User login
ALS Update: Drug Therapy Continues to Offer Little Benefit
SAVANNAH, GEORGIA — , nerve specialists learned.
The glutamate blocker riluzole (Rilutek), which became the first ALS drug to receive US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval in 1995, continues to be used, Michael D. Weiss, MD, professor of neurology at University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, said in a presentation at the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) 2024.
Weiss highlighted a 2012 Cochrane Library review that examined research and found the drug is “reasonably safe” and prolongs median survival by about 2-3 months. “About 12% develop liver disease. It’s pretty rare that we stop the medicine due to liver toxicity.”
Earlier Treatment Could Pay Dividends
A recent study “suggests we might be able to get more bang for our buck from riluzole” by initiating treatment earlier, Weiss said.
Researchers tracked 4778 patients with ALS, including 3446 (72.1%) who took riluzole. Those who took the drug survived a median 2 extra months (22.6 vs 20.2 months; P < .001). The data suggested that delaying riluzole initiation by 1 year (from 6 months to 18 months after diagnosis) reduced the median survival by 1.9 months (from 40.1 to 38.2 months).
There’s “a relatively significant additional benefit” to earlier treatment, Weiss said, although patients will vary on whether they think it’s meaningful. As for limitations, “there’s no clear impact on disease progression, and there’s a need for periodic monitoring of liver function profile.”
He added that there’s an out-of-pocket co-pay. “Even as a generic, it’s not that cheap. Depending on the source, it could cost anywhere from $1800 to $8400 a year.”
Edaravone Could Lack Relevant Benefit
No other ALS treatment appeared until 2017, when the FDA approved the novel antioxidant edaravone (Radicava). In 2022, the agency approved an oral suspension version, but a study published that year suggested there may not be a clinically relevant benefit.
The University of Washington, where Weiss works, offered the drug to 144 patients, according to an analysis. Eighty percent of the patients wanted it, but insurers refused to cover it for more than 20%. The average time to treatment with the drug was 28 days after patients said they wanted it.
That’s a “substantial delay,” Weiss said.
The cost is about $171,000 a year, he said, and assistance is limited for underinsured patients.*
Other Options
As Weiss noted, another drug, AMX0035 (Relyvrio), received FDA approval in 2022, but its manufacturer pulled it from the US/Canada market in April 2024 following poor phase 3 trial findings.
In 2023, the FDA approved another drug, the antisense oligonucleotide tofersen (Qalsody), in patients with ALS associated with a mutation in the superoxide dismutase 1 gene. According to the FDA, reductions in plasma neurofilament light concentration were “reasonably likely to predict a clinical benefit in patients.”
Only 1%-2% of patients with ALS fit the criteria to get the drug, Weiss said. He noted other limitations such as the cost ($180,000 a year), the need for lifelong monthly intrathecal injections, and serious neurological side effects in 7% of patients per a 2022 trial.
Weiss disclosed advisory board (Alexion, Ra [now UCB], argenx, Biogen, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Amylyx), data safety monitoring board (Sanofi, AI), consulting (Cytokinetics, CSL Behring), and speaker (Soleo) relationships.
*Correction, 10/23/2024: This story originally quoted Weiss as saying the maker of edaravone provides no assistance to underinsured patients. Weiss has clarified that he should have said this coverage is “limited.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAVANNAH, GEORGIA — , nerve specialists learned.
The glutamate blocker riluzole (Rilutek), which became the first ALS drug to receive US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval in 1995, continues to be used, Michael D. Weiss, MD, professor of neurology at University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, said in a presentation at the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) 2024.
Weiss highlighted a 2012 Cochrane Library review that examined research and found the drug is “reasonably safe” and prolongs median survival by about 2-3 months. “About 12% develop liver disease. It’s pretty rare that we stop the medicine due to liver toxicity.”
Earlier Treatment Could Pay Dividends
A recent study “suggests we might be able to get more bang for our buck from riluzole” by initiating treatment earlier, Weiss said.
Researchers tracked 4778 patients with ALS, including 3446 (72.1%) who took riluzole. Those who took the drug survived a median 2 extra months (22.6 vs 20.2 months; P < .001). The data suggested that delaying riluzole initiation by 1 year (from 6 months to 18 months after diagnosis) reduced the median survival by 1.9 months (from 40.1 to 38.2 months).
There’s “a relatively significant additional benefit” to earlier treatment, Weiss said, although patients will vary on whether they think it’s meaningful. As for limitations, “there’s no clear impact on disease progression, and there’s a need for periodic monitoring of liver function profile.”
He added that there’s an out-of-pocket co-pay. “Even as a generic, it’s not that cheap. Depending on the source, it could cost anywhere from $1800 to $8400 a year.”
Edaravone Could Lack Relevant Benefit
No other ALS treatment appeared until 2017, when the FDA approved the novel antioxidant edaravone (Radicava). In 2022, the agency approved an oral suspension version, but a study published that year suggested there may not be a clinically relevant benefit.
The University of Washington, where Weiss works, offered the drug to 144 patients, according to an analysis. Eighty percent of the patients wanted it, but insurers refused to cover it for more than 20%. The average time to treatment with the drug was 28 days after patients said they wanted it.
That’s a “substantial delay,” Weiss said.
The cost is about $171,000 a year, he said, and assistance is limited for underinsured patients.*
Other Options
As Weiss noted, another drug, AMX0035 (Relyvrio), received FDA approval in 2022, but its manufacturer pulled it from the US/Canada market in April 2024 following poor phase 3 trial findings.
In 2023, the FDA approved another drug, the antisense oligonucleotide tofersen (Qalsody), in patients with ALS associated with a mutation in the superoxide dismutase 1 gene. According to the FDA, reductions in plasma neurofilament light concentration were “reasonably likely to predict a clinical benefit in patients.”
Only 1%-2% of patients with ALS fit the criteria to get the drug, Weiss said. He noted other limitations such as the cost ($180,000 a year), the need for lifelong monthly intrathecal injections, and serious neurological side effects in 7% of patients per a 2022 trial.
Weiss disclosed advisory board (Alexion, Ra [now UCB], argenx, Biogen, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Amylyx), data safety monitoring board (Sanofi, AI), consulting (Cytokinetics, CSL Behring), and speaker (Soleo) relationships.
*Correction, 10/23/2024: This story originally quoted Weiss as saying the maker of edaravone provides no assistance to underinsured patients. Weiss has clarified that he should have said this coverage is “limited.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAVANNAH, GEORGIA — , nerve specialists learned.
The glutamate blocker riluzole (Rilutek), which became the first ALS drug to receive US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval in 1995, continues to be used, Michael D. Weiss, MD, professor of neurology at University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, said in a presentation at the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) 2024.
Weiss highlighted a 2012 Cochrane Library review that examined research and found the drug is “reasonably safe” and prolongs median survival by about 2-3 months. “About 12% develop liver disease. It’s pretty rare that we stop the medicine due to liver toxicity.”
Earlier Treatment Could Pay Dividends
A recent study “suggests we might be able to get more bang for our buck from riluzole” by initiating treatment earlier, Weiss said.
Researchers tracked 4778 patients with ALS, including 3446 (72.1%) who took riluzole. Those who took the drug survived a median 2 extra months (22.6 vs 20.2 months; P < .001). The data suggested that delaying riluzole initiation by 1 year (from 6 months to 18 months after diagnosis) reduced the median survival by 1.9 months (from 40.1 to 38.2 months).
There’s “a relatively significant additional benefit” to earlier treatment, Weiss said, although patients will vary on whether they think it’s meaningful. As for limitations, “there’s no clear impact on disease progression, and there’s a need for periodic monitoring of liver function profile.”
He added that there’s an out-of-pocket co-pay. “Even as a generic, it’s not that cheap. Depending on the source, it could cost anywhere from $1800 to $8400 a year.”
Edaravone Could Lack Relevant Benefit
No other ALS treatment appeared until 2017, when the FDA approved the novel antioxidant edaravone (Radicava). In 2022, the agency approved an oral suspension version, but a study published that year suggested there may not be a clinically relevant benefit.
The University of Washington, where Weiss works, offered the drug to 144 patients, according to an analysis. Eighty percent of the patients wanted it, but insurers refused to cover it for more than 20%. The average time to treatment with the drug was 28 days after patients said they wanted it.
That’s a “substantial delay,” Weiss said.
The cost is about $171,000 a year, he said, and assistance is limited for underinsured patients.*
Other Options
As Weiss noted, another drug, AMX0035 (Relyvrio), received FDA approval in 2022, but its manufacturer pulled it from the US/Canada market in April 2024 following poor phase 3 trial findings.
In 2023, the FDA approved another drug, the antisense oligonucleotide tofersen (Qalsody), in patients with ALS associated with a mutation in the superoxide dismutase 1 gene. According to the FDA, reductions in plasma neurofilament light concentration were “reasonably likely to predict a clinical benefit in patients.”
Only 1%-2% of patients with ALS fit the criteria to get the drug, Weiss said. He noted other limitations such as the cost ($180,000 a year), the need for lifelong monthly intrathecal injections, and serious neurological side effects in 7% of patients per a 2022 trial.
Weiss disclosed advisory board (Alexion, Ra [now UCB], argenx, Biogen, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Amylyx), data safety monitoring board (Sanofi, AI), consulting (Cytokinetics, CSL Behring), and speaker (Soleo) relationships.
*Correction, 10/23/2024: This story originally quoted Weiss as saying the maker of edaravone provides no assistance to underinsured patients. Weiss has clarified that he should have said this coverage is “limited.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AANEM 2024
A Brief Glimpse Into 80,000 Years of Human History
Like millions of other modern humans, my daughter and I stood in the backyard recently and watched comet C/2023 A3 (Tsuchinshan–ATLAS) with binoculars. It took a few minutes to locate, but once you see it is unmistakable.
It’s got a long (at least in human terms) orbit, roughly 80,000 years. So what was going on here, on our pale blue dot, the last time it graced our skies?
Well, here in Phoenix, the people were ... not here. Nor were they in Arizona, or North America, or pretty much the entire Western Hemisphere.
In fact, Homo sapiens were confined to Africa. The hardier Neanderthals had successfully moved into Eurasia, but our lineage was just starting to migrate there. There’s some evidence that we numbered maybe 10,000-15,000 at that point. Far more people saw the comet that night in the United States than our entire population count last time it swung by.
But we were moving up in the world. Our ancestors at the time had developed the first forms of jewelry, using seashells. There’s evidence that we’d learned to trade with other, distant, communities. We were using spears to put dinner on the table with less risk to ourselves than clubs posed.
And, in what’s now Kenya, in the same time frame, a pair of grieving parents carefully buried their 3-year-old child, wrapped in a covering and gently placed on a pillow.
Sadly, this isn’t a scene we’re unfamiliar with. Possibly the most famous painting of a physician is “The Doctor” (1891) by Luke Fildes, showing a physician trying to treat a seriously ill child while the parents look on helplessly.
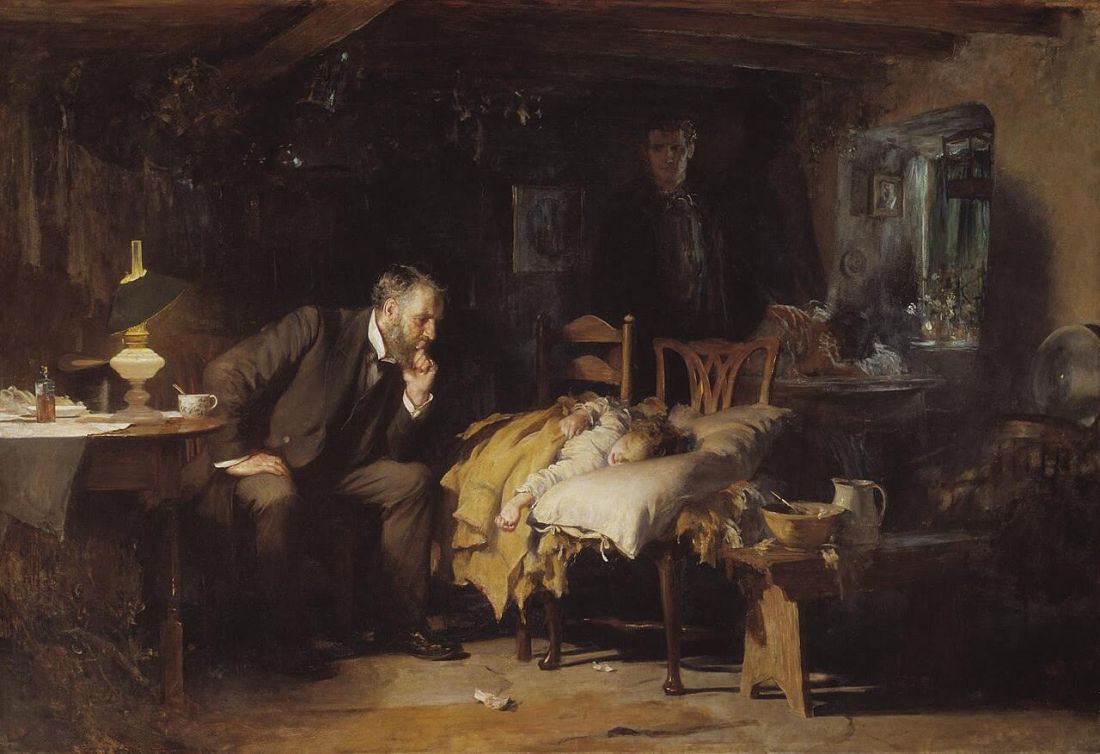

What did the Kenyan child die from? We’ll probably never know. Did they try to treat it? Most likely.
Humans, by nature, form societies. The size varies, but everyone has a role. There was probably some ancestor of Fildes’ doctor in the group who tried to help. Perhaps with prayers in an unknown tongue, or a preparation of certain leaves, or placing the child near a fire. When whatever they tried failed, the same person likely consoled the parents. Maybe they were involved in the burial, too.
The child would be found in 2017, giving us the first clear evidence of a ritual human burial in Africa. Just like today, we let go of our lost ones with ceremony. Perhaps the parents noticed the comet and thought it was their child’s spirit departing.
Now the comet is back. The planet hasn’t changed dramatically in 80,000 years (which isn’t much in geological time), but we have.
Would today’s doctors have been able to save the child? No idea, though we probably have a better chance than our professional ancestor did.
But our job hasn’t changed. Like us, the ancient practitioner probably tried to figure out why the child was sick and what could be done about it. When it was over they, and others, grieved with the parents.
The comet will be back in 80,000 years. On our scale, that’s a long time. The entire recorded history of our species is only 5,000 to 8,000 years. We’ve come a long way, but where we’re going in 80,000 years is anyone’s guess.
Will doctors in the year 82024 even know what we do now to care for people? Will they still be practicing on the third rock from the sun, or spread out across the galaxy? Will there even be doctors? (Probably, in one form or another.)
But We do our best to care, heal, and hope now, as we did then, and as our descendants will.
And, like my daughter and I did, no matter where we are, we will still look up at the sky with wonder.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Like millions of other modern humans, my daughter and I stood in the backyard recently and watched comet C/2023 A3 (Tsuchinshan–ATLAS) with binoculars. It took a few minutes to locate, but once you see it is unmistakable.
It’s got a long (at least in human terms) orbit, roughly 80,000 years. So what was going on here, on our pale blue dot, the last time it graced our skies?
Well, here in Phoenix, the people were ... not here. Nor were they in Arizona, or North America, or pretty much the entire Western Hemisphere.
In fact, Homo sapiens were confined to Africa. The hardier Neanderthals had successfully moved into Eurasia, but our lineage was just starting to migrate there. There’s some evidence that we numbered maybe 10,000-15,000 at that point. Far more people saw the comet that night in the United States than our entire population count last time it swung by.
But we were moving up in the world. Our ancestors at the time had developed the first forms of jewelry, using seashells. There’s evidence that we’d learned to trade with other, distant, communities. We were using spears to put dinner on the table with less risk to ourselves than clubs posed.
And, in what’s now Kenya, in the same time frame, a pair of grieving parents carefully buried their 3-year-old child, wrapped in a covering and gently placed on a pillow.
Sadly, this isn’t a scene we’re unfamiliar with. Possibly the most famous painting of a physician is “The Doctor” (1891) by Luke Fildes, showing a physician trying to treat a seriously ill child while the parents look on helplessly.

What did the Kenyan child die from? We’ll probably never know. Did they try to treat it? Most likely.
Humans, by nature, form societies. The size varies, but everyone has a role. There was probably some ancestor of Fildes’ doctor in the group who tried to help. Perhaps with prayers in an unknown tongue, or a preparation of certain leaves, or placing the child near a fire. When whatever they tried failed, the same person likely consoled the parents. Maybe they were involved in the burial, too.
The child would be found in 2017, giving us the first clear evidence of a ritual human burial in Africa. Just like today, we let go of our lost ones with ceremony. Perhaps the parents noticed the comet and thought it was their child’s spirit departing.
Now the comet is back. The planet hasn’t changed dramatically in 80,000 years (which isn’t much in geological time), but we have.
Would today’s doctors have been able to save the child? No idea, though we probably have a better chance than our professional ancestor did.
But our job hasn’t changed. Like us, the ancient practitioner probably tried to figure out why the child was sick and what could be done about it. When it was over they, and others, grieved with the parents.
The comet will be back in 80,000 years. On our scale, that’s a long time. The entire recorded history of our species is only 5,000 to 8,000 years. We’ve come a long way, but where we’re going in 80,000 years is anyone’s guess.
Will doctors in the year 82024 even know what we do now to care for people? Will they still be practicing on the third rock from the sun, or spread out across the galaxy? Will there even be doctors? (Probably, in one form or another.)
But We do our best to care, heal, and hope now, as we did then, and as our descendants will.
And, like my daughter and I did, no matter where we are, we will still look up at the sky with wonder.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Like millions of other modern humans, my daughter and I stood in the backyard recently and watched comet C/2023 A3 (Tsuchinshan–ATLAS) with binoculars. It took a few minutes to locate, but once you see it is unmistakable.
It’s got a long (at least in human terms) orbit, roughly 80,000 years. So what was going on here, on our pale blue dot, the last time it graced our skies?
Well, here in Phoenix, the people were ... not here. Nor were they in Arizona, or North America, or pretty much the entire Western Hemisphere.
In fact, Homo sapiens were confined to Africa. The hardier Neanderthals had successfully moved into Eurasia, but our lineage was just starting to migrate there. There’s some evidence that we numbered maybe 10,000-15,000 at that point. Far more people saw the comet that night in the United States than our entire population count last time it swung by.
But we were moving up in the world. Our ancestors at the time had developed the first forms of jewelry, using seashells. There’s evidence that we’d learned to trade with other, distant, communities. We were using spears to put dinner on the table with less risk to ourselves than clubs posed.
And, in what’s now Kenya, in the same time frame, a pair of grieving parents carefully buried their 3-year-old child, wrapped in a covering and gently placed on a pillow.
Sadly, this isn’t a scene we’re unfamiliar with. Possibly the most famous painting of a physician is “The Doctor” (1891) by Luke Fildes, showing a physician trying to treat a seriously ill child while the parents look on helplessly.

What did the Kenyan child die from? We’ll probably never know. Did they try to treat it? Most likely.
Humans, by nature, form societies. The size varies, but everyone has a role. There was probably some ancestor of Fildes’ doctor in the group who tried to help. Perhaps with prayers in an unknown tongue, or a preparation of certain leaves, or placing the child near a fire. When whatever they tried failed, the same person likely consoled the parents. Maybe they were involved in the burial, too.
The child would be found in 2017, giving us the first clear evidence of a ritual human burial in Africa. Just like today, we let go of our lost ones with ceremony. Perhaps the parents noticed the comet and thought it was their child’s spirit departing.
Now the comet is back. The planet hasn’t changed dramatically in 80,000 years (which isn’t much in geological time), but we have.
Would today’s doctors have been able to save the child? No idea, though we probably have a better chance than our professional ancestor did.
But our job hasn’t changed. Like us, the ancient practitioner probably tried to figure out why the child was sick and what could be done about it. When it was over they, and others, grieved with the parents.
The comet will be back in 80,000 years. On our scale, that’s a long time. The entire recorded history of our species is only 5,000 to 8,000 years. We’ve come a long way, but where we’re going in 80,000 years is anyone’s guess.
Will doctors in the year 82024 even know what we do now to care for people? Will they still be practicing on the third rock from the sun, or spread out across the galaxy? Will there even be doctors? (Probably, in one form or another.)
But We do our best to care, heal, and hope now, as we did then, and as our descendants will.
And, like my daughter and I did, no matter where we are, we will still look up at the sky with wonder.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
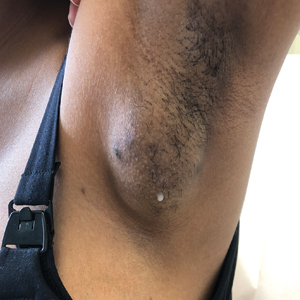
Spontaneously Draining Axillary Tumors in a Young Woman
THE DIAGNOSIS: Ectopic (Accessory) Breast Tissue
Ectopic (accessory) breast tissue (EBT) is a phenomenon caused by failed regression of one or more components of the embryonic mammary ridges— paired ectodermal thickenings that eventually develop into definitive breast tissue including the nipples, areolae, and parenchyma. Ectopic breast tissue is more common in women than men and is believed to be sporadic, although an autosomal-dominant inheritance mechanism with incomplete penetrance has been proposed for some cases.1 The reported incidence of EBT varies greatly among racial and ethnic groups but is most common in individuals of Asian descent. The incidence across all types of EBT is estimated at 0.25% to 6% in the general population.2
Observed clinical variations of EBT range from simple polythelia (additional nipple[s] without associated parenchyma) to complete polymastia (organized and differentiated accessory breasts). Some types of EBT are rarer than others: One report of gynecologic cancer screenings in 1660 patients found polymastia and polythelia incidences of 0.12% and 5.48%, respectively.3 Of the symptomatic variations, isolated parenchymal EBT without a nipple or areolar complex is the most common and may manifest clinically as unilateral or bilateral tender, mildly erythematous nodules or masses often located in the axillae. Ectopic breast tissue generally is observed along the milk line, a developmental regional designation corresponding to the embryologic mammary ridge and extending linearly from the anterior axilla to the inguinal fold on both sides of the body; however, there have been rare reports of EBT manifesting in areas outside the milk line, such as the face, neck, back, vulva, and extremities.2,3
Given that the underlying elements of EBT usually are hormone responsive (as with normal breast tissue), the initial symptom onset and subsequent manifestation frequently coincide with pubertal milestones, pregnancy, or lactation. Furthermore, some patients with EBT may experience symptom fluctuations in concordance with monthly menstrual phases. Many cases of EBT are selflimited and resolve within weeks to months after the end of a pregnancy or lactation, but some cases may persist. Continued observation and follow-up are advisable in all patients, as EBT symptoms often recur and the tissue is susceptible to the same disease processes that affect normal breasts, the most concerning of which is malignancy.4 Although the true incidence is limited by available data, primary ectopic breast malignancy has been estimated to account for 0.3% to 3.8% of diagnosed breast malignancies.2 Cases of malignancy arising from EBT often are of higher grade and poorer prognosis, a finding that may be attributable to diagnostic delays caused by oversight or misdiagnosis of EBT rather than inherent differences in the biologic profile of the tumors.2,4 Patients with a documented history of EBT may benefit from having their routine breast cancer screenings expanded to include areas with EBT foci.
Potential misdiagnoses for EBT include subcutaneous lipoma, axillary lymphadenopathy, abscess, hidradenitis suppurativa, or malignancy. Features that are suggestive of EBT include symptom association with hormone fluctuations (eg, menstrual phases), absence of fever, and lactescent rather than purulent drainage. Among reported EBT cases, spontaneous lactation rarely is described and, if present, often is associated with a history of prior trauma (eg, core needle biopsy or local abscess formation).5 This trauma creates an aberrant connection known as a milk fistula between the underlying parenchyma and the skin surface. Interestingly, our patient denied any history of axillary trauma, but she was noted to be lactating from an apparent milk fistula rather than an organized secretory duct system.
Though a patient history and clinical examination may be sufficient to diagnose EBT cases that are more physically apparent and well correlated with hormone fluctuations, many cases require additional diagnostic studies for confirmation. Of the tools available, ultrasonography generally is considered first-line due to its noninvasive nature, low cost, minimal risk, and high diagnostic value.2 Ultrasonography quickly differentiates between abscesses and cystlike processes, which may appear as discrete areas of decreased echogenicity, and breast tissue, which manifests with fibroglandular tissue and lobules of fat.2,6 Additionally, ultrasonography may demonstrate the secretion of milk through ducts or fistulae, if present. Should examination with ultrasonography prove inconclusive, follow-up studies using conventional radiographic mammography or magnetic resonance imaging may be warranted. Biopsy of EBT foci generally is not indicated unless first-line noninvasive studies fail to yield a conclusive diagnosis; however, biopsy also may be warranted if initial imaging is suggestive of malignancy arising from EBT.2
Management of EBT generally is conservative, and symptoms often resolve without intervention.4 Symptomatic relief may be achieved through techniques such as application of warm/cold compresses, avoidance of mechanical stimulation, and use of over-the-counter pain medicine. In cases that are persistent, frequently recurrent, or associated with severe symptoms or that cause considerable cosmetic impact, management with surgical excision and/or liposuction may be warranted.7 In our patient, the symptoms were not bothersome enough to warrant surgical intervention, so she was managed conservatively and did not return for follow-up.
- Leung AK. Familial supernumerary nipples. Am J Med Genet. 1988;31:631-635. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320310318
- Visconti G, Eltahir Y, Van Ginkel RJ, et al. Approach and management of primary ectopic breast carcinoma in the axilla: where are we? a comprehensive historical literature review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:E1-E11. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2010.08.015
- Göttlicher S. Incidence and location of polythelias, polymastias and mammae aberratae. a prospective one year study of 1,660 patients of a gynecologic practice. Article in German. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 1986;46:697-699. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1035944
- Ghosn SH, Khatri KA, Bhawan J. Bilateral aberrant axillary breast tissue mimicking lipomas: report of a case and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34(suppl 1):9-13. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00713.x
- Firat D, Idiz O, Isik A, et al. Spontaneous milk fistula from an accessory breast: an extremely rare case. Breast J. 2015;21:554-555. doi:10.1111/tbj.12452
- Lim HS, Kim SJ, Baek JM, et al. Sonographic findings of accessory breast tissue in axilla and related diseases. J Ultrasound Med. 2017;36:1469-1478. doi:10.7863/ultra.16.06056
- Gentile P, Izzo V, Cervelli V. Fibroadenoma in the bilateral accessory axillary breast. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2010;34:657-659. doi:10.1007/ s00266-010-9505-y
THE DIAGNOSIS: Ectopic (Accessory) Breast Tissue
Ectopic (accessory) breast tissue (EBT) is a phenomenon caused by failed regression of one or more components of the embryonic mammary ridges— paired ectodermal thickenings that eventually develop into definitive breast tissue including the nipples, areolae, and parenchyma. Ectopic breast tissue is more common in women than men and is believed to be sporadic, although an autosomal-dominant inheritance mechanism with incomplete penetrance has been proposed for some cases.1 The reported incidence of EBT varies greatly among racial and ethnic groups but is most common in individuals of Asian descent. The incidence across all types of EBT is estimated at 0.25% to 6% in the general population.2
Observed clinical variations of EBT range from simple polythelia (additional nipple[s] without associated parenchyma) to complete polymastia (organized and differentiated accessory breasts). Some types of EBT are rarer than others: One report of gynecologic cancer screenings in 1660 patients found polymastia and polythelia incidences of 0.12% and 5.48%, respectively.3 Of the symptomatic variations, isolated parenchymal EBT without a nipple or areolar complex is the most common and may manifest clinically as unilateral or bilateral tender, mildly erythematous nodules or masses often located in the axillae. Ectopic breast tissue generally is observed along the milk line, a developmental regional designation corresponding to the embryologic mammary ridge and extending linearly from the anterior axilla to the inguinal fold on both sides of the body; however, there have been rare reports of EBT manifesting in areas outside the milk line, such as the face, neck, back, vulva, and extremities.2,3
Given that the underlying elements of EBT usually are hormone responsive (as with normal breast tissue), the initial symptom onset and subsequent manifestation frequently coincide with pubertal milestones, pregnancy, or lactation. Furthermore, some patients with EBT may experience symptom fluctuations in concordance with monthly menstrual phases. Many cases of EBT are selflimited and resolve within weeks to months after the end of a pregnancy or lactation, but some cases may persist. Continued observation and follow-up are advisable in all patients, as EBT symptoms often recur and the tissue is susceptible to the same disease processes that affect normal breasts, the most concerning of which is malignancy.4 Although the true incidence is limited by available data, primary ectopic breast malignancy has been estimated to account for 0.3% to 3.8% of diagnosed breast malignancies.2 Cases of malignancy arising from EBT often are of higher grade and poorer prognosis, a finding that may be attributable to diagnostic delays caused by oversight or misdiagnosis of EBT rather than inherent differences in the biologic profile of the tumors.2,4 Patients with a documented history of EBT may benefit from having their routine breast cancer screenings expanded to include areas with EBT foci.
Potential misdiagnoses for EBT include subcutaneous lipoma, axillary lymphadenopathy, abscess, hidradenitis suppurativa, or malignancy. Features that are suggestive of EBT include symptom association with hormone fluctuations (eg, menstrual phases), absence of fever, and lactescent rather than purulent drainage. Among reported EBT cases, spontaneous lactation rarely is described and, if present, often is associated with a history of prior trauma (eg, core needle biopsy or local abscess formation).5 This trauma creates an aberrant connection known as a milk fistula between the underlying parenchyma and the skin surface. Interestingly, our patient denied any history of axillary trauma, but she was noted to be lactating from an apparent milk fistula rather than an organized secretory duct system.
Though a patient history and clinical examination may be sufficient to diagnose EBT cases that are more physically apparent and well correlated with hormone fluctuations, many cases require additional diagnostic studies for confirmation. Of the tools available, ultrasonography generally is considered first-line due to its noninvasive nature, low cost, minimal risk, and high diagnostic value.2 Ultrasonography quickly differentiates between abscesses and cystlike processes, which may appear as discrete areas of decreased echogenicity, and breast tissue, which manifests with fibroglandular tissue and lobules of fat.2,6 Additionally, ultrasonography may demonstrate the secretion of milk through ducts or fistulae, if present. Should examination with ultrasonography prove inconclusive, follow-up studies using conventional radiographic mammography or magnetic resonance imaging may be warranted. Biopsy of EBT foci generally is not indicated unless first-line noninvasive studies fail to yield a conclusive diagnosis; however, biopsy also may be warranted if initial imaging is suggestive of malignancy arising from EBT.2
Management of EBT generally is conservative, and symptoms often resolve without intervention.4 Symptomatic relief may be achieved through techniques such as application of warm/cold compresses, avoidance of mechanical stimulation, and use of over-the-counter pain medicine. In cases that are persistent, frequently recurrent, or associated with severe symptoms or that cause considerable cosmetic impact, management with surgical excision and/or liposuction may be warranted.7 In our patient, the symptoms were not bothersome enough to warrant surgical intervention, so she was managed conservatively and did not return for follow-up.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Ectopic (Accessory) Breast Tissue
Ectopic (accessory) breast tissue (EBT) is a phenomenon caused by failed regression of one or more components of the embryonic mammary ridges— paired ectodermal thickenings that eventually develop into definitive breast tissue including the nipples, areolae, and parenchyma. Ectopic breast tissue is more common in women than men and is believed to be sporadic, although an autosomal-dominant inheritance mechanism with incomplete penetrance has been proposed for some cases.1 The reported incidence of EBT varies greatly among racial and ethnic groups but is most common in individuals of Asian descent. The incidence across all types of EBT is estimated at 0.25% to 6% in the general population.2
Observed clinical variations of EBT range from simple polythelia (additional nipple[s] without associated parenchyma) to complete polymastia (organized and differentiated accessory breasts). Some types of EBT are rarer than others: One report of gynecologic cancer screenings in 1660 patients found polymastia and polythelia incidences of 0.12% and 5.48%, respectively.3 Of the symptomatic variations, isolated parenchymal EBT without a nipple or areolar complex is the most common and may manifest clinically as unilateral or bilateral tender, mildly erythematous nodules or masses often located in the axillae. Ectopic breast tissue generally is observed along the milk line, a developmental regional designation corresponding to the embryologic mammary ridge and extending linearly from the anterior axilla to the inguinal fold on both sides of the body; however, there have been rare reports of EBT manifesting in areas outside the milk line, such as the face, neck, back, vulva, and extremities.2,3
Given that the underlying elements of EBT usually are hormone responsive (as with normal breast tissue), the initial symptom onset and subsequent manifestation frequently coincide with pubertal milestones, pregnancy, or lactation. Furthermore, some patients with EBT may experience symptom fluctuations in concordance with monthly menstrual phases. Many cases of EBT are selflimited and resolve within weeks to months after the end of a pregnancy or lactation, but some cases may persist. Continued observation and follow-up are advisable in all patients, as EBT symptoms often recur and the tissue is susceptible to the same disease processes that affect normal breasts, the most concerning of which is malignancy.4 Although the true incidence is limited by available data, primary ectopic breast malignancy has been estimated to account for 0.3% to 3.8% of diagnosed breast malignancies.2 Cases of malignancy arising from EBT often are of higher grade and poorer prognosis, a finding that may be attributable to diagnostic delays caused by oversight or misdiagnosis of EBT rather than inherent differences in the biologic profile of the tumors.2,4 Patients with a documented history of EBT may benefit from having their routine breast cancer screenings expanded to include areas with EBT foci.
Potential misdiagnoses for EBT include subcutaneous lipoma, axillary lymphadenopathy, abscess, hidradenitis suppurativa, or malignancy. Features that are suggestive of EBT include symptom association with hormone fluctuations (eg, menstrual phases), absence of fever, and lactescent rather than purulent drainage. Among reported EBT cases, spontaneous lactation rarely is described and, if present, often is associated with a history of prior trauma (eg, core needle biopsy or local abscess formation).5 This trauma creates an aberrant connection known as a milk fistula between the underlying parenchyma and the skin surface. Interestingly, our patient denied any history of axillary trauma, but she was noted to be lactating from an apparent milk fistula rather than an organized secretory duct system.
Though a patient history and clinical examination may be sufficient to diagnose EBT cases that are more physically apparent and well correlated with hormone fluctuations, many cases require additional diagnostic studies for confirmation. Of the tools available, ultrasonography generally is considered first-line due to its noninvasive nature, low cost, minimal risk, and high diagnostic value.2 Ultrasonography quickly differentiates between abscesses and cystlike processes, which may appear as discrete areas of decreased echogenicity, and breast tissue, which manifests with fibroglandular tissue and lobules of fat.2,6 Additionally, ultrasonography may demonstrate the secretion of milk through ducts or fistulae, if present. Should examination with ultrasonography prove inconclusive, follow-up studies using conventional radiographic mammography or magnetic resonance imaging may be warranted. Biopsy of EBT foci generally is not indicated unless first-line noninvasive studies fail to yield a conclusive diagnosis; however, biopsy also may be warranted if initial imaging is suggestive of malignancy arising from EBT.2
Management of EBT generally is conservative, and symptoms often resolve without intervention.4 Symptomatic relief may be achieved through techniques such as application of warm/cold compresses, avoidance of mechanical stimulation, and use of over-the-counter pain medicine. In cases that are persistent, frequently recurrent, or associated with severe symptoms or that cause considerable cosmetic impact, management with surgical excision and/or liposuction may be warranted.7 In our patient, the symptoms were not bothersome enough to warrant surgical intervention, so she was managed conservatively and did not return for follow-up.
- Leung AK. Familial supernumerary nipples. Am J Med Genet. 1988;31:631-635. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320310318
- Visconti G, Eltahir Y, Van Ginkel RJ, et al. Approach and management of primary ectopic breast carcinoma in the axilla: where are we? a comprehensive historical literature review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:E1-E11. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2010.08.015
- Göttlicher S. Incidence and location of polythelias, polymastias and mammae aberratae. a prospective one year study of 1,660 patients of a gynecologic practice. Article in German. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 1986;46:697-699. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1035944
- Ghosn SH, Khatri KA, Bhawan J. Bilateral aberrant axillary breast tissue mimicking lipomas: report of a case and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34(suppl 1):9-13. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00713.x
- Firat D, Idiz O, Isik A, et al. Spontaneous milk fistula from an accessory breast: an extremely rare case. Breast J. 2015;21:554-555. doi:10.1111/tbj.12452
- Lim HS, Kim SJ, Baek JM, et al. Sonographic findings of accessory breast tissue in axilla and related diseases. J Ultrasound Med. 2017;36:1469-1478. doi:10.7863/ultra.16.06056
- Gentile P, Izzo V, Cervelli V. Fibroadenoma in the bilateral accessory axillary breast. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2010;34:657-659. doi:10.1007/ s00266-010-9505-y
- Leung AK. Familial supernumerary nipples. Am J Med Genet. 1988;31:631-635. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320310318
- Visconti G, Eltahir Y, Van Ginkel RJ, et al. Approach and management of primary ectopic breast carcinoma in the axilla: where are we? a comprehensive historical literature review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:E1-E11. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2010.08.015
- Göttlicher S. Incidence and location of polythelias, polymastias and mammae aberratae. a prospective one year study of 1,660 patients of a gynecologic practice. Article in German. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 1986;46:697-699. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1035944
- Ghosn SH, Khatri KA, Bhawan J. Bilateral aberrant axillary breast tissue mimicking lipomas: report of a case and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34(suppl 1):9-13. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00713.x
- Firat D, Idiz O, Isik A, et al. Spontaneous milk fistula from an accessory breast: an extremely rare case. Breast J. 2015;21:554-555. doi:10.1111/tbj.12452
- Lim HS, Kim SJ, Baek JM, et al. Sonographic findings of accessory breast tissue in axilla and related diseases. J Ultrasound Med. 2017;36:1469-1478. doi:10.7863/ultra.16.06056
- Gentile P, Izzo V, Cervelli V. Fibroadenoma in the bilateral accessory axillary breast. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2010;34:657-659. doi:10.1007/ s00266-010-9505-y
A 19-year-old G1P1A0 woman presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of bilateral axillary swelling, pain, and spontaneous drainage of approximately 2 weeks’ duration. The patient, who was 2 weeks postpartum, reported that the symptoms were associated with lactation when breastfeeding. She denied any personal or family history of hidradenitis suppurativa or other formally diagnosed dermatologic condition. Physical examination revealed a soft, mildly tender, well-circumscribed, nonfluctuant mobile mass in each axilla. Both lesions had a single central sinus tract with thin lactescent discharge that spontaneously drained and was expressible. A single thin hyperpigmented papule was noted on the anterior aspect of each mass.

EHR Prompt Helped Cut Acute Otitis Media Antibiotic Use by Half
LOS ANGELES — Embedding a new discharge order set into electronic health records (EHRs) with a preselected 5-day antibiotic course for children aged 2 years or older diagnosed with acute otitis media (AOM) cut antibiotic duration sharply, according to new data presented at the Infectious Disease Week (IDWeek) 2024 Annual Meeting.
“We were effectively able to cut antibiotic use in half by shortening the duration of treatment,” said lead author Joana Dimo, DO, a Pediatric Infectious Diseases fellow at the University of Colorado Denver/Children’s Hospital Colorado.
In the United States, 80% of children will experience otitis media during their lifetime. Untreated ear infections can lead to symptoms ranging from mild ear discharge to life-threatening conditions such as mastoiditis and intracranial abscesses.
Most Cases Resolve Without Antibiotics
Ear infections “are the leading reason for antibiotic prescriptions in kids,” Dimo noted, adding that 24% of all pediatric antibiotic prescriptions are for AOM. Amoxicillin is the preferred first-line treatment. “Research supports that 75% of children get better on their own without antibiotics, and when needed, short courses of just 5 days are safe and effective.”
Antibiotics can cause side effects such as diarrhea and rashes. “Each additional day of antibiotics that are not needed leads to more side effects,” Dimo said, as well as contributing to antibiotic resistance.
Dimo’s team implemented new EHR order sets across the University of Colorado/Children’s Hospital Colorado health network’s four emergency departments and four urgent care centers and included 31,929 patients in the study.
Then they conducted a retrospective review of patients 61 days to 18 years old who entered those settings and had confirmed AOM between January 2019 through December 2023, before and after the April 2021 intervention. The researchers also developed a guideline on managing ear infections to support clinicians as part of the intervention in December 2022.
Compliance Grew From 3% to 83%
Dimo said they found very few clinicians in their study had been prescribing according to current guidelines. Their results showed a jump from 3% to 83% in providers prescribing 5-day durations of antibiotics for children aged 2 years or older after their intervention.
The intervention did not lead to increased treatment failures or complications, she added. The team looked for diagnostic codes for mastoiditis, subperiosteal abscess, petrositis, labyrinthitis, meningitis, and intracranial abscess, and “none of our patients” developed any of those complications, Dimo said.
Dimo said the overall rate of prescribing, however, increased. Finding out why prescribing rates remained high throughout the study, before and after their intervention, is a question they are investigating in future work, she said.
Cost-Effective and Scalable
“The benefit of this strategy to other institutions is that it’s not labor-intensive. It’s cost-effective, and it can result in dramatic changes in antibiotic use,” Dimo said.
“In the outpatient setting, there’s still a lot of antibiotics being given unnecessarily to children with acute otitis media,” said William Schaffner, MD, infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University School of Medicine in Nashville, Tennessee, who was not part of the research. “The American Academy of Pediatrics has been working on that for about a decade — to get pediatricians attuned to when you use them. Most of these episodes of acute otitis media — it’s now well-established — are due to viral infections.”
He said that some physicians may still be defaulting to the longer doses — up to 10 days — that they may have learned in medical school or residency.
“The data would indicate that 5 days of treatment — when treatment is appropriate — is, in the vast majority of instances, sufficient,” Schaffner said.
The researchers “were remarkably successful,” he said, adding that another question is ripe for research. “They still have to get to this issue of whether all of these antibiotic starts were necessary.”
Not knowing whether antibiotic prescriptions in this study were warranted is a limitation of the study, Dimo said, as was not being able to track whether patients presented to institutions outside their own for a return visit or for complications.
She said she thinks one of the reasons for such a sharp increase in compliance was that clinicians in their system routinely use order sets, so using the new order sets easily became part of their workflow.
Dimo and Schaffner reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES — Embedding a new discharge order set into electronic health records (EHRs) with a preselected 5-day antibiotic course for children aged 2 years or older diagnosed with acute otitis media (AOM) cut antibiotic duration sharply, according to new data presented at the Infectious Disease Week (IDWeek) 2024 Annual Meeting.
“We were effectively able to cut antibiotic use in half by shortening the duration of treatment,” said lead author Joana Dimo, DO, a Pediatric Infectious Diseases fellow at the University of Colorado Denver/Children’s Hospital Colorado.
In the United States, 80% of children will experience otitis media during their lifetime. Untreated ear infections can lead to symptoms ranging from mild ear discharge to life-threatening conditions such as mastoiditis and intracranial abscesses.
Most Cases Resolve Without Antibiotics
Ear infections “are the leading reason for antibiotic prescriptions in kids,” Dimo noted, adding that 24% of all pediatric antibiotic prescriptions are for AOM. Amoxicillin is the preferred first-line treatment. “Research supports that 75% of children get better on their own without antibiotics, and when needed, short courses of just 5 days are safe and effective.”
Antibiotics can cause side effects such as diarrhea and rashes. “Each additional day of antibiotics that are not needed leads to more side effects,” Dimo said, as well as contributing to antibiotic resistance.
Dimo’s team implemented new EHR order sets across the University of Colorado/Children’s Hospital Colorado health network’s four emergency departments and four urgent care centers and included 31,929 patients in the study.
Then they conducted a retrospective review of patients 61 days to 18 years old who entered those settings and had confirmed AOM between January 2019 through December 2023, before and after the April 2021 intervention. The researchers also developed a guideline on managing ear infections to support clinicians as part of the intervention in December 2022.
Compliance Grew From 3% to 83%
Dimo said they found very few clinicians in their study had been prescribing according to current guidelines. Their results showed a jump from 3% to 83% in providers prescribing 5-day durations of antibiotics for children aged 2 years or older after their intervention.
The intervention did not lead to increased treatment failures or complications, she added. The team looked for diagnostic codes for mastoiditis, subperiosteal abscess, petrositis, labyrinthitis, meningitis, and intracranial abscess, and “none of our patients” developed any of those complications, Dimo said.
Dimo said the overall rate of prescribing, however, increased. Finding out why prescribing rates remained high throughout the study, before and after their intervention, is a question they are investigating in future work, she said.
Cost-Effective and Scalable
“The benefit of this strategy to other institutions is that it’s not labor-intensive. It’s cost-effective, and it can result in dramatic changes in antibiotic use,” Dimo said.
“In the outpatient setting, there’s still a lot of antibiotics being given unnecessarily to children with acute otitis media,” said William Schaffner, MD, infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University School of Medicine in Nashville, Tennessee, who was not part of the research. “The American Academy of Pediatrics has been working on that for about a decade — to get pediatricians attuned to when you use them. Most of these episodes of acute otitis media — it’s now well-established — are due to viral infections.”
He said that some physicians may still be defaulting to the longer doses — up to 10 days — that they may have learned in medical school or residency.
“The data would indicate that 5 days of treatment — when treatment is appropriate — is, in the vast majority of instances, sufficient,” Schaffner said.
The researchers “were remarkably successful,” he said, adding that another question is ripe for research. “They still have to get to this issue of whether all of these antibiotic starts were necessary.”
Not knowing whether antibiotic prescriptions in this study were warranted is a limitation of the study, Dimo said, as was not being able to track whether patients presented to institutions outside their own for a return visit or for complications.
She said she thinks one of the reasons for such a sharp increase in compliance was that clinicians in their system routinely use order sets, so using the new order sets easily became part of their workflow.
Dimo and Schaffner reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES — Embedding a new discharge order set into electronic health records (EHRs) with a preselected 5-day antibiotic course for children aged 2 years or older diagnosed with acute otitis media (AOM) cut antibiotic duration sharply, according to new data presented at the Infectious Disease Week (IDWeek) 2024 Annual Meeting.
“We were effectively able to cut antibiotic use in half by shortening the duration of treatment,” said lead author Joana Dimo, DO, a Pediatric Infectious Diseases fellow at the University of Colorado Denver/Children’s Hospital Colorado.
In the United States, 80% of children will experience otitis media during their lifetime. Untreated ear infections can lead to symptoms ranging from mild ear discharge to life-threatening conditions such as mastoiditis and intracranial abscesses.
Most Cases Resolve Without Antibiotics
Ear infections “are the leading reason for antibiotic prescriptions in kids,” Dimo noted, adding that 24% of all pediatric antibiotic prescriptions are for AOM. Amoxicillin is the preferred first-line treatment. “Research supports that 75% of children get better on their own without antibiotics, and when needed, short courses of just 5 days are safe and effective.”
Antibiotics can cause side effects such as diarrhea and rashes. “Each additional day of antibiotics that are not needed leads to more side effects,” Dimo said, as well as contributing to antibiotic resistance.
Dimo’s team implemented new EHR order sets across the University of Colorado/Children’s Hospital Colorado health network’s four emergency departments and four urgent care centers and included 31,929 patients in the study.
Then they conducted a retrospective review of patients 61 days to 18 years old who entered those settings and had confirmed AOM between January 2019 through December 2023, before and after the April 2021 intervention. The researchers also developed a guideline on managing ear infections to support clinicians as part of the intervention in December 2022.
Compliance Grew From 3% to 83%
Dimo said they found very few clinicians in their study had been prescribing according to current guidelines. Their results showed a jump from 3% to 83% in providers prescribing 5-day durations of antibiotics for children aged 2 years or older after their intervention.
The intervention did not lead to increased treatment failures or complications, she added. The team looked for diagnostic codes for mastoiditis, subperiosteal abscess, petrositis, labyrinthitis, meningitis, and intracranial abscess, and “none of our patients” developed any of those complications, Dimo said.
Dimo said the overall rate of prescribing, however, increased. Finding out why prescribing rates remained high throughout the study, before and after their intervention, is a question they are investigating in future work, she said.
Cost-Effective and Scalable
“The benefit of this strategy to other institutions is that it’s not labor-intensive. It’s cost-effective, and it can result in dramatic changes in antibiotic use,” Dimo said.
“In the outpatient setting, there’s still a lot of antibiotics being given unnecessarily to children with acute otitis media,” said William Schaffner, MD, infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University School of Medicine in Nashville, Tennessee, who was not part of the research. “The American Academy of Pediatrics has been working on that for about a decade — to get pediatricians attuned to when you use them. Most of these episodes of acute otitis media — it’s now well-established — are due to viral infections.”
He said that some physicians may still be defaulting to the longer doses — up to 10 days — that they may have learned in medical school or residency.
“The data would indicate that 5 days of treatment — when treatment is appropriate — is, in the vast majority of instances, sufficient,” Schaffner said.
The researchers “were remarkably successful,” he said, adding that another question is ripe for research. “They still have to get to this issue of whether all of these antibiotic starts were necessary.”
Not knowing whether antibiotic prescriptions in this study were warranted is a limitation of the study, Dimo said, as was not being able to track whether patients presented to institutions outside their own for a return visit or for complications.
She said she thinks one of the reasons for such a sharp increase in compliance was that clinicians in their system routinely use order sets, so using the new order sets easily became part of their workflow.
Dimo and Schaffner reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM IDWEEK 2024
Is It Possible To Treat Patients You Dislike?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
What do we do if we don’t like patients? We take the Hippocratic Oath as young students in Glasgow. We do that just before our graduation ceremony; we hold our hands up and repeat the Hippocratic Oath: “First, do no harm,” and so on.
I was thinking back over a long career. I’ve been a cancer doctor for 40 years and I quite like saying that.
I can only think genuinely over a couple of times in which I’ve acted reflexively when a patient has done something awful. The couple of times it happened, it was just terrible racist comments to junior doctors who were with me. Extraordinarily dreadful things such as, “I don’t want to be touched by ...” or something of that sort.
Without really thinking about it, you react as a normal citizen and say, “That’s absolutely awful. Apologize immediately or leave the consultation room, and never ever come back again.”
I remember that it happened once in Glasgow and once when I was a young professor in Birmingham, and it’s just an automatic gut reaction. The patient got a fright, and I immediately apologized and groveled around. In that relationship, we hold all the power, don’t we? Rather than being gentle about it, I was genuinely angry because of these ridiculous comments.
Otherwise, I think most of the doctor-patient relationships are predicated on nonromantic love. I think patients want us to love them as one would a son, mother, father, or daughter, because if we do, then we will do better for them and we’ll pull out all the stops. “Placebo” means “I will please.” I think in the vast majority of cases, at least in our National Health Service (NHS), patients come with trust and a sense of wanting to build that relationship. That may be changing, but not for me.
What about putting the boot on the other foot? What if the patients don’t like us rather than vice versa? As part of our accreditation appraisal process, from time to time we have to take patient surveys as to whether the patients felt that, after they had been seen in a consultation, they were treated with dignity, the quality of information given was appropriate, and they were treated with kindness.
It’s an excellent exercise. Without bragging about it, patients objectively, according to these measures, appreciate the service that I give. It’s like getting five-star reviews on Trustpilot, or whatever these things are, that allow you to review car salesmen and so on. I have always had five-star reviews across the board.
That, again, I thought was just a feature of that relationship, of patients wanting to please. These are patients who had been treated, who were in the outpatient department, who were in the midst of battle. Still, the scores are very high. I speak to my colleagues and that’s not uniformly the case. Patients actually do use these feedback forms, I think in a positive rather than negative way, reflecting back on the way that they were treated.
It has caused some of my colleagues to think quite hard about their personal style and approach to patients. That sense of feedback is important.
What about losing trust? If that’s at the heart of everything that we do, then what would be an objective measure of losing trust? Again, in our healthcare system, it has been exceedingly unusual for a patient to request a second opinion. Now, that’s changing. The government is trying to change it. Leaders of the NHS are trying to change it so that patients feel assured that they can seek second opinions.
Again, in all the years I’ve been a cancer doctor, it has been incredibly infrequent that somebody has sought a second opinion after I’ve said something. That may be a measure of trust. Again, I’ve lived through an NHS in which seeking second opinions was something of a rarity.
I’d be really interested to see what you think. In your own sphere of healthcare practice, is it possible for us to look after patients that we don’t like, or should we be honest and say, “I don’t like you. Our relationship has broken down. I want you to be seen by a colleague,” or “I want you to be nursed by somebody else”?
Has that happened? Is that something that you think is common or may become more common? What about when trust breaks down the other way? Can you think of instances in which the relationship, for whatever reason, just didn’t work and the patient had to move on because of that loss of trust and what underpinned it? I’d be really interested to know.
I seek to be informed rather than the other way around. Can we truly look after patients that we don’t like or can we rise above it as Hippocrates might have done?
Thanks for listening, as always. For the time being, over and out.
Dr. Kerr, Professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford; Professor of Cancer Medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom, disclosed ties with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers, Afrox, GlaxoSmithKline, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Genomic Health, Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
What do we do if we don’t like patients? We take the Hippocratic Oath as young students in Glasgow. We do that just before our graduation ceremony; we hold our hands up and repeat the Hippocratic Oath: “First, do no harm,” and so on.
I was thinking back over a long career. I’ve been a cancer doctor for 40 years and I quite like saying that.
I can only think genuinely over a couple of times in which I’ve acted reflexively when a patient has done something awful. The couple of times it happened, it was just terrible racist comments to junior doctors who were with me. Extraordinarily dreadful things such as, “I don’t want to be touched by ...” or something of that sort.
Without really thinking about it, you react as a normal citizen and say, “That’s absolutely awful. Apologize immediately or leave the consultation room, and never ever come back again.”
I remember that it happened once in Glasgow and once when I was a young professor in Birmingham, and it’s just an automatic gut reaction. The patient got a fright, and I immediately apologized and groveled around. In that relationship, we hold all the power, don’t we? Rather than being gentle about it, I was genuinely angry because of these ridiculous comments.
Otherwise, I think most of the doctor-patient relationships are predicated on nonromantic love. I think patients want us to love them as one would a son, mother, father, or daughter, because if we do, then we will do better for them and we’ll pull out all the stops. “Placebo” means “I will please.” I think in the vast majority of cases, at least in our National Health Service (NHS), patients come with trust and a sense of wanting to build that relationship. That may be changing, but not for me.
What about putting the boot on the other foot? What if the patients don’t like us rather than vice versa? As part of our accreditation appraisal process, from time to time we have to take patient surveys as to whether the patients felt that, after they had been seen in a consultation, they were treated with dignity, the quality of information given was appropriate, and they were treated with kindness.
It’s an excellent exercise. Without bragging about it, patients objectively, according to these measures, appreciate the service that I give. It’s like getting five-star reviews on Trustpilot, or whatever these things are, that allow you to review car salesmen and so on. I have always had five-star reviews across the board.
That, again, I thought was just a feature of that relationship, of patients wanting to please. These are patients who had been treated, who were in the outpatient department, who were in the midst of battle. Still, the scores are very high. I speak to my colleagues and that’s not uniformly the case. Patients actually do use these feedback forms, I think in a positive rather than negative way, reflecting back on the way that they were treated.
It has caused some of my colleagues to think quite hard about their personal style and approach to patients. That sense of feedback is important.
What about losing trust? If that’s at the heart of everything that we do, then what would be an objective measure of losing trust? Again, in our healthcare system, it has been exceedingly unusual for a patient to request a second opinion. Now, that’s changing. The government is trying to change it. Leaders of the NHS are trying to change it so that patients feel assured that they can seek second opinions.
Again, in all the years I’ve been a cancer doctor, it has been incredibly infrequent that somebody has sought a second opinion after I’ve said something. That may be a measure of trust. Again, I’ve lived through an NHS in which seeking second opinions was something of a rarity.
I’d be really interested to see what you think. In your own sphere of healthcare practice, is it possible for us to look after patients that we don’t like, or should we be honest and say, “I don’t like you. Our relationship has broken down. I want you to be seen by a colleague,” or “I want you to be nursed by somebody else”?
Has that happened? Is that something that you think is common or may become more common? What about when trust breaks down the other way? Can you think of instances in which the relationship, for whatever reason, just didn’t work and the patient had to move on because of that loss of trust and what underpinned it? I’d be really interested to know.
I seek to be informed rather than the other way around. Can we truly look after patients that we don’t like or can we rise above it as Hippocrates might have done?
Thanks for listening, as always. For the time being, over and out.
Dr. Kerr, Professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford; Professor of Cancer Medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom, disclosed ties with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers, Afrox, GlaxoSmithKline, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Genomic Health, Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
What do we do if we don’t like patients? We take the Hippocratic Oath as young students in Glasgow. We do that just before our graduation ceremony; we hold our hands up and repeat the Hippocratic Oath: “First, do no harm,” and so on.
I was thinking back over a long career. I’ve been a cancer doctor for 40 years and I quite like saying that.
I can only think genuinely over a couple of times in which I’ve acted reflexively when a patient has done something awful. The couple of times it happened, it was just terrible racist comments to junior doctors who were with me. Extraordinarily dreadful things such as, “I don’t want to be touched by ...” or something of that sort.
Without really thinking about it, you react as a normal citizen and say, “That’s absolutely awful. Apologize immediately or leave the consultation room, and never ever come back again.”
I remember that it happened once in Glasgow and once when I was a young professor in Birmingham, and it’s just an automatic gut reaction. The patient got a fright, and I immediately apologized and groveled around. In that relationship, we hold all the power, don’t we? Rather than being gentle about it, I was genuinely angry because of these ridiculous comments.
Otherwise, I think most of the doctor-patient relationships are predicated on nonromantic love. I think patients want us to love them as one would a son, mother, father, or daughter, because if we do, then we will do better for them and we’ll pull out all the stops. “Placebo” means “I will please.” I think in the vast majority of cases, at least in our National Health Service (NHS), patients come with trust and a sense of wanting to build that relationship. That may be changing, but not for me.
What about putting the boot on the other foot? What if the patients don’t like us rather than vice versa? As part of our accreditation appraisal process, from time to time we have to take patient surveys as to whether the patients felt that, after they had been seen in a consultation, they were treated with dignity, the quality of information given was appropriate, and they were treated with kindness.
It’s an excellent exercise. Without bragging about it, patients objectively, according to these measures, appreciate the service that I give. It’s like getting five-star reviews on Trustpilot, or whatever these things are, that allow you to review car salesmen and so on. I have always had five-star reviews across the board.
That, again, I thought was just a feature of that relationship, of patients wanting to please. These are patients who had been treated, who were in the outpatient department, who were in the midst of battle. Still, the scores are very high. I speak to my colleagues and that’s not uniformly the case. Patients actually do use these feedback forms, I think in a positive rather than negative way, reflecting back on the way that they were treated.
It has caused some of my colleagues to think quite hard about their personal style and approach to patients. That sense of feedback is important.
What about losing trust? If that’s at the heart of everything that we do, then what would be an objective measure of losing trust? Again, in our healthcare system, it has been exceedingly unusual for a patient to request a second opinion. Now, that’s changing. The government is trying to change it. Leaders of the NHS are trying to change it so that patients feel assured that they can seek second opinions.
Again, in all the years I’ve been a cancer doctor, it has been incredibly infrequent that somebody has sought a second opinion after I’ve said something. That may be a measure of trust. Again, I’ve lived through an NHS in which seeking second opinions was something of a rarity.
I’d be really interested to see what you think. In your own sphere of healthcare practice, is it possible for us to look after patients that we don’t like, or should we be honest and say, “I don’t like you. Our relationship has broken down. I want you to be seen by a colleague,” or “I want you to be nursed by somebody else”?
Has that happened? Is that something that you think is common or may become more common? What about when trust breaks down the other way? Can you think of instances in which the relationship, for whatever reason, just didn’t work and the patient had to move on because of that loss of trust and what underpinned it? I’d be really interested to know.
I seek to be informed rather than the other way around. Can we truly look after patients that we don’t like or can we rise above it as Hippocrates might have done?
Thanks for listening, as always. For the time being, over and out.
Dr. Kerr, Professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford; Professor of Cancer Medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom, disclosed ties with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers, Afrox, GlaxoSmithKline, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Genomic Health, Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ASA Releases New Primary Stroke Prevention Guideline
The first update in a decade, the 2024 Guideline for the Primary Prevention of Stroke, replaces the 2014 version and is intended to be a resource for clinicians to help them implement a variety of prevention strategies in patients with no previous history of stroke. It aligns with the American Heart Association’s Life’s Essential 8.
“This guideline is an important and timely update from 2014 for multiple reasons. First, there have been groundbreaking clinical trials that have been published with new medications to not only treat the target disease [including] diabetes/obesity and high cholesterol], but also lower the risk of stroke and heart disease,” said chair of the guideline writing group, Cheryl D. Bushnell, MD, MHS, FAHA, and vice chair of the research, Department of Neurology, Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
It was published online on October 21 in Stroke.
Up to 80% of Strokes Preventable
Estimates show that every year in the United States, more than 500,000 individuals have a first stroke. However, the guideline authors noted that up to 80% of strokes may be preventable. As a result, they called for better primary stroke prevention that includes improved screening and lifestyle changes.
This includes adoption of the Mediterranean diet, which has been shown to significantly reduce stroke risk, especially when supplemented with consumption of nuts and olive oil.
The guideline recommendations also emphasize the need for physical activity, which is “essential” for cardiovascular health and stroke reduction. The authors underscored this point and provided a new recommendation to screen for sedentary behavior and advise patients to avoid inactivity and engage in regular moderate to vigorous physical activity.
Another new recommendation is based on “robust” data that glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1s) significantly improve the management of type 2 diabetes, weight loss, and lower the risk for cardiovascular disease. As a result, guideline authors called for the use of GLP-1s in patients with diabetes and high cardiovascular risk or established cardiovascular disease.
“The glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists have been shown to not only drastically reduce blood sugars in patients with diabetes, but they also lead to significant weight loss in these patients, which has many downstream benefits. Together, this reduces the risk of stroke and other complications of diabetes,” said Bushnell.
She also noted that another drug class introduced since the 2014 guidelines were published, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors, have proven to be highly effective in lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. These medications have also been shown to reduce the risk for stroke.
At Least Two Meds Needed to Reduce BP
Effective blood pressure (BP) management is crucial for stroke prevention. Randomized controlled trials show that a single antihypertensive medication helps only about 30% of participants reach their BP target.
Most patients only achieve the desired BP target with two to three medications. In line with these data, the committee recommends using at least two antihypertensives for primary stroke prevention in most patients who require BP-lowering medications for hypertension.
In patients with antiphospholipid syndrome or systemic lupus erythematosus and no history of stroke or unprovoked venous thromboembolism, the authors recommended antiplatelet therapy to prevent stroke. They added that patients with antiphospholipid syndrome who have had a prior unprovoked venous thrombosis will likely benefit from vitamin K antagonist therapy (target international normalized ratio, 2-3) over direct oral anticoagulants.
Emphasis on Women’s Health
Preventing pregnancy-related stroke is achieved primarily by managing hypertension, the guideline authors noted. They recommended treating verified systolic BP over 160 mm Hg or diastolic BP over 110 mm Hg during pregnancy and up to 6 weeks postpartum to lower the risk for fatal maternal intracerebral hemorrhage.
They noted that adverse pregnancy outcomes are also common and linked to chronic hypertension, which increases stroke risk later in life. Therefore, they recommended screening for these outcomes to assess and manage vascular risk factors. The guideline includes a screening tool to help with this in clinical practice.
Endometriosis, premature ovarian failure (before age 40 years), and early-onset menopause (before age 45 years) are all associated with increased stroke risk. As a result, the guideline authors said screening for all three of these conditions is a “reasonable step in the evaluation and management of vascular risk factors in these individuals to reduce stroke risk.”
Finally, the guideline authors addressed primary stroke prevention in transgender individuals, noting that transgender women undergoing estrogen therapy for gender affirmation are at increased risk. They emphasized that evaluating and modifying risk factors could be beneficial for reducing stroke risk in this patient population.
Challenges Lie Ahead
Now that the guideline has been published, the challenge lies in determining how best to implement “its screening recommendations in primary care and other practices when these clinicians are already pushed to see as many patients as possible,” Bushnell said.
Development of screening tools that can be easily incorporated into the clinic visit or the electronic health record, as well as additional personnel to provide counseling, are probably needed to disseminate them, she added.
Bushnell also emphasized that the guideline includes a strong focus on social determinants of health and related social needs.
“We worked hard to use inclusive language and to consider populations historically excluded from research. In acknowledging that social determinants of health including access to healthcare, access to education, economic stability, neighborhood and geographic location, and social and community context have a tremendous influence on stroke risk, we describe how these factors are closely tied to the prevalence and management of many medical risks like obesity, hypertension, and diabetes.
“Our recommendations offer practical steps for screening and addressing essential health-related social needs, including access to nutritious food, stable housing, and reliable transportation, within clinical practice. By considering these factors more comprehensively, we believe we can make meaningful strides toward reducing the disparities in stroke risk,” said Bushnell.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The first update in a decade, the 2024 Guideline for the Primary Prevention of Stroke, replaces the 2014 version and is intended to be a resource for clinicians to help them implement a variety of prevention strategies in patients with no previous history of stroke. It aligns with the American Heart Association’s Life’s Essential 8.
“This guideline is an important and timely update from 2014 for multiple reasons. First, there have been groundbreaking clinical trials that have been published with new medications to not only treat the target disease [including] diabetes/obesity and high cholesterol], but also lower the risk of stroke and heart disease,” said chair of the guideline writing group, Cheryl D. Bushnell, MD, MHS, FAHA, and vice chair of the research, Department of Neurology, Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
It was published online on October 21 in Stroke.
Up to 80% of Strokes Preventable
Estimates show that every year in the United States, more than 500,000 individuals have a first stroke. However, the guideline authors noted that up to 80% of strokes may be preventable. As a result, they called for better primary stroke prevention that includes improved screening and lifestyle changes.
This includes adoption of the Mediterranean diet, which has been shown to significantly reduce stroke risk, especially when supplemented with consumption of nuts and olive oil.
The guideline recommendations also emphasize the need for physical activity, which is “essential” for cardiovascular health and stroke reduction. The authors underscored this point and provided a new recommendation to screen for sedentary behavior and advise patients to avoid inactivity and engage in regular moderate to vigorous physical activity.
Another new recommendation is based on “robust” data that glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1s) significantly improve the management of type 2 diabetes, weight loss, and lower the risk for cardiovascular disease. As a result, guideline authors called for the use of GLP-1s in patients with diabetes and high cardiovascular risk or established cardiovascular disease.
“The glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists have been shown to not only drastically reduce blood sugars in patients with diabetes, but they also lead to significant weight loss in these patients, which has many downstream benefits. Together, this reduces the risk of stroke and other complications of diabetes,” said Bushnell.
She also noted that another drug class introduced since the 2014 guidelines were published, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors, have proven to be highly effective in lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. These medications have also been shown to reduce the risk for stroke.
At Least Two Meds Needed to Reduce BP
Effective blood pressure (BP) management is crucial for stroke prevention. Randomized controlled trials show that a single antihypertensive medication helps only about 30% of participants reach their BP target.
Most patients only achieve the desired BP target with two to three medications. In line with these data, the committee recommends using at least two antihypertensives for primary stroke prevention in most patients who require BP-lowering medications for hypertension.
In patients with antiphospholipid syndrome or systemic lupus erythematosus and no history of stroke or unprovoked venous thromboembolism, the authors recommended antiplatelet therapy to prevent stroke. They added that patients with antiphospholipid syndrome who have had a prior unprovoked venous thrombosis will likely benefit from vitamin K antagonist therapy (target international normalized ratio, 2-3) over direct oral anticoagulants.
Emphasis on Women’s Health
Preventing pregnancy-related stroke is achieved primarily by managing hypertension, the guideline authors noted. They recommended treating verified systolic BP over 160 mm Hg or diastolic BP over 110 mm Hg during pregnancy and up to 6 weeks postpartum to lower the risk for fatal maternal intracerebral hemorrhage.
They noted that adverse pregnancy outcomes are also common and linked to chronic hypertension, which increases stroke risk later in life. Therefore, they recommended screening for these outcomes to assess and manage vascular risk factors. The guideline includes a screening tool to help with this in clinical practice.
Endometriosis, premature ovarian failure (before age 40 years), and early-onset menopause (before age 45 years) are all associated with increased stroke risk. As a result, the guideline authors said screening for all three of these conditions is a “reasonable step in the evaluation and management of vascular risk factors in these individuals to reduce stroke risk.”
Finally, the guideline authors addressed primary stroke prevention in transgender individuals, noting that transgender women undergoing estrogen therapy for gender affirmation are at increased risk. They emphasized that evaluating and modifying risk factors could be beneficial for reducing stroke risk in this patient population.
Challenges Lie Ahead
Now that the guideline has been published, the challenge lies in determining how best to implement “its screening recommendations in primary care and other practices when these clinicians are already pushed to see as many patients as possible,” Bushnell said.
Development of screening tools that can be easily incorporated into the clinic visit or the electronic health record, as well as additional personnel to provide counseling, are probably needed to disseminate them, she added.
Bushnell also emphasized that the guideline includes a strong focus on social determinants of health and related social needs.
“We worked hard to use inclusive language and to consider populations historically excluded from research. In acknowledging that social determinants of health including access to healthcare, access to education, economic stability, neighborhood and geographic location, and social and community context have a tremendous influence on stroke risk, we describe how these factors are closely tied to the prevalence and management of many medical risks like obesity, hypertension, and diabetes.
“Our recommendations offer practical steps for screening and addressing essential health-related social needs, including access to nutritious food, stable housing, and reliable transportation, within clinical practice. By considering these factors more comprehensively, we believe we can make meaningful strides toward reducing the disparities in stroke risk,” said Bushnell.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The first update in a decade, the 2024 Guideline for the Primary Prevention of Stroke, replaces the 2014 version and is intended to be a resource for clinicians to help them implement a variety of prevention strategies in patients with no previous history of stroke. It aligns with the American Heart Association’s Life’s Essential 8.
“This guideline is an important and timely update from 2014 for multiple reasons. First, there have been groundbreaking clinical trials that have been published with new medications to not only treat the target disease [including] diabetes/obesity and high cholesterol], but also lower the risk of stroke and heart disease,” said chair of the guideline writing group, Cheryl D. Bushnell, MD, MHS, FAHA, and vice chair of the research, Department of Neurology, Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
It was published online on October 21 in Stroke.
Up to 80% of Strokes Preventable
Estimates show that every year in the United States, more than 500,000 individuals have a first stroke. However, the guideline authors noted that up to 80% of strokes may be preventable. As a result, they called for better primary stroke prevention that includes improved screening and lifestyle changes.
This includes adoption of the Mediterranean diet, which has been shown to significantly reduce stroke risk, especially when supplemented with consumption of nuts and olive oil.
The guideline recommendations also emphasize the need for physical activity, which is “essential” for cardiovascular health and stroke reduction. The authors underscored this point and provided a new recommendation to screen for sedentary behavior and advise patients to avoid inactivity and engage in regular moderate to vigorous physical activity.
Another new recommendation is based on “robust” data that glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1s) significantly improve the management of type 2 diabetes, weight loss, and lower the risk for cardiovascular disease. As a result, guideline authors called for the use of GLP-1s in patients with diabetes and high cardiovascular risk or established cardiovascular disease.
“The glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists have been shown to not only drastically reduce blood sugars in patients with diabetes, but they also lead to significant weight loss in these patients, which has many downstream benefits. Together, this reduces the risk of stroke and other complications of diabetes,” said Bushnell.
She also noted that another drug class introduced since the 2014 guidelines were published, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors, have proven to be highly effective in lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. These medications have also been shown to reduce the risk for stroke.
At Least Two Meds Needed to Reduce BP
Effective blood pressure (BP) management is crucial for stroke prevention. Randomized controlled trials show that a single antihypertensive medication helps only about 30% of participants reach their BP target.
Most patients only achieve the desired BP target with two to three medications. In line with these data, the committee recommends using at least two antihypertensives for primary stroke prevention in most patients who require BP-lowering medications for hypertension.
In patients with antiphospholipid syndrome or systemic lupus erythematosus and no history of stroke or unprovoked venous thromboembolism, the authors recommended antiplatelet therapy to prevent stroke. They added that patients with antiphospholipid syndrome who have had a prior unprovoked venous thrombosis will likely benefit from vitamin K antagonist therapy (target international normalized ratio, 2-3) over direct oral anticoagulants.
Emphasis on Women’s Health
Preventing pregnancy-related stroke is achieved primarily by managing hypertension, the guideline authors noted. They recommended treating verified systolic BP over 160 mm Hg or diastolic BP over 110 mm Hg during pregnancy and up to 6 weeks postpartum to lower the risk for fatal maternal intracerebral hemorrhage.
They noted that adverse pregnancy outcomes are also common and linked to chronic hypertension, which increases stroke risk later in life. Therefore, they recommended screening for these outcomes to assess and manage vascular risk factors. The guideline includes a screening tool to help with this in clinical practice.
Endometriosis, premature ovarian failure (before age 40 years), and early-onset menopause (before age 45 years) are all associated with increased stroke risk. As a result, the guideline authors said screening for all three of these conditions is a “reasonable step in the evaluation and management of vascular risk factors in these individuals to reduce stroke risk.”
Finally, the guideline authors addressed primary stroke prevention in transgender individuals, noting that transgender women undergoing estrogen therapy for gender affirmation are at increased risk. They emphasized that evaluating and modifying risk factors could be beneficial for reducing stroke risk in this patient population.
Challenges Lie Ahead
Now that the guideline has been published, the challenge lies in determining how best to implement “its screening recommendations in primary care and other practices when these clinicians are already pushed to see as many patients as possible,” Bushnell said.
Development of screening tools that can be easily incorporated into the clinic visit or the electronic health record, as well as additional personnel to provide counseling, are probably needed to disseminate them, she added.
Bushnell also emphasized that the guideline includes a strong focus on social determinants of health and related social needs.
“We worked hard to use inclusive language and to consider populations historically excluded from research. In acknowledging that social determinants of health including access to healthcare, access to education, economic stability, neighborhood and geographic location, and social and community context have a tremendous influence on stroke risk, we describe how these factors are closely tied to the prevalence and management of many medical risks like obesity, hypertension, and diabetes.
“Our recommendations offer practical steps for screening and addressing essential health-related social needs, including access to nutritious food, stable housing, and reliable transportation, within clinical practice. By considering these factors more comprehensively, we believe we can make meaningful strides toward reducing the disparities in stroke risk,” said Bushnell.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Can Weight Loss Drugs Also Treat Addiction?
A new study provides more evidence that glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) used to treat diabetes and obesity could be repurposed for opioid use disorder (OUD) and alcohol use disorder (AUD).
Researchers found that patients with OUD or AUD who were taking semaglutide (Ozempic, Novo Nordisk) or similar medications for diabetes or weight-related conditions had a 40% lower rate of opioid overdose and a 50% lower rate of alcohol intoxication than their peers with OUD or AUD who were not taking these medications.
Their real-world study of more than 1 million adults with a history of OUD or AUD provide “foundational” estimates of the association between glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP)/GLP-1 RA prescriptions and opioid overdose/alcohol intoxication “and introduce the idea that GLP-1 RA and other related drugs should be investigated as a novel pharmacotherapy treatment option for individuals with OUD or AUD,” wrote the investigators, led by Fares Qeadan, PhD, Parkinson School of Health Sciences and Public Health, Loyola University Chicago, Maywood, Illinois.
The study was published online in the journal Addiction.
Protective Effect?
As previously reported by Medscape Medical News, earlier studies have pointed to a link between weight loss drugs and reduced overdose risk in people with OUD and decreased alcohol intake in people with AUD.
Until now, most studies on GLP-1 RAs and GIP agonists like tirzepatide (Mounjaro) to treat substance use disorders consisted of animal studies and small-scale clinical trials, investigators noted.
This new retrospective cohort study analyzed de-identified electronic health record data from the Oracle Health Real-World Data.
Participants, all aged 18 years or older, included 503,747 patients with a history of OUD, of whom 8103 had a GLP-1 RA or GIP prescription, and 817,309 patients with a history of AUD, of whom 5621 had a GLP-1 RA or GIP prescription.
Patients with OUD who were prescribed GLP-1 RAs had a 40% lower rate of opioid overdose than those without such prescriptions (adjusted incidence rate ratio [aIRR], 0.60; 95% CI, 0.43-0.83), the study team found.
In addition, patients with AUD and a GLP-1 RA prescription exhibited a 50% lower rate of alcohol intoxication (aIRR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.40-0.63).
The protective effect of GLP-1 RA on opioid overdose and alcohol intoxication was maintained across patients with comorbid conditions, such as type 2 diabetes and obesity.
“Future research should focus on prospective clinical trials to validate these findings, explore the underlying mechanisms, and determine the long-term efficacy and safety of GIP/GLP-1 RA medications in diverse populations,” Qeadan and colleagues concluded.
“Additionally, the study highlights the importance of interdisciplinary research in understanding the neurobiological links between metabolic disorders and problematic substance use, potentially leading to more effective treatment strategies within healthcare systems,” they added.
Questions Remain
In a statement from the UK nonprofit Science Media Centre, Matt Field, DPhil, professor of psychology, The University of Sheffield, in England, noted that the findings “add to those from other studies, particularly animal research, which suggest that this and similar drugs might one day be prescribed to help people with addiction.”
However, “a note of caution is that the outcomes are very extreme instances of substance intoxication,” added Field, who wasn’t involved in the study.
“Those outcomes are very different from the outcomes used when researchers test new treatments for addiction, in which case we might look at whether the treatment helps people to stop taking the substance altogether (complete abstinence), or if it helps people to reduce the amount of substance they consume, or how often they consume it. Those things could not be measured in this study,” he continued.
“This leaves open the possibility that while Ozempic may — for reasons currently unknown — prevent people from taking so much alcohol or heroin that they overdose and end up in hospital, it may not actually help them to reduce their substance use, or to abstain altogether,” Field said.
The study had no specific funding. The study authors and Field declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study provides more evidence that glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) used to treat diabetes and obesity could be repurposed for opioid use disorder (OUD) and alcohol use disorder (AUD).
Researchers found that patients with OUD or AUD who were taking semaglutide (Ozempic, Novo Nordisk) or similar medications for diabetes or weight-related conditions had a 40% lower rate of opioid overdose and a 50% lower rate of alcohol intoxication than their peers with OUD or AUD who were not taking these medications.
Their real-world study of more than 1 million adults with a history of OUD or AUD provide “foundational” estimates of the association between glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP)/GLP-1 RA prescriptions and opioid overdose/alcohol intoxication “and introduce the idea that GLP-1 RA and other related drugs should be investigated as a novel pharmacotherapy treatment option for individuals with OUD or AUD,” wrote the investigators, led by Fares Qeadan, PhD, Parkinson School of Health Sciences and Public Health, Loyola University Chicago, Maywood, Illinois.
The study was published online in the journal Addiction.
Protective Effect?
As previously reported by Medscape Medical News, earlier studies have pointed to a link between weight loss drugs and reduced overdose risk in people with OUD and decreased alcohol intake in people with AUD.
Until now, most studies on GLP-1 RAs and GIP agonists like tirzepatide (Mounjaro) to treat substance use disorders consisted of animal studies and small-scale clinical trials, investigators noted.
This new retrospective cohort study analyzed de-identified electronic health record data from the Oracle Health Real-World Data.
Participants, all aged 18 years or older, included 503,747 patients with a history of OUD, of whom 8103 had a GLP-1 RA or GIP prescription, and 817,309 patients with a history of AUD, of whom 5621 had a GLP-1 RA or GIP prescription.
Patients with OUD who were prescribed GLP-1 RAs had a 40% lower rate of opioid overdose than those without such prescriptions (adjusted incidence rate ratio [aIRR], 0.60; 95% CI, 0.43-0.83), the study team found.
In addition, patients with AUD and a GLP-1 RA prescription exhibited a 50% lower rate of alcohol intoxication (aIRR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.40-0.63).
The protective effect of GLP-1 RA on opioid overdose and alcohol intoxication was maintained across patients with comorbid conditions, such as type 2 diabetes and obesity.
“Future research should focus on prospective clinical trials to validate these findings, explore the underlying mechanisms, and determine the long-term efficacy and safety of GIP/GLP-1 RA medications in diverse populations,” Qeadan and colleagues concluded.
“Additionally, the study highlights the importance of interdisciplinary research in understanding the neurobiological links between metabolic disorders and problematic substance use, potentially leading to more effective treatment strategies within healthcare systems,” they added.
Questions Remain
In a statement from the UK nonprofit Science Media Centre, Matt Field, DPhil, professor of psychology, The University of Sheffield, in England, noted that the findings “add to those from other studies, particularly animal research, which suggest that this and similar drugs might one day be prescribed to help people with addiction.”
However, “a note of caution is that the outcomes are very extreme instances of substance intoxication,” added Field, who wasn’t involved in the study.
“Those outcomes are very different from the outcomes used when researchers test new treatments for addiction, in which case we might look at whether the treatment helps people to stop taking the substance altogether (complete abstinence), or if it helps people to reduce the amount of substance they consume, or how often they consume it. Those things could not be measured in this study,” he continued.
“This leaves open the possibility that while Ozempic may — for reasons currently unknown — prevent people from taking so much alcohol or heroin that they overdose and end up in hospital, it may not actually help them to reduce their substance use, or to abstain altogether,” Field said.
The study had no specific funding. The study authors and Field declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study provides more evidence that glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) used to treat diabetes and obesity could be repurposed for opioid use disorder (OUD) and alcohol use disorder (AUD).
Researchers found that patients with OUD or AUD who were taking semaglutide (Ozempic, Novo Nordisk) or similar medications for diabetes or weight-related conditions had a 40% lower rate of opioid overdose and a 50% lower rate of alcohol intoxication than their peers with OUD or AUD who were not taking these medications.
Their real-world study of more than 1 million adults with a history of OUD or AUD provide “foundational” estimates of the association between glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP)/GLP-1 RA prescriptions and opioid overdose/alcohol intoxication “and introduce the idea that GLP-1 RA and other related drugs should be investigated as a novel pharmacotherapy treatment option for individuals with OUD or AUD,” wrote the investigators, led by Fares Qeadan, PhD, Parkinson School of Health Sciences and Public Health, Loyola University Chicago, Maywood, Illinois.
The study was published online in the journal Addiction.
Protective Effect?
As previously reported by Medscape Medical News, earlier studies have pointed to a link between weight loss drugs and reduced overdose risk in people with OUD and decreased alcohol intake in people with AUD.
Until now, most studies on GLP-1 RAs and GIP agonists like tirzepatide (Mounjaro) to treat substance use disorders consisted of animal studies and small-scale clinical trials, investigators noted.
This new retrospective cohort study analyzed de-identified electronic health record data from the Oracle Health Real-World Data.
Participants, all aged 18 years or older, included 503,747 patients with a history of OUD, of whom 8103 had a GLP-1 RA or GIP prescription, and 817,309 patients with a history of AUD, of whom 5621 had a GLP-1 RA or GIP prescription.
Patients with OUD who were prescribed GLP-1 RAs had a 40% lower rate of opioid overdose than those without such prescriptions (adjusted incidence rate ratio [aIRR], 0.60; 95% CI, 0.43-0.83), the study team found.
In addition, patients with AUD and a GLP-1 RA prescription exhibited a 50% lower rate of alcohol intoxication (aIRR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.40-0.63).
The protective effect of GLP-1 RA on opioid overdose and alcohol intoxication was maintained across patients with comorbid conditions, such as type 2 diabetes and obesity.
“Future research should focus on prospective clinical trials to validate these findings, explore the underlying mechanisms, and determine the long-term efficacy and safety of GIP/GLP-1 RA medications in diverse populations,” Qeadan and colleagues concluded.
“Additionally, the study highlights the importance of interdisciplinary research in understanding the neurobiological links between metabolic disorders and problematic substance use, potentially leading to more effective treatment strategies within healthcare systems,” they added.
Questions Remain
In a statement from the UK nonprofit Science Media Centre, Matt Field, DPhil, professor of psychology, The University of Sheffield, in England, noted that the findings “add to those from other studies, particularly animal research, which suggest that this and similar drugs might one day be prescribed to help people with addiction.”
However, “a note of caution is that the outcomes are very extreme instances of substance intoxication,” added Field, who wasn’t involved in the study.
“Those outcomes are very different from the outcomes used when researchers test new treatments for addiction, in which case we might look at whether the treatment helps people to stop taking the substance altogether (complete abstinence), or if it helps people to reduce the amount of substance they consume, or how often they consume it. Those things could not be measured in this study,” he continued.
“This leaves open the possibility that while Ozempic may — for reasons currently unknown — prevent people from taking so much alcohol or heroin that they overdose and end up in hospital, it may not actually help them to reduce their substance use, or to abstain altogether,” Field said.
The study had no specific funding. The study authors and Field declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ADDICTION
A Single Jog Can Improve Glucose Metabolism in Young Adults
TOPLINE:
In healthy young adults, a single 30-minute bout of outdoor aerobic exercise significantly reduces fasting and 1-hour glucose levels during an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) the next day and improves insulin sensitivity.
METHODOLOGY:
- Recent studies have identified 1-hour post-load glucose concentration during an OGTT as a specific and early predictor of diabetes, and exercise has long been known for its metabolic benefits in people with and without diabetes.
- The researchers investigated the effect of a single bout of aerobic exercise on 1-hour post-load glucose levels during an OGTT in 32 young, healthy, normal-weight or marginally overweight individuals (mean age, 35 years; 14 women and 18 men) with a sedentary or moderately active lifestyle.
- The participants underwent an initial OGTT after at least 4 days of physical inactivity, followed by a second OGTT the day after a single 30-minute bout of aerobic exercise.
- The exercise session consisted of a light jog for 30 minutes, monitored using a metabolic holter to quantify energy expenditure and exercise intensity. The participants did not undertake any exercise outside the lab sessions.
- Blood glucose levels were measured, and insulin sensitivity and secretion were estimated using surrogate indices derived from OGTT glucose and insulin assays, including the Matsuda index, oral glucose insulin sensitivity (OGIS) index, and quantitative insulin sensitivity check index, as well as the homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) of insulin resistance and of beta-cell function (HOMA-B).
TAKEAWAY:
- Postexercise insulin levels also were significantly lower 1 hour after glucose load, decreasing from 57.4 IU/mL at baseline to 43.5 IU/mL the day after exercise (P = .01).
- Insulin sensitivity improved significantly after exercise, as indicated by increases in the Matsuda index (P = .02) and OGIS index (P = .04), along with a reduction in insulin resistance (P = .04).
- The study found a trend toward increased beta-cell function the day after an exercise bout, as indicated by a nonsignificant increase in HOMA-B from 144.7 at baseline to 167.1 after exercise.
IN PRACTICE:
“Improvement in 1-hour post-load plasma glucose following a single session of aerobic physical activity suggests that exercise could have a direct effect on T2D [type 2 diabetes] risk and cardiovascular risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Simona Moffa, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli IRCCS, Rome, and Gian Pio Sorice, Università Degli Studi di Bari “Aldo Moro,” Bari, Italy. It was published online in the Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.
LIMITATIONS:
The study had a limited sample size, which may affect the generalizability of the findings. C-peptide levels, which could have provided additional insights into insulin secretion, were not assessed in the study.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In healthy young adults, a single 30-minute bout of outdoor aerobic exercise significantly reduces fasting and 1-hour glucose levels during an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) the next day and improves insulin sensitivity.
METHODOLOGY:
- Recent studies have identified 1-hour post-load glucose concentration during an OGTT as a specific and early predictor of diabetes, and exercise has long been known for its metabolic benefits in people with and without diabetes.
- The researchers investigated the effect of a single bout of aerobic exercise on 1-hour post-load glucose levels during an OGTT in 32 young, healthy, normal-weight or marginally overweight individuals (mean age, 35 years; 14 women and 18 men) with a sedentary or moderately active lifestyle.
- The participants underwent an initial OGTT after at least 4 days of physical inactivity, followed by a second OGTT the day after a single 30-minute bout of aerobic exercise.
- The exercise session consisted of a light jog for 30 minutes, monitored using a metabolic holter to quantify energy expenditure and exercise intensity. The participants did not undertake any exercise outside the lab sessions.
- Blood glucose levels were measured, and insulin sensitivity and secretion were estimated using surrogate indices derived from OGTT glucose and insulin assays, including the Matsuda index, oral glucose insulin sensitivity (OGIS) index, and quantitative insulin sensitivity check index, as well as the homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) of insulin resistance and of beta-cell function (HOMA-B).
TAKEAWAY:
- Postexercise insulin levels also were significantly lower 1 hour after glucose load, decreasing from 57.4 IU/mL at baseline to 43.5 IU/mL the day after exercise (P = .01).
- Insulin sensitivity improved significantly after exercise, as indicated by increases in the Matsuda index (P = .02) and OGIS index (P = .04), along with a reduction in insulin resistance (P = .04).
- The study found a trend toward increased beta-cell function the day after an exercise bout, as indicated by a nonsignificant increase in HOMA-B from 144.7 at baseline to 167.1 after exercise.
IN PRACTICE:
“Improvement in 1-hour post-load plasma glucose following a single session of aerobic physical activity suggests that exercise could have a direct effect on T2D [type 2 diabetes] risk and cardiovascular risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Simona Moffa, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli IRCCS, Rome, and Gian Pio Sorice, Università Degli Studi di Bari “Aldo Moro,” Bari, Italy. It was published online in the Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.
LIMITATIONS:
The study had a limited sample size, which may affect the generalizability of the findings. C-peptide levels, which could have provided additional insights into insulin secretion, were not assessed in the study.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In healthy young adults, a single 30-minute bout of outdoor aerobic exercise significantly reduces fasting and 1-hour glucose levels during an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) the next day and improves insulin sensitivity.
METHODOLOGY:
- Recent studies have identified 1-hour post-load glucose concentration during an OGTT as a specific and early predictor of diabetes, and exercise has long been known for its metabolic benefits in people with and without diabetes.
- The researchers investigated the effect of a single bout of aerobic exercise on 1-hour post-load glucose levels during an OGTT in 32 young, healthy, normal-weight or marginally overweight individuals (mean age, 35 years; 14 women and 18 men) with a sedentary or moderately active lifestyle.
- The participants underwent an initial OGTT after at least 4 days of physical inactivity, followed by a second OGTT the day after a single 30-minute bout of aerobic exercise.
- The exercise session consisted of a light jog for 30 minutes, monitored using a metabolic holter to quantify energy expenditure and exercise intensity. The participants did not undertake any exercise outside the lab sessions.
- Blood glucose levels were measured, and insulin sensitivity and secretion were estimated using surrogate indices derived from OGTT glucose and insulin assays, including the Matsuda index, oral glucose insulin sensitivity (OGIS) index, and quantitative insulin sensitivity check index, as well as the homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) of insulin resistance and of beta-cell function (HOMA-B).
TAKEAWAY:
- Postexercise insulin levels also were significantly lower 1 hour after glucose load, decreasing from 57.4 IU/mL at baseline to 43.5 IU/mL the day after exercise (P = .01).
- Insulin sensitivity improved significantly after exercise, as indicated by increases in the Matsuda index (P = .02) and OGIS index (P = .04), along with a reduction in insulin resistance (P = .04).
- The study found a trend toward increased beta-cell function the day after an exercise bout, as indicated by a nonsignificant increase in HOMA-B from 144.7 at baseline to 167.1 after exercise.
IN PRACTICE:
“Improvement in 1-hour post-load plasma glucose following a single session of aerobic physical activity suggests that exercise could have a direct effect on T2D [type 2 diabetes] risk and cardiovascular risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Simona Moffa, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli IRCCS, Rome, and Gian Pio Sorice, Università Degli Studi di Bari “Aldo Moro,” Bari, Italy. It was published online in the Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.
LIMITATIONS:
The study had a limited sample size, which may affect the generalizability of the findings. C-peptide levels, which could have provided additional insights into insulin secretion, were not assessed in the study.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Metformin After Bariatric Surgery: Necessary or Not?
TOPLINE:
Patients who achieved an A1c level < 6.5% after metabolic bariatric surgery (MBS) maintained this target in the short and long terms, regardless of whether they continued or discontinued metformin after the procedure.
METHODOLOGY:
- MBS is effective in individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and obesity, but the recommendations for managing patients who achieve diabetes remission after bariatric surgery are not clear.
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using electronic health records from Clalit Health Services in Israel to assess the association between metformin continuation after MBS and the short- and long-term relapse of diabetes (2 and 5 years after surgery, respectively).
- They included 366 patients (aged ≥ 24 years; body mass index [BMI], ≥ 30) with obesity and T2D who received metformin and achieved A1c levels < 6.5% for up to 6 months after MBS.
- Patients who continued metformin (n = 122; ≥ 3 filled prescriptions; mean follow-up, 5.3 years) were matched and compared with those who discontinued it (n = 244; 0 prescriptions; mean follow-up, 5.8 years) after MBS.
- The primary outcome was the long-term relapse of diabetes, defined by an A1c level ≥ 6.5% during the follow-up period, and the secondary outcomes were short- and long-term A1c levels, changes in BMI, and all-cause mortality.
TAKEAWAY:
- After adjustment for patient variables, no significant association was found between metformin continuation after MBS and risk for relapse of diabetes (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.65).
- Patients in both groups maintained mean A1c levels < 6.5% during the short- and long-term follow-up periods, showing that discontinuing metformin did not impede glycemic control.
- No significant differences were noted between patients who continued or discontinued metformin in terms of weight loss.
- The mortality rate was low in both the groups, with no substantial difference noted between the groups that continued metformin (4.1%) or discontinued metformin (2.5%).
IN PRACTICE:
“The lack of a significant association of metformin continuation with A1c level observed in the current study supports the notion that metformin may not have an additional benefit after MBS,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Dror Dicker, MD, Internal Medicine Department D and Obesity Clinic, Hasharon Hospital, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, and published online in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The observational nature of the study and the lack of randomization may have introduced residual confounding. The small number of patients remaining in the final study population limited the generalizability of the findings. The follow-up period of approximately 5 years may not have been sufficient to observe the long-term effects of metformin continuation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received funding from Ariel University. Two authors disclosed receiving grants, personal fees, or nonfinancial support from various sources unrelated to this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients who achieved an A1c level < 6.5% after metabolic bariatric surgery (MBS) maintained this target in the short and long terms, regardless of whether they continued or discontinued metformin after the procedure.
METHODOLOGY:
- MBS is effective in individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and obesity, but the recommendations for managing patients who achieve diabetes remission after bariatric surgery are not clear.
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using electronic health records from Clalit Health Services in Israel to assess the association between metformin continuation after MBS and the short- and long-term relapse of diabetes (2 and 5 years after surgery, respectively).
- They included 366 patients (aged ≥ 24 years; body mass index [BMI], ≥ 30) with obesity and T2D who received metformin and achieved A1c levels < 6.5% for up to 6 months after MBS.
- Patients who continued metformin (n = 122; ≥ 3 filled prescriptions; mean follow-up, 5.3 years) were matched and compared with those who discontinued it (n = 244; 0 prescriptions; mean follow-up, 5.8 years) after MBS.
- The primary outcome was the long-term relapse of diabetes, defined by an A1c level ≥ 6.5% during the follow-up period, and the secondary outcomes were short- and long-term A1c levels, changes in BMI, and all-cause mortality.
TAKEAWAY:
- After adjustment for patient variables, no significant association was found between metformin continuation after MBS and risk for relapse of diabetes (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.65).
- Patients in both groups maintained mean A1c levels < 6.5% during the short- and long-term follow-up periods, showing that discontinuing metformin did not impede glycemic control.
- No significant differences were noted between patients who continued or discontinued metformin in terms of weight loss.
- The mortality rate was low in both the groups, with no substantial difference noted between the groups that continued metformin (4.1%) or discontinued metformin (2.5%).
IN PRACTICE:
“The lack of a significant association of metformin continuation with A1c level observed in the current study supports the notion that metformin may not have an additional benefit after MBS,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Dror Dicker, MD, Internal Medicine Department D and Obesity Clinic, Hasharon Hospital, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, and published online in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The observational nature of the study and the lack of randomization may have introduced residual confounding. The small number of patients remaining in the final study population limited the generalizability of the findings. The follow-up period of approximately 5 years may not have been sufficient to observe the long-term effects of metformin continuation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received funding from Ariel University. Two authors disclosed receiving grants, personal fees, or nonfinancial support from various sources unrelated to this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients who achieved an A1c level < 6.5% after metabolic bariatric surgery (MBS) maintained this target in the short and long terms, regardless of whether they continued or discontinued metformin after the procedure.
METHODOLOGY:
- MBS is effective in individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and obesity, but the recommendations for managing patients who achieve diabetes remission after bariatric surgery are not clear.
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using electronic health records from Clalit Health Services in Israel to assess the association between metformin continuation after MBS and the short- and long-term relapse of diabetes (2 and 5 years after surgery, respectively).
- They included 366 patients (aged ≥ 24 years; body mass index [BMI], ≥ 30) with obesity and T2D who received metformin and achieved A1c levels < 6.5% for up to 6 months after MBS.
- Patients who continued metformin (n = 122; ≥ 3 filled prescriptions; mean follow-up, 5.3 years) were matched and compared with those who discontinued it (n = 244; 0 prescriptions; mean follow-up, 5.8 years) after MBS.
- The primary outcome was the long-term relapse of diabetes, defined by an A1c level ≥ 6.5% during the follow-up period, and the secondary outcomes were short- and long-term A1c levels, changes in BMI, and all-cause mortality.
TAKEAWAY:
- After adjustment for patient variables, no significant association was found between metformin continuation after MBS and risk for relapse of diabetes (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.65).
- Patients in both groups maintained mean A1c levels < 6.5% during the short- and long-term follow-up periods, showing that discontinuing metformin did not impede glycemic control.
- No significant differences were noted between patients who continued or discontinued metformin in terms of weight loss.
- The mortality rate was low in both the groups, with no substantial difference noted between the groups that continued metformin (4.1%) or discontinued metformin (2.5%).
IN PRACTICE:
“The lack of a significant association of metformin continuation with A1c level observed in the current study supports the notion that metformin may not have an additional benefit after MBS,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Dror Dicker, MD, Internal Medicine Department D and Obesity Clinic, Hasharon Hospital, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, and published online in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The observational nature of the study and the lack of randomization may have introduced residual confounding. The small number of patients remaining in the final study population limited the generalizability of the findings. The follow-up period of approximately 5 years may not have been sufficient to observe the long-term effects of metformin continuation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received funding from Ariel University. Two authors disclosed receiving grants, personal fees, or nonfinancial support from various sources unrelated to this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VA Expanded Emergency Care Program Offers At-Home Clinical Evaluation
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has announced that tele-emergency care (tele-EC) is now available nationwide. According to the VA, the expansion has already helped > 61,000 callers with a 59.4% case resolution rate, meaning veterans’ needs were resolved without them having to travel to urgent care or an emergency department.
Tele-EC does not replace the need for in-person emergency evaluation, but offers quick, virtual triage assessments for veterans in rural areas or those with mobility and transportation challenges when in-person immediate care can be difficult to access. The program is a part of VA Health Connect, which connects the caller to a clinical triage nurse, who connects the veteran to tele-emergency care when clinically appropriate. Tele-EC practitioners evaluate the veteran over the phone or on video and recommend treatment or follow-up, including in-person care if needed. In life-threatening emergencies, the clinical triage nurse will call 911 and stay on the phone with the veteran until help arrives. The VA however, says the best step for a veteran experiencing a life-threatening emergency is to immediately contact 911 as opposed to seeking support via tele-EC.
The program can save time not only through on-the-spot evaluation, but by avoiding drive and wait times. “Sometimes, you’re not sure whether what you’re experiencing is a minor emergency or not — and tele-emergency care can help you resolve those questions,” VA Under Secretary for Health Shereef Elnahal, MD, says. “Veterans can get immediate, virtual triage with a VA medical provider who has direct access to their medical records. This avoids having to potentially drive to the nearest emergency department and wait to be evaluated, if appropriate.”
Veterans enrolled in VA health care can now access tele-EC nationwide by calling VA Health Connect and through the VA Health Chat app. Veterans can find their local VA Health Connect number by searching for their facility.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has announced that tele-emergency care (tele-EC) is now available nationwide. According to the VA, the expansion has already helped > 61,000 callers with a 59.4% case resolution rate, meaning veterans’ needs were resolved without them having to travel to urgent care or an emergency department.
Tele-EC does not replace the need for in-person emergency evaluation, but offers quick, virtual triage assessments for veterans in rural areas or those with mobility and transportation challenges when in-person immediate care can be difficult to access. The program is a part of VA Health Connect, which connects the caller to a clinical triage nurse, who connects the veteran to tele-emergency care when clinically appropriate. Tele-EC practitioners evaluate the veteran over the phone or on video and recommend treatment or follow-up, including in-person care if needed. In life-threatening emergencies, the clinical triage nurse will call 911 and stay on the phone with the veteran until help arrives. The VA however, says the best step for a veteran experiencing a life-threatening emergency is to immediately contact 911 as opposed to seeking support via tele-EC.
The program can save time not only through on-the-spot evaluation, but by avoiding drive and wait times. “Sometimes, you’re not sure whether what you’re experiencing is a minor emergency or not — and tele-emergency care can help you resolve those questions,” VA Under Secretary for Health Shereef Elnahal, MD, says. “Veterans can get immediate, virtual triage with a VA medical provider who has direct access to their medical records. This avoids having to potentially drive to the nearest emergency department and wait to be evaluated, if appropriate.”
Veterans enrolled in VA health care can now access tele-EC nationwide by calling VA Health Connect and through the VA Health Chat app. Veterans can find their local VA Health Connect number by searching for their facility.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has announced that tele-emergency care (tele-EC) is now available nationwide. According to the VA, the expansion has already helped > 61,000 callers with a 59.4% case resolution rate, meaning veterans’ needs were resolved without them having to travel to urgent care or an emergency department.
Tele-EC does not replace the need for in-person emergency evaluation, but offers quick, virtual triage assessments for veterans in rural areas or those with mobility and transportation challenges when in-person immediate care can be difficult to access. The program is a part of VA Health Connect, which connects the caller to a clinical triage nurse, who connects the veteran to tele-emergency care when clinically appropriate. Tele-EC practitioners evaluate the veteran over the phone or on video and recommend treatment or follow-up, including in-person care if needed. In life-threatening emergencies, the clinical triage nurse will call 911 and stay on the phone with the veteran until help arrives. The VA however, says the best step for a veteran experiencing a life-threatening emergency is to immediately contact 911 as opposed to seeking support via tele-EC.
The program can save time not only through on-the-spot evaluation, but by avoiding drive and wait times. “Sometimes, you’re not sure whether what you’re experiencing is a minor emergency or not — and tele-emergency care can help you resolve those questions,” VA Under Secretary for Health Shereef Elnahal, MD, says. “Veterans can get immediate, virtual triage with a VA medical provider who has direct access to their medical records. This avoids having to potentially drive to the nearest emergency department and wait to be evaluated, if appropriate.”
Veterans enrolled in VA health care can now access tele-EC nationwide by calling VA Health Connect and through the VA Health Chat app. Veterans can find their local VA Health Connect number by searching for their facility.