User login
Early, subtle, cardiac changes tied to midlife cognitive decline
new research suggests.
Cardiovascular disease risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes have been associated with an increased risk for cognitive impairment, but much less is known about heart structure and function and the risks for cognition.
“We showed for the first time that, even before the occurrence of cardiovascular disease, people with abnormalities in cardiac structure and function as early as in young adulthood have lower midlife cognition,” investigators Laure Rouch, PharmD, PhD, and Kristine Yaffe, MD, both with the department of psychiatry, University of California, San Francisco, said in a joint email.
“This study reminds us that heart health is key to brain health and that the overlap and interplay between the two is not limited to patients with end-stage heart disease,” Dr. Rouch and Dr. Yaffe said.
The findings were published online Jan. 26, 2022, in Neurology.
Heart/brain connection
The analysis included 2,653 participants in the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) study.
Echocardiograms were obtained at year 5, 25, and 30 study visits – at mean ages of 30, 50, and 55 years, respectively. At year 30, participants underwent a standard battery of tests measuring global cognition, processing speed, executive function, delayed verbal memory, and verbal fluency.
Over 25 years, there was an average increase in left ventricular mass of 0.27 g/m2 per year – from a mean of 80.5 g/m2 in year 5 to 86.0 g/m2 in year 30.
Left atrial volume increased by an average of 0.42 mL/m2 per year, from 16 mL/m2 in year 5 to 26 mL/m2 in year 30.
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) decreased by 0.11% per year, from 63.3% in year 5 to 59.7% in year 30.
After adjustment for demographics and education, an increase in left ventricular mass of at least 1 standard deviation over 25 years was associated with lower cognition on most tests (P ≤ .02).
An increase in left atrial volume over the study period was associated with lower global cognition (P = .04), whereas a decrease in LVEF was not associated with cognition. Further adjustment for cardiovascular risk factors yielded similar results.
“A more effective collaboration is needed between cardiologists and neurologists to promote healthy brain aging,” Dr. Rouch and Dr. Yaffe said.
“Echocardiography is a widely available, relatively inexpensive, and noninvasive imaging method that could be integrated into a risk assessment for cognitive impairment,” they added.
Looking ahead, the investigators noted there is a need for further research to determine whether interventions to improve cardiac structure and diastolic function could also benefit brain health.
They should also investigate the role of arterial stiffness and cerebral small vessel disease in the relationship between cardiac structure, function, and cognition, the researchers added.
First structural biomarker
Commenting on the study, Shaheen E. Lakhan, MD, PhD, a neurologist in Newton, Mass., said the study is important because, “thus far, the connections have really been physiological parameters,” such as blood pressure and cognitive health.
“This is really strong evidence of a structural cardiac biomarker that can be measured before and independent of changes in physiology or diseased state,” said Dr. Lakhan, who was not involved with the research.
As more and more interventions are being introduced for addressing disorders of cognition, “this potential structural finding may serve as a solid biomarker to determine” what lifestyle or drug therapy should be taken, he added.
Also weighing in on the findings, Pierre Fayad, MD, professor in the department of neurological sciences and director of the Nebraska Stroke Center, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, said CARDIA is “an important study” providing “precious data.”
The reported changes in cardiac structure and function “precede the clinical symptomatology, as the follow-up stops before they enter into later adulthood, where the risk of clinical events dramatically rises. Meaning these patients still have not had stroke, congestive heart failure, heart attack or dementia, but some of them could be on that trajectory later in their life,” Dr. Fayad told this news organization.
Documenting such changes over time is “valuable to give an insight into what leads us to such progression,” he noted.
How reliably predictive the findings are for eventual clinical cognitive impairment “will need to be confirmed and verified” in future studies, he added.
“If verified, it could be helpful to provide interventions to those with the left atrial volume enlargement marker and see their effectiveness at preventing eventual clinical cognitive impairment,” said Dr. Fayad.
The CARDIA study is supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute in collaboration with the University of Alabama at Birmingham, Northwestern University, the University of Minnesota, and the Kaiser Foundation Research Institute. Rouch, Lakhan, and Dr. Fayad have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Cardiovascular disease risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes have been associated with an increased risk for cognitive impairment, but much less is known about heart structure and function and the risks for cognition.
“We showed for the first time that, even before the occurrence of cardiovascular disease, people with abnormalities in cardiac structure and function as early as in young adulthood have lower midlife cognition,” investigators Laure Rouch, PharmD, PhD, and Kristine Yaffe, MD, both with the department of psychiatry, University of California, San Francisco, said in a joint email.
“This study reminds us that heart health is key to brain health and that the overlap and interplay between the two is not limited to patients with end-stage heart disease,” Dr. Rouch and Dr. Yaffe said.
The findings were published online Jan. 26, 2022, in Neurology.
Heart/brain connection
The analysis included 2,653 participants in the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) study.
Echocardiograms were obtained at year 5, 25, and 30 study visits – at mean ages of 30, 50, and 55 years, respectively. At year 30, participants underwent a standard battery of tests measuring global cognition, processing speed, executive function, delayed verbal memory, and verbal fluency.
Over 25 years, there was an average increase in left ventricular mass of 0.27 g/m2 per year – from a mean of 80.5 g/m2 in year 5 to 86.0 g/m2 in year 30.
Left atrial volume increased by an average of 0.42 mL/m2 per year, from 16 mL/m2 in year 5 to 26 mL/m2 in year 30.
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) decreased by 0.11% per year, from 63.3% in year 5 to 59.7% in year 30.
After adjustment for demographics and education, an increase in left ventricular mass of at least 1 standard deviation over 25 years was associated with lower cognition on most tests (P ≤ .02).
An increase in left atrial volume over the study period was associated with lower global cognition (P = .04), whereas a decrease in LVEF was not associated with cognition. Further adjustment for cardiovascular risk factors yielded similar results.
“A more effective collaboration is needed between cardiologists and neurologists to promote healthy brain aging,” Dr. Rouch and Dr. Yaffe said.
“Echocardiography is a widely available, relatively inexpensive, and noninvasive imaging method that could be integrated into a risk assessment for cognitive impairment,” they added.
Looking ahead, the investigators noted there is a need for further research to determine whether interventions to improve cardiac structure and diastolic function could also benefit brain health.
They should also investigate the role of arterial stiffness and cerebral small vessel disease in the relationship between cardiac structure, function, and cognition, the researchers added.
First structural biomarker
Commenting on the study, Shaheen E. Lakhan, MD, PhD, a neurologist in Newton, Mass., said the study is important because, “thus far, the connections have really been physiological parameters,” such as blood pressure and cognitive health.
“This is really strong evidence of a structural cardiac biomarker that can be measured before and independent of changes in physiology or diseased state,” said Dr. Lakhan, who was not involved with the research.
As more and more interventions are being introduced for addressing disorders of cognition, “this potential structural finding may serve as a solid biomarker to determine” what lifestyle or drug therapy should be taken, he added.
Also weighing in on the findings, Pierre Fayad, MD, professor in the department of neurological sciences and director of the Nebraska Stroke Center, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, said CARDIA is “an important study” providing “precious data.”
The reported changes in cardiac structure and function “precede the clinical symptomatology, as the follow-up stops before they enter into later adulthood, where the risk of clinical events dramatically rises. Meaning these patients still have not had stroke, congestive heart failure, heart attack or dementia, but some of them could be on that trajectory later in their life,” Dr. Fayad told this news organization.
Documenting such changes over time is “valuable to give an insight into what leads us to such progression,” he noted.
How reliably predictive the findings are for eventual clinical cognitive impairment “will need to be confirmed and verified” in future studies, he added.
“If verified, it could be helpful to provide interventions to those with the left atrial volume enlargement marker and see their effectiveness at preventing eventual clinical cognitive impairment,” said Dr. Fayad.
The CARDIA study is supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute in collaboration with the University of Alabama at Birmingham, Northwestern University, the University of Minnesota, and the Kaiser Foundation Research Institute. Rouch, Lakhan, and Dr. Fayad have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Cardiovascular disease risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes have been associated with an increased risk for cognitive impairment, but much less is known about heart structure and function and the risks for cognition.
“We showed for the first time that, even before the occurrence of cardiovascular disease, people with abnormalities in cardiac structure and function as early as in young adulthood have lower midlife cognition,” investigators Laure Rouch, PharmD, PhD, and Kristine Yaffe, MD, both with the department of psychiatry, University of California, San Francisco, said in a joint email.
“This study reminds us that heart health is key to brain health and that the overlap and interplay between the two is not limited to patients with end-stage heart disease,” Dr. Rouch and Dr. Yaffe said.
The findings were published online Jan. 26, 2022, in Neurology.
Heart/brain connection
The analysis included 2,653 participants in the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) study.
Echocardiograms were obtained at year 5, 25, and 30 study visits – at mean ages of 30, 50, and 55 years, respectively. At year 30, participants underwent a standard battery of tests measuring global cognition, processing speed, executive function, delayed verbal memory, and verbal fluency.
Over 25 years, there was an average increase in left ventricular mass of 0.27 g/m2 per year – from a mean of 80.5 g/m2 in year 5 to 86.0 g/m2 in year 30.
Left atrial volume increased by an average of 0.42 mL/m2 per year, from 16 mL/m2 in year 5 to 26 mL/m2 in year 30.
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) decreased by 0.11% per year, from 63.3% in year 5 to 59.7% in year 30.
After adjustment for demographics and education, an increase in left ventricular mass of at least 1 standard deviation over 25 years was associated with lower cognition on most tests (P ≤ .02).
An increase in left atrial volume over the study period was associated with lower global cognition (P = .04), whereas a decrease in LVEF was not associated with cognition. Further adjustment for cardiovascular risk factors yielded similar results.
“A more effective collaboration is needed between cardiologists and neurologists to promote healthy brain aging,” Dr. Rouch and Dr. Yaffe said.
“Echocardiography is a widely available, relatively inexpensive, and noninvasive imaging method that could be integrated into a risk assessment for cognitive impairment,” they added.
Looking ahead, the investigators noted there is a need for further research to determine whether interventions to improve cardiac structure and diastolic function could also benefit brain health.
They should also investigate the role of arterial stiffness and cerebral small vessel disease in the relationship between cardiac structure, function, and cognition, the researchers added.
First structural biomarker
Commenting on the study, Shaheen E. Lakhan, MD, PhD, a neurologist in Newton, Mass., said the study is important because, “thus far, the connections have really been physiological parameters,” such as blood pressure and cognitive health.
“This is really strong evidence of a structural cardiac biomarker that can be measured before and independent of changes in physiology or diseased state,” said Dr. Lakhan, who was not involved with the research.
As more and more interventions are being introduced for addressing disorders of cognition, “this potential structural finding may serve as a solid biomarker to determine” what lifestyle or drug therapy should be taken, he added.
Also weighing in on the findings, Pierre Fayad, MD, professor in the department of neurological sciences and director of the Nebraska Stroke Center, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, said CARDIA is “an important study” providing “precious data.”
The reported changes in cardiac structure and function “precede the clinical symptomatology, as the follow-up stops before they enter into later adulthood, where the risk of clinical events dramatically rises. Meaning these patients still have not had stroke, congestive heart failure, heart attack or dementia, but some of them could be on that trajectory later in their life,” Dr. Fayad told this news organization.
Documenting such changes over time is “valuable to give an insight into what leads us to such progression,” he noted.
How reliably predictive the findings are for eventual clinical cognitive impairment “will need to be confirmed and verified” in future studies, he added.
“If verified, it could be helpful to provide interventions to those with the left atrial volume enlargement marker and see their effectiveness at preventing eventual clinical cognitive impairment,” said Dr. Fayad.
The CARDIA study is supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute in collaboration with the University of Alabama at Birmingham, Northwestern University, the University of Minnesota, and the Kaiser Foundation Research Institute. Rouch, Lakhan, and Dr. Fayad have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Unraveling plaque changes in CAD With elevated Lp(a)
New research suggests serial coronary CT angiography (CCTA) can provide novel insights into the association between lipoprotein(a) and plaque progression over time in patients with advanced coronary artery disease.
Researchers examined data from 191 individuals with multivessel coronary disease receiving preventive statin (95%) and antiplatelet (100%) therapy in the single-center Scottish DIAMOND trial and compared CCTA at baseline and 12 months available for 160 patients.
As reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, patients with high Lp(a), defined as at least 70 mg/dL, had higher baseline high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and ASSIGN scores than those with low Lp(a) but had comparable coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores and total, calcific, noncalcific, and low-attenuation plaque (LAP) volumes.
At 1 year, however, LAP volume – a marker for necrotic core – increased by 26.2 mm3 in the high-Lp(a) group and decreased by –0.7 mm3 in the low-Lp(a) group (P = .020).
There was no significant difference in change in total, calcific, and noncalcific plaque volumes between groups.
In multivariate linear regression analysis adjusting for body mass index, ASSIGN score, and segment involvement score, LAP volume increased by 10.5% for each 50 mg/dL increment in Lp(a) (P = .034).
“It’s an exciting observation, because we’ve done previous studies where we’ve demonstrated the association of that particular plaque type with future myocardial infarction,” senior author Marc R. Dweck, MD, PhD, University of Amsterdam, told this news organization. “So, you’ve potentially got an explanation for the adverse prognosis associated with high lipoprotein(a) and its link to cardiovascular events and, in particular, myocardial infarction.”
The team’s recent SCOT-HEART analysis found that LAP burden was a stronger predictor of myocardial infarction (MI) than cardiovascular risk scores, stenosis severity, and CAC scoring, with MI risk nearly five-fold higher if LAP was above 4%.
As to why total, calcific, and noncalcific plaque volumes didn’t change significantly on repeat CCTA in the present study, Dr. Dweck said it’s possible that the sample was too small and follow-up too short but also that “total plaque volume is really dominated by the fibrous plaque, which doesn’t appear affected by Lp(a).” Nevertheless, Lp(a)’s effect on low-attenuation plaque was clearly present and supported by the change in fibro-fatty plaque, the next-most unstable plaque type.
At 1 year, fibro-fatty plaque volume was 55.0 mm3 in the high-Lp(a) group versus –25.0 mm3 in the low-Lp(a) group (P = .020).
Lp(a) was associated with fibro-fatty plaque progression in univariate analysis (β = 6.7%; P = .034) and showed a trend in multivariable analysis (β = 6.0%; P = .062).
“This study shows you can track changes in plaque over time and highlight important disease mechanisms and use them to understand the pathology of the disease,” Dr. Dweck said. “I’m very encouraged by this.”
What’s novel in the present study is that “it represents the beginning of our understanding of the role of Lp(a) in plaque progression,” Sotirios Tsimikas, MD, University of California, San Diego, and Jagat Narula, MD, PhD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, say in an accompanying commentary.
They note that prior studies, including the Dallas Heart Study, have struggled to find a strong association between Lp(a) with the extent or progression of CAC, despite elevated Lp(a) and CAC identifying higher-risk patients.
Similarly, a meta-analysis of intravascular ultrasound trials turned up only a 1.2% absolute difference in atheroma volume in patients with elevated Lp(a), and a recent optical coherence tomography study found an association of Lp(a) with thin-cap fibroatheromas but not lipid core.
With just 36 patients with elevated Lp(a), however, the current findings need validation in a larger data set, Dr. Tsimikas and Dr. Narula say.
Although Lp(a) is genetically elevated in about one in five individuals and measurement is recommended in European dyslipidemia guidelines, testing rates are low, in part because the argument has been that there are no Lp(a)-lowering therapies available, Dr. Dweck observed. That may change with the phase 3 cardiovascular outcomes Lp(a)HORIZON trial, which follows strong phase 2 results with the antisense agent AKCEA-APO(a)-LRx and is enrolling patients similar to the current cohort.
“Ultimately it comes down to that fundamental thing, that you need an action once you’ve done the test and then insurers will be happy to pay for it and clinicians will ask for it. That’s why that trial is so important,” Dr. Dweck said.
Dr. Tsimikas and Dr. Narula also point to the eagerly awaited results of that trial, expected in 2025. “A positive trial is likely to lead to additional trials and new drugs that may reinvigorate the use of imaging modalities that could go beyond plaque volume and atherosclerosis to also predict clinically relevant inflammation and atherothrombosis,” they conclude.
Dr. Dweck is supported by the British Heart Foundation and is the recipient of the Sir Jules Thorn Award for Biomedical Research 2015; has received speaker fees from Pfizer and Novartis; and has received consultancy fees from Novartis, Jupiter Bioventures, and Silence Therapeutics. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the paper. Dr. Tsimikas has a dual appointment at the University of California, San Diego, (UCSD) and Ionis Pharmaceuticals; is a coinventor and receives royalties from patents owned by UCSD; and is a cofounder and has an equity interest in Oxitope and its affiliates, Kleanthi Diagnostics, and Covicept Therapeutics. Dr. Narula reports having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research suggests serial coronary CT angiography (CCTA) can provide novel insights into the association between lipoprotein(a) and plaque progression over time in patients with advanced coronary artery disease.
Researchers examined data from 191 individuals with multivessel coronary disease receiving preventive statin (95%) and antiplatelet (100%) therapy in the single-center Scottish DIAMOND trial and compared CCTA at baseline and 12 months available for 160 patients.
As reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, patients with high Lp(a), defined as at least 70 mg/dL, had higher baseline high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and ASSIGN scores than those with low Lp(a) but had comparable coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores and total, calcific, noncalcific, and low-attenuation plaque (LAP) volumes.
At 1 year, however, LAP volume – a marker for necrotic core – increased by 26.2 mm3 in the high-Lp(a) group and decreased by –0.7 mm3 in the low-Lp(a) group (P = .020).
There was no significant difference in change in total, calcific, and noncalcific plaque volumes between groups.
In multivariate linear regression analysis adjusting for body mass index, ASSIGN score, and segment involvement score, LAP volume increased by 10.5% for each 50 mg/dL increment in Lp(a) (P = .034).
“It’s an exciting observation, because we’ve done previous studies where we’ve demonstrated the association of that particular plaque type with future myocardial infarction,” senior author Marc R. Dweck, MD, PhD, University of Amsterdam, told this news organization. “So, you’ve potentially got an explanation for the adverse prognosis associated with high lipoprotein(a) and its link to cardiovascular events and, in particular, myocardial infarction.”
The team’s recent SCOT-HEART analysis found that LAP burden was a stronger predictor of myocardial infarction (MI) than cardiovascular risk scores, stenosis severity, and CAC scoring, with MI risk nearly five-fold higher if LAP was above 4%.
As to why total, calcific, and noncalcific plaque volumes didn’t change significantly on repeat CCTA in the present study, Dr. Dweck said it’s possible that the sample was too small and follow-up too short but also that “total plaque volume is really dominated by the fibrous plaque, which doesn’t appear affected by Lp(a).” Nevertheless, Lp(a)’s effect on low-attenuation plaque was clearly present and supported by the change in fibro-fatty plaque, the next-most unstable plaque type.
At 1 year, fibro-fatty plaque volume was 55.0 mm3 in the high-Lp(a) group versus –25.0 mm3 in the low-Lp(a) group (P = .020).
Lp(a) was associated with fibro-fatty plaque progression in univariate analysis (β = 6.7%; P = .034) and showed a trend in multivariable analysis (β = 6.0%; P = .062).
“This study shows you can track changes in plaque over time and highlight important disease mechanisms and use them to understand the pathology of the disease,” Dr. Dweck said. “I’m very encouraged by this.”
What’s novel in the present study is that “it represents the beginning of our understanding of the role of Lp(a) in plaque progression,” Sotirios Tsimikas, MD, University of California, San Diego, and Jagat Narula, MD, PhD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, say in an accompanying commentary.
They note that prior studies, including the Dallas Heart Study, have struggled to find a strong association between Lp(a) with the extent or progression of CAC, despite elevated Lp(a) and CAC identifying higher-risk patients.
Similarly, a meta-analysis of intravascular ultrasound trials turned up only a 1.2% absolute difference in atheroma volume in patients with elevated Lp(a), and a recent optical coherence tomography study found an association of Lp(a) with thin-cap fibroatheromas but not lipid core.
With just 36 patients with elevated Lp(a), however, the current findings need validation in a larger data set, Dr. Tsimikas and Dr. Narula say.
Although Lp(a) is genetically elevated in about one in five individuals and measurement is recommended in European dyslipidemia guidelines, testing rates are low, in part because the argument has been that there are no Lp(a)-lowering therapies available, Dr. Dweck observed. That may change with the phase 3 cardiovascular outcomes Lp(a)HORIZON trial, which follows strong phase 2 results with the antisense agent AKCEA-APO(a)-LRx and is enrolling patients similar to the current cohort.
“Ultimately it comes down to that fundamental thing, that you need an action once you’ve done the test and then insurers will be happy to pay for it and clinicians will ask for it. That’s why that trial is so important,” Dr. Dweck said.
Dr. Tsimikas and Dr. Narula also point to the eagerly awaited results of that trial, expected in 2025. “A positive trial is likely to lead to additional trials and new drugs that may reinvigorate the use of imaging modalities that could go beyond plaque volume and atherosclerosis to also predict clinically relevant inflammation and atherothrombosis,” they conclude.
Dr. Dweck is supported by the British Heart Foundation and is the recipient of the Sir Jules Thorn Award for Biomedical Research 2015; has received speaker fees from Pfizer and Novartis; and has received consultancy fees from Novartis, Jupiter Bioventures, and Silence Therapeutics. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the paper. Dr. Tsimikas has a dual appointment at the University of California, San Diego, (UCSD) and Ionis Pharmaceuticals; is a coinventor and receives royalties from patents owned by UCSD; and is a cofounder and has an equity interest in Oxitope and its affiliates, Kleanthi Diagnostics, and Covicept Therapeutics. Dr. Narula reports having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research suggests serial coronary CT angiography (CCTA) can provide novel insights into the association between lipoprotein(a) and plaque progression over time in patients with advanced coronary artery disease.
Researchers examined data from 191 individuals with multivessel coronary disease receiving preventive statin (95%) and antiplatelet (100%) therapy in the single-center Scottish DIAMOND trial and compared CCTA at baseline and 12 months available for 160 patients.
As reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, patients with high Lp(a), defined as at least 70 mg/dL, had higher baseline high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and ASSIGN scores than those with low Lp(a) but had comparable coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores and total, calcific, noncalcific, and low-attenuation plaque (LAP) volumes.
At 1 year, however, LAP volume – a marker for necrotic core – increased by 26.2 mm3 in the high-Lp(a) group and decreased by –0.7 mm3 in the low-Lp(a) group (P = .020).
There was no significant difference in change in total, calcific, and noncalcific plaque volumes between groups.
In multivariate linear regression analysis adjusting for body mass index, ASSIGN score, and segment involvement score, LAP volume increased by 10.5% for each 50 mg/dL increment in Lp(a) (P = .034).
“It’s an exciting observation, because we’ve done previous studies where we’ve demonstrated the association of that particular plaque type with future myocardial infarction,” senior author Marc R. Dweck, MD, PhD, University of Amsterdam, told this news organization. “So, you’ve potentially got an explanation for the adverse prognosis associated with high lipoprotein(a) and its link to cardiovascular events and, in particular, myocardial infarction.”
The team’s recent SCOT-HEART analysis found that LAP burden was a stronger predictor of myocardial infarction (MI) than cardiovascular risk scores, stenosis severity, and CAC scoring, with MI risk nearly five-fold higher if LAP was above 4%.
As to why total, calcific, and noncalcific plaque volumes didn’t change significantly on repeat CCTA in the present study, Dr. Dweck said it’s possible that the sample was too small and follow-up too short but also that “total plaque volume is really dominated by the fibrous plaque, which doesn’t appear affected by Lp(a).” Nevertheless, Lp(a)’s effect on low-attenuation plaque was clearly present and supported by the change in fibro-fatty plaque, the next-most unstable plaque type.
At 1 year, fibro-fatty plaque volume was 55.0 mm3 in the high-Lp(a) group versus –25.0 mm3 in the low-Lp(a) group (P = .020).
Lp(a) was associated with fibro-fatty plaque progression in univariate analysis (β = 6.7%; P = .034) and showed a trend in multivariable analysis (β = 6.0%; P = .062).
“This study shows you can track changes in plaque over time and highlight important disease mechanisms and use them to understand the pathology of the disease,” Dr. Dweck said. “I’m very encouraged by this.”
What’s novel in the present study is that “it represents the beginning of our understanding of the role of Lp(a) in plaque progression,” Sotirios Tsimikas, MD, University of California, San Diego, and Jagat Narula, MD, PhD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, say in an accompanying commentary.
They note that prior studies, including the Dallas Heart Study, have struggled to find a strong association between Lp(a) with the extent or progression of CAC, despite elevated Lp(a) and CAC identifying higher-risk patients.
Similarly, a meta-analysis of intravascular ultrasound trials turned up only a 1.2% absolute difference in atheroma volume in patients with elevated Lp(a), and a recent optical coherence tomography study found an association of Lp(a) with thin-cap fibroatheromas but not lipid core.
With just 36 patients with elevated Lp(a), however, the current findings need validation in a larger data set, Dr. Tsimikas and Dr. Narula say.
Although Lp(a) is genetically elevated in about one in five individuals and measurement is recommended in European dyslipidemia guidelines, testing rates are low, in part because the argument has been that there are no Lp(a)-lowering therapies available, Dr. Dweck observed. That may change with the phase 3 cardiovascular outcomes Lp(a)HORIZON trial, which follows strong phase 2 results with the antisense agent AKCEA-APO(a)-LRx and is enrolling patients similar to the current cohort.
“Ultimately it comes down to that fundamental thing, that you need an action once you’ve done the test and then insurers will be happy to pay for it and clinicians will ask for it. That’s why that trial is so important,” Dr. Dweck said.
Dr. Tsimikas and Dr. Narula also point to the eagerly awaited results of that trial, expected in 2025. “A positive trial is likely to lead to additional trials and new drugs that may reinvigorate the use of imaging modalities that could go beyond plaque volume and atherosclerosis to also predict clinically relevant inflammation and atherothrombosis,” they conclude.
Dr. Dweck is supported by the British Heart Foundation and is the recipient of the Sir Jules Thorn Award for Biomedical Research 2015; has received speaker fees from Pfizer and Novartis; and has received consultancy fees from Novartis, Jupiter Bioventures, and Silence Therapeutics. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the paper. Dr. Tsimikas has a dual appointment at the University of California, San Diego, (UCSD) and Ionis Pharmaceuticals; is a coinventor and receives royalties from patents owned by UCSD; and is a cofounder and has an equity interest in Oxitope and its affiliates, Kleanthi Diagnostics, and Covicept Therapeutics. Dr. Narula reports having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AHA advice for diabetes patients to stay heart healthy
A new document from the American Heart Association summarizes the latest research on cardiovascular risk factor management in type 2 diabetes, including medications, lifestyle, and social determinants of health.
Despite the availability of effective therapies for improving cardiovascular risk, in the United States fewer than one in five people with type 2 diabetes and without known cardiovascular disease meet control targets for a combination of A1c, blood pressure, LDL cholesterol, and nonsmoking status.
That proportion drops to less than 1 in 10 if body mass index less than 30 kg/m2 is included among the targets, and even less than that among individuals with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, Joshua J. Joseph, MD, and colleagues point out in their paper, published online Jan. 10 in Circulation.
“This new scientific statement is an urgent call to action to follow the latest evidence-based approaches and to develop new best practices to advance type 2 diabetes treatment and care and reduce cardiovascular disease risk,” wrote Dr. Joseph, assistant professor of medicine in the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism at The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, and coauthors.
The statement is not a guideline but an expert analysis that may inform future clinical practice guidelines, according to a press release from the AHA.
The new statement reviews evidence through June 2020 for lifestyle management of diabetes and weight, glycemic targets and control, blood pressure management, lipid management, antithrombotic therapy, and screening for cardiovascular and renal complications, including imaging. It also discusses the clinical implications of recent cardiovascular outcomes trials of newer glucose-lowering medications.
However, Dr. Joseph and colleagues point out, clinical care and treatment account for just 10%-20% of modifiable contributors to health outcomes. The other 80%-90% relate to social determinants of health, including health-related behaviors, socioeconomic factors, environmental factors, and racism.
“If we are to continue to advance the management of cardiovascular risk factors, we must also address the [social determinants of health] in the delivery of health care,” they noted.
Overall, they advise a patient-centered approach, meaning “reframing our clinical encounters to think about patients as people who live in families, communities, and societies that must be considered in their cardiovascular risk management.”
“People with [type 2 diabetes] face numerous barriers to health including access to care and equitable care, which must be considered when developing individualized care plans with our patients,” Dr. Joseph said in the AHA press release.
Lifestyle, medications for lowering A1c, BP, lipids
For lifestyle management, the authors say, “culturally appropriate recommendations through diabetes self-management education and support and medical nutrition therapy are key to meeting individualized goals for behavioral change and diabetes self-management.”
The document summarizes recommendations from other professional societies regarding glycemic targets and glucose lowering medications, i.e., target A1c levels of either < 7% or < 6.5% for the majority, with adjustments based on individual factors, such as life expectancy. It advises on use of metformin as first-line therapy followed by a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor or a glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist for those with established cardiovascular disease or risk factors.
“Cost may be a barrier to taking some [type 2 diabetes] medications as prescribed; however, many of these medications are now more commonly covered by more health insurance plans,” Dr. Joseph said.
“Another barrier is recognition by patients that these newer [type 2 diabetes] medications are also effective in reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, heart failure, and kidney disease.”
Blood pressure treatment guidelines differ between those of the AHA/American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Diabetes Association (ADA), most notably that the AHA/ACC guidelines advise a general target of < 130/80 mm Hg, whereas ADA advises < 140/90 mm Hg or < 130/80 mm Hg for those with high risk if it can be safely achieved.
The decision should be “patient-centered with shared decision-making,” Dr. Joseph and colleagues advised.
For lipid-lowering, the document cites the 2018 ACC/AHA cholesterol guidelines, which include advising statins as first-line therapy for both primary and secondary prevention in diabetes, with highest intensity statins used in those at highest risk. But again, treatment should be individualized, and other agents should be used for patients in whom statins don’t work or aren’t tolerated.
And while use of antiplatelets – that is, aspirin – is well established as secondary prevention in type 2 diabetes, given new data suggesting that the risk for major bleeding could outweigh the benefits for primary prevention, “the relative benefits of antithrombotic approaches need to be weighed carefully against risks using a patient-centered approach,” the authors advised.
Among the many imaging tests available to facilitate cardiovascular risk stratification in type 2 diabetes, coronary artery calcification (CAC) CT screening is one of the few with sufficient data to support routine use in selected patients. The National Lipid Association, for example, recommends escalation to high-intensity statin for CAC > 100.
“One avenue to continue to address and advance diabetes management is through breaking down the four walls of the clinic or hospital through community engagement, clinic-to-community connections, and academic-community-government partnerships that may help address and support modifiable lifestyle behaviors such as physical activity, nutrition, smoking cessation and stress management,” Dr. Joseph concluded.
The AHA receives funding primarily from individuals. Foundations and corporations, including pharmaceutical, device manufacturers, and other companies, also make donations and fund AHA programs and events. The AHA’s strict policies prevent these relationships from influencing the science content. Revenues from pharmaceutical and biotech companies, device manufacturers, and health insurance providers and the AHA’s financial information are available on the association’s website. Dr. Joseph has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new document from the American Heart Association summarizes the latest research on cardiovascular risk factor management in type 2 diabetes, including medications, lifestyle, and social determinants of health.
Despite the availability of effective therapies for improving cardiovascular risk, in the United States fewer than one in five people with type 2 diabetes and without known cardiovascular disease meet control targets for a combination of A1c, blood pressure, LDL cholesterol, and nonsmoking status.
That proportion drops to less than 1 in 10 if body mass index less than 30 kg/m2 is included among the targets, and even less than that among individuals with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, Joshua J. Joseph, MD, and colleagues point out in their paper, published online Jan. 10 in Circulation.
“This new scientific statement is an urgent call to action to follow the latest evidence-based approaches and to develop new best practices to advance type 2 diabetes treatment and care and reduce cardiovascular disease risk,” wrote Dr. Joseph, assistant professor of medicine in the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism at The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, and coauthors.
The statement is not a guideline but an expert analysis that may inform future clinical practice guidelines, according to a press release from the AHA.
The new statement reviews evidence through June 2020 for lifestyle management of diabetes and weight, glycemic targets and control, blood pressure management, lipid management, antithrombotic therapy, and screening for cardiovascular and renal complications, including imaging. It also discusses the clinical implications of recent cardiovascular outcomes trials of newer glucose-lowering medications.
However, Dr. Joseph and colleagues point out, clinical care and treatment account for just 10%-20% of modifiable contributors to health outcomes. The other 80%-90% relate to social determinants of health, including health-related behaviors, socioeconomic factors, environmental factors, and racism.
“If we are to continue to advance the management of cardiovascular risk factors, we must also address the [social determinants of health] in the delivery of health care,” they noted.
Overall, they advise a patient-centered approach, meaning “reframing our clinical encounters to think about patients as people who live in families, communities, and societies that must be considered in their cardiovascular risk management.”
“People with [type 2 diabetes] face numerous barriers to health including access to care and equitable care, which must be considered when developing individualized care plans with our patients,” Dr. Joseph said in the AHA press release.
Lifestyle, medications for lowering A1c, BP, lipids
For lifestyle management, the authors say, “culturally appropriate recommendations through diabetes self-management education and support and medical nutrition therapy are key to meeting individualized goals for behavioral change and diabetes self-management.”
The document summarizes recommendations from other professional societies regarding glycemic targets and glucose lowering medications, i.e., target A1c levels of either < 7% or < 6.5% for the majority, with adjustments based on individual factors, such as life expectancy. It advises on use of metformin as first-line therapy followed by a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor or a glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist for those with established cardiovascular disease or risk factors.
“Cost may be a barrier to taking some [type 2 diabetes] medications as prescribed; however, many of these medications are now more commonly covered by more health insurance plans,” Dr. Joseph said.
“Another barrier is recognition by patients that these newer [type 2 diabetes] medications are also effective in reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, heart failure, and kidney disease.”
Blood pressure treatment guidelines differ between those of the AHA/American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Diabetes Association (ADA), most notably that the AHA/ACC guidelines advise a general target of < 130/80 mm Hg, whereas ADA advises < 140/90 mm Hg or < 130/80 mm Hg for those with high risk if it can be safely achieved.
The decision should be “patient-centered with shared decision-making,” Dr. Joseph and colleagues advised.
For lipid-lowering, the document cites the 2018 ACC/AHA cholesterol guidelines, which include advising statins as first-line therapy for both primary and secondary prevention in diabetes, with highest intensity statins used in those at highest risk. But again, treatment should be individualized, and other agents should be used for patients in whom statins don’t work or aren’t tolerated.
And while use of antiplatelets – that is, aspirin – is well established as secondary prevention in type 2 diabetes, given new data suggesting that the risk for major bleeding could outweigh the benefits for primary prevention, “the relative benefits of antithrombotic approaches need to be weighed carefully against risks using a patient-centered approach,” the authors advised.
Among the many imaging tests available to facilitate cardiovascular risk stratification in type 2 diabetes, coronary artery calcification (CAC) CT screening is one of the few with sufficient data to support routine use in selected patients. The National Lipid Association, for example, recommends escalation to high-intensity statin for CAC > 100.
“One avenue to continue to address and advance diabetes management is through breaking down the four walls of the clinic or hospital through community engagement, clinic-to-community connections, and academic-community-government partnerships that may help address and support modifiable lifestyle behaviors such as physical activity, nutrition, smoking cessation and stress management,” Dr. Joseph concluded.
The AHA receives funding primarily from individuals. Foundations and corporations, including pharmaceutical, device manufacturers, and other companies, also make donations and fund AHA programs and events. The AHA’s strict policies prevent these relationships from influencing the science content. Revenues from pharmaceutical and biotech companies, device manufacturers, and health insurance providers and the AHA’s financial information are available on the association’s website. Dr. Joseph has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new document from the American Heart Association summarizes the latest research on cardiovascular risk factor management in type 2 diabetes, including medications, lifestyle, and social determinants of health.
Despite the availability of effective therapies for improving cardiovascular risk, in the United States fewer than one in five people with type 2 diabetes and without known cardiovascular disease meet control targets for a combination of A1c, blood pressure, LDL cholesterol, and nonsmoking status.
That proportion drops to less than 1 in 10 if body mass index less than 30 kg/m2 is included among the targets, and even less than that among individuals with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, Joshua J. Joseph, MD, and colleagues point out in their paper, published online Jan. 10 in Circulation.
“This new scientific statement is an urgent call to action to follow the latest evidence-based approaches and to develop new best practices to advance type 2 diabetes treatment and care and reduce cardiovascular disease risk,” wrote Dr. Joseph, assistant professor of medicine in the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism at The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, and coauthors.
The statement is not a guideline but an expert analysis that may inform future clinical practice guidelines, according to a press release from the AHA.
The new statement reviews evidence through June 2020 for lifestyle management of diabetes and weight, glycemic targets and control, blood pressure management, lipid management, antithrombotic therapy, and screening for cardiovascular and renal complications, including imaging. It also discusses the clinical implications of recent cardiovascular outcomes trials of newer glucose-lowering medications.
However, Dr. Joseph and colleagues point out, clinical care and treatment account for just 10%-20% of modifiable contributors to health outcomes. The other 80%-90% relate to social determinants of health, including health-related behaviors, socioeconomic factors, environmental factors, and racism.
“If we are to continue to advance the management of cardiovascular risk factors, we must also address the [social determinants of health] in the delivery of health care,” they noted.
Overall, they advise a patient-centered approach, meaning “reframing our clinical encounters to think about patients as people who live in families, communities, and societies that must be considered in their cardiovascular risk management.”
“People with [type 2 diabetes] face numerous barriers to health including access to care and equitable care, which must be considered when developing individualized care plans with our patients,” Dr. Joseph said in the AHA press release.
Lifestyle, medications for lowering A1c, BP, lipids
For lifestyle management, the authors say, “culturally appropriate recommendations through diabetes self-management education and support and medical nutrition therapy are key to meeting individualized goals for behavioral change and diabetes self-management.”
The document summarizes recommendations from other professional societies regarding glycemic targets and glucose lowering medications, i.e., target A1c levels of either < 7% or < 6.5% for the majority, with adjustments based on individual factors, such as life expectancy. It advises on use of metformin as first-line therapy followed by a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor or a glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist for those with established cardiovascular disease or risk factors.
“Cost may be a barrier to taking some [type 2 diabetes] medications as prescribed; however, many of these medications are now more commonly covered by more health insurance plans,” Dr. Joseph said.
“Another barrier is recognition by patients that these newer [type 2 diabetes] medications are also effective in reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, heart failure, and kidney disease.”
Blood pressure treatment guidelines differ between those of the AHA/American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Diabetes Association (ADA), most notably that the AHA/ACC guidelines advise a general target of < 130/80 mm Hg, whereas ADA advises < 140/90 mm Hg or < 130/80 mm Hg for those with high risk if it can be safely achieved.
The decision should be “patient-centered with shared decision-making,” Dr. Joseph and colleagues advised.
For lipid-lowering, the document cites the 2018 ACC/AHA cholesterol guidelines, which include advising statins as first-line therapy for both primary and secondary prevention in diabetes, with highest intensity statins used in those at highest risk. But again, treatment should be individualized, and other agents should be used for patients in whom statins don’t work or aren’t tolerated.
And while use of antiplatelets – that is, aspirin – is well established as secondary prevention in type 2 diabetes, given new data suggesting that the risk for major bleeding could outweigh the benefits for primary prevention, “the relative benefits of antithrombotic approaches need to be weighed carefully against risks using a patient-centered approach,” the authors advised.
Among the many imaging tests available to facilitate cardiovascular risk stratification in type 2 diabetes, coronary artery calcification (CAC) CT screening is one of the few with sufficient data to support routine use in selected patients. The National Lipid Association, for example, recommends escalation to high-intensity statin for CAC > 100.
“One avenue to continue to address and advance diabetes management is through breaking down the four walls of the clinic or hospital through community engagement, clinic-to-community connections, and academic-community-government partnerships that may help address and support modifiable lifestyle behaviors such as physical activity, nutrition, smoking cessation and stress management,” Dr. Joseph concluded.
The AHA receives funding primarily from individuals. Foundations and corporations, including pharmaceutical, device manufacturers, and other companies, also make donations and fund AHA programs and events. The AHA’s strict policies prevent these relationships from influencing the science content. Revenues from pharmaceutical and biotech companies, device manufacturers, and health insurance providers and the AHA’s financial information are available on the association’s website. Dr. Joseph has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Valentin Fuster: ‘Atherosclerosis starts in the femoral artery’
Advances in technology and genomics have given rise to many issues, such as the extent to which genetic and lifestyle factors contribute to the individual-level risk for coronary artery disease, and the extent one’s genetic risk can be offset by a healthy lifestyle.
Over the years, Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, director of Mount Sinai Heart and physician-in-chief at the Mount Sinai Hospital, both in New York, has focused much of his research on this topic. At the virtual ACC Latin America 2021 conference, the cardiologist spoke about his hypotheses and findings during his opening plenary on imaging genomics, an emerging field that is rapidly identifying genes that influence the brain, cognition, and risk for disease.
Dr. Fuster discussed his research (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77:2777-91; J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:1617-27; J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73:1371-82; J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70:2979-91; Circulation. 2015;131:2104-13) and spoke about his innovative program that looks at cardiovascular health in people from young children to senior citizens. The work has been a process of learning and discovery. “We’re beginning to understand how the disease can develop earlier and how we can prevent it from getting worse. There’s nothing more beneficial than beginning to see how the disease starts in the arteries – something that we’re able to do with imaging technologies that, in the next 2 years, will be available worldwide.” And “by using imaging biomarkers in conjunction with genomic biomarkers, we’re beginning to get an idea earlier on as to whether the person is at risk.”
We need to be talking more about health and healthy arteries and trying to come up with epistemologies that are more modern, Dr. Fuster said. “To be able to see who we actually are is fascinating, and all of this is completely new” with imaging genomics.
Developing cardiovascular disease can be identified in people aged 40-60 years when seven risk factors – obesity, metabolic syndrome, blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, and poor nutrition” – are grouped together, he explained. In their 2015 study, Dr. Fuster and colleagues explored, using high-quality three-dimensional ultrasonography, five areas of the body – right and left carotids, aorta, and right and left iliofemorals – in more than 4,000 people with no history of cardiovascular disease.
“The first thing I want to point out is that the disease originates in a territory that is not commonly evaluated. And we had no idea. We only learned about this development through imaging tests, assessing plaques. The disease starts in the femoral artery and, in fact, it starts with an inflammatory process – seen at autopsy – that can lead to fibrosis and, in later years, can form lipid-rich vulnerable plaque,” he said.
His work has shown an increase in disease progression in groups of people who have been monitored for 20 years. What is most interesting is the way lesions are silent and evolve as the years go by.
“Atherosclerosis appears as a silent phenomenon initially and worsens in the presence of risk factors that trigger its progression,” he said.
But can subclinical disease be identified in people who have few or no risk factors? “What we call normal is not, in fact, normal,” said Dr. Fuster. To not have subclinical disease, LDL cholesterol needs to be 70 mg/dL and hemoglobin A1c needs to be 5%-6%, according to a 2020 study by Dr. Fuster and colleagues.
“The fact that we’re seeing people with no apparent risk factors develop atherosclerosis is the reason what we consider normal is not,” he said. It is necessary to take into account what happened in the first 40 years of these individuals’ lives, he added.
Dr. Fuster presented findings on 6,000 people aged 60-100 years underwent three-dimensional ultrasonography and were monitored for 12 years. The data have yet to be published, but they indicate that, with this disease, more than just risk factors are at play; atherosclerosis is related to what happens early on in one’s life.
In their 2016 study of more than 55,000 participants, Dr. Fuster and associates quantified the genetic risk for coronary artery disease with a polygenic risk score derived from an analysis of up to 50 genetic polymorphisms that had been associated with coronary artery disease in previous studies. On the basis of this score, the participants were divided into subgroups by genetic risk: low, intermediate, and high. Genetic and lifestyle factors were independently associated with susceptibility to coronary artery disease. For participants at high genetic risk, a favorable lifestyle was associated with a relative risk for coronary artery disease nearly 50% lower than an unfavorable lifestyle.
The risk factors cause the bone marrow to be activated and, when this happens, an inflammatory process occurs in the arteries. This activation is a defense mechanism designed to help monocytes heal the arteries. “When we’re dealing with a disease in the arteries, inflammation starts in the bone marrow, where cholesterol is deposited, and there are macrophages that, because there’s too much to clean up and they can’t keep up, will actually kill themselves. When that happens, they will release substances that will damage the arteries,” Dr. Fuster reported.
In elderly people, risk factors have an impact not only on the great vessels, they can also lead to cerebral small vessel disease.
“The problem is that, before, we didn’t have the technology to make this observation. And this is something critical with respect to late-onset dementia,” he said, citing a 2016 study on Alzheimer’s disease. Even if risk factors are increasing, the person will not necessarily develop the disease, but there is a greater chance that they will.
Education
Playful activities have a major impact in childhood. With this in mind, Dr. Fuster instituted a 6-month, 60-hour educational program for children aged 3-6 years. The approach was aimed at teaching children about healthy eating habits and how the human body works. “Children are able to absorb everything we say, but then at age 10, it all goes away,” he said. With another intervention that involved the same children, he showed that the benefits were greater than those seen in the first intervention.
“Our hypothesis is that, regardless of age, any program that has to do with prevention needs to be repeated,” Dr. Fuster said. “Repetition will bring more benefits every x years. That’s what we’re learning.
“We learned that when these children go home, they tell their parents what to do. The program had a greater impact on the children than their parents. So we need to use repetition in prevention efforts directed at young children. And we need to remember that the later we start this kind of work, the less impact it will have. The sooner things start, the greater the benefit and the lower the cost,” he concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Advances in technology and genomics have given rise to many issues, such as the extent to which genetic and lifestyle factors contribute to the individual-level risk for coronary artery disease, and the extent one’s genetic risk can be offset by a healthy lifestyle.
Over the years, Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, director of Mount Sinai Heart and physician-in-chief at the Mount Sinai Hospital, both in New York, has focused much of his research on this topic. At the virtual ACC Latin America 2021 conference, the cardiologist spoke about his hypotheses and findings during his opening plenary on imaging genomics, an emerging field that is rapidly identifying genes that influence the brain, cognition, and risk for disease.
Dr. Fuster discussed his research (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77:2777-91; J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:1617-27; J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73:1371-82; J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70:2979-91; Circulation. 2015;131:2104-13) and spoke about his innovative program that looks at cardiovascular health in people from young children to senior citizens. The work has been a process of learning and discovery. “We’re beginning to understand how the disease can develop earlier and how we can prevent it from getting worse. There’s nothing more beneficial than beginning to see how the disease starts in the arteries – something that we’re able to do with imaging technologies that, in the next 2 years, will be available worldwide.” And “by using imaging biomarkers in conjunction with genomic biomarkers, we’re beginning to get an idea earlier on as to whether the person is at risk.”
We need to be talking more about health and healthy arteries and trying to come up with epistemologies that are more modern, Dr. Fuster said. “To be able to see who we actually are is fascinating, and all of this is completely new” with imaging genomics.
Developing cardiovascular disease can be identified in people aged 40-60 years when seven risk factors – obesity, metabolic syndrome, blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, and poor nutrition” – are grouped together, he explained. In their 2015 study, Dr. Fuster and colleagues explored, using high-quality three-dimensional ultrasonography, five areas of the body – right and left carotids, aorta, and right and left iliofemorals – in more than 4,000 people with no history of cardiovascular disease.
“The first thing I want to point out is that the disease originates in a territory that is not commonly evaluated. And we had no idea. We only learned about this development through imaging tests, assessing plaques. The disease starts in the femoral artery and, in fact, it starts with an inflammatory process – seen at autopsy – that can lead to fibrosis and, in later years, can form lipid-rich vulnerable plaque,” he said.
His work has shown an increase in disease progression in groups of people who have been monitored for 20 years. What is most interesting is the way lesions are silent and evolve as the years go by.
“Atherosclerosis appears as a silent phenomenon initially and worsens in the presence of risk factors that trigger its progression,” he said.
But can subclinical disease be identified in people who have few or no risk factors? “What we call normal is not, in fact, normal,” said Dr. Fuster. To not have subclinical disease, LDL cholesterol needs to be 70 mg/dL and hemoglobin A1c needs to be 5%-6%, according to a 2020 study by Dr. Fuster and colleagues.
“The fact that we’re seeing people with no apparent risk factors develop atherosclerosis is the reason what we consider normal is not,” he said. It is necessary to take into account what happened in the first 40 years of these individuals’ lives, he added.
Dr. Fuster presented findings on 6,000 people aged 60-100 years underwent three-dimensional ultrasonography and were monitored for 12 years. The data have yet to be published, but they indicate that, with this disease, more than just risk factors are at play; atherosclerosis is related to what happens early on in one’s life.
In their 2016 study of more than 55,000 participants, Dr. Fuster and associates quantified the genetic risk for coronary artery disease with a polygenic risk score derived from an analysis of up to 50 genetic polymorphisms that had been associated with coronary artery disease in previous studies. On the basis of this score, the participants were divided into subgroups by genetic risk: low, intermediate, and high. Genetic and lifestyle factors were independently associated with susceptibility to coronary artery disease. For participants at high genetic risk, a favorable lifestyle was associated with a relative risk for coronary artery disease nearly 50% lower than an unfavorable lifestyle.
The risk factors cause the bone marrow to be activated and, when this happens, an inflammatory process occurs in the arteries. This activation is a defense mechanism designed to help monocytes heal the arteries. “When we’re dealing with a disease in the arteries, inflammation starts in the bone marrow, where cholesterol is deposited, and there are macrophages that, because there’s too much to clean up and they can’t keep up, will actually kill themselves. When that happens, they will release substances that will damage the arteries,” Dr. Fuster reported.
In elderly people, risk factors have an impact not only on the great vessels, they can also lead to cerebral small vessel disease.
“The problem is that, before, we didn’t have the technology to make this observation. And this is something critical with respect to late-onset dementia,” he said, citing a 2016 study on Alzheimer’s disease. Even if risk factors are increasing, the person will not necessarily develop the disease, but there is a greater chance that they will.
Education
Playful activities have a major impact in childhood. With this in mind, Dr. Fuster instituted a 6-month, 60-hour educational program for children aged 3-6 years. The approach was aimed at teaching children about healthy eating habits and how the human body works. “Children are able to absorb everything we say, but then at age 10, it all goes away,” he said. With another intervention that involved the same children, he showed that the benefits were greater than those seen in the first intervention.
“Our hypothesis is that, regardless of age, any program that has to do with prevention needs to be repeated,” Dr. Fuster said. “Repetition will bring more benefits every x years. That’s what we’re learning.
“We learned that when these children go home, they tell their parents what to do. The program had a greater impact on the children than their parents. So we need to use repetition in prevention efforts directed at young children. And we need to remember that the later we start this kind of work, the less impact it will have. The sooner things start, the greater the benefit and the lower the cost,” he concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Advances in technology and genomics have given rise to many issues, such as the extent to which genetic and lifestyle factors contribute to the individual-level risk for coronary artery disease, and the extent one’s genetic risk can be offset by a healthy lifestyle.
Over the years, Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, director of Mount Sinai Heart and physician-in-chief at the Mount Sinai Hospital, both in New York, has focused much of his research on this topic. At the virtual ACC Latin America 2021 conference, the cardiologist spoke about his hypotheses and findings during his opening plenary on imaging genomics, an emerging field that is rapidly identifying genes that influence the brain, cognition, and risk for disease.
Dr. Fuster discussed his research (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77:2777-91; J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:1617-27; J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73:1371-82; J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70:2979-91; Circulation. 2015;131:2104-13) and spoke about his innovative program that looks at cardiovascular health in people from young children to senior citizens. The work has been a process of learning and discovery. “We’re beginning to understand how the disease can develop earlier and how we can prevent it from getting worse. There’s nothing more beneficial than beginning to see how the disease starts in the arteries – something that we’re able to do with imaging technologies that, in the next 2 years, will be available worldwide.” And “by using imaging biomarkers in conjunction with genomic biomarkers, we’re beginning to get an idea earlier on as to whether the person is at risk.”
We need to be talking more about health and healthy arteries and trying to come up with epistemologies that are more modern, Dr. Fuster said. “To be able to see who we actually are is fascinating, and all of this is completely new” with imaging genomics.
Developing cardiovascular disease can be identified in people aged 40-60 years when seven risk factors – obesity, metabolic syndrome, blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, and poor nutrition” – are grouped together, he explained. In their 2015 study, Dr. Fuster and colleagues explored, using high-quality three-dimensional ultrasonography, five areas of the body – right and left carotids, aorta, and right and left iliofemorals – in more than 4,000 people with no history of cardiovascular disease.
“The first thing I want to point out is that the disease originates in a territory that is not commonly evaluated. And we had no idea. We only learned about this development through imaging tests, assessing plaques. The disease starts in the femoral artery and, in fact, it starts with an inflammatory process – seen at autopsy – that can lead to fibrosis and, in later years, can form lipid-rich vulnerable plaque,” he said.
His work has shown an increase in disease progression in groups of people who have been monitored for 20 years. What is most interesting is the way lesions are silent and evolve as the years go by.
“Atherosclerosis appears as a silent phenomenon initially and worsens in the presence of risk factors that trigger its progression,” he said.
But can subclinical disease be identified in people who have few or no risk factors? “What we call normal is not, in fact, normal,” said Dr. Fuster. To not have subclinical disease, LDL cholesterol needs to be 70 mg/dL and hemoglobin A1c needs to be 5%-6%, according to a 2020 study by Dr. Fuster and colleagues.
“The fact that we’re seeing people with no apparent risk factors develop atherosclerosis is the reason what we consider normal is not,” he said. It is necessary to take into account what happened in the first 40 years of these individuals’ lives, he added.
Dr. Fuster presented findings on 6,000 people aged 60-100 years underwent three-dimensional ultrasonography and were monitored for 12 years. The data have yet to be published, but they indicate that, with this disease, more than just risk factors are at play; atherosclerosis is related to what happens early on in one’s life.
In their 2016 study of more than 55,000 participants, Dr. Fuster and associates quantified the genetic risk for coronary artery disease with a polygenic risk score derived from an analysis of up to 50 genetic polymorphisms that had been associated with coronary artery disease in previous studies. On the basis of this score, the participants were divided into subgroups by genetic risk: low, intermediate, and high. Genetic and lifestyle factors were independently associated with susceptibility to coronary artery disease. For participants at high genetic risk, a favorable lifestyle was associated with a relative risk for coronary artery disease nearly 50% lower than an unfavorable lifestyle.
The risk factors cause the bone marrow to be activated and, when this happens, an inflammatory process occurs in the arteries. This activation is a defense mechanism designed to help monocytes heal the arteries. “When we’re dealing with a disease in the arteries, inflammation starts in the bone marrow, where cholesterol is deposited, and there are macrophages that, because there’s too much to clean up and they can’t keep up, will actually kill themselves. When that happens, they will release substances that will damage the arteries,” Dr. Fuster reported.
In elderly people, risk factors have an impact not only on the great vessels, they can also lead to cerebral small vessel disease.
“The problem is that, before, we didn’t have the technology to make this observation. And this is something critical with respect to late-onset dementia,” he said, citing a 2016 study on Alzheimer’s disease. Even if risk factors are increasing, the person will not necessarily develop the disease, but there is a greater chance that they will.
Education
Playful activities have a major impact in childhood. With this in mind, Dr. Fuster instituted a 6-month, 60-hour educational program for children aged 3-6 years. The approach was aimed at teaching children about healthy eating habits and how the human body works. “Children are able to absorb everything we say, but then at age 10, it all goes away,” he said. With another intervention that involved the same children, he showed that the benefits were greater than those seen in the first intervention.
“Our hypothesis is that, regardless of age, any program that has to do with prevention needs to be repeated,” Dr. Fuster said. “Repetition will bring more benefits every x years. That’s what we’re learning.
“We learned that when these children go home, they tell their parents what to do. The program had a greater impact on the children than their parents. So we need to use repetition in prevention efforts directed at young children. And we need to remember that the later we start this kind of work, the less impact it will have. The sooner things start, the greater the benefit and the lower the cost,” he concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
D-dimer thresholds rule out PE in meta-analysis
In a patient suspected to have a PE, “diagnosis is made radiographically, usually with CT pulmonary angiogram, or V/Q scan,” Suman Pal, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview.
“Validated clinical decision tools such as Wells’ score or Geneva score may be used to identify patients at low pretest probability of PE who may initially get a D-dimer level check, followed by imaging only if D-dimer level is elevated,” explained Dr. Pal, who was not involved with the new research, which was published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
According to the authors of the new paper, while current diagnostic strategies in patients with suspected PE include use of a validated clinical decision rule (CDR) and D-dimer testing to rule out PE without imaging tests, the effectiveness of D-dimer tests in older patients, inpatients, cancer patients, and other high-risk groups has not been well-studied.
Lead author of the paper, Milou A.M. Stals, MD, and colleagues said their goal was to evaluate the safety and efficiency of the Wells rule and revised Geneva score in combination with D-dimer tests, and also the YEARS algorithm for D-dimer thresholds, in their paper.
Dr. Stals, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, and the coinvestigators conducted an international systemic review and individual patient data meta-analysis that included 16 studies and 20,553 patients, with all studies having been published between Jan. 1, 1995, and Jan. 1, 2021. Their primary outcomes were the safety and efficiency of each of these three strategies.
In the review, the researchers defined safety as the 3-month incidence of venous thromboembolism after PE was ruled out without imaging at baseline. They defined efficiency as the proportion patients for whom PE was ruled out based on D-dimer thresholds without imaging.
Overall, efficiency was highest in the subset of patients aged younger than 40 years, ranging from 47% to 68% in this group. Efficiency was lowest in patients aged 80 years and older (6.0%-23%), and in patients with cancer (9.6%-26%).
The efficiency was higher when D-dimer thresholds based on pretest probability were used, compared with when fixed or age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds were used.
The key finding was the significant variability in performance of the diagnostic strategies, the researchers said.
“The predicted failure rate was generally highest for strategies incorporating adapted D-dimer thresholds. However, at the same time, predicted overall efficiency was substantially higher with these strategies versus strategies with a fixed D-dimer threshold as well,” they said. Given that the benefits of each of the three diagnostic strategies depends on their correct application, the researchers recommended that an individual hospitalist choose one strategy for their institution.
“Whether clinicians should rely on the Wells rule, the YEARS algorithm, or the revised Geneva score becomes a matter of local preference and experience,” Dr. Stals and colleagues wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including between-study differences in scoring predictors and D-dimer assays. Another limitation was that differential verification biases for classifying fatal events and PE may have contributed to overestimation of failure rates of the adapted D-dimer thresholds.
Strengths of the study included its large sample size and original data on pretest probability, and that data support the use of any of the three strategies for ruling out PE in the identified subgroups without the need for imaging tests, the authors wrote.
“Pending the results of ongoing diagnostic randomized trials, physicians and guideline committees should balance the interlink between safety and efficiency of available diagnostic strategies,” they concluded.
Adapted D-dimer benefits some patients
“Clearly, increasing the D-dimer cutoff will lower the number of patients who require radiographic imaging (improved specificity), but this comes with a risk for missing PE (lower sensitivity). Is this risk worth taking?” Daniel J. Brotman, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, asked in an editorial accompanying the new study.
Dr. Brotman was not surprised by the study findings.
“Conditions that predispose to thrombosis through activated hemostasis – such as advanced age, cancer, inflammation, prolonged hospitalization, and trauma – drive D-dimer levels higher independent of the presence or absence of radiographically apparent thrombosis,” he said. However, these patients are unlikely to have normal D-dimer levels regardless of the cutoff used.
Adapted D-dimer cutoffs may benefit some patients, including those with contraindications or limited access to imaging, said Dr. Brotman. D-dimer may be used for risk stratification regardless of PE, since patients with marginally elevated D-dimers have better prognoses than those with higher D-dimer elevations, even if a small PE is missed.
Dr. Brotman wrote that increasing D-dimer cutoffs for high-risk patients in the subgroups analyzed may spare some patients radiographic testing, but doing so carries an increased risk for diagnostic failure. Overall, “the important work by Stals and colleagues offers reassurance that modifying D-dimer thresholds according to age or pretest probability is safe enough for widespread practice, even in high-risk groups.”
Focus on single strategy ‘based on local needs’
“Several validated clinical decision tools, along with age or pretest probability adjusted D-dimer threshold are currently in use as diagnostic strategies for ruling out pulmonary embolism,” Dr. Pal said in an interview.
The current study is important because of limited data on the performance of these strategies in specific subgroups of patients whose risk of PE may differ from the overall patient population, he noted.
“Different diagnostic strategies for PE have a variable performance in patients with differences of age, active cancer, and history of VTE,” said Dr. Pal. “However, in this study, no clear preference for one strategy over others could be established for these subgroups, and clinicians should continue to follow institution-specific guidance.
“A single strategy should be adopted at each institution based on local needs and used as the standard of care until further data are available,” he said.
“The use of D-dimer to rule out PE, either with fixed threshold or age-adjusted thresholds, can be confounded in clinical settings by other comorbid conditions such as sepsis, recent surgery, and more recently, COVID-19,” he said.
“Since the findings of this study do not show a clear benefit of one diagnostic strategy over others in the analyzed subgroups of patients, further prospective head-to-head comparison among the subgroups of interest would be helpful to guide clinical decision making,” Dr. Pal added.
YEARS-specific study supports D-dimer safety and value
A recent paper published in JAMA supported the results of the meta-analysis. In that study, Yonathan Freund, MD, of Sorbonne Université, Paris, and colleagues focused on the YEARS strategy combined with age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds as a way to rule out PE in PERC-positive ED patients.
The authors of this paper randomized 18 EDs to either a protocol of intervention followed by control, or control followed by intervention. The study population included 726 patients in the intervention group and 688 in the control group.
The intervention strategy to rule out PE consisted of assessing the YEARS criteria and D-dimer testing. PE was ruled out in patients with no YEARS criteria and a D-dimer level below 1,000 ng/mL and in patients with one or more YEARS criteria and D-dimers below an age-adjusted threshold (defined as age times 10 ng/mL in patients aged 50 years and older).
The control strategy consisted of D-dimer testing for all patients with the threshold at age-adjusted levels; D-dimers about these levels prompted chest imaging.
Overall, the risk of a missed VTE at 3 months was noninferior between the groups (0.15% in the intervention group and 0.80% in the controls).
“The intervention was associated with a statistically significant reduction in chest imaging use,” the researchers wrote.
This study’s findings were limited by randomization at the center level, rather than the patient level, and the use of imaging on some patients despite negative D-dimer tests, the researchers wrote. However, their findings support those of previous studies and especially support the safety of the intervention, in an emergency medicine setting, as no PEs occurred in patients with a YEARS score of zero who underwent the intervention.
Downsides to applying algorithms to every patient explained
In an editorial accompanying the JAMA study, Marcel Levi, MD, and Nick van Es, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Center, emphasized the challenges of diagnosing PE given that many patients present with nonspecific clinical manifestations and without typical signs and symptoms. High-resolution CT pulmonary angiography allows for a fast and easy diagnosis in an emergency setting. However, efforts are ongoing to develop alternative strategies that avoid unnecessary scanning for potential PE patients, many of whom have alternative diagnoses such as pulmonary infections, cardiac conditions, pleural disease, or musculoskeletal problems.
On review of the JAMA study using the YEARS rule with adjusted D-dimer thresholds, the editorialists noted that the data were robust and indicated a 10% reduction in chest imaging. They also emphasized the potential to overwhelm busy clinicians with more algorithms.
“Blindly applying algorithms to every patient may be less appropriate or even undesirable in specific situations in which deviation from the rules on clinical grounds is indicated,” but a complex imaging approach may be time consuming and challenging in the acute setting, and a simple algorithm may be safe and efficient in many cases, they wrote. “From a patient perspective, a negative diagnostic algorithm for pulmonary embolism does not diminish the physician’s obligation to consider other diagnoses that explain the symptoms, for which chest CT scans may still be needed and helpful.”
The Annals of Internal Medicine study was supported by the Dutch Research Council. The JAMA study was supported by the French Health Ministry. Dr. Stals, Dr. Freund, Dr. Pal, Dr. Levi, and Dr. van Es had no financial conflicts to disclose.
In a patient suspected to have a PE, “diagnosis is made radiographically, usually with CT pulmonary angiogram, or V/Q scan,” Suman Pal, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview.
“Validated clinical decision tools such as Wells’ score or Geneva score may be used to identify patients at low pretest probability of PE who may initially get a D-dimer level check, followed by imaging only if D-dimer level is elevated,” explained Dr. Pal, who was not involved with the new research, which was published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
According to the authors of the new paper, while current diagnostic strategies in patients with suspected PE include use of a validated clinical decision rule (CDR) and D-dimer testing to rule out PE without imaging tests, the effectiveness of D-dimer tests in older patients, inpatients, cancer patients, and other high-risk groups has not been well-studied.
Lead author of the paper, Milou A.M. Stals, MD, and colleagues said their goal was to evaluate the safety and efficiency of the Wells rule and revised Geneva score in combination with D-dimer tests, and also the YEARS algorithm for D-dimer thresholds, in their paper.
Dr. Stals, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, and the coinvestigators conducted an international systemic review and individual patient data meta-analysis that included 16 studies and 20,553 patients, with all studies having been published between Jan. 1, 1995, and Jan. 1, 2021. Their primary outcomes were the safety and efficiency of each of these three strategies.
In the review, the researchers defined safety as the 3-month incidence of venous thromboembolism after PE was ruled out without imaging at baseline. They defined efficiency as the proportion patients for whom PE was ruled out based on D-dimer thresholds without imaging.
Overall, efficiency was highest in the subset of patients aged younger than 40 years, ranging from 47% to 68% in this group. Efficiency was lowest in patients aged 80 years and older (6.0%-23%), and in patients with cancer (9.6%-26%).
The efficiency was higher when D-dimer thresholds based on pretest probability were used, compared with when fixed or age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds were used.
The key finding was the significant variability in performance of the diagnostic strategies, the researchers said.
“The predicted failure rate was generally highest for strategies incorporating adapted D-dimer thresholds. However, at the same time, predicted overall efficiency was substantially higher with these strategies versus strategies with a fixed D-dimer threshold as well,” they said. Given that the benefits of each of the three diagnostic strategies depends on their correct application, the researchers recommended that an individual hospitalist choose one strategy for their institution.
“Whether clinicians should rely on the Wells rule, the YEARS algorithm, or the revised Geneva score becomes a matter of local preference and experience,” Dr. Stals and colleagues wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including between-study differences in scoring predictors and D-dimer assays. Another limitation was that differential verification biases for classifying fatal events and PE may have contributed to overestimation of failure rates of the adapted D-dimer thresholds.
Strengths of the study included its large sample size and original data on pretest probability, and that data support the use of any of the three strategies for ruling out PE in the identified subgroups without the need for imaging tests, the authors wrote.
“Pending the results of ongoing diagnostic randomized trials, physicians and guideline committees should balance the interlink between safety and efficiency of available diagnostic strategies,” they concluded.
Adapted D-dimer benefits some patients
“Clearly, increasing the D-dimer cutoff will lower the number of patients who require radiographic imaging (improved specificity), but this comes with a risk for missing PE (lower sensitivity). Is this risk worth taking?” Daniel J. Brotman, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, asked in an editorial accompanying the new study.
Dr. Brotman was not surprised by the study findings.
“Conditions that predispose to thrombosis through activated hemostasis – such as advanced age, cancer, inflammation, prolonged hospitalization, and trauma – drive D-dimer levels higher independent of the presence or absence of radiographically apparent thrombosis,” he said. However, these patients are unlikely to have normal D-dimer levels regardless of the cutoff used.
Adapted D-dimer cutoffs may benefit some patients, including those with contraindications or limited access to imaging, said Dr. Brotman. D-dimer may be used for risk stratification regardless of PE, since patients with marginally elevated D-dimers have better prognoses than those with higher D-dimer elevations, even if a small PE is missed.
Dr. Brotman wrote that increasing D-dimer cutoffs for high-risk patients in the subgroups analyzed may spare some patients radiographic testing, but doing so carries an increased risk for diagnostic failure. Overall, “the important work by Stals and colleagues offers reassurance that modifying D-dimer thresholds according to age or pretest probability is safe enough for widespread practice, even in high-risk groups.”
Focus on single strategy ‘based on local needs’
“Several validated clinical decision tools, along with age or pretest probability adjusted D-dimer threshold are currently in use as diagnostic strategies for ruling out pulmonary embolism,” Dr. Pal said in an interview.
The current study is important because of limited data on the performance of these strategies in specific subgroups of patients whose risk of PE may differ from the overall patient population, he noted.
“Different diagnostic strategies for PE have a variable performance in patients with differences of age, active cancer, and history of VTE,” said Dr. Pal. “However, in this study, no clear preference for one strategy over others could be established for these subgroups, and clinicians should continue to follow institution-specific guidance.
“A single strategy should be adopted at each institution based on local needs and used as the standard of care until further data are available,” he said.
“The use of D-dimer to rule out PE, either with fixed threshold or age-adjusted thresholds, can be confounded in clinical settings by other comorbid conditions such as sepsis, recent surgery, and more recently, COVID-19,” he said.
“Since the findings of this study do not show a clear benefit of one diagnostic strategy over others in the analyzed subgroups of patients, further prospective head-to-head comparison among the subgroups of interest would be helpful to guide clinical decision making,” Dr. Pal added.
YEARS-specific study supports D-dimer safety and value
A recent paper published in JAMA supported the results of the meta-analysis. In that study, Yonathan Freund, MD, of Sorbonne Université, Paris, and colleagues focused on the YEARS strategy combined with age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds as a way to rule out PE in PERC-positive ED patients.
The authors of this paper randomized 18 EDs to either a protocol of intervention followed by control, or control followed by intervention. The study population included 726 patients in the intervention group and 688 in the control group.
The intervention strategy to rule out PE consisted of assessing the YEARS criteria and D-dimer testing. PE was ruled out in patients with no YEARS criteria and a D-dimer level below 1,000 ng/mL and in patients with one or more YEARS criteria and D-dimers below an age-adjusted threshold (defined as age times 10 ng/mL in patients aged 50 years and older).
The control strategy consisted of D-dimer testing for all patients with the threshold at age-adjusted levels; D-dimers about these levels prompted chest imaging.
Overall, the risk of a missed VTE at 3 months was noninferior between the groups (0.15% in the intervention group and 0.80% in the controls).
“The intervention was associated with a statistically significant reduction in chest imaging use,” the researchers wrote.
This study’s findings were limited by randomization at the center level, rather than the patient level, and the use of imaging on some patients despite negative D-dimer tests, the researchers wrote. However, their findings support those of previous studies and especially support the safety of the intervention, in an emergency medicine setting, as no PEs occurred in patients with a YEARS score of zero who underwent the intervention.
Downsides to applying algorithms to every patient explained
In an editorial accompanying the JAMA study, Marcel Levi, MD, and Nick van Es, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Center, emphasized the challenges of diagnosing PE given that many patients present with nonspecific clinical manifestations and without typical signs and symptoms. High-resolution CT pulmonary angiography allows for a fast and easy diagnosis in an emergency setting. However, efforts are ongoing to develop alternative strategies that avoid unnecessary scanning for potential PE patients, many of whom have alternative diagnoses such as pulmonary infections, cardiac conditions, pleural disease, or musculoskeletal problems.
On review of the JAMA study using the YEARS rule with adjusted D-dimer thresholds, the editorialists noted that the data were robust and indicated a 10% reduction in chest imaging. They also emphasized the potential to overwhelm busy clinicians with more algorithms.
“Blindly applying algorithms to every patient may be less appropriate or even undesirable in specific situations in which deviation from the rules on clinical grounds is indicated,” but a complex imaging approach may be time consuming and challenging in the acute setting, and a simple algorithm may be safe and efficient in many cases, they wrote. “From a patient perspective, a negative diagnostic algorithm for pulmonary embolism does not diminish the physician’s obligation to consider other diagnoses that explain the symptoms, for which chest CT scans may still be needed and helpful.”
The Annals of Internal Medicine study was supported by the Dutch Research Council. The JAMA study was supported by the French Health Ministry. Dr. Stals, Dr. Freund, Dr. Pal, Dr. Levi, and Dr. van Es had no financial conflicts to disclose.
In a patient suspected to have a PE, “diagnosis is made radiographically, usually with CT pulmonary angiogram, or V/Q scan,” Suman Pal, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview.
“Validated clinical decision tools such as Wells’ score or Geneva score may be used to identify patients at low pretest probability of PE who may initially get a D-dimer level check, followed by imaging only if D-dimer level is elevated,” explained Dr. Pal, who was not involved with the new research, which was published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
According to the authors of the new paper, while current diagnostic strategies in patients with suspected PE include use of a validated clinical decision rule (CDR) and D-dimer testing to rule out PE without imaging tests, the effectiveness of D-dimer tests in older patients, inpatients, cancer patients, and other high-risk groups has not been well-studied.
Lead author of the paper, Milou A.M. Stals, MD, and colleagues said their goal was to evaluate the safety and efficiency of the Wells rule and revised Geneva score in combination with D-dimer tests, and also the YEARS algorithm for D-dimer thresholds, in their paper.
Dr. Stals, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, and the coinvestigators conducted an international systemic review and individual patient data meta-analysis that included 16 studies and 20,553 patients, with all studies having been published between Jan. 1, 1995, and Jan. 1, 2021. Their primary outcomes were the safety and efficiency of each of these three strategies.
In the review, the researchers defined safety as the 3-month incidence of venous thromboembolism after PE was ruled out without imaging at baseline. They defined efficiency as the proportion patients for whom PE was ruled out based on D-dimer thresholds without imaging.
Overall, efficiency was highest in the subset of patients aged younger than 40 years, ranging from 47% to 68% in this group. Efficiency was lowest in patients aged 80 years and older (6.0%-23%), and in patients with cancer (9.6%-26%).
The efficiency was higher when D-dimer thresholds based on pretest probability were used, compared with when fixed or age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds were used.
The key finding was the significant variability in performance of the diagnostic strategies, the researchers said.
“The predicted failure rate was generally highest for strategies incorporating adapted D-dimer thresholds. However, at the same time, predicted overall efficiency was substantially higher with these strategies versus strategies with a fixed D-dimer threshold as well,” they said. Given that the benefits of each of the three diagnostic strategies depends on their correct application, the researchers recommended that an individual hospitalist choose one strategy for their institution.
“Whether clinicians should rely on the Wells rule, the YEARS algorithm, or the revised Geneva score becomes a matter of local preference and experience,” Dr. Stals and colleagues wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including between-study differences in scoring predictors and D-dimer assays. Another limitation was that differential verification biases for classifying fatal events and PE may have contributed to overestimation of failure rates of the adapted D-dimer thresholds.
Strengths of the study included its large sample size and original data on pretest probability, and that data support the use of any of the three strategies for ruling out PE in the identified subgroups without the need for imaging tests, the authors wrote.
“Pending the results of ongoing diagnostic randomized trials, physicians and guideline committees should balance the interlink between safety and efficiency of available diagnostic strategies,” they concluded.
Adapted D-dimer benefits some patients
“Clearly, increasing the D-dimer cutoff will lower the number of patients who require radiographic imaging (improved specificity), but this comes with a risk for missing PE (lower sensitivity). Is this risk worth taking?” Daniel J. Brotman, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, asked in an editorial accompanying the new study.
Dr. Brotman was not surprised by the study findings.
“Conditions that predispose to thrombosis through activated hemostasis – such as advanced age, cancer, inflammation, prolonged hospitalization, and trauma – drive D-dimer levels higher independent of the presence or absence of radiographically apparent thrombosis,” he said. However, these patients are unlikely to have normal D-dimer levels regardless of the cutoff used.
Adapted D-dimer cutoffs may benefit some patients, including those with contraindications or limited access to imaging, said Dr. Brotman. D-dimer may be used for risk stratification regardless of PE, since patients with marginally elevated D-dimers have better prognoses than those with higher D-dimer elevations, even if a small PE is missed.
Dr. Brotman wrote that increasing D-dimer cutoffs for high-risk patients in the subgroups analyzed may spare some patients radiographic testing, but doing so carries an increased risk for diagnostic failure. Overall, “the important work by Stals and colleagues offers reassurance that modifying D-dimer thresholds according to age or pretest probability is safe enough for widespread practice, even in high-risk groups.”
Focus on single strategy ‘based on local needs’
“Several validated clinical decision tools, along with age or pretest probability adjusted D-dimer threshold are currently in use as diagnostic strategies for ruling out pulmonary embolism,” Dr. Pal said in an interview.
The current study is important because of limited data on the performance of these strategies in specific subgroups of patients whose risk of PE may differ from the overall patient population, he noted.
“Different diagnostic strategies for PE have a variable performance in patients with differences of age, active cancer, and history of VTE,” said Dr. Pal. “However, in this study, no clear preference for one strategy over others could be established for these subgroups, and clinicians should continue to follow institution-specific guidance.
“A single strategy should be adopted at each institution based on local needs and used as the standard of care until further data are available,” he said.
“The use of D-dimer to rule out PE, either with fixed threshold or age-adjusted thresholds, can be confounded in clinical settings by other comorbid conditions such as sepsis, recent surgery, and more recently, COVID-19,” he said.
“Since the findings of this study do not show a clear benefit of one diagnostic strategy over others in the analyzed subgroups of patients, further prospective head-to-head comparison among the subgroups of interest would be helpful to guide clinical decision making,” Dr. Pal added.
YEARS-specific study supports D-dimer safety and value
A recent paper published in JAMA supported the results of the meta-analysis. In that study, Yonathan Freund, MD, of Sorbonne Université, Paris, and colleagues focused on the YEARS strategy combined with age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds as a way to rule out PE in PERC-positive ED patients.
The authors of this paper randomized 18 EDs to either a protocol of intervention followed by control, or control followed by intervention. The study population included 726 patients in the intervention group and 688 in the control group.
The intervention strategy to rule out PE consisted of assessing the YEARS criteria and D-dimer testing. PE was ruled out in patients with no YEARS criteria and a D-dimer level below 1,000 ng/mL and in patients with one or more YEARS criteria and D-dimers below an age-adjusted threshold (defined as age times 10 ng/mL in patients aged 50 years and older).
The control strategy consisted of D-dimer testing for all patients with the threshold at age-adjusted levels; D-dimers about these levels prompted chest imaging.
Overall, the risk of a missed VTE at 3 months was noninferior between the groups (0.15% in the intervention group and 0.80% in the controls).
“The intervention was associated with a statistically significant reduction in chest imaging use,” the researchers wrote.
This study’s findings were limited by randomization at the center level, rather than the patient level, and the use of imaging on some patients despite negative D-dimer tests, the researchers wrote. However, their findings support those of previous studies and especially support the safety of the intervention, in an emergency medicine setting, as no PEs occurred in patients with a YEARS score of zero who underwent the intervention.
Downsides to applying algorithms to every patient explained
In an editorial accompanying the JAMA study, Marcel Levi, MD, and Nick van Es, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Center, emphasized the challenges of diagnosing PE given that many patients present with nonspecific clinical manifestations and without typical signs and symptoms. High-resolution CT pulmonary angiography allows for a fast and easy diagnosis in an emergency setting. However, efforts are ongoing to develop alternative strategies that avoid unnecessary scanning for potential PE patients, many of whom have alternative diagnoses such as pulmonary infections, cardiac conditions, pleural disease, or musculoskeletal problems.
On review of the JAMA study using the YEARS rule with adjusted D-dimer thresholds, the editorialists noted that the data were robust and indicated a 10% reduction in chest imaging. They also emphasized the potential to overwhelm busy clinicians with more algorithms.
“Blindly applying algorithms to every patient may be less appropriate or even undesirable in specific situations in which deviation from the rules on clinical grounds is indicated,” but a complex imaging approach may be time consuming and challenging in the acute setting, and a simple algorithm may be safe and efficient in many cases, they wrote. “From a patient perspective, a negative diagnostic algorithm for pulmonary embolism does not diminish the physician’s obligation to consider other diagnoses that explain the symptoms, for which chest CT scans may still be needed and helpful.”
The Annals of Internal Medicine study was supported by the Dutch Research Council. The JAMA study was supported by the French Health Ministry. Dr. Stals, Dr. Freund, Dr. Pal, Dr. Levi, and Dr. van Es had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Exercise reduces arm and shoulder problems after breast cancer surgery
However, according to a U.K. study published by The BMJ on Nov. 10, women who exercised shortly after having nonreconstructive breast cancer surgery experienced less pain and regained better shoulder and arm mobility at 1 year than those who did not exercise.
“Hospitals should consider training physiotherapists in the PROSPER program to offer this structured, prescribed exercise program to women undergoing axillary clearance surgery and those having radiotherapy to the axilla,” said lead author Julie Bruce, PhD, a specialist in surgical epidemiology with the University of Warwick, Coventry, England.
Up to one-third of women experience adverse effects to their lymphatic and musculoskeletal systems after breast cancer surgery and radiotherapy targeting the axilla. A study of 2,411 women in Denmark found that pain remained for up to 7 years after breast cancer treatment. U.K. guidelines for the management of breast cancer recommend referral to physical therapy if such problems develop, but the best timing and intensity along with the safety of postoperative exercise remain uncertain. A review of the literature in 2019 found a lack of adequate evidence to support the use of postoperative exercise after breast cancer surgery. Moreover, concerns with such exercise have been reported, such as increased risks of postoperative wound complications and lymphedema.
“The study was conducted to address uncertainty whether early postoperative exercise after women at high risk of shoulder and arm problems after nonreconstructive surgery was safe, clinically, and cost-effective. Previous studies were small, and no large high-quality randomized controlled trials had been undertaken with this patient population in the U.K.,” Dr. Bruce said.
In UK PROSPER, a multicenter, randomized controlled trial, researchers investigated the effects of an exercise program compared with usual care for 392 women (mean age 58) undergoing breast cancer surgery at 17 National Health Service (NHS) cancer centers. The women were randomly assigned to usual care with structured exercise or usual care alone. Structured exercise, introduced 7-10 days postoperatively, consisted of a physical therapy–led exercise program comprising stretching, strengthening, and physical activity, along with behavioral change techniques to support exercise adherence. Two further appointments were offered 1 and 3 months later. Outcomes included upper limb function, as measured by the Disability of Arm, Hand, and Shoulder (DASH) questionnaire at 12 months, complications, health related quality of life, and cost effectiveness.
At 12 months, women in the exercise group showed improved upper limb function compared with those who received usual care (mean DASH 16.3 for exercise, 23.7 for usual care; adjusted mean difference 7.81, 95% confidence interval, 3.17-12.44; P = .001). Compared with the usual care group, women in the exercise group reported lower pain intensity, fewer arm disability symptoms, and better health related quality of life.
“We found that arm function, measured using the DASH scale, improved over time and found surprisingly, these differences between treatment groups persisted at 12 months,” Dr. Bruce said. “There was no increased risk of neuropathic pain or lymphedema, so we concluded that the structured exercise program introduced from the seventh postoperative day was safe. Strengthening exercises were introduced from 1 month postoperatively.”
While the authors noted that the study was limited as participants and physical therapists knew which treatment they were receiving, they stressed that the study included a larger sample size than that of previous trials, along with a long follow-up period.
“We know that some women develop late lymphedema. Our findings are based on follow-up at 12 months. We hope to undertake longer-term follow up of our patient sample in the future,” Dr. Bruce said.
The authors declared support from the UK National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Technology Assessment Programme.
However, according to a U.K. study published by The BMJ on Nov. 10, women who exercised shortly after having nonreconstructive breast cancer surgery experienced less pain and regained better shoulder and arm mobility at 1 year than those who did not exercise.
“Hospitals should consider training physiotherapists in the PROSPER program to offer this structured, prescribed exercise program to women undergoing axillary clearance surgery and those having radiotherapy to the axilla,” said lead author Julie Bruce, PhD, a specialist in surgical epidemiology with the University of Warwick, Coventry, England.
Up to one-third of women experience adverse effects to their lymphatic and musculoskeletal systems after breast cancer surgery and radiotherapy targeting the axilla. A study of 2,411 women in Denmark found that pain remained for up to 7 years after breast cancer treatment. U.K. guidelines for the management of breast cancer recommend referral to physical therapy if such problems develop, but the best timing and intensity along with the safety of postoperative exercise remain uncertain. A review of the literature in 2019 found a lack of adequate evidence to support the use of postoperative exercise after breast cancer surgery. Moreover, concerns with such exercise have been reported, such as increased risks of postoperative wound complications and lymphedema.
“The study was conducted to address uncertainty whether early postoperative exercise after women at high risk of shoulder and arm problems after nonreconstructive surgery was safe, clinically, and cost-effective. Previous studies were small, and no large high-quality randomized controlled trials had been undertaken with this patient population in the U.K.,” Dr. Bruce said.
In UK PROSPER, a multicenter, randomized controlled trial, researchers investigated the effects of an exercise program compared with usual care for 392 women (mean age 58) undergoing breast cancer surgery at 17 National Health Service (NHS) cancer centers. The women were randomly assigned to usual care with structured exercise or usual care alone. Structured exercise, introduced 7-10 days postoperatively, consisted of a physical therapy–led exercise program comprising stretching, strengthening, and physical activity, along with behavioral change techniques to support exercise adherence. Two further appointments were offered 1 and 3 months later. Outcomes included upper limb function, as measured by the Disability of Arm, Hand, and Shoulder (DASH) questionnaire at 12 months, complications, health related quality of life, and cost effectiveness.
At 12 months, women in the exercise group showed improved upper limb function compared with those who received usual care (mean DASH 16.3 for exercise, 23.7 for usual care; adjusted mean difference 7.81, 95% confidence interval, 3.17-12.44; P = .001). Compared with the usual care group, women in the exercise group reported lower pain intensity, fewer arm disability symptoms, and better health related quality of life.
“We found that arm function, measured using the DASH scale, improved over time and found surprisingly, these differences between treatment groups persisted at 12 months,” Dr. Bruce said. “There was no increased risk of neuropathic pain or lymphedema, so we concluded that the structured exercise program introduced from the seventh postoperative day was safe. Strengthening exercises were introduced from 1 month postoperatively.”
While the authors noted that the study was limited as participants and physical therapists knew which treatment they were receiving, they stressed that the study included a larger sample size than that of previous trials, along with a long follow-up period.
“We know that some women develop late lymphedema. Our findings are based on follow-up at 12 months. We hope to undertake longer-term follow up of our patient sample in the future,” Dr. Bruce said.
The authors declared support from the UK National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Technology Assessment Programme.
However, according to a U.K. study published by The BMJ on Nov. 10, women who exercised shortly after having nonreconstructive breast cancer surgery experienced less pain and regained better shoulder and arm mobility at 1 year than those who did not exercise.
“Hospitals should consider training physiotherapists in the PROSPER program to offer this structured, prescribed exercise program to women undergoing axillary clearance surgery and those having radiotherapy to the axilla,” said lead author Julie Bruce, PhD, a specialist in surgical epidemiology with the University of Warwick, Coventry, England.
Up to one-third of women experience adverse effects to their lymphatic and musculoskeletal systems after breast cancer surgery and radiotherapy targeting the axilla. A study of 2,411 women in Denmark found that pain remained for up to 7 years after breast cancer treatment. U.K. guidelines for the management of breast cancer recommend referral to physical therapy if such problems develop, but the best timing and intensity along with the safety of postoperative exercise remain uncertain. A review of the literature in 2019 found a lack of adequate evidence to support the use of postoperative exercise after breast cancer surgery. Moreover, concerns with such exercise have been reported, such as increased risks of postoperative wound complications and lymphedema.
“The study was conducted to address uncertainty whether early postoperative exercise after women at high risk of shoulder and arm problems after nonreconstructive surgery was safe, clinically, and cost-effective. Previous studies were small, and no large high-quality randomized controlled trials had been undertaken with this patient population in the U.K.,” Dr. Bruce said.
In UK PROSPER, a multicenter, randomized controlled trial, researchers investigated the effects of an exercise program compared with usual care for 392 women (mean age 58) undergoing breast cancer surgery at 17 National Health Service (NHS) cancer centers. The women were randomly assigned to usual care with structured exercise or usual care alone. Structured exercise, introduced 7-10 days postoperatively, consisted of a physical therapy–led exercise program comprising stretching, strengthening, and physical activity, along with behavioral change techniques to support exercise adherence. Two further appointments were offered 1 and 3 months later. Outcomes included upper limb function, as measured by the Disability of Arm, Hand, and Shoulder (DASH) questionnaire at 12 months, complications, health related quality of life, and cost effectiveness.
At 12 months, women in the exercise group showed improved upper limb function compared with those who received usual care (mean DASH 16.3 for exercise, 23.7 for usual care; adjusted mean difference 7.81, 95% confidence interval, 3.17-12.44; P = .001). Compared with the usual care group, women in the exercise group reported lower pain intensity, fewer arm disability symptoms, and better health related quality of life.
“We found that arm function, measured using the DASH scale, improved over time and found surprisingly, these differences between treatment groups persisted at 12 months,” Dr. Bruce said. “There was no increased risk of neuropathic pain or lymphedema, so we concluded that the structured exercise program introduced from the seventh postoperative day was safe. Strengthening exercises were introduced from 1 month postoperatively.”
While the authors noted that the study was limited as participants and physical therapists knew which treatment they were receiving, they stressed that the study included a larger sample size than that of previous trials, along with a long follow-up period.
“We know that some women develop late lymphedema. Our findings are based on follow-up at 12 months. We hope to undertake longer-term follow up of our patient sample in the future,” Dr. Bruce said.
The authors declared support from the UK National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Technology Assessment Programme.
FROM THE BMJ
Fully endovascular mitral valve replacement a limited success in feasibility study
It remains early days for transcatheter mitral-valve replacement (TMVR) as a minimally invasive way to treat severe, mitral regurgitation (MR), but it’s even earlier days for TMVR as an endovascular procedure. Most of the technique’s limited experience with a dedicated mitral prosthesis has involved transapical delivery.
But now a 15-patient study of transfemoral, transeptal TMVR – with a prosthesis designed for the mitral position and previously tested only transapically – has shown good 30-day results in that MR was essentially abolished with virtually no paravalvular leakage.
Nor were there adverse clinical events such as death, stroke, reintervention, or new need for a pacemaker in any of the high-surgical-risk patients with MR in this feasibility study of the transfemoral Intrepid TMVR System (Medtronic). Implantation failed, however, in one patient who then received a surgical valve via sternotomy.
The current cohort is part of a larger ongoing trial that will track whether patients implanted transfemorally with the Intrepid also show reverse remodeling and good clinical outcomes over at least a year. That study, called APOLLO, is one of several exploring dedicated TMVR valves from different companies, with names like SUMMIT, MISCEND, and TIARA-2.
Currently, TMVR is approved in the United States only using one device designed for the aortic position and only for treating failed surgical mitral bioprostheses in high-risk patients.
If the Intrepid transfemoral system has an Achilles’ heel, at least in the current iteration, it might be its 35 F catheter delivery system that requires surgical access to the femoral vein. Seven of the patients in the small series experienced major bleeding events, including six at the femoral access site, listed as major vascular complications.
Overall, the study’s patients “were extremely sick with a lot of comorbidity. A lot of them had atrial fibrillation, a lot of them were on anticoagulation to start with,” observed Firas Zahr, MD, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, as part of his presentation of the study at Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics (TCT) 2021, held virtually as well as onsite in Orlando, Florida.
All had moderate-to-severe, usually primary MR; two thirds of the cohort had been in NYHA class III or IV at baseline, and 40% had been hospitalized for heart failure within the past year. Eight had a history of cardiovascular surgery, and eight had diabetes. Their mean Society of Thoracic Surgeons Predicted Risk of Mortality (STS-PROM) score was 4.7, Dr. Zahr reported.
“At 30 days, there was a significant improvement in their heart failure classification; the vast majority of the patients were [NYHA] class I and class II,” said Dr. Zahr, who is also lead author on the study’s Nov. 6 publication in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
Observers of the study at TCT 2021 seemed enthusiastic about the study’s results but recognized that TMVR in its current form still has formidable limitations.
“This is clearly an exciting look into the future and very reassuring to a degree, aside from the complications, which are somewhat expected as we go with 30-plus French devices,” Rajiv Tayal, MD, MPH, said at a press conference on the Intrepid study held before Dr. Zahr’s formal presentation. Dr. Tayal is an interventional cardiologist with Valley Health System, Ridgewood, New Jersey, and New York Medical College, Valhalla.
“I think we’ve all learned that transapical [access] is just not a viable procedure for a lot of these patients, and so we’ve got to get to transfemoral,” Susheel K. Kodali, MD, interventional cardiologist at New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, said at the same forum.
A 35 F device “is going to be too big,” he said. However, “it is the first step to iterate to a smaller device.” Dr. Kodali said his center contributed a patient to the study, and he is listed as a coauthor on the publication.
The delivery system’s large profile is only part of the vascular complication issue. Not only did the procedure require surgical cutdown for venous access, but “we were fairly aggressive in anticoagulating these patients with the fear of thrombus formation,” Dr. Zahr said in the discussion following his presentation.
“A postprocedure anticoagulation regimen is recommended within the protocol, but ultimate therapy was left to the discretion of the treating site physician,” the published report states, noting that all 14 patients with successful TMVR were discharged on warfarin. They included 12 who were also put on a single antiplatelet and one given dual antiplatelet therapy on top of the oral anticoagulant.
“One thing that we learned is that we probably should standardize our approach to perioperative anticoagulation,” Dr. Zahr observed. Also, a 29 F sheath for the system is in the works, “and we’re hoping that with smaller sheath size, and hopefully going even to percutaneous, might have an impact on lowering the vascular complications.”
Explanations for the “higher-than-expected vascular complication rate” remains somewhat unclear, agreed an editorial accompanying the study’s publication, “but may include a learning curve with the system, the large introducer sheath, the need for surgical cutdown, and postprocedural anticoagulation.”
For trans-septal TMVR to become a default approach, “venous access will need to be achieved percutaneously and vascular complications need to be infrequent,” contends the editorial, with lead author Mohamad Alkhouli, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
“These data provide a glimpse into the future of TMVR. The excellent short-term safety and effectiveness of this still very early-stage procedure represent a major step forward in the field,” they write.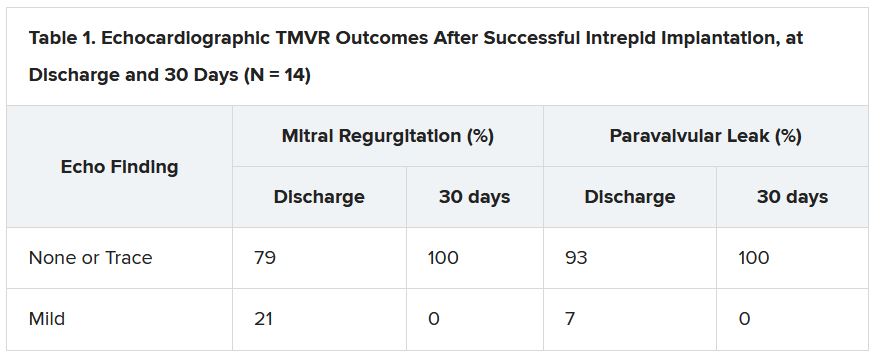
“The main question that the Intrepid early feasibility data raise is whether transfemoral, trans-septal TMVR will evolve to become the preferred strategy over transapical TMVR,” as occurred with transcatheter aortic-valve replacement (TAVR), the editorial states. “The answer is likely yes, but a few matters specific to trans-septal route will need be addressed first.”
Among those matters: The 35 F catheter leaves behind a considerable atrial septal defect (ASD). At operator discretion in this series, 11 patients received an ASD closure device.
None of the remaining four patients “developed significant heart failure or right ventricular dysfunction,” Dr. Zahr observed. “So, it seems like those patients who had their ASD left open tolerated it fairly well, at least until 30 days.”
But “we still need to learn what to do with those ASDs,” he said. “What is an acceptable residual shunt and what is an acceptable ASD size is to be determined.”
In general, the editorial notes, “the TMVR population has a high prevalence of cardiomyopathy, and a large residual iatrogenic ASD may lead to worsening volume overload and heart failure decompensation in some patients.”
Insertion of a closure device has its own issues, it continues. “Closure of the ASD might impede future access to the left atrium, which could impact life-long management of this high-risk population. A large septal occluder may hinder potentially needed procedures such as paravalvular leak closure, left atrial appendage closure, or pulmonary vein isolation.”
Patients like those in the current series, Dr. Kodali observed, will face “a lifetime of management challenges, and you want to make sure you don’t take away other options.”
The study was funded by Medtronic. Dr. Zahr reported institutional grant support from Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic. Dr. Kodali disclosed consultant fees from Admedus and Dura Biotech; equity in Dura Biotech, Microinterventional Devices, Thubrika Aortic Valve, Supira, Admedus, TriFlo, and Anona; and institutional grant support from Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, and JenaValve. The editorial writers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tayal disclosed consultant fees or honoraria from or serving on a speakers bureau for Abiomed, Edwards Lifesciences, Abbott Vascular, and Shockwave Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It remains early days for transcatheter mitral-valve replacement (TMVR) as a minimally invasive way to treat severe, mitral regurgitation (MR), but it’s even earlier days for TMVR as an endovascular procedure. Most of the technique’s limited experience with a dedicated mitral prosthesis has involved transapical delivery.
But now a 15-patient study of transfemoral, transeptal TMVR – with a prosthesis designed for the mitral position and previously tested only transapically – has shown good 30-day results in that MR was essentially abolished with virtually no paravalvular leakage.
Nor were there adverse clinical events such as death, stroke, reintervention, or new need for a pacemaker in any of the high-surgical-risk patients with MR in this feasibility study of the transfemoral Intrepid TMVR System (Medtronic). Implantation failed, however, in one patient who then received a surgical valve via sternotomy.
The current cohort is part of a larger ongoing trial that will track whether patients implanted transfemorally with the Intrepid also show reverse remodeling and good clinical outcomes over at least a year. That study, called APOLLO, is one of several exploring dedicated TMVR valves from different companies, with names like SUMMIT, MISCEND, and TIARA-2.
Currently, TMVR is approved in the United States only using one device designed for the aortic position and only for treating failed surgical mitral bioprostheses in high-risk patients.
If the Intrepid transfemoral system has an Achilles’ heel, at least in the current iteration, it might be its 35 F catheter delivery system that requires surgical access to the femoral vein. Seven of the patients in the small series experienced major bleeding events, including six at the femoral access site, listed as major vascular complications.
Overall, the study’s patients “were extremely sick with a lot of comorbidity. A lot of them had atrial fibrillation, a lot of them were on anticoagulation to start with,” observed Firas Zahr, MD, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, as part of his presentation of the study at Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics (TCT) 2021, held virtually as well as onsite in Orlando, Florida.
All had moderate-to-severe, usually primary MR; two thirds of the cohort had been in NYHA class III or IV at baseline, and 40% had been hospitalized for heart failure within the past year. Eight had a history of cardiovascular surgery, and eight had diabetes. Their mean Society of Thoracic Surgeons Predicted Risk of Mortality (STS-PROM) score was 4.7, Dr. Zahr reported.
“At 30 days, there was a significant improvement in their heart failure classification; the vast majority of the patients were [NYHA] class I and class II,” said Dr. Zahr, who is also lead author on the study’s Nov. 6 publication in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
Observers of the study at TCT 2021 seemed enthusiastic about the study’s results but recognized that TMVR in its current form still has formidable limitations.
“This is clearly an exciting look into the future and very reassuring to a degree, aside from the complications, which are somewhat expected as we go with 30-plus French devices,” Rajiv Tayal, MD, MPH, said at a press conference on the Intrepid study held before Dr. Zahr’s formal presentation. Dr. Tayal is an interventional cardiologist with Valley Health System, Ridgewood, New Jersey, and New York Medical College, Valhalla.
“I think we’ve all learned that transapical [access] is just not a viable procedure for a lot of these patients, and so we’ve got to get to transfemoral,” Susheel K. Kodali, MD, interventional cardiologist at New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, said at the same forum.
A 35 F device “is going to be too big,” he said. However, “it is the first step to iterate to a smaller device.” Dr. Kodali said his center contributed a patient to the study, and he is listed as a coauthor on the publication.
The delivery system’s large profile is only part of the vascular complication issue. Not only did the procedure require surgical cutdown for venous access, but “we were fairly aggressive in anticoagulating these patients with the fear of thrombus formation,” Dr. Zahr said in the discussion following his presentation.
“A postprocedure anticoagulation regimen is recommended within the protocol, but ultimate therapy was left to the discretion of the treating site physician,” the published report states, noting that all 14 patients with successful TMVR were discharged on warfarin. They included 12 who were also put on a single antiplatelet and one given dual antiplatelet therapy on top of the oral anticoagulant.
“One thing that we learned is that we probably should standardize our approach to perioperative anticoagulation,” Dr. Zahr observed. Also, a 29 F sheath for the system is in the works, “and we’re hoping that with smaller sheath size, and hopefully going even to percutaneous, might have an impact on lowering the vascular complications.”
Explanations for the “higher-than-expected vascular complication rate” remains somewhat unclear, agreed an editorial accompanying the study’s publication, “but may include a learning curve with the system, the large introducer sheath, the need for surgical cutdown, and postprocedural anticoagulation.”
For trans-septal TMVR to become a default approach, “venous access will need to be achieved percutaneously and vascular complications need to be infrequent,” contends the editorial, with lead author Mohamad Alkhouli, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
“These data provide a glimpse into the future of TMVR. The excellent short-term safety and effectiveness of this still very early-stage procedure represent a major step forward in the field,” they write.
“The main question that the Intrepid early feasibility data raise is whether transfemoral, trans-septal TMVR will evolve to become the preferred strategy over transapical TMVR,” as occurred with transcatheter aortic-valve replacement (TAVR), the editorial states. “The answer is likely yes, but a few matters specific to trans-septal route will need be addressed first.”
Among those matters: The 35 F catheter leaves behind a considerable atrial septal defect (ASD). At operator discretion in this series, 11 patients received an ASD closure device.
None of the remaining four patients “developed significant heart failure or right ventricular dysfunction,” Dr. Zahr observed. “So, it seems like those patients who had their ASD left open tolerated it fairly well, at least until 30 days.”
But “we still need to learn what to do with those ASDs,” he said. “What is an acceptable residual shunt and what is an acceptable ASD size is to be determined.”
In general, the editorial notes, “the TMVR population has a high prevalence of cardiomyopathy, and a large residual iatrogenic ASD may lead to worsening volume overload and heart failure decompensation in some patients.”
Insertion of a closure device has its own issues, it continues. “Closure of the ASD might impede future access to the left atrium, which could impact life-long management of this high-risk population. A large septal occluder may hinder potentially needed procedures such as paravalvular leak closure, left atrial appendage closure, or pulmonary vein isolation.”
Patients like those in the current series, Dr. Kodali observed, will face “a lifetime of management challenges, and you want to make sure you don’t take away other options.”
The study was funded by Medtronic. Dr. Zahr reported institutional grant support from Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic. Dr. Kodali disclosed consultant fees from Admedus and Dura Biotech; equity in Dura Biotech, Microinterventional Devices, Thubrika Aortic Valve, Supira, Admedus, TriFlo, and Anona; and institutional grant support from Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, and JenaValve. The editorial writers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tayal disclosed consultant fees or honoraria from or serving on a speakers bureau for Abiomed, Edwards Lifesciences, Abbott Vascular, and Shockwave Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It remains early days for transcatheter mitral-valve replacement (TMVR) as a minimally invasive way to treat severe, mitral regurgitation (MR), but it’s even earlier days for TMVR as an endovascular procedure. Most of the technique’s limited experience with a dedicated mitral prosthesis has involved transapical delivery.
But now a 15-patient study of transfemoral, transeptal TMVR – with a prosthesis designed for the mitral position and previously tested only transapically – has shown good 30-day results in that MR was essentially abolished with virtually no paravalvular leakage.
Nor were there adverse clinical events such as death, stroke, reintervention, or new need for a pacemaker in any of the high-surgical-risk patients with MR in this feasibility study of the transfemoral Intrepid TMVR System (Medtronic). Implantation failed, however, in one patient who then received a surgical valve via sternotomy.
The current cohort is part of a larger ongoing trial that will track whether patients implanted transfemorally with the Intrepid also show reverse remodeling and good clinical outcomes over at least a year. That study, called APOLLO, is one of several exploring dedicated TMVR valves from different companies, with names like SUMMIT, MISCEND, and TIARA-2.
Currently, TMVR is approved in the United States only using one device designed for the aortic position and only for treating failed surgical mitral bioprostheses in high-risk patients.
If the Intrepid transfemoral system has an Achilles’ heel, at least in the current iteration, it might be its 35 F catheter delivery system that requires surgical access to the femoral vein. Seven of the patients in the small series experienced major bleeding events, including six at the femoral access site, listed as major vascular complications.
Overall, the study’s patients “were extremely sick with a lot of comorbidity. A lot of them had atrial fibrillation, a lot of them were on anticoagulation to start with,” observed Firas Zahr, MD, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, as part of his presentation of the study at Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics (TCT) 2021, held virtually as well as onsite in Orlando, Florida.
All had moderate-to-severe, usually primary MR; two thirds of the cohort had been in NYHA class III or IV at baseline, and 40% had been hospitalized for heart failure within the past year. Eight had a history of cardiovascular surgery, and eight had diabetes. Their mean Society of Thoracic Surgeons Predicted Risk of Mortality (STS-PROM) score was 4.7, Dr. Zahr reported.
“At 30 days, there was a significant improvement in their heart failure classification; the vast majority of the patients were [NYHA] class I and class II,” said Dr. Zahr, who is also lead author on the study’s Nov. 6 publication in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
Observers of the study at TCT 2021 seemed enthusiastic about the study’s results but recognized that TMVR in its current form still has formidable limitations.
“This is clearly an exciting look into the future and very reassuring to a degree, aside from the complications, which are somewhat expected as we go with 30-plus French devices,” Rajiv Tayal, MD, MPH, said at a press conference on the Intrepid study held before Dr. Zahr’s formal presentation. Dr. Tayal is an interventional cardiologist with Valley Health System, Ridgewood, New Jersey, and New York Medical College, Valhalla.
“I think we’ve all learned that transapical [access] is just not a viable procedure for a lot of these patients, and so we’ve got to get to transfemoral,” Susheel K. Kodali, MD, interventional cardiologist at New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, said at the same forum.
A 35 F device “is going to be too big,” he said. However, “it is the first step to iterate to a smaller device.” Dr. Kodali said his center contributed a patient to the study, and he is listed as a coauthor on the publication.
The delivery system’s large profile is only part of the vascular complication issue. Not only did the procedure require surgical cutdown for venous access, but “we were fairly aggressive in anticoagulating these patients with the fear of thrombus formation,” Dr. Zahr said in the discussion following his presentation.
“A postprocedure anticoagulation regimen is recommended within the protocol, but ultimate therapy was left to the discretion of the treating site physician,” the published report states, noting that all 14 patients with successful TMVR were discharged on warfarin. They included 12 who were also put on a single antiplatelet and one given dual antiplatelet therapy on top of the oral anticoagulant.
“One thing that we learned is that we probably should standardize our approach to perioperative anticoagulation,” Dr. Zahr observed. Also, a 29 F sheath for the system is in the works, “and we’re hoping that with smaller sheath size, and hopefully going even to percutaneous, might have an impact on lowering the vascular complications.”
Explanations for the “higher-than-expected vascular complication rate” remains somewhat unclear, agreed an editorial accompanying the study’s publication, “but may include a learning curve with the system, the large introducer sheath, the need for surgical cutdown, and postprocedural anticoagulation.”
For trans-septal TMVR to become a default approach, “venous access will need to be achieved percutaneously and vascular complications need to be infrequent,” contends the editorial, with lead author Mohamad Alkhouli, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
“These data provide a glimpse into the future of TMVR. The excellent short-term safety and effectiveness of this still very early-stage procedure represent a major step forward in the field,” they write.
“The main question that the Intrepid early feasibility data raise is whether transfemoral, trans-septal TMVR will evolve to become the preferred strategy over transapical TMVR,” as occurred with transcatheter aortic-valve replacement (TAVR), the editorial states. “The answer is likely yes, but a few matters specific to trans-septal route will need be addressed first.”
Among those matters: The 35 F catheter leaves behind a considerable atrial septal defect (ASD). At operator discretion in this series, 11 patients received an ASD closure device.
None of the remaining four patients “developed significant heart failure or right ventricular dysfunction,” Dr. Zahr observed. “So, it seems like those patients who had their ASD left open tolerated it fairly well, at least until 30 days.”
But “we still need to learn what to do with those ASDs,” he said. “What is an acceptable residual shunt and what is an acceptable ASD size is to be determined.”
In general, the editorial notes, “the TMVR population has a high prevalence of cardiomyopathy, and a large residual iatrogenic ASD may lead to worsening volume overload and heart failure decompensation in some patients.”
Insertion of a closure device has its own issues, it continues. “Closure of the ASD might impede future access to the left atrium, which could impact life-long management of this high-risk population. A large septal occluder may hinder potentially needed procedures such as paravalvular leak closure, left atrial appendage closure, or pulmonary vein isolation.”
Patients like those in the current series, Dr. Kodali observed, will face “a lifetime of management challenges, and you want to make sure you don’t take away other options.”
The study was funded by Medtronic. Dr. Zahr reported institutional grant support from Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic. Dr. Kodali disclosed consultant fees from Admedus and Dura Biotech; equity in Dura Biotech, Microinterventional Devices, Thubrika Aortic Valve, Supira, Admedus, TriFlo, and Anona; and institutional grant support from Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, and JenaValve. The editorial writers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tayal disclosed consultant fees or honoraria from or serving on a speakers bureau for Abiomed, Edwards Lifesciences, Abbott Vascular, and Shockwave Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AHA 2021 puts scientific dialogue, health equity center stage
Virtual platforms democratized scientific meetings during the COVID-19 pandemic but, as any meeting-goer will tell you, it’s the questions from the floor and the back-and-forth of an expert panel that often reveal the importance of and/or problems with a presentation. It’s the scrutiny that makes the science resonate, especially in this postfactual era.
The all-virtual American Heart Association Scientific Sessions 2021 is looking to recreate the engagement of an in-person meeting by offering more live interactive events. They range from seven late-breaking science (LBS) sessions to Saturday’s fireside chat on the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines and Monday’s dive into the controversial new AHA/American College of Cardiology Chest Pain guidelines.
To help digest the latest science, attendees will be able to have their questions answered in real-time via Slido, meet with the trialists, and hear live commentary from key opinion leaders after the live events. A networking function will also allow attendees and exhibitors to chat or meet virtually.
“In this day and age, many people pretty quickly can get access to the science but it’s what I call the IC sort of phenomenon – the presentation of the information, the context of the information, putting it into how I’m going to use it in my practice, and then the critical appraisal – that’s what most people want at the Scientific Sessions,” program committee chair Manesh R. Patel, MD, of Duke University School of Medicine, said in an interview. “We’re all craving ways in which we can interact with one another to put things in context.”
Plans for a hybrid in-person meeting in Boston were scuttled in September because of the Delta variant surge, but the theme of the meeting remained: “One World. Together for Science.” Attendees will be able to access more than 500 live and on-demand sessions including 117 oral abstracts, 286 poster sessions, 59 moderated digital posters, and over a dozen sessions focused on strategies to promote health equity.
“Last year there was a Presidential Session and a statement on structural racism, so we wanted to take the next step and say, What are the ways in which people are starting to interact and do things to make a difference?” explained Dr. Patel. “So, this year, you’ll see different versions of that from the Main Event session, which has some case vignettes and a panel discussion, to other health equity sessions that describe not just COVID care, but blood pressure care, maternal-fetal medicine, and congenital kids. Wherever we can, we’ve tried to infuse it throughout the sessions and will continue to.”
Late-breaking science
The LBS sessions kick off at 9:30 a.m. ET Saturday with AVATAR, a randomized trial of aortic valve replacement vs. watchful waiting in severe aortic stenosis proved asymptomatic through exercise testing.
“The findings of that trial, depending on what they are, could certainly impact clinical practice because it’s a very common scenario in which we have elderly patients with aortic valve stenosis that might be severe but they may not be symptomatic,” he said.
It’s followed by a randomized trial from the Cardiothoracic Surgical Trials Network, examining whether tricuspid repair at the time of mitral valve surgery leads to beneficial outcomes. “I think it’s a pretty important study,” Dr. Patel said, “because it’ll again affect how we think about our clinical practice.”
Rounding out the LBS.01 session is RAPID CABG, comparing early vs. delayed coronary bypass graft surgery (CABG) in patients with acute coronary syndromes on ticagrelor, and the pivotal U.S. VEST trial of an external support device already approved in Europe for saphenous vein grafts during CABG.
Saturday’s LBS.02 at 3:00 p.m. ET is devoted to hypertension and looks at how the COVID-19 pandemic affected blood pressure control. There’s also a study of remotely delivered hypertension and lipid management in 10,000 patients across the Partners Healthcare System and a cluster randomized trial of a village doctor–led blood pressure intervention in rural China.
Sunday’s LBS.03 at 8:00 a.m. ET is focused on atrial arrhythmias, starting with the CRAVE trial examining the effect of caffeine consumption on cardiac ectopy burden in 108 patients using an N-of-1 design and 2-day blocks on and off caffeine. “There’s an ability to identify a dose response that you get arrhythmias when you increase the amount of coffee you drink vs. not in an individual, so I think that will be likely discussed a lot and worth paying attention to,” Dr. Patel said.
The session also includes GIRAF, a comparison of cognitive outcomes with dabigatran (Pradaxa) vs. warfarin (Coumadin) in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AF); PALACS, a randomized trial examining whether left-sided pericardiotomy prevents AF after cardiac surgery; and AMAZE, which study sponsor AtriCure revealed missed its primary efficacy endpoint of freedom from AF with the LARIAT suture delivery device for left atrial appendage closure plus pulmonary vein isolation.
LBS.04 at 3:30 p.m. ET Sunday takes on digital health, with results from the nonrandomized Fitbit Heart Study on AF notifications from 450,000 participants wearing a single-lead ECG patch. “A lot of technologies claim that they can detect things, and we should ask that people go through the rigorous evaluation to see if they in fact do. So, in that respect, I think it›s an important step,” observed Dr. Patel.
Also on tap is I-STOP-AFib, another N-of-1 study using mobile apps and the AliveCor device to identify individual AF triggers; and REVeAL-HF, a 4,000-patient study examining whether electronic alerts that provide clinicians with prognostic information on their heart failure (HF) patients will reduce mortality and 30-day HF hospitalizations.
LBS.05 at 5:00 p.m. ET provides new information from EMPEROR-Preserved in HF with preserved ejection fraction and main results from EMPULSE, also using the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance) in 530 patients hospitalized for acute HF.
The session also features CHIEF-HF, a randomized trial leveraging mobile technologies to test whether 12 weeks of another SGLT2 inhibitor, canagliflozin (Invokana), is superior to placebo for improving HF symptoms; and DREAM-HF, a comparison of transendocardial delivery of allogeneic mesenchymal precursor cells vs. a sham comparator in chronic HF as a result of left ventricular systolic dysfunction.
Monday’s LBS.06 at 8:00 a.m. ET details the safety and cholesterol-lowering efficacy of MK-0616, an investigational oral PCSK9 inhibitor. “It’s just a phase 2 [trial], but there’s interest in an oral PCSK9 inhibitor, given that the current ones are subcutaneous,” Dr. Patel said.
Results will also be presented from PREPARE-IT 2, which tested icosapent ethyl vs. placebo in outpatients with COVID-19. In the recently reported PREPARE-IT 1, a loading dose of icosapent ethyl failed to reduce the risk of hospitalization with SARS-CoV-2 infection among at-risk individuals.
LBS.07 at 11:00 a.m. Monday completes the late-breakers with new results from ASCEND, this time examining the effect of aspirin on dementia and cognitive impairment in patients with diabetes.
Next up is a look at the effectiveness of P2Y12 inhibitors in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in the adaptive ACTIV-4a trial, followed by results of the pivotal phase 3 REVERSE-IT trial of bentracimab, a recombinant human monoclonal antibody antigen fragment designed to reverse the antiplatelet activity of ticagrelor in the event of major bleeding or when urgent surgery is needed.
Closing out the session is AXIOMATIC-TKR, a double-blind comparison of the safety and efficacy of the investigational oral factor XI anticoagulant JNJ-70033093 vs. subcutaneous enoxaparin (Lovenox) in elective total knee replacement.
For those searching for more AHA-related science online, the Resuscitation Science Symposium (ReSS) will run from this Friday through Sunday and the Quality of Care and Outcomes Research (QCOR) Scientific Sessions will take the stage next Monday, Nov. 15.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Virtual platforms democratized scientific meetings during the COVID-19 pandemic but, as any meeting-goer will tell you, it’s the questions from the floor and the back-and-forth of an expert panel that often reveal the importance of and/or problems with a presentation. It’s the scrutiny that makes the science resonate, especially in this postfactual era.
The all-virtual American Heart Association Scientific Sessions 2021 is looking to recreate the engagement of an in-person meeting by offering more live interactive events. They range from seven late-breaking science (LBS) sessions to Saturday’s fireside chat on the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines and Monday’s dive into the controversial new AHA/American College of Cardiology Chest Pain guidelines.
To help digest the latest science, attendees will be able to have their questions answered in real-time via Slido, meet with the trialists, and hear live commentary from key opinion leaders after the live events. A networking function will also allow attendees and exhibitors to chat or meet virtually.
“In this day and age, many people pretty quickly can get access to the science but it’s what I call the IC sort of phenomenon – the presentation of the information, the context of the information, putting it into how I’m going to use it in my practice, and then the critical appraisal – that’s what most people want at the Scientific Sessions,” program committee chair Manesh R. Patel, MD, of Duke University School of Medicine, said in an interview. “We’re all craving ways in which we can interact with one another to put things in context.”
Plans for a hybrid in-person meeting in Boston were scuttled in September because of the Delta variant surge, but the theme of the meeting remained: “One World. Together for Science.” Attendees will be able to access more than 500 live and on-demand sessions including 117 oral abstracts, 286 poster sessions, 59 moderated digital posters, and over a dozen sessions focused on strategies to promote health equity.
“Last year there was a Presidential Session and a statement on structural racism, so we wanted to take the next step and say, What are the ways in which people are starting to interact and do things to make a difference?” explained Dr. Patel. “So, this year, you’ll see different versions of that from the Main Event session, which has some case vignettes and a panel discussion, to other health equity sessions that describe not just COVID care, but blood pressure care, maternal-fetal medicine, and congenital kids. Wherever we can, we’ve tried to infuse it throughout the sessions and will continue to.”
Late-breaking science
The LBS sessions kick off at 9:30 a.m. ET Saturday with AVATAR, a randomized trial of aortic valve replacement vs. watchful waiting in severe aortic stenosis proved asymptomatic through exercise testing.
“The findings of that trial, depending on what they are, could certainly impact clinical practice because it’s a very common scenario in which we have elderly patients with aortic valve stenosis that might be severe but they may not be symptomatic,” he said.
It’s followed by a randomized trial from the Cardiothoracic Surgical Trials Network, examining whether tricuspid repair at the time of mitral valve surgery leads to beneficial outcomes. “I think it’s a pretty important study,” Dr. Patel said, “because it’ll again affect how we think about our clinical practice.”
Rounding out the LBS.01 session is RAPID CABG, comparing early vs. delayed coronary bypass graft surgery (CABG) in patients with acute coronary syndromes on ticagrelor, and the pivotal U.S. VEST trial of an external support device already approved in Europe for saphenous vein grafts during CABG.
Saturday’s LBS.02 at 3:00 p.m. ET is devoted to hypertension and looks at how the COVID-19 pandemic affected blood pressure control. There’s also a study of remotely delivered hypertension and lipid management in 10,000 patients across the Partners Healthcare System and a cluster randomized trial of a village doctor–led blood pressure intervention in rural China.
Sunday’s LBS.03 at 8:00 a.m. ET is focused on atrial arrhythmias, starting with the CRAVE trial examining the effect of caffeine consumption on cardiac ectopy burden in 108 patients using an N-of-1 design and 2-day blocks on and off caffeine. “There’s an ability to identify a dose response that you get arrhythmias when you increase the amount of coffee you drink vs. not in an individual, so I think that will be likely discussed a lot and worth paying attention to,” Dr. Patel said.
The session also includes GIRAF, a comparison of cognitive outcomes with dabigatran (Pradaxa) vs. warfarin (Coumadin) in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AF); PALACS, a randomized trial examining whether left-sided pericardiotomy prevents AF after cardiac surgery; and AMAZE, which study sponsor AtriCure revealed missed its primary efficacy endpoint of freedom from AF with the LARIAT suture delivery device for left atrial appendage closure plus pulmonary vein isolation.
LBS.04 at 3:30 p.m. ET Sunday takes on digital health, with results from the nonrandomized Fitbit Heart Study on AF notifications from 450,000 participants wearing a single-lead ECG patch. “A lot of technologies claim that they can detect things, and we should ask that people go through the rigorous evaluation to see if they in fact do. So, in that respect, I think it›s an important step,” observed Dr. Patel.
Also on tap is I-STOP-AFib, another N-of-1 study using mobile apps and the AliveCor device to identify individual AF triggers; and REVeAL-HF, a 4,000-patient study examining whether electronic alerts that provide clinicians with prognostic information on their heart failure (HF) patients will reduce mortality and 30-day HF hospitalizations.
LBS.05 at 5:00 p.m. ET provides new information from EMPEROR-Preserved in HF with preserved ejection fraction and main results from EMPULSE, also using the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance) in 530 patients hospitalized for acute HF.
The session also features CHIEF-HF, a randomized trial leveraging mobile technologies to test whether 12 weeks of another SGLT2 inhibitor, canagliflozin (Invokana), is superior to placebo for improving HF symptoms; and DREAM-HF, a comparison of transendocardial delivery of allogeneic mesenchymal precursor cells vs. a sham comparator in chronic HF as a result of left ventricular systolic dysfunction.
Monday’s LBS.06 at 8:00 a.m. ET details the safety and cholesterol-lowering efficacy of MK-0616, an investigational oral PCSK9 inhibitor. “It’s just a phase 2 [trial], but there’s interest in an oral PCSK9 inhibitor, given that the current ones are subcutaneous,” Dr. Patel said.
Results will also be presented from PREPARE-IT 2, which tested icosapent ethyl vs. placebo in outpatients with COVID-19. In the recently reported PREPARE-IT 1, a loading dose of icosapent ethyl failed to reduce the risk of hospitalization with SARS-CoV-2 infection among at-risk individuals.
LBS.07 at 11:00 a.m. Monday completes the late-breakers with new results from ASCEND, this time examining the effect of aspirin on dementia and cognitive impairment in patients with diabetes.
Next up is a look at the effectiveness of P2Y12 inhibitors in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in the adaptive ACTIV-4a trial, followed by results of the pivotal phase 3 REVERSE-IT trial of bentracimab, a recombinant human monoclonal antibody antigen fragment designed to reverse the antiplatelet activity of ticagrelor in the event of major bleeding or when urgent surgery is needed.
Closing out the session is AXIOMATIC-TKR, a double-blind comparison of the safety and efficacy of the investigational oral factor XI anticoagulant JNJ-70033093 vs. subcutaneous enoxaparin (Lovenox) in elective total knee replacement.
For those searching for more AHA-related science online, the Resuscitation Science Symposium (ReSS) will run from this Friday through Sunday and the Quality of Care and Outcomes Research (QCOR) Scientific Sessions will take the stage next Monday, Nov. 15.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Virtual platforms democratized scientific meetings during the COVID-19 pandemic but, as any meeting-goer will tell you, it’s the questions from the floor and the back-and-forth of an expert panel that often reveal the importance of and/or problems with a presentation. It’s the scrutiny that makes the science resonate, especially in this postfactual era.
The all-virtual American Heart Association Scientific Sessions 2021 is looking to recreate the engagement of an in-person meeting by offering more live interactive events. They range from seven late-breaking science (LBS) sessions to Saturday’s fireside chat on the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines and Monday’s dive into the controversial new AHA/American College of Cardiology Chest Pain guidelines.
To help digest the latest science, attendees will be able to have their questions answered in real-time via Slido, meet with the trialists, and hear live commentary from key opinion leaders after the live events. A networking function will also allow attendees and exhibitors to chat or meet virtually.
“In this day and age, many people pretty quickly can get access to the science but it’s what I call the IC sort of phenomenon – the presentation of the information, the context of the information, putting it into how I’m going to use it in my practice, and then the critical appraisal – that’s what most people want at the Scientific Sessions,” program committee chair Manesh R. Patel, MD, of Duke University School of Medicine, said in an interview. “We’re all craving ways in which we can interact with one another to put things in context.”
Plans for a hybrid in-person meeting in Boston were scuttled in September because of the Delta variant surge, but the theme of the meeting remained: “One World. Together for Science.” Attendees will be able to access more than 500 live and on-demand sessions including 117 oral abstracts, 286 poster sessions, 59 moderated digital posters, and over a dozen sessions focused on strategies to promote health equity.
“Last year there was a Presidential Session and a statement on structural racism, so we wanted to take the next step and say, What are the ways in which people are starting to interact and do things to make a difference?” explained Dr. Patel. “So, this year, you’ll see different versions of that from the Main Event session, which has some case vignettes and a panel discussion, to other health equity sessions that describe not just COVID care, but blood pressure care, maternal-fetal medicine, and congenital kids. Wherever we can, we’ve tried to infuse it throughout the sessions and will continue to.”
Late-breaking science
The LBS sessions kick off at 9:30 a.m. ET Saturday with AVATAR, a randomized trial of aortic valve replacement vs. watchful waiting in severe aortic stenosis proved asymptomatic through exercise testing.
“The findings of that trial, depending on what they are, could certainly impact clinical practice because it’s a very common scenario in which we have elderly patients with aortic valve stenosis that might be severe but they may not be symptomatic,” he said.
It’s followed by a randomized trial from the Cardiothoracic Surgical Trials Network, examining whether tricuspid repair at the time of mitral valve surgery leads to beneficial outcomes. “I think it’s a pretty important study,” Dr. Patel said, “because it’ll again affect how we think about our clinical practice.”
Rounding out the LBS.01 session is RAPID CABG, comparing early vs. delayed coronary bypass graft surgery (CABG) in patients with acute coronary syndromes on ticagrelor, and the pivotal U.S. VEST trial of an external support device already approved in Europe for saphenous vein grafts during CABG.
Saturday’s LBS.02 at 3:00 p.m. ET is devoted to hypertension and looks at how the COVID-19 pandemic affected blood pressure control. There’s also a study of remotely delivered hypertension and lipid management in 10,000 patients across the Partners Healthcare System and a cluster randomized trial of a village doctor–led blood pressure intervention in rural China.
Sunday’s LBS.03 at 8:00 a.m. ET is focused on atrial arrhythmias, starting with the CRAVE trial examining the effect of caffeine consumption on cardiac ectopy burden in 108 patients using an N-of-1 design and 2-day blocks on and off caffeine. “There’s an ability to identify a dose response that you get arrhythmias when you increase the amount of coffee you drink vs. not in an individual, so I think that will be likely discussed a lot and worth paying attention to,” Dr. Patel said.
The session also includes GIRAF, a comparison of cognitive outcomes with dabigatran (Pradaxa) vs. warfarin (Coumadin) in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AF); PALACS, a randomized trial examining whether left-sided pericardiotomy prevents AF after cardiac surgery; and AMAZE, which study sponsor AtriCure revealed missed its primary efficacy endpoint of freedom from AF with the LARIAT suture delivery device for left atrial appendage closure plus pulmonary vein isolation.
LBS.04 at 3:30 p.m. ET Sunday takes on digital health, with results from the nonrandomized Fitbit Heart Study on AF notifications from 450,000 participants wearing a single-lead ECG patch. “A lot of technologies claim that they can detect things, and we should ask that people go through the rigorous evaluation to see if they in fact do. So, in that respect, I think it›s an important step,” observed Dr. Patel.
Also on tap is I-STOP-AFib, another N-of-1 study using mobile apps and the AliveCor device to identify individual AF triggers; and REVeAL-HF, a 4,000-patient study examining whether electronic alerts that provide clinicians with prognostic information on their heart failure (HF) patients will reduce mortality and 30-day HF hospitalizations.
LBS.05 at 5:00 p.m. ET provides new information from EMPEROR-Preserved in HF with preserved ejection fraction and main results from EMPULSE, also using the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance) in 530 patients hospitalized for acute HF.
The session also features CHIEF-HF, a randomized trial leveraging mobile technologies to test whether 12 weeks of another SGLT2 inhibitor, canagliflozin (Invokana), is superior to placebo for improving HF symptoms; and DREAM-HF, a comparison of transendocardial delivery of allogeneic mesenchymal precursor cells vs. a sham comparator in chronic HF as a result of left ventricular systolic dysfunction.
Monday’s LBS.06 at 8:00 a.m. ET details the safety and cholesterol-lowering efficacy of MK-0616, an investigational oral PCSK9 inhibitor. “It’s just a phase 2 [trial], but there’s interest in an oral PCSK9 inhibitor, given that the current ones are subcutaneous,” Dr. Patel said.
Results will also be presented from PREPARE-IT 2, which tested icosapent ethyl vs. placebo in outpatients with COVID-19. In the recently reported PREPARE-IT 1, a loading dose of icosapent ethyl failed to reduce the risk of hospitalization with SARS-CoV-2 infection among at-risk individuals.
LBS.07 at 11:00 a.m. Monday completes the late-breakers with new results from ASCEND, this time examining the effect of aspirin on dementia and cognitive impairment in patients with diabetes.
Next up is a look at the effectiveness of P2Y12 inhibitors in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in the adaptive ACTIV-4a trial, followed by results of the pivotal phase 3 REVERSE-IT trial of bentracimab, a recombinant human monoclonal antibody antigen fragment designed to reverse the antiplatelet activity of ticagrelor in the event of major bleeding or when urgent surgery is needed.
Closing out the session is AXIOMATIC-TKR, a double-blind comparison of the safety and efficacy of the investigational oral factor XI anticoagulant JNJ-70033093 vs. subcutaneous enoxaparin (Lovenox) in elective total knee replacement.
For those searching for more AHA-related science online, the Resuscitation Science Symposium (ReSS) will run from this Friday through Sunday and the Quality of Care and Outcomes Research (QCOR) Scientific Sessions will take the stage next Monday, Nov. 15.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2021
At 5 years, iFR found as effective and safe as FFR for guiding PCI intervention
The rate of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) over 5 years is similar whether revascularization is guided by instantaneous wave-free ratio (iFR) or fractional flow reserve (FFR), according to long-term results of the iFR-SWEDEHEART study.
“The results are about the same as reported at 12 months. There were no significant differences in any outcome we evaluated,” according to Matthias Götberg, MD, PhD.
When the initial results of the noninferiority iFR-SWEDEHEART trial were published after 1 year of follow-up, the primary MACE endpoint of death from any-cause nonfatal myocardial infarction, or unplanned revascularization, was met by 6.7% and 6.1% of those randomized to iFR or FFR, respectively.
These outcomes were not significantly different and placed iFR well within the predefined boundaries of noninferiority (P = .007).
In this new and final follow-up of iFR-SWEDEHEART, which evaluated the same 2,019 patients who were alive at 1 year (none were lost to follow-up), the MACE endpoint was met by 21.5% and 19.9% of those managed with iFR and FFR, respectively. The hazard ratio (1.09) had a wide 95% confidence interval (0.90-1.31) that did not approach statistical significance.
No differences seen across outcomes
When broken down into the MACE components, there were no differences between iFR and FFR, respectively, for all-cause death (9.4% vs. 7.9%), MI (5.8% vs. 5.7%) or unplanned revascularization (11.6% vs. 11.3%).
Across predefined subgroups, such as those defined by age, gender, stable versus unstable angina, and presence of risk factors such as diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and smoking, there were also no significant differences in outcome.
At the time iFR-SWEDEHART was initiated, FFR had already been accepted as more effective than angiographic assessment to identify lesion ischemia and the need for percutaneous intervention (PCI). The iFR-SWEDEHEART trial tested iFR, a relatively new technology at the time, as a noninferior alternative. Unlike FFR, which requires adenosine to dilate the vessel, adding cost and patient discomfort, iFR measures the resting pressure gradient across the coronary lesion, and it is generally easier to perform.
“The advantage of iFR is that it provides an instantaneous lesion assessment without the need for adenosine,” Dr. Götberg explained in presenting the results at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, held virtually and live in Orlando.
When the procedural results were compared in the published study at 1 year, it was noted that the mean number of lesions evaluated per patient was higher (1.55 vs. 1.43; P = .002), but the proportion of lesions found functionally significant was lower (29.2% vs. 36.8%; P < .0001) among those randomized to iFR than in the FFR group.
While most other procedural characteristics, such as PCI access route, fluoroscopy time, and contrast use did not differ significantly, fewer stents were placed in patients managed with iFR (1.58 vs. 1.73; P = .048), and a reduction in the average procedural time of a few minutes approached significance (P = .09).
Patient discomfort is greater with FFR
Patient discomfort measured during the procedure did differ, according to Dr. Götberg, an interventional cardiologist at Skåne University Hospital, Lund, Sweden.
Only about 30% in the FFR group reported no discomfort. Most of the others reported mild or moderate discomfort, but nearly 10% characterized the discomfort as severe. In the iFR group, more than 95% reported no discomfort. All of the remaining patients reported discomfort level as mild.
Because differences in MACE would be most likely to occur in the first year after revascularization, the similarity of the 1- and 5-year results were expected, according to Dr. Götberg. However, a 5-year follow-up was considered prudent given the relatively limited experience with iFR when the study was designed. This technique is now well established and widely used.
The study supports the premise that quicker and easier-to-obtain results with iFR are obtained without sacrificing greater relative risk of failing to identify a vulnerable lesion, according to Dr. Götberg.
Nevertheless, iFR and FFR “are not an exact match,” according to Jennifer A. Rymer, MD, an interventional cardiologist and assistant professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C. Although she called this trial an “excellent” demonstration of comparable utility in distinguishing lesions that do not require intervention from those that do, she implied that some clinicians might still prefer FFR for other reasons.
For example, FFR provides information about coronary flow reserve and microvascular resistance that are relevant to the underlying pathophysiology in a diseased vessel, according to Shmuel Banai, MD, head of interventional cardiology, Tel Aviv Medical Center. Recognizing that this information is not as readily generated by iFR, he is among those who plan to continue to use FFR despite these results.
However, for those who are now routinely performing iFR for the purposes of guiding revascularization, “these data are reassuring,” said David Kandzari, MD, director of interventional cardiology, Piedmont Hart Institute, Atlanta. The 5-year data essentially eliminate the likelihood that iFR relative to FFR increases the risk of missing functionally significant lesions for revascularization procedures.
Dr. Götberg reports financial relationships with Abbott, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Phillips Healthcare. Dr. Rymer reports no potential financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Banai has a financial relationship with Neovasc. Dr. Kandzari reports financial relationships with Ablative Solutions and Medtronic.
The rate of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) over 5 years is similar whether revascularization is guided by instantaneous wave-free ratio (iFR) or fractional flow reserve (FFR), according to long-term results of the iFR-SWEDEHEART study.
“The results are about the same as reported at 12 months. There were no significant differences in any outcome we evaluated,” according to Matthias Götberg, MD, PhD.
When the initial results of the noninferiority iFR-SWEDEHEART trial were published after 1 year of follow-up, the primary MACE endpoint of death from any-cause nonfatal myocardial infarction, or unplanned revascularization, was met by 6.7% and 6.1% of those randomized to iFR or FFR, respectively.
These outcomes were not significantly different and placed iFR well within the predefined boundaries of noninferiority (P = .007).
In this new and final follow-up of iFR-SWEDEHEART, which evaluated the same 2,019 patients who were alive at 1 year (none were lost to follow-up), the MACE endpoint was met by 21.5% and 19.9% of those managed with iFR and FFR, respectively. The hazard ratio (1.09) had a wide 95% confidence interval (0.90-1.31) that did not approach statistical significance.
No differences seen across outcomes
When broken down into the MACE components, there were no differences between iFR and FFR, respectively, for all-cause death (9.4% vs. 7.9%), MI (5.8% vs. 5.7%) or unplanned revascularization (11.6% vs. 11.3%).
Across predefined subgroups, such as those defined by age, gender, stable versus unstable angina, and presence of risk factors such as diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and smoking, there were also no significant differences in outcome.
At the time iFR-SWEDEHART was initiated, FFR had already been accepted as more effective than angiographic assessment to identify lesion ischemia and the need for percutaneous intervention (PCI). The iFR-SWEDEHEART trial tested iFR, a relatively new technology at the time, as a noninferior alternative. Unlike FFR, which requires adenosine to dilate the vessel, adding cost and patient discomfort, iFR measures the resting pressure gradient across the coronary lesion, and it is generally easier to perform.
“The advantage of iFR is that it provides an instantaneous lesion assessment without the need for adenosine,” Dr. Götberg explained in presenting the results at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, held virtually and live in Orlando.
When the procedural results were compared in the published study at 1 year, it was noted that the mean number of lesions evaluated per patient was higher (1.55 vs. 1.43; P = .002), but the proportion of lesions found functionally significant was lower (29.2% vs. 36.8%; P < .0001) among those randomized to iFR than in the FFR group.
While most other procedural characteristics, such as PCI access route, fluoroscopy time, and contrast use did not differ significantly, fewer stents were placed in patients managed with iFR (1.58 vs. 1.73; P = .048), and a reduction in the average procedural time of a few minutes approached significance (P = .09).
Patient discomfort is greater with FFR
Patient discomfort measured during the procedure did differ, according to Dr. Götberg, an interventional cardiologist at Skåne University Hospital, Lund, Sweden.
Only about 30% in the FFR group reported no discomfort. Most of the others reported mild or moderate discomfort, but nearly 10% characterized the discomfort as severe. In the iFR group, more than 95% reported no discomfort. All of the remaining patients reported discomfort level as mild.
Because differences in MACE would be most likely to occur in the first year after revascularization, the similarity of the 1- and 5-year results were expected, according to Dr. Götberg. However, a 5-year follow-up was considered prudent given the relatively limited experience with iFR when the study was designed. This technique is now well established and widely used.
The study supports the premise that quicker and easier-to-obtain results with iFR are obtained without sacrificing greater relative risk of failing to identify a vulnerable lesion, according to Dr. Götberg.
Nevertheless, iFR and FFR “are not an exact match,” according to Jennifer A. Rymer, MD, an interventional cardiologist and assistant professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C. Although she called this trial an “excellent” demonstration of comparable utility in distinguishing lesions that do not require intervention from those that do, she implied that some clinicians might still prefer FFR for other reasons.
For example, FFR provides information about coronary flow reserve and microvascular resistance that are relevant to the underlying pathophysiology in a diseased vessel, according to Shmuel Banai, MD, head of interventional cardiology, Tel Aviv Medical Center. Recognizing that this information is not as readily generated by iFR, he is among those who plan to continue to use FFR despite these results.
However, for those who are now routinely performing iFR for the purposes of guiding revascularization, “these data are reassuring,” said David Kandzari, MD, director of interventional cardiology, Piedmont Hart Institute, Atlanta. The 5-year data essentially eliminate the likelihood that iFR relative to FFR increases the risk of missing functionally significant lesions for revascularization procedures.
Dr. Götberg reports financial relationships with Abbott, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Phillips Healthcare. Dr. Rymer reports no potential financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Banai has a financial relationship with Neovasc. Dr. Kandzari reports financial relationships with Ablative Solutions and Medtronic.
The rate of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) over 5 years is similar whether revascularization is guided by instantaneous wave-free ratio (iFR) or fractional flow reserve (FFR), according to long-term results of the iFR-SWEDEHEART study.
“The results are about the same as reported at 12 months. There were no significant differences in any outcome we evaluated,” according to Matthias Götberg, MD, PhD.
When the initial results of the noninferiority iFR-SWEDEHEART trial were published after 1 year of follow-up, the primary MACE endpoint of death from any-cause nonfatal myocardial infarction, or unplanned revascularization, was met by 6.7% and 6.1% of those randomized to iFR or FFR, respectively.
These outcomes were not significantly different and placed iFR well within the predefined boundaries of noninferiority (P = .007).
In this new and final follow-up of iFR-SWEDEHEART, which evaluated the same 2,019 patients who were alive at 1 year (none were lost to follow-up), the MACE endpoint was met by 21.5% and 19.9% of those managed with iFR and FFR, respectively. The hazard ratio (1.09) had a wide 95% confidence interval (0.90-1.31) that did not approach statistical significance.
No differences seen across outcomes
When broken down into the MACE components, there were no differences between iFR and FFR, respectively, for all-cause death (9.4% vs. 7.9%), MI (5.8% vs. 5.7%) or unplanned revascularization (11.6% vs. 11.3%).
Across predefined subgroups, such as those defined by age, gender, stable versus unstable angina, and presence of risk factors such as diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and smoking, there were also no significant differences in outcome.
At the time iFR-SWEDEHART was initiated, FFR had already been accepted as more effective than angiographic assessment to identify lesion ischemia and the need for percutaneous intervention (PCI). The iFR-SWEDEHEART trial tested iFR, a relatively new technology at the time, as a noninferior alternative. Unlike FFR, which requires adenosine to dilate the vessel, adding cost and patient discomfort, iFR measures the resting pressure gradient across the coronary lesion, and it is generally easier to perform.
“The advantage of iFR is that it provides an instantaneous lesion assessment without the need for adenosine,” Dr. Götberg explained in presenting the results at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, held virtually and live in Orlando.
When the procedural results were compared in the published study at 1 year, it was noted that the mean number of lesions evaluated per patient was higher (1.55 vs. 1.43; P = .002), but the proportion of lesions found functionally significant was lower (29.2% vs. 36.8%; P < .0001) among those randomized to iFR than in the FFR group.
While most other procedural characteristics, such as PCI access route, fluoroscopy time, and contrast use did not differ significantly, fewer stents were placed in patients managed with iFR (1.58 vs. 1.73; P = .048), and a reduction in the average procedural time of a few minutes approached significance (P = .09).
Patient discomfort is greater with FFR
Patient discomfort measured during the procedure did differ, according to Dr. Götberg, an interventional cardiologist at Skåne University Hospital, Lund, Sweden.
Only about 30% in the FFR group reported no discomfort. Most of the others reported mild or moderate discomfort, but nearly 10% characterized the discomfort as severe. In the iFR group, more than 95% reported no discomfort. All of the remaining patients reported discomfort level as mild.
Because differences in MACE would be most likely to occur in the first year after revascularization, the similarity of the 1- and 5-year results were expected, according to Dr. Götberg. However, a 5-year follow-up was considered prudent given the relatively limited experience with iFR when the study was designed. This technique is now well established and widely used.
The study supports the premise that quicker and easier-to-obtain results with iFR are obtained without sacrificing greater relative risk of failing to identify a vulnerable lesion, according to Dr. Götberg.
Nevertheless, iFR and FFR “are not an exact match,” according to Jennifer A. Rymer, MD, an interventional cardiologist and assistant professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C. Although she called this trial an “excellent” demonstration of comparable utility in distinguishing lesions that do not require intervention from those that do, she implied that some clinicians might still prefer FFR for other reasons.
For example, FFR provides information about coronary flow reserve and microvascular resistance that are relevant to the underlying pathophysiology in a diseased vessel, according to Shmuel Banai, MD, head of interventional cardiology, Tel Aviv Medical Center. Recognizing that this information is not as readily generated by iFR, he is among those who plan to continue to use FFR despite these results.
However, for those who are now routinely performing iFR for the purposes of guiding revascularization, “these data are reassuring,” said David Kandzari, MD, director of interventional cardiology, Piedmont Hart Institute, Atlanta. The 5-year data essentially eliminate the likelihood that iFR relative to FFR increases the risk of missing functionally significant lesions for revascularization procedures.
Dr. Götberg reports financial relationships with Abbott, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Phillips Healthcare. Dr. Rymer reports no potential financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Banai has a financial relationship with Neovasc. Dr. Kandzari reports financial relationships with Ablative Solutions and Medtronic.
FROM TCT 2021
FFR-guided PCI falls short vs. surgery in multivessel disease: FAME 3
Coronary stenting guided by fractional flow reserve (FFR) readings, considered to reflect the targeted lesion’s functional impact, was no match for coronary bypass surgery (CABG) in patients with multivessel disease (MVD) in a major international randomized trial.
Indeed, FFR-guided percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) using one of the latest drug-eluting stents (DES) seemed to perform poorly in the trial, compared with surgery, apparently upping the risk for clinical events by 50% over 1 year.
Designed statistically for noninferiority, the third Fractional Flow Reserve Versus Angiography for Multivessel Evaluation (FAME 3) trial, with 1,500 randomized patients, showed that FFR-guided PCI was “not noninferior” to CABG. Of those randomized to PCI, 10.6% met the 1-year primary endpoint of major adverse cardiac or cerebrovascular events (MACCE), compared with only 6.9% of patients assigned to CABG.
The trial enrolled only patients with three-vessel coronary disease with no left-main coronary artery involvement, who were declared by their institution’s multidisciplinary heart team to be appropriate for either form of revascularization.
One of the roles of FFR for PCI guidance is to identify significant lesions “that are underrecognized by the angiogram,” which is less likely to happen in patients with very complex coronary anatomy, study chair William F. Fearon, MD, Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview.
“That’s what we saw in a subgroup analysis based on SYNTAX score,” an index of lesion complexity. “In patients with very high SYNTAX scores, CABG outperformed FFR-guided PCI. But if you look at patients with low SYNTAX scores, actually, FFR-guided PCI outperformed CABG for 1-year MACCE.”
Dr. Fearon is lead author on the study’s Nov. 4, 2021, publication in the New England Journal of Medicine, its release timed to coincide with his presentation of the trial at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, held virtually and live in Orlando and sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
He noted that FAME-3 “wasn’t designed or powered to test for superiority,” so its results do not imply CABG is superior to FFR-PCI in patients with MVD, and remains “inconclusive” on that question.
“I think what this study does is provide both the physician and patients more contemporary data and information on options and expected outcomes in multivessel disease. So if you are a patient who has less complex disease, I think you can feel comfortable that you will get an equivalent result with FFR-guided PCI.” But, at least based on FAME-3, Dr. Fearon said, CABG provides better outcomes in patients with more complex disease.
“I think there are still patients that look at trade-offs. Some patients will accept a higher event rate in order to avoid a long recovery, and vice versa.” So the trial may allow patients and physicians to make more informed decisions, he said.
A main message of FAME-3 “is that we’re getting very good results with three-vessel PCI, but better results with surgery,” Ran Kornowski, MD, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, and Tel Aviv University, said as a discussant following Dr. Fearon’s presentation of the trial. The subanalysis by SYNTAX score, he agreed, probably could be used as part of shared decision-making with patients.
Not all that surprising
“It’s a well-designed study, with a lot of patients,” said surgeon Frank W. Sellke, MD, of Rhode Island Hospital, Miriam Hospital, and Brown University, all in Providence.
“I don’t think it’s all that surprising,” he said in an interview. “It’s very consistent with what other studies have shown, that for three-vessel disease, surgery tends to have the edge,” even when pitted against FFR-guided PCI.
Indeed, pressure-wire FFR-PCI has a spotty history, even as an alternative to standard angiography-based PCI. For example, it has performed well in registry and other cohort studies but showed no advantage in the all-comers RIPCORD-2 trial or in the setting of complete revascularization PCI for acute MI in FLOWER-MI. And it emitted an increased-mortality signal in the prematurely halted FUTURE trial.
In FAME-3, “the 1-year follow-up was the best chance for FFR-PCI to be noninferior to CABG. The CABG advantage is only going to get better with time if prior experience and pathobiology is true,” Sanjay Kaul, MD, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
Overall, “the quality and quantity of evidence is insufficient to support FFR-guided PCI” in patients with complex coronary artery disease (CAD), he said. “I would also argue that the evidence for FFR-guided PCI for simple CAD is also not high quality.”
Dr. Kaul also blasted the claim that FFR-PCI was seen to perform better against CABG in patients with low SYNTAX scores. “In general, one cannot use a positive subgroup in a null or negative trial, as is the case with FAME-3, to ‘rescue’ the treatment intervention.” Such a positive subgroup finding, he said, “would at best be deemed hypothesis-generating and not hypothesis validating.”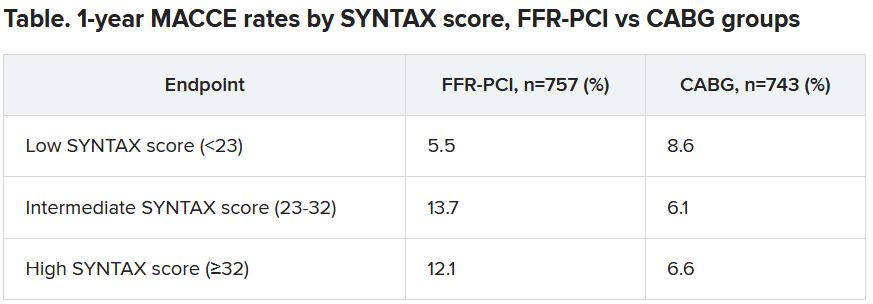
Dr. Fearon agreed that the subgroup analysis by SYNTAX score, though prespecified, was only hypothesis generating. “But I think that other studies have shown the same thing – that in less complex disease, the two strategies appear to perform in a similar fashion.”
The FAME-3 trial’s 1,500 patients were randomly assigned at 48 centers to undergo standard CABG or FFR-guided PCI with Resolute Integrity (Medtronic) zotarolimus-eluting DES. Lesions with a pressure-wire FFR of 0.80 or less were stented and those with higher FFR readings were deferred.
The 1-year hazard ratio for the primary endpoint—a composite of death from any cause, MI, stroke, or repeat revascularization – was 1.5 (95% confidence interval, 1.1-2.2) with a noninferiority P value of .35 for the comparison of FFR-PCI versus CABG.
FFR-guided PCI fared significantly better than CABG for some safety endpoints, including major bleeding (1.6% vs 3.8%, P < .01), arrhythmia including atrial fibrillation (2.4% vs. 14.1%, P < .001), acute kidney injury (0.1% vs 0.9%, P < .04), and 30-day rehospitalization (5.5% vs 10.2%, P < .001).
Did the primary endpoint favor CABG?
At a media briefing prior to Dr. Fearon’s TCT 2021 presentation of the trail, Roxana Mehran, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, proposed that the inclusion of repeat revascularization in the trial’s composite primary endpoint tilted the outcome in favor of CABG. “To me, the FAME-3 results are predictable because repeat revascularization is in the equation.”
It’s well recognized that the endpoint is less likely after CABG than PCI. The latter treats focal lesions that are a limited part of a coronary artery in which CAD is still likely progressing. CABG, on the other hand, can bypass longer segments of diseased artery.
Indeed, as Dr. Fearon reported, the rates of death, MI, or stroke excluding repeat revascularization were 7.3% with FFR-PCI and 5.2% for CABG, for an HR of 1.4 (95% CI, 0.9-2.1).
Dr. Mehran also proposed that intravascular-ultrasound (IVUS) guidance, had it been part of the trial, could potentially have boosted the performance of FFR-PCI.
Repeat revascularization, Dr. Kaul agreed, “should not have been included” in the trial’s primary endpoint. It had been added “to amplify events and to minimize sample size. Not including revascularization would render the sample size prohibitive. There is always give and take in designing clinical trials.”
And he agreed that “IVUS-based PCI optimization would have further improved PCI outcomes.” However, “IVUS plus FFR adds to the procedural burden and limited resources available.” Dr. Fearon said when interviewed that the trial’s definition of procedural MI, a component of the primary endpoint, might potentially be seen as controversial. Procedural MIs in both the PCI and CABG groups were required to meet the standards of CABG-related type-5 MI according to the third and fourth Universal Definitions. The had also had to be accompanied by “a significant finding like new Q waves or a new wall-motion abnormality on echocardiography,” he said.
“That’s fairly strict. Because of that, we had a low rate of periprocedural MI and it was similar between the two groups, around 1.5% in both arms.”
FAME-3 was funded by Medtronic and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Kaul disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kornowsky receives royalties from or holds intellectual property rights with CathWorks. Dr. Mehran disclosed financial ties to numerous pharmaceutical and device companies, and that she, her spouse, or her institution hold equity in Elixir Medical, Applied Therapeutics, and ControlRad.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Coronary stenting guided by fractional flow reserve (FFR) readings, considered to reflect the targeted lesion’s functional impact, was no match for coronary bypass surgery (CABG) in patients with multivessel disease (MVD) in a major international randomized trial.
Indeed, FFR-guided percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) using one of the latest drug-eluting stents (DES) seemed to perform poorly in the trial, compared with surgery, apparently upping the risk for clinical events by 50% over 1 year.
Designed statistically for noninferiority, the third Fractional Flow Reserve Versus Angiography for Multivessel Evaluation (FAME 3) trial, with 1,500 randomized patients, showed that FFR-guided PCI was “not noninferior” to CABG. Of those randomized to PCI, 10.6% met the 1-year primary endpoint of major adverse cardiac or cerebrovascular events (MACCE), compared with only 6.9% of patients assigned to CABG.
The trial enrolled only patients with three-vessel coronary disease with no left-main coronary artery involvement, who were declared by their institution’s multidisciplinary heart team to be appropriate for either form of revascularization.
One of the roles of FFR for PCI guidance is to identify significant lesions “that are underrecognized by the angiogram,” which is less likely to happen in patients with very complex coronary anatomy, study chair William F. Fearon, MD, Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview.
“That’s what we saw in a subgroup analysis based on SYNTAX score,” an index of lesion complexity. “In patients with very high SYNTAX scores, CABG outperformed FFR-guided PCI. But if you look at patients with low SYNTAX scores, actually, FFR-guided PCI outperformed CABG for 1-year MACCE.”
Dr. Fearon is lead author on the study’s Nov. 4, 2021, publication in the New England Journal of Medicine, its release timed to coincide with his presentation of the trial at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, held virtually and live in Orlando and sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
He noted that FAME-3 “wasn’t designed or powered to test for superiority,” so its results do not imply CABG is superior to FFR-PCI in patients with MVD, and remains “inconclusive” on that question.
“I think what this study does is provide both the physician and patients more contemporary data and information on options and expected outcomes in multivessel disease. So if you are a patient who has less complex disease, I think you can feel comfortable that you will get an equivalent result with FFR-guided PCI.” But, at least based on FAME-3, Dr. Fearon said, CABG provides better outcomes in patients with more complex disease.
“I think there are still patients that look at trade-offs. Some patients will accept a higher event rate in order to avoid a long recovery, and vice versa.” So the trial may allow patients and physicians to make more informed decisions, he said.
A main message of FAME-3 “is that we’re getting very good results with three-vessel PCI, but better results with surgery,” Ran Kornowski, MD, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, and Tel Aviv University, said as a discussant following Dr. Fearon’s presentation of the trial. The subanalysis by SYNTAX score, he agreed, probably could be used as part of shared decision-making with patients.
Not all that surprising
“It’s a well-designed study, with a lot of patients,” said surgeon Frank W. Sellke, MD, of Rhode Island Hospital, Miriam Hospital, and Brown University, all in Providence.
“I don’t think it’s all that surprising,” he said in an interview. “It’s very consistent with what other studies have shown, that for three-vessel disease, surgery tends to have the edge,” even when pitted against FFR-guided PCI.
Indeed, pressure-wire FFR-PCI has a spotty history, even as an alternative to standard angiography-based PCI. For example, it has performed well in registry and other cohort studies but showed no advantage in the all-comers RIPCORD-2 trial or in the setting of complete revascularization PCI for acute MI in FLOWER-MI. And it emitted an increased-mortality signal in the prematurely halted FUTURE trial.
In FAME-3, “the 1-year follow-up was the best chance for FFR-PCI to be noninferior to CABG. The CABG advantage is only going to get better with time if prior experience and pathobiology is true,” Sanjay Kaul, MD, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
Overall, “the quality and quantity of evidence is insufficient to support FFR-guided PCI” in patients with complex coronary artery disease (CAD), he said. “I would also argue that the evidence for FFR-guided PCI for simple CAD is also not high quality.”
Dr. Kaul also blasted the claim that FFR-PCI was seen to perform better against CABG in patients with low SYNTAX scores. “In general, one cannot use a positive subgroup in a null or negative trial, as is the case with FAME-3, to ‘rescue’ the treatment intervention.” Such a positive subgroup finding, he said, “would at best be deemed hypothesis-generating and not hypothesis validating.”
Dr. Fearon agreed that the subgroup analysis by SYNTAX score, though prespecified, was only hypothesis generating. “But I think that other studies have shown the same thing – that in less complex disease, the two strategies appear to perform in a similar fashion.”
The FAME-3 trial’s 1,500 patients were randomly assigned at 48 centers to undergo standard CABG or FFR-guided PCI with Resolute Integrity (Medtronic) zotarolimus-eluting DES. Lesions with a pressure-wire FFR of 0.80 or less were stented and those with higher FFR readings were deferred.
The 1-year hazard ratio for the primary endpoint—a composite of death from any cause, MI, stroke, or repeat revascularization – was 1.5 (95% confidence interval, 1.1-2.2) with a noninferiority P value of .35 for the comparison of FFR-PCI versus CABG.
FFR-guided PCI fared significantly better than CABG for some safety endpoints, including major bleeding (1.6% vs 3.8%, P < .01), arrhythmia including atrial fibrillation (2.4% vs. 14.1%, P < .001), acute kidney injury (0.1% vs 0.9%, P < .04), and 30-day rehospitalization (5.5% vs 10.2%, P < .001).
Did the primary endpoint favor CABG?
At a media briefing prior to Dr. Fearon’s TCT 2021 presentation of the trail, Roxana Mehran, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, proposed that the inclusion of repeat revascularization in the trial’s composite primary endpoint tilted the outcome in favor of CABG. “To me, the FAME-3 results are predictable because repeat revascularization is in the equation.”
It’s well recognized that the endpoint is less likely after CABG than PCI. The latter treats focal lesions that are a limited part of a coronary artery in which CAD is still likely progressing. CABG, on the other hand, can bypass longer segments of diseased artery.
Indeed, as Dr. Fearon reported, the rates of death, MI, or stroke excluding repeat revascularization were 7.3% with FFR-PCI and 5.2% for CABG, for an HR of 1.4 (95% CI, 0.9-2.1).
Dr. Mehran also proposed that intravascular-ultrasound (IVUS) guidance, had it been part of the trial, could potentially have boosted the performance of FFR-PCI.
Repeat revascularization, Dr. Kaul agreed, “should not have been included” in the trial’s primary endpoint. It had been added “to amplify events and to minimize sample size. Not including revascularization would render the sample size prohibitive. There is always give and take in designing clinical trials.”
And he agreed that “IVUS-based PCI optimization would have further improved PCI outcomes.” However, “IVUS plus FFR adds to the procedural burden and limited resources available.” Dr. Fearon said when interviewed that the trial’s definition of procedural MI, a component of the primary endpoint, might potentially be seen as controversial. Procedural MIs in both the PCI and CABG groups were required to meet the standards of CABG-related type-5 MI according to the third and fourth Universal Definitions. The had also had to be accompanied by “a significant finding like new Q waves or a new wall-motion abnormality on echocardiography,” he said.
“That’s fairly strict. Because of that, we had a low rate of periprocedural MI and it was similar between the two groups, around 1.5% in both arms.”
FAME-3 was funded by Medtronic and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Kaul disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kornowsky receives royalties from or holds intellectual property rights with CathWorks. Dr. Mehran disclosed financial ties to numerous pharmaceutical and device companies, and that she, her spouse, or her institution hold equity in Elixir Medical, Applied Therapeutics, and ControlRad.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Coronary stenting guided by fractional flow reserve (FFR) readings, considered to reflect the targeted lesion’s functional impact, was no match for coronary bypass surgery (CABG) in patients with multivessel disease (MVD) in a major international randomized trial.
Indeed, FFR-guided percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) using one of the latest drug-eluting stents (DES) seemed to perform poorly in the trial, compared with surgery, apparently upping the risk for clinical events by 50% over 1 year.
Designed statistically for noninferiority, the third Fractional Flow Reserve Versus Angiography for Multivessel Evaluation (FAME 3) trial, with 1,500 randomized patients, showed that FFR-guided PCI was “not noninferior” to CABG. Of those randomized to PCI, 10.6% met the 1-year primary endpoint of major adverse cardiac or cerebrovascular events (MACCE), compared with only 6.9% of patients assigned to CABG.
The trial enrolled only patients with three-vessel coronary disease with no left-main coronary artery involvement, who were declared by their institution’s multidisciplinary heart team to be appropriate for either form of revascularization.
One of the roles of FFR for PCI guidance is to identify significant lesions “that are underrecognized by the angiogram,” which is less likely to happen in patients with very complex coronary anatomy, study chair William F. Fearon, MD, Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview.
“That’s what we saw in a subgroup analysis based on SYNTAX score,” an index of lesion complexity. “In patients with very high SYNTAX scores, CABG outperformed FFR-guided PCI. But if you look at patients with low SYNTAX scores, actually, FFR-guided PCI outperformed CABG for 1-year MACCE.”
Dr. Fearon is lead author on the study’s Nov. 4, 2021, publication in the New England Journal of Medicine, its release timed to coincide with his presentation of the trial at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, held virtually and live in Orlando and sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
He noted that FAME-3 “wasn’t designed or powered to test for superiority,” so its results do not imply CABG is superior to FFR-PCI in patients with MVD, and remains “inconclusive” on that question.
“I think what this study does is provide both the physician and patients more contemporary data and information on options and expected outcomes in multivessel disease. So if you are a patient who has less complex disease, I think you can feel comfortable that you will get an equivalent result with FFR-guided PCI.” But, at least based on FAME-3, Dr. Fearon said, CABG provides better outcomes in patients with more complex disease.
“I think there are still patients that look at trade-offs. Some patients will accept a higher event rate in order to avoid a long recovery, and vice versa.” So the trial may allow patients and physicians to make more informed decisions, he said.
A main message of FAME-3 “is that we’re getting very good results with three-vessel PCI, but better results with surgery,” Ran Kornowski, MD, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, and Tel Aviv University, said as a discussant following Dr. Fearon’s presentation of the trial. The subanalysis by SYNTAX score, he agreed, probably could be used as part of shared decision-making with patients.
Not all that surprising
“It’s a well-designed study, with a lot of patients,” said surgeon Frank W. Sellke, MD, of Rhode Island Hospital, Miriam Hospital, and Brown University, all in Providence.
“I don’t think it’s all that surprising,” he said in an interview. “It’s very consistent with what other studies have shown, that for three-vessel disease, surgery tends to have the edge,” even when pitted against FFR-guided PCI.
Indeed, pressure-wire FFR-PCI has a spotty history, even as an alternative to standard angiography-based PCI. For example, it has performed well in registry and other cohort studies but showed no advantage in the all-comers RIPCORD-2 trial or in the setting of complete revascularization PCI for acute MI in FLOWER-MI. And it emitted an increased-mortality signal in the prematurely halted FUTURE trial.
In FAME-3, “the 1-year follow-up was the best chance for FFR-PCI to be noninferior to CABG. The CABG advantage is only going to get better with time if prior experience and pathobiology is true,” Sanjay Kaul, MD, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
Overall, “the quality and quantity of evidence is insufficient to support FFR-guided PCI” in patients with complex coronary artery disease (CAD), he said. “I would also argue that the evidence for FFR-guided PCI for simple CAD is also not high quality.”
Dr. Kaul also blasted the claim that FFR-PCI was seen to perform better against CABG in patients with low SYNTAX scores. “In general, one cannot use a positive subgroup in a null or negative trial, as is the case with FAME-3, to ‘rescue’ the treatment intervention.” Such a positive subgroup finding, he said, “would at best be deemed hypothesis-generating and not hypothesis validating.”
Dr. Fearon agreed that the subgroup analysis by SYNTAX score, though prespecified, was only hypothesis generating. “But I think that other studies have shown the same thing – that in less complex disease, the two strategies appear to perform in a similar fashion.”
The FAME-3 trial’s 1,500 patients were randomly assigned at 48 centers to undergo standard CABG or FFR-guided PCI with Resolute Integrity (Medtronic) zotarolimus-eluting DES. Lesions with a pressure-wire FFR of 0.80 or less were stented and those with higher FFR readings were deferred.
The 1-year hazard ratio for the primary endpoint—a composite of death from any cause, MI, stroke, or repeat revascularization – was 1.5 (95% confidence interval, 1.1-2.2) with a noninferiority P value of .35 for the comparison of FFR-PCI versus CABG.
FFR-guided PCI fared significantly better than CABG for some safety endpoints, including major bleeding (1.6% vs 3.8%, P < .01), arrhythmia including atrial fibrillation (2.4% vs. 14.1%, P < .001), acute kidney injury (0.1% vs 0.9%, P < .04), and 30-day rehospitalization (5.5% vs 10.2%, P < .001).
Did the primary endpoint favor CABG?
At a media briefing prior to Dr. Fearon’s TCT 2021 presentation of the trail, Roxana Mehran, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, proposed that the inclusion of repeat revascularization in the trial’s composite primary endpoint tilted the outcome in favor of CABG. “To me, the FAME-3 results are predictable because repeat revascularization is in the equation.”
It’s well recognized that the endpoint is less likely after CABG than PCI. The latter treats focal lesions that are a limited part of a coronary artery in which CAD is still likely progressing. CABG, on the other hand, can bypass longer segments of diseased artery.
Indeed, as Dr. Fearon reported, the rates of death, MI, or stroke excluding repeat revascularization were 7.3% with FFR-PCI and 5.2% for CABG, for an HR of 1.4 (95% CI, 0.9-2.1).
Dr. Mehran also proposed that intravascular-ultrasound (IVUS) guidance, had it been part of the trial, could potentially have boosted the performance of FFR-PCI.
Repeat revascularization, Dr. Kaul agreed, “should not have been included” in the trial’s primary endpoint. It had been added “to amplify events and to minimize sample size. Not including revascularization would render the sample size prohibitive. There is always give and take in designing clinical trials.”
And he agreed that “IVUS-based PCI optimization would have further improved PCI outcomes.” However, “IVUS plus FFR adds to the procedural burden and limited resources available.” Dr. Fearon said when interviewed that the trial’s definition of procedural MI, a component of the primary endpoint, might potentially be seen as controversial. Procedural MIs in both the PCI and CABG groups were required to meet the standards of CABG-related type-5 MI according to the third and fourth Universal Definitions. The had also had to be accompanied by “a significant finding like new Q waves or a new wall-motion abnormality on echocardiography,” he said.
“That’s fairly strict. Because of that, we had a low rate of periprocedural MI and it was similar between the two groups, around 1.5% in both arms.”
FAME-3 was funded by Medtronic and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Kaul disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kornowsky receives royalties from or holds intellectual property rights with CathWorks. Dr. Mehran disclosed financial ties to numerous pharmaceutical and device companies, and that she, her spouse, or her institution hold equity in Elixir Medical, Applied Therapeutics, and ControlRad.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.