User login
A Paradox? Higher Male Fertility Seen With Inflammatory Arthritis
TOPLINE:
Men with an inflammatory arthritis (IA) diagnosis are less likely to be childless than healthy comparators, according to an epidemiological study.
METHODS:
- 10,865 men in the Norwegian Arthritis Registry were compared with 54,325 men without IA, matched by age and location.
- In the arthritis group, 37% had rheumatoid arthritis, 33% had psoriatic arthritis, and 30% had spondyloarthritis.
- Researchers used childlessness and number of children as proxies for male fertility.
TAKEAWAY:
- 21% of men with IA were childless compared with 27% in the healthy cohort (P < .001).
- On an average, a man with IA had 1.80 children whereas a man in the control group had 1.69 children (P < .001).
- These findings were consistent over time, but the most pronounced difference between groups was seen in men diagnosed after the year 2000.
IN PRACTICE:
The finding “is novel and generates new hypotheses regarding associations between fertility, inflammatory rheumatic diseases, and immune-modulating drugs,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Gudrun David Sigmo, of the department of rheumatology at Stavanger (Norway) University Hospital, and colleagues had their work published online on January 23, 2024, in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis relied on administrative data, and researchers did not have data on confounding factors.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the nonprofit organizations Aslaug Anders fond, Astri og Edvard Riisøens legat, Det alminnelige medisinske forskningsfond, Pahles legat, and Fagsenter for medisins-ke kvalitetsregistre i Helse Vest. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Men with an inflammatory arthritis (IA) diagnosis are less likely to be childless than healthy comparators, according to an epidemiological study.
METHODS:
- 10,865 men in the Norwegian Arthritis Registry were compared with 54,325 men without IA, matched by age and location.
- In the arthritis group, 37% had rheumatoid arthritis, 33% had psoriatic arthritis, and 30% had spondyloarthritis.
- Researchers used childlessness and number of children as proxies for male fertility.
TAKEAWAY:
- 21% of men with IA were childless compared with 27% in the healthy cohort (P < .001).
- On an average, a man with IA had 1.80 children whereas a man in the control group had 1.69 children (P < .001).
- These findings were consistent over time, but the most pronounced difference between groups was seen in men diagnosed after the year 2000.
IN PRACTICE:
The finding “is novel and generates new hypotheses regarding associations between fertility, inflammatory rheumatic diseases, and immune-modulating drugs,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Gudrun David Sigmo, of the department of rheumatology at Stavanger (Norway) University Hospital, and colleagues had their work published online on January 23, 2024, in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis relied on administrative data, and researchers did not have data on confounding factors.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the nonprofit organizations Aslaug Anders fond, Astri og Edvard Riisøens legat, Det alminnelige medisinske forskningsfond, Pahles legat, and Fagsenter for medisins-ke kvalitetsregistre i Helse Vest. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Men with an inflammatory arthritis (IA) diagnosis are less likely to be childless than healthy comparators, according to an epidemiological study.
METHODS:
- 10,865 men in the Norwegian Arthritis Registry were compared with 54,325 men without IA, matched by age and location.
- In the arthritis group, 37% had rheumatoid arthritis, 33% had psoriatic arthritis, and 30% had spondyloarthritis.
- Researchers used childlessness and number of children as proxies for male fertility.
TAKEAWAY:
- 21% of men with IA were childless compared with 27% in the healthy cohort (P < .001).
- On an average, a man with IA had 1.80 children whereas a man in the control group had 1.69 children (P < .001).
- These findings were consistent over time, but the most pronounced difference between groups was seen in men diagnosed after the year 2000.
IN PRACTICE:
The finding “is novel and generates new hypotheses regarding associations between fertility, inflammatory rheumatic diseases, and immune-modulating drugs,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Gudrun David Sigmo, of the department of rheumatology at Stavanger (Norway) University Hospital, and colleagues had their work published online on January 23, 2024, in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis relied on administrative data, and researchers did not have data on confounding factors.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the nonprofit organizations Aslaug Anders fond, Astri og Edvard Riisøens legat, Det alminnelige medisinske forskningsfond, Pahles legat, and Fagsenter for medisins-ke kvalitetsregistre i Helse Vest. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vibrating Belt Receives Approval to Help Women With Osteopenia Keep Bone Strength
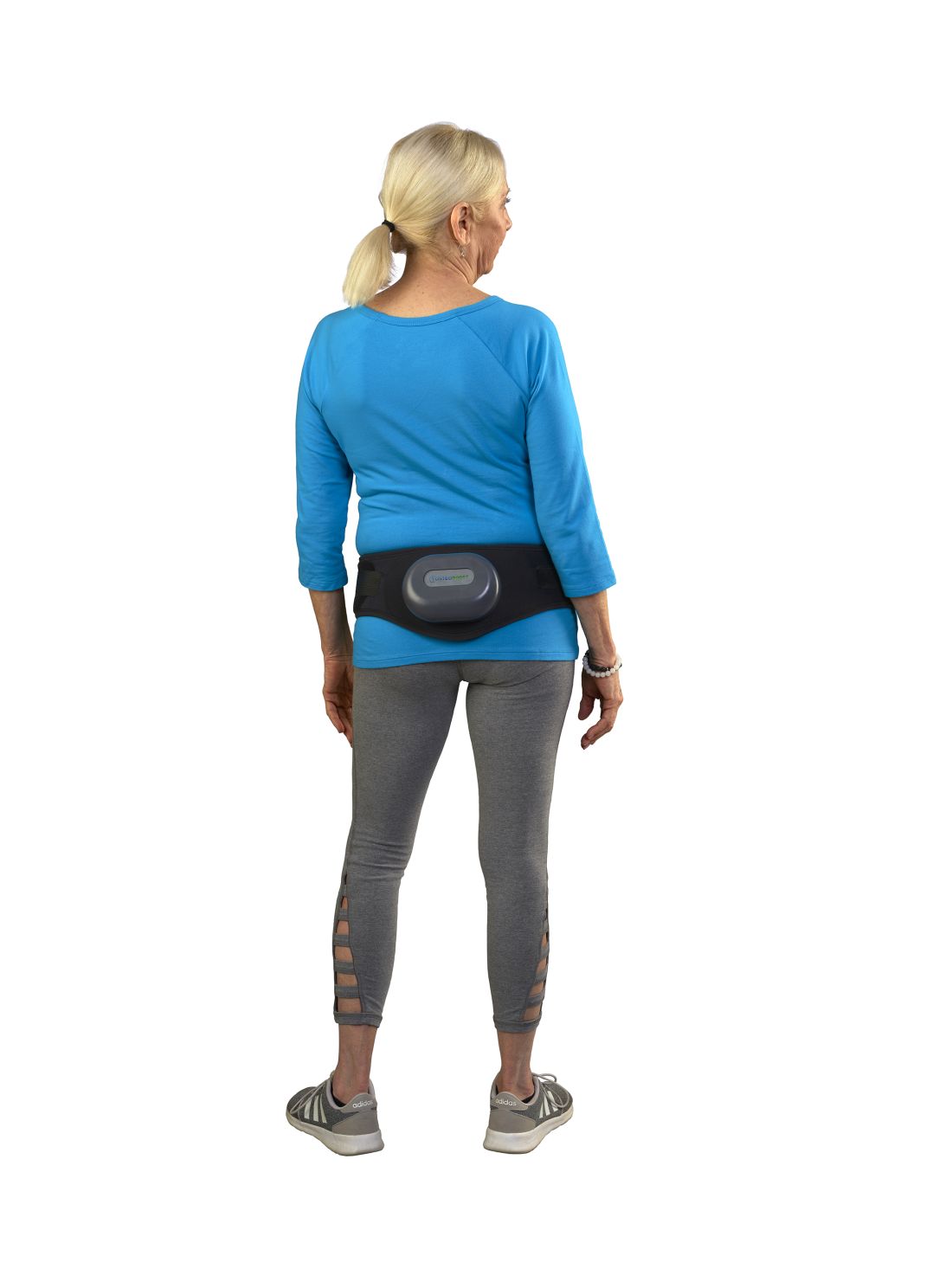
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a wearable belt device for postmenopausal women with osteopenia, the precursor to osteoporosis, according to the company’s manufacturer, Bone Health Technologies.
According to the company, the device (Osteoboost) is the first nonpharmacologic device-based, prescription-only treatment for postmenopausal women with low bone density. It has not been tested for ability to reduce fracture risk.
The device is worn around the hips and delivers calibrated mild vibrations to the hips and lumbar spine to help preserve bone strength and density. A vibration pack is mounted to the back of the belt.
FDA approval, announced on January 18, was based on the findings of a National Institutes of Health–funded double-blinded, sham-controlled study of 126 women with low bone density conducted at the University of Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha. The data were shared at the 2023 Endocrine Society and American Society for Bone and Mineral Research annual meetings and published in the Journal of the Endocrine Society.
Lead investigator Laura D. Bilek, PT, PhD, associate dean for research and associate professor at the University of Nebraska, and colleagues wrote that the primary outcome measurement was the change in vertebral strength measured by CT scans for women who used the device a minimum of three times per week compared with a sham group who wore a belt that emitted sound but had no vibrations.
Compressive strength and volumetric density of the first lumbar vertebra were analyzed.
In the active-belt group, women lost, on average, 0.48% bone strength, while those in the sham group lost nearly 2.84% (P = .014), about five times as much. Results also showed that participants in the active treatment group who used the device three times per week lost 0.29% bone mineral density (BMD) compared with the 1.97% BMD lost in the control group. No adverse events were reported in the study.
Sonali Khandelwal, MD, a rheumatologist at Rush University in Chicago, told this news organization there’s considerable fear among some patients about long-term use of available medications for bone health, “so any modality that is nontherapeutic — not a pill — is always exciting.”
The endpoints of the study are one good measure, she said, but she emphasized that it will be important to show that the improved bone density from the belt that is described in this study “is a true marker of decreased fracture risk.”
Because there are no apparent side effects, she said it may be effective in combination with weight-bearing exercise, vitamin D and calcium, and/or medication, depending on severity of bone loss.
Current medications on the market for osteoporosis have been shown to improve bone strength and reduce fracture risk, she noted.
“It could help; I just don’t think we have enough evidence that it will completely treat the bone loss,” Dr. Khandelwal said.
She said she sees the potential population most interested in the belt as premenopausal women with a family history of bone loss who may not meet the level of bone loss for medical management but are interested in prevention.
“I also think of individuals who might already meet medication needs but are completely averse to being on medication,” she said. The bulk of her practice is treating bone loss, she said, estimating that 20% of her patients do not want to be on medication.
Bone Health Technologies CEO Laura Yecies, MBA, told this news organization the company has not yet set the price for the device and noted that because it will be available by prescription only, out-of-pocket costs and copays will differ. She said the company expects to begin shipping later this year. Requests for update notifications can be made at the company’s website.
Dr. Bilek told this news organization the device was tested for a year, so it’s unclear how long people with osteopenia would need to wear the belt for maximum benefit.
The theory behind the mechanism of action, she said, “is that the vibration actually inhibits the cells [osteoclasts] that take away bone mass.”
The researchers included only postmenopausal women with osteopenia in the study, but Dr. Bilek said she would like to test the device on other groups, such as men with prostate cancer getting testosterone-blocking therapy, which can result in loss of bone density. An estimated 34 million people in the United States have osteopenia.
Dr. Bilek said a next step for the study is to enroll a more diverse cohort at an additional center to test the device because most of the women in this one were White.
She noted that women’s bone mass peaks at age 30 and then starts to decline.
“When women hit menopause, there’s a really rapid decline [in bone strength] for the next 5-7 years and then the decline levels off. If we can slow that decline, hopefully that woman’s bone density is maintained at a higher level throughout their life,” Dr. Bilek said.
Dr. Bilek is a scientific adviser to Bone Health Technologies. She and many coauthors of the study received grants or fees from the company and own stock in or are employees of the company. Ms. Yecies is the founder and CEO of Bone Health Technologies. Dr. Khandelwal had no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a wearable belt device for postmenopausal women with osteopenia, the precursor to osteoporosis, according to the company’s manufacturer, Bone Health Technologies.
According to the company, the device (Osteoboost) is the first nonpharmacologic device-based, prescription-only treatment for postmenopausal women with low bone density. It has not been tested for ability to reduce fracture risk.
The device is worn around the hips and delivers calibrated mild vibrations to the hips and lumbar spine to help preserve bone strength and density. A vibration pack is mounted to the back of the belt.
FDA approval, announced on January 18, was based on the findings of a National Institutes of Health–funded double-blinded, sham-controlled study of 126 women with low bone density conducted at the University of Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha. The data were shared at the 2023 Endocrine Society and American Society for Bone and Mineral Research annual meetings and published in the Journal of the Endocrine Society.
Lead investigator Laura D. Bilek, PT, PhD, associate dean for research and associate professor at the University of Nebraska, and colleagues wrote that the primary outcome measurement was the change in vertebral strength measured by CT scans for women who used the device a minimum of three times per week compared with a sham group who wore a belt that emitted sound but had no vibrations.
Compressive strength and volumetric density of the first lumbar vertebra were analyzed.
In the active-belt group, women lost, on average, 0.48% bone strength, while those in the sham group lost nearly 2.84% (P = .014), about five times as much. Results also showed that participants in the active treatment group who used the device three times per week lost 0.29% bone mineral density (BMD) compared with the 1.97% BMD lost in the control group. No adverse events were reported in the study.
Sonali Khandelwal, MD, a rheumatologist at Rush University in Chicago, told this news organization there’s considerable fear among some patients about long-term use of available medications for bone health, “so any modality that is nontherapeutic — not a pill — is always exciting.”
The endpoints of the study are one good measure, she said, but she emphasized that it will be important to show that the improved bone density from the belt that is described in this study “is a true marker of decreased fracture risk.”
Because there are no apparent side effects, she said it may be effective in combination with weight-bearing exercise, vitamin D and calcium, and/or medication, depending on severity of bone loss.
Current medications on the market for osteoporosis have been shown to improve bone strength and reduce fracture risk, she noted.
“It could help; I just don’t think we have enough evidence that it will completely treat the bone loss,” Dr. Khandelwal said.
She said she sees the potential population most interested in the belt as premenopausal women with a family history of bone loss who may not meet the level of bone loss for medical management but are interested in prevention.
“I also think of individuals who might already meet medication needs but are completely averse to being on medication,” she said. The bulk of her practice is treating bone loss, she said, estimating that 20% of her patients do not want to be on medication.
Bone Health Technologies CEO Laura Yecies, MBA, told this news organization the company has not yet set the price for the device and noted that because it will be available by prescription only, out-of-pocket costs and copays will differ. She said the company expects to begin shipping later this year. Requests for update notifications can be made at the company’s website.
Dr. Bilek told this news organization the device was tested for a year, so it’s unclear how long people with osteopenia would need to wear the belt for maximum benefit.
The theory behind the mechanism of action, she said, “is that the vibration actually inhibits the cells [osteoclasts] that take away bone mass.”
The researchers included only postmenopausal women with osteopenia in the study, but Dr. Bilek said she would like to test the device on other groups, such as men with prostate cancer getting testosterone-blocking therapy, which can result in loss of bone density. An estimated 34 million people in the United States have osteopenia.
Dr. Bilek said a next step for the study is to enroll a more diverse cohort at an additional center to test the device because most of the women in this one were White.
She noted that women’s bone mass peaks at age 30 and then starts to decline.
“When women hit menopause, there’s a really rapid decline [in bone strength] for the next 5-7 years and then the decline levels off. If we can slow that decline, hopefully that woman’s bone density is maintained at a higher level throughout their life,” Dr. Bilek said.
Dr. Bilek is a scientific adviser to Bone Health Technologies. She and many coauthors of the study received grants or fees from the company and own stock in or are employees of the company. Ms. Yecies is the founder and CEO of Bone Health Technologies. Dr. Khandelwal had no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a wearable belt device for postmenopausal women with osteopenia, the precursor to osteoporosis, according to the company’s manufacturer, Bone Health Technologies.
According to the company, the device (Osteoboost) is the first nonpharmacologic device-based, prescription-only treatment for postmenopausal women with low bone density. It has not been tested for ability to reduce fracture risk.
The device is worn around the hips and delivers calibrated mild vibrations to the hips and lumbar spine to help preserve bone strength and density. A vibration pack is mounted to the back of the belt.
FDA approval, announced on January 18, was based on the findings of a National Institutes of Health–funded double-blinded, sham-controlled study of 126 women with low bone density conducted at the University of Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha. The data were shared at the 2023 Endocrine Society and American Society for Bone and Mineral Research annual meetings and published in the Journal of the Endocrine Society.
Lead investigator Laura D. Bilek, PT, PhD, associate dean for research and associate professor at the University of Nebraska, and colleagues wrote that the primary outcome measurement was the change in vertebral strength measured by CT scans for women who used the device a minimum of three times per week compared with a sham group who wore a belt that emitted sound but had no vibrations.
Compressive strength and volumetric density of the first lumbar vertebra were analyzed.
In the active-belt group, women lost, on average, 0.48% bone strength, while those in the sham group lost nearly 2.84% (P = .014), about five times as much. Results also showed that participants in the active treatment group who used the device three times per week lost 0.29% bone mineral density (BMD) compared with the 1.97% BMD lost in the control group. No adverse events were reported in the study.
Sonali Khandelwal, MD, a rheumatologist at Rush University in Chicago, told this news organization there’s considerable fear among some patients about long-term use of available medications for bone health, “so any modality that is nontherapeutic — not a pill — is always exciting.”
The endpoints of the study are one good measure, she said, but she emphasized that it will be important to show that the improved bone density from the belt that is described in this study “is a true marker of decreased fracture risk.”
Because there are no apparent side effects, she said it may be effective in combination with weight-bearing exercise, vitamin D and calcium, and/or medication, depending on severity of bone loss.
Current medications on the market for osteoporosis have been shown to improve bone strength and reduce fracture risk, she noted.
“It could help; I just don’t think we have enough evidence that it will completely treat the bone loss,” Dr. Khandelwal said.
She said she sees the potential population most interested in the belt as premenopausal women with a family history of bone loss who may not meet the level of bone loss for medical management but are interested in prevention.
“I also think of individuals who might already meet medication needs but are completely averse to being on medication,” she said. The bulk of her practice is treating bone loss, she said, estimating that 20% of her patients do not want to be on medication.
Bone Health Technologies CEO Laura Yecies, MBA, told this news organization the company has not yet set the price for the device and noted that because it will be available by prescription only, out-of-pocket costs and copays will differ. She said the company expects to begin shipping later this year. Requests for update notifications can be made at the company’s website.
Dr. Bilek told this news organization the device was tested for a year, so it’s unclear how long people with osteopenia would need to wear the belt for maximum benefit.
The theory behind the mechanism of action, she said, “is that the vibration actually inhibits the cells [osteoclasts] that take away bone mass.”
The researchers included only postmenopausal women with osteopenia in the study, but Dr. Bilek said she would like to test the device on other groups, such as men with prostate cancer getting testosterone-blocking therapy, which can result in loss of bone density. An estimated 34 million people in the United States have osteopenia.
Dr. Bilek said a next step for the study is to enroll a more diverse cohort at an additional center to test the device because most of the women in this one were White.
She noted that women’s bone mass peaks at age 30 and then starts to decline.
“When women hit menopause, there’s a really rapid decline [in bone strength] for the next 5-7 years and then the decline levels off. If we can slow that decline, hopefully that woman’s bone density is maintained at a higher level throughout their life,” Dr. Bilek said.
Dr. Bilek is a scientific adviser to Bone Health Technologies. She and many coauthors of the study received grants or fees from the company and own stock in or are employees of the company. Ms. Yecies is the founder and CEO of Bone Health Technologies. Dr. Khandelwal had no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is RA Disease Activity Assessed Too Little After Starting TNFi?
TOPLINE:
Less than half of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) initiating a first-line tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) in clinical practice had a recorded composite disease activity assessment at the start of the treatment, and many remained on that treatment for years without evidence recorded in their electronic medical record of achieving low-disease activity or remission.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers reviewed data from 1651 adults aged 18 years and older with moderate to severe RA at baseline or follow-up in the electronic medical record database of the American Rheumatology Network, a large community network of independent practices with > 200 rheumatologists across the United States.
- Patients received a TNFi as their first advanced therapy between January 2014 and August 2021 and were assessed for measurement of disease activity with the Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) or Routine Assessment of Patient Index Data 3 (RAPID3) at baseline and follow-up visits.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among the patients with moderate to severe RA, 47.2% of patients remained on first-line TNFi therapy 1 year after initiation despite no evidence of achieving treatment targets of low disease activity or remission (defined as CDAI ≤ 10 and/or RAPID3 ≤ 2).
- Approximately one third of patients remained on TNFi therapy for 2 (38.1%) or 3 (35.4%) years after initiation despite not achieving these targets. The median times to TNFi discontinuation was 30.4 months and to subsequent therapy initiation 68.3 months.
- A total of 52% discontinued their initial TNFi during the study period; among those who started a second therapy, 15% restarted the same TNFi, 45.6% started another TNFi, 27.6% started a non-TNFi biologic, and 11.5% started a Janus kinase inhibitor.
- The most common reported reasons for discontinuation were a combination of efficacy and intolerance, efficacy only, and intolerance only (26.9%, 25.3%, and 20.3%, respectively).
- Persistent pain was the most common reason for efficacy-related discontinuation (39.0%), followed by persistent inflammation/swelling and overall general discomfort (31.8% for both).
IN PRACTICE:
“Consistent monitoring of treatment response and timely switch to effective therapy as appropriate is needed in patients with RA initiating their first advanced therapies,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Colin Edgerton, MD, of Articularis Healthcare Group and American Rheumatology Network, Charleston, South Carolina, reported their work on January 14, 2024, in ACR Open Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design, incomplete data from electronic medical records, and reliance on physician documentation for drivers of discontinuation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by AbbVie. Lead author Edgerton also disclosed relationships with Novartis and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Less than half of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) initiating a first-line tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) in clinical practice had a recorded composite disease activity assessment at the start of the treatment, and many remained on that treatment for years without evidence recorded in their electronic medical record of achieving low-disease activity or remission.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers reviewed data from 1651 adults aged 18 years and older with moderate to severe RA at baseline or follow-up in the electronic medical record database of the American Rheumatology Network, a large community network of independent practices with > 200 rheumatologists across the United States.
- Patients received a TNFi as their first advanced therapy between January 2014 and August 2021 and were assessed for measurement of disease activity with the Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) or Routine Assessment of Patient Index Data 3 (RAPID3) at baseline and follow-up visits.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among the patients with moderate to severe RA, 47.2% of patients remained on first-line TNFi therapy 1 year after initiation despite no evidence of achieving treatment targets of low disease activity or remission (defined as CDAI ≤ 10 and/or RAPID3 ≤ 2).
- Approximately one third of patients remained on TNFi therapy for 2 (38.1%) or 3 (35.4%) years after initiation despite not achieving these targets. The median times to TNFi discontinuation was 30.4 months and to subsequent therapy initiation 68.3 months.
- A total of 52% discontinued their initial TNFi during the study period; among those who started a second therapy, 15% restarted the same TNFi, 45.6% started another TNFi, 27.6% started a non-TNFi biologic, and 11.5% started a Janus kinase inhibitor.
- The most common reported reasons for discontinuation were a combination of efficacy and intolerance, efficacy only, and intolerance only (26.9%, 25.3%, and 20.3%, respectively).
- Persistent pain was the most common reason for efficacy-related discontinuation (39.0%), followed by persistent inflammation/swelling and overall general discomfort (31.8% for both).
IN PRACTICE:
“Consistent monitoring of treatment response and timely switch to effective therapy as appropriate is needed in patients with RA initiating their first advanced therapies,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Colin Edgerton, MD, of Articularis Healthcare Group and American Rheumatology Network, Charleston, South Carolina, reported their work on January 14, 2024, in ACR Open Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design, incomplete data from electronic medical records, and reliance on physician documentation for drivers of discontinuation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by AbbVie. Lead author Edgerton also disclosed relationships with Novartis and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Less than half of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) initiating a first-line tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) in clinical practice had a recorded composite disease activity assessment at the start of the treatment, and many remained on that treatment for years without evidence recorded in their electronic medical record of achieving low-disease activity or remission.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers reviewed data from 1651 adults aged 18 years and older with moderate to severe RA at baseline or follow-up in the electronic medical record database of the American Rheumatology Network, a large community network of independent practices with > 200 rheumatologists across the United States.
- Patients received a TNFi as their first advanced therapy between January 2014 and August 2021 and were assessed for measurement of disease activity with the Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) or Routine Assessment of Patient Index Data 3 (RAPID3) at baseline and follow-up visits.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among the patients with moderate to severe RA, 47.2% of patients remained on first-line TNFi therapy 1 year after initiation despite no evidence of achieving treatment targets of low disease activity or remission (defined as CDAI ≤ 10 and/or RAPID3 ≤ 2).
- Approximately one third of patients remained on TNFi therapy for 2 (38.1%) or 3 (35.4%) years after initiation despite not achieving these targets. The median times to TNFi discontinuation was 30.4 months and to subsequent therapy initiation 68.3 months.
- A total of 52% discontinued their initial TNFi during the study period; among those who started a second therapy, 15% restarted the same TNFi, 45.6% started another TNFi, 27.6% started a non-TNFi biologic, and 11.5% started a Janus kinase inhibitor.
- The most common reported reasons for discontinuation were a combination of efficacy and intolerance, efficacy only, and intolerance only (26.9%, 25.3%, and 20.3%, respectively).
- Persistent pain was the most common reason for efficacy-related discontinuation (39.0%), followed by persistent inflammation/swelling and overall general discomfort (31.8% for both).
IN PRACTICE:
“Consistent monitoring of treatment response and timely switch to effective therapy as appropriate is needed in patients with RA initiating their first advanced therapies,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Colin Edgerton, MD, of Articularis Healthcare Group and American Rheumatology Network, Charleston, South Carolina, reported their work on January 14, 2024, in ACR Open Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design, incomplete data from electronic medical records, and reliance on physician documentation for drivers of discontinuation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by AbbVie. Lead author Edgerton also disclosed relationships with Novartis and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cutaneous lupus, dermatomyositis: Excitement growing around emerging therapies
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — Advances in treating medical conditions rarely emerge in a straight line. Oftentimes, progress comes in fits and starts, and therapies to treat cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) and dermatomyositis are no exception.
Beyond approved treatments that deserve more attention, like belimumab, approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in 2011, and Octagam 10%, an intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) preparation approved for dermatomyositis in 2021, anticipation is growing for emerging therapies and their potential to provide relief to patients, Anthony Fernandez, MD, PhD, said at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference. The tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor deucravacitinib, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors brepocitinib and baricitinib, and the monoclonal antibody anifrolumab, he noted, are prime examples.
“. In my opinion, this is the start of what will be the most exciting decade in the history of these two diseases,” said Dr. Fernandez, director of medical dermatology at the Cleveland Clinic.
Emerging Treatments for Cutaneous Lupus
Although SLE can involve many organ systems, the skin is one of the most affected. There are specific cutaneous lesions categorized as either acute cutaneous lupus, subacute cutaneous lupus, or chronic cutaneous lupus.
The oral TYK2 inhibitor deucravacitinib, for example, should be able to dampen interleukin responses in people with CLE, Dr. Fernandez said. Deucravacitinib was approved by the FDA to treat psoriasis in September 2022.
A phase 2 study published in 2023 focused on this agent for relief of systemic lupus. Improvements in cutaneous disease were a secondary endpoint. The trial demonstrated that the patients treated with deucravacitinib achieved a 56%-70% CLASI-50 response, depending on dosing, compared with a 17% response among those on placebo at week 48.
Based on the trial results, recruitment has begun for a phase 2 trial to evaluate deucravacitinib, compared with placebo, in patients with discoid and/or subacute cutaneous lupus. “This may be another medicine we have available to give to any of our patients with cutaneous lupus,” Dr. Fernandez said.
Anifrolumab Appears Promising
The FDA approval of anifrolumab, a type I interferon (IFN) receptor antagonist, for treating moderate to severe SLE in July 2021, for example, is good news for dermatologists and their patients, added Dr. Fernandez. “Almost immediately after approval, case studies showed marked improvement in patients with refractory cutaneous lupus.” While the therapy was approved for treating systemic lupus, it allows for off-label treatment of the cutaneous predominant form of the disease, he said.
Furthermore, the manufacturer of anifrolumab, AstraZeneca, is launching the LAVENDER clinical trial to assess the monoclonal antibody specifically for treating CLE. “This is a big deal because we may be able to prescribe anifrolumab for our cutaneous lupus patients who don’t have systemic lupus,” Dr. Fernandez said.
Phase 3 data supported use the of anifrolumab in systemic lupus, including the TULIP-2 trial, which demonstrated its superiority to placebo for reducing severity of systemic disease and lowering corticosteroid use. A study published in March 2023 of 11 patients showed that they had a “very fast response” to the agent, Dr. Fernandez said, with a 50% or greater improvement in the Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index activity score reached by all participants at week 16. Improvements of 50% or more in this scoring system are considered clinically meaningful, he added.
Upcoming Dermatomyositis Treatments
Why highlight emerging therapies for CLE and dermatomyositis in the same ODAC presentation? Although distinct conditions, these autoimmune conditions are both mediated by type 1 IFN inflammation.
Dermatomyositis is a relatively rare immune-mediated disease that most commonly affects the skin and muscle. Doctors score disease presentation, activity, and clinical improvements on a scale similar to CLASI for cutaneous lupus, the CDASI or Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index. Among people with CDASI activity scores of at least 14, which is the threshold for moderate to severe disease, a 20% improvement is clinically meaningful, Dr. Fernandez said. In addition, a 40% or greater improvement correlates with significant improvements in quality of life.
There is now more evidence for the use of IVIG to treat dermatomyositis. “Among those of us who treat dermatomyositis on a regular basis, we believe IVIG is the most potent treatment. We’ve known that for a long time,” Dr. Fernandez said.
Despite this tenet, for years, there was only one placebo-controlled trial, published in 1993, that evaluated IVIG treatment for dermatomyositis, and it included only 15 participants. That was until October 2022, he said, when the New England Journal of Medicine published a study comparing a specific brand of IVIG (Octagam) with placebo in 95 people with dermatomyositis.
In the study, 79% of participants treated with IVIG had a total improvement score of at least 20 (minimal improvement), the primary endpoint, at 16 weeks, compared with 44% of those receiving a placebo. Those treated with IVIG also had significant improvements in the CDASI score, a secondary endpoint, compared with those on placebo, he said.
Based on results of this trial, the FDA approved Octagam 10% for dermatomyositis in adults. Dr. Fernandez noted the approval is restricted to the brand of IVIG in the trial, not all IVIG products. However, “the FDA approval is most important to us because it gives us ammunition to fight for insurers to approve IVIG when we feel our patients with dermatomyositis need it,” regardless of the brand.
The Potential of JAK1 Inhibitors
An open-label study of the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib, published in December 2020, showed that mean changes in CDASI activity scores at 12 weeks were statistically significant compared with baseline in 10 people with dermatomyositis. “The importance of this study is that it is proof of concept that JAK inhibition can be effective for treating dermatomyositis, especially with active skin disease,” Dr. Fernandez said.
In addition, two large phase 3 trials are evaluating JAK inhibitor safety and efficacy for treating dermatomyositis. One is the VALOR trial, currently recruiting people with recalcitrant dermatomyositis to evaluate treatment with brepocitinib. Researchers in France are looking at another JAK inhibitor, baricitinib, for treating relapsing or treatment-naive dermatomyositis. Recruitment for the BIRD clinical trial is ongoing.
Monoclonal Antibody Showing Promise
“When it comes to looking specifically at dermatomyositis cutaneous disease, it’s been found that the levels of IFN beta correlate best with not only lesional skin type 1 IFN inflammatory signatures but also overall clinical disease activity,” Dr. Fernandez said. This correlation is stronger than for any other IFN-1-type cytokine active in the disorder.
“Perhaps blocking IFN beta might be best way to get control of dermatomyositis activity,” he added.
With that in mind, a phase 2 trial of dazukibart presented at the American Academy of Dermatology 2023 annual meeting highlighted the promise of this agent that targets type 1 IFN beta.
The primary endpoint was improvement in CDASI at 12 weeks. “This medication has remarkable efficacy,” Dr. Fernandez said. “We were one of the sites for this trial. Despite being blinded, there was no question about who was receiving drug and who was receiving placebo.”
“A minimal clinical improvement in disease activity was seen in more than 90%, so almost every patient who received this medication had meaningful improvement,” he added.
Based on the results, the manufacturer, Pfizer, is recruiting participants for a phase 3 trial to further assess dazukibart in dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Dr. Fernandez said, “This is a story you should pay attention to if you treat any dermatomyositis patients at all.”
Regarding these emerging therapies for CLE and dermatomyositis, “This looks very much like the early days of psoriasis, in the early 2000s, when there was a lot of activity developing treatments,” Dr. Fernandez said. “I will predict that within 10 years, we will have multiple novel agents available that will probably work better than anything we have today.”
Dr. Fernandez reported receiving grant and/or research support from Alexion, Incyte, Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Pfizer, and Priovant Therapeutics; acting as a consultant or advisory board member for AbbVie, Biogen, Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals; and being a member of the speaker bureau or receiving honoraria for non-CME from AbbVie, Kyowa Kirin, and Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — Advances in treating medical conditions rarely emerge in a straight line. Oftentimes, progress comes in fits and starts, and therapies to treat cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) and dermatomyositis are no exception.
Beyond approved treatments that deserve more attention, like belimumab, approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in 2011, and Octagam 10%, an intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) preparation approved for dermatomyositis in 2021, anticipation is growing for emerging therapies and their potential to provide relief to patients, Anthony Fernandez, MD, PhD, said at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference. The tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor deucravacitinib, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors brepocitinib and baricitinib, and the monoclonal antibody anifrolumab, he noted, are prime examples.
“. In my opinion, this is the start of what will be the most exciting decade in the history of these two diseases,” said Dr. Fernandez, director of medical dermatology at the Cleveland Clinic.
Emerging Treatments for Cutaneous Lupus
Although SLE can involve many organ systems, the skin is one of the most affected. There are specific cutaneous lesions categorized as either acute cutaneous lupus, subacute cutaneous lupus, or chronic cutaneous lupus.
The oral TYK2 inhibitor deucravacitinib, for example, should be able to dampen interleukin responses in people with CLE, Dr. Fernandez said. Deucravacitinib was approved by the FDA to treat psoriasis in September 2022.
A phase 2 study published in 2023 focused on this agent for relief of systemic lupus. Improvements in cutaneous disease were a secondary endpoint. The trial demonstrated that the patients treated with deucravacitinib achieved a 56%-70% CLASI-50 response, depending on dosing, compared with a 17% response among those on placebo at week 48.
Based on the trial results, recruitment has begun for a phase 2 trial to evaluate deucravacitinib, compared with placebo, in patients with discoid and/or subacute cutaneous lupus. “This may be another medicine we have available to give to any of our patients with cutaneous lupus,” Dr. Fernandez said.
Anifrolumab Appears Promising
The FDA approval of anifrolumab, a type I interferon (IFN) receptor antagonist, for treating moderate to severe SLE in July 2021, for example, is good news for dermatologists and their patients, added Dr. Fernandez. “Almost immediately after approval, case studies showed marked improvement in patients with refractory cutaneous lupus.” While the therapy was approved for treating systemic lupus, it allows for off-label treatment of the cutaneous predominant form of the disease, he said.
Furthermore, the manufacturer of anifrolumab, AstraZeneca, is launching the LAVENDER clinical trial to assess the monoclonal antibody specifically for treating CLE. “This is a big deal because we may be able to prescribe anifrolumab for our cutaneous lupus patients who don’t have systemic lupus,” Dr. Fernandez said.
Phase 3 data supported use the of anifrolumab in systemic lupus, including the TULIP-2 trial, which demonstrated its superiority to placebo for reducing severity of systemic disease and lowering corticosteroid use. A study published in March 2023 of 11 patients showed that they had a “very fast response” to the agent, Dr. Fernandez said, with a 50% or greater improvement in the Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index activity score reached by all participants at week 16. Improvements of 50% or more in this scoring system are considered clinically meaningful, he added.
Upcoming Dermatomyositis Treatments
Why highlight emerging therapies for CLE and dermatomyositis in the same ODAC presentation? Although distinct conditions, these autoimmune conditions are both mediated by type 1 IFN inflammation.
Dermatomyositis is a relatively rare immune-mediated disease that most commonly affects the skin and muscle. Doctors score disease presentation, activity, and clinical improvements on a scale similar to CLASI for cutaneous lupus, the CDASI or Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index. Among people with CDASI activity scores of at least 14, which is the threshold for moderate to severe disease, a 20% improvement is clinically meaningful, Dr. Fernandez said. In addition, a 40% or greater improvement correlates with significant improvements in quality of life.
There is now more evidence for the use of IVIG to treat dermatomyositis. “Among those of us who treat dermatomyositis on a regular basis, we believe IVIG is the most potent treatment. We’ve known that for a long time,” Dr. Fernandez said.
Despite this tenet, for years, there was only one placebo-controlled trial, published in 1993, that evaluated IVIG treatment for dermatomyositis, and it included only 15 participants. That was until October 2022, he said, when the New England Journal of Medicine published a study comparing a specific brand of IVIG (Octagam) with placebo in 95 people with dermatomyositis.
In the study, 79% of participants treated with IVIG had a total improvement score of at least 20 (minimal improvement), the primary endpoint, at 16 weeks, compared with 44% of those receiving a placebo. Those treated with IVIG also had significant improvements in the CDASI score, a secondary endpoint, compared with those on placebo, he said.
Based on results of this trial, the FDA approved Octagam 10% for dermatomyositis in adults. Dr. Fernandez noted the approval is restricted to the brand of IVIG in the trial, not all IVIG products. However, “the FDA approval is most important to us because it gives us ammunition to fight for insurers to approve IVIG when we feel our patients with dermatomyositis need it,” regardless of the brand.
The Potential of JAK1 Inhibitors
An open-label study of the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib, published in December 2020, showed that mean changes in CDASI activity scores at 12 weeks were statistically significant compared with baseline in 10 people with dermatomyositis. “The importance of this study is that it is proof of concept that JAK inhibition can be effective for treating dermatomyositis, especially with active skin disease,” Dr. Fernandez said.
In addition, two large phase 3 trials are evaluating JAK inhibitor safety and efficacy for treating dermatomyositis. One is the VALOR trial, currently recruiting people with recalcitrant dermatomyositis to evaluate treatment with brepocitinib. Researchers in France are looking at another JAK inhibitor, baricitinib, for treating relapsing or treatment-naive dermatomyositis. Recruitment for the BIRD clinical trial is ongoing.
Monoclonal Antibody Showing Promise
“When it comes to looking specifically at dermatomyositis cutaneous disease, it’s been found that the levels of IFN beta correlate best with not only lesional skin type 1 IFN inflammatory signatures but also overall clinical disease activity,” Dr. Fernandez said. This correlation is stronger than for any other IFN-1-type cytokine active in the disorder.
“Perhaps blocking IFN beta might be best way to get control of dermatomyositis activity,” he added.
With that in mind, a phase 2 trial of dazukibart presented at the American Academy of Dermatology 2023 annual meeting highlighted the promise of this agent that targets type 1 IFN beta.
The primary endpoint was improvement in CDASI at 12 weeks. “This medication has remarkable efficacy,” Dr. Fernandez said. “We were one of the sites for this trial. Despite being blinded, there was no question about who was receiving drug and who was receiving placebo.”
“A minimal clinical improvement in disease activity was seen in more than 90%, so almost every patient who received this medication had meaningful improvement,” he added.
Based on the results, the manufacturer, Pfizer, is recruiting participants for a phase 3 trial to further assess dazukibart in dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Dr. Fernandez said, “This is a story you should pay attention to if you treat any dermatomyositis patients at all.”
Regarding these emerging therapies for CLE and dermatomyositis, “This looks very much like the early days of psoriasis, in the early 2000s, when there was a lot of activity developing treatments,” Dr. Fernandez said. “I will predict that within 10 years, we will have multiple novel agents available that will probably work better than anything we have today.”
Dr. Fernandez reported receiving grant and/or research support from Alexion, Incyte, Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Pfizer, and Priovant Therapeutics; acting as a consultant or advisory board member for AbbVie, Biogen, Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals; and being a member of the speaker bureau or receiving honoraria for non-CME from AbbVie, Kyowa Kirin, and Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — Advances in treating medical conditions rarely emerge in a straight line. Oftentimes, progress comes in fits and starts, and therapies to treat cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) and dermatomyositis are no exception.
Beyond approved treatments that deserve more attention, like belimumab, approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in 2011, and Octagam 10%, an intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) preparation approved for dermatomyositis in 2021, anticipation is growing for emerging therapies and their potential to provide relief to patients, Anthony Fernandez, MD, PhD, said at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference. The tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor deucravacitinib, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors brepocitinib and baricitinib, and the monoclonal antibody anifrolumab, he noted, are prime examples.
“. In my opinion, this is the start of what will be the most exciting decade in the history of these two diseases,” said Dr. Fernandez, director of medical dermatology at the Cleveland Clinic.
Emerging Treatments for Cutaneous Lupus
Although SLE can involve many organ systems, the skin is one of the most affected. There are specific cutaneous lesions categorized as either acute cutaneous lupus, subacute cutaneous lupus, or chronic cutaneous lupus.
The oral TYK2 inhibitor deucravacitinib, for example, should be able to dampen interleukin responses in people with CLE, Dr. Fernandez said. Deucravacitinib was approved by the FDA to treat psoriasis in September 2022.
A phase 2 study published in 2023 focused on this agent for relief of systemic lupus. Improvements in cutaneous disease were a secondary endpoint. The trial demonstrated that the patients treated with deucravacitinib achieved a 56%-70% CLASI-50 response, depending on dosing, compared with a 17% response among those on placebo at week 48.
Based on the trial results, recruitment has begun for a phase 2 trial to evaluate deucravacitinib, compared with placebo, in patients with discoid and/or subacute cutaneous lupus. “This may be another medicine we have available to give to any of our patients with cutaneous lupus,” Dr. Fernandez said.
Anifrolumab Appears Promising
The FDA approval of anifrolumab, a type I interferon (IFN) receptor antagonist, for treating moderate to severe SLE in July 2021, for example, is good news for dermatologists and their patients, added Dr. Fernandez. “Almost immediately after approval, case studies showed marked improvement in patients with refractory cutaneous lupus.” While the therapy was approved for treating systemic lupus, it allows for off-label treatment of the cutaneous predominant form of the disease, he said.
Furthermore, the manufacturer of anifrolumab, AstraZeneca, is launching the LAVENDER clinical trial to assess the monoclonal antibody specifically for treating CLE. “This is a big deal because we may be able to prescribe anifrolumab for our cutaneous lupus patients who don’t have systemic lupus,” Dr. Fernandez said.
Phase 3 data supported use the of anifrolumab in systemic lupus, including the TULIP-2 trial, which demonstrated its superiority to placebo for reducing severity of systemic disease and lowering corticosteroid use. A study published in March 2023 of 11 patients showed that they had a “very fast response” to the agent, Dr. Fernandez said, with a 50% or greater improvement in the Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index activity score reached by all participants at week 16. Improvements of 50% or more in this scoring system are considered clinically meaningful, he added.
Upcoming Dermatomyositis Treatments
Why highlight emerging therapies for CLE and dermatomyositis in the same ODAC presentation? Although distinct conditions, these autoimmune conditions are both mediated by type 1 IFN inflammation.
Dermatomyositis is a relatively rare immune-mediated disease that most commonly affects the skin and muscle. Doctors score disease presentation, activity, and clinical improvements on a scale similar to CLASI for cutaneous lupus, the CDASI or Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index. Among people with CDASI activity scores of at least 14, which is the threshold for moderate to severe disease, a 20% improvement is clinically meaningful, Dr. Fernandez said. In addition, a 40% or greater improvement correlates with significant improvements in quality of life.
There is now more evidence for the use of IVIG to treat dermatomyositis. “Among those of us who treat dermatomyositis on a regular basis, we believe IVIG is the most potent treatment. We’ve known that for a long time,” Dr. Fernandez said.
Despite this tenet, for years, there was only one placebo-controlled trial, published in 1993, that evaluated IVIG treatment for dermatomyositis, and it included only 15 participants. That was until October 2022, he said, when the New England Journal of Medicine published a study comparing a specific brand of IVIG (Octagam) with placebo in 95 people with dermatomyositis.
In the study, 79% of participants treated with IVIG had a total improvement score of at least 20 (minimal improvement), the primary endpoint, at 16 weeks, compared with 44% of those receiving a placebo. Those treated with IVIG also had significant improvements in the CDASI score, a secondary endpoint, compared with those on placebo, he said.
Based on results of this trial, the FDA approved Octagam 10% for dermatomyositis in adults. Dr. Fernandez noted the approval is restricted to the brand of IVIG in the trial, not all IVIG products. However, “the FDA approval is most important to us because it gives us ammunition to fight for insurers to approve IVIG when we feel our patients with dermatomyositis need it,” regardless of the brand.
The Potential of JAK1 Inhibitors
An open-label study of the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib, published in December 2020, showed that mean changes in CDASI activity scores at 12 weeks were statistically significant compared with baseline in 10 people with dermatomyositis. “The importance of this study is that it is proof of concept that JAK inhibition can be effective for treating dermatomyositis, especially with active skin disease,” Dr. Fernandez said.
In addition, two large phase 3 trials are evaluating JAK inhibitor safety and efficacy for treating dermatomyositis. One is the VALOR trial, currently recruiting people with recalcitrant dermatomyositis to evaluate treatment with brepocitinib. Researchers in France are looking at another JAK inhibitor, baricitinib, for treating relapsing or treatment-naive dermatomyositis. Recruitment for the BIRD clinical trial is ongoing.
Monoclonal Antibody Showing Promise
“When it comes to looking specifically at dermatomyositis cutaneous disease, it’s been found that the levels of IFN beta correlate best with not only lesional skin type 1 IFN inflammatory signatures but also overall clinical disease activity,” Dr. Fernandez said. This correlation is stronger than for any other IFN-1-type cytokine active in the disorder.
“Perhaps blocking IFN beta might be best way to get control of dermatomyositis activity,” he added.
With that in mind, a phase 2 trial of dazukibart presented at the American Academy of Dermatology 2023 annual meeting highlighted the promise of this agent that targets type 1 IFN beta.
The primary endpoint was improvement in CDASI at 12 weeks. “This medication has remarkable efficacy,” Dr. Fernandez said. “We were one of the sites for this trial. Despite being blinded, there was no question about who was receiving drug and who was receiving placebo.”
“A minimal clinical improvement in disease activity was seen in more than 90%, so almost every patient who received this medication had meaningful improvement,” he added.
Based on the results, the manufacturer, Pfizer, is recruiting participants for a phase 3 trial to further assess dazukibart in dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Dr. Fernandez said, “This is a story you should pay attention to if you treat any dermatomyositis patients at all.”
Regarding these emerging therapies for CLE and dermatomyositis, “This looks very much like the early days of psoriasis, in the early 2000s, when there was a lot of activity developing treatments,” Dr. Fernandez said. “I will predict that within 10 years, we will have multiple novel agents available that will probably work better than anything we have today.”
Dr. Fernandez reported receiving grant and/or research support from Alexion, Incyte, Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Pfizer, and Priovant Therapeutics; acting as a consultant or advisory board member for AbbVie, Biogen, Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals; and being a member of the speaker bureau or receiving honoraria for non-CME from AbbVie, Kyowa Kirin, and Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ODAC 2024
Dana-Farber Moves to Retract, Correct Dozens of Cancer Papers Amid Allegations
News of the investigation follows a blog post by British molecular biologist Sholto David, MD, who flagged almost 60 papers published between 1997 and 2017 that contained image manipulation and other errors. Some of the papers were published by Dana-Farber’s chief executive officer, Laurie Glimcher, MD, and chief operating officer, William Hahn, MD, on topics including multiple myeloma and immune cells.
Mr. David, who blogs about research integrity, highlighted numerous errors and irregularities, including copying and pasting images across multiple experiments to represent different days within the same experiment, sometimes rotating or stretching images.
In one case, Mr. David equated the manipulation with tactics used by “hapless Chinese papermills” and concluded that “a swathe of research coming out of [Dana-Farber] authored by the most senior researchers and managers appears to be hopelessly corrupt with errors that are obvious from just a cursory reading the papers.”
“Imagine what mistakes might be found in the raw data if anyone was allowed to look!” he wrote.
Barrett Rollins, MD, PhD, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute’s research integrity officer, declined to comment on whether the errors represent scientific misconduct, according to STAT. Rollins told ScienceInsider that the “presence of image discrepancies in a paper is not evidence of an author’s intent to deceive.”
Access to new artificial intelligence tools is making it easier for data sleuths, like Mr. David, to unearth data manipulation and errors.
The current investigation closely follows two other investigations into the published work of Harvard University’s former president, Claudine Gay, and Stanford University’s former president, Marc Tessier-Lavigne, which led both to resign their posts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
News of the investigation follows a blog post by British molecular biologist Sholto David, MD, who flagged almost 60 papers published between 1997 and 2017 that contained image manipulation and other errors. Some of the papers were published by Dana-Farber’s chief executive officer, Laurie Glimcher, MD, and chief operating officer, William Hahn, MD, on topics including multiple myeloma and immune cells.
Mr. David, who blogs about research integrity, highlighted numerous errors and irregularities, including copying and pasting images across multiple experiments to represent different days within the same experiment, sometimes rotating or stretching images.
In one case, Mr. David equated the manipulation with tactics used by “hapless Chinese papermills” and concluded that “a swathe of research coming out of [Dana-Farber] authored by the most senior researchers and managers appears to be hopelessly corrupt with errors that are obvious from just a cursory reading the papers.”
“Imagine what mistakes might be found in the raw data if anyone was allowed to look!” he wrote.
Barrett Rollins, MD, PhD, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute’s research integrity officer, declined to comment on whether the errors represent scientific misconduct, according to STAT. Rollins told ScienceInsider that the “presence of image discrepancies in a paper is not evidence of an author’s intent to deceive.”
Access to new artificial intelligence tools is making it easier for data sleuths, like Mr. David, to unearth data manipulation and errors.
The current investigation closely follows two other investigations into the published work of Harvard University’s former president, Claudine Gay, and Stanford University’s former president, Marc Tessier-Lavigne, which led both to resign their posts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
News of the investigation follows a blog post by British molecular biologist Sholto David, MD, who flagged almost 60 papers published between 1997 and 2017 that contained image manipulation and other errors. Some of the papers were published by Dana-Farber’s chief executive officer, Laurie Glimcher, MD, and chief operating officer, William Hahn, MD, on topics including multiple myeloma and immune cells.
Mr. David, who blogs about research integrity, highlighted numerous errors and irregularities, including copying and pasting images across multiple experiments to represent different days within the same experiment, sometimes rotating or stretching images.
In one case, Mr. David equated the manipulation with tactics used by “hapless Chinese papermills” and concluded that “a swathe of research coming out of [Dana-Farber] authored by the most senior researchers and managers appears to be hopelessly corrupt with errors that are obvious from just a cursory reading the papers.”
“Imagine what mistakes might be found in the raw data if anyone was allowed to look!” he wrote.
Barrett Rollins, MD, PhD, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute’s research integrity officer, declined to comment on whether the errors represent scientific misconduct, according to STAT. Rollins told ScienceInsider that the “presence of image discrepancies in a paper is not evidence of an author’s intent to deceive.”
Access to new artificial intelligence tools is making it easier for data sleuths, like Mr. David, to unearth data manipulation and errors.
The current investigation closely follows two other investigations into the published work of Harvard University’s former president, Claudine Gay, and Stanford University’s former president, Marc Tessier-Lavigne, which led both to resign their posts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea May Promote Early Bone Loss
TOPLINE:
Indicators of early bone loss were significantly higher in adults with severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) than in those with mild or moderate OSA and controls.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers enrolled 90 men aged 30-59 years who were patients at a single sleep and respiratory center between August 2017 and February 2019; the average age was 47.1 years, and the average body mass index was 25.7 kg/m2.
- The study population included 25 individuals with mild OSA, 21 with moderate OSA, 34 with severe OSA, and 10 controls without OSA.
- Bone loss was assessed using high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography and blood samples. The researchers collected information on metabolic and inflammatory bone turnover indicators, as well as bone geometric parameters, bone microstructure parameters, and measures of bone mineral density (BMD).
TAKEAWAY:
- Total volumetric bone mineral density was significantly lower in patients with OSA than in controls and significantly different among OSA groups, as were the meta trabecular volumetric BMD, trabecular thickness (Tb.Th), and cortical thickness (Ct.Th).
- Differences in bone microstructure between patients with OSA and controls were most evident in measures of Tb.Th and Ct.Th.
- No significant differences appeared in blood bone turnover indicators or inflammation indicators among the groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“A study with a larger sample is necessary to further assess the relationship and mechanisms between OSA and osteoporosis,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Yixian Qiao, MD, of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China. The study was published online in BMC Pulmonary Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design, small sample size, and inability to control for several key confounders such as nutritional status and amount of exercise, as well as the exclusion of women and elderly individuals, limited the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Projects of China. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Indicators of early bone loss were significantly higher in adults with severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) than in those with mild or moderate OSA and controls.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers enrolled 90 men aged 30-59 years who were patients at a single sleep and respiratory center between August 2017 and February 2019; the average age was 47.1 years, and the average body mass index was 25.7 kg/m2.
- The study population included 25 individuals with mild OSA, 21 with moderate OSA, 34 with severe OSA, and 10 controls without OSA.
- Bone loss was assessed using high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography and blood samples. The researchers collected information on metabolic and inflammatory bone turnover indicators, as well as bone geometric parameters, bone microstructure parameters, and measures of bone mineral density (BMD).
TAKEAWAY:
- Total volumetric bone mineral density was significantly lower in patients with OSA than in controls and significantly different among OSA groups, as were the meta trabecular volumetric BMD, trabecular thickness (Tb.Th), and cortical thickness (Ct.Th).
- Differences in bone microstructure between patients with OSA and controls were most evident in measures of Tb.Th and Ct.Th.
- No significant differences appeared in blood bone turnover indicators or inflammation indicators among the groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“A study with a larger sample is necessary to further assess the relationship and mechanisms between OSA and osteoporosis,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Yixian Qiao, MD, of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China. The study was published online in BMC Pulmonary Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design, small sample size, and inability to control for several key confounders such as nutritional status and amount of exercise, as well as the exclusion of women and elderly individuals, limited the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Projects of China. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Indicators of early bone loss were significantly higher in adults with severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) than in those with mild or moderate OSA and controls.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers enrolled 90 men aged 30-59 years who were patients at a single sleep and respiratory center between August 2017 and February 2019; the average age was 47.1 years, and the average body mass index was 25.7 kg/m2.
- The study population included 25 individuals with mild OSA, 21 with moderate OSA, 34 with severe OSA, and 10 controls without OSA.
- Bone loss was assessed using high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography and blood samples. The researchers collected information on metabolic and inflammatory bone turnover indicators, as well as bone geometric parameters, bone microstructure parameters, and measures of bone mineral density (BMD).
TAKEAWAY:
- Total volumetric bone mineral density was significantly lower in patients with OSA than in controls and significantly different among OSA groups, as were the meta trabecular volumetric BMD, trabecular thickness (Tb.Th), and cortical thickness (Ct.Th).
- Differences in bone microstructure between patients with OSA and controls were most evident in measures of Tb.Th and Ct.Th.
- No significant differences appeared in blood bone turnover indicators or inflammation indicators among the groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“A study with a larger sample is necessary to further assess the relationship and mechanisms between OSA and osteoporosis,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Yixian Qiao, MD, of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China. The study was published online in BMC Pulmonary Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design, small sample size, and inability to control for several key confounders such as nutritional status and amount of exercise, as well as the exclusion of women and elderly individuals, limited the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Projects of China. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer Identified as a New Cardiovascular Risk Factor
A history of cancer is an independent predictor of major cardiovascular events in patients undergoing coronary angioplasty. Cancer should be considered a new cardiovascular risk factor in primary and secondary prevention, according to a study presented at the 2023 American Heart Association Congress in Philadelphia.
, for example, equating it to the situation of a patient with diabetes or chronic renal failure,” said lead author Renzo Melchiori, MD, a cardiologist at the University Hospital Austral in Pilar, Argentina.
The researchers also advocate for intensifying cardiovascular control measures in secondary prevention for these patients, reconsidering goals, and ensuring compliance with prescribed pharmacological regimens and healthy lifestyle habits.
“Previously, when a patient had oncological pathology, thinking about associated cardiovascular risk seemed somewhat superfluous. But today, oncological diseases are treated so effectively, increasing survival and life expectancy, that we begin to focus on what happens with the arteries of these patients after treatment,” said Dr. Melchiori.
Higher Incidence Density
The retrospective analysis included 937 patients of both sexes aged 18 years and older who underwent coronary angioplasty for acute coronary syndrome between 2008 and 2022 at a university hospital. Of these participants, 89 (9.5%) had a history of cancer, with a median time since oncologic diagnosis of around 2 years for solid and hematologic tumors. Most participants had treated and resolved cancer.
Over a median follow-up of 45 months (range, 14-72 months), the cumulative incidence rates of a major cardiovascular event (nonfatal stroke, nonfatal acute myocardial infarction, cardiovascular death, or new angioplasty) were 22.2% (155/698) and 28.4% (25/88) in the groups without and with a history of cancer, respectively. The incidence density was significantly higher in the group with an oncologic history than in the group without such a history: 0.78 events/100 patients/month vs 0.48 events/100 patients/month (P = .01).
Kaplan-Meier analysis showed a higher probability of a major cardiovascular event in the group of patients with cancer or a history of cancer (P = .0086). In multivariate Cox regression analysis, cancer history was an independent predictor of major cardiovascular events adjusted for other risk factors such as age, hypertension, diabetes, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, and family history (hazard ratio, 1.66; P = .025).
Dr. Melchiori clarified that the increased incidence of cardiovascular events in patients with cancer or a history of cancer cannot be attributed to differences in percutaneous intervention or the indication or compliance of post-treatment pharmacological therapy.
In addition, the specialist acknowledged that due to the sample size, discrimination by cancer type, disease stage, or therapeutic strategies couldn’t be performed. A subanalysis, which has not been presented, indicated that the effect could not be explained solely by the application of radiotherapy or chemotherapy in the 90 days before angioplasty — two factors that cause arterial inflammation.
Intensifying Prevention Measures
Two independent experts told this news organization that the new study is "interesting" and reinforces the close connection between oncologic and cardiovascular pathology.
Andrés Daniele, MD, cardiologist and president of the Argentine Cardio-Oncology Association, a local chapter of the International Cardio-Oncology Society, emphasized that the study “reiterates an observation seen in other works: A higher rate of atherosclerotic pathology and cardiovascular events in patients with a history of cancer. And that has a reason to be: Both pathologies present common risk factors, and on the other hand, there is greater endothelial dysfunction secondary to the inflammatory syndrome and oncologic therapies.”
“There needs to be a continuum in the intensification of measures in primary and secondary cardiovascular prevention in cancer survivors, whether in remission or with chronic disease. We need to be very aggressive in managing risk factors and insist that patients who have had a cardiovascular event enter cardiovascular rehabilitation therapies,” said Dr. Daniele, who also heads the Cardio-Oncology Department at the centenary Roffo Institute of Oncology at the University of Buenos Aires, Argentina.
The study provides a valuable contribution because “we need to understand the epidemiology and natural history of patients with cancer at risk of developing cardiovascular complications to implement personalized cardiovascular prevention strategies,” said Teresa López Fernández, MD, cardiologist, coordinator of the Cardio-Oncology Program at La Paz University Hospital in Madrid, member of the Cardio-Oncology Working Group of the Spanish Society of Cardiology, member of the board of the International Cardio-Oncology Society, and cochair of the first clinical practice guidelines in cardio-oncology of the European Society of Cardiology.
“We have to be aware that perhaps we should not guide ourselves in these patients with the usual risk stratification scores as cancer or cardiotoxic treatment are not included as variables. However, they require our attention and effort to improve their quality and quantity of life, avoiding potentially preventable cardiovascular events that could negatively impact the survival achieved thanks to advances in cancer treatments,” said Dr. López Fernández.
Dr. Melchiori and Dr. Daniele declared no relevant economic conflicts of interest. Dr. López Fernández reported relationships with Daiichi Sankyo, Almirall España, Janssen-Cilag, Bayer, Roche, Philips, and Incyte.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A history of cancer is an independent predictor of major cardiovascular events in patients undergoing coronary angioplasty. Cancer should be considered a new cardiovascular risk factor in primary and secondary prevention, according to a study presented at the 2023 American Heart Association Congress in Philadelphia.
, for example, equating it to the situation of a patient with diabetes or chronic renal failure,” said lead author Renzo Melchiori, MD, a cardiologist at the University Hospital Austral in Pilar, Argentina.
The researchers also advocate for intensifying cardiovascular control measures in secondary prevention for these patients, reconsidering goals, and ensuring compliance with prescribed pharmacological regimens and healthy lifestyle habits.
“Previously, when a patient had oncological pathology, thinking about associated cardiovascular risk seemed somewhat superfluous. But today, oncological diseases are treated so effectively, increasing survival and life expectancy, that we begin to focus on what happens with the arteries of these patients after treatment,” said Dr. Melchiori.
Higher Incidence Density
The retrospective analysis included 937 patients of both sexes aged 18 years and older who underwent coronary angioplasty for acute coronary syndrome between 2008 and 2022 at a university hospital. Of these participants, 89 (9.5%) had a history of cancer, with a median time since oncologic diagnosis of around 2 years for solid and hematologic tumors. Most participants had treated and resolved cancer.
Over a median follow-up of 45 months (range, 14-72 months), the cumulative incidence rates of a major cardiovascular event (nonfatal stroke, nonfatal acute myocardial infarction, cardiovascular death, or new angioplasty) were 22.2% (155/698) and 28.4% (25/88) in the groups without and with a history of cancer, respectively. The incidence density was significantly higher in the group with an oncologic history than in the group without such a history: 0.78 events/100 patients/month vs 0.48 events/100 patients/month (P = .01).
Kaplan-Meier analysis showed a higher probability of a major cardiovascular event in the group of patients with cancer or a history of cancer (P = .0086). In multivariate Cox regression analysis, cancer history was an independent predictor of major cardiovascular events adjusted for other risk factors such as age, hypertension, diabetes, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, and family history (hazard ratio, 1.66; P = .025).
Dr. Melchiori clarified that the increased incidence of cardiovascular events in patients with cancer or a history of cancer cannot be attributed to differences in percutaneous intervention or the indication or compliance of post-treatment pharmacological therapy.
In addition, the specialist acknowledged that due to the sample size, discrimination by cancer type, disease stage, or therapeutic strategies couldn’t be performed. A subanalysis, which has not been presented, indicated that the effect could not be explained solely by the application of radiotherapy or chemotherapy in the 90 days before angioplasty — two factors that cause arterial inflammation.
Intensifying Prevention Measures
Two independent experts told this news organization that the new study is "interesting" and reinforces the close connection between oncologic and cardiovascular pathology.
Andrés Daniele, MD, cardiologist and president of the Argentine Cardio-Oncology Association, a local chapter of the International Cardio-Oncology Society, emphasized that the study “reiterates an observation seen in other works: A higher rate of atherosclerotic pathology and cardiovascular events in patients with a history of cancer. And that has a reason to be: Both pathologies present common risk factors, and on the other hand, there is greater endothelial dysfunction secondary to the inflammatory syndrome and oncologic therapies.”
“There needs to be a continuum in the intensification of measures in primary and secondary cardiovascular prevention in cancer survivors, whether in remission or with chronic disease. We need to be very aggressive in managing risk factors and insist that patients who have had a cardiovascular event enter cardiovascular rehabilitation therapies,” said Dr. Daniele, who also heads the Cardio-Oncology Department at the centenary Roffo Institute of Oncology at the University of Buenos Aires, Argentina.
The study provides a valuable contribution because “we need to understand the epidemiology and natural history of patients with cancer at risk of developing cardiovascular complications to implement personalized cardiovascular prevention strategies,” said Teresa López Fernández, MD, cardiologist, coordinator of the Cardio-Oncology Program at La Paz University Hospital in Madrid, member of the Cardio-Oncology Working Group of the Spanish Society of Cardiology, member of the board of the International Cardio-Oncology Society, and cochair of the first clinical practice guidelines in cardio-oncology of the European Society of Cardiology.
“We have to be aware that perhaps we should not guide ourselves in these patients with the usual risk stratification scores as cancer or cardiotoxic treatment are not included as variables. However, they require our attention and effort to improve their quality and quantity of life, avoiding potentially preventable cardiovascular events that could negatively impact the survival achieved thanks to advances in cancer treatments,” said Dr. López Fernández.
Dr. Melchiori and Dr. Daniele declared no relevant economic conflicts of interest. Dr. López Fernández reported relationships with Daiichi Sankyo, Almirall España, Janssen-Cilag, Bayer, Roche, Philips, and Incyte.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A history of cancer is an independent predictor of major cardiovascular events in patients undergoing coronary angioplasty. Cancer should be considered a new cardiovascular risk factor in primary and secondary prevention, according to a study presented at the 2023 American Heart Association Congress in Philadelphia.
, for example, equating it to the situation of a patient with diabetes or chronic renal failure,” said lead author Renzo Melchiori, MD, a cardiologist at the University Hospital Austral in Pilar, Argentina.
The researchers also advocate for intensifying cardiovascular control measures in secondary prevention for these patients, reconsidering goals, and ensuring compliance with prescribed pharmacological regimens and healthy lifestyle habits.
“Previously, when a patient had oncological pathology, thinking about associated cardiovascular risk seemed somewhat superfluous. But today, oncological diseases are treated so effectively, increasing survival and life expectancy, that we begin to focus on what happens with the arteries of these patients after treatment,” said Dr. Melchiori.
Higher Incidence Density
The retrospective analysis included 937 patients of both sexes aged 18 years and older who underwent coronary angioplasty for acute coronary syndrome between 2008 and 2022 at a university hospital. Of these participants, 89 (9.5%) had a history of cancer, with a median time since oncologic diagnosis of around 2 years for solid and hematologic tumors. Most participants had treated and resolved cancer.
Over a median follow-up of 45 months (range, 14-72 months), the cumulative incidence rates of a major cardiovascular event (nonfatal stroke, nonfatal acute myocardial infarction, cardiovascular death, or new angioplasty) were 22.2% (155/698) and 28.4% (25/88) in the groups without and with a history of cancer, respectively. The incidence density was significantly higher in the group with an oncologic history than in the group without such a history: 0.78 events/100 patients/month vs 0.48 events/100 patients/month (P = .01).
Kaplan-Meier analysis showed a higher probability of a major cardiovascular event in the group of patients with cancer or a history of cancer (P = .0086). In multivariate Cox regression analysis, cancer history was an independent predictor of major cardiovascular events adjusted for other risk factors such as age, hypertension, diabetes, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, and family history (hazard ratio, 1.66; P = .025).
Dr. Melchiori clarified that the increased incidence of cardiovascular events in patients with cancer or a history of cancer cannot be attributed to differences in percutaneous intervention or the indication or compliance of post-treatment pharmacological therapy.
In addition, the specialist acknowledged that due to the sample size, discrimination by cancer type, disease stage, or therapeutic strategies couldn’t be performed. A subanalysis, which has not been presented, indicated that the effect could not be explained solely by the application of radiotherapy or chemotherapy in the 90 days before angioplasty — two factors that cause arterial inflammation.
Intensifying Prevention Measures
Two independent experts told this news organization that the new study is "interesting" and reinforces the close connection between oncologic and cardiovascular pathology.
Andrés Daniele, MD, cardiologist and president of the Argentine Cardio-Oncology Association, a local chapter of the International Cardio-Oncology Society, emphasized that the study “reiterates an observation seen in other works: A higher rate of atherosclerotic pathology and cardiovascular events in patients with a history of cancer. And that has a reason to be: Both pathologies present common risk factors, and on the other hand, there is greater endothelial dysfunction secondary to the inflammatory syndrome and oncologic therapies.”
“There needs to be a continuum in the intensification of measures in primary and secondary cardiovascular prevention in cancer survivors, whether in remission or with chronic disease. We need to be very aggressive in managing risk factors and insist that patients who have had a cardiovascular event enter cardiovascular rehabilitation therapies,” said Dr. Daniele, who also heads the Cardio-Oncology Department at the centenary Roffo Institute of Oncology at the University of Buenos Aires, Argentina.
The study provides a valuable contribution because “we need to understand the epidemiology and natural history of patients with cancer at risk of developing cardiovascular complications to implement personalized cardiovascular prevention strategies,” said Teresa López Fernández, MD, cardiologist, coordinator of the Cardio-Oncology Program at La Paz University Hospital in Madrid, member of the Cardio-Oncology Working Group of the Spanish Society of Cardiology, member of the board of the International Cardio-Oncology Society, and cochair of the first clinical practice guidelines in cardio-oncology of the European Society of Cardiology.
“We have to be aware that perhaps we should not guide ourselves in these patients with the usual risk stratification scores as cancer or cardiotoxic treatment are not included as variables. However, they require our attention and effort to improve their quality and quantity of life, avoiding potentially preventable cardiovascular events that could negatively impact the survival achieved thanks to advances in cancer treatments,” said Dr. López Fernández.
Dr. Melchiori and Dr. Daniele declared no relevant economic conflicts of interest. Dr. López Fernández reported relationships with Daiichi Sankyo, Almirall España, Janssen-Cilag, Bayer, Roche, Philips, and Incyte.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Licensing Hurdles Keep Foreign-Trained Docs in Nonphysician Roles
Foreign-trained doctors can supplement the nation’s waning physician workforce and bring diverse perspectives to patient care, but a new study finds that most never enter comparable roles after immigration, raising questions about the feasibility of educational and licensing pathways for international medical graduates (IMGs).
Conducted by the Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis and the nonprofit Upwardly Global, the study analyzed the data of 300 physicians who immigrated to the United States between 2004 and 2022.
Although 85% of IMGs found employment, only 1 in 3 became a medical resident or doctor.
Despite the study’s small sample size, it highlights the hurdles IMGs face, the authors noted.
If unable to complete these steps, IMGs may pursue other healthcare jobs for which they’re overqualified and underpaid, given their experience. The study found that 23% of IMGs who were not on track to become physicians worked as medical assistants. Others became clinical researchers, medical interpreters, and case managers.
Russian ob/gyn Maxim Nikolaevskiy moved to the US in 2018 and understands why some IMGs switch career paths. His wife, who also trained as a physician in Russia, opted to enroll in a respiratory therapy program after they immigrated to Minnesota, whereas he found work as a research coordinator. The pressure to find housing, enroll their kids in school, and establish new routines took much of their focus.
Dr. Nikolaevskiy told this news organization that IMGs often struggle to find a residency program willing to consider their unique career trajectory, which looks markedly different from that of someone trained in the US.
“Multiple residency programs refuse IMGs’ applications, saying they graduated too long ago, without understanding they worked as a physician before,” he said. Immigrant doctors accepting nonphysician jobs once in the US, often out of financial necessity, only adds to this confusion.
New federal and state legislation aim to reduce practice barriers for IMGs and shore up physician shortages and access for some of the nation›s most vulnerable counties.
The Conrad State 30 and Physician Access Reauthorization Act, supported by the American Medical Association, would revamp the J-1 visa waiver program to permit more immigrant physicians to work in medically underserved areas instead of returning to their home countries.
Last year, Alabama streamlined rules to allow IMGs to practice earlier. Effective July 1, those residing in Tennessee may skip residency requirements and receive a temporary medical license once they pass the state medical board and prove they have completed a 3-year postgraduate training program in their licensing country or recently fulfilled physician duties outside the US.
Washington state now issues 2-year medical licenses to foreign-trained doctors, no residency required, with the possibility of renewal. Doctors must meet other requirements, including passing all steps of the USMLE and establishing a practice agreement with a supervising physician. Illinois recently passed a similar law that will take effect in January 2025.
Beyond laws, communities can embrace IMGs and offer career guidance and clinical opportunities. Daniel Weber, MD, founded the International Healthcare Professionals Program in Lancaster, Pennsylvania, to provide this critical support.
“It is daunting to master a new language and pass medical licensing and English proficiency exams while working full time to support themselves and their families,” Dr. Weber said.
Some participants have entered US residency training programs, but Weber told this news organization that many others have earned nursing degrees and are on track to become nurse practitioners.
More than 5 years after leaving Russia, Dr. Nikolaevskiy is inching closer to practicing medicine again.
He recently completed the Bridge to Residency for Immigrant International Doctor Graduates (BRIIDGE) program at the University of Minnesota Medical School. The 9-month program offers clinical experiences in community settings, outpatient primary care, and inpatient general medicine and pediatrics, clearing the way for him to apply for family medicine residency and possibly match in this cycle.
“If not for the BRIIDGE program, I would still be [doing] medical monitoring in clinical trials or pharmacovigilance jobs. I’m grateful for the clinical experience and the people and institutions ready to give me a second chance,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Foreign-trained doctors can supplement the nation’s waning physician workforce and bring diverse perspectives to patient care, but a new study finds that most never enter comparable roles after immigration, raising questions about the feasibility of educational and licensing pathways for international medical graduates (IMGs).
Conducted by the Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis and the nonprofit Upwardly Global, the study analyzed the data of 300 physicians who immigrated to the United States between 2004 and 2022.
Although 85% of IMGs found employment, only 1 in 3 became a medical resident or doctor.
Despite the study’s small sample size, it highlights the hurdles IMGs face, the authors noted.
If unable to complete these steps, IMGs may pursue other healthcare jobs for which they’re overqualified and underpaid, given their experience. The study found that 23% of IMGs who were not on track to become physicians worked as medical assistants. Others became clinical researchers, medical interpreters, and case managers.
Russian ob/gyn Maxim Nikolaevskiy moved to the US in 2018 and understands why some IMGs switch career paths. His wife, who also trained as a physician in Russia, opted to enroll in a respiratory therapy program after they immigrated to Minnesota, whereas he found work as a research coordinator. The pressure to find housing, enroll their kids in school, and establish new routines took much of their focus.
Dr. Nikolaevskiy told this news organization that IMGs often struggle to find a residency program willing to consider their unique career trajectory, which looks markedly different from that of someone trained in the US.
“Multiple residency programs refuse IMGs’ applications, saying they graduated too long ago, without understanding they worked as a physician before,” he said. Immigrant doctors accepting nonphysician jobs once in the US, often out of financial necessity, only adds to this confusion.
New federal and state legislation aim to reduce practice barriers for IMGs and shore up physician shortages and access for some of the nation›s most vulnerable counties.
The Conrad State 30 and Physician Access Reauthorization Act, supported by the American Medical Association, would revamp the J-1 visa waiver program to permit more immigrant physicians to work in medically underserved areas instead of returning to their home countries.
Last year, Alabama streamlined rules to allow IMGs to practice earlier. Effective July 1, those residing in Tennessee may skip residency requirements and receive a temporary medical license once they pass the state medical board and prove they have completed a 3-year postgraduate training program in their licensing country or recently fulfilled physician duties outside the US.
Washington state now issues 2-year medical licenses to foreign-trained doctors, no residency required, with the possibility of renewal. Doctors must meet other requirements, including passing all steps of the USMLE and establishing a practice agreement with a supervising physician. Illinois recently passed a similar law that will take effect in January 2025.
Beyond laws, communities can embrace IMGs and offer career guidance and clinical opportunities. Daniel Weber, MD, founded the International Healthcare Professionals Program in Lancaster, Pennsylvania, to provide this critical support.
“It is daunting to master a new language and pass medical licensing and English proficiency exams while working full time to support themselves and their families,” Dr. Weber said.
Some participants have entered US residency training programs, but Weber told this news organization that many others have earned nursing degrees and are on track to become nurse practitioners.
More than 5 years after leaving Russia, Dr. Nikolaevskiy is inching closer to practicing medicine again.
He recently completed the Bridge to Residency for Immigrant International Doctor Graduates (BRIIDGE) program at the University of Minnesota Medical School. The 9-month program offers clinical experiences in community settings, outpatient primary care, and inpatient general medicine and pediatrics, clearing the way for him to apply for family medicine residency and possibly match in this cycle.
“If not for the BRIIDGE program, I would still be [doing] medical monitoring in clinical trials or pharmacovigilance jobs. I’m grateful for the clinical experience and the people and institutions ready to give me a second chance,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Foreign-trained doctors can supplement the nation’s waning physician workforce and bring diverse perspectives to patient care, but a new study finds that most never enter comparable roles after immigration, raising questions about the feasibility of educational and licensing pathways for international medical graduates (IMGs).
Conducted by the Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis and the nonprofit Upwardly Global, the study analyzed the data of 300 physicians who immigrated to the United States between 2004 and 2022.
Although 85% of IMGs found employment, only 1 in 3 became a medical resident or doctor.
Despite the study’s small sample size, it highlights the hurdles IMGs face, the authors noted.
If unable to complete these steps, IMGs may pursue other healthcare jobs for which they’re overqualified and underpaid, given their experience. The study found that 23% of IMGs who were not on track to become physicians worked as medical assistants. Others became clinical researchers, medical interpreters, and case managers.
Russian ob/gyn Maxim Nikolaevskiy moved to the US in 2018 and understands why some IMGs switch career paths. His wife, who also trained as a physician in Russia, opted to enroll in a respiratory therapy program after they immigrated to Minnesota, whereas he found work as a research coordinator. The pressure to find housing, enroll their kids in school, and establish new routines took much of their focus.
Dr. Nikolaevskiy told this news organization that IMGs often struggle to find a residency program willing to consider their unique career trajectory, which looks markedly different from that of someone trained in the US.
“Multiple residency programs refuse IMGs’ applications, saying they graduated too long ago, without understanding they worked as a physician before,” he said. Immigrant doctors accepting nonphysician jobs once in the US, often out of financial necessity, only adds to this confusion.
New federal and state legislation aim to reduce practice barriers for IMGs and shore up physician shortages and access for some of the nation›s most vulnerable counties.
The Conrad State 30 and Physician Access Reauthorization Act, supported by the American Medical Association, would revamp the J-1 visa waiver program to permit more immigrant physicians to work in medically underserved areas instead of returning to their home countries.
Last year, Alabama streamlined rules to allow IMGs to practice earlier. Effective July 1, those residing in Tennessee may skip residency requirements and receive a temporary medical license once they pass the state medical board and prove they have completed a 3-year postgraduate training program in their licensing country or recently fulfilled physician duties outside the US.
Washington state now issues 2-year medical licenses to foreign-trained doctors, no residency required, with the possibility of renewal. Doctors must meet other requirements, including passing all steps of the USMLE and establishing a practice agreement with a supervising physician. Illinois recently passed a similar law that will take effect in January 2025.
Beyond laws, communities can embrace IMGs and offer career guidance and clinical opportunities. Daniel Weber, MD, founded the International Healthcare Professionals Program in Lancaster, Pennsylvania, to provide this critical support.
“It is daunting to master a new language and pass medical licensing and English proficiency exams while working full time to support themselves and their families,” Dr. Weber said.
Some participants have entered US residency training programs, but Weber told this news organization that many others have earned nursing degrees and are on track to become nurse practitioners.
More than 5 years after leaving Russia, Dr. Nikolaevskiy is inching closer to practicing medicine again.
He recently completed the Bridge to Residency for Immigrant International Doctor Graduates (BRIIDGE) program at the University of Minnesota Medical School. The 9-month program offers clinical experiences in community settings, outpatient primary care, and inpatient general medicine and pediatrics, clearing the way for him to apply for family medicine residency and possibly match in this cycle.
“If not for the BRIIDGE program, I would still be [doing] medical monitoring in clinical trials or pharmacovigilance jobs. I’m grateful for the clinical experience and the people and institutions ready to give me a second chance,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Ultrasound Monitoring of IBD May Prompt Faster Treatment Change
, according to a small retrospective analysis.
“Current disease monitoring tools have significant limitations,” said Noa Krugliak Cleveland, MD, director of the intestinal ultrasound program at the University of Chicago. “Intestinal ultrasound is an innovative technology that enables point-of-care assessment.”
Dr. Cleveland presented the findings at the October 2023 American College of Gastroenterology’s annual scientific meeting in Vancouver, Canada.
The analysis was based on 30 patients with IBD in an ongoing real-world prospective study of upadacitinib (Rinvoq, Abbvie) who were not in clinical remission at week 8. For 11 patients, routine clinical care included IUS; the other 19 patients were monitored using a conventional approach.
In the study, both groups were almost evenly split in terms of diagnosis. In the IUS group, four patients had Crohn’s disease and five had ulcerative colitis. In the conventional management group, six had Crohn’s disease and five had ulcerative colitis.
The primary endpoint was time to treatment change.
For the secondary endpoint, the researchers defined clinical remission as a Simple Clinical Colitis Activity Index ≤ 2, or Harvey-Bradshaw Index ≤ 4, and by IUS as bowel wall thickness ≤ 3 mm in the colon or terminal ileum and no hyperemia by color Doppler signal.
The average time to treatment change in the IUS group was 1.1 days, compared with 16.6 days for the conventional management group, Dr. Cleveland reported.
The average time to clinical remission was 26.8 days for the IUS group, compared with 55.3 days for the conventional management group.
The delays in treatment change in the conventional management group were attributed to awaiting test results and endoscopy procedures, as well as communications among clinical team members.
Strength of this research project included its prospective data collection and the experienced sonographers who participated, Dr. Cleveland and colleagues said. Limitations included retrospective analysis, a small number of patients on a single therapy, and the potential for bias in patient selection. Studies of other therapies and a prospective trial are underway.
During the presentation, Dr. Cleveland commented about what kinds of treatment changes were made for patients in the study. They commonly involved extending the induction time, and, in some cases, patients were switched to another treatment, she said.
In an interview, Michael Dolinger, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, said more research needs to be done to show whether IUS will improve outcomes.
“They’re showing that they make more changes sooner,” he said. “Does that actually affect and improve outcomes? That’s the big question.”
Dr. Dolinger said the concept for using IUS is that it helps physicians catch disease flares earlier and respond faster with changes to the treatment plan, thus preventing the buildup of chronic bowel damage.
“That’s the concept, but that concept is actually not so proven in reality” yet, he said. “But I do believe that they’re on the right path.”
In Dr. Dolinger’s view, adding ultrasound provides a more patient-centric approach to care of people with IBD. With more traditional approaches, patients often are waiting for results of tests done outside of the visit, such as MRI.
“With ultrasound, I am walking them through the results as it’s happening in real time during the clinic visit,” Dr. Dolinger said. ”I am showing them on the screen, allowing them to ask questions. They’re telling me about their symptoms, as I’m putting the probe on where it may hurt, as I’m showing them inflammation or healing. And that changes the whole conversation.”
The study received support from the Mutchnik Family Foundation. Dr. Cleveland reported financial relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb, Neurologica, and Takeda. Her coauthors reported financial relationships with multiple drug and device makers. Dr. Dolinger said he is a consultant for Samsung’s Neurologica Corp., which makes ultrasound equipment.
, according to a small retrospective analysis.
“Current disease monitoring tools have significant limitations,” said Noa Krugliak Cleveland, MD, director of the intestinal ultrasound program at the University of Chicago. “Intestinal ultrasound is an innovative technology that enables point-of-care assessment.”
Dr. Cleveland presented the findings at the October 2023 American College of Gastroenterology’s annual scientific meeting in Vancouver, Canada.
The analysis was based on 30 patients with IBD in an ongoing real-world prospective study of upadacitinib (Rinvoq, Abbvie) who were not in clinical remission at week 8. For 11 patients, routine clinical care included IUS; the other 19 patients were monitored using a conventional approach.
In the study, both groups were almost evenly split in terms of diagnosis. In the IUS group, four patients had Crohn’s disease and five had ulcerative colitis. In the conventional management group, six had Crohn’s disease and five had ulcerative colitis.
The primary endpoint was time to treatment change.
For the secondary endpoint, the researchers defined clinical remission as a Simple Clinical Colitis Activity Index ≤ 2, or Harvey-Bradshaw Index ≤ 4, and by IUS as bowel wall thickness ≤ 3 mm in the colon or terminal ileum and no hyperemia by color Doppler signal.
The average time to treatment change in the IUS group was 1.1 days, compared with 16.6 days for the conventional management group, Dr. Cleveland reported.
The average time to clinical remission was 26.8 days for the IUS group, compared with 55.3 days for the conventional management group.
The delays in treatment change in the conventional management group were attributed to awaiting test results and endoscopy procedures, as well as communications among clinical team members.
Strength of this research project included its prospective data collection and the experienced sonographers who participated, Dr. Cleveland and colleagues said. Limitations included retrospective analysis, a small number of patients on a single therapy, and the potential for bias in patient selection. Studies of other therapies and a prospective trial are underway.
During the presentation, Dr. Cleveland commented about what kinds of treatment changes were made for patients in the study. They commonly involved extending the induction time, and, in some cases, patients were switched to another treatment, she said.
In an interview, Michael Dolinger, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, said more research needs to be done to show whether IUS will improve outcomes.
“They’re showing that they make more changes sooner,” he said. “Does that actually affect and improve outcomes? That’s the big question.”
Dr. Dolinger said the concept for using IUS is that it helps physicians catch disease flares earlier and respond faster with changes to the treatment plan, thus preventing the buildup of chronic bowel damage.
“That’s the concept, but that concept is actually not so proven in reality” yet, he said. “But I do believe that they’re on the right path.”
In Dr. Dolinger’s view, adding ultrasound provides a more patient-centric approach to care of people with IBD. With more traditional approaches, patients often are waiting for results of tests done outside of the visit, such as MRI.
“With ultrasound, I am walking them through the results as it’s happening in real time during the clinic visit,” Dr. Dolinger said. ”I am showing them on the screen, allowing them to ask questions. They’re telling me about their symptoms, as I’m putting the probe on where it may hurt, as I’m showing them inflammation or healing. And that changes the whole conversation.”
The study received support from the Mutchnik Family Foundation. Dr. Cleveland reported financial relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb, Neurologica, and Takeda. Her coauthors reported financial relationships with multiple drug and device makers. Dr. Dolinger said he is a consultant for Samsung’s Neurologica Corp., which makes ultrasound equipment.
, according to a small retrospective analysis.
“Current disease monitoring tools have significant limitations,” said Noa Krugliak Cleveland, MD, director of the intestinal ultrasound program at the University of Chicago. “Intestinal ultrasound is an innovative technology that enables point-of-care assessment.”
Dr. Cleveland presented the findings at the October 2023 American College of Gastroenterology’s annual scientific meeting in Vancouver, Canada.
The analysis was based on 30 patients with IBD in an ongoing real-world prospective study of upadacitinib (Rinvoq, Abbvie) who were not in clinical remission at week 8. For 11 patients, routine clinical care included IUS; the other 19 patients were monitored using a conventional approach.
In the study, both groups were almost evenly split in terms of diagnosis. In the IUS group, four patients had Crohn’s disease and five had ulcerative colitis. In the conventional management group, six had Crohn’s disease and five had ulcerative colitis.
The primary endpoint was time to treatment change.
For the secondary endpoint, the researchers defined clinical remission as a Simple Clinical Colitis Activity Index ≤ 2, or Harvey-Bradshaw Index ≤ 4, and by IUS as bowel wall thickness ≤ 3 mm in the colon or terminal ileum and no hyperemia by color Doppler signal.
The average time to treatment change in the IUS group was 1.1 days, compared with 16.6 days for the conventional management group, Dr. Cleveland reported.
The average time to clinical remission was 26.8 days for the IUS group, compared with 55.3 days for the conventional management group.
The delays in treatment change in the conventional management group were attributed to awaiting test results and endoscopy procedures, as well as communications among clinical team members.
Strength of this research project included its prospective data collection and the experienced sonographers who participated, Dr. Cleveland and colleagues said. Limitations included retrospective analysis, a small number of patients on a single therapy, and the potential for bias in patient selection. Studies of other therapies and a prospective trial are underway.
During the presentation, Dr. Cleveland commented about what kinds of treatment changes were made for patients in the study. They commonly involved extending the induction time, and, in some cases, patients were switched to another treatment, she said.
In an interview, Michael Dolinger, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, said more research needs to be done to show whether IUS will improve outcomes.
“They’re showing that they make more changes sooner,” he said. “Does that actually affect and improve outcomes? That’s the big question.”
Dr. Dolinger said the concept for using IUS is that it helps physicians catch disease flares earlier and respond faster with changes to the treatment plan, thus preventing the buildup of chronic bowel damage.
“That’s the concept, but that concept is actually not so proven in reality” yet, he said. “But I do believe that they’re on the right path.”
In Dr. Dolinger’s view, adding ultrasound provides a more patient-centric approach to care of people with IBD. With more traditional approaches, patients often are waiting for results of tests done outside of the visit, such as MRI.
“With ultrasound, I am walking them through the results as it’s happening in real time during the clinic visit,” Dr. Dolinger said. ”I am showing them on the screen, allowing them to ask questions. They’re telling me about their symptoms, as I’m putting the probe on where it may hurt, as I’m showing them inflammation or healing. And that changes the whole conversation.”
The study received support from the Mutchnik Family Foundation. Dr. Cleveland reported financial relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb, Neurologica, and Takeda. Her coauthors reported financial relationships with multiple drug and device makers. Dr. Dolinger said he is a consultant for Samsung’s Neurologica Corp., which makes ultrasound equipment.
FROM ACG 2023
Association Between LDL-C and Androgenetic Alopecia Among Female Patients in a Specialty Alopecia Clinic
To the Editor:
Female pattern hair loss (FPHL), or androgenetic alopecia (AGA), is the most common form of alopecia worldwide and is characterized by a reduction of hair follicles spent in the anagen phase of growth as well as progressive terminal hair loss.1 It is caused by an excessive response to androgens and leads to the characteristic distribution of hair loss in both sexes. Studies have shown a notable association between AGA and markers of metabolic syndrome such as dyslipidemia, insulin resistance, and obesity in age- and sex-matched controls.2,3 However, research describing the relationship between AGA severity and these markers is scarce.
To understand the relationship between FPHL severity and abnormal cholesterol levels, we performed a retrospective chart review of patients diagnosed with FPHL at a specialty alopecia clinic from June 2022 to December 2022. Patient age and age at onset of FPHL were collected. The severity of FPHL was measured using the Sinclair scale (score range, 1–5) and unidentifiable patient photographs. Laboratory values were collected; abnormal cholesterol was defined by the American Heart Association as having a low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level of 100 mg/dL or higher.4 Finally, data on medication use were noted to understand patient treatment status (Table).
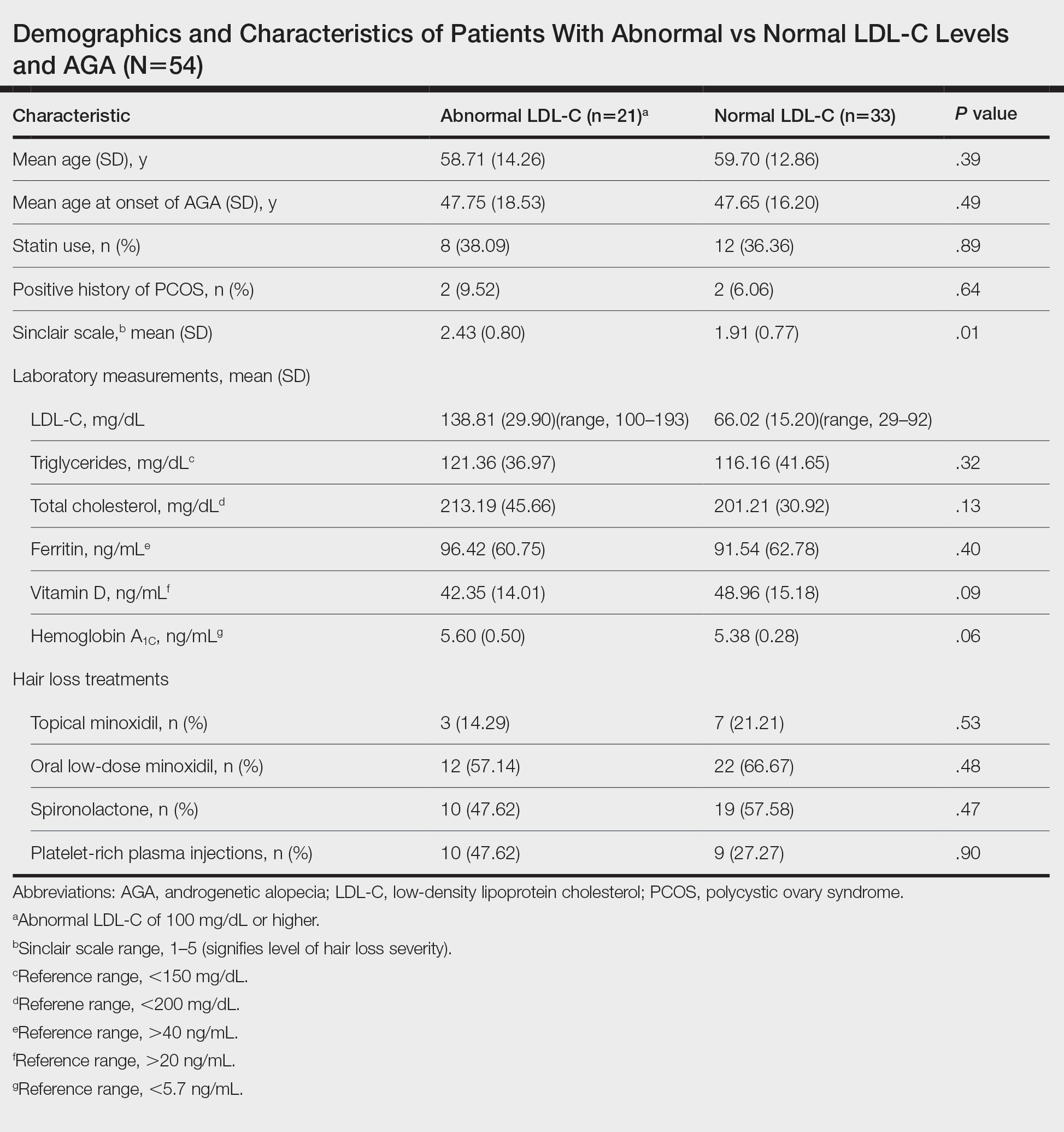
We identified 54 female patients with FPHL with an average age of 59 years (range, 34–80 years). Thirty-three females (61.11%) had a normal LDL-C level and 21 (38.89%) had an abnormal level. The mean (SD) LDL-C level was 66.02 (15.20) mg/dL (range, 29–92 mg/dL) in the group with normal levels and 138.81 (29.90) mg/dL (range, 100–193 mg/dL) in the group with abnormal levels. Patients with abnormal LDL-C had significantly higher Sinclair scale scores compared to those with normal levels (2.43 vs 1.91; P=.01). There were no significant differences in patient age (58.71 vs 59.70 years; P=.39), age at onset of AGA (47.75 vs 47.65 years; P=.49), history of polycystic ovary syndrome (9.52% vs 6.06%; P=.64), or statin use (38.09% vs 36.36%; P=.89) between patients with abnormal and normal LDL-C levels, respectively. There also were no significant differences in ferritin (96.42 vs 91.54 ng/mL; P=.40), vitamin D (42.35 vs 48.96 ng/mL; P=.09), or hemoglobin A1c levels (5.60 ng/mL vs 5.38 ng/mL; P=.06)—variables that could have confounded this relationship. Triglycerides were within reference range in both groups (121.36 vs 116.16 mg/dL; P=.32), while total cholesterol was mildly elevated in both groups but not significantly different (213.19 vs 201.21 mg/dL; P=.13). Use of hair loss treatments such as topical minoxidil (14.29% vs 21.21%; P=.53), oral low-dose minoxidil (57.14% vs 66.67%; P=.48), oral spironolactone (47.62% vs 57.58%; P=.47), and platelet-rich plasma injections (47.62% vs 27.27%; P=.90) were not significantly different across both groups.
The data suggest a significant (P<.05) association between abnormal LDL-C and hair loss severity in FPHL patients. Our study was limited by its small sample size and lack of causality; however, it coincides with and reiterates the findings established in the literature. The mechanism of the association between hyperlipidemia and AGA is not well understood but is thought to stem from the homology between cholesterol and androgens. Increased cholesterol release from dermal adipocytes and subsequent absorption into hair follicle cell populations may increase hair follicle steroidogenesis, thereby accelerating the anagen-catagen transition and inducing AGA. Alternatively, impaired cholesterol homeostasis may disrupt normal hair follicle cycling by interrupting signaling pathways in follicle proliferation and differentiation.5 Adequate control and monitoring of LDL-C levels may be important, particularly in patients with more severe FPHL.
- Herskovitz I, Tosti A. Female pattern hair loss. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2013;11:E9860. doi:10.5812/ijem.9860
- El Sayed MH, Abdallah MA, Aly DG, et al. Association of metabolic syndrome with female pattern hair loss in women: a case-control study. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:1131-1137. doi:10.1111/ijd.13303
- Kim MW, Shin IS, Yoon HS, et al. Lipid profile in patients with androgenetic alopecia: a meta-analysis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:942-951. doi:10.1111/jdv.14000
- Birtcher KK, Ballantyne CM. Cardiology patient page. measurement of cholesterol: a patient perspective. Circulation. 2004;110:E296-E297. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000141564.89465.4E
- Palmer MA, Blakeborough L, Harries M, et al. Cholesterol homeostasis: links to hair follicle biology and hair disorders. Exp Dermatol. 2020;29:299-311. doi:10.1111/exd.13993
To the Editor:
Female pattern hair loss (FPHL), or androgenetic alopecia (AGA), is the most common form of alopecia worldwide and is characterized by a reduction of hair follicles spent in the anagen phase of growth as well as progressive terminal hair loss.1 It is caused by an excessive response to androgens and leads to the characteristic distribution of hair loss in both sexes. Studies have shown a notable association between AGA and markers of metabolic syndrome such as dyslipidemia, insulin resistance, and obesity in age- and sex-matched controls.2,3 However, research describing the relationship between AGA severity and these markers is scarce.
To understand the relationship between FPHL severity and abnormal cholesterol levels, we performed a retrospective chart review of patients diagnosed with FPHL at a specialty alopecia clinic from June 2022 to December 2022. Patient age and age at onset of FPHL were collected. The severity of FPHL was measured using the Sinclair scale (score range, 1–5) and unidentifiable patient photographs. Laboratory values were collected; abnormal cholesterol was defined by the American Heart Association as having a low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level of 100 mg/dL or higher.4 Finally, data on medication use were noted to understand patient treatment status (Table).

We identified 54 female patients with FPHL with an average age of 59 years (range, 34–80 years). Thirty-three females (61.11%) had a normal LDL-C level and 21 (38.89%) had an abnormal level. The mean (SD) LDL-C level was 66.02 (15.20) mg/dL (range, 29–92 mg/dL) in the group with normal levels and 138.81 (29.90) mg/dL (range, 100–193 mg/dL) in the group with abnormal levels. Patients with abnormal LDL-C had significantly higher Sinclair scale scores compared to those with normal levels (2.43 vs 1.91; P=.01). There were no significant differences in patient age (58.71 vs 59.70 years; P=.39), age at onset of AGA (47.75 vs 47.65 years; P=.49), history of polycystic ovary syndrome (9.52% vs 6.06%; P=.64), or statin use (38.09% vs 36.36%; P=.89) between patients with abnormal and normal LDL-C levels, respectively. There also were no significant differences in ferritin (96.42 vs 91.54 ng/mL; P=.40), vitamin D (42.35 vs 48.96 ng/mL; P=.09), or hemoglobin A1c levels (5.60 ng/mL vs 5.38 ng/mL; P=.06)—variables that could have confounded this relationship. Triglycerides were within reference range in both groups (121.36 vs 116.16 mg/dL; P=.32), while total cholesterol was mildly elevated in both groups but not significantly different (213.19 vs 201.21 mg/dL; P=.13). Use of hair loss treatments such as topical minoxidil (14.29% vs 21.21%; P=.53), oral low-dose minoxidil (57.14% vs 66.67%; P=.48), oral spironolactone (47.62% vs 57.58%; P=.47), and platelet-rich plasma injections (47.62% vs 27.27%; P=.90) were not significantly different across both groups.
The data suggest a significant (P<.05) association between abnormal LDL-C and hair loss severity in FPHL patients. Our study was limited by its small sample size and lack of causality; however, it coincides with and reiterates the findings established in the literature. The mechanism of the association between hyperlipidemia and AGA is not well understood but is thought to stem from the homology between cholesterol and androgens. Increased cholesterol release from dermal adipocytes and subsequent absorption into hair follicle cell populations may increase hair follicle steroidogenesis, thereby accelerating the anagen-catagen transition and inducing AGA. Alternatively, impaired cholesterol homeostasis may disrupt normal hair follicle cycling by interrupting signaling pathways in follicle proliferation and differentiation.5 Adequate control and monitoring of LDL-C levels may be important, particularly in patients with more severe FPHL.
To the Editor:
Female pattern hair loss (FPHL), or androgenetic alopecia (AGA), is the most common form of alopecia worldwide and is characterized by a reduction of hair follicles spent in the anagen phase of growth as well as progressive terminal hair loss.1 It is caused by an excessive response to androgens and leads to the characteristic distribution of hair loss in both sexes. Studies have shown a notable association between AGA and markers of metabolic syndrome such as dyslipidemia, insulin resistance, and obesity in age- and sex-matched controls.2,3 However, research describing the relationship between AGA severity and these markers is scarce.
To understand the relationship between FPHL severity and abnormal cholesterol levels, we performed a retrospective chart review of patients diagnosed with FPHL at a specialty alopecia clinic from June 2022 to December 2022. Patient age and age at onset of FPHL were collected. The severity of FPHL was measured using the Sinclair scale (score range, 1–5) and unidentifiable patient photographs. Laboratory values were collected; abnormal cholesterol was defined by the American Heart Association as having a low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level of 100 mg/dL or higher.4 Finally, data on medication use were noted to understand patient treatment status (Table).

We identified 54 female patients with FPHL with an average age of 59 years (range, 34–80 years). Thirty-three females (61.11%) had a normal LDL-C level and 21 (38.89%) had an abnormal level. The mean (SD) LDL-C level was 66.02 (15.20) mg/dL (range, 29–92 mg/dL) in the group with normal levels and 138.81 (29.90) mg/dL (range, 100–193 mg/dL) in the group with abnormal levels. Patients with abnormal LDL-C had significantly higher Sinclair scale scores compared to those with normal levels (2.43 vs 1.91; P=.01). There were no significant differences in patient age (58.71 vs 59.70 years; P=.39), age at onset of AGA (47.75 vs 47.65 years; P=.49), history of polycystic ovary syndrome (9.52% vs 6.06%; P=.64), or statin use (38.09% vs 36.36%; P=.89) between patients with abnormal and normal LDL-C levels, respectively. There also were no significant differences in ferritin (96.42 vs 91.54 ng/mL; P=.40), vitamin D (42.35 vs 48.96 ng/mL; P=.09), or hemoglobin A1c levels (5.60 ng/mL vs 5.38 ng/mL; P=.06)—variables that could have confounded this relationship. Triglycerides were within reference range in both groups (121.36 vs 116.16 mg/dL; P=.32), while total cholesterol was mildly elevated in both groups but not significantly different (213.19 vs 201.21 mg/dL; P=.13). Use of hair loss treatments such as topical minoxidil (14.29% vs 21.21%; P=.53), oral low-dose minoxidil (57.14% vs 66.67%; P=.48), oral spironolactone (47.62% vs 57.58%; P=.47), and platelet-rich plasma injections (47.62% vs 27.27%; P=.90) were not significantly different across both groups.
The data suggest a significant (P<.05) association between abnormal LDL-C and hair loss severity in FPHL patients. Our study was limited by its small sample size and lack of causality; however, it coincides with and reiterates the findings established in the literature. The mechanism of the association between hyperlipidemia and AGA is not well understood but is thought to stem from the homology between cholesterol and androgens. Increased cholesterol release from dermal adipocytes and subsequent absorption into hair follicle cell populations may increase hair follicle steroidogenesis, thereby accelerating the anagen-catagen transition and inducing AGA. Alternatively, impaired cholesterol homeostasis may disrupt normal hair follicle cycling by interrupting signaling pathways in follicle proliferation and differentiation.5 Adequate control and monitoring of LDL-C levels may be important, particularly in patients with more severe FPHL.
- Herskovitz I, Tosti A. Female pattern hair loss. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2013;11:E9860. doi:10.5812/ijem.9860
- El Sayed MH, Abdallah MA, Aly DG, et al. Association of metabolic syndrome with female pattern hair loss in women: a case-control study. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:1131-1137. doi:10.1111/ijd.13303
- Kim MW, Shin IS, Yoon HS, et al. Lipid profile in patients with androgenetic alopecia: a meta-analysis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:942-951. doi:10.1111/jdv.14000
- Birtcher KK, Ballantyne CM. Cardiology patient page. measurement of cholesterol: a patient perspective. Circulation. 2004;110:E296-E297. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000141564.89465.4E
- Palmer MA, Blakeborough L, Harries M, et al. Cholesterol homeostasis: links to hair follicle biology and hair disorders. Exp Dermatol. 2020;29:299-311. doi:10.1111/exd.13993
- Herskovitz I, Tosti A. Female pattern hair loss. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2013;11:E9860. doi:10.5812/ijem.9860
- El Sayed MH, Abdallah MA, Aly DG, et al. Association of metabolic syndrome with female pattern hair loss in women: a case-control study. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:1131-1137. doi:10.1111/ijd.13303
- Kim MW, Shin IS, Yoon HS, et al. Lipid profile in patients with androgenetic alopecia: a meta-analysis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:942-951. doi:10.1111/jdv.14000
- Birtcher KK, Ballantyne CM. Cardiology patient page. measurement of cholesterol: a patient perspective. Circulation. 2004;110:E296-E297. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000141564.89465.4E
- Palmer MA, Blakeborough L, Harries M, et al. Cholesterol homeostasis: links to hair follicle biology and hair disorders. Exp Dermatol. 2020;29:299-311. doi:10.1111/exd.13993
Practice Points
- Associations have been shown between hair loss and markers of bad health such as insulin resistance and high cholesterol. Research has not yet shown the relationship between hair loss severity and these markers, particularly cholesterol.






