), according to a CDC statement, and will support seven new regional laboratories with specialized capabilities allowing rapid detection and identification of emerging antibiotic resistant threats.
The CDC said it would distribute funds to all 50 state health departments, six local health departments (Chicago, the District of Columbia, Houston, Los Angeles County, New York City, and Philadelphia), and Puerto Rico, beginning Aug. 1, 2016. The agency said the grants would allow every state health department lab to test for carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae and ultimately perform whole genome sequencing on intestinal bacteria, including Salmonella, Shigella, and many Campylobacter strains.
The agency intends to provide support teams in nine state health departments for rapid response activities designed to “quickly identify and respond to the threat” of antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea in the United States, and will support high-level expertise to implement antimicrobial resistance activities in six states.
The CDC also said the promised funding would strengthen states’ ability to conduct foodborne disease tracking, investigation, and prevention, as it includes increased support for the PulseNet and OutbreakNet systems and for the Integrated Food Safety Centers of Excellence, as well as support for the National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS).
Global partnerships
Complementing the new CDC grants was an announcement from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services that it would partner with the Wellcome Trust of London, the AMR Centre of Alderley Park (Cheshire, U.K.), and Boston University School of Law to create one of the world’s largest public-private partnerships focused on preclinical discovery and development of new antimicrobial products.
According to an HHS statement, the Combating Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria Biopharmaceutical Accelerator (CARB-X) will bring together “multiple domestic and international partners and capabilities to find potential antibiotics and move them through preclinical testing to enable safety and efficacy testing in humans and greatly reducing the business risk,” to make antimicrobial development more attractive to private sector investment.
HHS said the federal Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) would provide $30 million during the first year of CARB-X, and up to $250 million during the 5-year project. CARB-X will provide funding for research and development, and technical assistance for companies with innovative and promising solutions to antibiotic resistance, HHS said.
“Our hope is that the combination of technical expertise and life science entrepreneurship experience within the CARB-X’s life science accelerators will remove barriers for companies pursuing the development of the next novel drug, diagnostic, or vaccine to combat this public health threat,” said Joe Larsen, PhD, acting BARDA deputy director, in the HHS statement.
On Twitter @richpizzi
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is providing $67 million to help U.S. health departments address antibiotic resistance and related patient safety concerns.
The new funding was made available through the CDC’s Epidemiology and Laboratory Capacity for Infectious Diseases Cooperative Agreement (ELC), according to a CDC statement, and will support seven new regional laboratories with specialized capabilities allowing rapid detection and identification of emerging antibiotic resistant threats.
The CDC said it would distribute funds to all 50 state health departments, six local health departments (Chicago, the District of Columbia, Houston, Los Angeles County, New York City, and Philadelphia), and Puerto Rico, beginning Aug. 1, 2016. The agency said the grants would allow every state health department lab to test for carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae and ultimately perform whole genome sequencing on intestinal bacteria, including Salmonella, Shigella, and many Campylobacter strains.
The agency intends to provide support teams in nine state health departments for rapid response activities designed to “quickly identify and respond to the threat” of antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea in the United States, and will support high-level expertise to implement antimicrobial resistance activities in six states.
The CDC also said the promised funding would strengthen states’ ability to conduct foodborne disease tracking, investigation, and prevention, as it includes increased support for the PulseNet and OutbreakNet systems and for the Integrated Food Safety Centers of Excellence, as well as support for the National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS).
Global partnerships
Complementing the new CDC grants was an announcement from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services that it would partner with the Wellcome Trust of London, the AMR Centre of Alderley Park (Cheshire, U.K.), and Boston University School of Law to create one of the world’s largest public-private partnerships focused on preclinical discovery and development of new antimicrobial products.
According to an HHS statement, the Combating Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria Biopharmaceutical Accelerator (CARB-X) will bring together “multiple domestic and international partners and capabilities to find potential antibiotics and move them through preclinical testing to enable safety and efficacy testing in humans and greatly reducing the business risk,” to make antimicrobial development more attractive to private sector investment.
HHS said the federal Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) would provide $30 million during the first year of CARB-X, and up to $250 million during the 5-year project. CARB-X will provide funding for research and development, and technical assistance for companies with innovative and promising solutions to antibiotic resistance, HHS said.
“Our hope is that the combination of technical expertise and life science entrepreneurship experience within the CARB-X’s life science accelerators will remove barriers for companies pursuing the development of the next novel drug, diagnostic, or vaccine to combat this public health threat,” said Joe Larsen, PhD, acting BARDA deputy director, in the HHS statement.
On Twitter @richpizzi
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is providing $67 million to help U.S. health departments address antibiotic resistance and related patient safety concerns.
The new funding was made available through the CDC’s Epidemiology and Laboratory Capacity for Infectious Diseases Cooperative Agreement (ELC), according to a CDC statement, and will support seven new regional laboratories with specialized capabilities allowing rapid detection and identification of emerging antibiotic resistant threats.
The CDC said it would distribute funds to all 50 state health departments, six local health departments (Chicago, the District of Columbia, Houston, Los Angeles County, New York City, and Philadelphia), and Puerto Rico, beginning Aug. 1, 2016. The agency said the grants would allow every state health department lab to test for carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae and ultimately perform whole genome sequencing on intestinal bacteria, including Salmonella, Shigella, and many Campylobacter strains.
The agency intends to provide support teams in nine state health departments for rapid response activities designed to “quickly identify and respond to the threat” of antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea in the United States, and will support high-level expertise to implement antimicrobial resistance activities in six states.
The CDC also said the promised funding would strengthen states’ ability to conduct foodborne disease tracking, investigation, and prevention, as it includes increased support for the PulseNet and OutbreakNet systems and for the Integrated Food Safety Centers of Excellence, as well as support for the National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS).
Global partnerships
Complementing the new CDC grants was an announcement from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services that it would partner with the Wellcome Trust of London, the AMR Centre of Alderley Park (Cheshire, U.K.), and Boston University School of Law to create one of the world’s largest public-private partnerships focused on preclinical discovery and development of new antimicrobial products.
According to an HHS statement, the Combating Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria Biopharmaceutical Accelerator (CARB-X) will bring together “multiple domestic and international partners and capabilities to find potential antibiotics and move them through preclinical testing to enable safety and efficacy testing in humans and greatly reducing the business risk,” to make antimicrobial development more attractive to private sector investment.
HHS said the federal Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) would provide $30 million during the first year of CARB-X, and up to $250 million during the 5-year project. CARB-X will provide funding for research and development, and technical assistance for companies with innovative and promising solutions to antibiotic resistance, HHS said.
“Our hope is that the combination of technical expertise and life science entrepreneurship experience within the CARB-X’s life science accelerators will remove barriers for companies pursuing the development of the next novel drug, diagnostic, or vaccine to combat this public health threat,” said Joe Larsen, PhD, acting BARDA deputy director, in the HHS statement.
On Twitter @richpizzi