User login
PCOS in mothers tied to health problems in children
Children whose mothers have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have increased rates of hospitalization for various conditions, including asthma, pneumonia, and ear infection, a study of more than 1 million children shows.
The associations were not particularly strong, according to the researchers. But they raise questions about the reasons for the increased risk and whether interventions such as diet, exercise, or medications could lead to healthier outcomes for children whose mothers have PCOS.
“The findings suggest that maternal PCOS may have a negative impact on offspring development, enough to lead to a measurable increase in the risk of childhood hospitalization,” study coauthor Nathalie Auger, MD, associate professor of epidemiology at University of Montreal, and colleagues reported in Human Reproduction.
“They are minor differences, just enough that we can statistically identify them. They’re not something where everyone should be worrying at this point,” Dr. Auger told this news organization.
Still, some of the hospitalizations, such as those related to infection or allergy, could be prevented with earlier ambulatory care, so some degree of greater awareness among parents and clinicians may be warranted, she said.
Thirteen years of follow-up
PCOS – a reproductive disorder characterized by irregular periods, increased male hormones, and metabolic complications – affects some 10% of women. People with the condition are at increased risk for obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Although prior research has shown that maternal PCOS may be associated with higher body mass index and attention deficit disorder in children, data on long-term childhood health outcomes have been limited, Dr. Auger’s group noted.
To examine illness in children exposed to maternal PCOS, the investigators analyzed hospitalization rates for nearly 1.04 million children in Quebec between 2006 and 2020; 7,160 of the children had mothers with PCOS.
In all, 275,354 children were hospitalized during 13 years of follow-up, including 2,314 whose mothers had PCOS.
Children exposed to PCOS were hospitalized at a rate of 68.9 per 1,000 person-years – roughly 50% more often than the rate of 45.3 per 1,000 person-years for children not exposed to maternal PCOS.
In an analysis that adjusted for maternal characteristics, childhood hospitalization for any reason was 1.32 times more likely for children exposed to maternal PCOS.
Hospitalizations linked to infectious diseases – such as for bronchitis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, nephritis, otitis media, or meningitis – were 1.31 times more likely among children exposed to PCOS. Allergy-related hospitalizations, such as for allergic asthma and anaphylaxis, were 1.47 times more likely, according to the researchers.
Metabolic hospitalizations were 1.59 times more likely. For gastrointestinal hospitalizations, the hazard ratio was 1.72. For central nervous system hospitalizations, it was 1.74.
The associations were stronger in earlier childhood, and results were similar for boys and girls, the investigators reported.
Hospitalizations for cardiovascular disease, musculoskeletal conditions, or malignancy were not increased.
‘Surprising’ links
“The findings are surprising in that some of the conditions that they showed increased risk for, like asthma and some infections, are not conditions that we think of as being typically associated with PCOS,” said Andrea E. Dunaif, MD, chief of the Hilda and J. Lester Gabrilove Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Bone Disease at Mount Sinai Health System, New York, who was not part of the study team.
Earlier studies of offspring of women with PCOS have suggested that children may be at increased risk for insulin resistance and obesity.
Differences in genetics, intrauterine environments, patterns of health care use by women with PCOS, and behavioral factors, such as diet and how children are raised, are variables that could have contributed to the different hospitalization rates among children exposed to maternal PCOS, Dr. Auger said.
“Everything is interconnected,” she said.
The study was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Auger has received a career award from Fonds de Recherche du Québec-Santé. Dr. Dunaif has consulted for Novo Nordisk and Fractyl Laboratories (now Fractyl Health).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children whose mothers have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have increased rates of hospitalization for various conditions, including asthma, pneumonia, and ear infection, a study of more than 1 million children shows.
The associations were not particularly strong, according to the researchers. But they raise questions about the reasons for the increased risk and whether interventions such as diet, exercise, or medications could lead to healthier outcomes for children whose mothers have PCOS.
“The findings suggest that maternal PCOS may have a negative impact on offspring development, enough to lead to a measurable increase in the risk of childhood hospitalization,” study coauthor Nathalie Auger, MD, associate professor of epidemiology at University of Montreal, and colleagues reported in Human Reproduction.
“They are minor differences, just enough that we can statistically identify them. They’re not something where everyone should be worrying at this point,” Dr. Auger told this news organization.
Still, some of the hospitalizations, such as those related to infection or allergy, could be prevented with earlier ambulatory care, so some degree of greater awareness among parents and clinicians may be warranted, she said.
Thirteen years of follow-up
PCOS – a reproductive disorder characterized by irregular periods, increased male hormones, and metabolic complications – affects some 10% of women. People with the condition are at increased risk for obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Although prior research has shown that maternal PCOS may be associated with higher body mass index and attention deficit disorder in children, data on long-term childhood health outcomes have been limited, Dr. Auger’s group noted.
To examine illness in children exposed to maternal PCOS, the investigators analyzed hospitalization rates for nearly 1.04 million children in Quebec between 2006 and 2020; 7,160 of the children had mothers with PCOS.
In all, 275,354 children were hospitalized during 13 years of follow-up, including 2,314 whose mothers had PCOS.
Children exposed to PCOS were hospitalized at a rate of 68.9 per 1,000 person-years – roughly 50% more often than the rate of 45.3 per 1,000 person-years for children not exposed to maternal PCOS.
In an analysis that adjusted for maternal characteristics, childhood hospitalization for any reason was 1.32 times more likely for children exposed to maternal PCOS.
Hospitalizations linked to infectious diseases – such as for bronchitis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, nephritis, otitis media, or meningitis – were 1.31 times more likely among children exposed to PCOS. Allergy-related hospitalizations, such as for allergic asthma and anaphylaxis, were 1.47 times more likely, according to the researchers.
Metabolic hospitalizations were 1.59 times more likely. For gastrointestinal hospitalizations, the hazard ratio was 1.72. For central nervous system hospitalizations, it was 1.74.
The associations were stronger in earlier childhood, and results were similar for boys and girls, the investigators reported.
Hospitalizations for cardiovascular disease, musculoskeletal conditions, or malignancy were not increased.
‘Surprising’ links
“The findings are surprising in that some of the conditions that they showed increased risk for, like asthma and some infections, are not conditions that we think of as being typically associated with PCOS,” said Andrea E. Dunaif, MD, chief of the Hilda and J. Lester Gabrilove Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Bone Disease at Mount Sinai Health System, New York, who was not part of the study team.
Earlier studies of offspring of women with PCOS have suggested that children may be at increased risk for insulin resistance and obesity.
Differences in genetics, intrauterine environments, patterns of health care use by women with PCOS, and behavioral factors, such as diet and how children are raised, are variables that could have contributed to the different hospitalization rates among children exposed to maternal PCOS, Dr. Auger said.
“Everything is interconnected,” she said.
The study was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Auger has received a career award from Fonds de Recherche du Québec-Santé. Dr. Dunaif has consulted for Novo Nordisk and Fractyl Laboratories (now Fractyl Health).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children whose mothers have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have increased rates of hospitalization for various conditions, including asthma, pneumonia, and ear infection, a study of more than 1 million children shows.
The associations were not particularly strong, according to the researchers. But they raise questions about the reasons for the increased risk and whether interventions such as diet, exercise, or medications could lead to healthier outcomes for children whose mothers have PCOS.
“The findings suggest that maternal PCOS may have a negative impact on offspring development, enough to lead to a measurable increase in the risk of childhood hospitalization,” study coauthor Nathalie Auger, MD, associate professor of epidemiology at University of Montreal, and colleagues reported in Human Reproduction.
“They are minor differences, just enough that we can statistically identify them. They’re not something where everyone should be worrying at this point,” Dr. Auger told this news organization.
Still, some of the hospitalizations, such as those related to infection or allergy, could be prevented with earlier ambulatory care, so some degree of greater awareness among parents and clinicians may be warranted, she said.
Thirteen years of follow-up
PCOS – a reproductive disorder characterized by irregular periods, increased male hormones, and metabolic complications – affects some 10% of women. People with the condition are at increased risk for obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Although prior research has shown that maternal PCOS may be associated with higher body mass index and attention deficit disorder in children, data on long-term childhood health outcomes have been limited, Dr. Auger’s group noted.
To examine illness in children exposed to maternal PCOS, the investigators analyzed hospitalization rates for nearly 1.04 million children in Quebec between 2006 and 2020; 7,160 of the children had mothers with PCOS.
In all, 275,354 children were hospitalized during 13 years of follow-up, including 2,314 whose mothers had PCOS.
Children exposed to PCOS were hospitalized at a rate of 68.9 per 1,000 person-years – roughly 50% more often than the rate of 45.3 per 1,000 person-years for children not exposed to maternal PCOS.
In an analysis that adjusted for maternal characteristics, childhood hospitalization for any reason was 1.32 times more likely for children exposed to maternal PCOS.
Hospitalizations linked to infectious diseases – such as for bronchitis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, nephritis, otitis media, or meningitis – were 1.31 times more likely among children exposed to PCOS. Allergy-related hospitalizations, such as for allergic asthma and anaphylaxis, were 1.47 times more likely, according to the researchers.
Metabolic hospitalizations were 1.59 times more likely. For gastrointestinal hospitalizations, the hazard ratio was 1.72. For central nervous system hospitalizations, it was 1.74.
The associations were stronger in earlier childhood, and results were similar for boys and girls, the investigators reported.
Hospitalizations for cardiovascular disease, musculoskeletal conditions, or malignancy were not increased.
‘Surprising’ links
“The findings are surprising in that some of the conditions that they showed increased risk for, like asthma and some infections, are not conditions that we think of as being typically associated with PCOS,” said Andrea E. Dunaif, MD, chief of the Hilda and J. Lester Gabrilove Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Bone Disease at Mount Sinai Health System, New York, who was not part of the study team.
Earlier studies of offspring of women with PCOS have suggested that children may be at increased risk for insulin resistance and obesity.
Differences in genetics, intrauterine environments, patterns of health care use by women with PCOS, and behavioral factors, such as diet and how children are raised, are variables that could have contributed to the different hospitalization rates among children exposed to maternal PCOS, Dr. Auger said.
“Everything is interconnected,” she said.
The study was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Auger has received a career award from Fonds de Recherche du Québec-Santé. Dr. Dunaif has consulted for Novo Nordisk and Fractyl Laboratories (now Fractyl Health).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HUMAN REPRODUCTION
Some have heavier periods after COVID vaccine
Many women who got a COVID-19 vaccine have reported heavier bleeding during their periods since they had the shots.
A team of researchers investigated the trend and set out to find out who among the vaccinated were more likely to experience the menstruation changes.
The researchers were led by Katharine M.N. Lee, PhD, MS, of the division of public health sciences at Washington University in St. Louis. Their findings were published ahead of print in Science Advances.
The investigators analyzed more than 139,000 responses from an online survey from both currently and formerly menstruating women.
They found that, among people who have regular periods, about the same percentage had heavier bleeding after they got a COVID vaccine as had no change in bleeding after the vaccine (44% vs. 42%, respectively).
“A much smaller portion had lighter periods,” they write.
The phenomenon has been difficult to study because questions about changes in menstruation are not a standard part of vaccine trials.
Date of last period is often tracked in clinical trials to make sure a participant is not pregnant, but the questions about periods often stop there.
Additionally, periods are different for everyone and can be influenced by all sorts of environmental factors, so making associations regarding exposures is problematic.
No changes found to fertility
The authors emphasized that, generally, changes to menstrual bleeding are not uncommon nor dangerous. They also emphasized that the changes in bleeding don’t mean changes to fertility.
The uterine reproductive system is flexible when the body is under stress, they note.
“We know that running a marathon may influence hormone concentrations in the short term while not rendering that person infertile,” the authors write.
However, they acknowledge that investigating these reports is critical in building trust in medicine.
This report includes information that hasn’t been available through the clinical trial follow-up process.
For instance, the authors write, “To the best of our knowledge, our work is the first to examine breakthrough bleeding after vaccination in either pre- or postmenopausal people.”
Reports of changes to periods after vaccination started emerging in 2021. But without data, reports were largely dismissed, fueling criticism from those waging campaigns against COVID vaccines.
Dr. Lee and colleagues gathered data from those who responded to the online survey and detailed some trends.
People who were bleeding more heavily after vaccination were more likely to be older, Hispanic, had vaccine side effects of fever and fatigue, had been pregnant at some point, or had given birth.
People with regular periods who had endometriosis, prolonged bleeding during their periods, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) or fibroids were also more likely to have increased bleeding after a COVID vaccine.
Breakthrough bleeding
For people who don’t menstruate, but have not reached menopause, breakthrough bleeding happened more often in women who had been pregnant and/or had given birth.
Among respondents who were postmenopausal, breakthrough bleeding happened more often in younger people and/or those who are Hispanic.
More than a third of the respondents (39%) who use gender-affirming hormones that eliminate menstruation reported breakthrough bleeding after vaccination.
The majority of premenopausal people on long-acting, reversible contraception (71%) and the majority of postmenopausal respondents (66%) had breakthrough bleeding as well.
The authors note that you can’t compare the percentages who report these experiences in the survey with the incidence of those who would experience changes in menstrual bleeding in the general population.
The nature of the online survey means it may be naturally biased because the people who responded may be more often those who noted some change in their own menstrual experiences, particularly if that involved discomfort, pain, or fear.
Researchers also acknowledge that Black, Indigenous, Latinx, and other respondents of color are underrepresented in this research and that represents a limitation in the work.
Alison Edelman, MD, MPH, with the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, was not involved with Dr. Lee and associates’ study but has also studied the relationship between COVID vaccines and menstruation.
Her team’s study found that COVID vaccination is associated with a small change in time between periods but not length of periods.
She said about the work by Dr. Lee and colleagues, “This work really elevates the voices of the public and what they’re experiencing.”
The association makes sense, Dr. Edelman says, in that the reproductive system and the immune system talk to each other and inflammation in the immune system is going to be noticed by the system governing periods.
Lack of data on the relationship between exposures and menstruation didn’t start with COVID. “There has been a signal in the population before with other vaccines that’s been dismissed,” she said.
Tracking menstruation information in clinical trials can help physicians counsel women on what may be coming with any vaccine and alleviate fears and vaccine hesitancy, Dr. Edelman explained. It can also help vaccine developers know what to include in information about their product.
“When you are counseled about what to expect, it’s not as scary. That provides trust in the system,” she said. She likened it to original lack of data on whether COVID-19 vaccines would affect pregnancy.
“We have great science now that COVID vaccine does not affect fertility and [vaccine] does not impact pregnancy.”
Another important aspect of this paper is that it included subgroups not studied before regarding menstruation and breakthrough bleeding, such as those taking gender-affirming hormones, she added.
Menstruation has been often overlooked as important in clinical trial exposures but Dr. Edelman hopes this recent attention and question will escalate and prompt more research.
“I’m hoping with the immense outpouring from the public about how important this is, that future studies will look at this a little bit better,” she says.
She said when the National Institutes of Health opened up funding for trials on COVID-19 vaccines and menstruation, researchers got flooded with requests from women to share their stories.
“As a researcher – I’ve been doing research for over 20 years – that’s not something that usually happens. I would love to have that happen for every research project.”
The authors and Dr. Edelman declare that they have no competing interests. This research was supported in part by the University of Illinois Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, the University of Illinois Interdisciplinary Health Sciences Institute, the National Institutes of Health, the Foundation for Barnes-Jewish Hospital, and the Siteman Cancer Center.
Many women who got a COVID-19 vaccine have reported heavier bleeding during their periods since they had the shots.
A team of researchers investigated the trend and set out to find out who among the vaccinated were more likely to experience the menstruation changes.
The researchers were led by Katharine M.N. Lee, PhD, MS, of the division of public health sciences at Washington University in St. Louis. Their findings were published ahead of print in Science Advances.
The investigators analyzed more than 139,000 responses from an online survey from both currently and formerly menstruating women.
They found that, among people who have regular periods, about the same percentage had heavier bleeding after they got a COVID vaccine as had no change in bleeding after the vaccine (44% vs. 42%, respectively).
“A much smaller portion had lighter periods,” they write.
The phenomenon has been difficult to study because questions about changes in menstruation are not a standard part of vaccine trials.
Date of last period is often tracked in clinical trials to make sure a participant is not pregnant, but the questions about periods often stop there.
Additionally, periods are different for everyone and can be influenced by all sorts of environmental factors, so making associations regarding exposures is problematic.
No changes found to fertility
The authors emphasized that, generally, changes to menstrual bleeding are not uncommon nor dangerous. They also emphasized that the changes in bleeding don’t mean changes to fertility.
The uterine reproductive system is flexible when the body is under stress, they note.
“We know that running a marathon may influence hormone concentrations in the short term while not rendering that person infertile,” the authors write.
However, they acknowledge that investigating these reports is critical in building trust in medicine.
This report includes information that hasn’t been available through the clinical trial follow-up process.
For instance, the authors write, “To the best of our knowledge, our work is the first to examine breakthrough bleeding after vaccination in either pre- or postmenopausal people.”
Reports of changes to periods after vaccination started emerging in 2021. But without data, reports were largely dismissed, fueling criticism from those waging campaigns against COVID vaccines.
Dr. Lee and colleagues gathered data from those who responded to the online survey and detailed some trends.
People who were bleeding more heavily after vaccination were more likely to be older, Hispanic, had vaccine side effects of fever and fatigue, had been pregnant at some point, or had given birth.
People with regular periods who had endometriosis, prolonged bleeding during their periods, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) or fibroids were also more likely to have increased bleeding after a COVID vaccine.
Breakthrough bleeding
For people who don’t menstruate, but have not reached menopause, breakthrough bleeding happened more often in women who had been pregnant and/or had given birth.
Among respondents who were postmenopausal, breakthrough bleeding happened more often in younger people and/or those who are Hispanic.
More than a third of the respondents (39%) who use gender-affirming hormones that eliminate menstruation reported breakthrough bleeding after vaccination.
The majority of premenopausal people on long-acting, reversible contraception (71%) and the majority of postmenopausal respondents (66%) had breakthrough bleeding as well.
The authors note that you can’t compare the percentages who report these experiences in the survey with the incidence of those who would experience changes in menstrual bleeding in the general population.
The nature of the online survey means it may be naturally biased because the people who responded may be more often those who noted some change in their own menstrual experiences, particularly if that involved discomfort, pain, or fear.
Researchers also acknowledge that Black, Indigenous, Latinx, and other respondents of color are underrepresented in this research and that represents a limitation in the work.
Alison Edelman, MD, MPH, with the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, was not involved with Dr. Lee and associates’ study but has also studied the relationship between COVID vaccines and menstruation.
Her team’s study found that COVID vaccination is associated with a small change in time between periods but not length of periods.
She said about the work by Dr. Lee and colleagues, “This work really elevates the voices of the public and what they’re experiencing.”
The association makes sense, Dr. Edelman says, in that the reproductive system and the immune system talk to each other and inflammation in the immune system is going to be noticed by the system governing periods.
Lack of data on the relationship between exposures and menstruation didn’t start with COVID. “There has been a signal in the population before with other vaccines that’s been dismissed,” she said.
Tracking menstruation information in clinical trials can help physicians counsel women on what may be coming with any vaccine and alleviate fears and vaccine hesitancy, Dr. Edelman explained. It can also help vaccine developers know what to include in information about their product.
“When you are counseled about what to expect, it’s not as scary. That provides trust in the system,” she said. She likened it to original lack of data on whether COVID-19 vaccines would affect pregnancy.
“We have great science now that COVID vaccine does not affect fertility and [vaccine] does not impact pregnancy.”
Another important aspect of this paper is that it included subgroups not studied before regarding menstruation and breakthrough bleeding, such as those taking gender-affirming hormones, she added.
Menstruation has been often overlooked as important in clinical trial exposures but Dr. Edelman hopes this recent attention and question will escalate and prompt more research.
“I’m hoping with the immense outpouring from the public about how important this is, that future studies will look at this a little bit better,” she says.
She said when the National Institutes of Health opened up funding for trials on COVID-19 vaccines and menstruation, researchers got flooded with requests from women to share their stories.
“As a researcher – I’ve been doing research for over 20 years – that’s not something that usually happens. I would love to have that happen for every research project.”
The authors and Dr. Edelman declare that they have no competing interests. This research was supported in part by the University of Illinois Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, the University of Illinois Interdisciplinary Health Sciences Institute, the National Institutes of Health, the Foundation for Barnes-Jewish Hospital, and the Siteman Cancer Center.
Many women who got a COVID-19 vaccine have reported heavier bleeding during their periods since they had the shots.
A team of researchers investigated the trend and set out to find out who among the vaccinated were more likely to experience the menstruation changes.
The researchers were led by Katharine M.N. Lee, PhD, MS, of the division of public health sciences at Washington University in St. Louis. Their findings were published ahead of print in Science Advances.
The investigators analyzed more than 139,000 responses from an online survey from both currently and formerly menstruating women.
They found that, among people who have regular periods, about the same percentage had heavier bleeding after they got a COVID vaccine as had no change in bleeding after the vaccine (44% vs. 42%, respectively).
“A much smaller portion had lighter periods,” they write.
The phenomenon has been difficult to study because questions about changes in menstruation are not a standard part of vaccine trials.
Date of last period is often tracked in clinical trials to make sure a participant is not pregnant, but the questions about periods often stop there.
Additionally, periods are different for everyone and can be influenced by all sorts of environmental factors, so making associations regarding exposures is problematic.
No changes found to fertility
The authors emphasized that, generally, changes to menstrual bleeding are not uncommon nor dangerous. They also emphasized that the changes in bleeding don’t mean changes to fertility.
The uterine reproductive system is flexible when the body is under stress, they note.
“We know that running a marathon may influence hormone concentrations in the short term while not rendering that person infertile,” the authors write.
However, they acknowledge that investigating these reports is critical in building trust in medicine.
This report includes information that hasn’t been available through the clinical trial follow-up process.
For instance, the authors write, “To the best of our knowledge, our work is the first to examine breakthrough bleeding after vaccination in either pre- or postmenopausal people.”
Reports of changes to periods after vaccination started emerging in 2021. But without data, reports were largely dismissed, fueling criticism from those waging campaigns against COVID vaccines.
Dr. Lee and colleagues gathered data from those who responded to the online survey and detailed some trends.
People who were bleeding more heavily after vaccination were more likely to be older, Hispanic, had vaccine side effects of fever and fatigue, had been pregnant at some point, or had given birth.
People with regular periods who had endometriosis, prolonged bleeding during their periods, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) or fibroids were also more likely to have increased bleeding after a COVID vaccine.
Breakthrough bleeding
For people who don’t menstruate, but have not reached menopause, breakthrough bleeding happened more often in women who had been pregnant and/or had given birth.
Among respondents who were postmenopausal, breakthrough bleeding happened more often in younger people and/or those who are Hispanic.
More than a third of the respondents (39%) who use gender-affirming hormones that eliminate menstruation reported breakthrough bleeding after vaccination.
The majority of premenopausal people on long-acting, reversible contraception (71%) and the majority of postmenopausal respondents (66%) had breakthrough bleeding as well.
The authors note that you can’t compare the percentages who report these experiences in the survey with the incidence of those who would experience changes in menstrual bleeding in the general population.
The nature of the online survey means it may be naturally biased because the people who responded may be more often those who noted some change in their own menstrual experiences, particularly if that involved discomfort, pain, or fear.
Researchers also acknowledge that Black, Indigenous, Latinx, and other respondents of color are underrepresented in this research and that represents a limitation in the work.
Alison Edelman, MD, MPH, with the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, was not involved with Dr. Lee and associates’ study but has also studied the relationship between COVID vaccines and menstruation.
Her team’s study found that COVID vaccination is associated with a small change in time between periods but not length of periods.
She said about the work by Dr. Lee and colleagues, “This work really elevates the voices of the public and what they’re experiencing.”
The association makes sense, Dr. Edelman says, in that the reproductive system and the immune system talk to each other and inflammation in the immune system is going to be noticed by the system governing periods.
Lack of data on the relationship between exposures and menstruation didn’t start with COVID. “There has been a signal in the population before with other vaccines that’s been dismissed,” she said.
Tracking menstruation information in clinical trials can help physicians counsel women on what may be coming with any vaccine and alleviate fears and vaccine hesitancy, Dr. Edelman explained. It can also help vaccine developers know what to include in information about their product.
“When you are counseled about what to expect, it’s not as scary. That provides trust in the system,” she said. She likened it to original lack of data on whether COVID-19 vaccines would affect pregnancy.
“We have great science now that COVID vaccine does not affect fertility and [vaccine] does not impact pregnancy.”
Another important aspect of this paper is that it included subgroups not studied before regarding menstruation and breakthrough bleeding, such as those taking gender-affirming hormones, she added.
Menstruation has been often overlooked as important in clinical trial exposures but Dr. Edelman hopes this recent attention and question will escalate and prompt more research.
“I’m hoping with the immense outpouring from the public about how important this is, that future studies will look at this a little bit better,” she says.
She said when the National Institutes of Health opened up funding for trials on COVID-19 vaccines and menstruation, researchers got flooded with requests from women to share their stories.
“As a researcher – I’ve been doing research for over 20 years – that’s not something that usually happens. I would love to have that happen for every research project.”
The authors and Dr. Edelman declare that they have no competing interests. This research was supported in part by the University of Illinois Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, the University of Illinois Interdisciplinary Health Sciences Institute, the National Institutes of Health, the Foundation for Barnes-Jewish Hospital, and the Siteman Cancer Center.
FROM SCIENCE ADVANCES
Best practices for evaluating pelvic pain in patients with Essure tubal occlusion devices
The evaluation and management of chronic pelvic pain in patients with a history of Essure device (Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc, Whippany, New Jersey) insertion have posed many challenges for both clinicians and patients. The availability of high-quality, evidence-based clinical guidance has been limited. We have reviewed the currently available published data, and here provide an overview of takeaways, as well as share our perspective and approach on evaluating and managing chronic pelvic pain in this unique patient population.
The device
The Essure microinsert is a hysteroscopically placed device that facilitates permanent sterilization by occluding the bilateral proximal fallopian tubes. The microinsert has an inner and outer nitinol coil that attaches the device to the proximal fallopian tube to ensure retention. The inner coil releases polyethylene terephthalate fibers that cause tubal fiber proliferation to occlude the lumen of the fallopian tube and achieve sterilization.
The device was first approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2002. In subsequent years, the device was well received and widely used, with approximately 750,000 women worldwide undergoing Essure placement.1,2 Shortly after approval, many adverse events (AEs), including pelvic pain and abnormal uterine bleeding, were reported, resulting in a public meeting of the FDA Obstetrics and Gynecology Devices Panel in September 2015. A postmarket surveillance study on the device ensued to assess complication rates including unplanned pregnancy, pelvic pain, and surgery for removal. In February 2016, the FDA issued a black box warning and a patient decision checklist.3,4 In December 2018, Bayer stopped selling and distributing Essure in the United States.5 A 4-year follow-up surveillance study on Essure was submitted to the FDA in March 2020.
Adverse outcomes
Common AEs related to the Essure device include heavy uterine bleeding, pelvic pain, and other quality-of-life symptoms such as fatigue and weight gain.6-8 The main safety endpoints for the mandated FDA postmarket 522 surveillance studies were chronic lower abdominal and pelvic pain; abnormal uterine bleeding; hypersensitivity; allergic reaction, as well as autoimmune disorders incorporating inflammatory markers and human leukocyte antigen; and gynecologic surgery for device removal.9 Postmarket surveillence has shown that most AEs are related to placement complications or pelvic pain after Essure insertion. However, there have been several reports of autoimmune diseases categorized as serious AEs, such as new-onset systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and worsening ulcerative colitis, after Essure insertion.5
Evaluation of symptoms
Prevalence of pelvic pain following device placement
We conducted a PubMed and MEDLINE search from January 2000 to May 2020, which identified 43 studies citing AEs related to device placement, including pelvic or abdominal pain, abnormal uterine bleeding, hypersensitivity, and autoimmune disorders. A particularly debilitating and frequently cited AE was new-onset pelvic pain or worsening of preexisting pelvic pain. Perforation of the uterus or fallopian tube, resulting in displacement of the device into the peritoneal cavity, or fragmentation of the microinsert was reported as a serious AE that occurred after device placement. However, due to the complexity of chronic pelvic pain pathogenesis, the effect of the insert on patients with existing chronic pelvic pain remains unknown.
Authors of a large retrospective study found that approximately 2.7% of 1,430 patients developed new-onset or worsening pelvic pain after device placement. New-onset pelvic pain in 1% of patients was thought to be secondary to device placement, without a coexisting pathology or diagnosis.10
In a retrospective study by Clark and colleagues, 22 of 50 women (44%) with pelvic pain after microinsert placement were found to have at least one other cause of pelvic pain. The most common alternative diagnoses were endometriosis, adenomyosis, salpingitis, and adhesive disease. Nine of the 50 patients (18%) were found to have endometriosis upon surgical removal of the microinsert.7
Another case series examined outcomes in 29 patients undergoing laparoscopic device removal due to new-onset pelvic pain. Intraoperative findings included endometriosis in 5 patients (17.2%) and pelvic adhesions in 3 (10.3%).2 Chronic pelvic pain secondary to endometriosis may be exacerbated with Essure insertion due to discontinuation of hormonal birth control after device placement,7 and this diagnosis along with adenomyosis should be strongly considered in patients whose pelvic pain began when hormonal contraception was discontinued after placement of the device.
Continue to: Risk factors...
Risk factors
Authors of a retrospective cohort study found that patients with prior diagnosis of a chronic pain syndrome, low back pain, headaches, or fibromyalgia were 5 to 6 times more likely to report acute and chronic pain after hysteroscopic sterilization with Essure.11 Since chronic pain is often thought to be driven by a hyperalgesic state of the central nervous system, as previously shown in patients with conditions such as vulvodynia, interstitial cystitis, and fibromyalgia,12 a hyperalgesic state can potentially explain why some patients are more susceptible to developing worsening pain.
Van Limburg and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study with prospective follow-up on 284 women who underwent Essure sterilization. Among these patients, 48% reported negative AEs; risk factors included young age at placement, increasing gravidity, and no prior abdominal surgery.13
Onset of pain
The timing and onset of pelvic pain vary widely, suggesting there is no particular time frame for this AE after device placement.2,6,14-18 A case series by Arjona and colleagues analyzed the incidence of chronic pelvic pain in 4,274 patients after Essure sterilization. Seven patients (0.16%) reported chronic pelvic pain that necessitated device removal. In 6 of the women, the pelvic pain began within 1 week of device placement. In 3 of the 6 cases, the surgeon reported the removal procedures as “difficult.” In all 6 cases, the level of pelvic pain increased with time and was not alleviated with standard analgesic medications.6
In another case series of 26 patients, the authors evaluated patients undergoing laparoscopic removal of Essure secondary to pelvic pain and reported that the time range for symptom presentation was immediate to 85 months. Thirteen of 26 patients (50%) reported pain onset within less than 1 month of device placement, 5 of 26 patients (19.2%) reported pain between 1 and 12 months after device placement, and 8 of 26 patients (30.8%) reported pain onset more than 12 months after microinsert placement.2 In this study, 17.2% of operative reports indicated difficulty with device placement. It is unclear whether difficulty with placement was associated with development of subsequent abdominal or pelvic pain; however, the relevance of initial insertion difficulty diminished with longer follow-up.
Workup and evaluation
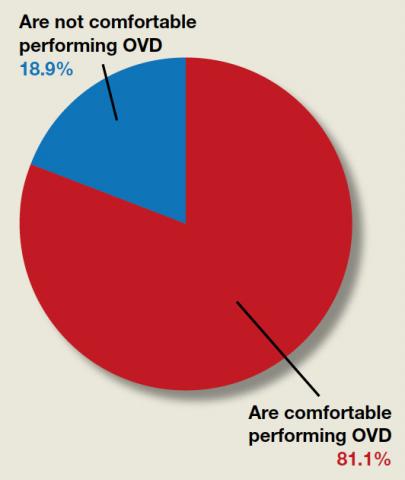
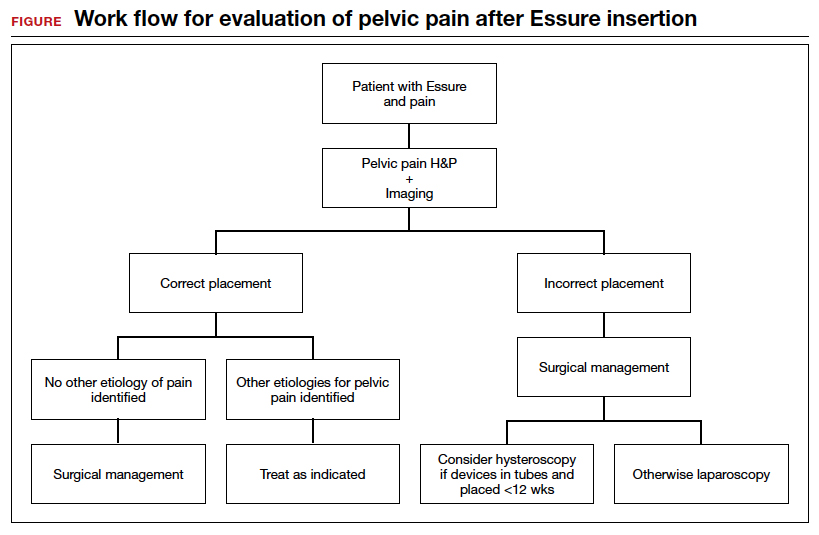
We found 5 studies that provided some framework for evaluating a patient with new-onset or worsening pelvic pain after microinsert placement. Overall, correct placement and functionality of the device should be confirmed by either hysterosalpingogram (HSG) or transvaginal ultrasonography (TVUS). The gold standard to determine tubal occlusion is the HSG. However, TVUS may be a dependable alternative, and either test can accurately demonstrate Essure location.19 Patients often prefer TVUS over HSG due to the low cost, minimal discomfort, and short examination time.1 TVUS is a noninvasive and reasonable test to start the initial assessment. The Essure devices are highly echogenic on pelvic ultrasound and easily identifiable by the proximity of the device to the uterotubal junction and its relationship with the surrounding soft tissue. If the device perforates the peritoneal cavity, then the echogenic bowel can impede adequate visualization of the Essure microinsert. If the Essure insert is not visualized on TVUS, an HSG will not only confirm placement but also test insert functionality. After confirming correct placement of the device, the provider can proceed with standard workup for chronic pelvic pain.
If one or more of the devices are malpositioned, the devices are generally presumed to be the etiology of the new pain. Multiple case reports demonstrate pain due to Essure misconfiguration or perforation with subsequent resolution of symptoms after device removal.18,20,21 A case study by Alcantara and colleagues described a patient with chronic pelvic pain and an Essure coil that was curved in an elliptical shape, not adhering to the anatomic course of the fallopian tube. The patient reported pain resolution after laparoscopic removal of the device.20 Another case report by Mahmoud et al described a subserosal malpositioned device that caused acute pelvic pain 4 months after sterilization. The patient reported resolution of pain after the microinsert was removed via laparoscopy.21 These reports highlight the importance of considering malpositioned devices as the etiology of new pelvic pain after Essure placement.
Continue to: Device removal and patient outcomes...
Device removal and patient outcomes
Removal
Several studies that we evaluated included a discussion on the methods for Essure removal. which are divided into 2 general categories: hysteroscopy and laparoscopy.
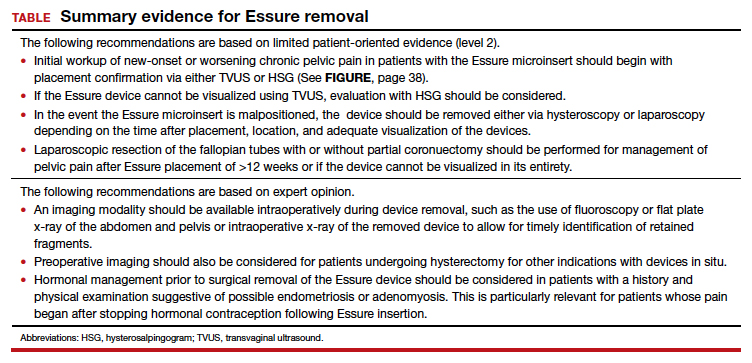
Hysteroscopic removal is generally used when the device was placed less than 12 weeks prior to removal.7,19 After 12 weeks, removal is more difficult due to fibrosis within the fallopian tubes. A risk with hysteroscopic removal is failure to remove all fibers, which allows inflammation and fibrosis to continue.7 This risk is mitigated via laparoscopic hysterectomy or mini-cornuectomy with bilateral salpingectomy, where the devices can be removed en bloc and without excessive traction.
Laparoscopic Essure removal procedures described in the literature include salpingostomy and traction on the device, salpingectomy, and salpingectomy with mini-cornuectomy. The incision and traction method is typically performed via a 2- to 3-cm incision on the antimesial edge of the fallopian tube along with a circumferential incision to surround the interstitial tubal area. The implant is carefully extracted from the fallopian tube and cornua, and a salpingectomy is then performed.22 The implant is removed prior to the salpingectomy to ensure that the Essure device is removed in its entirety prior to performing a salpingectomy.
A prospective observational study evaluated laparoscopic removal of Essure devices in 80 women with or without cornual excision. Results suggest that the incision and traction method poses more technical difficulties than the cornuectomy approach.23 Surgeons reported significant difficulty controlling the tensile pressure with traction, whereas use of the cornuectomy approach eliminated this risk and decreased the risk of fragmentation and incomplete removal.23,24
Charavil and colleagues demonstrated in a prospective observational study that a vaginal hysterectomy with bilateral salpingectomy is a feasible approach to Essure removal. Twenty-six vaginal hysterectomies with bilateral salpingectomy and Essure removal were performed without conversion to laparoscopy or laparotomy. The surgeons performed an en bloc removal of each hemiuterus along with the ipsilateral tube, which ensured complete removal of the Essure device. Each case was confirmed with an x-ray of the surgical specimen.25
If device fragmentation occurs, there are different methods recommended for locating fragments. A case report of bilateral uterine perforation after uncomplicated Essure placement used a preoperative computed tomography (CT) scan to locate the Essure fragments, but no intraoperative imaging was performed to confirm complete fragment removal.26 The patient continued reporting chronic pelvic pain and ultimately underwent exploratory laparotomy with intraoperative fluoroscopy. Using fluoroscopy, investigators identified omental fragments that were missed on preoperative CT imaging. Fluoroscopy is not commonly used intraoperatively, but it may have added benefit for localizing retained fragments.
A retrospective cohort study reviewed the use of intraoperative x-ray of the removed specimen to confirm complete Essure removal.27 If an x-ray of the removed specimen showed incomplete removal, an intraoperative pelvic x-ray was performed to locate missing fragments. X-ray of the removed devices confirmed complete removal in 63 of 72 patients (87.5%). Six of 9 women with an unsatisfactory specimen x-ray had no residual fragments identified during pelvic x-ray, and the device removal was deemed adequate. The remaining 3 women had radiologic evidence of incomplete device removal and required additional dissection for complete removal. Overall, use of x-ray or fluoroscopy is a relatively safe and accessible way to ensure complete removal of the Essure device and is worth consideration, especially when retained device fragments are suspected.
Symptom resolution
We reviewed 5 studies that examined pain outcomes after removal of the Essure devices. Casey et al found that 23 of 26 patients (88.5%) reported significant pain relief at the postoperative visit, while 3 of 26 (11.5%) reported persistent pelvic pain.2 Two of 3 case series examined other outcomes in addition to postoperative pelvic pain, including sexual function and activities of daily living.7,14 In the first case series by Brito and colleagues, 8 of 11 patients (72.7%) reported an improvement in pelvic pain, ability to perform daily activities, sexual life, and overall quality of life after Essure removal. For the remaining 3 patients with persistent pelvic pain after surgical removal of the device, 2 patients reported worsening pain symptoms and dyspareunia.14 In this study, 5 of 11 patients reported a history of chronic pelvic pain at baseline. In a retrospective case series by Clark et al, 28 of 32 women (87.5%) reported some improvement in all domains, with 24 of 32 patients (75%) reporting almost total or complete improvement in quality of life, sexual life, pelvic pain, and scores related to activities of daily living. Pain and quality-of-life scores were similar for women who underwent uterine-preserving surgery and for those who underwent hysterectomy. Ten of 32 women (31.3%) reported persistent or worsening symptoms after the Essure removal surgery. In these patients, the authors recommended consideration of other autoimmune and hypersensitivity etiologies.7
In a retrospective cohort study by Kamencic et al from 2002 to 2013 of 1,430 patients who underwent Essure placement with postplacement imaging, 62 patients (4.3%) required a second surgery after Essure placement due to pelvic pain.10 This study also found that 4 of 62 patients (0.3%) had no other obvious cause for the pelvic pain. All 4 of these women had complete resolution of their pain with removal of the Essure microinsert device. A prospective observational study by Chene e
Summary
Although Essure products were withdrawn from the market in the United States in 2018, many patients still experience significant AEs associated with the device. The goal of the perspectives and data presented here is to assist clinicians in addressing and managing the pain experienced by patients after device insertion. ●
- Connor VF. Essure: a review six years later. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2009;16:282-290. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2009.02.009.
- Casey J, Aguirre F, Yunker A. Outcomes of laparoscopic removal of the Essure sterilization device for pelvic pain: a case series. Contraception. 2016;94:190-192. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2016.03.017.
- Jackson I. Essure device removed entirely from market, with 99% of unused birth control implants retrieved: FDA. AboutLawsuits.com. January 13, 2020. https://www.aboutlawsuits.com/Essure-removal-update-166509. Accessed June 7, 2022.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Labeling for permanent hysteroscopically-placed tubal implants intended for sterilization. October 31, 2016. https://www.fda.gov/media/96315/download. Accessed June 7, 2022.
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA activities related to Essure. March 14, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/essure-permanent-birth-control/fda-activities-related-essure. Accessed June 8, 2022.
- Arjona Berral JE, Rodríguez Jiménez B, Velasco Sánchez E, et al. Essure and chronic pelvic pain: a population-based cohort. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2014;34:712-713. doi:10.3109/01443615.2014.92075.
- Clark NV, Rademaker D, Mushinski AA, et al. Essure removal for the treatment of device-attributed symptoms: an expanded case series and follow-up survey. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24:971-976. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2017.05.015.
- Sills ES, Rickers NS, Li X. Surgical management after hysteroscopic sterilization: minimally invasive approach incorporating intraoperative fluoroscopy for symptomatic patients with >2 Essure devices. Surg Technol Int. 2018;32:156-161.
- Administration USF and D. 522 Postmarket Surveillance Studies. Center for Devices and Radiological Health; 2020.
- Kamencic H, Thiel L, Karreman E, et al. Does Essure cause significant de novo pain? A retrospective review of indications for second surgeries after Essure placement. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2016;23:1158-1162. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2016.08.823.
- Yunker AC, Ritch JM, Robinson EF, et al. Incidence and risk factors for chronic pelvic pain after hysteroscopic sterilization. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015;22:390-994. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2014.06.007.
- Phillips K, Clauw DJ. Central pain mechanisms in chronic pain states--maybe it is all in their head. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2011;25:141-154. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2011.02.005.
- van Limburg Stirum EVJ, Clark NV, Lindsey A, et al. Factors associated with negative patient experiences with Essure sterilization. JSLS. 2020;24(1):e2019.00065. doi:10.4293/JSLS.2019.00065.
- Brito LG, Cohen SL, Goggins ER, et al. Essure surgical removal and subsequent symptom resolution: case series and follow-up survey. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015;22:910-913. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2015.03.018.
- Maassen LW, van Gastel DM, Haveman I, et al. Removal of Essure sterilization devices: a retrospective cohort study in the Netherlands. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:1056-1062. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2018.10.009.
- Sills ES, Palermo GD. Surgical excision of Essure devices with ESHRE class IIb uterine malformation: sequential hysteroscopic-laparoscopic approach to the septate uterus. Facts Views Vis Obgyn. 2016;8:49-52.
- Ricci G, Restaino S, Di Lorenzo G, et al. Risk of Essure microinsert abdominal migration: case report and review of literature. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2014;10:963-968. doi:10.2147/TCRM.S65634.
- Borley J, Shabajee N, Tan TL. A kink is not always a perforation: assessing Essure hysteroscopic sterilization placement. Fertil Steril. 2011;95:2429.e15-7. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.02.006.
- Djeffal H, Blouet M, Pizzoferato AC, et al. Imaging findings in Essure-related complications: a pictorial review.7Br J Radiol. 2018;91(1090):20170686. doi:10.1259/bjr.20170686.
- Lora Alcantara I, Rezai S, Kirby C, et al. Essure surgical removal and subsequent resolution of chronic pelvic pain: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2016;2016:6961202. doi:10.1155/2016/6961202.
- Mahmoud MS, Fridman D, Merhi ZO. Subserosal misplacement of Essure device manifested by late-onset acute pelvic pain. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:2038.e1-3. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.07.1677.
- Tissot M, Petry S, Lecointre L, et al. Two surgical techniques for Essure device ablation: the hysteroscopic way and the laparoscopic way by salpingectomy with tubal interstitial resection. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26(4):603. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2018.07.017.
- Chene G, Cerruto E, Moret S, et al. Quality of life after laparoscopic removal of Essure sterilization devices. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol X. 2019;3:100054. doi:10.1016/j.eurox.2019.100054.
- Thiel L, Rattray D, Thiel J. Laparoscopic cornuectomy as a technique for removal of Essure microinserts. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24(1):10. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2016.07.004.
- Charavil A, Agostini A, Rambeaud C, et al. Vaginal hysterectomy with salpingectomy for Essure insert removal. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;2:695-701. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2018.07.019.
- Howard DL, Christenson PJ, Strickland JL. Use of intraoperative fluoroscopy during laparotomy to identify fragments of retained Essure microinserts: case report. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2012;19:667-670. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2012.04.007.
- Miquel L, Crochet P, Francini S, et al. Laparoscopic Essure device removal by en bloc salpingectomy-cornuectomy with intraoperative x-ray checking: a retrospective cohort study. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020;27:697-703. doi:10.1016/j. jmig.2019.06.006.
The evaluation and management of chronic pelvic pain in patients with a history of Essure device (Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc, Whippany, New Jersey) insertion have posed many challenges for both clinicians and patients. The availability of high-quality, evidence-based clinical guidance has been limited. We have reviewed the currently available published data, and here provide an overview of takeaways, as well as share our perspective and approach on evaluating and managing chronic pelvic pain in this unique patient population.
The device
The Essure microinsert is a hysteroscopically placed device that facilitates permanent sterilization by occluding the bilateral proximal fallopian tubes. The microinsert has an inner and outer nitinol coil that attaches the device to the proximal fallopian tube to ensure retention. The inner coil releases polyethylene terephthalate fibers that cause tubal fiber proliferation to occlude the lumen of the fallopian tube and achieve sterilization.
The device was first approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2002. In subsequent years, the device was well received and widely used, with approximately 750,000 women worldwide undergoing Essure placement.1,2 Shortly after approval, many adverse events (AEs), including pelvic pain and abnormal uterine bleeding, were reported, resulting in a public meeting of the FDA Obstetrics and Gynecology Devices Panel in September 2015. A postmarket surveillance study on the device ensued to assess complication rates including unplanned pregnancy, pelvic pain, and surgery for removal. In February 2016, the FDA issued a black box warning and a patient decision checklist.3,4 In December 2018, Bayer stopped selling and distributing Essure in the United States.5 A 4-year follow-up surveillance study on Essure was submitted to the FDA in March 2020.
Adverse outcomes
Common AEs related to the Essure device include heavy uterine bleeding, pelvic pain, and other quality-of-life symptoms such as fatigue and weight gain.6-8 The main safety endpoints for the mandated FDA postmarket 522 surveillance studies were chronic lower abdominal and pelvic pain; abnormal uterine bleeding; hypersensitivity; allergic reaction, as well as autoimmune disorders incorporating inflammatory markers and human leukocyte antigen; and gynecologic surgery for device removal.9 Postmarket surveillence has shown that most AEs are related to placement complications or pelvic pain after Essure insertion. However, there have been several reports of autoimmune diseases categorized as serious AEs, such as new-onset systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and worsening ulcerative colitis, after Essure insertion.5
Evaluation of symptoms
Prevalence of pelvic pain following device placement
We conducted a PubMed and MEDLINE search from January 2000 to May 2020, which identified 43 studies citing AEs related to device placement, including pelvic or abdominal pain, abnormal uterine bleeding, hypersensitivity, and autoimmune disorders. A particularly debilitating and frequently cited AE was new-onset pelvic pain or worsening of preexisting pelvic pain. Perforation of the uterus or fallopian tube, resulting in displacement of the device into the peritoneal cavity, or fragmentation of the microinsert was reported as a serious AE that occurred after device placement. However, due to the complexity of chronic pelvic pain pathogenesis, the effect of the insert on patients with existing chronic pelvic pain remains unknown.
Authors of a large retrospective study found that approximately 2.7% of 1,430 patients developed new-onset or worsening pelvic pain after device placement. New-onset pelvic pain in 1% of patients was thought to be secondary to device placement, without a coexisting pathology or diagnosis.10
In a retrospective study by Clark and colleagues, 22 of 50 women (44%) with pelvic pain after microinsert placement were found to have at least one other cause of pelvic pain. The most common alternative diagnoses were endometriosis, adenomyosis, salpingitis, and adhesive disease. Nine of the 50 patients (18%) were found to have endometriosis upon surgical removal of the microinsert.7
Another case series examined outcomes in 29 patients undergoing laparoscopic device removal due to new-onset pelvic pain. Intraoperative findings included endometriosis in 5 patients (17.2%) and pelvic adhesions in 3 (10.3%).2 Chronic pelvic pain secondary to endometriosis may be exacerbated with Essure insertion due to discontinuation of hormonal birth control after device placement,7 and this diagnosis along with adenomyosis should be strongly considered in patients whose pelvic pain began when hormonal contraception was discontinued after placement of the device.
Continue to: Risk factors...
Risk factors
Authors of a retrospective cohort study found that patients with prior diagnosis of a chronic pain syndrome, low back pain, headaches, or fibromyalgia were 5 to 6 times more likely to report acute and chronic pain after hysteroscopic sterilization with Essure.11 Since chronic pain is often thought to be driven by a hyperalgesic state of the central nervous system, as previously shown in patients with conditions such as vulvodynia, interstitial cystitis, and fibromyalgia,12 a hyperalgesic state can potentially explain why some patients are more susceptible to developing worsening pain.
Van Limburg and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study with prospective follow-up on 284 women who underwent Essure sterilization. Among these patients, 48% reported negative AEs; risk factors included young age at placement, increasing gravidity, and no prior abdominal surgery.13
Onset of pain
The timing and onset of pelvic pain vary widely, suggesting there is no particular time frame for this AE after device placement.2,6,14-18 A case series by Arjona and colleagues analyzed the incidence of chronic pelvic pain in 4,274 patients after Essure sterilization. Seven patients (0.16%) reported chronic pelvic pain that necessitated device removal. In 6 of the women, the pelvic pain began within 1 week of device placement. In 3 of the 6 cases, the surgeon reported the removal procedures as “difficult.” In all 6 cases, the level of pelvic pain increased with time and was not alleviated with standard analgesic medications.6
In another case series of 26 patients, the authors evaluated patients undergoing laparoscopic removal of Essure secondary to pelvic pain and reported that the time range for symptom presentation was immediate to 85 months. Thirteen of 26 patients (50%) reported pain onset within less than 1 month of device placement, 5 of 26 patients (19.2%) reported pain between 1 and 12 months after device placement, and 8 of 26 patients (30.8%) reported pain onset more than 12 months after microinsert placement.2 In this study, 17.2% of operative reports indicated difficulty with device placement. It is unclear whether difficulty with placement was associated with development of subsequent abdominal or pelvic pain; however, the relevance of initial insertion difficulty diminished with longer follow-up.
Workup and evaluation
We found 5 studies that provided some framework for evaluating a patient with new-onset or worsening pelvic pain after microinsert placement. Overall, correct placement and functionality of the device should be confirmed by either hysterosalpingogram (HSG) or transvaginal ultrasonography (TVUS). The gold standard to determine tubal occlusion is the HSG. However, TVUS may be a dependable alternative, and either test can accurately demonstrate Essure location.19 Patients often prefer TVUS over HSG due to the low cost, minimal discomfort, and short examination time.1 TVUS is a noninvasive and reasonable test to start the initial assessment. The Essure devices are highly echogenic on pelvic ultrasound and easily identifiable by the proximity of the device to the uterotubal junction and its relationship with the surrounding soft tissue. If the device perforates the peritoneal cavity, then the echogenic bowel can impede adequate visualization of the Essure microinsert. If the Essure insert is not visualized on TVUS, an HSG will not only confirm placement but also test insert functionality. After confirming correct placement of the device, the provider can proceed with standard workup for chronic pelvic pain.
If one or more of the devices are malpositioned, the devices are generally presumed to be the etiology of the new pain. Multiple case reports demonstrate pain due to Essure misconfiguration or perforation with subsequent resolution of symptoms after device removal.18,20,21 A case study by Alcantara and colleagues described a patient with chronic pelvic pain and an Essure coil that was curved in an elliptical shape, not adhering to the anatomic course of the fallopian tube. The patient reported pain resolution after laparoscopic removal of the device.20 Another case report by Mahmoud et al described a subserosal malpositioned device that caused acute pelvic pain 4 months after sterilization. The patient reported resolution of pain after the microinsert was removed via laparoscopy.21 These reports highlight the importance of considering malpositioned devices as the etiology of new pelvic pain after Essure placement.

Continue to: Device removal and patient outcomes...
Device removal and patient outcomes
Removal
Several studies that we evaluated included a discussion on the methods for Essure removal. which are divided into 2 general categories: hysteroscopy and laparoscopy.
Hysteroscopic removal is generally used when the device was placed less than 12 weeks prior to removal.7,19 After 12 weeks, removal is more difficult due to fibrosis within the fallopian tubes. A risk with hysteroscopic removal is failure to remove all fibers, which allows inflammation and fibrosis to continue.7 This risk is mitigated via laparoscopic hysterectomy or mini-cornuectomy with bilateral salpingectomy, where the devices can be removed en bloc and without excessive traction.
Laparoscopic Essure removal procedures described in the literature include salpingostomy and traction on the device, salpingectomy, and salpingectomy with mini-cornuectomy. The incision and traction method is typically performed via a 2- to 3-cm incision on the antimesial edge of the fallopian tube along with a circumferential incision to surround the interstitial tubal area. The implant is carefully extracted from the fallopian tube and cornua, and a salpingectomy is then performed.22 The implant is removed prior to the salpingectomy to ensure that the Essure device is removed in its entirety prior to performing a salpingectomy.
A prospective observational study evaluated laparoscopic removal of Essure devices in 80 women with or without cornual excision. Results suggest that the incision and traction method poses more technical difficulties than the cornuectomy approach.23 Surgeons reported significant difficulty controlling the tensile pressure with traction, whereas use of the cornuectomy approach eliminated this risk and decreased the risk of fragmentation and incomplete removal.23,24
Charavil and colleagues demonstrated in a prospective observational study that a vaginal hysterectomy with bilateral salpingectomy is a feasible approach to Essure removal. Twenty-six vaginal hysterectomies with bilateral salpingectomy and Essure removal were performed without conversion to laparoscopy or laparotomy. The surgeons performed an en bloc removal of each hemiuterus along with the ipsilateral tube, which ensured complete removal of the Essure device. Each case was confirmed with an x-ray of the surgical specimen.25
If device fragmentation occurs, there are different methods recommended for locating fragments. A case report of bilateral uterine perforation after uncomplicated Essure placement used a preoperative computed tomography (CT) scan to locate the Essure fragments, but no intraoperative imaging was performed to confirm complete fragment removal.26 The patient continued reporting chronic pelvic pain and ultimately underwent exploratory laparotomy with intraoperative fluoroscopy. Using fluoroscopy, investigators identified omental fragments that were missed on preoperative CT imaging. Fluoroscopy is not commonly used intraoperatively, but it may have added benefit for localizing retained fragments.
A retrospective cohort study reviewed the use of intraoperative x-ray of the removed specimen to confirm complete Essure removal.27 If an x-ray of the removed specimen showed incomplete removal, an intraoperative pelvic x-ray was performed to locate missing fragments. X-ray of the removed devices confirmed complete removal in 63 of 72 patients (87.5%). Six of 9 women with an unsatisfactory specimen x-ray had no residual fragments identified during pelvic x-ray, and the device removal was deemed adequate. The remaining 3 women had radiologic evidence of incomplete device removal and required additional dissection for complete removal. Overall, use of x-ray or fluoroscopy is a relatively safe and accessible way to ensure complete removal of the Essure device and is worth consideration, especially when retained device fragments are suspected.

Symptom resolution
We reviewed 5 studies that examined pain outcomes after removal of the Essure devices. Casey et al found that 23 of 26 patients (88.5%) reported significant pain relief at the postoperative visit, while 3 of 26 (11.5%) reported persistent pelvic pain.2 Two of 3 case series examined other outcomes in addition to postoperative pelvic pain, including sexual function and activities of daily living.7,14 In the first case series by Brito and colleagues, 8 of 11 patients (72.7%) reported an improvement in pelvic pain, ability to perform daily activities, sexual life, and overall quality of life after Essure removal. For the remaining 3 patients with persistent pelvic pain after surgical removal of the device, 2 patients reported worsening pain symptoms and dyspareunia.14 In this study, 5 of 11 patients reported a history of chronic pelvic pain at baseline. In a retrospective case series by Clark et al, 28 of 32 women (87.5%) reported some improvement in all domains, with 24 of 32 patients (75%) reporting almost total or complete improvement in quality of life, sexual life, pelvic pain, and scores related to activities of daily living. Pain and quality-of-life scores were similar for women who underwent uterine-preserving surgery and for those who underwent hysterectomy. Ten of 32 women (31.3%) reported persistent or worsening symptoms after the Essure removal surgery. In these patients, the authors recommended consideration of other autoimmune and hypersensitivity etiologies.7
In a retrospective cohort study by Kamencic et al from 2002 to 2013 of 1,430 patients who underwent Essure placement with postplacement imaging, 62 patients (4.3%) required a second surgery after Essure placement due to pelvic pain.10 This study also found that 4 of 62 patients (0.3%) had no other obvious cause for the pelvic pain. All 4 of these women had complete resolution of their pain with removal of the Essure microinsert device. A prospective observational study by Chene e
Summary
Although Essure products were withdrawn from the market in the United States in 2018, many patients still experience significant AEs associated with the device. The goal of the perspectives and data presented here is to assist clinicians in addressing and managing the pain experienced by patients after device insertion. ●
The evaluation and management of chronic pelvic pain in patients with a history of Essure device (Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc, Whippany, New Jersey) insertion have posed many challenges for both clinicians and patients. The availability of high-quality, evidence-based clinical guidance has been limited. We have reviewed the currently available published data, and here provide an overview of takeaways, as well as share our perspective and approach on evaluating and managing chronic pelvic pain in this unique patient population.
The device
The Essure microinsert is a hysteroscopically placed device that facilitates permanent sterilization by occluding the bilateral proximal fallopian tubes. The microinsert has an inner and outer nitinol coil that attaches the device to the proximal fallopian tube to ensure retention. The inner coil releases polyethylene terephthalate fibers that cause tubal fiber proliferation to occlude the lumen of the fallopian tube and achieve sterilization.
The device was first approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2002. In subsequent years, the device was well received and widely used, with approximately 750,000 women worldwide undergoing Essure placement.1,2 Shortly after approval, many adverse events (AEs), including pelvic pain and abnormal uterine bleeding, were reported, resulting in a public meeting of the FDA Obstetrics and Gynecology Devices Panel in September 2015. A postmarket surveillance study on the device ensued to assess complication rates including unplanned pregnancy, pelvic pain, and surgery for removal. In February 2016, the FDA issued a black box warning and a patient decision checklist.3,4 In December 2018, Bayer stopped selling and distributing Essure in the United States.5 A 4-year follow-up surveillance study on Essure was submitted to the FDA in March 2020.
Adverse outcomes
Common AEs related to the Essure device include heavy uterine bleeding, pelvic pain, and other quality-of-life symptoms such as fatigue and weight gain.6-8 The main safety endpoints for the mandated FDA postmarket 522 surveillance studies were chronic lower abdominal and pelvic pain; abnormal uterine bleeding; hypersensitivity; allergic reaction, as well as autoimmune disorders incorporating inflammatory markers and human leukocyte antigen; and gynecologic surgery for device removal.9 Postmarket surveillence has shown that most AEs are related to placement complications or pelvic pain after Essure insertion. However, there have been several reports of autoimmune diseases categorized as serious AEs, such as new-onset systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and worsening ulcerative colitis, after Essure insertion.5
Evaluation of symptoms
Prevalence of pelvic pain following device placement
We conducted a PubMed and MEDLINE search from January 2000 to May 2020, which identified 43 studies citing AEs related to device placement, including pelvic or abdominal pain, abnormal uterine bleeding, hypersensitivity, and autoimmune disorders. A particularly debilitating and frequently cited AE was new-onset pelvic pain or worsening of preexisting pelvic pain. Perforation of the uterus or fallopian tube, resulting in displacement of the device into the peritoneal cavity, or fragmentation of the microinsert was reported as a serious AE that occurred after device placement. However, due to the complexity of chronic pelvic pain pathogenesis, the effect of the insert on patients with existing chronic pelvic pain remains unknown.
Authors of a large retrospective study found that approximately 2.7% of 1,430 patients developed new-onset or worsening pelvic pain after device placement. New-onset pelvic pain in 1% of patients was thought to be secondary to device placement, without a coexisting pathology or diagnosis.10
In a retrospective study by Clark and colleagues, 22 of 50 women (44%) with pelvic pain after microinsert placement were found to have at least one other cause of pelvic pain. The most common alternative diagnoses were endometriosis, adenomyosis, salpingitis, and adhesive disease. Nine of the 50 patients (18%) were found to have endometriosis upon surgical removal of the microinsert.7
Another case series examined outcomes in 29 patients undergoing laparoscopic device removal due to new-onset pelvic pain. Intraoperative findings included endometriosis in 5 patients (17.2%) and pelvic adhesions in 3 (10.3%).2 Chronic pelvic pain secondary to endometriosis may be exacerbated with Essure insertion due to discontinuation of hormonal birth control after device placement,7 and this diagnosis along with adenomyosis should be strongly considered in patients whose pelvic pain began when hormonal contraception was discontinued after placement of the device.
Continue to: Risk factors...
Risk factors
Authors of a retrospective cohort study found that patients with prior diagnosis of a chronic pain syndrome, low back pain, headaches, or fibromyalgia were 5 to 6 times more likely to report acute and chronic pain after hysteroscopic sterilization with Essure.11 Since chronic pain is often thought to be driven by a hyperalgesic state of the central nervous system, as previously shown in patients with conditions such as vulvodynia, interstitial cystitis, and fibromyalgia,12 a hyperalgesic state can potentially explain why some patients are more susceptible to developing worsening pain.
Van Limburg and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study with prospective follow-up on 284 women who underwent Essure sterilization. Among these patients, 48% reported negative AEs; risk factors included young age at placement, increasing gravidity, and no prior abdominal surgery.13
Onset of pain
The timing and onset of pelvic pain vary widely, suggesting there is no particular time frame for this AE after device placement.2,6,14-18 A case series by Arjona and colleagues analyzed the incidence of chronic pelvic pain in 4,274 patients after Essure sterilization. Seven patients (0.16%) reported chronic pelvic pain that necessitated device removal. In 6 of the women, the pelvic pain began within 1 week of device placement. In 3 of the 6 cases, the surgeon reported the removal procedures as “difficult.” In all 6 cases, the level of pelvic pain increased with time and was not alleviated with standard analgesic medications.6
In another case series of 26 patients, the authors evaluated patients undergoing laparoscopic removal of Essure secondary to pelvic pain and reported that the time range for symptom presentation was immediate to 85 months. Thirteen of 26 patients (50%) reported pain onset within less than 1 month of device placement, 5 of 26 patients (19.2%) reported pain between 1 and 12 months after device placement, and 8 of 26 patients (30.8%) reported pain onset more than 12 months after microinsert placement.2 In this study, 17.2% of operative reports indicated difficulty with device placement. It is unclear whether difficulty with placement was associated with development of subsequent abdominal or pelvic pain; however, the relevance of initial insertion difficulty diminished with longer follow-up.
Workup and evaluation
We found 5 studies that provided some framework for evaluating a patient with new-onset or worsening pelvic pain after microinsert placement. Overall, correct placement and functionality of the device should be confirmed by either hysterosalpingogram (HSG) or transvaginal ultrasonography (TVUS). The gold standard to determine tubal occlusion is the HSG. However, TVUS may be a dependable alternative, and either test can accurately demonstrate Essure location.19 Patients often prefer TVUS over HSG due to the low cost, minimal discomfort, and short examination time.1 TVUS is a noninvasive and reasonable test to start the initial assessment. The Essure devices are highly echogenic on pelvic ultrasound and easily identifiable by the proximity of the device to the uterotubal junction and its relationship with the surrounding soft tissue. If the device perforates the peritoneal cavity, then the echogenic bowel can impede adequate visualization of the Essure microinsert. If the Essure insert is not visualized on TVUS, an HSG will not only confirm placement but also test insert functionality. After confirming correct placement of the device, the provider can proceed with standard workup for chronic pelvic pain.
If one or more of the devices are malpositioned, the devices are generally presumed to be the etiology of the new pain. Multiple case reports demonstrate pain due to Essure misconfiguration or perforation with subsequent resolution of symptoms after device removal.18,20,21 A case study by Alcantara and colleagues described a patient with chronic pelvic pain and an Essure coil that was curved in an elliptical shape, not adhering to the anatomic course of the fallopian tube. The patient reported pain resolution after laparoscopic removal of the device.20 Another case report by Mahmoud et al described a subserosal malpositioned device that caused acute pelvic pain 4 months after sterilization. The patient reported resolution of pain after the microinsert was removed via laparoscopy.21 These reports highlight the importance of considering malpositioned devices as the etiology of new pelvic pain after Essure placement.

Continue to: Device removal and patient outcomes...
Device removal and patient outcomes
Removal
Several studies that we evaluated included a discussion on the methods for Essure removal. which are divided into 2 general categories: hysteroscopy and laparoscopy.
Hysteroscopic removal is generally used when the device was placed less than 12 weeks prior to removal.7,19 After 12 weeks, removal is more difficult due to fibrosis within the fallopian tubes. A risk with hysteroscopic removal is failure to remove all fibers, which allows inflammation and fibrosis to continue.7 This risk is mitigated via laparoscopic hysterectomy or mini-cornuectomy with bilateral salpingectomy, where the devices can be removed en bloc and without excessive traction.
Laparoscopic Essure removal procedures described in the literature include salpingostomy and traction on the device, salpingectomy, and salpingectomy with mini-cornuectomy. The incision and traction method is typically performed via a 2- to 3-cm incision on the antimesial edge of the fallopian tube along with a circumferential incision to surround the interstitial tubal area. The implant is carefully extracted from the fallopian tube and cornua, and a salpingectomy is then performed.22 The implant is removed prior to the salpingectomy to ensure that the Essure device is removed in its entirety prior to performing a salpingectomy.
A prospective observational study evaluated laparoscopic removal of Essure devices in 80 women with or without cornual excision. Results suggest that the incision and traction method poses more technical difficulties than the cornuectomy approach.23 Surgeons reported significant difficulty controlling the tensile pressure with traction, whereas use of the cornuectomy approach eliminated this risk and decreased the risk of fragmentation and incomplete removal.23,24
Charavil and colleagues demonstrated in a prospective observational study that a vaginal hysterectomy with bilateral salpingectomy is a feasible approach to Essure removal. Twenty-six vaginal hysterectomies with bilateral salpingectomy and Essure removal were performed without conversion to laparoscopy or laparotomy. The surgeons performed an en bloc removal of each hemiuterus along with the ipsilateral tube, which ensured complete removal of the Essure device. Each case was confirmed with an x-ray of the surgical specimen.25
If device fragmentation occurs, there are different methods recommended for locating fragments. A case report of bilateral uterine perforation after uncomplicated Essure placement used a preoperative computed tomography (CT) scan to locate the Essure fragments, but no intraoperative imaging was performed to confirm complete fragment removal.26 The patient continued reporting chronic pelvic pain and ultimately underwent exploratory laparotomy with intraoperative fluoroscopy. Using fluoroscopy, investigators identified omental fragments that were missed on preoperative CT imaging. Fluoroscopy is not commonly used intraoperatively, but it may have added benefit for localizing retained fragments.
A retrospective cohort study reviewed the use of intraoperative x-ray of the removed specimen to confirm complete Essure removal.27 If an x-ray of the removed specimen showed incomplete removal, an intraoperative pelvic x-ray was performed to locate missing fragments. X-ray of the removed devices confirmed complete removal in 63 of 72 patients (87.5%). Six of 9 women with an unsatisfactory specimen x-ray had no residual fragments identified during pelvic x-ray, and the device removal was deemed adequate. The remaining 3 women had radiologic evidence of incomplete device removal and required additional dissection for complete removal. Overall, use of x-ray or fluoroscopy is a relatively safe and accessible way to ensure complete removal of the Essure device and is worth consideration, especially when retained device fragments are suspected.

Symptom resolution
We reviewed 5 studies that examined pain outcomes after removal of the Essure devices. Casey et al found that 23 of 26 patients (88.5%) reported significant pain relief at the postoperative visit, while 3 of 26 (11.5%) reported persistent pelvic pain.2 Two of 3 case series examined other outcomes in addition to postoperative pelvic pain, including sexual function and activities of daily living.7,14 In the first case series by Brito and colleagues, 8 of 11 patients (72.7%) reported an improvement in pelvic pain, ability to perform daily activities, sexual life, and overall quality of life after Essure removal. For the remaining 3 patients with persistent pelvic pain after surgical removal of the device, 2 patients reported worsening pain symptoms and dyspareunia.14 In this study, 5 of 11 patients reported a history of chronic pelvic pain at baseline. In a retrospective case series by Clark et al, 28 of 32 women (87.5%) reported some improvement in all domains, with 24 of 32 patients (75%) reporting almost total or complete improvement in quality of life, sexual life, pelvic pain, and scores related to activities of daily living. Pain and quality-of-life scores were similar for women who underwent uterine-preserving surgery and for those who underwent hysterectomy. Ten of 32 women (31.3%) reported persistent or worsening symptoms after the Essure removal surgery. In these patients, the authors recommended consideration of other autoimmune and hypersensitivity etiologies.7
In a retrospective cohort study by Kamencic et al from 2002 to 2013 of 1,430 patients who underwent Essure placement with postplacement imaging, 62 patients (4.3%) required a second surgery after Essure placement due to pelvic pain.10 This study also found that 4 of 62 patients (0.3%) had no other obvious cause for the pelvic pain. All 4 of these women had complete resolution of their pain with removal of the Essure microinsert device. A prospective observational study by Chene e
Summary
Although Essure products were withdrawn from the market in the United States in 2018, many patients still experience significant AEs associated with the device. The goal of the perspectives and data presented here is to assist clinicians in addressing and managing the pain experienced by patients after device insertion. ●
- Connor VF. Essure: a review six years later. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2009;16:282-290. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2009.02.009.
- Casey J, Aguirre F, Yunker A. Outcomes of laparoscopic removal of the Essure sterilization device for pelvic pain: a case series. Contraception. 2016;94:190-192. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2016.03.017.
- Jackson I. Essure device removed entirely from market, with 99% of unused birth control implants retrieved: FDA. AboutLawsuits.com. January 13, 2020. https://www.aboutlawsuits.com/Essure-removal-update-166509. Accessed June 7, 2022.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Labeling for permanent hysteroscopically-placed tubal implants intended for sterilization. October 31, 2016. https://www.fda.gov/media/96315/download. Accessed June 7, 2022.
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA activities related to Essure. March 14, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/essure-permanent-birth-control/fda-activities-related-essure. Accessed June 8, 2022.
- Arjona Berral JE, Rodríguez Jiménez B, Velasco Sánchez E, et al. Essure and chronic pelvic pain: a population-based cohort. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2014;34:712-713. doi:10.3109/01443615.2014.92075.
- Clark NV, Rademaker D, Mushinski AA, et al. Essure removal for the treatment of device-attributed symptoms: an expanded case series and follow-up survey. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24:971-976. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2017.05.015.
- Sills ES, Rickers NS, Li X. Surgical management after hysteroscopic sterilization: minimally invasive approach incorporating intraoperative fluoroscopy for symptomatic patients with >2 Essure devices. Surg Technol Int. 2018;32:156-161.
- Administration USF and D. 522 Postmarket Surveillance Studies. Center for Devices and Radiological Health; 2020.
- Kamencic H, Thiel L, Karreman E, et al. Does Essure cause significant de novo pain? A retrospective review of indications for second surgeries after Essure placement. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2016;23:1158-1162. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2016.08.823.
- Yunker AC, Ritch JM, Robinson EF, et al. Incidence and risk factors for chronic pelvic pain after hysteroscopic sterilization. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015;22:390-994. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2014.06.007.
- Phillips K, Clauw DJ. Central pain mechanisms in chronic pain states--maybe it is all in their head. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2011;25:141-154. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2011.02.005.
- van Limburg Stirum EVJ, Clark NV, Lindsey A, et al. Factors associated with negative patient experiences with Essure sterilization. JSLS. 2020;24(1):e2019.00065. doi:10.4293/JSLS.2019.00065.
- Brito LG, Cohen SL, Goggins ER, et al. Essure surgical removal and subsequent symptom resolution: case series and follow-up survey. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015;22:910-913. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2015.03.018.
- Maassen LW, van Gastel DM, Haveman I, et al. Removal of Essure sterilization devices: a retrospective cohort study in the Netherlands. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:1056-1062. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2018.10.009.
- Sills ES, Palermo GD. Surgical excision of Essure devices with ESHRE class IIb uterine malformation: sequential hysteroscopic-laparoscopic approach to the septate uterus. Facts Views Vis Obgyn. 2016;8:49-52.
- Ricci G, Restaino S, Di Lorenzo G, et al. Risk of Essure microinsert abdominal migration: case report and review of literature. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2014;10:963-968. doi:10.2147/TCRM.S65634.
- Borley J, Shabajee N, Tan TL. A kink is not always a perforation: assessing Essure hysteroscopic sterilization placement. Fertil Steril. 2011;95:2429.e15-7. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.02.006.
- Djeffal H, Blouet M, Pizzoferato AC, et al. Imaging findings in Essure-related complications: a pictorial review.7Br J Radiol. 2018;91(1090):20170686. doi:10.1259/bjr.20170686.
- Lora Alcantara I, Rezai S, Kirby C, et al. Essure surgical removal and subsequent resolution of chronic pelvic pain: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2016;2016:6961202. doi:10.1155/2016/6961202.
- Mahmoud MS, Fridman D, Merhi ZO. Subserosal misplacement of Essure device manifested by late-onset acute pelvic pain. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:2038.e1-3. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.07.1677.
- Tissot M, Petry S, Lecointre L, et al. Two surgical techniques for Essure device ablation: the hysteroscopic way and the laparoscopic way by salpingectomy with tubal interstitial resection. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26(4):603. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2018.07.017.
- Chene G, Cerruto E, Moret S, et al. Quality of life after laparoscopic removal of Essure sterilization devices. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol X. 2019;3:100054. doi:10.1016/j.eurox.2019.100054.
- Thiel L, Rattray D, Thiel J. Laparoscopic cornuectomy as a technique for removal of Essure microinserts. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24(1):10. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2016.07.004.
- Charavil A, Agostini A, Rambeaud C, et al. Vaginal hysterectomy with salpingectomy for Essure insert removal. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;2:695-701. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2018.07.019.
- Howard DL, Christenson PJ, Strickland JL. Use of intraoperative fluoroscopy during laparotomy to identify fragments of retained Essure microinserts: case report. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2012;19:667-670. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2012.04.007.
- Miquel L, Crochet P, Francini S, et al. Laparoscopic Essure device removal by en bloc salpingectomy-cornuectomy with intraoperative x-ray checking: a retrospective cohort study. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020;27:697-703. doi:10.1016/j. jmig.2019.06.006.
- Connor VF. Essure: a review six years later. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2009;16:282-290. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2009.02.009.
- Casey J, Aguirre F, Yunker A. Outcomes of laparoscopic removal of the Essure sterilization device for pelvic pain: a case series. Contraception. 2016;94:190-192. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2016.03.017.
- Jackson I. Essure device removed entirely from market, with 99% of unused birth control implants retrieved: FDA. AboutLawsuits.com. January 13, 2020. https://www.aboutlawsuits.com/Essure-removal-update-166509. Accessed June 7, 2022.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Labeling for permanent hysteroscopically-placed tubal implants intended for sterilization. October 31, 2016. https://www.fda.gov/media/96315/download. Accessed June 7, 2022.
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA activities related to Essure. March 14, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/essure-permanent-birth-control/fda-activities-related-essure. Accessed June 8, 2022.
- Arjona Berral JE, Rodríguez Jiménez B, Velasco Sánchez E, et al. Essure and chronic pelvic pain: a population-based cohort. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2014;34:712-713. doi:10.3109/01443615.2014.92075.
- Clark NV, Rademaker D, Mushinski AA, et al. Essure removal for the treatment of device-attributed symptoms: an expanded case series and follow-up survey. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24:971-976. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2017.05.015.
- Sills ES, Rickers NS, Li X. Surgical management after hysteroscopic sterilization: minimally invasive approach incorporating intraoperative fluoroscopy for symptomatic patients with >2 Essure devices. Surg Technol Int. 2018;32:156-161.
- Administration USF and D. 522 Postmarket Surveillance Studies. Center for Devices and Radiological Health; 2020.
- Kamencic H, Thiel L, Karreman E, et al. Does Essure cause significant de novo pain? A retrospective review of indications for second surgeries after Essure placement. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2016;23:1158-1162. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2016.08.823.
- Yunker AC, Ritch JM, Robinson EF, et al. Incidence and risk factors for chronic pelvic pain after hysteroscopic sterilization. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015;22:390-994. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2014.06.007.
- Phillips K, Clauw DJ. Central pain mechanisms in chronic pain states--maybe it is all in their head. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2011;25:141-154. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2011.02.005.
- van Limburg Stirum EVJ, Clark NV, Lindsey A, et al. Factors associated with negative patient experiences with Essure sterilization. JSLS. 2020;24(1):e2019.00065. doi:10.4293/JSLS.2019.00065.
- Brito LG, Cohen SL, Goggins ER, et al. Essure surgical removal and subsequent symptom resolution: case series and follow-up survey. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015;22:910-913. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2015.03.018.
- Maassen LW, van Gastel DM, Haveman I, et al. Removal of Essure sterilization devices: a retrospective cohort study in the Netherlands. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:1056-1062. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2018.10.009.
- Sills ES, Palermo GD. Surgical excision of Essure devices with ESHRE class IIb uterine malformation: sequential hysteroscopic-laparoscopic approach to the septate uterus. Facts Views Vis Obgyn. 2016;8:49-52.
- Ricci G, Restaino S, Di Lorenzo G, et al. Risk of Essure microinsert abdominal migration: case report and review of literature. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2014;10:963-968. doi:10.2147/TCRM.S65634.
- Borley J, Shabajee N, Tan TL. A kink is not always a perforation: assessing Essure hysteroscopic sterilization placement. Fertil Steril. 2011;95:2429.e15-7. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.02.006.
- Djeffal H, Blouet M, Pizzoferato AC, et al. Imaging findings in Essure-related complications: a pictorial review.7Br J Radiol. 2018;91(1090):20170686. doi:10.1259/bjr.20170686.
- Lora Alcantara I, Rezai S, Kirby C, et al. Essure surgical removal and subsequent resolution of chronic pelvic pain: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2016;2016:6961202. doi:10.1155/2016/6961202.
- Mahmoud MS, Fridman D, Merhi ZO. Subserosal misplacement of Essure device manifested by late-onset acute pelvic pain. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:2038.e1-3. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.07.1677.
- Tissot M, Petry S, Lecointre L, et al. Two surgical techniques for Essure device ablation: the hysteroscopic way and the laparoscopic way by salpingectomy with tubal interstitial resection. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26(4):603. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2018.07.017.
- Chene G, Cerruto E, Moret S, et al. Quality of life after laparoscopic removal of Essure sterilization devices. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol X. 2019;3:100054. doi:10.1016/j.eurox.2019.100054.
- Thiel L, Rattray D, Thiel J. Laparoscopic cornuectomy as a technique for removal of Essure microinserts. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24(1):10. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2016.07.004.
- Charavil A, Agostini A, Rambeaud C, et al. Vaginal hysterectomy with salpingectomy for Essure insert removal. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;2:695-701. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2018.07.019.
- Howard DL, Christenson PJ, Strickland JL. Use of intraoperative fluoroscopy during laparotomy to identify fragments of retained Essure microinserts: case report. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2012;19:667-670. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2012.04.007.
- Miquel L, Crochet P, Francini S, et al. Laparoscopic Essure device removal by en bloc salpingectomy-cornuectomy with intraoperative x-ray checking: a retrospective cohort study. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020;27:697-703. doi:10.1016/j. jmig.2019.06.006.
Misoprostol: Clinical pharmacology in obstetrics and gynecology
Oxytocin and prostaglandins are critically important regulators of uterine contraction. Obstetrician-gynecologists commonly prescribe oxytocin and prostaglandin agonists (misoprostol, dinoprostone) to stimulate uterine contraction for the induction of labor, prevention and treatment of postpartum hemorrhage, and treatment of miscarriage and fetal demise. The focus of this editorial is the clinical pharmacology of misoprostol.
Misoprostol is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the prevention and treatment of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug–induced gastric ulcers and for patients at high risk for gastric ulcers, including those with a history of gastric ulcers. The approved misoprostol route and dose for this indication is oral administration of 200 µg four times daily with food.1 Recent food intake and antacid use reduces the absorption of orally administered misoprostol. There are no FDA-approved indications for the use of misoprostol as a single agent in obstetrics and gynecology. The FDA has approved the combination of mifepristone and misoprostol for medication abortion in the first trimester. In contrast to misoprostol, PGE2 (dinoprostone) is approved by the FDA as a vaginal insert containing 10 mg of dinoprostone for the initiation and/or continuation of cervical ripening in patients at or near term in whom there is a medical or obstetric indication for induction of labor (Cervidil; Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc, Parsippany, New Jersey).2
Pharmacology of misoprostol
Misoprostol is a prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) agonist analogue. Prostaglandin E1 (alprostadil) is rapidly metabolized, has a half-life in the range of minutes and is not orally active, requiring administration by intravenous infusion or injection. It is indicated to maintain a patent ductus arteriosus in newborns with ductal-dependent circulation and to treat erectile dysfunction.3 In contrast to PGE1, misoprostol has a methyl ester group at carbon-1 (C-1) that increases potency and duration of action. Misoprostol also has no hydroxyl group at C-15, replacing that moiety with the addition of both a methyl- and hydroxyl- group at C-16 (FIGURE). These molecular changes improve oral activity and increase duration of action.4 Pure misoprostol is a viscous oil. It is formulated into tables by dispersing the oil on hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose before compounding into tablets. Unlike naturally occurring prostaglandins (PGE1), misoprostol tablets are stabile at room temperature for years.4
Following absorption, the methyl ester at C-1 is enzymatically cleaved, yielding misoprostol acid, the active drug.4 Misoprostol binds to the E prostanoid receptor 3 (EP-3).5 Activation of myometrial EP-3 receptor induces an increase in intracellular phosphoinositol turnover and calcium mobilization, resulting in an increase in intracellular-free calcium, triggering actin-myosin contractility.6 The increase in free calcium is propagated cell-to-cell through gap junctions that link the myometrial cells to facilitate the generation of a coordinated contraction.
Misoprostol: Various routes of administration are not equal
Misoprostol can be given by an oral, buccal, vaginal, or rectal route of administration. To study the effect of the route of administration on uterine tone and contractility, investigators randomly assigned patients at 8 to 11 weeks’ gestation to receive misoprostol 400 µg as a single dose by the oral or vaginal route. Uterine tone and contractility were measured using an intrauterine pressure transducer. Compared to vaginal administration, oral administration of misprostol was associated with rapid attainment of peak plasma level at 30 minutes, followed by a decline in concentration by 60 minutes. This rapid onset and rapid offset of plasma concentration was paralleled by the onset of uterine tone within 8 minutes, but surprisingly no sustained uterine contractions.7 By contrast, following vaginal administration of misoprostol, serum levels rose slowly and peaked in 1 to 2 hours. Uterine tone increased within 21 minutes, and sustained uterine contractions were recorded for 4 hours.7 The rapid rise and fall in plasma misoprostol following oral administration and the more sustained plasma misoprostol concentration over 4 hours has been previously reported.8 In a second study involving patients 8 to 11 weeks’ gestation, the effect of a single dose of misoprostol 400 µg by an oral or vaginal route on uterine contractility was compared using an intrauterine pressure transducer.9 Confirming previous results, the time from misoprostol administration to increased uterine tone was more rapid with oral than with vaginal administration (8 min vs 19 min). Over the course of 4 hours, uterine contraction activity was greater with vaginal than with oral administration (454 vs 166 Montevideo units).9
Both studies reported that oral administration of misoprostol resulted in more rapid onset and offset of action than vaginal administration. Oral administration of a single dose of misoprostol 400 µg did not result in sustained uterine contractions in most patients in the first trimester. Vaginal administration produced a slower onset of increased uterine tone but sustained uterine contractions over 4 hours. Compared with vaginal administration of misoprostol, the rapid onset and offset of action of oral misoprostol may reduce the rate of tachysystole and changes in fetal heart rate observed with vaginal administration.10
An important finding is that buccal and vaginal administration of misoprostol have similar effects on uterine tone in the first trimester.11 To study the effect of buccal and vaginal administration of misoprostol on uterine tone, patients 6 to 13 weeks’ gestation were randomly allocated to receive a single dose of misoprostol 400 µg by a buccal or vaginal route.11 Uterine activity over 5 hours following administration was assessed using an intrauterine pressure transducer. Uterine tone 20 to 30 minutes after buccal or vaginal administration of misoprostol (400 µg) was 27 and 28 mm Hg, respectively. Peak uterine tone, as measured by an intrauterine pressure transducer, for buccal and vaginal administration of misoprostol was 49 mm Hg and 54 mm Hg, respectively. Total Alexandria units (AU) over 5 hours following buccal or vaginal administration was 6,537 AU and 6,090 AU, respectively.11
An AU is calculated as the average amplitude of the contractions (mm Hg) multiplied by the average duration of the contractions (min) multiplied by average frequency of contraction over 10 minutes.12 By contrast, a Montevideo unit does not include an assessment of contraction duration and is calculated as average amplitude of contractions (mm Hg) multiplied by frequency of uterine contractions over 10 minutes.12
In contrast to buccal or vaginal administration, rectal administration of misoprostol resulted in much lower peak uterine tone and contractility as measured by a pressure transducer. Uterine tone 20 to 30 minutes after vaginal and rectal administration of misoprostol (400 µg) was 28 and 19 mm Hg, respectively.11 Peak uterine tone, as measured by an intrauterine pressure transducer, for vaginal and rectal administration of misoprostol was 54 and 31 mm Hg, respectively. AUs over 5 hours following vaginal and rectal administration was 6,090 AU and 2,768 AU, respectively.11 Compared with buccal and vaginal administration of misoprostol, rectal administration produced less sustained uterine contractions in the first trimester of pregnancy. To achieve maximal sustained uterine contractions, buccal and vaginal routes of administration are superior to oral and rectal administration.
Continue to: Misoprostol and cervical ripening...
Misoprostol and cervical ripening
Misoprostol is commonly used to soften and ripen the cervix. Some of the cervical ripening effects of misoprostol are likely due to increased uterine tone. In addition, misoprostol may have a direct effect on the collagen structure of the cervix. To study the effect of misoprostol on the cervix, pregnant patients in the first trimester were randomly assigned to receive misoprostol 200 µg by vaginal self-administration, isosorbide mononitrate (IMN) 40 mg by vaginal self-administration or no treatment the evening prior to pregnancy termination.13 The following day, before uterine evacuation, a cervical biopsy was obtained for electron microscopy studies and immunohistochemistry to assess the presence of enzymes involved in collagen degradation, including matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP-1) and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9). Electron microscopy demonstrated that pretreatment with misoprostol resulted in a pronounced splitting and disorganization of collagen fibers.13 Compared with misoprostol treatment, IMN produced less splitting and disorganization of collagen fibers, and in the no treatment group, no marked changes in the collagen framework were observed.
Compared with no treatment, misoprostol and IMN pretreatment were associated with marked increases in MMP-1 and MMP-9 as assessed by immunohistochemistry. Misoprostol pretreatment also resulted in a significant increase in interleukin-8 concentration compared with IMN pretreatment and no treatment (8.8 vs 2.7 vs 2.4 pg/mg tissue), respectively.13 Other investigators have also reported that misoprostol increased cervical leukocyte influx and collagen disrupting enzymes MMP-8 and MMP-9.14,15
An open-label clinical trial compared the efficacy of misoprostol versus Foley catheter for labor induction at term in 1,859 patients ≥ 37 weeks’ gestation with a Bishop score <6.16 Patients were randomly allocated to misoprostol (50 µg orally every 4 hours up to 3 times in 24 hours) versus placement of a 16 F or 18 F Foley catheter introduced through the cervix, filled with 30 mL of sodium chloride or water. The investigators reported that oral misoprostol and Foley catheter cervical ripening had similar safety and effectiveness for cervical ripening as a prelude to induction of labor, including no statistically significant differences in 5-minute Apgar score <7, umbilical cord artery pH ≤ 7.05, postpartum hemorrhage, or cesarean birth rate.16
Bottom line
Misoprostol and oxytocin are commonly prescribed in obstetric practice for cervical ripening and induction of labor, respectively. The dose and route of administration of misoprostol influences the effect on the uterus. For cervical ripening, where rapid onset and offset may help to reduce the risk of uterine tachysystole and worrisome fetal heart rate changes, low-dose (50 µg) oral administration of misoprostol may be a preferred dose and route. For the treatment of miscarriage and fetal demise, to stimulate sustained uterine contractions over many hours, buccal and vaginal administration of misoprostol are preferred. Rectal administration is generally inferior to buccal and vaginal administration for stimulating sustained uterine contractions and its uses should be limited. ●
Common side effects of misoprostol are abdominal cramping, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headache, and fever. Elevated temperature following misoprostol administration is a concerning side effect that may require further investigation to rule out an infection, especially if the elevated temperature persists for > 4 hours. The preoptic area of the anterior hypothalamus (POAH) plays a major role in thermoregulation. When an infection causes an increase in endogenous pyrogens, including interleukin-1β, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor, prostaglandins are generated in the region of the POAH, increasing the thermoregulatory set point, triggering cutaneous vasoconstriction and shivering and non-shivering thermogenesis.1 Misoprostol, especially at doses >400 µg commonly causes both patient-reported chills and temperature elevation >38° C.
In a study comparing misoprostol and oxytocin for the management of the third stage of labor, 597 patients were randomly allocated to receive oxytocin 10 units by intramuscular injection or misoprostol 400 µg or 600 µg by the oral route.2 Patient-reported shivering occurred in 13%, 19%, and 28% of patients receiving oxytocin, misoprostol 400 µg and misoprostol 800 µg, respectively. A recorded temperature >38° C occurred within 1 hour of medication administration in approximately 3%, 2%, and 7.5% of patients receiving oxytocin, misoprostol 400 µg, and misoprostol 800 µg, respectively. In another study, 453 patients scheduled for a cesarean birth were randomly allocated to receive 1 of 3 doses of rectal misoprostol 200 μg, 400 μg, or 600 μg before incision. Fever was detected in 2.6%, 9.9%, and 5.1% of the patients receiving misoprostol 200 μg, 400 μg, or 600 μg, respectively.3
References
1. Aronoff DM, Neilson EG. Antipyretics: mechanisms of action and clinical use in fever suppression. Am J Med. 2001;111:304-315. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(01)00834-8.
2. Lumbiganon P, Hofmeyr J, Gumezoglu AM, et al. Misoprostol dose-related shivering and pyrexia in the third stage of labor. WHO Collaborative Trial of Misoprostol in the Management of the Third Stage of Labor. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1999;106:304-308. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1999.tb08266.x.
3. Sweed M, El-Said M, Abou-Gamrah AA, et al. Comparison between 200, 400 and 600 microgram rectal misoprostol before cesarean section: a randomized clinical trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019;45:585-591. doi: 10.1111 /jog.13883.
- Cytotec [package insert]. Chicago, IL: GD Searle & Co. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2002/19268slr037.pdf. Accessed June 20, 2022.
- Cervidil [package insert]. St Louis, MO: Forrest Pharmaceuticals Inc.; May 2006. Accessed June 20, 2022.
- Caverject [package insert]. New York, NY: Pfizer Inc.; March 2014. Accessed June 20, 2022.
- Collins PW. Misoprostol: discovery, development and clinical applications. Med Res Rev. 1990;10:149-172. doi: 10.1002/med.2610100202.
- Audit M, White KI, Breton B, et al. Crystal structure of misoprostol bound to the labor inducer prostaglandin E2 receptor. Nat Chem Biol. 2019;15:11-17. doi: 10.1038/s41589-018-0160-y.
- Pallliser KH, Hirst JJ, Ooi G, et al. Prostaglandin E and F receptor expression and myometrial sensitivity in labor onset in the sheep. Biol Reprod. 2005;72:937-943. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.104.035311.
- Gemzell-Danilesson K, Marions L, Rodriguez A, et al. Comparison between oral and vaginal administration of misoprostol on uterine contractility. Obstet Gynecol. 1999;93:275-280. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(98)00436-0.
- Zieman M, Fong SK, Benowitz NL, et al. Absorption kinetics of misoprostol with oral or vaginal administration. Obstet Gynecol. 1997;90:88-92. doi: 10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00111-7.
- Aronsson A, Bygdeman M, Gemzell-Danielsson K. Effects of misoprostol on uterine contractility following different routes of administration. Hum Reprod. 2004;19:81-84. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deh005.
- Young DC, Delaney T, Armson BA, et al. Oral misoprostol, low dose vaginal misoprostol and vaginal dinoprostone for labor induction: randomized controlled trial. PLOS One. 2020;15:e0227245. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227245.
- Meckstroth KR, Whitaker AK, Bertisch S, et al. Misoprostol administered by epithelial routes. Drug absorption and uterine response. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;108:582-590. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000230398.32794.9d.
- el-Sahwi S, Gaafar AA, Toppozada HK. A new unit for evaluation of uterine activity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1967;98:900-903. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(67)90074-9.
- Vukas N, Ekerhovd E, Abrahamsson G, et al. Cervical priming in the first trimester: morphological and biochemical effects of misoprostol and isosorbide mononitrate. Acta Obstet Gyecol. 2009;88:43-51. doi: 10.1080/00016340802585440.
- Aronsson A, Ulfgren AK, Stabi B, et al. The effect of orally and vaginally administered misoprostol on inflammatory mediators and cervical ripening during early pregnancy. Contraception. 2005;72:33-39. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2005.02.012.
- Denison FC, Riley SC, Elliott CL, et al. The effect of mifepristone administration on leukocyte populations, matrix metalloproteinases and inflammatory mediators in the first trimester cervix. Mol Hum Reprod. 2000;6:541-548. doi: 10.1093/molehr/6.6.541.
- ten Eikelder MLG, Rengerink KO, Jozwiak M, et al. Induction of labour at term with oral misoprostol versus a Foley catheter (PROBAAT-II): a multicentre randomised controlled non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2016;387:1619-1628. doi: 10.1016 /S0140-6736(16)00084-2.
Oxytocin and prostaglandins are critically important regulators of uterine contraction. Obstetrician-gynecologists commonly prescribe oxytocin and prostaglandin agonists (misoprostol, dinoprostone) to stimulate uterine contraction for the induction of labor, prevention and treatment of postpartum hemorrhage, and treatment of miscarriage and fetal demise. The focus of this editorial is the clinical pharmacology of misoprostol.
Misoprostol is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the prevention and treatment of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug–induced gastric ulcers and for patients at high risk for gastric ulcers, including those with a history of gastric ulcers. The approved misoprostol route and dose for this indication is oral administration of 200 µg four times daily with food.1 Recent food intake and antacid use reduces the absorption of orally administered misoprostol. There are no FDA-approved indications for the use of misoprostol as a single agent in obstetrics and gynecology. The FDA has approved the combination of mifepristone and misoprostol for medication abortion in the first trimester. In contrast to misoprostol, PGE2 (dinoprostone) is approved by the FDA as a vaginal insert containing 10 mg of dinoprostone for the initiation and/or continuation of cervical ripening in patients at or near term in whom there is a medical or obstetric indication for induction of labor (Cervidil; Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc, Parsippany, New Jersey).2
Pharmacology of misoprostol
Misoprostol is a prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) agonist analogue. Prostaglandin E1 (alprostadil) is rapidly metabolized, has a half-life in the range of minutes and is not orally active, requiring administration by intravenous infusion or injection. It is indicated to maintain a patent ductus arteriosus in newborns with ductal-dependent circulation and to treat erectile dysfunction.3 In contrast to PGE1, misoprostol has a methyl ester group at carbon-1 (C-1) that increases potency and duration of action. Misoprostol also has no hydroxyl group at C-15, replacing that moiety with the addition of both a methyl- and hydroxyl- group at C-16 (FIGURE). These molecular changes improve oral activity and increase duration of action.4 Pure misoprostol is a viscous oil. It is formulated into tables by dispersing the oil on hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose before compounding into tablets. Unlike naturally occurring prostaglandins (PGE1), misoprostol tablets are stabile at room temperature for years.4
Following absorption, the methyl ester at C-1 is enzymatically cleaved, yielding misoprostol acid, the active drug.4 Misoprostol binds to the E prostanoid receptor 3 (EP-3).5 Activation of myometrial EP-3 receptor induces an increase in intracellular phosphoinositol turnover and calcium mobilization, resulting in an increase in intracellular-free calcium, triggering actin-myosin contractility.6 The increase in free calcium is propagated cell-to-cell through gap junctions that link the myometrial cells to facilitate the generation of a coordinated contraction.

Misoprostol: Various routes of administration are not equal
Misoprostol can be given by an oral, buccal, vaginal, or rectal route of administration. To study the effect of the route of administration on uterine tone and contractility, investigators randomly assigned patients at 8 to 11 weeks’ gestation to receive misoprostol 400 µg as a single dose by the oral or vaginal route. Uterine tone and contractility were measured using an intrauterine pressure transducer. Compared to vaginal administration, oral administration of misprostol was associated with rapid attainment of peak plasma level at 30 minutes, followed by a decline in concentration by 60 minutes. This rapid onset and rapid offset of plasma concentration was paralleled by the onset of uterine tone within 8 minutes, but surprisingly no sustained uterine contractions.7 By contrast, following vaginal administration of misoprostol, serum levels rose slowly and peaked in 1 to 2 hours. Uterine tone increased within 21 minutes, and sustained uterine contractions were recorded for 4 hours.7 The rapid rise and fall in plasma misoprostol following oral administration and the more sustained plasma misoprostol concentration over 4 hours has been previously reported.8 In a second study involving patients 8 to 11 weeks’ gestation, the effect of a single dose of misoprostol 400 µg by an oral or vaginal route on uterine contractility was compared using an intrauterine pressure transducer.9 Confirming previous results, the time from misoprostol administration to increased uterine tone was more rapid with oral than with vaginal administration (8 min vs 19 min). Over the course of 4 hours, uterine contraction activity was greater with vaginal than with oral administration (454 vs 166 Montevideo units).9
Both studies reported that oral administration of misoprostol resulted in more rapid onset and offset of action than vaginal administration. Oral administration of a single dose of misoprostol 400 µg did not result in sustained uterine contractions in most patients in the first trimester. Vaginal administration produced a slower onset of increased uterine tone but sustained uterine contractions over 4 hours. Compared with vaginal administration of misoprostol, the rapid onset and offset of action of oral misoprostol may reduce the rate of tachysystole and changes in fetal heart rate observed with vaginal administration.10
An important finding is that buccal and vaginal administration of misoprostol have similar effects on uterine tone in the first trimester.11 To study the effect of buccal and vaginal administration of misoprostol on uterine tone, patients 6 to 13 weeks’ gestation were randomly allocated to receive a single dose of misoprostol 400 µg by a buccal or vaginal route.11 Uterine activity over 5 hours following administration was assessed using an intrauterine pressure transducer. Uterine tone 20 to 30 minutes after buccal or vaginal administration of misoprostol (400 µg) was 27 and 28 mm Hg, respectively. Peak uterine tone, as measured by an intrauterine pressure transducer, for buccal and vaginal administration of misoprostol was 49 mm Hg and 54 mm Hg, respectively. Total Alexandria units (AU) over 5 hours following buccal or vaginal administration was 6,537 AU and 6,090 AU, respectively.11
An AU is calculated as the average amplitude of the contractions (mm Hg) multiplied by the average duration of the contractions (min) multiplied by average frequency of contraction over 10 minutes.12 By contrast, a Montevideo unit does not include an assessment of contraction duration and is calculated as average amplitude of contractions (mm Hg) multiplied by frequency of uterine contractions over 10 minutes.12
In contrast to buccal or vaginal administration, rectal administration of misoprostol resulted in much lower peak uterine tone and contractility as measured by a pressure transducer. Uterine tone 20 to 30 minutes after vaginal and rectal administration of misoprostol (400 µg) was 28 and 19 mm Hg, respectively.11 Peak uterine tone, as measured by an intrauterine pressure transducer, for vaginal and rectal administration of misoprostol was 54 and 31 mm Hg, respectively. AUs over 5 hours following vaginal and rectal administration was 6,090 AU and 2,768 AU, respectively.11 Compared with buccal and vaginal administration of misoprostol, rectal administration produced less sustained uterine contractions in the first trimester of pregnancy. To achieve maximal sustained uterine contractions, buccal and vaginal routes of administration are superior to oral and rectal administration.
Continue to: Misoprostol and cervical ripening...
Misoprostol and cervical ripening
Misoprostol is commonly used to soften and ripen the cervix. Some of the cervical ripening effects of misoprostol are likely due to increased uterine tone. In addition, misoprostol may have a direct effect on the collagen structure of the cervix. To study the effect of misoprostol on the cervix, pregnant patients in the first trimester were randomly assigned to receive misoprostol 200 µg by vaginal self-administration, isosorbide mononitrate (IMN) 40 mg by vaginal self-administration or no treatment the evening prior to pregnancy termination.13 The following day, before uterine evacuation, a cervical biopsy was obtained for electron microscopy studies and immunohistochemistry to assess the presence of enzymes involved in collagen degradation, including matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP-1) and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9). Electron microscopy demonstrated that pretreatment with misoprostol resulted in a pronounced splitting and disorganization of collagen fibers.13 Compared with misoprostol treatment, IMN produced less splitting and disorganization of collagen fibers, and in the no treatment group, no marked changes in the collagen framework were observed.
Compared with no treatment, misoprostol and IMN pretreatment were associated with marked increases in MMP-1 and MMP-9 as assessed by immunohistochemistry. Misoprostol pretreatment also resulted in a significant increase in interleukin-8 concentration compared with IMN pretreatment and no treatment (8.8 vs 2.7 vs 2.4 pg/mg tissue), respectively.13 Other investigators have also reported that misoprostol increased cervical leukocyte influx and collagen disrupting enzymes MMP-8 and MMP-9.14,15
An open-label clinical trial compared the efficacy of misoprostol versus Foley catheter for labor induction at term in 1,859 patients ≥ 37 weeks’ gestation with a Bishop score <6.16 Patients were randomly allocated to misoprostol (50 µg orally every 4 hours up to 3 times in 24 hours) versus placement of a 16 F or 18 F Foley catheter introduced through the cervix, filled with 30 mL of sodium chloride or water. The investigators reported that oral misoprostol and Foley catheter cervical ripening had similar safety and effectiveness for cervical ripening as a prelude to induction of labor, including no statistically significant differences in 5-minute Apgar score <7, umbilical cord artery pH ≤ 7.05, postpartum hemorrhage, or cesarean birth rate.16
Bottom line
Misoprostol and oxytocin are commonly prescribed in obstetric practice for cervical ripening and induction of labor, respectively. The dose and route of administration of misoprostol influences the effect on the uterus. For cervical ripening, where rapid onset and offset may help to reduce the risk of uterine tachysystole and worrisome fetal heart rate changes, low-dose (50 µg) oral administration of misoprostol may be a preferred dose and route. For the treatment of miscarriage and fetal demise, to stimulate sustained uterine contractions over many hours, buccal and vaginal administration of misoprostol are preferred. Rectal administration is generally inferior to buccal and vaginal administration for stimulating sustained uterine contractions and its uses should be limited. ●
Common side effects of misoprostol are abdominal cramping, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headache, and fever. Elevated temperature following misoprostol administration is a concerning side effect that may require further investigation to rule out an infection, especially if the elevated temperature persists for > 4 hours. The preoptic area of the anterior hypothalamus (POAH) plays a major role in thermoregulation. When an infection causes an increase in endogenous pyrogens, including interleukin-1β, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor, prostaglandins are generated in the region of the POAH, increasing the thermoregulatory set point, triggering cutaneous vasoconstriction and shivering and non-shivering thermogenesis.1 Misoprostol, especially at doses >400 µg commonly causes both patient-reported chills and temperature elevation >38° C.
In a study comparing misoprostol and oxytocin for the management of the third stage of labor, 597 patients were randomly allocated to receive oxytocin 10 units by intramuscular injection or misoprostol 400 µg or 600 µg by the oral route.2 Patient-reported shivering occurred in 13%, 19%, and 28% of patients receiving oxytocin, misoprostol 400 µg and misoprostol 800 µg, respectively. A recorded temperature >38° C occurred within 1 hour of medication administration in approximately 3%, 2%, and 7.5% of patients receiving oxytocin, misoprostol 400 µg, and misoprostol 800 µg, respectively. In another study, 453 patients scheduled for a cesarean birth were randomly allocated to receive 1 of 3 doses of rectal misoprostol 200 μg, 400 μg, or 600 μg before incision. Fever was detected in 2.6%, 9.9%, and 5.1% of the patients receiving misoprostol 200 μg, 400 μg, or 600 μg, respectively.3
References
1. Aronoff DM, Neilson EG. Antipyretics: mechanisms of action and clinical use in fever suppression. Am J Med. 2001;111:304-315. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(01)00834-8.
2. Lumbiganon P, Hofmeyr J, Gumezoglu AM, et al. Misoprostol dose-related shivering and pyrexia in the third stage of labor. WHO Collaborative Trial of Misoprostol in the Management of the Third Stage of Labor. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1999;106:304-308. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1999.tb08266.x.
3. Sweed M, El-Said M, Abou-Gamrah AA, et al. Comparison between 200, 400 and 600 microgram rectal misoprostol before cesarean section: a randomized clinical trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019;45:585-591. doi: 10.1111 /jog.13883.
Oxytocin and prostaglandins are critically important regulators of uterine contraction. Obstetrician-gynecologists commonly prescribe oxytocin and prostaglandin agonists (misoprostol, dinoprostone) to stimulate uterine contraction for the induction of labor, prevention and treatment of postpartum hemorrhage, and treatment of miscarriage and fetal demise. The focus of this editorial is the clinical pharmacology of misoprostol.
Misoprostol is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the prevention and treatment of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug–induced gastric ulcers and for patients at high risk for gastric ulcers, including those with a history of gastric ulcers. The approved misoprostol route and dose for this indication is oral administration of 200 µg four times daily with food.1 Recent food intake and antacid use reduces the absorption of orally administered misoprostol. There are no FDA-approved indications for the use of misoprostol as a single agent in obstetrics and gynecology. The FDA has approved the combination of mifepristone and misoprostol for medication abortion in the first trimester. In contrast to misoprostol, PGE2 (dinoprostone) is approved by the FDA as a vaginal insert containing 10 mg of dinoprostone for the initiation and/or continuation of cervical ripening in patients at or near term in whom there is a medical or obstetric indication for induction of labor (Cervidil; Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc, Parsippany, New Jersey).2
Pharmacology of misoprostol
Misoprostol is a prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) agonist analogue. Prostaglandin E1 (alprostadil) is rapidly metabolized, has a half-life in the range of minutes and is not orally active, requiring administration by intravenous infusion or injection. It is indicated to maintain a patent ductus arteriosus in newborns with ductal-dependent circulation and to treat erectile dysfunction.3 In contrast to PGE1, misoprostol has a methyl ester group at carbon-1 (C-1) that increases potency and duration of action. Misoprostol also has no hydroxyl group at C-15, replacing that moiety with the addition of both a methyl- and hydroxyl- group at C-16 (FIGURE). These molecular changes improve oral activity and increase duration of action.4 Pure misoprostol is a viscous oil. It is formulated into tables by dispersing the oil on hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose before compounding into tablets. Unlike naturally occurring prostaglandins (PGE1), misoprostol tablets are stabile at room temperature for years.4
Following absorption, the methyl ester at C-1 is enzymatically cleaved, yielding misoprostol acid, the active drug.4 Misoprostol binds to the E prostanoid receptor 3 (EP-3).5 Activation of myometrial EP-3 receptor induces an increase in intracellular phosphoinositol turnover and calcium mobilization, resulting in an increase in intracellular-free calcium, triggering actin-myosin contractility.6 The increase in free calcium is propagated cell-to-cell through gap junctions that link the myometrial cells to facilitate the generation of a coordinated contraction.

Misoprostol: Various routes of administration are not equal
Misoprostol can be given by an oral, buccal, vaginal, or rectal route of administration. To study the effect of the route of administration on uterine tone and contractility, investigators randomly assigned patients at 8 to 11 weeks’ gestation to receive misoprostol 400 µg as a single dose by the oral or vaginal route. Uterine tone and contractility were measured using an intrauterine pressure transducer. Compared to vaginal administration, oral administration of misprostol was associated with rapid attainment of peak plasma level at 30 minutes, followed by a decline in concentration by 60 minutes. This rapid onset and rapid offset of plasma concentration was paralleled by the onset of uterine tone within 8 minutes, but surprisingly no sustained uterine contractions.7 By contrast, following vaginal administration of misoprostol, serum levels rose slowly and peaked in 1 to 2 hours. Uterine tone increased within 21 minutes, and sustained uterine contractions were recorded for 4 hours.7 The rapid rise and fall in plasma misoprostol following oral administration and the more sustained plasma misoprostol concentration over 4 hours has been previously reported.8 In a second study involving patients 8 to 11 weeks’ gestation, the effect of a single dose of misoprostol 400 µg by an oral or vaginal route on uterine contractility was compared using an intrauterine pressure transducer.9 Confirming previous results, the time from misoprostol administration to increased uterine tone was more rapid with oral than with vaginal administration (8 min vs 19 min). Over the course of 4 hours, uterine contraction activity was greater with vaginal than with oral administration (454 vs 166 Montevideo units).9
Both studies reported that oral administration of misoprostol resulted in more rapid onset and offset of action than vaginal administration. Oral administration of a single dose of misoprostol 400 µg did not result in sustained uterine contractions in most patients in the first trimester. Vaginal administration produced a slower onset of increased uterine tone but sustained uterine contractions over 4 hours. Compared with vaginal administration of misoprostol, the rapid onset and offset of action of oral misoprostol may reduce the rate of tachysystole and changes in fetal heart rate observed with vaginal administration.10
An important finding is that buccal and vaginal administration of misoprostol have similar effects on uterine tone in the first trimester.11 To study the effect of buccal and vaginal administration of misoprostol on uterine tone, patients 6 to 13 weeks’ gestation were randomly allocated to receive a single dose of misoprostol 400 µg by a buccal or vaginal route.11 Uterine activity over 5 hours following administration was assessed using an intrauterine pressure transducer. Uterine tone 20 to 30 minutes after buccal or vaginal administration of misoprostol (400 µg) was 27 and 28 mm Hg, respectively. Peak uterine tone, as measured by an intrauterine pressure transducer, for buccal and vaginal administration of misoprostol was 49 mm Hg and 54 mm Hg, respectively. Total Alexandria units (AU) over 5 hours following buccal or vaginal administration was 6,537 AU and 6,090 AU, respectively.11
An AU is calculated as the average amplitude of the contractions (mm Hg) multiplied by the average duration of the contractions (min) multiplied by average frequency of contraction over 10 minutes.12 By contrast, a Montevideo unit does not include an assessment of contraction duration and is calculated as average amplitude of contractions (mm Hg) multiplied by frequency of uterine contractions over 10 minutes.12
In contrast to buccal or vaginal administration, rectal administration of misoprostol resulted in much lower peak uterine tone and contractility as measured by a pressure transducer. Uterine tone 20 to 30 minutes after vaginal and rectal administration of misoprostol (400 µg) was 28 and 19 mm Hg, respectively.11 Peak uterine tone, as measured by an intrauterine pressure transducer, for vaginal and rectal administration of misoprostol was 54 and 31 mm Hg, respectively. AUs over 5 hours following vaginal and rectal administration was 6,090 AU and 2,768 AU, respectively.11 Compared with buccal and vaginal administration of misoprostol, rectal administration produced less sustained uterine contractions in the first trimester of pregnancy. To achieve maximal sustained uterine contractions, buccal and vaginal routes of administration are superior to oral and rectal administration.
Continue to: Misoprostol and cervical ripening...
Misoprostol and cervical ripening
Misoprostol is commonly used to soften and ripen the cervix. Some of the cervical ripening effects of misoprostol are likely due to increased uterine tone. In addition, misoprostol may have a direct effect on the collagen structure of the cervix. To study the effect of misoprostol on the cervix, pregnant patients in the first trimester were randomly assigned to receive misoprostol 200 µg by vaginal self-administration, isosorbide mononitrate (IMN) 40 mg by vaginal self-administration or no treatment the evening prior to pregnancy termination.13 The following day, before uterine evacuation, a cervical biopsy was obtained for electron microscopy studies and immunohistochemistry to assess the presence of enzymes involved in collagen degradation, including matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP-1) and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9). Electron microscopy demonstrated that pretreatment with misoprostol resulted in a pronounced splitting and disorganization of collagen fibers.13 Compared with misoprostol treatment, IMN produced less splitting and disorganization of collagen fibers, and in the no treatment group, no marked changes in the collagen framework were observed.
Compared with no treatment, misoprostol and IMN pretreatment were associated with marked increases in MMP-1 and MMP-9 as assessed by immunohistochemistry. Misoprostol pretreatment also resulted in a significant increase in interleukin-8 concentration compared with IMN pretreatment and no treatment (8.8 vs 2.7 vs 2.4 pg/mg tissue), respectively.13 Other investigators have also reported that misoprostol increased cervical leukocyte influx and collagen disrupting enzymes MMP-8 and MMP-9.14,15
An open-label clinical trial compared the efficacy of misoprostol versus Foley catheter for labor induction at term in 1,859 patients ≥ 37 weeks’ gestation with a Bishop score <6.16 Patients were randomly allocated to misoprostol (50 µg orally every 4 hours up to 3 times in 24 hours) versus placement of a 16 F or 18 F Foley catheter introduced through the cervix, filled with 30 mL of sodium chloride or water. The investigators reported that oral misoprostol and Foley catheter cervical ripening had similar safety and effectiveness for cervical ripening as a prelude to induction of labor, including no statistically significant differences in 5-minute Apgar score <7, umbilical cord artery pH ≤ 7.05, postpartum hemorrhage, or cesarean birth rate.16
Bottom line
Misoprostol and oxytocin are commonly prescribed in obstetric practice for cervical ripening and induction of labor, respectively. The dose and route of administration of misoprostol influences the effect on the uterus. For cervical ripening, where rapid onset and offset may help to reduce the risk of uterine tachysystole and worrisome fetal heart rate changes, low-dose (50 µg) oral administration of misoprostol may be a preferred dose and route. For the treatment of miscarriage and fetal demise, to stimulate sustained uterine contractions over many hours, buccal and vaginal administration of misoprostol are preferred. Rectal administration is generally inferior to buccal and vaginal administration for stimulating sustained uterine contractions and its uses should be limited. ●
Common side effects of misoprostol are abdominal cramping, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headache, and fever. Elevated temperature following misoprostol administration is a concerning side effect that may require further investigation to rule out an infection, especially if the elevated temperature persists for > 4 hours. The preoptic area of the anterior hypothalamus (POAH) plays a major role in thermoregulation. When an infection causes an increase in endogenous pyrogens, including interleukin-1β, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor, prostaglandins are generated in the region of the POAH, increasing the thermoregulatory set point, triggering cutaneous vasoconstriction and shivering and non-shivering thermogenesis.1 Misoprostol, especially at doses >400 µg commonly causes both patient-reported chills and temperature elevation >38° C.
In a study comparing misoprostol and oxytocin for the management of the third stage of labor, 597 patients were randomly allocated to receive oxytocin 10 units by intramuscular injection or misoprostol 400 µg or 600 µg by the oral route.2 Patient-reported shivering occurred in 13%, 19%, and 28% of patients receiving oxytocin, misoprostol 400 µg and misoprostol 800 µg, respectively. A recorded temperature >38° C occurred within 1 hour of medication administration in approximately 3%, 2%, and 7.5% of patients receiving oxytocin, misoprostol 400 µg, and misoprostol 800 µg, respectively. In another study, 453 patients scheduled for a cesarean birth were randomly allocated to receive 1 of 3 doses of rectal misoprostol 200 μg, 400 μg, or 600 μg before incision. Fever was detected in 2.6%, 9.9%, and 5.1% of the patients receiving misoprostol 200 μg, 400 μg, or 600 μg, respectively.3
References
1. Aronoff DM, Neilson EG. Antipyretics: mechanisms of action and clinical use in fever suppression. Am J Med. 2001;111:304-315. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(01)00834-8.
2. Lumbiganon P, Hofmeyr J, Gumezoglu AM, et al. Misoprostol dose-related shivering and pyrexia in the third stage of labor. WHO Collaborative Trial of Misoprostol in the Management of the Third Stage of Labor. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1999;106:304-308. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1999.tb08266.x.
3. Sweed M, El-Said M, Abou-Gamrah AA, et al. Comparison between 200, 400 and 600 microgram rectal misoprostol before cesarean section: a randomized clinical trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019;45:585-591. doi: 10.1111 /jog.13883.
- Cytotec [package insert]. Chicago, IL: GD Searle & Co. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2002/19268slr037.pdf. Accessed June 20, 2022.
- Cervidil [package insert]. St Louis, MO: Forrest Pharmaceuticals Inc.; May 2006. Accessed June 20, 2022.
- Caverject [package insert]. New York, NY: Pfizer Inc.; March 2014. Accessed June 20, 2022.
- Collins PW. Misoprostol: discovery, development and clinical applications. Med Res Rev. 1990;10:149-172. doi: 10.1002/med.2610100202.
- Audit M, White KI, Breton B, et al. Crystal structure of misoprostol bound to the labor inducer prostaglandin E2 receptor. Nat Chem Biol. 2019;15:11-17. doi: 10.1038/s41589-018-0160-y.
- Pallliser KH, Hirst JJ, Ooi G, et al. Prostaglandin E and F receptor expression and myometrial sensitivity in labor onset in the sheep. Biol Reprod. 2005;72:937-943. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.104.035311.
- Gemzell-Danilesson K, Marions L, Rodriguez A, et al. Comparison between oral and vaginal administration of misoprostol on uterine contractility. Obstet Gynecol. 1999;93:275-280. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(98)00436-0.
- Zieman M, Fong SK, Benowitz NL, et al. Absorption kinetics of misoprostol with oral or vaginal administration. Obstet Gynecol. 1997;90:88-92. doi: 10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00111-7.
- Aronsson A, Bygdeman M, Gemzell-Danielsson K. Effects of misoprostol on uterine contractility following different routes of administration. Hum Reprod. 2004;19:81-84. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deh005.
- Young DC, Delaney T, Armson BA, et al. Oral misoprostol, low dose vaginal misoprostol and vaginal dinoprostone for labor induction: randomized controlled trial. PLOS One. 2020;15:e0227245. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227245.
- Meckstroth KR, Whitaker AK, Bertisch S, et al. Misoprostol administered by epithelial routes. Drug absorption and uterine response. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;108:582-590. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000230398.32794.9d.
- el-Sahwi S, Gaafar AA, Toppozada HK. A new unit for evaluation of uterine activity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1967;98:900-903. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(67)90074-9.
- Vukas N, Ekerhovd E, Abrahamsson G, et al. Cervical priming in the first trimester: morphological and biochemical effects of misoprostol and isosorbide mononitrate. Acta Obstet Gyecol. 2009;88:43-51. doi: 10.1080/00016340802585440.
- Aronsson A, Ulfgren AK, Stabi B, et al. The effect of orally and vaginally administered misoprostol on inflammatory mediators and cervical ripening during early pregnancy. Contraception. 2005;72:33-39. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2005.02.012.
- Denison FC, Riley SC, Elliott CL, et al. The effect of mifepristone administration on leukocyte populations, matrix metalloproteinases and inflammatory mediators in the first trimester cervix. Mol Hum Reprod. 2000;6:541-548. doi: 10.1093/molehr/6.6.541.
- ten Eikelder MLG, Rengerink KO, Jozwiak M, et al. Induction of labour at term with oral misoprostol versus a Foley catheter (PROBAAT-II): a multicentre randomised controlled non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2016;387:1619-1628. doi: 10.1016 /S0140-6736(16)00084-2.
- Cytotec [package insert]. Chicago, IL: GD Searle & Co. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2002/19268slr037.pdf. Accessed June 20, 2022.
- Cervidil [package insert]. St Louis, MO: Forrest Pharmaceuticals Inc.; May 2006. Accessed June 20, 2022.
- Caverject [package insert]. New York, NY: Pfizer Inc.; March 2014. Accessed June 20, 2022.
- Collins PW. Misoprostol: discovery, development and clinical applications. Med Res Rev. 1990;10:149-172. doi: 10.1002/med.2610100202.
- Audit M, White KI, Breton B, et al. Crystal structure of misoprostol bound to the labor inducer prostaglandin E2 receptor. Nat Chem Biol. 2019;15:11-17. doi: 10.1038/s41589-018-0160-y.
- Pallliser KH, Hirst JJ, Ooi G, et al. Prostaglandin E and F receptor expression and myometrial sensitivity in labor onset in the sheep. Biol Reprod. 2005;72:937-943. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.104.035311.
- Gemzell-Danilesson K, Marions L, Rodriguez A, et al. Comparison between oral and vaginal administration of misoprostol on uterine contractility. Obstet Gynecol. 1999;93:275-280. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(98)00436-0.
- Zieman M, Fong SK, Benowitz NL, et al. Absorption kinetics of misoprostol with oral or vaginal administration. Obstet Gynecol. 1997;90:88-92. doi: 10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00111-7.
- Aronsson A, Bygdeman M, Gemzell-Danielsson K. Effects of misoprostol on uterine contractility following different routes of administration. Hum Reprod. 2004;19:81-84. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deh005.
- Young DC, Delaney T, Armson BA, et al. Oral misoprostol, low dose vaginal misoprostol and vaginal dinoprostone for labor induction: randomized controlled trial. PLOS One. 2020;15:e0227245. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227245.
- Meckstroth KR, Whitaker AK, Bertisch S, et al. Misoprostol administered by epithelial routes. Drug absorption and uterine response. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;108:582-590. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000230398.32794.9d.
- el-Sahwi S, Gaafar AA, Toppozada HK. A new unit for evaluation of uterine activity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1967;98:900-903. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(67)90074-9.
- Vukas N, Ekerhovd E, Abrahamsson G, et al. Cervical priming in the first trimester: morphological and biochemical effects of misoprostol and isosorbide mononitrate. Acta Obstet Gyecol. 2009;88:43-51. doi: 10.1080/00016340802585440.
- Aronsson A, Ulfgren AK, Stabi B, et al. The effect of orally and vaginally administered misoprostol on inflammatory mediators and cervical ripening during early pregnancy. Contraception. 2005;72:33-39. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2005.02.012.
- Denison FC, Riley SC, Elliott CL, et al. The effect of mifepristone administration on leukocyte populations, matrix metalloproteinases and inflammatory mediators in the first trimester cervix. Mol Hum Reprod. 2000;6:541-548. doi: 10.1093/molehr/6.6.541.
- ten Eikelder MLG, Rengerink KO, Jozwiak M, et al. Induction of labour at term with oral misoprostol versus a Foley catheter (PROBAAT-II): a multicentre randomised controlled non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2016;387:1619-1628. doi: 10.1016 /S0140-6736(16)00084-2.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and more linked to lower CRC risk
Estrogen exposure helps protect against colorectal cancer (CRC), and in some instances, the protection is site specific, a new analysis finds.
In a 17-year study involving almost 5,000 women, researchers from Germany found that hormone replacement therapy, oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and menopause at age 50 or older were all significantly associated with reductions in CRC risk.
Interestingly, the reduced risk of CRC observed for pregnancy and breastfeeding only applied to proximal colon cancer, while the association with oral contraceptive use was confined to the distal colon and rectum.
The results were published online in JNCI Cancer Spectrum.
CRC is the second most common cause of cancer death. It is responsible for more than one million deaths globally, according to the latest figures from the Global Burden of Disease 2019 Cancer Collaboration.
And sex seems to make a difference. The Global Burden analysis, echoing previous data, found that CRC is less common among women and that fewer women die from the disease.
Little, however, is known about the mechanisms of estrogen signaling in CRC or the impact of reproductive factors on CRC, despite a large amount of literature linking CRC risk to exogenous estrogens, such as hormone replacement therapy and oral contraceptives.
In the current analysis, the team recruited 2,650 patients with CRC from 20 German cancer centers between 2003 and 2020. Researchers used standardized questionnaires to garner the women’s reproductive histories.
A matched control group of 2,175 participants who did not have a history of CRC was randomly selected from population registries. All analyses were adjusted for known CRC risk factors, such as age; body mass index; education level; family history; having previously undergone large-bowel endoscopy; diabetes; and smoking status.
The researchers found that each pregnancy was associated with a small but significant 9% reduction in CRC risk (odds ratio, 0.91), specifically in the proximal colon (OR, 0.86).
Overall, breastfeeding for a year or longer was associated with a significantly lower CRC risk, compared with never breastfeeding (OR, 0.74), but the results were only significant for the proximal colon (OR, 0.58).
Oral contraceptive use for 9 years or longer was associated with a lower CRC risk (OR, 0.75) but was only significant for the distal colon (OR, 0.63). Hormone replacement therapy was associated with a lower risk of CRC irrespective of tumor location (OR, 0.76). And using both was linked to a 42% CRC risk reduction (OR, 0.58).
Although age at menarche was not associated with CRC risk, menopause at age 50 or older was associated with a significant 17% lower risk of CRC.
In an email interview, lead author Tobias Niedermaier, PhD, expressed surprise at two of the findings. The first was the small association between pregnancies and CRC risk, “despite the strong increase in estrogen levels during pregnancy,” he said. He speculated that pregnancy-related increases in insulin levels may have “largely offset the protection effects of estrogen exposure during pregnancy.”
The second surprise was that the age at menarche did not have a bearing on CRC risk, which could be because “exposure to estrogen levels in younger ages [is] less relevant with respect to CRC risk, because CRC typically develops at comparably old age.”
John Marshall, MD, who was not involved in the research, commented that such studies “put a lot of pressure on people to perform in a certain way to modify their personal risk of something.” However, “we would not recommend people alter their life choices for reproduction for this,” said Dr. Marshall, chief of the Division of Hematology/Oncology at Georgetown University, Washington, D.C.
Dr. Niedermaier agreed that “while this knowledge will certainly not change a woman’s decision on family planning,” he noted that the findings “could influence current CRC screening strategies, for example, by risk-adapted screening intervals [and] start and stop ages of screening.”
Dr. Niedermaier and colleagues’ work was funded by the German Research Council, the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research, and the Interdisciplinary Research Program of the National Center for Tumor Diseases. Dr. Niedermaier has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Marshall writes a column that appears regularly on Medscape: Marshall on Oncology. He has served as speaker or member of a speakers’ bureau for Genentech, Amgen, Bayer, Celgene Corporation, and Caris Life Sciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Estrogen exposure helps protect against colorectal cancer (CRC), and in some instances, the protection is site specific, a new analysis finds.
In a 17-year study involving almost 5,000 women, researchers from Germany found that hormone replacement therapy, oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and menopause at age 50 or older were all significantly associated with reductions in CRC risk.
Interestingly, the reduced risk of CRC observed for pregnancy and breastfeeding only applied to proximal colon cancer, while the association with oral contraceptive use was confined to the distal colon and rectum.
The results were published online in JNCI Cancer Spectrum.
CRC is the second most common cause of cancer death. It is responsible for more than one million deaths globally, according to the latest figures from the Global Burden of Disease 2019 Cancer Collaboration.
And sex seems to make a difference. The Global Burden analysis, echoing previous data, found that CRC is less common among women and that fewer women die from the disease.
Little, however, is known about the mechanisms of estrogen signaling in CRC or the impact of reproductive factors on CRC, despite a large amount of literature linking CRC risk to exogenous estrogens, such as hormone replacement therapy and oral contraceptives.
In the current analysis, the team recruited 2,650 patients with CRC from 20 German cancer centers between 2003 and 2020. Researchers used standardized questionnaires to garner the women’s reproductive histories.
A matched control group of 2,175 participants who did not have a history of CRC was randomly selected from population registries. All analyses were adjusted for known CRC risk factors, such as age; body mass index; education level; family history; having previously undergone large-bowel endoscopy; diabetes; and smoking status.
The researchers found that each pregnancy was associated with a small but significant 9% reduction in CRC risk (odds ratio, 0.91), specifically in the proximal colon (OR, 0.86).
Overall, breastfeeding for a year or longer was associated with a significantly lower CRC risk, compared with never breastfeeding (OR, 0.74), but the results were only significant for the proximal colon (OR, 0.58).
Oral contraceptive use for 9 years or longer was associated with a lower CRC risk (OR, 0.75) but was only significant for the distal colon (OR, 0.63). Hormone replacement therapy was associated with a lower risk of CRC irrespective of tumor location (OR, 0.76). And using both was linked to a 42% CRC risk reduction (OR, 0.58).
Although age at menarche was not associated with CRC risk, menopause at age 50 or older was associated with a significant 17% lower risk of CRC.
In an email interview, lead author Tobias Niedermaier, PhD, expressed surprise at two of the findings. The first was the small association between pregnancies and CRC risk, “despite the strong increase in estrogen levels during pregnancy,” he said. He speculated that pregnancy-related increases in insulin levels may have “largely offset the protection effects of estrogen exposure during pregnancy.”
The second surprise was that the age at menarche did not have a bearing on CRC risk, which could be because “exposure to estrogen levels in younger ages [is] less relevant with respect to CRC risk, because CRC typically develops at comparably old age.”
John Marshall, MD, who was not involved in the research, commented that such studies “put a lot of pressure on people to perform in a certain way to modify their personal risk of something.” However, “we would not recommend people alter their life choices for reproduction for this,” said Dr. Marshall, chief of the Division of Hematology/Oncology at Georgetown University, Washington, D.C.
Dr. Niedermaier agreed that “while this knowledge will certainly not change a woman’s decision on family planning,” he noted that the findings “could influence current CRC screening strategies, for example, by risk-adapted screening intervals [and] start and stop ages of screening.”
Dr. Niedermaier and colleagues’ work was funded by the German Research Council, the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research, and the Interdisciplinary Research Program of the National Center for Tumor Diseases. Dr. Niedermaier has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Marshall writes a column that appears regularly on Medscape: Marshall on Oncology. He has served as speaker or member of a speakers’ bureau for Genentech, Amgen, Bayer, Celgene Corporation, and Caris Life Sciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Estrogen exposure helps protect against colorectal cancer (CRC), and in some instances, the protection is site specific, a new analysis finds.
In a 17-year study involving almost 5,000 women, researchers from Germany found that hormone replacement therapy, oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and menopause at age 50 or older were all significantly associated with reductions in CRC risk.
Interestingly, the reduced risk of CRC observed for pregnancy and breastfeeding only applied to proximal colon cancer, while the association with oral contraceptive use was confined to the distal colon and rectum.
The results were published online in JNCI Cancer Spectrum.
CRC is the second most common cause of cancer death. It is responsible for more than one million deaths globally, according to the latest figures from the Global Burden of Disease 2019 Cancer Collaboration.
And sex seems to make a difference. The Global Burden analysis, echoing previous data, found that CRC is less common among women and that fewer women die from the disease.
Little, however, is known about the mechanisms of estrogen signaling in CRC or the impact of reproductive factors on CRC, despite a large amount of literature linking CRC risk to exogenous estrogens, such as hormone replacement therapy and oral contraceptives.
In the current analysis, the team recruited 2,650 patients with CRC from 20 German cancer centers between 2003 and 2020. Researchers used standardized questionnaires to garner the women’s reproductive histories.
A matched control group of 2,175 participants who did not have a history of CRC was randomly selected from population registries. All analyses were adjusted for known CRC risk factors, such as age; body mass index; education level; family history; having previously undergone large-bowel endoscopy; diabetes; and smoking status.
The researchers found that each pregnancy was associated with a small but significant 9% reduction in CRC risk (odds ratio, 0.91), specifically in the proximal colon (OR, 0.86).
Overall, breastfeeding for a year or longer was associated with a significantly lower CRC risk, compared with never breastfeeding (OR, 0.74), but the results were only significant for the proximal colon (OR, 0.58).
Oral contraceptive use for 9 years or longer was associated with a lower CRC risk (OR, 0.75) but was only significant for the distal colon (OR, 0.63). Hormone replacement therapy was associated with a lower risk of CRC irrespective of tumor location (OR, 0.76). And using both was linked to a 42% CRC risk reduction (OR, 0.58).
Although age at menarche was not associated with CRC risk, menopause at age 50 or older was associated with a significant 17% lower risk of CRC.
In an email interview, lead author Tobias Niedermaier, PhD, expressed surprise at two of the findings. The first was the small association between pregnancies and CRC risk, “despite the strong increase in estrogen levels during pregnancy,” he said. He speculated that pregnancy-related increases in insulin levels may have “largely offset the protection effects of estrogen exposure during pregnancy.”
The second surprise was that the age at menarche did not have a bearing on CRC risk, which could be because “exposure to estrogen levels in younger ages [is] less relevant with respect to CRC risk, because CRC typically develops at comparably old age.”
John Marshall, MD, who was not involved in the research, commented that such studies “put a lot of pressure on people to perform in a certain way to modify their personal risk of something.” However, “we would not recommend people alter their life choices for reproduction for this,” said Dr. Marshall, chief of the Division of Hematology/Oncology at Georgetown University, Washington, D.C.
Dr. Niedermaier agreed that “while this knowledge will certainly not change a woman’s decision on family planning,” he noted that the findings “could influence current CRC screening strategies, for example, by risk-adapted screening intervals [and] start and stop ages of screening.”
Dr. Niedermaier and colleagues’ work was funded by the German Research Council, the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research, and the Interdisciplinary Research Program of the National Center for Tumor Diseases. Dr. Niedermaier has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Marshall writes a column that appears regularly on Medscape: Marshall on Oncology. He has served as speaker or member of a speakers’ bureau for Genentech, Amgen, Bayer, Celgene Corporation, and Caris Life Sciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Menstrual phase impacts exercise effects in type 1 diabetes
Women with type 1 diabetes may need additional glucose after exercise during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, compared with other times, according to a study in nine women.
“We know that exercise is very beneficial for people with type 1 diabetes; we also know that fear of hypoglycemia is a major barrier to exercise in this population,” said Jane E. Yardley, PhD, in a presentation at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association, New Orleans. Women with type 1 diabetes (T1D) perceive more barriers, compared with men, she added.
The menstrual cycle could be an additional barrier to exercise for women with T1D because it increases glucose fluctuations that have not been well documented in the literature to date, said Dr. Yardley, of the University of Alberta, Augustana.
The follicular phase of the menstrual cycle lasts from menses to the midcycle, about 14 days later. This is followed by the luteal phase, which lasts until approximately day 28, Dr. Yardley explained. Data on insulin sensitivity have shown that the late luteal phase is associated with “a little less insulin sensitivity” in women with T1D, she noted.
To assess the relationship between menstrual cycle, glucose control, and exercise, Dr. Yardley and colleagues compared the effects of a moderate aerobic exercise on glycemic responses between the early follicular and late luteal phases of the menstrual cycle in nine female participants with T1D.
The exercise involved 45 minutes of aerobic cycling at 50% of predetermined peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak) for 45 min. The mean age of the participants was 30.2 years, the mean hemoglobin A1C was 7.4%, and the mean VO2peak was 32.5 mL/kg per min. The women reported regular menstrual cycles, and none were using oral contraceptives.
Blood samples were collected before and immediately after exercise and after an hour of recovery. Participants wore continuous glucose monitors for at least 1 hour before and after exercise.
Menstrual cycle was confirmed via estrogen, estradiol, and progesterone.
Insulin levels varied greatly among the study participants, but the differences were not significant, Dr. Yardley said. Glucose levels consistently decreased during exercise and increased after exercise, she noted.
No significant difference in glucose was observed between the follicular and luteal phases.
However, “this needs to be interpreted in the context of the safety profiles that are in place in our lab,” which include carbohydrate supplements for individuals whose blood glucose levels drop below 4.5 mmol/L, she said.
In the current study, 6 of 9 participants required additional carbohydrates during the luteal phase, but only 1 participant needed additional carbohydrates during the follicular phase, she noted. For this reason, no differences were noted. “We actually prevented changes,” she said.
No significant differences were noted in mean glucose levels or number of hypoglycemic episodes at any of the time points between the two phases.
“One place where we did see a difference was in hyperglycemia 24 hours after exercise,” Dr. Yardley said. Level 1 hyperglycemia 24 hours after exercise was significantly more frequent in the follicular phase, compared with the luteal phase (P = .028).
The study findings were limited by the small sample size and homogenous population, and more research is needed to interpret the data, said Dr. Yardley.
However, the need for more glucose supplementation to prevent hypoglycemia during the luteal phase suggests a higher hypoglycemic risk associated with aerobic exercise during this time, she said.
In addition, the results suggest that the menstrual cycle should be taken into consideration when female participants are involved in exercise studies, she noted.
Study supports personalized exercise plans
“It is important to evaluate effects of exercise in people with type 1 diabetes and evaluate whether there is a difference those effects in men and women,” said Helena W. Rodbard, MD, an endocrinologist in private practice in Rockville, Md., in an interview. “There is also a need to evaluate to what extent the changes in blood glucose patterns in women in response to exercise differ depending on the phase of the ovarian cycle,” said Dr. Rodbard, who was not involved in the study.
In the current study, “the researchers observed a decline in glucose during a 45-minute period of moderate aerobic exercise, cycling at 50% VO2peak followed by an increase during a 60-minute recovery period. There was a suggestive finding, in the nine subjects, that more carbohydrate supplementation was needed during the late luteal phase of the menstrual cycle than during the follicular phase,” Dr. Rodbard noted. “In contrast, the authors reported a significantly increased degree of hyperglycemia during the recovery phase for subjects during the follicular phase. These findings are consistent with and extend several recent studies from Dr. Yardley and coworkers, who have been focused on this area of research,” she said.
“This study provides provocative evidence that glucose responses to aerobic exercise in women may depend on the timing in relationship to their ovarian cycle,” said Dr. Rodbard. “These findings are based on a small group of subjects and were present in some but not all subjects. Clinicians should encourage women to evaluate and record their experiences during and after exercise in terms of need for carbohydrate supplementation for documented or symptomatic hypoglycemia and in terms of glucose changes as recorded using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), both in relation to type of exercise and in relation to time in the menstrual cycle,” she said.
The findings also highlight the importance of individualized therapy that is “based on subjective inputs combined with analysis of CGM data during and following exercise,” said Dr. Rodbard. “It is likely that use of Automated Insulin Delivery (AID) will be helpful in achieving this level of individualization in view of the wide range of types, intensity, and duration of physical activity and exercise in which people with T1D engage and the myriad factors that can influence the glycemic response,” she said.
Looking ahead, “the authors and others should expand the present series of subjects using aerobic exercise and examine other types of exercise as well,” Dr. Rodbard noted. “It will be important to evaluate the consistency of these changes in glucose patterns within individuals on multiple occasions, and it would be helpful to repeat the studies in women using oral contraceptives.”
Dr. Yardley disclosed research support from Abbott, Dexcom, and LifeScan and disclosed serving on the speaker’s bureau for Abbott Diabetes. Dr. Rodbard had no financial conflicts to disclose. She serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Clinical Endocrinology News.
Women with type 1 diabetes may need additional glucose after exercise during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, compared with other times, according to a study in nine women.
“We know that exercise is very beneficial for people with type 1 diabetes; we also know that fear of hypoglycemia is a major barrier to exercise in this population,” said Jane E. Yardley, PhD, in a presentation at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association, New Orleans. Women with type 1 diabetes (T1D) perceive more barriers, compared with men, she added.
The menstrual cycle could be an additional barrier to exercise for women with T1D because it increases glucose fluctuations that have not been well documented in the literature to date, said Dr. Yardley, of the University of Alberta, Augustana.
The follicular phase of the menstrual cycle lasts from menses to the midcycle, about 14 days later. This is followed by the luteal phase, which lasts until approximately day 28, Dr. Yardley explained. Data on insulin sensitivity have shown that the late luteal phase is associated with “a little less insulin sensitivity” in women with T1D, she noted.
To assess the relationship between menstrual cycle, glucose control, and exercise, Dr. Yardley and colleagues compared the effects of a moderate aerobic exercise on glycemic responses between the early follicular and late luteal phases of the menstrual cycle in nine female participants with T1D.
The exercise involved 45 minutes of aerobic cycling at 50% of predetermined peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak) for 45 min. The mean age of the participants was 30.2 years, the mean hemoglobin A1C was 7.4%, and the mean VO2peak was 32.5 mL/kg per min. The women reported regular menstrual cycles, and none were using oral contraceptives.
Blood samples were collected before and immediately after exercise and after an hour of recovery. Participants wore continuous glucose monitors for at least 1 hour before and after exercise.
Menstrual cycle was confirmed via estrogen, estradiol, and progesterone.
Insulin levels varied greatly among the study participants, but the differences were not significant, Dr. Yardley said. Glucose levels consistently decreased during exercise and increased after exercise, she noted.
No significant difference in glucose was observed between the follicular and luteal phases.
However, “this needs to be interpreted in the context of the safety profiles that are in place in our lab,” which include carbohydrate supplements for individuals whose blood glucose levels drop below 4.5 mmol/L, she said.
In the current study, 6 of 9 participants required additional carbohydrates during the luteal phase, but only 1 participant needed additional carbohydrates during the follicular phase, she noted. For this reason, no differences were noted. “We actually prevented changes,” she said.
No significant differences were noted in mean glucose levels or number of hypoglycemic episodes at any of the time points between the two phases.
“One place where we did see a difference was in hyperglycemia 24 hours after exercise,” Dr. Yardley said. Level 1 hyperglycemia 24 hours after exercise was significantly more frequent in the follicular phase, compared with the luteal phase (P = .028).
The study findings were limited by the small sample size and homogenous population, and more research is needed to interpret the data, said Dr. Yardley.
However, the need for more glucose supplementation to prevent hypoglycemia during the luteal phase suggests a higher hypoglycemic risk associated with aerobic exercise during this time, she said.
In addition, the results suggest that the menstrual cycle should be taken into consideration when female participants are involved in exercise studies, she noted.
Study supports personalized exercise plans
“It is important to evaluate effects of exercise in people with type 1 diabetes and evaluate whether there is a difference those effects in men and women,” said Helena W. Rodbard, MD, an endocrinologist in private practice in Rockville, Md., in an interview. “There is also a need to evaluate to what extent the changes in blood glucose patterns in women in response to exercise differ depending on the phase of the ovarian cycle,” said Dr. Rodbard, who was not involved in the study.
In the current study, “the researchers observed a decline in glucose during a 45-minute period of moderate aerobic exercise, cycling at 50% VO2peak followed by an increase during a 60-minute recovery period. There was a suggestive finding, in the nine subjects, that more carbohydrate supplementation was needed during the late luteal phase of the menstrual cycle than during the follicular phase,” Dr. Rodbard noted. “In contrast, the authors reported a significantly increased degree of hyperglycemia during the recovery phase for subjects during the follicular phase. These findings are consistent with and extend several recent studies from Dr. Yardley and coworkers, who have been focused on this area of research,” she said.
“This study provides provocative evidence that glucose responses to aerobic exercise in women may depend on the timing in relationship to their ovarian cycle,” said Dr. Rodbard. “These findings are based on a small group of subjects and were present in some but not all subjects. Clinicians should encourage women to evaluate and record their experiences during and after exercise in terms of need for carbohydrate supplementation for documented or symptomatic hypoglycemia and in terms of glucose changes as recorded using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), both in relation to type of exercise and in relation to time in the menstrual cycle,” she said.
The findings also highlight the importance of individualized therapy that is “based on subjective inputs combined with analysis of CGM data during and following exercise,” said Dr. Rodbard. “It is likely that use of Automated Insulin Delivery (AID) will be helpful in achieving this level of individualization in view of the wide range of types, intensity, and duration of physical activity and exercise in which people with T1D engage and the myriad factors that can influence the glycemic response,” she said.
Looking ahead, “the authors and others should expand the present series of subjects using aerobic exercise and examine other types of exercise as well,” Dr. Rodbard noted. “It will be important to evaluate the consistency of these changes in glucose patterns within individuals on multiple occasions, and it would be helpful to repeat the studies in women using oral contraceptives.”
Dr. Yardley disclosed research support from Abbott, Dexcom, and LifeScan and disclosed serving on the speaker’s bureau for Abbott Diabetes. Dr. Rodbard had no financial conflicts to disclose. She serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Clinical Endocrinology News.
Women with type 1 diabetes may need additional glucose after exercise during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, compared with other times, according to a study in nine women.
“We know that exercise is very beneficial for people with type 1 diabetes; we also know that fear of hypoglycemia is a major barrier to exercise in this population,” said Jane E. Yardley, PhD, in a presentation at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association, New Orleans. Women with type 1 diabetes (T1D) perceive more barriers, compared with men, she added.
The menstrual cycle could be an additional barrier to exercise for women with T1D because it increases glucose fluctuations that have not been well documented in the literature to date, said Dr. Yardley, of the University of Alberta, Augustana.
The follicular phase of the menstrual cycle lasts from menses to the midcycle, about 14 days later. This is followed by the luteal phase, which lasts until approximately day 28, Dr. Yardley explained. Data on insulin sensitivity have shown that the late luteal phase is associated with “a little less insulin sensitivity” in women with T1D, she noted.
To assess the relationship between menstrual cycle, glucose control, and exercise, Dr. Yardley and colleagues compared the effects of a moderate aerobic exercise on glycemic responses between the early follicular and late luteal phases of the menstrual cycle in nine female participants with T1D.
The exercise involved 45 minutes of aerobic cycling at 50% of predetermined peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak) for 45 min. The mean age of the participants was 30.2 years, the mean hemoglobin A1C was 7.4%, and the mean VO2peak was 32.5 mL/kg per min. The women reported regular menstrual cycles, and none were using oral contraceptives.
Blood samples were collected before and immediately after exercise and after an hour of recovery. Participants wore continuous glucose monitors for at least 1 hour before and after exercise.
Menstrual cycle was confirmed via estrogen, estradiol, and progesterone.
Insulin levels varied greatly among the study participants, but the differences were not significant, Dr. Yardley said. Glucose levels consistently decreased during exercise and increased after exercise, she noted.
No significant difference in glucose was observed between the follicular and luteal phases.
However, “this needs to be interpreted in the context of the safety profiles that are in place in our lab,” which include carbohydrate supplements for individuals whose blood glucose levels drop below 4.5 mmol/L, she said.
In the current study, 6 of 9 participants required additional carbohydrates during the luteal phase, but only 1 participant needed additional carbohydrates during the follicular phase, she noted. For this reason, no differences were noted. “We actually prevented changes,” she said.
No significant differences were noted in mean glucose levels or number of hypoglycemic episodes at any of the time points between the two phases.
“One place where we did see a difference was in hyperglycemia 24 hours after exercise,” Dr. Yardley said. Level 1 hyperglycemia 24 hours after exercise was significantly more frequent in the follicular phase, compared with the luteal phase (P = .028).
The study findings were limited by the small sample size and homogenous population, and more research is needed to interpret the data, said Dr. Yardley.
However, the need for more glucose supplementation to prevent hypoglycemia during the luteal phase suggests a higher hypoglycemic risk associated with aerobic exercise during this time, she said.
In addition, the results suggest that the menstrual cycle should be taken into consideration when female participants are involved in exercise studies, she noted.
Study supports personalized exercise plans
“It is important to evaluate effects of exercise in people with type 1 diabetes and evaluate whether there is a difference those effects in men and women,” said Helena W. Rodbard, MD, an endocrinologist in private practice in Rockville, Md., in an interview. “There is also a need to evaluate to what extent the changes in blood glucose patterns in women in response to exercise differ depending on the phase of the ovarian cycle,” said Dr. Rodbard, who was not involved in the study.
In the current study, “the researchers observed a decline in glucose during a 45-minute period of moderate aerobic exercise, cycling at 50% VO2peak followed by an increase during a 60-minute recovery period. There was a suggestive finding, in the nine subjects, that more carbohydrate supplementation was needed during the late luteal phase of the menstrual cycle than during the follicular phase,” Dr. Rodbard noted. “In contrast, the authors reported a significantly increased degree of hyperglycemia during the recovery phase for subjects during the follicular phase. These findings are consistent with and extend several recent studies from Dr. Yardley and coworkers, who have been focused on this area of research,” she said.
“This study provides provocative evidence that glucose responses to aerobic exercise in women may depend on the timing in relationship to their ovarian cycle,” said Dr. Rodbard. “These findings are based on a small group of subjects and were present in some but not all subjects. Clinicians should encourage women to evaluate and record their experiences during and after exercise in terms of need for carbohydrate supplementation for documented or symptomatic hypoglycemia and in terms of glucose changes as recorded using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), both in relation to type of exercise and in relation to time in the menstrual cycle,” she said.
The findings also highlight the importance of individualized therapy that is “based on subjective inputs combined with analysis of CGM data during and following exercise,” said Dr. Rodbard. “It is likely that use of Automated Insulin Delivery (AID) will be helpful in achieving this level of individualization in view of the wide range of types, intensity, and duration of physical activity and exercise in which people with T1D engage and the myriad factors that can influence the glycemic response,” she said.
Looking ahead, “the authors and others should expand the present series of subjects using aerobic exercise and examine other types of exercise as well,” Dr. Rodbard noted. “It will be important to evaluate the consistency of these changes in glucose patterns within individuals on multiple occasions, and it would be helpful to repeat the studies in women using oral contraceptives.”
Dr. Yardley disclosed research support from Abbott, Dexcom, and LifeScan and disclosed serving on the speaker’s bureau for Abbott Diabetes. Dr. Rodbard had no financial conflicts to disclose. She serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Clinical Endocrinology News.
FROM ADA 2022
Alabama cites Roe decision in call to ban transgender health care
Alabama urged a federal court on June 28 to drop its block on the state’s ban on gender-affirming care for transgender youth, citing the Supreme Court’s recent decision to overturn Roe v. Wade.
Alabama Attorney General Steve Marshall said the high court ruled that abortion isn’t protected under the 14th Amendment because it’s not “deeply rooted” in the nation’s history, which he noted could be said about access to gender-affirming care as well, according to Axios.
“No one – adult or child – has a right to transitioning treatments that is deeply rooted in our Nation’s history and tradition,” he wrote in a court document.
“The State can thus regulate or prohibit those interventions for children, even if an adult wants the drugs for his child,” he wrote.
In May, a federal judge blocked part of Alabama’s Senate Bill 184, which makes it a felony for someone to “engage in or cause” certain types of medical care for transgender youths. The law, which was put in place in April, allows for criminal prosecution against doctors, parents, guardians, and anyone else who provides care to a minor. The penalties could result in up to 10 years in prison and up to $15,000 in fines.
At that time, U.S. District Judge Liles Burke issued an injunction to stop Alabama from enforcing the law and allow challenges, including one filed by the Department of Justice. Mr. Burke said the state provided “no credible evidence to show that transitioning medications are ‘experimental.’ ”
“While Defendants offer some evidence that transitioning medications pose certain risks, the uncontradicted record evidence is that at least twenty-two major medical associations in the United States endorse transitioning medications as well-established, evidence-based treatments for gender dysphoria in minors,” he wrote in the ruling.
Medical organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Psychological Association, and American Medical Association have urged governors to oppose legislation this year that would restrict gender-affirming medical care, saying that such laws could have negative effects on the mental health of transgender youths.
But on June 28, Mr. Marshall focused on the Constitution and what he believes the recent overturn of Roe implies.
“Just as the parental relationship does not unlock a Due Process right allowing parents to obtain medical marijuana or abortions for their children, neither does it unlock a right to transitioning treatments,” he wrote.
“The Constitution reserves to the State – not courts or medical interest groups – the authority to determine that these sterilizing interventions are too dangerous for minors,” he said.
Since the Supreme Court overturned Roe, people have expressed concerns that lawsuits could now target several rights that are protected under the 14th Amendment, including same-sex relationships, marriage equality, and access to contraceptives.
Justice Clarence Thomas, who wrote a concurring opinion to the majority decision, said the Supreme Court, “in future cases” should reconsider “substantive due process precedents” under previous landmark cases such as Griswold v. Connecticut, Lawrence v. Texas, and Obergefell v. Hodges.
At the same time, Justice Brett Kavanaugh, who also wrote a concurring opinion, said the decision to overturn Roe was only focused on abortion, saying it “does not mean the overruling of those precedents, and does not threaten or cast doubt on those precedents.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Alabama urged a federal court on June 28 to drop its block on the state’s ban on gender-affirming care for transgender youth, citing the Supreme Court’s recent decision to overturn Roe v. Wade.
Alabama Attorney General Steve Marshall said the high court ruled that abortion isn’t protected under the 14th Amendment because it’s not “deeply rooted” in the nation’s history, which he noted could be said about access to gender-affirming care as well, according to Axios.
“No one – adult or child – has a right to transitioning treatments that is deeply rooted in our Nation’s history and tradition,” he wrote in a court document.
“The State can thus regulate or prohibit those interventions for children, even if an adult wants the drugs for his child,” he wrote.
In May, a federal judge blocked part of Alabama’s Senate Bill 184, which makes it a felony for someone to “engage in or cause” certain types of medical care for transgender youths. The law, which was put in place in April, allows for criminal prosecution against doctors, parents, guardians, and anyone else who provides care to a minor. The penalties could result in up to 10 years in prison and up to $15,000 in fines.
At that time, U.S. District Judge Liles Burke issued an injunction to stop Alabama from enforcing the law and allow challenges, including one filed by the Department of Justice. Mr. Burke said the state provided “no credible evidence to show that transitioning medications are ‘experimental.’ ”
“While Defendants offer some evidence that transitioning medications pose certain risks, the uncontradicted record evidence is that at least twenty-two major medical associations in the United States endorse transitioning medications as well-established, evidence-based treatments for gender dysphoria in minors,” he wrote in the ruling.
Medical organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Psychological Association, and American Medical Association have urged governors to oppose legislation this year that would restrict gender-affirming medical care, saying that such laws could have negative effects on the mental health of transgender youths.
But on June 28, Mr. Marshall focused on the Constitution and what he believes the recent overturn of Roe implies.
“Just as the parental relationship does not unlock a Due Process right allowing parents to obtain medical marijuana or abortions for their children, neither does it unlock a right to transitioning treatments,” he wrote.
“The Constitution reserves to the State – not courts or medical interest groups – the authority to determine that these sterilizing interventions are too dangerous for minors,” he said.
Since the Supreme Court overturned Roe, people have expressed concerns that lawsuits could now target several rights that are protected under the 14th Amendment, including same-sex relationships, marriage equality, and access to contraceptives.
Justice Clarence Thomas, who wrote a concurring opinion to the majority decision, said the Supreme Court, “in future cases” should reconsider “substantive due process precedents” under previous landmark cases such as Griswold v. Connecticut, Lawrence v. Texas, and Obergefell v. Hodges.
At the same time, Justice Brett Kavanaugh, who also wrote a concurring opinion, said the decision to overturn Roe was only focused on abortion, saying it “does not mean the overruling of those precedents, and does not threaten or cast doubt on those precedents.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Alabama urged a federal court on June 28 to drop its block on the state’s ban on gender-affirming care for transgender youth, citing the Supreme Court’s recent decision to overturn Roe v. Wade.
Alabama Attorney General Steve Marshall said the high court ruled that abortion isn’t protected under the 14th Amendment because it’s not “deeply rooted” in the nation’s history, which he noted could be said about access to gender-affirming care as well, according to Axios.
“No one – adult or child – has a right to transitioning treatments that is deeply rooted in our Nation’s history and tradition,” he wrote in a court document.
“The State can thus regulate or prohibit those interventions for children, even if an adult wants the drugs for his child,” he wrote.
In May, a federal judge blocked part of Alabama’s Senate Bill 184, which makes it a felony for someone to “engage in or cause” certain types of medical care for transgender youths. The law, which was put in place in April, allows for criminal prosecution against doctors, parents, guardians, and anyone else who provides care to a minor. The penalties could result in up to 10 years in prison and up to $15,000 in fines.
At that time, U.S. District Judge Liles Burke issued an injunction to stop Alabama from enforcing the law and allow challenges, including one filed by the Department of Justice. Mr. Burke said the state provided “no credible evidence to show that transitioning medications are ‘experimental.’ ”
“While Defendants offer some evidence that transitioning medications pose certain risks, the uncontradicted record evidence is that at least twenty-two major medical associations in the United States endorse transitioning medications as well-established, evidence-based treatments for gender dysphoria in minors,” he wrote in the ruling.
Medical organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Psychological Association, and American Medical Association have urged governors to oppose legislation this year that would restrict gender-affirming medical care, saying that such laws could have negative effects on the mental health of transgender youths.
But on June 28, Mr. Marshall focused on the Constitution and what he believes the recent overturn of Roe implies.
“Just as the parental relationship does not unlock a Due Process right allowing parents to obtain medical marijuana or abortions for their children, neither does it unlock a right to transitioning treatments,” he wrote.
“The Constitution reserves to the State – not courts or medical interest groups – the authority to determine that these sterilizing interventions are too dangerous for minors,” he said.
Since the Supreme Court overturned Roe, people have expressed concerns that lawsuits could now target several rights that are protected under the 14th Amendment, including same-sex relationships, marriage equality, and access to contraceptives.
Justice Clarence Thomas, who wrote a concurring opinion to the majority decision, said the Supreme Court, “in future cases” should reconsider “substantive due process precedents” under previous landmark cases such as Griswold v. Connecticut, Lawrence v. Texas, and Obergefell v. Hodges.
At the same time, Justice Brett Kavanaugh, who also wrote a concurring opinion, said the decision to overturn Roe was only focused on abortion, saying it “does not mean the overruling of those precedents, and does not threaten or cast doubt on those precedents.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Are ObGyns comfortable performing operative vaginal delivery as an alternative to cesarean delivery?
“[Operative vaginal delivery] was used in only 3% of all US births in 2013, a shift from approximately 30% in 1987,” reported Hayley M. Miller, MD, and Danielle M. Panelli, MD, in the June issue of OBG Management. In their article, “How are maternal and neonatal outcomes impacted by the contemporary practice of operative vaginal delivery [OVD],” the authors mentioned that level of experience by the operator can bias reported complication rates of OVD. Although they examined evidence that found the absolute risk of neonatal trauma to be low following OVD, perineal lacerations “appeared to remain a major driver of maternal morbidity….” Given the current infrequency of OVD, they urged that training be prioritized so OVD can be offered as a safe alternative to cesarean delivery. OBG Management followed up with a poll for readers to ask, “Are you comfortable performing OVD as an alternative to cesarean?”
A total of 302 readers cast their vote:
81.1% (245 readers) said yes
18.9% (57 readers) said no
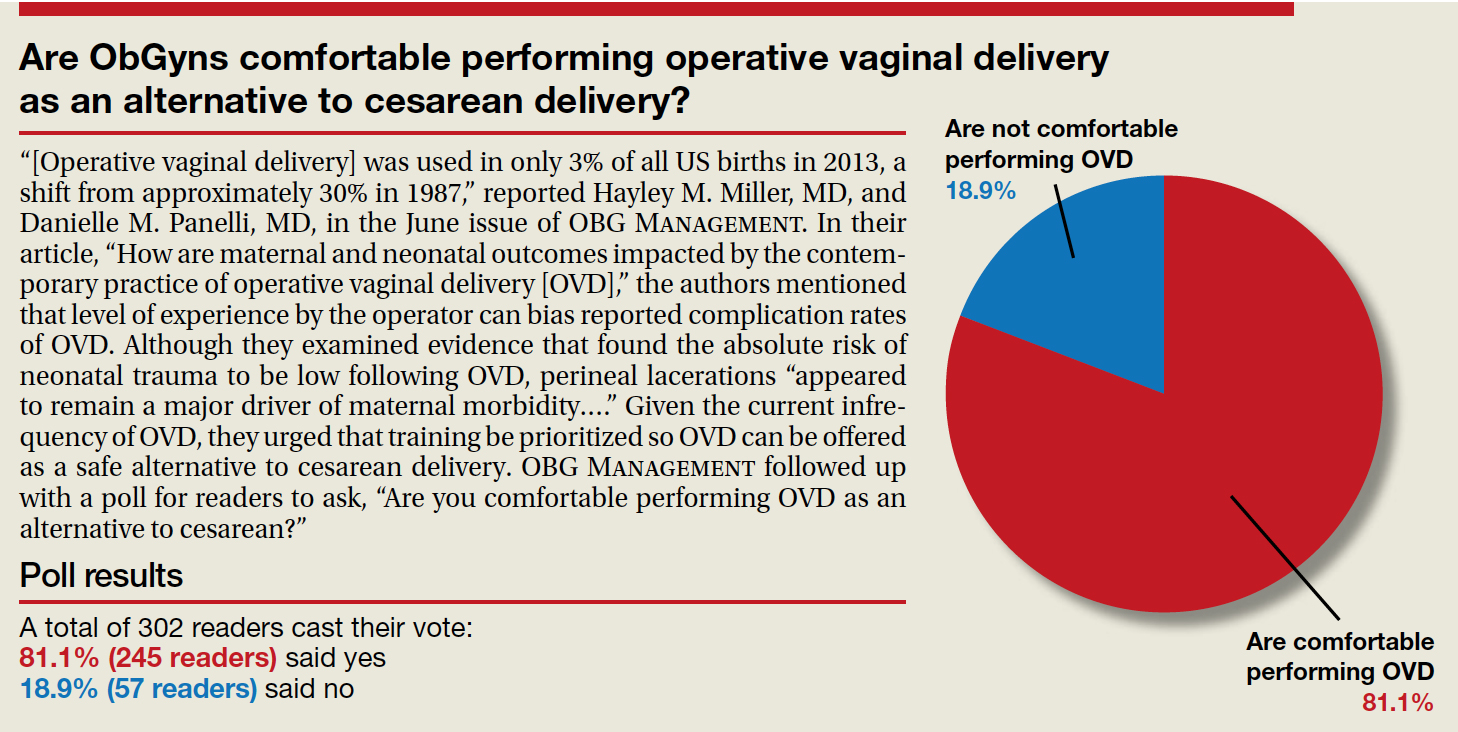
“[Operative vaginal delivery] was used in only 3% of all US births in 2013, a shift from approximately 30% in 1987,” reported Hayley M. Miller, MD, and Danielle M. Panelli, MD, in the June issue of OBG Management. In their article, “How are maternal and neonatal outcomes impacted by the contemporary practice of operative vaginal delivery [OVD],” the authors mentioned that level of experience by the operator can bias reported complication rates of OVD. Although they examined evidence that found the absolute risk of neonatal trauma to be low following OVD, perineal lacerations “appeared to remain a major driver of maternal morbidity….” Given the current infrequency of OVD, they urged that training be prioritized so OVD can be offered as a safe alternative to cesarean delivery. OBG Management followed up with a poll for readers to ask, “Are you comfortable performing OVD as an alternative to cesarean?”
A total of 302 readers cast their vote:
81.1% (245 readers) said yes
18.9% (57 readers) said no

“[Operative vaginal delivery] was used in only 3% of all US births in 2013, a shift from approximately 30% in 1987,” reported Hayley M. Miller, MD, and Danielle M. Panelli, MD, in the June issue of OBG Management. In their article, “How are maternal and neonatal outcomes impacted by the contemporary practice of operative vaginal delivery [OVD],” the authors mentioned that level of experience by the operator can bias reported complication rates of OVD. Although they examined evidence that found the absolute risk of neonatal trauma to be low following OVD, perineal lacerations “appeared to remain a major driver of maternal morbidity….” Given the current infrequency of OVD, they urged that training be prioritized so OVD can be offered as a safe alternative to cesarean delivery. OBG Management followed up with a poll for readers to ask, “Are you comfortable performing OVD as an alternative to cesarean?”
A total of 302 readers cast their vote:
81.1% (245 readers) said yes
18.9% (57 readers) said no

COVID-19 Pandemic stress affected ovulation, not menstruation
ATLANTA – Disturbances in ovulation that didn’t produce any actual changes in the menstrual cycle of women were extremely common during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic and were linked to emotional stress, according to the findings of an “experiment of nature” that allowed for comparison with women a decade earlier.
Findings from two studies of reproductive-age women, one conducted in 2006-2008 and the other in 2020-2021, were presented by Jerilynn C. Prior, MD, at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
The comparison of the two time periods yielded several novel findings. “I was taught in medical school that when women don’t eat enough they lose their period. But what we now understand is there’s a graded response to various stressors, acting through the hypothalamus in a common pathway. There is a gradation of disturbances, some of which are subclinical or not obvious,” said Dr. Prior, professor of endocrinology and metabolism at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver.
Moreover, women’s menstrual cycle lengths didn’t differ across the two time periods, despite a dramatic 63% decrement in normal ovulatory function related to increased depression, anxiety, and outside stresses that the women reported in diaries.
“Assuming that regular cycles need normal ovulation is something we should just get out of our minds. It changes our concept about what’s normal if we only know about the cycle length,” she observed.
It will be critical going forward to see whether the ovulatory disturbances have resolved as the pandemic has shifted “because there’s strong evidence that ovulatory disturbances, even with normal cycle length, are related to bone loss and some evidence it’s related to early heart attacks, breast and endometrial cancers,” Dr. Prior said during a press conference.
Asked to comment, session moderator Genevieve Neal-Perry, MD, PhD, told this news organization: “I think what we can take away is that stress itself is a modifier of the way the brain and the gonads communicate with each other, and that then has an impact on ovulatory function.”
Dr. Neal-Perry noted that the association of stress and ovulatory disruption has been reported in various ways previously, but “clearly it doesn’t affect everyone. What we don’t know is who is most susceptible. There have been some studies showing a genetic predisposition and a genetic anomaly that actually makes them more susceptible to the impact of stress on the reproductive system.”
But the lack of data on weight change in the study cohorts is a limitation. “To me one of the more important questions was what was going on with weight. Just looking at a static number doesn’t tell you whether there were changes. We know that weight gain or weight loss can stress the reproductive axis,” noted Dr. Neal-Parry of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
‘Experiment of nature’ revealed invisible effect of pandemic stress
The women in both cohorts of the Menstruation Ovulation Study (MOS) were healthy volunteers aged 19-35 years recruited from the metropolitan Vancouver region. All were menstruating monthly and none were taking hormonal birth control. Recruitment for the second cohort had begun just prior to the March 2020 COVID-19 pandemic lockdown.
Interviewer-administered questionnaires (CaMos) covering demographics, socioeconomic status, and reproductive history, and daily diaries kept by the women (menstrual cycle diary) were identical for both cohorts.
Assessments of ovulation differed for the two studies but were cross-validated. For the earlier time period, ovulation was assessed by a threefold increase in follicular-to-luteal urinary progesterone (PdG). For the pandemic-era study, the validated quantitative basal temperature (QBT) method was used.
There were 301 women in the earlier cohort and 125 during the pandemic. Both were an average age of about 29 years and had a body mass index of about 24.3 kg/m2 (within the normal range). The pandemic cohort was more racially/ethnically diverse than the earlier one and more in-line with recent census data.
More of the women were nulliparous during the pandemic than earlier (92.7% vs. 80.4%; P = .002).
The distribution of menstrual cycle lengths didn’t differ, with both cohorts averaging about 30 days (P = .893). However, while 90% of the women in the earlier cohort ovulated normally, only 37% did during the pandemic, a highly significant difference (P < .0001).
Thus, during the pandemic, 63% of women had “silent ovulatory disturbances,” either with short luteal phases after ovulation or no ovulation, compared with just 10% in the earlier cohort, “which is remarkable, unbelievable actually,” Dr. Prior remarked.
The difference wasn’t explained by any of the demographic information collected either, including socioeconomic status, lifestyle, or reproductive history variables.
And it wasn’t because of COVID-19 vaccination, as the vaccine wasn’t available when most of the women were recruited, and of the 79 who were recruited during vaccine availability, only two received a COVID-19 vaccine during the study (and both had normal ovulation).
Employment changes, caring responsibilities, and worry likely causes
The information from the diaries was more revealing. Several diary components were far more common during the pandemic, including negative mood (feeling depressed or anxious, sleep problems, and outside stresses), self-worth, interest in sex, energy level, and appetite. All were significantly different between the two cohorts (P < .001) and between those with and without ovulatory disturbances.
“So menstrual cycle lengths and long cycles didn’t differ, but there was a much higher prevalence of silent or subclinical ovulatory disturbances, and these were related to the increased stresses that women recorded in their diaries. This means that the estrogen levels were pretty close to normal but the progesterone levels were remarkably decreased,” Dr. Prior said.
Interestingly, reported menstrual cramps were also significantly more common during the pandemic and associated with ovulatory disruption.
“That is a new observation because previously we’ve always thought that you needed to ovulate in order to even have cramps,” she commented.
Asked whether COVID-19 itself might have played a role, Dr. Prior said no woman in the study tested positive for the virus or had long COVID.
“As far as I’m aware, it was the changes in employment … and caring for elders and worry about illness in somebody you loved that was related,” she said.
Asked what she thinks the result would be if the study were conducted now, she said: “I don’t know. We’re still in a stressful time with inflation and not complete recovery, so probably the issue is still very present.”
Dr. Prior and Dr. Neal-Perry have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ATLANTA – Disturbances in ovulation that didn’t produce any actual changes in the menstrual cycle of women were extremely common during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic and were linked to emotional stress, according to the findings of an “experiment of nature” that allowed for comparison with women a decade earlier.
Findings from two studies of reproductive-age women, one conducted in 2006-2008 and the other in 2020-2021, were presented by Jerilynn C. Prior, MD, at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
The comparison of the two time periods yielded several novel findings. “I was taught in medical school that when women don’t eat enough they lose their period. But what we now understand is there’s a graded response to various stressors, acting through the hypothalamus in a common pathway. There is a gradation of disturbances, some of which are subclinical or not obvious,” said Dr. Prior, professor of endocrinology and metabolism at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver.
Moreover, women’s menstrual cycle lengths didn’t differ across the two time periods, despite a dramatic 63% decrement in normal ovulatory function related to increased depression, anxiety, and outside stresses that the women reported in diaries.
“Assuming that regular cycles need normal ovulation is something we should just get out of our minds. It changes our concept about what’s normal if we only know about the cycle length,” she observed.
It will be critical going forward to see whether the ovulatory disturbances have resolved as the pandemic has shifted “because there’s strong evidence that ovulatory disturbances, even with normal cycle length, are related to bone loss and some evidence it’s related to early heart attacks, breast and endometrial cancers,” Dr. Prior said during a press conference.
Asked to comment, session moderator Genevieve Neal-Perry, MD, PhD, told this news organization: “I think what we can take away is that stress itself is a modifier of the way the brain and the gonads communicate with each other, and that then has an impact on ovulatory function.”
Dr. Neal-Perry noted that the association of stress and ovulatory disruption has been reported in various ways previously, but “clearly it doesn’t affect everyone. What we don’t know is who is most susceptible. There have been some studies showing a genetic predisposition and a genetic anomaly that actually makes them more susceptible to the impact of stress on the reproductive system.”
But the lack of data on weight change in the study cohorts is a limitation. “To me one of the more important questions was what was going on with weight. Just looking at a static number doesn’t tell you whether there were changes. We know that weight gain or weight loss can stress the reproductive axis,” noted Dr. Neal-Parry of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
‘Experiment of nature’ revealed invisible effect of pandemic stress
The women in both cohorts of the Menstruation Ovulation Study (MOS) were healthy volunteers aged 19-35 years recruited from the metropolitan Vancouver region. All were menstruating monthly and none were taking hormonal birth control. Recruitment for the second cohort had begun just prior to the March 2020 COVID-19 pandemic lockdown.
Interviewer-administered questionnaires (CaMos) covering demographics, socioeconomic status, and reproductive history, and daily diaries kept by the women (menstrual cycle diary) were identical for both cohorts.
Assessments of ovulation differed for the two studies but were cross-validated. For the earlier time period, ovulation was assessed by a threefold increase in follicular-to-luteal urinary progesterone (PdG). For the pandemic-era study, the validated quantitative basal temperature (QBT) method was used.
There were 301 women in the earlier cohort and 125 during the pandemic. Both were an average age of about 29 years and had a body mass index of about 24.3 kg/m2 (within the normal range). The pandemic cohort was more racially/ethnically diverse than the earlier one and more in-line with recent census data.
More of the women were nulliparous during the pandemic than earlier (92.7% vs. 80.4%; P = .002).
The distribution of menstrual cycle lengths didn’t differ, with both cohorts averaging about 30 days (P = .893). However, while 90% of the women in the earlier cohort ovulated normally, only 37% did during the pandemic, a highly significant difference (P < .0001).
Thus, during the pandemic, 63% of women had “silent ovulatory disturbances,” either with short luteal phases after ovulation or no ovulation, compared with just 10% in the earlier cohort, “which is remarkable, unbelievable actually,” Dr. Prior remarked.
The difference wasn’t explained by any of the demographic information collected either, including socioeconomic status, lifestyle, or reproductive history variables.
And it wasn’t because of COVID-19 vaccination, as the vaccine wasn’t available when most of the women were recruited, and of the 79 who were recruited during vaccine availability, only two received a COVID-19 vaccine during the study (and both had normal ovulation).
Employment changes, caring responsibilities, and worry likely causes
The information from the diaries was more revealing. Several diary components were far more common during the pandemic, including negative mood (feeling depressed or anxious, sleep problems, and outside stresses), self-worth, interest in sex, energy level, and appetite. All were significantly different between the two cohorts (P < .001) and between those with and without ovulatory disturbances.
“So menstrual cycle lengths and long cycles didn’t differ, but there was a much higher prevalence of silent or subclinical ovulatory disturbances, and these were related to the increased stresses that women recorded in their diaries. This means that the estrogen levels were pretty close to normal but the progesterone levels were remarkably decreased,” Dr. Prior said.
Interestingly, reported menstrual cramps were also significantly more common during the pandemic and associated with ovulatory disruption.
“That is a new observation because previously we’ve always thought that you needed to ovulate in order to even have cramps,” she commented.
Asked whether COVID-19 itself might have played a role, Dr. Prior said no woman in the study tested positive for the virus or had long COVID.
“As far as I’m aware, it was the changes in employment … and caring for elders and worry about illness in somebody you loved that was related,” she said.
Asked what she thinks the result would be if the study were conducted now, she said: “I don’t know. We’re still in a stressful time with inflation and not complete recovery, so probably the issue is still very present.”
Dr. Prior and Dr. Neal-Perry have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ATLANTA – Disturbances in ovulation that didn’t produce any actual changes in the menstrual cycle of women were extremely common during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic and were linked to emotional stress, according to the findings of an “experiment of nature” that allowed for comparison with women a decade earlier.
Findings from two studies of reproductive-age women, one conducted in 2006-2008 and the other in 2020-2021, were presented by Jerilynn C. Prior, MD, at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
The comparison of the two time periods yielded several novel findings. “I was taught in medical school that when women don’t eat enough they lose their period. But what we now understand is there’s a graded response to various stressors, acting through the hypothalamus in a common pathway. There is a gradation of disturbances, some of which are subclinical or not obvious,” said Dr. Prior, professor of endocrinology and metabolism at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver.
Moreover, women’s menstrual cycle lengths didn’t differ across the two time periods, despite a dramatic 63% decrement in normal ovulatory function related to increased depression, anxiety, and outside stresses that the women reported in diaries.
“Assuming that regular cycles need normal ovulation is something we should just get out of our minds. It changes our concept about what’s normal if we only know about the cycle length,” she observed.
It will be critical going forward to see whether the ovulatory disturbances have resolved as the pandemic has shifted “because there’s strong evidence that ovulatory disturbances, even with normal cycle length, are related to bone loss and some evidence it’s related to early heart attacks, breast and endometrial cancers,” Dr. Prior said during a press conference.
Asked to comment, session moderator Genevieve Neal-Perry, MD, PhD, told this news organization: “I think what we can take away is that stress itself is a modifier of the way the brain and the gonads communicate with each other, and that then has an impact on ovulatory function.”
Dr. Neal-Perry noted that the association of stress and ovulatory disruption has been reported in various ways previously, but “clearly it doesn’t affect everyone. What we don’t know is who is most susceptible. There have been some studies showing a genetic predisposition and a genetic anomaly that actually makes them more susceptible to the impact of stress on the reproductive system.”
But the lack of data on weight change in the study cohorts is a limitation. “To me one of the more important questions was what was going on with weight. Just looking at a static number doesn’t tell you whether there were changes. We know that weight gain or weight loss can stress the reproductive axis,” noted Dr. Neal-Parry of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
‘Experiment of nature’ revealed invisible effect of pandemic stress
The women in both cohorts of the Menstruation Ovulation Study (MOS) were healthy volunteers aged 19-35 years recruited from the metropolitan Vancouver region. All were menstruating monthly and none were taking hormonal birth control. Recruitment for the second cohort had begun just prior to the March 2020 COVID-19 pandemic lockdown.
Interviewer-administered questionnaires (CaMos) covering demographics, socioeconomic status, and reproductive history, and daily diaries kept by the women (menstrual cycle diary) were identical for both cohorts.
Assessments of ovulation differed for the two studies but were cross-validated. For the earlier time period, ovulation was assessed by a threefold increase in follicular-to-luteal urinary progesterone (PdG). For the pandemic-era study, the validated quantitative basal temperature (QBT) method was used.
There were 301 women in the earlier cohort and 125 during the pandemic. Both were an average age of about 29 years and had a body mass index of about 24.3 kg/m2 (within the normal range). The pandemic cohort was more racially/ethnically diverse than the earlier one and more in-line with recent census data.
More of the women were nulliparous during the pandemic than earlier (92.7% vs. 80.4%; P = .002).
The distribution of menstrual cycle lengths didn’t differ, with both cohorts averaging about 30 days (P = .893). However, while 90% of the women in the earlier cohort ovulated normally, only 37% did during the pandemic, a highly significant difference (P < .0001).
Thus, during the pandemic, 63% of women had “silent ovulatory disturbances,” either with short luteal phases after ovulation or no ovulation, compared with just 10% in the earlier cohort, “which is remarkable, unbelievable actually,” Dr. Prior remarked.
The difference wasn’t explained by any of the demographic information collected either, including socioeconomic status, lifestyle, or reproductive history variables.
And it wasn’t because of COVID-19 vaccination, as the vaccine wasn’t available when most of the women were recruited, and of the 79 who were recruited during vaccine availability, only two received a COVID-19 vaccine during the study (and both had normal ovulation).
Employment changes, caring responsibilities, and worry likely causes
The information from the diaries was more revealing. Several diary components were far more common during the pandemic, including negative mood (feeling depressed or anxious, sleep problems, and outside stresses), self-worth, interest in sex, energy level, and appetite. All were significantly different between the two cohorts (P < .001) and between those with and without ovulatory disturbances.
“So menstrual cycle lengths and long cycles didn’t differ, but there was a much higher prevalence of silent or subclinical ovulatory disturbances, and these were related to the increased stresses that women recorded in their diaries. This means that the estrogen levels were pretty close to normal but the progesterone levels were remarkably decreased,” Dr. Prior said.
Interestingly, reported menstrual cramps were also significantly more common during the pandemic and associated with ovulatory disruption.
“That is a new observation because previously we’ve always thought that you needed to ovulate in order to even have cramps,” she commented.
Asked whether COVID-19 itself might have played a role, Dr. Prior said no woman in the study tested positive for the virus or had long COVID.
“As far as I’m aware, it was the changes in employment … and caring for elders and worry about illness in somebody you loved that was related,” she said.
Asked what she thinks the result would be if the study were conducted now, she said: “I don’t know. We’re still in a stressful time with inflation and not complete recovery, so probably the issue is still very present.”
Dr. Prior and Dr. Neal-Perry have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ENDO 2022
HPV vaccination with Cervarix ‘unmasks’ cervical lesions from non-vax strains
Vaccines against human papillomavirus have been hailed as a success: they have been shown to decrease the incidence of cervical lesions associated with the HPV types that are in the vaccine.
However,
An expert not involved in the research said the new data “tell us to be a little bit careful.” Although the HPV types not included in the vaccine are rarer and less aggressive, they can still cause cancer.
The data come from the Costa Rica HPV Vaccine Trial, which involved more than 10,000 women aged 18-25 years. The HPV vaccine used in the trial was Cervarix, from GlaxoSmithKline. It covers the two leading causes of cervical cancer, HPV-16 and -18, and provides partial protection against three other genotypes.
After a follow-up of 11 years, among vaccinated women, there was an excess of precancerous cervical lesions caused by genotypes not included in the vaccine, resulting in negative vaccine efficacy for those HPV variants.
The increase wasn’t enough to offset the overall benefit of vaccination when all genotypes were considered, said the researchers, led by Jaimie Shing, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md.
Vaccinated women “still had long-term absolute reductions in high-grade lesions,” they pointed out.
The net protection “remained considerable, emphasizing the importance of HPV vaccination for cervical cancer prevention,” the team concluded.
The findings were published online in The Lancet Oncology.
The results are likely the first evidence to date of “clinical unmasking” with HPV vaccination, meaning that protection against the strains covered by the vaccine leaves women more prone to attack from other carcinogenic HPV variants.
This phenomenon “could attenuate long-term reductions in high-grade disease following successful implementation of HPV vaccination programs,” the investigators commented.
Highlighting a need for caution
The take-home message from the trial is that “we have to be careful,” said Marc Steben, MD, co-President of HPV Global Action and a professor at the University of Montreal.
He noted that the Cervarix HPV vaccine used in the trial is not the vaccine that is used now in developed nations.
The current standard HPV vaccine is Gardasil 9 (Merck), which offers broader coverage against nine HPV types (types 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, and 58).
There are 12 main carcinogenic HPV genotypes, so unmasking of other strains is still possible with Gardasil 9, he said.
There is another issue, Dr. Steben added. The success of HPV vaccinations - a nearly 90% reduction in invasive cervical cancer in women who are vaccinated at a young age – has led to questions about the future role of routine cervical cancer screening.
“Some people are saying that if we achieve 90% coverage, we might” eliminate community transmission and no longer need to screen, he said.
These trial results “tell us to be a little bit careful,” Dr. Steben continued. Those HPV types that are less aggressive and rarer than HPV-16 and -18 “can still cause cancer and might be there and surprise us. It could take more time than we thought” to get to the point where screening can be eliminated.
“There might be a little problem if we stop too early,” he said.
Study details
During the period 2004-2005, the investigators randomly assigned 3,727 women aged 18-25 years to receive Cervarix and 3,739 to a control group that received the hepatitis A vaccine; after 4 years, the control group also received Cervarix and exited the study. They were replaced by an unvaccinated control group of 2,836 women. The new control group and the original HPV vaccine group were followed for an additional 7 years.
In years 7-11 of the trial, the investigators found 9.2 additional cervical intraepithelial neoplasias of grade 2 or worse (CIN2+) from HPV types not covered by Cervarix per 1,000 vaccinated women in comparison with unvaccinated participants. This corresponds to –71.2% negative vaccine efficacy against CIN2+ lesions of HPV types not covered by the vaccine.
There were 8.3 additional CIN3+ lesions from nontargeted HPV strains per 1,000 vaccinated women in comparison with unvaccinated participants, which corresponds to –135% negative vaccine efficacy.
Overall, however, there was a net benefit of vaccination, with 27 fewer CIN2+ lesions when all HPV genotypes – vaccine covered or not – were considered per 1,000 vaccinated women over the entire 11 years of follow-up.
There were also 8.7 fewer CIN3+ lesions across all genotypes per 1,000 vaccinated women, but the benefit was not statistically significant.
Among the study limits, the team was unable to evaluate the effect of clinical unmasking on cervical cancer, because women were treated for high-grade cervical lesions before cases could progress to cervical cancer.
The trial was funded by the National Cancer Institute and the National Institutes of Health Office of Research on Women’s Health. GlaxoSmithKline provided the Cervarix vaccine and supported aspects of the trial. Two authors are named inventors on U.S. government–owned HPV vaccine patents with expired licenses to GlaxoSmithKline and Merck. Dr. Steben is an adviser/speaker for many companies, including GlaxoSmithKline and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vaccines against human papillomavirus have been hailed as a success: they have been shown to decrease the incidence of cervical lesions associated with the HPV types that are in the vaccine.
However,
An expert not involved in the research said the new data “tell us to be a little bit careful.” Although the HPV types not included in the vaccine are rarer and less aggressive, they can still cause cancer.
The data come from the Costa Rica HPV Vaccine Trial, which involved more than 10,000 women aged 18-25 years. The HPV vaccine used in the trial was Cervarix, from GlaxoSmithKline. It covers the two leading causes of cervical cancer, HPV-16 and -18, and provides partial protection against three other genotypes.
After a follow-up of 11 years, among vaccinated women, there was an excess of precancerous cervical lesions caused by genotypes not included in the vaccine, resulting in negative vaccine efficacy for those HPV variants.
The increase wasn’t enough to offset the overall benefit of vaccination when all genotypes were considered, said the researchers, led by Jaimie Shing, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md.
Vaccinated women “still had long-term absolute reductions in high-grade lesions,” they pointed out.
The net protection “remained considerable, emphasizing the importance of HPV vaccination for cervical cancer prevention,” the team concluded.
The findings were published online in The Lancet Oncology.
The results are likely the first evidence to date of “clinical unmasking” with HPV vaccination, meaning that protection against the strains covered by the vaccine leaves women more prone to attack from other carcinogenic HPV variants.
This phenomenon “could attenuate long-term reductions in high-grade disease following successful implementation of HPV vaccination programs,” the investigators commented.
Highlighting a need for caution
The take-home message from the trial is that “we have to be careful,” said Marc Steben, MD, co-President of HPV Global Action and a professor at the University of Montreal.
He noted that the Cervarix HPV vaccine used in the trial is not the vaccine that is used now in developed nations.
The current standard HPV vaccine is Gardasil 9 (Merck), which offers broader coverage against nine HPV types (types 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, and 58).
There are 12 main carcinogenic HPV genotypes, so unmasking of other strains is still possible with Gardasil 9, he said.
There is another issue, Dr. Steben added. The success of HPV vaccinations - a nearly 90% reduction in invasive cervical cancer in women who are vaccinated at a young age – has led to questions about the future role of routine cervical cancer screening.
“Some people are saying that if we achieve 90% coverage, we might” eliminate community transmission and no longer need to screen, he said.
These trial results “tell us to be a little bit careful,” Dr. Steben continued. Those HPV types that are less aggressive and rarer than HPV-16 and -18 “can still cause cancer and might be there and surprise us. It could take more time than we thought” to get to the point where screening can be eliminated.
“There might be a little problem if we stop too early,” he said.
Study details
During the period 2004-2005, the investigators randomly assigned 3,727 women aged 18-25 years to receive Cervarix and 3,739 to a control group that received the hepatitis A vaccine; after 4 years, the control group also received Cervarix and exited the study. They were replaced by an unvaccinated control group of 2,836 women. The new control group and the original HPV vaccine group were followed for an additional 7 years.
In years 7-11 of the trial, the investigators found 9.2 additional cervical intraepithelial neoplasias of grade 2 or worse (CIN2+) from HPV types not covered by Cervarix per 1,000 vaccinated women in comparison with unvaccinated participants. This corresponds to –71.2% negative vaccine efficacy against CIN2+ lesions of HPV types not covered by the vaccine.
There were 8.3 additional CIN3+ lesions from nontargeted HPV strains per 1,000 vaccinated women in comparison with unvaccinated participants, which corresponds to –135% negative vaccine efficacy.
Overall, however, there was a net benefit of vaccination, with 27 fewer CIN2+ lesions when all HPV genotypes – vaccine covered or not – were considered per 1,000 vaccinated women over the entire 11 years of follow-up.
There were also 8.7 fewer CIN3+ lesions across all genotypes per 1,000 vaccinated women, but the benefit was not statistically significant.
Among the study limits, the team was unable to evaluate the effect of clinical unmasking on cervical cancer, because women were treated for high-grade cervical lesions before cases could progress to cervical cancer.
The trial was funded by the National Cancer Institute and the National Institutes of Health Office of Research on Women’s Health. GlaxoSmithKline provided the Cervarix vaccine and supported aspects of the trial. Two authors are named inventors on U.S. government–owned HPV vaccine patents with expired licenses to GlaxoSmithKline and Merck. Dr. Steben is an adviser/speaker for many companies, including GlaxoSmithKline and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vaccines against human papillomavirus have been hailed as a success: they have been shown to decrease the incidence of cervical lesions associated with the HPV types that are in the vaccine.
However,
An expert not involved in the research said the new data “tell us to be a little bit careful.” Although the HPV types not included in the vaccine are rarer and less aggressive, they can still cause cancer.
The data come from the Costa Rica HPV Vaccine Trial, which involved more than 10,000 women aged 18-25 years. The HPV vaccine used in the trial was Cervarix, from GlaxoSmithKline. It covers the two leading causes of cervical cancer, HPV-16 and -18, and provides partial protection against three other genotypes.
After a follow-up of 11 years, among vaccinated women, there was an excess of precancerous cervical lesions caused by genotypes not included in the vaccine, resulting in negative vaccine efficacy for those HPV variants.
The increase wasn’t enough to offset the overall benefit of vaccination when all genotypes were considered, said the researchers, led by Jaimie Shing, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md.
Vaccinated women “still had long-term absolute reductions in high-grade lesions,” they pointed out.
The net protection “remained considerable, emphasizing the importance of HPV vaccination for cervical cancer prevention,” the team concluded.
The findings were published online in The Lancet Oncology.
The results are likely the first evidence to date of “clinical unmasking” with HPV vaccination, meaning that protection against the strains covered by the vaccine leaves women more prone to attack from other carcinogenic HPV variants.
This phenomenon “could attenuate long-term reductions in high-grade disease following successful implementation of HPV vaccination programs,” the investigators commented.
Highlighting a need for caution
The take-home message from the trial is that “we have to be careful,” said Marc Steben, MD, co-President of HPV Global Action and a professor at the University of Montreal.
He noted that the Cervarix HPV vaccine used in the trial is not the vaccine that is used now in developed nations.
The current standard HPV vaccine is Gardasil 9 (Merck), which offers broader coverage against nine HPV types (types 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, and 58).
There are 12 main carcinogenic HPV genotypes, so unmasking of other strains is still possible with Gardasil 9, he said.
There is another issue, Dr. Steben added. The success of HPV vaccinations - a nearly 90% reduction in invasive cervical cancer in women who are vaccinated at a young age – has led to questions about the future role of routine cervical cancer screening.
“Some people are saying that if we achieve 90% coverage, we might” eliminate community transmission and no longer need to screen, he said.
These trial results “tell us to be a little bit careful,” Dr. Steben continued. Those HPV types that are less aggressive and rarer than HPV-16 and -18 “can still cause cancer and might be there and surprise us. It could take more time than we thought” to get to the point where screening can be eliminated.
“There might be a little problem if we stop too early,” he said.
Study details
During the period 2004-2005, the investigators randomly assigned 3,727 women aged 18-25 years to receive Cervarix and 3,739 to a control group that received the hepatitis A vaccine; after 4 years, the control group also received Cervarix and exited the study. They were replaced by an unvaccinated control group of 2,836 women. The new control group and the original HPV vaccine group were followed for an additional 7 years.
In years 7-11 of the trial, the investigators found 9.2 additional cervical intraepithelial neoplasias of grade 2 or worse (CIN2+) from HPV types not covered by Cervarix per 1,000 vaccinated women in comparison with unvaccinated participants. This corresponds to –71.2% negative vaccine efficacy against CIN2+ lesions of HPV types not covered by the vaccine.
There were 8.3 additional CIN3+ lesions from nontargeted HPV strains per 1,000 vaccinated women in comparison with unvaccinated participants, which corresponds to –135% negative vaccine efficacy.
Overall, however, there was a net benefit of vaccination, with 27 fewer CIN2+ lesions when all HPV genotypes – vaccine covered or not – were considered per 1,000 vaccinated women over the entire 11 years of follow-up.
There were also 8.7 fewer CIN3+ lesions across all genotypes per 1,000 vaccinated women, but the benefit was not statistically significant.
Among the study limits, the team was unable to evaluate the effect of clinical unmasking on cervical cancer, because women were treated for high-grade cervical lesions before cases could progress to cervical cancer.
The trial was funded by the National Cancer Institute and the National Institutes of Health Office of Research on Women’s Health. GlaxoSmithKline provided the Cervarix vaccine and supported aspects of the trial. Two authors are named inventors on U.S. government–owned HPV vaccine patents with expired licenses to GlaxoSmithKline and Merck. Dr. Steben is an adviser/speaker for many companies, including GlaxoSmithKline and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET ONCOLOGY