User login
For MD-IQ use only
Not a Professional Degree? A New Federal Policy Could Exacerbate the Nursing Shortage
The statistics are shocking: 138,000 registered nurses (RNs) have left the workforce since 2022 and at least 40% plan to retire or leave the profession in the next 5 years — and new updates from the Department of Education could make the national nursing crisis even worse.
The reason? Nursing is no longer considered a professional degree.
A recent Department of Education rulemaking session omitted advanced nursing programs (as well as physician assistance programs, physical therapy, occupational therapy, audiology, social work, and public health programs) from the definition of professional degrees and limited the amount of student loan funding available to pursue advanced practice degrees like Master of Science in Nursing and Doctor of Nursing Practice.
“We have a primary care crisis in this country,” said Deborah Trautman PhD, RN, president and chief executive officer of the American Association of Colleges of Nursing (AACN). “The omission is not only harmful for nursing; the omission is not good for anyone who needs healthcare.”
Limiting Loan Access
The One Big, Beautiful Bill Act eliminated the Grad PLUS student loan program and amended the list of professional degrees to exclude advanced practice nursing. Although the change doesn’t affect the licensure or legal standing of nurses, it alters access to financial aid and limits advanced education opportunities.
Starting on July 1, 2026, graduate students will be limited to a total of $100,000 in federal student loans, a decrease from the previous cap of $138,500 but loan caps for graduate students in professional degree programs will increase to $200,000. The changes led the National Association of Student Financial Aid Administrators to declare, “Many will be shut out of graduate education.”
“It would force people who need loan support and don’t have a sufficient amount through a federal loan to seek [private loans], but federal loans have better interest rates and/or other conditions, and some students may not qualify for the private loans,” Trautman said. “The risk then is that students may not pursue these advanced nursing degrees because of the financial barriers that they will face.”
The Department of Education disagrees. In a statement, the federal department said, “Placing a cap on loans will push the remaining graduate nursing programs to reduce their program costs, ensuring that nurses will not be saddled with unmanageable student loan debt.” So far, Trautman has seen “no evidence” that limiting access to advanced nursing programs would reduce tuition costs.
Industry-Wide Impacts
Trautman worries that omitting nursing from the list of professional degrees will reduce access to care.
Nurse practitioners are providing primary care in rural and underserved areas; certified registered nurse anesthetists make up more than 50% of anesthesia providers in the US (a number that jumps to 80% in rural areas); and the percentage of births attended by certified nurse midwives is growing fast.
“These are nurses…who are working to achieve better patient outcomes and to make the health system work better for all of us,” Trautman said. “And we would be compromising this workforce that is so critical to our nation.”
Limiting the federal student loan borrowing cap for advanced nursing degrees could also exacerbate the nursing faculty shortage. In 2023, more than 65,000 qualified applicants were denied admission to baccalaureate and graduate nursing programs; insufficient number of faculty was the top reason.
Colleges depend on nurses with advanced degrees to fill faculty vacancies. In fact, more than 80% of open positions required or preferred a doctoral degree, according to AACN. Removing nursing from the list of professional degree programs and limiting access to student loans will make it even harder to fill vacancies, limiting the number of new nurses entering the profession.
“We’re finalizing the results of [a new national survey] that showed overwhelming feedback from our member deans and students who believe enrollment in advanced nursing programs is going be impacted,” said Trautman. “We’re going to see the faculty shortage worsen; we’re going see increased financial burdens to our students, and we believe it’s going to undermine the stability of the healthcare workforce.”
Industry associations, including the American Nurses Association, American Academy of Nursing, and American Organization for Nursing Leadership have released statements opposing the change and advocating for graduate nursing degrees to be added to the list of professional programs. Trautman hopes that public pressure and cross-sector support will lead the Department of Education to reverse its current position.
“It’s the wrong decision,” she said. “There is an opportunity to make this right, and that is to include nursing on that professional list.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The statistics are shocking: 138,000 registered nurses (RNs) have left the workforce since 2022 and at least 40% plan to retire or leave the profession in the next 5 years — and new updates from the Department of Education could make the national nursing crisis even worse.
The reason? Nursing is no longer considered a professional degree.
A recent Department of Education rulemaking session omitted advanced nursing programs (as well as physician assistance programs, physical therapy, occupational therapy, audiology, social work, and public health programs) from the definition of professional degrees and limited the amount of student loan funding available to pursue advanced practice degrees like Master of Science in Nursing and Doctor of Nursing Practice.
“We have a primary care crisis in this country,” said Deborah Trautman PhD, RN, president and chief executive officer of the American Association of Colleges of Nursing (AACN). “The omission is not only harmful for nursing; the omission is not good for anyone who needs healthcare.”
Limiting Loan Access
The One Big, Beautiful Bill Act eliminated the Grad PLUS student loan program and amended the list of professional degrees to exclude advanced practice nursing. Although the change doesn’t affect the licensure or legal standing of nurses, it alters access to financial aid and limits advanced education opportunities.
Starting on July 1, 2026, graduate students will be limited to a total of $100,000 in federal student loans, a decrease from the previous cap of $138,500 but loan caps for graduate students in professional degree programs will increase to $200,000. The changes led the National Association of Student Financial Aid Administrators to declare, “Many will be shut out of graduate education.”
“It would force people who need loan support and don’t have a sufficient amount through a federal loan to seek [private loans], but federal loans have better interest rates and/or other conditions, and some students may not qualify for the private loans,” Trautman said. “The risk then is that students may not pursue these advanced nursing degrees because of the financial barriers that they will face.”
The Department of Education disagrees. In a statement, the federal department said, “Placing a cap on loans will push the remaining graduate nursing programs to reduce their program costs, ensuring that nurses will not be saddled with unmanageable student loan debt.” So far, Trautman has seen “no evidence” that limiting access to advanced nursing programs would reduce tuition costs.
Industry-Wide Impacts
Trautman worries that omitting nursing from the list of professional degrees will reduce access to care.
Nurse practitioners are providing primary care in rural and underserved areas; certified registered nurse anesthetists make up more than 50% of anesthesia providers in the US (a number that jumps to 80% in rural areas); and the percentage of births attended by certified nurse midwives is growing fast.
“These are nurses…who are working to achieve better patient outcomes and to make the health system work better for all of us,” Trautman said. “And we would be compromising this workforce that is so critical to our nation.”
Limiting the federal student loan borrowing cap for advanced nursing degrees could also exacerbate the nursing faculty shortage. In 2023, more than 65,000 qualified applicants were denied admission to baccalaureate and graduate nursing programs; insufficient number of faculty was the top reason.
Colleges depend on nurses with advanced degrees to fill faculty vacancies. In fact, more than 80% of open positions required or preferred a doctoral degree, according to AACN. Removing nursing from the list of professional degree programs and limiting access to student loans will make it even harder to fill vacancies, limiting the number of new nurses entering the profession.
“We’re finalizing the results of [a new national survey] that showed overwhelming feedback from our member deans and students who believe enrollment in advanced nursing programs is going be impacted,” said Trautman. “We’re going to see the faculty shortage worsen; we’re going see increased financial burdens to our students, and we believe it’s going to undermine the stability of the healthcare workforce.”
Industry associations, including the American Nurses Association, American Academy of Nursing, and American Organization for Nursing Leadership have released statements opposing the change and advocating for graduate nursing degrees to be added to the list of professional programs. Trautman hopes that public pressure and cross-sector support will lead the Department of Education to reverse its current position.
“It’s the wrong decision,” she said. “There is an opportunity to make this right, and that is to include nursing on that professional list.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The statistics are shocking: 138,000 registered nurses (RNs) have left the workforce since 2022 and at least 40% plan to retire or leave the profession in the next 5 years — and new updates from the Department of Education could make the national nursing crisis even worse.
The reason? Nursing is no longer considered a professional degree.
A recent Department of Education rulemaking session omitted advanced nursing programs (as well as physician assistance programs, physical therapy, occupational therapy, audiology, social work, and public health programs) from the definition of professional degrees and limited the amount of student loan funding available to pursue advanced practice degrees like Master of Science in Nursing and Doctor of Nursing Practice.
“We have a primary care crisis in this country,” said Deborah Trautman PhD, RN, president and chief executive officer of the American Association of Colleges of Nursing (AACN). “The omission is not only harmful for nursing; the omission is not good for anyone who needs healthcare.”
Limiting Loan Access
The One Big, Beautiful Bill Act eliminated the Grad PLUS student loan program and amended the list of professional degrees to exclude advanced practice nursing. Although the change doesn’t affect the licensure or legal standing of nurses, it alters access to financial aid and limits advanced education opportunities.
Starting on July 1, 2026, graduate students will be limited to a total of $100,000 in federal student loans, a decrease from the previous cap of $138,500 but loan caps for graduate students in professional degree programs will increase to $200,000. The changes led the National Association of Student Financial Aid Administrators to declare, “Many will be shut out of graduate education.”
“It would force people who need loan support and don’t have a sufficient amount through a federal loan to seek [private loans], but federal loans have better interest rates and/or other conditions, and some students may not qualify for the private loans,” Trautman said. “The risk then is that students may not pursue these advanced nursing degrees because of the financial barriers that they will face.”
The Department of Education disagrees. In a statement, the federal department said, “Placing a cap on loans will push the remaining graduate nursing programs to reduce their program costs, ensuring that nurses will not be saddled with unmanageable student loan debt.” So far, Trautman has seen “no evidence” that limiting access to advanced nursing programs would reduce tuition costs.
Industry-Wide Impacts
Trautman worries that omitting nursing from the list of professional degrees will reduce access to care.
Nurse practitioners are providing primary care in rural and underserved areas; certified registered nurse anesthetists make up more than 50% of anesthesia providers in the US (a number that jumps to 80% in rural areas); and the percentage of births attended by certified nurse midwives is growing fast.
“These are nurses…who are working to achieve better patient outcomes and to make the health system work better for all of us,” Trautman said. “And we would be compromising this workforce that is so critical to our nation.”
Limiting the federal student loan borrowing cap for advanced nursing degrees could also exacerbate the nursing faculty shortage. In 2023, more than 65,000 qualified applicants were denied admission to baccalaureate and graduate nursing programs; insufficient number of faculty was the top reason.
Colleges depend on nurses with advanced degrees to fill faculty vacancies. In fact, more than 80% of open positions required or preferred a doctoral degree, according to AACN. Removing nursing from the list of professional degree programs and limiting access to student loans will make it even harder to fill vacancies, limiting the number of new nurses entering the profession.
“We’re finalizing the results of [a new national survey] that showed overwhelming feedback from our member deans and students who believe enrollment in advanced nursing programs is going be impacted,” said Trautman. “We’re going to see the faculty shortage worsen; we’re going see increased financial burdens to our students, and we believe it’s going to undermine the stability of the healthcare workforce.”
Industry associations, including the American Nurses Association, American Academy of Nursing, and American Organization for Nursing Leadership have released statements opposing the change and advocating for graduate nursing degrees to be added to the list of professional programs. Trautman hopes that public pressure and cross-sector support will lead the Department of Education to reverse its current position.
“It’s the wrong decision,” she said. “There is an opportunity to make this right, and that is to include nursing on that professional list.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Interview Tips for Dermatology Applicants From Dr. Scott Worswick
What qualities are dermatology programs looking for that may be different from 5 years ago?
DR. WORSWICK: Every dermatology residency program is different, and as a result, each program is looking for different qualities in its applicants. Overall, I don’t think there has been a huge change in what programs are generally looking for, though. While each program may have a particular trait it values more than another, in general, programs are looking to find residents who will be competent and caring doctors, who work well in teams, and who could be future leaders in our field.
What are common mistakes you see in dermatology residency interviews, and how can applicants avoid them?
DR. WORSWICK: Most dermatology applicants are highly accomplished and empathic soon-to-be physicians, so I haven’t found a lot of “mistakes” from this incredible group of people that we have the privilege of interviewing. From time to time, an applicant will lie in an interview, usually out of a desire to appear to be a certain way, and occasionally, they may be nervous and stumble over their words. The former is a really big problem when it happens, and I would recommend that applicants be honest in all their encounters. The latter is not a major problem, and in some cases, might be avoided by lots of practice in advance.
What types of questions do you recommend applicants ask their interviewers to demonstrate genuine interest in the program?
DR. WORSWICK: Because of the signaling system, I think that programs assume interest at baseline once an applicant has sent the signal. So, “demonstrating interest” is generally not something I would recommend to applicants during the interview day. It is important for applicants to determine on interview day if a program is a fit for them, so applicants should showcase their unique strengths and skills and find out about what makes any given program different from another. The match generally works well and gets applicants into a program that closely aligns with their strengths and interests. So, think of interview day as your time to figure out how good a fit a program is for you, and not the other way around.
How can applicants who feel they don't have standout research or leadership credentials differentiate themselves in the interview?
DR. WORSWICK: While leadership, and less so research experience, is a trait valued highly by most if not all dermatology programs, it is only a part of what an applicant can offer a program. Most programs employ holistic review and consider several factors, probably most commonly grades in medical school, leadership experience, mentorship, teaching, volunteering, Step 2 scores, and letters of recommendation. Any given applicant does not need to excel in all of these. If an applicant has not done a lot of research, they may not match into a research-heavy program, but it doesn’t mean they won’t match. They should determine in which areas they shine and signal the programs that align with those interests/strengths.
How should applicants discuss nontraditional experiences in a way that adds value rather than raising red flags?
DR. WORSWICK: In general, my recommendation would be to explain what happened leading up to the change or challenge so that someone reading the application clearly understands the circumstances of the experience, then add value to the description by explaining what was learned and how this might relate to the applicant being a dermatology resident. For example, if a resident took time off for financial reasons and had to work as a medical assitant for a year, a concise description that explains the need for the leave (financial) as well as what value was gained (a year of hands-on patient care experience that validated their choice of going into medicine) could be very helpful.
What qualities are dermatology programs looking for that may be different from 5 years ago?
DR. WORSWICK: Every dermatology residency program is different, and as a result, each program is looking for different qualities in its applicants. Overall, I don’t think there has been a huge change in what programs are generally looking for, though. While each program may have a particular trait it values more than another, in general, programs are looking to find residents who will be competent and caring doctors, who work well in teams, and who could be future leaders in our field.
What are common mistakes you see in dermatology residency interviews, and how can applicants avoid them?
DR. WORSWICK: Most dermatology applicants are highly accomplished and empathic soon-to-be physicians, so I haven’t found a lot of “mistakes” from this incredible group of people that we have the privilege of interviewing. From time to time, an applicant will lie in an interview, usually out of a desire to appear to be a certain way, and occasionally, they may be nervous and stumble over their words. The former is a really big problem when it happens, and I would recommend that applicants be honest in all their encounters. The latter is not a major problem, and in some cases, might be avoided by lots of practice in advance.
What types of questions do you recommend applicants ask their interviewers to demonstrate genuine interest in the program?
DR. WORSWICK: Because of the signaling system, I think that programs assume interest at baseline once an applicant has sent the signal. So, “demonstrating interest” is generally not something I would recommend to applicants during the interview day. It is important for applicants to determine on interview day if a program is a fit for them, so applicants should showcase their unique strengths and skills and find out about what makes any given program different from another. The match generally works well and gets applicants into a program that closely aligns with their strengths and interests. So, think of interview day as your time to figure out how good a fit a program is for you, and not the other way around.
How can applicants who feel they don't have standout research or leadership credentials differentiate themselves in the interview?
DR. WORSWICK: While leadership, and less so research experience, is a trait valued highly by most if not all dermatology programs, it is only a part of what an applicant can offer a program. Most programs employ holistic review and consider several factors, probably most commonly grades in medical school, leadership experience, mentorship, teaching, volunteering, Step 2 scores, and letters of recommendation. Any given applicant does not need to excel in all of these. If an applicant has not done a lot of research, they may not match into a research-heavy program, but it doesn’t mean they won’t match. They should determine in which areas they shine and signal the programs that align with those interests/strengths.
How should applicants discuss nontraditional experiences in a way that adds value rather than raising red flags?
DR. WORSWICK: In general, my recommendation would be to explain what happened leading up to the change or challenge so that someone reading the application clearly understands the circumstances of the experience, then add value to the description by explaining what was learned and how this might relate to the applicant being a dermatology resident. For example, if a resident took time off for financial reasons and had to work as a medical assitant for a year, a concise description that explains the need for the leave (financial) as well as what value was gained (a year of hands-on patient care experience that validated their choice of going into medicine) could be very helpful.
What qualities are dermatology programs looking for that may be different from 5 years ago?
DR. WORSWICK: Every dermatology residency program is different, and as a result, each program is looking for different qualities in its applicants. Overall, I don’t think there has been a huge change in what programs are generally looking for, though. While each program may have a particular trait it values more than another, in general, programs are looking to find residents who will be competent and caring doctors, who work well in teams, and who could be future leaders in our field.
What are common mistakes you see in dermatology residency interviews, and how can applicants avoid them?
DR. WORSWICK: Most dermatology applicants are highly accomplished and empathic soon-to-be physicians, so I haven’t found a lot of “mistakes” from this incredible group of people that we have the privilege of interviewing. From time to time, an applicant will lie in an interview, usually out of a desire to appear to be a certain way, and occasionally, they may be nervous and stumble over their words. The former is a really big problem when it happens, and I would recommend that applicants be honest in all their encounters. The latter is not a major problem, and in some cases, might be avoided by lots of practice in advance.
What types of questions do you recommend applicants ask their interviewers to demonstrate genuine interest in the program?
DR. WORSWICK: Because of the signaling system, I think that programs assume interest at baseline once an applicant has sent the signal. So, “demonstrating interest” is generally not something I would recommend to applicants during the interview day. It is important for applicants to determine on interview day if a program is a fit for them, so applicants should showcase their unique strengths and skills and find out about what makes any given program different from another. The match generally works well and gets applicants into a program that closely aligns with their strengths and interests. So, think of interview day as your time to figure out how good a fit a program is for you, and not the other way around.
How can applicants who feel they don't have standout research or leadership credentials differentiate themselves in the interview?
DR. WORSWICK: While leadership, and less so research experience, is a trait valued highly by most if not all dermatology programs, it is only a part of what an applicant can offer a program. Most programs employ holistic review and consider several factors, probably most commonly grades in medical school, leadership experience, mentorship, teaching, volunteering, Step 2 scores, and letters of recommendation. Any given applicant does not need to excel in all of these. If an applicant has not done a lot of research, they may not match into a research-heavy program, but it doesn’t mean they won’t match. They should determine in which areas they shine and signal the programs that align with those interests/strengths.
How should applicants discuss nontraditional experiences in a way that adds value rather than raising red flags?
DR. WORSWICK: In general, my recommendation would be to explain what happened leading up to the change or challenge so that someone reading the application clearly understands the circumstances of the experience, then add value to the description by explaining what was learned and how this might relate to the applicant being a dermatology resident. For example, if a resident took time off for financial reasons and had to work as a medical assitant for a year, a concise description that explains the need for the leave (financial) as well as what value was gained (a year of hands-on patient care experience that validated their choice of going into medicine) could be very helpful.
Millipede Burns: An Unusual Cause of Purplish Toes
To the Editor:
Millipedes do not have nearly as many feet as their name would suggest; most have fewer than 100.1 They are not actually insects; they are a wormlike arthropod in the Diplopoda class. Generally these harmless animals can be a welcome resident in gardens because they break down decaying plant material and rejuvenate the soil.1 However, they are less welcome in the home or underfoot because of what happens when these invertebrates are threatened or crushed.2
Millipedes, which typically have at least 30 pairs of legs, have 2 defense mechanisms: (1) body coiling to withstand external pressure, and (2) secretion of fluids with insecticidal properties from specialized glands distributed along their body.3 These secretions, which are used by the millipede to defend against predators, contain organic compounds including benzoquinone. When these secretions come into contact with skin, pigmentary changes resembling a burn or necrosis and irritation to the skin (pain, burning, itching) occur.4,5
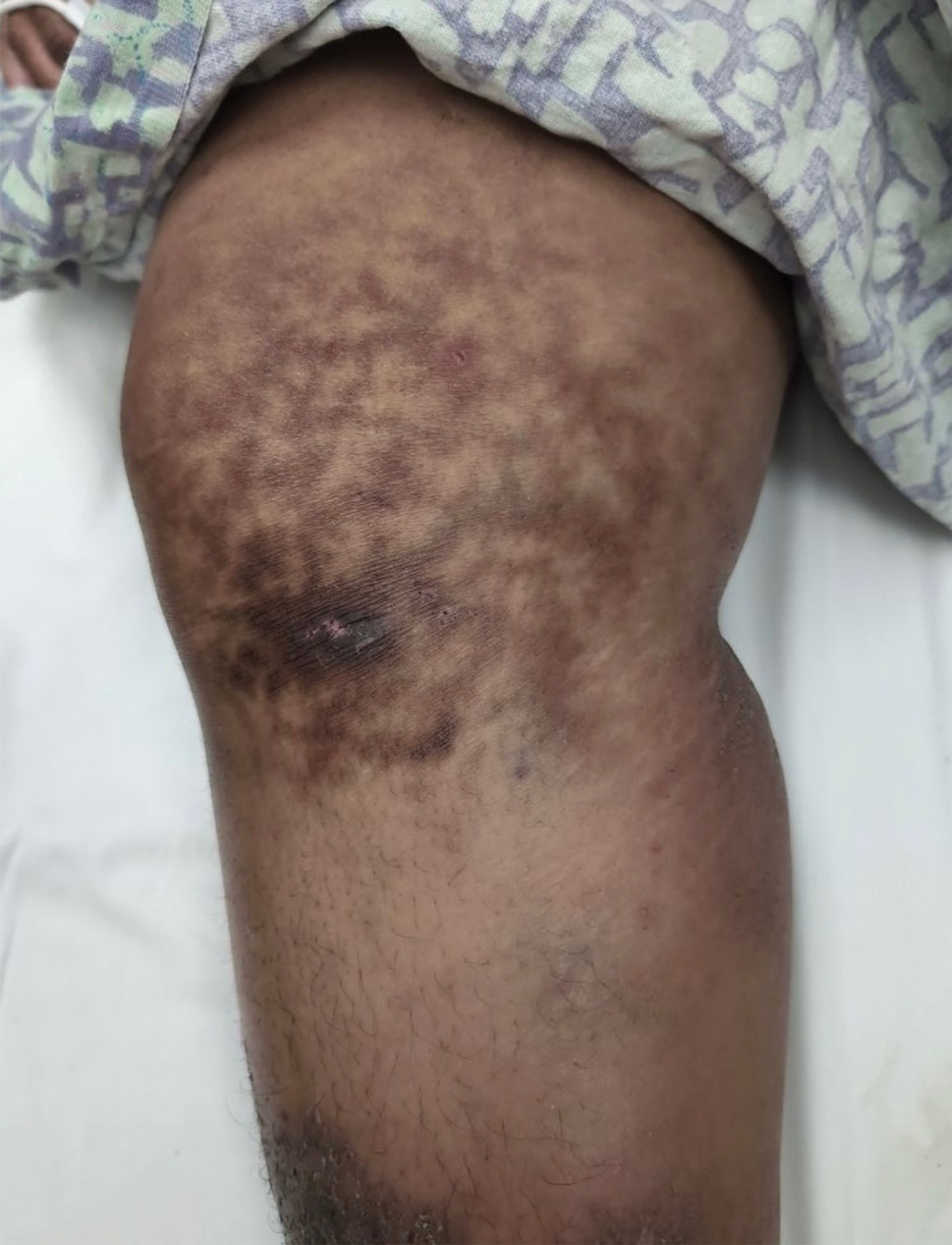
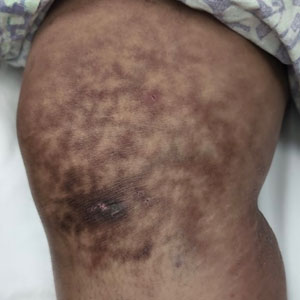
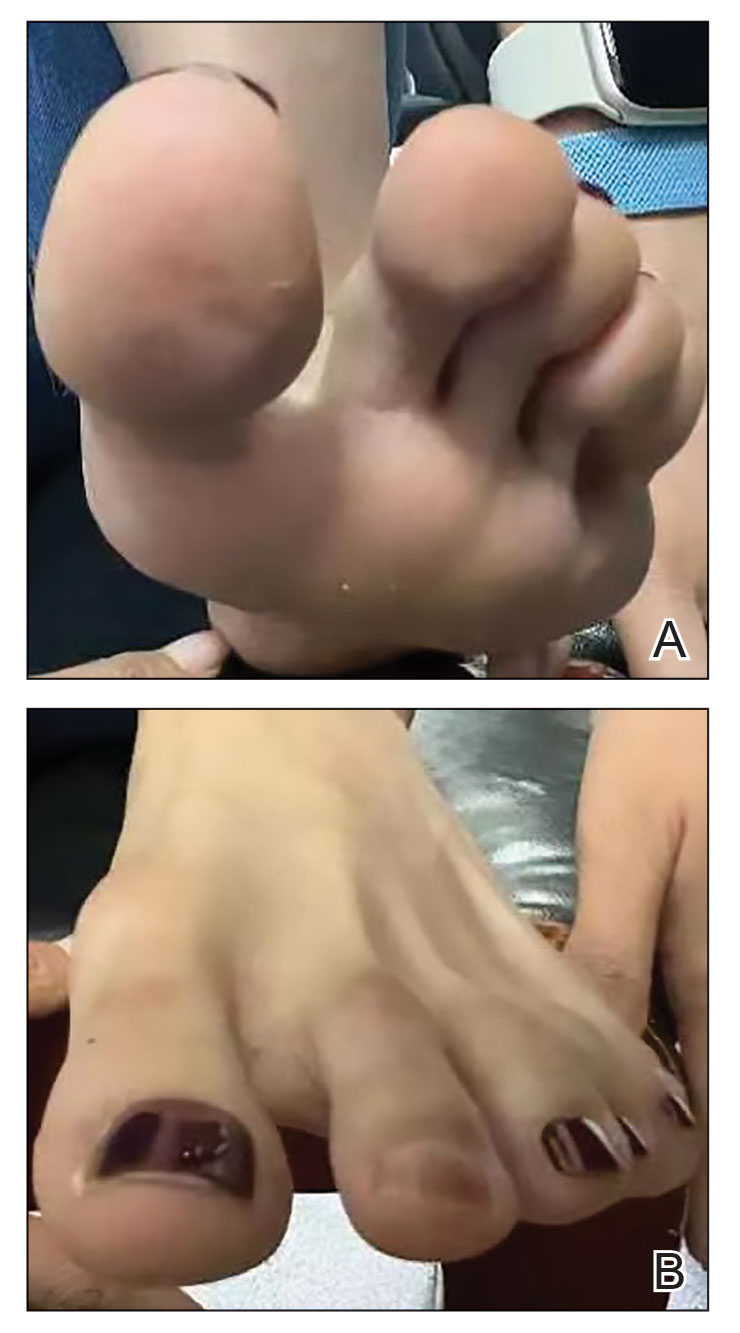
Millipedes typically are found in tropical and temperate regions worldwide, such as the Amazon rainforest, Southeast Asia, tropical areas of Africa, forests, grasslands, and gardens in North America and Europe.6 They also are found in every US state as well as Puerto Rico.1 Millipedes are nocturnal, favor dark places, and can make their way into residential areas, including homes, basements, gardens, and yards.2,6 Although millipede burns commonly are reported in tropical regions, we present a case in China.6A 33-year-old woman presented with purplish-red discoloration on all 5 toes on the left foot. The patient recounted that she discovered a millipede in her shoe earlier in the day, removed it, and crushed it with her bare foot. That night, while taking a bath, she noticed that the toes had turned purplish-red (Figure 1). The patient brought the crushed millipede with her to the emergency department where she sought treatment. The dermatologist confirmed that it was a millipede; however, the team was unable to determine the specific species because it had been crushed (Figure 2).
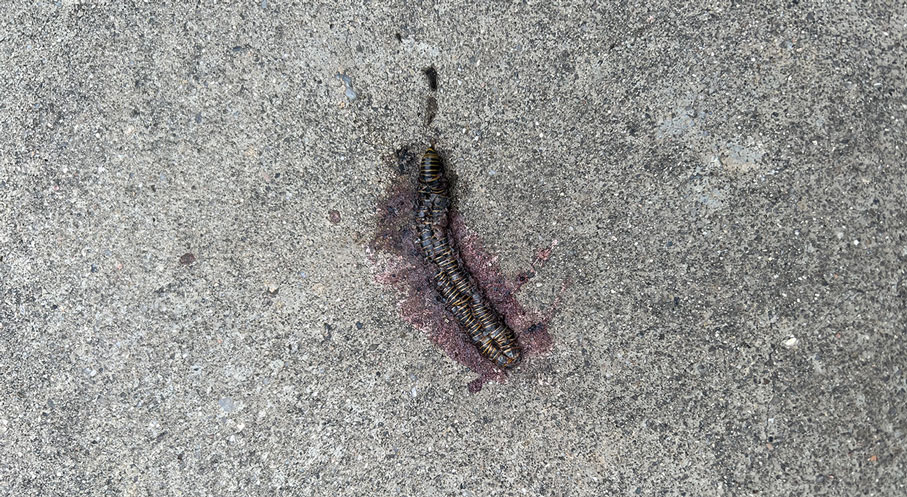
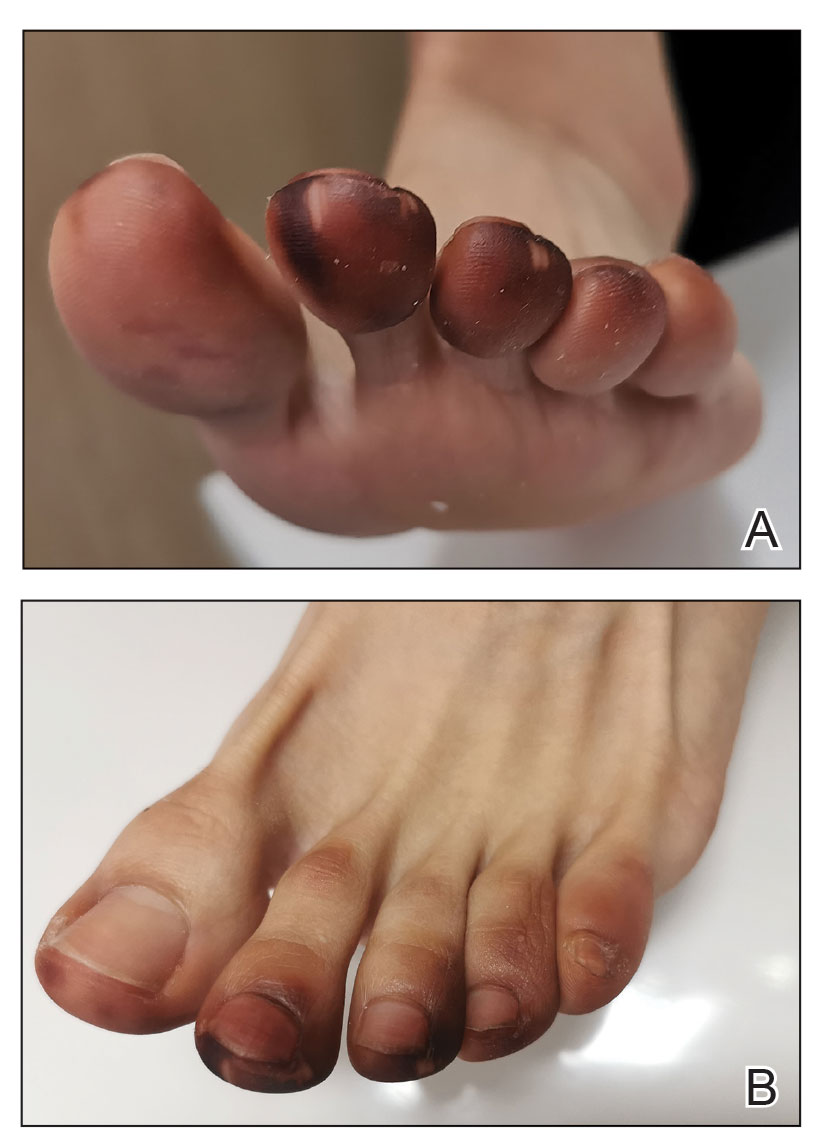

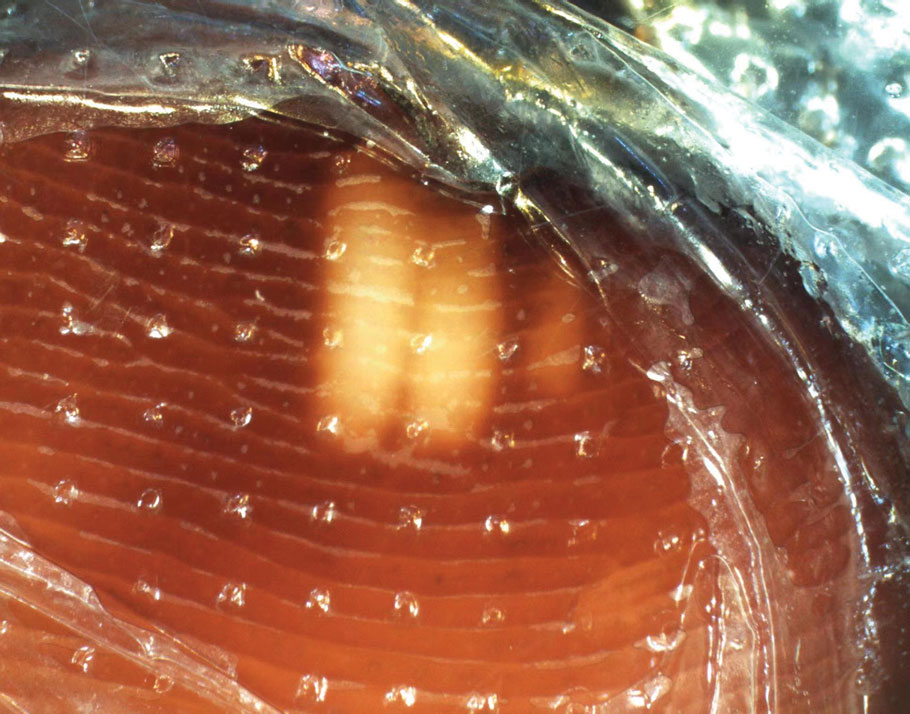
Physical examination of the affected toes showed a clear boundary and iodinelike staining. The patient did not report pain. The stained skin had a normal temperature, pulse, texture, and sensation. Dermoscopy revealed multiple black-brown patches on the toes (Figure 3). The pigmented area gradually faded over a 1-month period. Superficial damage to the toenail revealed evidence of black-brown pigmentation on both the nail and the skin underneath. The diagnosis in the dermoscopy report suggested exogenous pigmentation of the toes. The patient was advised that no treatment was needed and that the condition would resolve on its own. At 1-month follow-up, the patient’s toes had returned to their normal color (Figure 4).
The feet are common sites of millipede burns; other exposed areas, such as the arms, face, and eyes, also are potential sites of involvement.5 The cutaneous pigmentary changes seen on our patient’s foot were a result of the millipede’s defense mechanism—secreted toxic chemicals that stained the foot. It is important to note that the pigmentation was not associated with the death of the millipede, as the millipede was still alive upon initial contact with the patient’s foot in her shoe.
When a patient presents with pigmentary changes, several conditions must be ruled out—notably acute arterial thrombosis. Patients with this condition will describe acute pain and weakness in the area of involvement. Physicians inspecting the area will note coldness and pallor in the affected limb as well as a diminished or absent pulse. In severe cases, the skin may exhibit a purplish-red appearance.5 Millipede burns also should be distinguished from bacterial endocarditis and cryoglobulinemia.7 All 3 conditions can manifest with redness, swelling, blisters, and purpuralike changes. Positive blood culture is an important diagnostic basis for bacterial endocarditis; in addition, routine blood tests will demonstrate a decrease in red blood cells and hemoglobin, and routine urinalysis may show proteinuria and microscopic hematuria. Patients with cryoglobulinemia will have a positive cryoglobulin assay, increased IgM, and often decreased complement.7 It also is worth noting that millipede burns might resemble child abuse in pediatric patients, necessitating further evaluation.5
It is unusual to see a millipede burn in nontropical regions. Therefore, the identification of our patient’s millipede burn was notable and serves as a reminder to keep this diagnosis in the differential when caring for patients with pigmentary changes. An accurate diagnosis hinges on being alert to a millipede exposure history and recognizing the clinical manifestations. For affected patients, it may be beneficial to recommend they advise friends and relatives to avoid skin contact with millipedes and most importantly to avoid stepping on them with bare feet.
Millipedes. National Wildlife Federation. Accessed October 15, 2025. https://www.nwf.org/Educational-Resources/Wildlife-Guide/Invertebrates/Millipedes
Pennini SN, Rebello PFB, Guerra MdGVB, et al. Millipede accident with unusual dermatological lesion. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94:765-767. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2019.10.003
Lima CAJ, Cardoso JLC, Magela A, et al. Exogenous pigmentation in toes feigning ischemia of the extremities: a diagnostic challenge brought by arthropods of the Diplopoda Class (“millipedes“). An Bras Dermatol. 2010;85:391-392. doi:10.1590/s0365-05962910000300018
De Capitani EM, Vieira RJ, Bucaretchi F, et al. Human accidents involving Rhinocricus spp., a common millipede genus observed in urban areas of Brazil. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2011;49:187-190. doi:10.3109/15563650.2011.560855
Lacy FA, Elston DM. What’s eating you? millipede burns. Cutis. 2019;103:195-196.
Neto ASH, Filho FB, Martins G. Skin lesions simulating blue toe syndrome caused by prolonged contact with a millipede. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2014;47:257-258. doi:10.1590/0037-8682-0212-2013
Sampaio FMS, Valviesse VRGdA, Lyra-da-Silva JO, et al. Pain and hyperpigmentation of the toes: a quiz. hyperpigmentation of the toes caused by millipedes. Acta Derm Venereol. 2014;94:253-254. doi:10.2340/00015555-1645
To the Editor:
Millipedes do not have nearly as many feet as their name would suggest; most have fewer than 100.1 They are not actually insects; they are a wormlike arthropod in the Diplopoda class. Generally these harmless animals can be a welcome resident in gardens because they break down decaying plant material and rejuvenate the soil.1 However, they are less welcome in the home or underfoot because of what happens when these invertebrates are threatened or crushed.2
Millipedes, which typically have at least 30 pairs of legs, have 2 defense mechanisms: (1) body coiling to withstand external pressure, and (2) secretion of fluids with insecticidal properties from specialized glands distributed along their body.3 These secretions, which are used by the millipede to defend against predators, contain organic compounds including benzoquinone. When these secretions come into contact with skin, pigmentary changes resembling a burn or necrosis and irritation to the skin (pain, burning, itching) occur.4,5
Millipedes typically are found in tropical and temperate regions worldwide, such as the Amazon rainforest, Southeast Asia, tropical areas of Africa, forests, grasslands, and gardens in North America and Europe.6 They also are found in every US state as well as Puerto Rico.1 Millipedes are nocturnal, favor dark places, and can make their way into residential areas, including homes, basements, gardens, and yards.2,6 Although millipede burns commonly are reported in tropical regions, we present a case in China.6A 33-year-old woman presented with purplish-red discoloration on all 5 toes on the left foot. The patient recounted that she discovered a millipede in her shoe earlier in the day, removed it, and crushed it with her bare foot. That night, while taking a bath, she noticed that the toes had turned purplish-red (Figure 1). The patient brought the crushed millipede with her to the emergency department where she sought treatment. The dermatologist confirmed that it was a millipede; however, the team was unable to determine the specific species because it had been crushed (Figure 2).


Physical examination of the affected toes showed a clear boundary and iodinelike staining. The patient did not report pain. The stained skin had a normal temperature, pulse, texture, and sensation. Dermoscopy revealed multiple black-brown patches on the toes (Figure 3). The pigmented area gradually faded over a 1-month period. Superficial damage to the toenail revealed evidence of black-brown pigmentation on both the nail and the skin underneath. The diagnosis in the dermoscopy report suggested exogenous pigmentation of the toes. The patient was advised that no treatment was needed and that the condition would resolve on its own. At 1-month follow-up, the patient’s toes had returned to their normal color (Figure 4).


The feet are common sites of millipede burns; other exposed areas, such as the arms, face, and eyes, also are potential sites of involvement.5 The cutaneous pigmentary changes seen on our patient’s foot were a result of the millipede’s defense mechanism—secreted toxic chemicals that stained the foot. It is important to note that the pigmentation was not associated with the death of the millipede, as the millipede was still alive upon initial contact with the patient’s foot in her shoe.
When a patient presents with pigmentary changes, several conditions must be ruled out—notably acute arterial thrombosis. Patients with this condition will describe acute pain and weakness in the area of involvement. Physicians inspecting the area will note coldness and pallor in the affected limb as well as a diminished or absent pulse. In severe cases, the skin may exhibit a purplish-red appearance.5 Millipede burns also should be distinguished from bacterial endocarditis and cryoglobulinemia.7 All 3 conditions can manifest with redness, swelling, blisters, and purpuralike changes. Positive blood culture is an important diagnostic basis for bacterial endocarditis; in addition, routine blood tests will demonstrate a decrease in red blood cells and hemoglobin, and routine urinalysis may show proteinuria and microscopic hematuria. Patients with cryoglobulinemia will have a positive cryoglobulin assay, increased IgM, and often decreased complement.7 It also is worth noting that millipede burns might resemble child abuse in pediatric patients, necessitating further evaluation.5
It is unusual to see a millipede burn in nontropical regions. Therefore, the identification of our patient’s millipede burn was notable and serves as a reminder to keep this diagnosis in the differential when caring for patients with pigmentary changes. An accurate diagnosis hinges on being alert to a millipede exposure history and recognizing the clinical manifestations. For affected patients, it may be beneficial to recommend they advise friends and relatives to avoid skin contact with millipedes and most importantly to avoid stepping on them with bare feet.
To the Editor:
Millipedes do not have nearly as many feet as their name would suggest; most have fewer than 100.1 They are not actually insects; they are a wormlike arthropod in the Diplopoda class. Generally these harmless animals can be a welcome resident in gardens because they break down decaying plant material and rejuvenate the soil.1 However, they are less welcome in the home or underfoot because of what happens when these invertebrates are threatened or crushed.2
Millipedes, which typically have at least 30 pairs of legs, have 2 defense mechanisms: (1) body coiling to withstand external pressure, and (2) secretion of fluids with insecticidal properties from specialized glands distributed along their body.3 These secretions, which are used by the millipede to defend against predators, contain organic compounds including benzoquinone. When these secretions come into contact with skin, pigmentary changes resembling a burn or necrosis and irritation to the skin (pain, burning, itching) occur.4,5
Millipedes typically are found in tropical and temperate regions worldwide, such as the Amazon rainforest, Southeast Asia, tropical areas of Africa, forests, grasslands, and gardens in North America and Europe.6 They also are found in every US state as well as Puerto Rico.1 Millipedes are nocturnal, favor dark places, and can make their way into residential areas, including homes, basements, gardens, and yards.2,6 Although millipede burns commonly are reported in tropical regions, we present a case in China.6A 33-year-old woman presented with purplish-red discoloration on all 5 toes on the left foot. The patient recounted that she discovered a millipede in her shoe earlier in the day, removed it, and crushed it with her bare foot. That night, while taking a bath, she noticed that the toes had turned purplish-red (Figure 1). The patient brought the crushed millipede with her to the emergency department where she sought treatment. The dermatologist confirmed that it was a millipede; however, the team was unable to determine the specific species because it had been crushed (Figure 2).


Physical examination of the affected toes showed a clear boundary and iodinelike staining. The patient did not report pain. The stained skin had a normal temperature, pulse, texture, and sensation. Dermoscopy revealed multiple black-brown patches on the toes (Figure 3). The pigmented area gradually faded over a 1-month period. Superficial damage to the toenail revealed evidence of black-brown pigmentation on both the nail and the skin underneath. The diagnosis in the dermoscopy report suggested exogenous pigmentation of the toes. The patient was advised that no treatment was needed and that the condition would resolve on its own. At 1-month follow-up, the patient’s toes had returned to their normal color (Figure 4).


The feet are common sites of millipede burns; other exposed areas, such as the arms, face, and eyes, also are potential sites of involvement.5 The cutaneous pigmentary changes seen on our patient’s foot were a result of the millipede’s defense mechanism—secreted toxic chemicals that stained the foot. It is important to note that the pigmentation was not associated with the death of the millipede, as the millipede was still alive upon initial contact with the patient’s foot in her shoe.
When a patient presents with pigmentary changes, several conditions must be ruled out—notably acute arterial thrombosis. Patients with this condition will describe acute pain and weakness in the area of involvement. Physicians inspecting the area will note coldness and pallor in the affected limb as well as a diminished or absent pulse. In severe cases, the skin may exhibit a purplish-red appearance.5 Millipede burns also should be distinguished from bacterial endocarditis and cryoglobulinemia.7 All 3 conditions can manifest with redness, swelling, blisters, and purpuralike changes. Positive blood culture is an important diagnostic basis for bacterial endocarditis; in addition, routine blood tests will demonstrate a decrease in red blood cells and hemoglobin, and routine urinalysis may show proteinuria and microscopic hematuria. Patients with cryoglobulinemia will have a positive cryoglobulin assay, increased IgM, and often decreased complement.7 It also is worth noting that millipede burns might resemble child abuse in pediatric patients, necessitating further evaluation.5
It is unusual to see a millipede burn in nontropical regions. Therefore, the identification of our patient’s millipede burn was notable and serves as a reminder to keep this diagnosis in the differential when caring for patients with pigmentary changes. An accurate diagnosis hinges on being alert to a millipede exposure history and recognizing the clinical manifestations. For affected patients, it may be beneficial to recommend they advise friends and relatives to avoid skin contact with millipedes and most importantly to avoid stepping on them with bare feet.
Millipedes. National Wildlife Federation. Accessed October 15, 2025. https://www.nwf.org/Educational-Resources/Wildlife-Guide/Invertebrates/Millipedes
Pennini SN, Rebello PFB, Guerra MdGVB, et al. Millipede accident with unusual dermatological lesion. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94:765-767. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2019.10.003
Lima CAJ, Cardoso JLC, Magela A, et al. Exogenous pigmentation in toes feigning ischemia of the extremities: a diagnostic challenge brought by arthropods of the Diplopoda Class (“millipedes“). An Bras Dermatol. 2010;85:391-392. doi:10.1590/s0365-05962910000300018
De Capitani EM, Vieira RJ, Bucaretchi F, et al. Human accidents involving Rhinocricus spp., a common millipede genus observed in urban areas of Brazil. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2011;49:187-190. doi:10.3109/15563650.2011.560855
Lacy FA, Elston DM. What’s eating you? millipede burns. Cutis. 2019;103:195-196.
Neto ASH, Filho FB, Martins G. Skin lesions simulating blue toe syndrome caused by prolonged contact with a millipede. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2014;47:257-258. doi:10.1590/0037-8682-0212-2013
Sampaio FMS, Valviesse VRGdA, Lyra-da-Silva JO, et al. Pain and hyperpigmentation of the toes: a quiz. hyperpigmentation of the toes caused by millipedes. Acta Derm Venereol. 2014;94:253-254. doi:10.2340/00015555-1645
Millipedes. National Wildlife Federation. Accessed October 15, 2025. https://www.nwf.org/Educational-Resources/Wildlife-Guide/Invertebrates/Millipedes
Pennini SN, Rebello PFB, Guerra MdGVB, et al. Millipede accident with unusual dermatological lesion. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94:765-767. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2019.10.003
Lima CAJ, Cardoso JLC, Magela A, et al. Exogenous pigmentation in toes feigning ischemia of the extremities: a diagnostic challenge brought by arthropods of the Diplopoda Class (“millipedes“). An Bras Dermatol. 2010;85:391-392. doi:10.1590/s0365-05962910000300018
De Capitani EM, Vieira RJ, Bucaretchi F, et al. Human accidents involving Rhinocricus spp., a common millipede genus observed in urban areas of Brazil. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2011;49:187-190. doi:10.3109/15563650.2011.560855
Lacy FA, Elston DM. What’s eating you? millipede burns. Cutis. 2019;103:195-196.
Neto ASH, Filho FB, Martins G. Skin lesions simulating blue toe syndrome caused by prolonged contact with a millipede. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2014;47:257-258. doi:10.1590/0037-8682-0212-2013
Sampaio FMS, Valviesse VRGdA, Lyra-da-Silva JO, et al. Pain and hyperpigmentation of the toes: a quiz. hyperpigmentation of the toes caused by millipedes. Acta Derm Venereol. 2014;94:253-254. doi:10.2340/00015555-1645
PRACTICE POINTS
- Millipede burns can resemble ischemia. The most common site of a millipede burn is the feet.
- Diagnosing a millipede burn hinges on obtaining a detailed history, viewing the site under a dermatoscope, and carefully assessing the temperature and pulse of the affected area.
Poly-L-Lactic Acid Reconstitution Technique to Reduce Needle Obstruction
Poly-L-Lactic Acid Reconstitution Technique to Reduce Needle Obstruction
Practice Gap
Poly-L-lactic acid is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for addressing fat loss due to HAART in patients with HIV.2,3 When used as a dermal filler for correction of facial lipoatrophy, PLLA is well tolerated and has been shown to improve quality of life.2,3 Poly-L-lactic acid is available for clinical use as microparticles of lyophilized alpha hydroxy acid polymers. Once injected (after the carrier substance is absorbed), PLLA induces an inflammatory response that ultimately leads to the production of new collagen.3 Unfortunately, PLLA microparticles often obstruct needles and make the product difficult to use, potentially hindering effective injection; thus, it is in the best interest of the patient to mitigate needle obstruction during this procedure. In this article, we describe a simple and effective way to mitigate this problem by utilizing a water bath to warm the filler prior to injection.
Technique
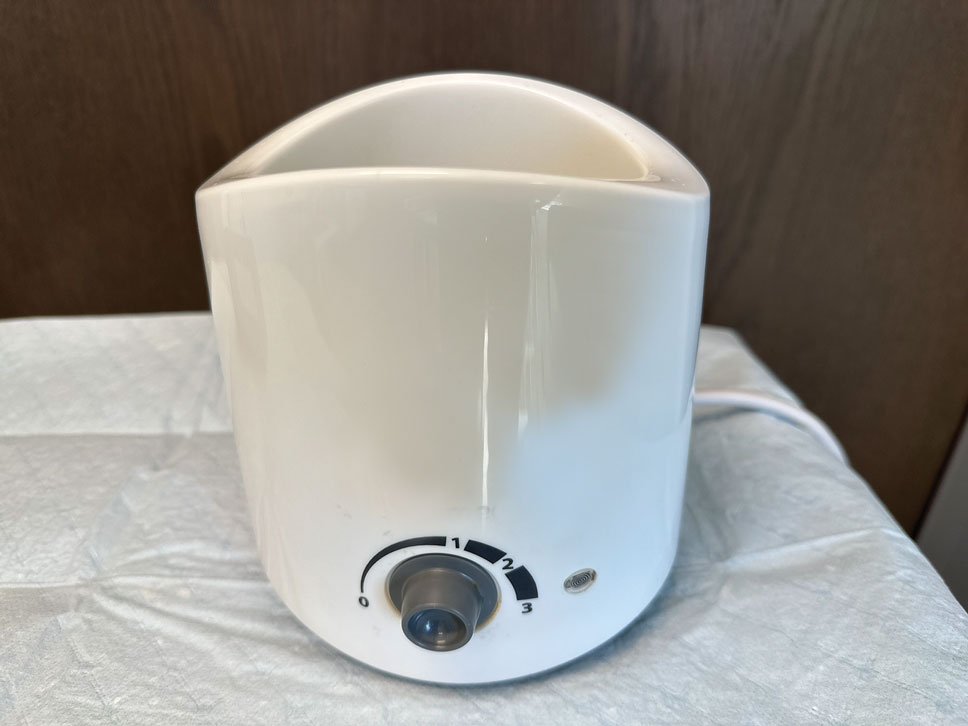
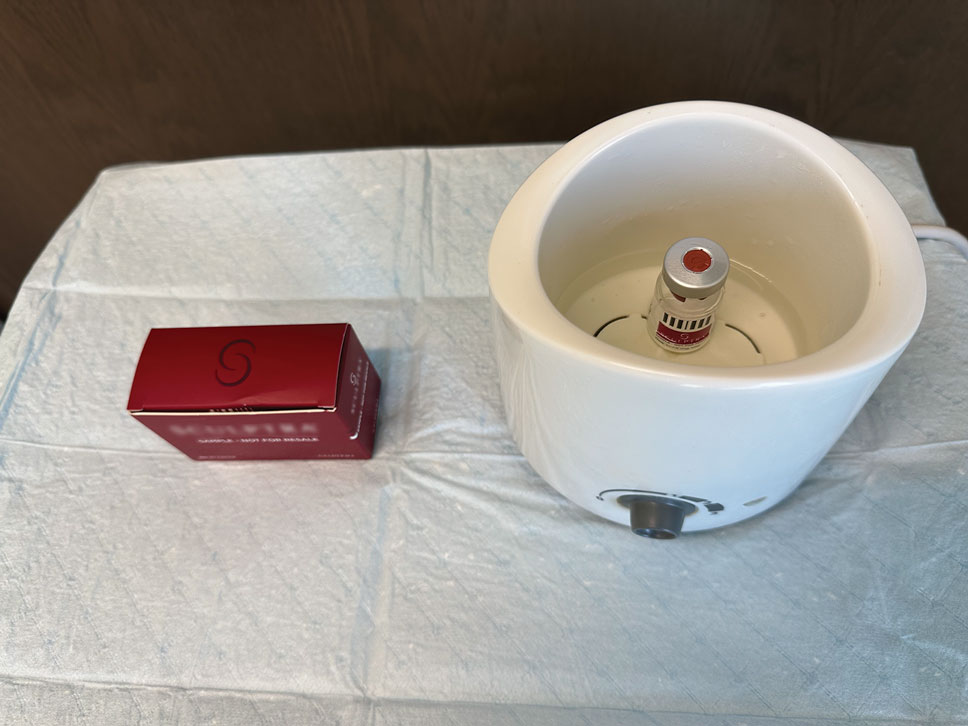
The required supplies include a thermostatic water bath, reconstituted PLLA, a syringe, and a 26-gauge injection needle. Because laboratory-grade heated water baths typically cost between $300 and $3000,4 we recommend using a more affordable, commercially available thermostatic water bath (eg, baby bottle warmer)(Figure 1) to warm the filler prior to injection, as the optimal temperature for this technique can still be achieved while remaining cost effective. Vials of PLLA reconstituted with 7 mL of sterile water and 2 mL lidocaine hydrochloride 1% should be labeled with the date of reconstitution and manually agitated for 30 seconds. The reconstituted product should be stored for 24 hours to ensure even suspension and powder saturation.5 On the day of the procedure, the vial should be placed into the water bath (heated to 100 °C) for 10 minutes prior to injection (Figure 2) and agitated again immediately before withdrawal into the syringe. The clinician then should sterilize the rubber top and draw the product from the warmed vial using the same size needle that will be used for injection. Although a larger gauge needle may make drawing up the product easier in typical practice, drawing and injecting with the same gauge needle helps prevent larger particles from clogging a smaller injection needle. Using a 26-gauge injection needle for withdrawal further reduces clogging by serving as a filter to prevent larger product particles from entering the injection syringe. The vials of PLLA can be kept in the water bath throughout the procedure between uses to keep the filler at a consistent temperature.

Practice Implications
Although many clinicians reduce needle obstructions by warming PLLA before injection, a published protocol currently is not available. One consideration when utilizing this technique is the limited data on the clinical stability and efficacy of PLLA at varying temperatures. Two studies recommend bringing the reconstituted vial to room temperature prior to injection, while others have documented an endothermic melting point in the range of 120 °C to 180
- James J, Carruthers A, Carruthers J. HIV-associated facial lipoatrophy. Dermatol Surg. 2002;28:979-986. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2002.02099.x
- Duracinsky M, Leclercq P, Herrmann S, et al. Safety of poly-L-lactic acid (New-Fill®) in the treatment of facial lipoatrophy: a large observational study among HIV-positive patients. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;14:474. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-14-474
- Sickles CK, Nassereddin A, Patel P, et al. Poly-L-lactic acid. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated February 28, 2024. Accessed October 31, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507871/
- Laboratory equipment: Water bath. Global Lab Supply. (n.d.). http://www.globallabsupply.com/Water-Bath-s/2122.htm
- Lin MJ, Dubin DP, Goldberg DJ, et al. Practices in the usage and reconstitution of poly-L-lactic acid. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:880-886.
- Vleggaar D, Fitzgerald R, Lorenc ZP, et al. Consensus recommendations on the use of injectable poly-L-lactic acid for facial and nonfacial volumization. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:s44-51.
- Sedush NG, Kalinin KT, Azarkevich PN, et al. Physicochemical characteristics and hydrolytic degradation of polylactic acid dermal fillers: a comparative study. Cosmetics. 2023;10:110. doi:10.3390/cosmetics10040110
Practice Gap
Poly-L-lactic acid is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for addressing fat loss due to HAART in patients with HIV.2,3 When used as a dermal filler for correction of facial lipoatrophy, PLLA is well tolerated and has been shown to improve quality of life.2,3 Poly-L-lactic acid is available for clinical use as microparticles of lyophilized alpha hydroxy acid polymers. Once injected (after the carrier substance is absorbed), PLLA induces an inflammatory response that ultimately leads to the production of new collagen.3 Unfortunately, PLLA microparticles often obstruct needles and make the product difficult to use, potentially hindering effective injection; thus, it is in the best interest of the patient to mitigate needle obstruction during this procedure. In this article, we describe a simple and effective way to mitigate this problem by utilizing a water bath to warm the filler prior to injection.
Technique
The required supplies include a thermostatic water bath, reconstituted PLLA, a syringe, and a 26-gauge injection needle. Because laboratory-grade heated water baths typically cost between $300 and $3000,4 we recommend using a more affordable, commercially available thermostatic water bath (eg, baby bottle warmer)(Figure 1) to warm the filler prior to injection, as the optimal temperature for this technique can still be achieved while remaining cost effective. Vials of PLLA reconstituted with 7 mL of sterile water and 2 mL lidocaine hydrochloride 1% should be labeled with the date of reconstitution and manually agitated for 30 seconds. The reconstituted product should be stored for 24 hours to ensure even suspension and powder saturation.5 On the day of the procedure, the vial should be placed into the water bath (heated to 100 °C) for 10 minutes prior to injection (Figure 2) and agitated again immediately before withdrawal into the syringe. The clinician then should sterilize the rubber top and draw the product from the warmed vial using the same size needle that will be used for injection. Although a larger gauge needle may make drawing up the product easier in typical practice, drawing and injecting with the same gauge needle helps prevent larger particles from clogging a smaller injection needle. Using a 26-gauge injection needle for withdrawal further reduces clogging by serving as a filter to prevent larger product particles from entering the injection syringe. The vials of PLLA can be kept in the water bath throughout the procedure between uses to keep the filler at a consistent temperature.


Practice Implications
Although many clinicians reduce needle obstructions by warming PLLA before injection, a published protocol currently is not available. One consideration when utilizing this technique is the limited data on the clinical stability and efficacy of PLLA at varying temperatures. Two studies recommend bringing the reconstituted vial to room temperature prior to injection, while others have documented an endothermic melting point in the range of 120 °C to 180
Practice Gap
Poly-L-lactic acid is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for addressing fat loss due to HAART in patients with HIV.2,3 When used as a dermal filler for correction of facial lipoatrophy, PLLA is well tolerated and has been shown to improve quality of life.2,3 Poly-L-lactic acid is available for clinical use as microparticles of lyophilized alpha hydroxy acid polymers. Once injected (after the carrier substance is absorbed), PLLA induces an inflammatory response that ultimately leads to the production of new collagen.3 Unfortunately, PLLA microparticles often obstruct needles and make the product difficult to use, potentially hindering effective injection; thus, it is in the best interest of the patient to mitigate needle obstruction during this procedure. In this article, we describe a simple and effective way to mitigate this problem by utilizing a water bath to warm the filler prior to injection.
Technique
The required supplies include a thermostatic water bath, reconstituted PLLA, a syringe, and a 26-gauge injection needle. Because laboratory-grade heated water baths typically cost between $300 and $3000,4 we recommend using a more affordable, commercially available thermostatic water bath (eg, baby bottle warmer)(Figure 1) to warm the filler prior to injection, as the optimal temperature for this technique can still be achieved while remaining cost effective. Vials of PLLA reconstituted with 7 mL of sterile water and 2 mL lidocaine hydrochloride 1% should be labeled with the date of reconstitution and manually agitated for 30 seconds. The reconstituted product should be stored for 24 hours to ensure even suspension and powder saturation.5 On the day of the procedure, the vial should be placed into the water bath (heated to 100 °C) for 10 minutes prior to injection (Figure 2) and agitated again immediately before withdrawal into the syringe. The clinician then should sterilize the rubber top and draw the product from the warmed vial using the same size needle that will be used for injection. Although a larger gauge needle may make drawing up the product easier in typical practice, drawing and injecting with the same gauge needle helps prevent larger particles from clogging a smaller injection needle. Using a 26-gauge injection needle for withdrawal further reduces clogging by serving as a filter to prevent larger product particles from entering the injection syringe. The vials of PLLA can be kept in the water bath throughout the procedure between uses to keep the filler at a consistent temperature.


Practice Implications
Although many clinicians reduce needle obstructions by warming PLLA before injection, a published protocol currently is not available. One consideration when utilizing this technique is the limited data on the clinical stability and efficacy of PLLA at varying temperatures. Two studies recommend bringing the reconstituted vial to room temperature prior to injection, while others have documented an endothermic melting point in the range of 120 °C to 180
- James J, Carruthers A, Carruthers J. HIV-associated facial lipoatrophy. Dermatol Surg. 2002;28:979-986. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2002.02099.x
- Duracinsky M, Leclercq P, Herrmann S, et al. Safety of poly-L-lactic acid (New-Fill®) in the treatment of facial lipoatrophy: a large observational study among HIV-positive patients. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;14:474. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-14-474
- Sickles CK, Nassereddin A, Patel P, et al. Poly-L-lactic acid. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated February 28, 2024. Accessed October 31, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507871/
- Laboratory equipment: Water bath. Global Lab Supply. (n.d.). http://www.globallabsupply.com/Water-Bath-s/2122.htm
- Lin MJ, Dubin DP, Goldberg DJ, et al. Practices in the usage and reconstitution of poly-L-lactic acid. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:880-886.
- Vleggaar D, Fitzgerald R, Lorenc ZP, et al. Consensus recommendations on the use of injectable poly-L-lactic acid for facial and nonfacial volumization. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:s44-51.
- Sedush NG, Kalinin KT, Azarkevich PN, et al. Physicochemical characteristics and hydrolytic degradation of polylactic acid dermal fillers: a comparative study. Cosmetics. 2023;10:110. doi:10.3390/cosmetics10040110
- James J, Carruthers A, Carruthers J. HIV-associated facial lipoatrophy. Dermatol Surg. 2002;28:979-986. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2002.02099.x
- Duracinsky M, Leclercq P, Herrmann S, et al. Safety of poly-L-lactic acid (New-Fill®) in the treatment of facial lipoatrophy: a large observational study among HIV-positive patients. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;14:474. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-14-474
- Sickles CK, Nassereddin A, Patel P, et al. Poly-L-lactic acid. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated February 28, 2024. Accessed October 31, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507871/
- Laboratory equipment: Water bath. Global Lab Supply. (n.d.). http://www.globallabsupply.com/Water-Bath-s/2122.htm
- Lin MJ, Dubin DP, Goldberg DJ, et al. Practices in the usage and reconstitution of poly-L-lactic acid. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:880-886.
- Vleggaar D, Fitzgerald R, Lorenc ZP, et al. Consensus recommendations on the use of injectable poly-L-lactic acid for facial and nonfacial volumization. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:s44-51.
- Sedush NG, Kalinin KT, Azarkevich PN, et al. Physicochemical characteristics and hydrolytic degradation of polylactic acid dermal fillers: a comparative study. Cosmetics. 2023;10:110. doi:10.3390/cosmetics10040110
Poly-L-Lactic Acid Reconstitution Technique to Reduce Needle Obstruction
Poly-L-Lactic Acid Reconstitution Technique to Reduce Needle Obstruction
Cost Analysis of Dermatology Residency Applications From 2021 to 2024 Using the Texas Seeking Transparency in Application to Residency Database
Cost Analysis of Dermatology Residency Applications From 2021 to 2024 Using the Texas Seeking Transparency in Application to Residency Database
To the Editor:
Residency applicants, especially in competitive specialties such as dermatology, face major financial barriers due to the high costs of applications, interviews, and away rotations.1 While several studies have examined application costs of other specialties, few have analyzed expenses associated with dermatology applications.1,2 There are no data examining costs following the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020; thus, our study evaluated dermatology application cost trends from 2021 to 2024 and compared them to other specialties to identify strategies to reduce the financial burden on applicants.
Self-reported total application costs, application fees, interview expenses, and away rotation costs from 2021 to 2024 were collected from the Texas Seeking Transparency in Application to Residency (STAR) database powered by the UT Southwestern Medical Center (Dallas, Texas).3 The mean total application expenses per year were compared among specialties, and an analysis of variance was used to determine if the differences were statistically significant.
The number of applicants who recorded information in the Texas STAR database was 110 in 2021, 163 in 2022, 136 in 2023, and 129 in 2024.3 The total dermatology application expenses increased from $2805 in 2021 to $6231 in 2024; interview costs increased from $404 in 2021 to $911 in 2024; and away rotation costs increased from $850 in 2021 to $3812 in 2024 (all P<.05)(Table). There was no significant change in application fees during the study period ($2176 in 2021 to $2125 in 2024 [P=.58]). Dermatology had the fourth highest average total cost over the study period compared to all other specialties, increasing from $2250 in 2021 to $5250 in 2024, following orthopedic surgery ($2250 in 2021 to $6750 in 2024), plastic surgery ($2250 in 2021 to $9750 in 2024), and neurosurgery ($1750 in 2021 to $11,250 in 2024).

Our study found that dermatology residency application costs have increased significantly from 2021 to 2024, primarily driven by rising interview and away rotation expenses (both P<.05). This trend places dermatology among the most expensive fields to apply to for residency. A cross-sectional survey of dermatology residency program directors identified away rotations as one of the top 5 selection criteria, underscoring their importance in the matching process.4 In addition, a cross-sectional analysis of 345 dermatology residents found that 26.2% matched at institutions where they had mentors, including those they connected with through away rotations.5,6 Overall, the high cost of away rotations partially may reflect the competitive nature of the specialty, as building connections at programs may enhance the chances of matching. These costs also can vary based on geography, as rotating in high-cost urban centers can be more expensive than in rural areas; however, rural rotations may be less common due to limited program availability and applicant preferences. For example, nearly 50% of 2024 Electronic Residency Application Service applicants indicated a preference for urban settings, while fewer than 5% selected rural settings.7 Additionally, the high costs associated with applying to residency programs and completing away rotations can disproportionately impact students from rural backgrounds and underrepresented minorities, who may have fewer financial resources.
In our study, the lower application-related expenses in 2021 (during the pandemic) compared to those of 2024 (postpandemic) likely stem from the Association of American Medical Colleges’ recommendation to conduct virtual interviews during the pandemic.8 In 2024, some dermatology programs returned to in-person interviews, with some applicants consequently incurring higher costs related to travel, lodging, and other associated expenses.8 A cost-analysis study of 4153 dermatology applicants from 2016 to 2021 found that the average application costs were $1759 per applicant during the pandemic, when virtual interviews replaced in-person ones, whereas costs were $8476 per applicant during periods with in-person interviews and no COVID-19 restrictions.2 However, we did not observe a significant change in application fees over our study period, likely because the pandemic did not affect application numbers. A cross-sectional analysis of dermatology applicants during the pandemic similarly reported reductions in application-related expenses during the period when interviews were conducted virtually,9 supporting the trend observed in our study. Overall, our findings taken together with other studies highlight the pandemic’s role in reducing expenses and underscore the potential for exploring additional cost-saving measures.
Implementing strategies to reduce these financial burdens—including virtual interviews, increasing student funding for away rotations, and limiting the number of applications individual students can submit—could help alleviate socioeconomic disparities. The new signaling system for residency programs aims to reduce the number of applications submitted, as applicants typically receive interviews only from the limited number of programs they signal, reducing overall application costs. However, our data from the Texas STAR database suggest that application numbers remained relatively stable from 2021 to 2024, indicating that, despite signaling, many applicants still may apply broadly in hopes of improving their chances in an increasingly competitive field. Although a definitive solution to reducing the financial burden on dermatology applicants remains elusive, these strategies can raise awareness and encourage important dialogues.
Limitations of our study include the voluntary nature of the Texas STAR survey, leading to potential voluntary response bias, as well as the small sample size. Students who choose to submit cost data may differ systematically from those who do not; for example, students who match may be more likely to report their outcomes, while those who do not match may be less likely to participate, potentially introducing selection bias. In addition, general awareness of the Texas STAR survey may vary across institutions and among students, further limiting the number of students who participate. Additionally, 2021 was the only presignaling year included, making it difficult to assess longer-term trends. Despite these limitations, the Texas STAR database remains a valuable resource for analyzing general residency application expenses and trends, as it offers comprehensive data from more than 100 medical schools and includes many variables.3
In conclusion, our study found that total dermatology residency application costs have increased significantly from 2021 to 2024 (all P<.05), making dermatology among the most expensive specialties for applying. This study sets the foundation for future survey-based research for applicants and program directors on strategies to alleviate financial burdens.
- Mansouri B, Walker GD, Mitchell J, et al. The cost of applying to dermatology residency: 2014 data estimates. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:754-756. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.10.049
- Gorgy M, Shah S, Arbuiso S, et al. Comparison of cost changes due to the COVID-19 pandemic for dermatology residency applications in the USA. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022;47:600-602. doi:10.1111/ced.15001<.li>
- UT Southwestern. Texas STAR. 2024. Accessed November 5, 2025. https://www.utsouthwestern.edu/education/medical-school/about-the-school/student-affairs/texas-star.html
- Baldwin K, Weidner Z, Ahn J, et al. Are away rotations critical for a successful match in orthopaedic surgery? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:3340-3345. doi:10.1007/s11999-009-0920-9
- Yeh C, Desai AD, Wilson BN, et al. Cross-sectional analysis of scholarly work and mentor relationships in matched dermatology residency applicants. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1437-1439. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.861
- Gorouhi F, Alikhan A, Rezaei A, et al. Dermatology residency selection criteria with an emphasis on program characteristics: a national program director survey. Dermatol Res Pract. 2014;2014:692760. doi:10.1155/2014/692760
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Decoding geographic and setting preferences in residency selection. January 18, 2024. Accessed October 27, 2025. https://www.aamc.org/services/eras-institutions/geographic-preferences
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Virtual interviews: tips for program directors. Updated May 14, 2020. https://med.stanford.edu/content/dam/sm/gme/program_portal/pd/pd_meet/2019-2020/8-6-20-Virtual_Interview_Tips_for_Program_Directors_05142020.pdf
- Williams GE, Zimmerman JM, Wiggins CJ, et al. The indelible marks on dermatology: impacts of COVID-19 on dermatology residency match using the Texas STAR database. Clin Dermatol. 2023;41:215-218. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2022.12.001
To the Editor:
Residency applicants, especially in competitive specialties such as dermatology, face major financial barriers due to the high costs of applications, interviews, and away rotations.1 While several studies have examined application costs of other specialties, few have analyzed expenses associated with dermatology applications.1,2 There are no data examining costs following the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020; thus, our study evaluated dermatology application cost trends from 2021 to 2024 and compared them to other specialties to identify strategies to reduce the financial burden on applicants.
Self-reported total application costs, application fees, interview expenses, and away rotation costs from 2021 to 2024 were collected from the Texas Seeking Transparency in Application to Residency (STAR) database powered by the UT Southwestern Medical Center (Dallas, Texas).3 The mean total application expenses per year were compared among specialties, and an analysis of variance was used to determine if the differences were statistically significant.
The number of applicants who recorded information in the Texas STAR database was 110 in 2021, 163 in 2022, 136 in 2023, and 129 in 2024.3 The total dermatology application expenses increased from $2805 in 2021 to $6231 in 2024; interview costs increased from $404 in 2021 to $911 in 2024; and away rotation costs increased from $850 in 2021 to $3812 in 2024 (all P<.05)(Table). There was no significant change in application fees during the study period ($2176 in 2021 to $2125 in 2024 [P=.58]). Dermatology had the fourth highest average total cost over the study period compared to all other specialties, increasing from $2250 in 2021 to $5250 in 2024, following orthopedic surgery ($2250 in 2021 to $6750 in 2024), plastic surgery ($2250 in 2021 to $9750 in 2024), and neurosurgery ($1750 in 2021 to $11,250 in 2024).

Our study found that dermatology residency application costs have increased significantly from 2021 to 2024, primarily driven by rising interview and away rotation expenses (both P<.05). This trend places dermatology among the most expensive fields to apply to for residency. A cross-sectional survey of dermatology residency program directors identified away rotations as one of the top 5 selection criteria, underscoring their importance in the matching process.4 In addition, a cross-sectional analysis of 345 dermatology residents found that 26.2% matched at institutions where they had mentors, including those they connected with through away rotations.5,6 Overall, the high cost of away rotations partially may reflect the competitive nature of the specialty, as building connections at programs may enhance the chances of matching. These costs also can vary based on geography, as rotating in high-cost urban centers can be more expensive than in rural areas; however, rural rotations may be less common due to limited program availability and applicant preferences. For example, nearly 50% of 2024 Electronic Residency Application Service applicants indicated a preference for urban settings, while fewer than 5% selected rural settings.7 Additionally, the high costs associated with applying to residency programs and completing away rotations can disproportionately impact students from rural backgrounds and underrepresented minorities, who may have fewer financial resources.
In our study, the lower application-related expenses in 2021 (during the pandemic) compared to those of 2024 (postpandemic) likely stem from the Association of American Medical Colleges’ recommendation to conduct virtual interviews during the pandemic.8 In 2024, some dermatology programs returned to in-person interviews, with some applicants consequently incurring higher costs related to travel, lodging, and other associated expenses.8 A cost-analysis study of 4153 dermatology applicants from 2016 to 2021 found that the average application costs were $1759 per applicant during the pandemic, when virtual interviews replaced in-person ones, whereas costs were $8476 per applicant during periods with in-person interviews and no COVID-19 restrictions.2 However, we did not observe a significant change in application fees over our study period, likely because the pandemic did not affect application numbers. A cross-sectional analysis of dermatology applicants during the pandemic similarly reported reductions in application-related expenses during the period when interviews were conducted virtually,9 supporting the trend observed in our study. Overall, our findings taken together with other studies highlight the pandemic’s role in reducing expenses and underscore the potential for exploring additional cost-saving measures.
Implementing strategies to reduce these financial burdens—including virtual interviews, increasing student funding for away rotations, and limiting the number of applications individual students can submit—could help alleviate socioeconomic disparities. The new signaling system for residency programs aims to reduce the number of applications submitted, as applicants typically receive interviews only from the limited number of programs they signal, reducing overall application costs. However, our data from the Texas STAR database suggest that application numbers remained relatively stable from 2021 to 2024, indicating that, despite signaling, many applicants still may apply broadly in hopes of improving their chances in an increasingly competitive field. Although a definitive solution to reducing the financial burden on dermatology applicants remains elusive, these strategies can raise awareness and encourage important dialogues.
Limitations of our study include the voluntary nature of the Texas STAR survey, leading to potential voluntary response bias, as well as the small sample size. Students who choose to submit cost data may differ systematically from those who do not; for example, students who match may be more likely to report their outcomes, while those who do not match may be less likely to participate, potentially introducing selection bias. In addition, general awareness of the Texas STAR survey may vary across institutions and among students, further limiting the number of students who participate. Additionally, 2021 was the only presignaling year included, making it difficult to assess longer-term trends. Despite these limitations, the Texas STAR database remains a valuable resource for analyzing general residency application expenses and trends, as it offers comprehensive data from more than 100 medical schools and includes many variables.3
In conclusion, our study found that total dermatology residency application costs have increased significantly from 2021 to 2024 (all P<.05), making dermatology among the most expensive specialties for applying. This study sets the foundation for future survey-based research for applicants and program directors on strategies to alleviate financial burdens.
To the Editor:
Residency applicants, especially in competitive specialties such as dermatology, face major financial barriers due to the high costs of applications, interviews, and away rotations.1 While several studies have examined application costs of other specialties, few have analyzed expenses associated with dermatology applications.1,2 There are no data examining costs following the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020; thus, our study evaluated dermatology application cost trends from 2021 to 2024 and compared them to other specialties to identify strategies to reduce the financial burden on applicants.
Self-reported total application costs, application fees, interview expenses, and away rotation costs from 2021 to 2024 were collected from the Texas Seeking Transparency in Application to Residency (STAR) database powered by the UT Southwestern Medical Center (Dallas, Texas).3 The mean total application expenses per year were compared among specialties, and an analysis of variance was used to determine if the differences were statistically significant.
The number of applicants who recorded information in the Texas STAR database was 110 in 2021, 163 in 2022, 136 in 2023, and 129 in 2024.3 The total dermatology application expenses increased from $2805 in 2021 to $6231 in 2024; interview costs increased from $404 in 2021 to $911 in 2024; and away rotation costs increased from $850 in 2021 to $3812 in 2024 (all P<.05)(Table). There was no significant change in application fees during the study period ($2176 in 2021 to $2125 in 2024 [P=.58]). Dermatology had the fourth highest average total cost over the study period compared to all other specialties, increasing from $2250 in 2021 to $5250 in 2024, following orthopedic surgery ($2250 in 2021 to $6750 in 2024), plastic surgery ($2250 in 2021 to $9750 in 2024), and neurosurgery ($1750 in 2021 to $11,250 in 2024).

Our study found that dermatology residency application costs have increased significantly from 2021 to 2024, primarily driven by rising interview and away rotation expenses (both P<.05). This trend places dermatology among the most expensive fields to apply to for residency. A cross-sectional survey of dermatology residency program directors identified away rotations as one of the top 5 selection criteria, underscoring their importance in the matching process.4 In addition, a cross-sectional analysis of 345 dermatology residents found that 26.2% matched at institutions where they had mentors, including those they connected with through away rotations.5,6 Overall, the high cost of away rotations partially may reflect the competitive nature of the specialty, as building connections at programs may enhance the chances of matching. These costs also can vary based on geography, as rotating in high-cost urban centers can be more expensive than in rural areas; however, rural rotations may be less common due to limited program availability and applicant preferences. For example, nearly 50% of 2024 Electronic Residency Application Service applicants indicated a preference for urban settings, while fewer than 5% selected rural settings.7 Additionally, the high costs associated with applying to residency programs and completing away rotations can disproportionately impact students from rural backgrounds and underrepresented minorities, who may have fewer financial resources.
In our study, the lower application-related expenses in 2021 (during the pandemic) compared to those of 2024 (postpandemic) likely stem from the Association of American Medical Colleges’ recommendation to conduct virtual interviews during the pandemic.8 In 2024, some dermatology programs returned to in-person interviews, with some applicants consequently incurring higher costs related to travel, lodging, and other associated expenses.8 A cost-analysis study of 4153 dermatology applicants from 2016 to 2021 found that the average application costs were $1759 per applicant during the pandemic, when virtual interviews replaced in-person ones, whereas costs were $8476 per applicant during periods with in-person interviews and no COVID-19 restrictions.2 However, we did not observe a significant change in application fees over our study period, likely because the pandemic did not affect application numbers. A cross-sectional analysis of dermatology applicants during the pandemic similarly reported reductions in application-related expenses during the period when interviews were conducted virtually,9 supporting the trend observed in our study. Overall, our findings taken together with other studies highlight the pandemic’s role in reducing expenses and underscore the potential for exploring additional cost-saving measures.
Implementing strategies to reduce these financial burdens—including virtual interviews, increasing student funding for away rotations, and limiting the number of applications individual students can submit—could help alleviate socioeconomic disparities. The new signaling system for residency programs aims to reduce the number of applications submitted, as applicants typically receive interviews only from the limited number of programs they signal, reducing overall application costs. However, our data from the Texas STAR database suggest that application numbers remained relatively stable from 2021 to 2024, indicating that, despite signaling, many applicants still may apply broadly in hopes of improving their chances in an increasingly competitive field. Although a definitive solution to reducing the financial burden on dermatology applicants remains elusive, these strategies can raise awareness and encourage important dialogues.
Limitations of our study include the voluntary nature of the Texas STAR survey, leading to potential voluntary response bias, as well as the small sample size. Students who choose to submit cost data may differ systematically from those who do not; for example, students who match may be more likely to report their outcomes, while those who do not match may be less likely to participate, potentially introducing selection bias. In addition, general awareness of the Texas STAR survey may vary across institutions and among students, further limiting the number of students who participate. Additionally, 2021 was the only presignaling year included, making it difficult to assess longer-term trends. Despite these limitations, the Texas STAR database remains a valuable resource for analyzing general residency application expenses and trends, as it offers comprehensive data from more than 100 medical schools and includes many variables.3
In conclusion, our study found that total dermatology residency application costs have increased significantly from 2021 to 2024 (all P<.05), making dermatology among the most expensive specialties for applying. This study sets the foundation for future survey-based research for applicants and program directors on strategies to alleviate financial burdens.
- Mansouri B, Walker GD, Mitchell J, et al. The cost of applying to dermatology residency: 2014 data estimates. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:754-756. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.10.049
- Gorgy M, Shah S, Arbuiso S, et al. Comparison of cost changes due to the COVID-19 pandemic for dermatology residency applications in the USA. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022;47:600-602. doi:10.1111/ced.15001<.li>
- UT Southwestern. Texas STAR. 2024. Accessed November 5, 2025. https://www.utsouthwestern.edu/education/medical-school/about-the-school/student-affairs/texas-star.html
- Baldwin K, Weidner Z, Ahn J, et al. Are away rotations critical for a successful match in orthopaedic surgery? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:3340-3345. doi:10.1007/s11999-009-0920-9
- Yeh C, Desai AD, Wilson BN, et al. Cross-sectional analysis of scholarly work and mentor relationships in matched dermatology residency applicants. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1437-1439. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.861
- Gorouhi F, Alikhan A, Rezaei A, et al. Dermatology residency selection criteria with an emphasis on program characteristics: a national program director survey. Dermatol Res Pract. 2014;2014:692760. doi:10.1155/2014/692760
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Decoding geographic and setting preferences in residency selection. January 18, 2024. Accessed October 27, 2025. https://www.aamc.org/services/eras-institutions/geographic-preferences
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Virtual interviews: tips for program directors. Updated May 14, 2020. https://med.stanford.edu/content/dam/sm/gme/program_portal/pd/pd_meet/2019-2020/8-6-20-Virtual_Interview_Tips_for_Program_Directors_05142020.pdf
- Williams GE, Zimmerman JM, Wiggins CJ, et al. The indelible marks on dermatology: impacts of COVID-19 on dermatology residency match using the Texas STAR database. Clin Dermatol. 2023;41:215-218. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2022.12.001
- Mansouri B, Walker GD, Mitchell J, et al. The cost of applying to dermatology residency: 2014 data estimates. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:754-756. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.10.049
- Gorgy M, Shah S, Arbuiso S, et al. Comparison of cost changes due to the COVID-19 pandemic for dermatology residency applications in the USA. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022;47:600-602. doi:10.1111/ced.15001<.li>
- UT Southwestern. Texas STAR. 2024. Accessed November 5, 2025. https://www.utsouthwestern.edu/education/medical-school/about-the-school/student-affairs/texas-star.html
- Baldwin K, Weidner Z, Ahn J, et al. Are away rotations critical for a successful match in orthopaedic surgery? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:3340-3345. doi:10.1007/s11999-009-0920-9
- Yeh C, Desai AD, Wilson BN, et al. Cross-sectional analysis of scholarly work and mentor relationships in matched dermatology residency applicants. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1437-1439. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.861
- Gorouhi F, Alikhan A, Rezaei A, et al. Dermatology residency selection criteria with an emphasis on program characteristics: a national program director survey. Dermatol Res Pract. 2014;2014:692760. doi:10.1155/2014/692760
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Decoding geographic and setting preferences in residency selection. January 18, 2024. Accessed October 27, 2025. https://www.aamc.org/services/eras-institutions/geographic-preferences
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Virtual interviews: tips for program directors. Updated May 14, 2020. https://med.stanford.edu/content/dam/sm/gme/program_portal/pd/pd_meet/2019-2020/8-6-20-Virtual_Interview_Tips_for_Program_Directors_05142020.pdf
- Williams GE, Zimmerman JM, Wiggins CJ, et al. The indelible marks on dermatology: impacts of COVID-19 on dermatology residency match using the Texas STAR database. Clin Dermatol. 2023;41:215-218. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2022.12.001
Cost Analysis of Dermatology Residency Applications From 2021 to 2024 Using the Texas Seeking Transparency in Application to Residency Database
Cost Analysis of Dermatology Residency Applications From 2021 to 2024 Using the Texas Seeking Transparency in Application to Residency Database
PRACTICE POINTS
- Dermatology application costs increased from 2021 to 2024, largely due to expenses related to away rotations and, in some cases, a return to in-person interviews.
- Away rotations play a critical role in the dermatology match; however, they also contribute substantially to financial burden.
- The cost-saving impact of virtual interviews during the COVID-19 pandemic highlights a meaningful opportunity for future cost reduction.
- Further interventions are needed to meaningfully reduce financial burden and promote equity.
Finding Your Voice in Advocacy
Dear Friends,
Since moving to Missouri a little over 2 years ago, I got involved with the Missouri GI Society. They held their inaugural in-person meeting in September, and it was exciting to see and meet gastroenterologists and associates from all over the state. The meeting sparked conversations about challenges in practices and ways to improve patient care. It was incredibly inspiring to see the beginnings and bright future of a society motivated to mobilize change in the community. On a national scale, AGA Advocacy Day 2025 this fall was another example of how to make an impact for the field. I am grateful that local and national GI communities can be a platform for our voices.
In this issue’s “In Focus,” Dr. Colleen R. Kelly discusses the approach for weight management for the gastroenterologist, including how to discuss lifestyle modifications, anti-obesity medications, endoscopic therapies, and bariatric surgeries. In the “Short Clinical Review,” Dr. Ekta Gupta, Dr. Carol Burke, and Dr. Carole Macaron review available non-invasive blood and stool tests for colorectal cancer screening, including guidelines recommendations and evidence supporting each modality.
In the “Early Career” section, Dr. Mayada Ismail shares her personal journey in making the difficult decision of leaving her first job as an early career gastroenterologist, outlining the challenges and lessons learned along the way.
Dr. Alicia Muratore, Dr. Emily V. Wechsler, and Dr. Eric D. Shah provide a practical guide to tech and device development in the “Finance/Legal” section of this issue, outlining everything from intellectual property ownership to building the right team, and selecting the right incubator.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]) or Danielle Kiefer ([email protected]), Communications/Managing Editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: screening colonoscopy for colorectal cancer was only first introduced in the mid-1990s with Medicare coverage for high-risk individuals starting in 1998, followed by coverage for average-risk patients in 2001.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
Dear Friends,
Since moving to Missouri a little over 2 years ago, I got involved with the Missouri GI Society. They held their inaugural in-person meeting in September, and it was exciting to see and meet gastroenterologists and associates from all over the state. The meeting sparked conversations about challenges in practices and ways to improve patient care. It was incredibly inspiring to see the beginnings and bright future of a society motivated to mobilize change in the community. On a national scale, AGA Advocacy Day 2025 this fall was another example of how to make an impact for the field. I am grateful that local and national GI communities can be a platform for our voices.
In this issue’s “In Focus,” Dr. Colleen R. Kelly discusses the approach for weight management for the gastroenterologist, including how to discuss lifestyle modifications, anti-obesity medications, endoscopic therapies, and bariatric surgeries. In the “Short Clinical Review,” Dr. Ekta Gupta, Dr. Carol Burke, and Dr. Carole Macaron review available non-invasive blood and stool tests for colorectal cancer screening, including guidelines recommendations and evidence supporting each modality.
In the “Early Career” section, Dr. Mayada Ismail shares her personal journey in making the difficult decision of leaving her first job as an early career gastroenterologist, outlining the challenges and lessons learned along the way.
Dr. Alicia Muratore, Dr. Emily V. Wechsler, and Dr. Eric D. Shah provide a practical guide to tech and device development in the “Finance/Legal” section of this issue, outlining everything from intellectual property ownership to building the right team, and selecting the right incubator.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]) or Danielle Kiefer ([email protected]), Communications/Managing Editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: screening colonoscopy for colorectal cancer was only first introduced in the mid-1990s with Medicare coverage for high-risk individuals starting in 1998, followed by coverage for average-risk patients in 2001.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
Dear Friends,
Since moving to Missouri a little over 2 years ago, I got involved with the Missouri GI Society. They held their inaugural in-person meeting in September, and it was exciting to see and meet gastroenterologists and associates from all over the state. The meeting sparked conversations about challenges in practices and ways to improve patient care. It was incredibly inspiring to see the beginnings and bright future of a society motivated to mobilize change in the community. On a national scale, AGA Advocacy Day 2025 this fall was another example of how to make an impact for the field. I am grateful that local and national GI communities can be a platform for our voices.
In this issue’s “In Focus,” Dr. Colleen R. Kelly discusses the approach for weight management for the gastroenterologist, including how to discuss lifestyle modifications, anti-obesity medications, endoscopic therapies, and bariatric surgeries. In the “Short Clinical Review,” Dr. Ekta Gupta, Dr. Carol Burke, and Dr. Carole Macaron review available non-invasive blood and stool tests for colorectal cancer screening, including guidelines recommendations and evidence supporting each modality.
In the “Early Career” section, Dr. Mayada Ismail shares her personal journey in making the difficult decision of leaving her first job as an early career gastroenterologist, outlining the challenges and lessons learned along the way.
Dr. Alicia Muratore, Dr. Emily V. Wechsler, and Dr. Eric D. Shah provide a practical guide to tech and device development in the “Finance/Legal” section of this issue, outlining everything from intellectual property ownership to building the right team, and selecting the right incubator.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]) or Danielle Kiefer ([email protected]), Communications/Managing Editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: screening colonoscopy for colorectal cancer was only first introduced in the mid-1990s with Medicare coverage for high-risk individuals starting in 1998, followed by coverage for average-risk patients in 2001.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
‘So You Have an Idea…’: A Practical Guide to Tech and Device Development for the Early Career GI
You are in the middle of a busy clinic day and think, “there has to be a better way to do this.” Suddenly, a better way to do something becomes obvious. Maybe it’s a tool that simplifies documentation, a device that improves patient comfort, or an app that bridges a clinical gap. Many physicians, especially early career gastroenterologists, have ideas like this, but few know what to do next.
This article is for the curious innovator at the beginning of their clinical career. It offers practical, real-world guidance on developing a clinical product: whether that be hardware, software, or a hybrid. It outlines what questions to ask, who to consult, and how to protect your work, using personal insights and business principles learned through lived experience.
1. Understand Intellectual Property (IP): Know Its Value and Ownership
What is IP?
Intellectual property refers to your original creations: inventions, designs, software, and more. This is what you want to protect legally through patents, trademarks, or copyrights.
Who owns your idea?
This is the first and most important question to ask. If you are employed (especially by a hospital or academic center), your contract may already give your employer rights to any inventions you create, even those developed in your personal time.
What to ask:
- Does my employment contract include an “assignment of inventions” clause?
- Does the institution claim rights to anything developed with institutional resources?
- Are there moonlighting or external activity policies that affect this?
If you are developing an idea on your personal time, with your own resources, and outside your scope of clinical duties, it might still be considered “theirs” under some contracts. Early legal consultation is critical. A specialized IP attorney can help you understand what you own and how to protect it. This should be done early, ideally before you start building anything.
2. Lawyers Aren’t Optional: They’re Essential Early Partners
You do not need a full legal team, but you do need a lawyer early. An early consultation with an IP attorney can clarify your rights, guide your filing process (e.g. provisional patents), and help you avoid costly missteps.
Do this before sharing your idea publicly, including in academic presentations, pitch competitions, or even on social media. Public disclosure can start a clock ticking for application to protect your IP.
3. Build a Founding Team with Intent
Think of your startup team like a long-term relationship: you’re committing to build something together through uncertainty, tension, and change.
Strong early-stage teams often include:
- The Visionary – understands the clinical need and vision
- The Builder – engineer, developer, or designer
- The Doer – project manager or operations lead
Before forming a company, clearly define:
- Ownership (equity percentages)
- Roles and responsibilities
- Time commitments
- What happens if someone exits
Have these discussions early and document your agreements. Avoid informal “handshake” deals that can lead to serious disputes later.
4. You Don’t Need to Know Everything on Day One
You do not need to know how to write code, build a prototype, or get FDA clearance on day one. Successful innovators are humble learners. Use a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), a simple, functional version of your idea, to test assumptions and gather feedback. Iterate based on what you learn. Do not chase perfection; pursue progress. Consider using online accelerators like Y Combinator’s startup school or AGA’s Center for GI Innovation and Technology.
5. Incubators: Use them Strategically
Incubators can offer mentorship, seed funding, legal support, and technical resources, but they vary widely in value (see Table 1). Many may want equity, and not all offer when you truly need.
Ask Yourself:
- Do I need technical help, business mentorship, or just accountability?
- What does this incubator offer in terms of IP protection, exposure, and connections?
- Do I understand the equity trade-off?
- What services and funding do they provide?
- Do they take equity? How much and when?
- What’s their track record with similar ventures?
- Are their incentives aligned with your vision?
6. Academic Institutions: Partners or Pitfalls?
Universities can provide credibility, resources, and early funding through their tech transfer office (TTO).
Key Questions to Ask:
- Will my IP be managed by the TTO?
- How much say do I have in licensing decisions?
- Are there royalty-sharing agreements in place?
- Can I form a startup while employed here?
You may need to negotiate if you want to commercialize your idea independently.
7. Do it for Purpose, Not Payday
Most founders end up owning only a small percentage of their company by the time a product reaches the market. Do not expect to get rich. Do it because it solves a problem you care about. If it happens to come with a nice paycheck, then that is an added bonus.
Your clinical training and insight give you a unique edge. You already know what’s broken. Use that as your compass.
Conclusion
Innovation isn’t about brilliance, it’s about curiosity, structure, and tenacity (see Table 2). Start small. Protect your work. Choose the right partners. Most importantly, stay anchored in your mission to make GI care better.
Dr. Muratore is based at UNC Rex Digestive Health, Raleigh, North Carolina. She has no conflicts related to this article. Dr. Wechsler is based at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. She holds a patent assigned to Trustees of Dartmouth College. Dr. Shah is based at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan. He consults for Ardelyx, Laborie, Neuraxis, Salix, Sanofi, and Takeda and holds a patent with the Regents of the University of Michigan.
You are in the middle of a busy clinic day and think, “there has to be a better way to do this.” Suddenly, a better way to do something becomes obvious. Maybe it’s a tool that simplifies documentation, a device that improves patient comfort, or an app that bridges a clinical gap. Many physicians, especially early career gastroenterologists, have ideas like this, but few know what to do next.
This article is for the curious innovator at the beginning of their clinical career. It offers practical, real-world guidance on developing a clinical product: whether that be hardware, software, or a hybrid. It outlines what questions to ask, who to consult, and how to protect your work, using personal insights and business principles learned through lived experience.
1. Understand Intellectual Property (IP): Know Its Value and Ownership
What is IP?
Intellectual property refers to your original creations: inventions, designs, software, and more. This is what you want to protect legally through patents, trademarks, or copyrights.
Who owns your idea?
This is the first and most important question to ask. If you are employed (especially by a hospital or academic center), your contract may already give your employer rights to any inventions you create, even those developed in your personal time.
What to ask:
- Does my employment contract include an “assignment of inventions” clause?
- Does the institution claim rights to anything developed with institutional resources?
- Are there moonlighting or external activity policies that affect this?
If you are developing an idea on your personal time, with your own resources, and outside your scope of clinical duties, it might still be considered “theirs” under some contracts. Early legal consultation is critical. A specialized IP attorney can help you understand what you own and how to protect it. This should be done early, ideally before you start building anything.
2. Lawyers Aren’t Optional: They’re Essential Early Partners
You do not need a full legal team, but you do need a lawyer early. An early consultation with an IP attorney can clarify your rights, guide your filing process (e.g. provisional patents), and help you avoid costly missteps.
Do this before sharing your idea publicly, including in academic presentations, pitch competitions, or even on social media. Public disclosure can start a clock ticking for application to protect your IP.
3. Build a Founding Team with Intent
Think of your startup team like a long-term relationship: you’re committing to build something together through uncertainty, tension, and change.
Strong early-stage teams often include:
- The Visionary – understands the clinical need and vision
- The Builder – engineer, developer, or designer
- The Doer – project manager or operations lead
Before forming a company, clearly define:
- Ownership (equity percentages)
- Roles and responsibilities
- Time commitments
- What happens if someone exits
Have these discussions early and document your agreements. Avoid informal “handshake” deals that can lead to serious disputes later.
4. You Don’t Need to Know Everything on Day One
You do not need to know how to write code, build a prototype, or get FDA clearance on day one. Successful innovators are humble learners. Use a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), a simple, functional version of your idea, to test assumptions and gather feedback. Iterate based on what you learn. Do not chase perfection; pursue progress. Consider using online accelerators like Y Combinator’s startup school or AGA’s Center for GI Innovation and Technology.
5. Incubators: Use them Strategically
Incubators can offer mentorship, seed funding, legal support, and technical resources, but they vary widely in value (see Table 1). Many may want equity, and not all offer when you truly need.
Ask Yourself:
- Do I need technical help, business mentorship, or just accountability?
- What does this incubator offer in terms of IP protection, exposure, and connections?
- Do I understand the equity trade-off?
- What services and funding do they provide?
- Do they take equity? How much and when?
- What’s their track record with similar ventures?
- Are their incentives aligned with your vision?
6. Academic Institutions: Partners or Pitfalls?
Universities can provide credibility, resources, and early funding through their tech transfer office (TTO).
Key Questions to Ask:
- Will my IP be managed by the TTO?
- How much say do I have in licensing decisions?
- Are there royalty-sharing agreements in place?
- Can I form a startup while employed here?
You may need to negotiate if you want to commercialize your idea independently.
7. Do it for Purpose, Not Payday
Most founders end up owning only a small percentage of their company by the time a product reaches the market. Do not expect to get rich. Do it because it solves a problem you care about. If it happens to come with a nice paycheck, then that is an added bonus.
Your clinical training and insight give you a unique edge. You already know what’s broken. Use that as your compass.
Conclusion
Innovation isn’t about brilliance, it’s about curiosity, structure, and tenacity (see Table 2). Start small. Protect your work. Choose the right partners. Most importantly, stay anchored in your mission to make GI care better.
Dr. Muratore is based at UNC Rex Digestive Health, Raleigh, North Carolina. She has no conflicts related to this article. Dr. Wechsler is based at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. She holds a patent assigned to Trustees of Dartmouth College. Dr. Shah is based at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan. He consults for Ardelyx, Laborie, Neuraxis, Salix, Sanofi, and Takeda and holds a patent with the Regents of the University of Michigan.
You are in the middle of a busy clinic day and think, “there has to be a better way to do this.” Suddenly, a better way to do something becomes obvious. Maybe it’s a tool that simplifies documentation, a device that improves patient comfort, or an app that bridges a clinical gap. Many physicians, especially early career gastroenterologists, have ideas like this, but few know what to do next.
This article is for the curious innovator at the beginning of their clinical career. It offers practical, real-world guidance on developing a clinical product: whether that be hardware, software, or a hybrid. It outlines what questions to ask, who to consult, and how to protect your work, using personal insights and business principles learned through lived experience.
1. Understand Intellectual Property (IP): Know Its Value and Ownership
What is IP?
Intellectual property refers to your original creations: inventions, designs, software, and more. This is what you want to protect legally through patents, trademarks, or copyrights.
Who owns your idea?
This is the first and most important question to ask. If you are employed (especially by a hospital or academic center), your contract may already give your employer rights to any inventions you create, even those developed in your personal time.
What to ask:
- Does my employment contract include an “assignment of inventions” clause?
- Does the institution claim rights to anything developed with institutional resources?
- Are there moonlighting or external activity policies that affect this?
If you are developing an idea on your personal time, with your own resources, and outside your scope of clinical duties, it might still be considered “theirs” under some contracts. Early legal consultation is critical. A specialized IP attorney can help you understand what you own and how to protect it. This should be done early, ideally before you start building anything.
2. Lawyers Aren’t Optional: They’re Essential Early Partners
You do not need a full legal team, but you do need a lawyer early. An early consultation with an IP attorney can clarify your rights, guide your filing process (e.g. provisional patents), and help you avoid costly missteps.
Do this before sharing your idea publicly, including in academic presentations, pitch competitions, or even on social media. Public disclosure can start a clock ticking for application to protect your IP.
3. Build a Founding Team with Intent
Think of your startup team like a long-term relationship: you’re committing to build something together through uncertainty, tension, and change.
Strong early-stage teams often include:
- The Visionary – understands the clinical need and vision
- The Builder – engineer, developer, or designer
- The Doer – project manager or operations lead
Before forming a company, clearly define:
- Ownership (equity percentages)
- Roles and responsibilities
- Time commitments
- What happens if someone exits
Have these discussions early and document your agreements. Avoid informal “handshake” deals that can lead to serious disputes later.
4. You Don’t Need to Know Everything on Day One
You do not need to know how to write code, build a prototype, or get FDA clearance on day one. Successful innovators are humble learners. Use a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), a simple, functional version of your idea, to test assumptions and gather feedback. Iterate based on what you learn. Do not chase perfection; pursue progress. Consider using online accelerators like Y Combinator’s startup school or AGA’s Center for GI Innovation and Technology.
5. Incubators: Use them Strategically
Incubators can offer mentorship, seed funding, legal support, and technical resources, but they vary widely in value (see Table 1). Many may want equity, and not all offer when you truly need.
Ask Yourself:
- Do I need technical help, business mentorship, or just accountability?
- What does this incubator offer in terms of IP protection, exposure, and connections?
- Do I understand the equity trade-off?
- What services and funding do they provide?
- Do they take equity? How much and when?
- What’s their track record with similar ventures?
- Are their incentives aligned with your vision?
6. Academic Institutions: Partners or Pitfalls?
Universities can provide credibility, resources, and early funding through their tech transfer office (TTO).
Key Questions to Ask:
- Will my IP be managed by the TTO?
- How much say do I have in licensing decisions?
- Are there royalty-sharing agreements in place?
- Can I form a startup while employed here?
You may need to negotiate if you want to commercialize your idea independently.
7. Do it for Purpose, Not Payday
Most founders end up owning only a small percentage of their company by the time a product reaches the market. Do not expect to get rich. Do it because it solves a problem you care about. If it happens to come with a nice paycheck, then that is an added bonus.
Your clinical training and insight give you a unique edge. You already know what’s broken. Use that as your compass.
Conclusion
Innovation isn’t about brilliance, it’s about curiosity, structure, and tenacity (see Table 2). Start small. Protect your work. Choose the right partners. Most importantly, stay anchored in your mission to make GI care better.
Dr. Muratore is based at UNC Rex Digestive Health, Raleigh, North Carolina. She has no conflicts related to this article. Dr. Wechsler is based at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. She holds a patent assigned to Trustees of Dartmouth College. Dr. Shah is based at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan. He consults for Ardelyx, Laborie, Neuraxis, Salix, Sanofi, and Takeda and holds a patent with the Regents of the University of Michigan.
When Your First Job Isn’t Forever: Lessons from My Journey and What Early-Career GIs Need to Know
Introduction
For many of us in gastroenterology, landing that first attending job feels like the ultimate victory lap — the reward for all those years of training. We sign the contract, relocate, and imagine this will be our “forever job.” Reality often plays out differently.
In fact, 43% of physicians change jobs within five years, while 83% changed employers at least once in their careers.1 Even within our field — which is always in demand — turnover is high; 1 in 3 gastroenterologists are planning to leave their current role within two years.2 Why does this happen? More importantly, how do we navigate this transition with clarity and confidence as an early-career GI?
My Story: When I Dared to Change My “Forever Job”
When I signed my first attending contract, I didn’t negotiate a single thing. My priorities were simple: family in Toronto and visa requirements. After a decade of medical school, residency, and fellowship, everything else felt secondary. I was happy to be back home.
The job itself was good — reasonable hours, flexible colleagues, and ample opportunity to enhance my procedural skills. As I started carving out my niche in endobariatrics, the support I needed to grow further was not there. I kept telling myself that this job fulfilled my values and I needed to be patient: “this is my forever job. I am close to my family and that’s what matters.”
Then, during a suturing course at the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, I had a casual chat with the course director (now my boss). It took me by surprise, but as the conversation continued, he offered me a job. It was tempting: the chance to build my own endobariatrics program with real institutional backing. The catch? It was in a city I had never been to, with no family or friends around. I politely said “no, thank you, I can’t.” He smiled, gave me his number, and said, “think about it.”
For the first time, I allowed myself to ask, “could I really leave my forever job?”
The Power of a Circle and a Spreadsheet
I leaned on my circle — a close group of fellowship friends who each took a turn being someone’s lifeline. We have monthly Zoom calls to talk about jobs, family, and career aspirations. When I shared my dilemma, I realized I wasn’t alone; one friend was also unhappy with her first job. Suddenly, we were asking one another, “can we really leave?”
I hired a career consultant familiar with physician visa issues — hands down, the best money I ever invested. The job search felt like dating: each interview was a first date; some needed a second or third date before I knew if it could be a match.
After every interview, I’d jump on Zoom with my circle. We’d screen-share my giant Excel spreadsheet — our decision matrix — with columns for everything I cared about:
- Institute
- Administrative Time
- Endobariatric support
- Director Title
- Salary
- On-call
- Vacation
- Proximity to airport
- Cost of living
- RVU percentage
- Endoscopy center buy-in
- Contract duration
- Support staff
- CME
We scored each job, line by line, and not a single job checked all the boxes. As I sat there in a state of decision paralysis, it became clear that this was not a simple decision.
The GI Community: A Small, Supportive World
The GI community is incredibly close-knit and kind-hearted. At every conference, I made a point to chat with as many colleagues as I could, to hear their perspectives on jobs and how they made tough career moves. Those conversations were real — no Google search or Excel sheet could offer the perspective and insight I gained by simply asking and leaning on the GI community.
Meanwhile, the person who had first offered me that job kept checking in, catching up at conferences, and bonding over our love for food and baking. With him, I never felt like I was being ‘interviewed’ — I felt valued. It did not feel like he was trying to fill a position with just anyone to improve the call pool. He genuinely wanted to understand what my goals were and how I envisioned my future. Through those conversations, he reminded me of my original passions, which were sidelined when so immersed in the daily routine.
I’ve learned that feeling valued doesn’t come from grand gestures in recruitment. It’s in the quiet signs of respect, trust, and being seen. He wasn’t looking for just anyone; he was looking for someone whose goals aligned with his group’s and someone in whom he wanted to invest. While others might chase the highest salary, the most flexible schedule, or the strongest ancillary support, I realized I valued something I did not realize that I was lacking until then: mentorship.
What I Learned: There is No Such Thing As “The Perfect Job”
After a full year of spreadsheets, Zoom calls, conference chats, and overthinking, I came to a big realization: there’s no perfect job — there’s no such thing as an ideal “forever job.” The only constant for humans is change. Our circumstances change, our priorities shift, our interests shuffle, and our finances evolve. The best job is simply the one that fits the stage of life you’re in at that given moment. For me, mentorship and growth became my top priorities, even if it meant moving away from family.
What Physicians Value Most in a Second Job
After their first job, early-career gastroenterologists often reevaluate what really matters. Recent surveys highlight four key priorities:
- Work-life balance:
In a 2022 CompHealth Group healthcare survey, 85% of physicians ranked work-life balance as their top job priority.3
- Mentorship and growth:
Nearly 1 in 3 physicians cited lack of mentorship or career advancement as their reason for leaving a first job, per the 2023 MGMA/Jackson Physician Search report.4
- Compensation:
While not always the main reason for leaving, 77% of physicians now list compensation as a top priority — a big jump from prior years.3
- Practice support:
Poor infrastructure, administrative overload, or understaffed teams are common dealbreakers. In the second job, physicians look for well-run practices with solid support staff and reduced burnout risk.5
Conclusion
Welcome the uncertainty, talk to your circle, lean on your community, and use a spreadsheet if you need to — but don’t forget to trust your gut. There’s no forever job or the perfect path, only the next move that feels most true to who you are in that moment.
Dr. Ismail (@mayyismail) is Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine (Gastroenterology) at Temple University in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. She declares no conflicts of interest.
References
1. CHG Healthcare. Survey: 62% of physicians made a career change in the last two years. CHG Healthcare blog. June 10, 2024. Accessed August 5, 2025.
2. Berg S. Physicians in these 10 specialties are less likely to quit. AMA News. Published June 24, 2025. Accessed July 2025.
3. Saley C. Survey: Work/life balance is #1 priority in physicians’ job search. CHG Healthcare Insights. March 10, 2022. Accessed August 2025.
4. Medical Group Management Association; Jackson Physician Search. Early‑Career Physician Recruiting & Retention Playbook. October 23, 2023. Accessed August 2025.
5. Von Rosenvinge EC, et al. A crisis in scope: Recruitment and retention challenges reported by VA gastroenterology section chiefs. Fed Pract. 2024 Aug. doi:10.12788/fp.0504.
Introduction
For many of us in gastroenterology, landing that first attending job feels like the ultimate victory lap — the reward for all those years of training. We sign the contract, relocate, and imagine this will be our “forever job.” Reality often plays out differently.
In fact, 43% of physicians change jobs within five years, while 83% changed employers at least once in their careers.1 Even within our field — which is always in demand — turnover is high; 1 in 3 gastroenterologists are planning to leave their current role within two years.2 Why does this happen? More importantly, how do we navigate this transition with clarity and confidence as an early-career GI?
My Story: When I Dared to Change My “Forever Job”
When I signed my first attending contract, I didn’t negotiate a single thing. My priorities were simple: family in Toronto and visa requirements. After a decade of medical school, residency, and fellowship, everything else felt secondary. I was happy to be back home.
The job itself was good — reasonable hours, flexible colleagues, and ample opportunity to enhance my procedural skills. As I started carving out my niche in endobariatrics, the support I needed to grow further was not there. I kept telling myself that this job fulfilled my values and I needed to be patient: “this is my forever job. I am close to my family and that’s what matters.”
Then, during a suturing course at the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, I had a casual chat with the course director (now my boss). It took me by surprise, but as the conversation continued, he offered me a job. It was tempting: the chance to build my own endobariatrics program with real institutional backing. The catch? It was in a city I had never been to, with no family or friends around. I politely said “no, thank you, I can’t.” He smiled, gave me his number, and said, “think about it.”
For the first time, I allowed myself to ask, “could I really leave my forever job?”
The Power of a Circle and a Spreadsheet
I leaned on my circle — a close group of fellowship friends who each took a turn being someone’s lifeline. We have monthly Zoom calls to talk about jobs, family, and career aspirations. When I shared my dilemma, I realized I wasn’t alone; one friend was also unhappy with her first job. Suddenly, we were asking one another, “can we really leave?”
I hired a career consultant familiar with physician visa issues — hands down, the best money I ever invested. The job search felt like dating: each interview was a first date; some needed a second or third date before I knew if it could be a match.
After every interview, I’d jump on Zoom with my circle. We’d screen-share my giant Excel spreadsheet — our decision matrix — with columns for everything I cared about:
- Institute
- Administrative Time
- Endobariatric support
- Director Title
- Salary
- On-call
- Vacation
- Proximity to airport
- Cost of living
- RVU percentage
- Endoscopy center buy-in
- Contract duration
- Support staff
- CME
We scored each job, line by line, and not a single job checked all the boxes. As I sat there in a state of decision paralysis, it became clear that this was not a simple decision.
The GI Community: A Small, Supportive World
The GI community is incredibly close-knit and kind-hearted. At every conference, I made a point to chat with as many colleagues as I could, to hear their perspectives on jobs and how they made tough career moves. Those conversations were real — no Google search or Excel sheet could offer the perspective and insight I gained by simply asking and leaning on the GI community.
Meanwhile, the person who had first offered me that job kept checking in, catching up at conferences, and bonding over our love for food and baking. With him, I never felt like I was being ‘interviewed’ — I felt valued. It did not feel like he was trying to fill a position with just anyone to improve the call pool. He genuinely wanted to understand what my goals were and how I envisioned my future. Through those conversations, he reminded me of my original passions, which were sidelined when so immersed in the daily routine.
I’ve learned that feeling valued doesn’t come from grand gestures in recruitment. It’s in the quiet signs of respect, trust, and being seen. He wasn’t looking for just anyone; he was looking for someone whose goals aligned with his group’s and someone in whom he wanted to invest. While others might chase the highest salary, the most flexible schedule, or the strongest ancillary support, I realized I valued something I did not realize that I was lacking until then: mentorship.
What I Learned: There is No Such Thing As “The Perfect Job”
After a full year of spreadsheets, Zoom calls, conference chats, and overthinking, I came to a big realization: there’s no perfect job — there’s no such thing as an ideal “forever job.” The only constant for humans is change. Our circumstances change, our priorities shift, our interests shuffle, and our finances evolve. The best job is simply the one that fits the stage of life you’re in at that given moment. For me, mentorship and growth became my top priorities, even if it meant moving away from family.
What Physicians Value Most in a Second Job
After their first job, early-career gastroenterologists often reevaluate what really matters. Recent surveys highlight four key priorities:
- Work-life balance:
In a 2022 CompHealth Group healthcare survey, 85% of physicians ranked work-life balance as their top job priority.3
- Mentorship and growth:
Nearly 1 in 3 physicians cited lack of mentorship or career advancement as their reason for leaving a first job, per the 2023 MGMA/Jackson Physician Search report.4
- Compensation:
While not always the main reason for leaving, 77% of physicians now list compensation as a top priority — a big jump from prior years.3
- Practice support:
Poor infrastructure, administrative overload, or understaffed teams are common dealbreakers. In the second job, physicians look for well-run practices with solid support staff and reduced burnout risk.5
Conclusion
Welcome the uncertainty, talk to your circle, lean on your community, and use a spreadsheet if you need to — but don’t forget to trust your gut. There’s no forever job or the perfect path, only the next move that feels most true to who you are in that moment.
Dr. Ismail (@mayyismail) is Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine (Gastroenterology) at Temple University in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. She declares no conflicts of interest.
References
1. CHG Healthcare. Survey: 62% of physicians made a career change in the last two years. CHG Healthcare blog. June 10, 2024. Accessed August 5, 2025.
2. Berg S. Physicians in these 10 specialties are less likely to quit. AMA News. Published June 24, 2025. Accessed July 2025.
3. Saley C. Survey: Work/life balance is #1 priority in physicians’ job search. CHG Healthcare Insights. March 10, 2022. Accessed August 2025.
4. Medical Group Management Association; Jackson Physician Search. Early‑Career Physician Recruiting & Retention Playbook. October 23, 2023. Accessed August 2025.
5. Von Rosenvinge EC, et al. A crisis in scope: Recruitment and retention challenges reported by VA gastroenterology section chiefs. Fed Pract. 2024 Aug. doi:10.12788/fp.0504.
Introduction
For many of us in gastroenterology, landing that first attending job feels like the ultimate victory lap — the reward for all those years of training. We sign the contract, relocate, and imagine this will be our “forever job.” Reality often plays out differently.
In fact, 43% of physicians change jobs within five years, while 83% changed employers at least once in their careers.1 Even within our field — which is always in demand — turnover is high; 1 in 3 gastroenterologists are planning to leave their current role within two years.2 Why does this happen? More importantly, how do we navigate this transition with clarity and confidence as an early-career GI?
My Story: When I Dared to Change My “Forever Job”
When I signed my first attending contract, I didn’t negotiate a single thing. My priorities were simple: family in Toronto and visa requirements. After a decade of medical school, residency, and fellowship, everything else felt secondary. I was happy to be back home.
The job itself was good — reasonable hours, flexible colleagues, and ample opportunity to enhance my procedural skills. As I started carving out my niche in endobariatrics, the support I needed to grow further was not there. I kept telling myself that this job fulfilled my values and I needed to be patient: “this is my forever job. I am close to my family and that’s what matters.”
Then, during a suturing course at the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, I had a casual chat with the course director (now my boss). It took me by surprise, but as the conversation continued, he offered me a job. It was tempting: the chance to build my own endobariatrics program with real institutional backing. The catch? It was in a city I had never been to, with no family or friends around. I politely said “no, thank you, I can’t.” He smiled, gave me his number, and said, “think about it.”
For the first time, I allowed myself to ask, “could I really leave my forever job?”
The Power of a Circle and a Spreadsheet
I leaned on my circle — a close group of fellowship friends who each took a turn being someone’s lifeline. We have monthly Zoom calls to talk about jobs, family, and career aspirations. When I shared my dilemma, I realized I wasn’t alone; one friend was also unhappy with her first job. Suddenly, we were asking one another, “can we really leave?”
I hired a career consultant familiar with physician visa issues — hands down, the best money I ever invested. The job search felt like dating: each interview was a first date; some needed a second or third date before I knew if it could be a match.
After every interview, I’d jump on Zoom with my circle. We’d screen-share my giant Excel spreadsheet — our decision matrix — with columns for everything I cared about:
- Institute
- Administrative Time
- Endobariatric support
- Director Title
- Salary
- On-call
- Vacation
- Proximity to airport
- Cost of living
- RVU percentage
- Endoscopy center buy-in
- Contract duration
- Support staff
- CME
We scored each job, line by line, and not a single job checked all the boxes. As I sat there in a state of decision paralysis, it became clear that this was not a simple decision.
The GI Community: A Small, Supportive World
The GI community is incredibly close-knit and kind-hearted. At every conference, I made a point to chat with as many colleagues as I could, to hear their perspectives on jobs and how they made tough career moves. Those conversations were real — no Google search or Excel sheet could offer the perspective and insight I gained by simply asking and leaning on the GI community.
Meanwhile, the person who had first offered me that job kept checking in, catching up at conferences, and bonding over our love for food and baking. With him, I never felt like I was being ‘interviewed’ — I felt valued. It did not feel like he was trying to fill a position with just anyone to improve the call pool. He genuinely wanted to understand what my goals were and how I envisioned my future. Through those conversations, he reminded me of my original passions, which were sidelined when so immersed in the daily routine.
I’ve learned that feeling valued doesn’t come from grand gestures in recruitment. It’s in the quiet signs of respect, trust, and being seen. He wasn’t looking for just anyone; he was looking for someone whose goals aligned with his group’s and someone in whom he wanted to invest. While others might chase the highest salary, the most flexible schedule, or the strongest ancillary support, I realized I valued something I did not realize that I was lacking until then: mentorship.
What I Learned: There is No Such Thing As “The Perfect Job”
After a full year of spreadsheets, Zoom calls, conference chats, and overthinking, I came to a big realization: there’s no perfect job — there’s no such thing as an ideal “forever job.” The only constant for humans is change. Our circumstances change, our priorities shift, our interests shuffle, and our finances evolve. The best job is simply the one that fits the stage of life you’re in at that given moment. For me, mentorship and growth became my top priorities, even if it meant moving away from family.
What Physicians Value Most in a Second Job
After their first job, early-career gastroenterologists often reevaluate what really matters. Recent surveys highlight four key priorities:
- Work-life balance:
In a 2022 CompHealth Group healthcare survey, 85% of physicians ranked work-life balance as their top job priority.3
- Mentorship and growth:
Nearly 1 in 3 physicians cited lack of mentorship or career advancement as their reason for leaving a first job, per the 2023 MGMA/Jackson Physician Search report.4
- Compensation:
While not always the main reason for leaving, 77% of physicians now list compensation as a top priority — a big jump from prior years.3
- Practice support:
Poor infrastructure, administrative overload, or understaffed teams are common dealbreakers. In the second job, physicians look for well-run practices with solid support staff and reduced burnout risk.5
Conclusion
Welcome the uncertainty, talk to your circle, lean on your community, and use a spreadsheet if you need to — but don’t forget to trust your gut. There’s no forever job or the perfect path, only the next move that feels most true to who you are in that moment.
Dr. Ismail (@mayyismail) is Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine (Gastroenterology) at Temple University in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. She declares no conflicts of interest.
References
1. CHG Healthcare. Survey: 62% of physicians made a career change in the last two years. CHG Healthcare blog. June 10, 2024. Accessed August 5, 2025.
2. Berg S. Physicians in these 10 specialties are less likely to quit. AMA News. Published June 24, 2025. Accessed July 2025.
3. Saley C. Survey: Work/life balance is #1 priority in physicians’ job search. CHG Healthcare Insights. March 10, 2022. Accessed August 2025.
4. Medical Group Management Association; Jackson Physician Search. Early‑Career Physician Recruiting & Retention Playbook. October 23, 2023. Accessed August 2025.
5. Von Rosenvinge EC, et al. A crisis in scope: Recruitment and retention challenges reported by VA gastroenterology section chiefs. Fed Pract. 2024 Aug. doi:10.12788/fp.0504.
The Patient Portal That Patients Can’t Navigate
Beth Cavanaugh, 79, was starting a new medication when she ran into a modern hurdle: Her doctor’s office required all follow–up questions, even those about side effects of the drug, to go through the patient portal.
Cavanaugh said she did not know how to set up or use the system.
“I tried to explain that, but the receptionist said that was the only way to contact the doctor. I felt lost,” said Cavanaugh, a retired psychotherapist near Albany, New York.
Cavanaugh is far from alone. Many older people balk at the idea of communicating with their physicians over the internet. They may have limited digital skills, have physical challenges, or simply prefer human connection.
As medicine leans harder on electronic portals and telehealth, these patients are finding themselves shut out of their own care. Experts warn this approach deepens inequities in access to care and can worsen health outcomes.
Clinicians should “offer options for various types of communication, such as phone calls or texts, because whenever an older adult — or anyone, for that matter — is given a choice, they feel more empowered and more committed to their care,” said Susan Wehry, MD, associate clinical professor at the University of New England College of Osteopathic Medicine in Biddeford, Maine.
Tech Support
Use of medical communication tools varies among older adults. One study in JAMA Network Open found nearly two thirds of those older than 65 years who filled out surveys via phone or internet had used a patient portal, while a little under half used telehealth, and only 44% used a medical health application.
Older patients tend to fall into two camps, said Neela Patel, MD, MPH, CMD, chief of the Division of Geriatrics and Supportive Care at the UT Health San Antonio.
Her patients “are at two extremes of the spectrum — some technologically savvy and others with limited digital literacy or limited or no access to the Internet,” Patel, who is also the vice chair of the Health Systems Innovations and Technology Committee of the American Geriatric Society, said.
Patel’s practice has dedicated staff to help patients master certain technologies. For example, a pharmacist teaches patients how to use a glucometer and a blood pressure cuff. Other staff teach them how to use smartphone apps that track blood pressure or glucose.
She usually sees patients in person before offering telehealth as an option, ensuring the person has “enough digital literacy to utilize them and that the patient can see and hear the visit.”
If technological limitations impede a telehealth appointment, clinicians can help patients navigate their computer screen. Patel recounted the story of an older woman who was unable to come to the clinic in person, so had a telehealth visit instead.
“She had trouble hearing me, so I asked her to share her screen with me. I walked her through how to do that. Then I showed her where the ‘volume’ button was located. It turns out her volume was at zero,” Patel said. “Once that was adjusted, we were able to proceed with the appointment.”
Educating older adults on how to use health technology does not have to fall upon clinicians and their staff, according to Wehry. She routinely refers her patients to community resources to help them develop digital skills.
Local libraries and community centers often offer digital education. Some retirement communities and assisted living facilities also have tech support personnel or classes available to residents.
Wehry refers some of her patients to the National Digital Equity Center which teaches older adults how to hold a telehealth visit.
Roughly 90% of Patel’s patients are signed up for the patient portal, but they may not be operating the technology, she said. She advises these patients to ask their children or caregivers for help as appropriate.
Teaching patients to use the communication technology early on can also be helpful in other ways. If patients who have been technologically proficient start having difficulty, “it’s a clue there may be cognitive changes, and we follow up on those,” Patel said.
Additional resources to help older adults develop digital competence include Cyber Seniors, Older Adults Technology Services, AARP, AARP Find Digital Courses, Area Agencies on Aging, and Senior Navigator.
Human Touch
Some older adults may simply want a more traditional means of communicating with their clinician. A review of 29 papers, encompassing over 6200 adults older than 60 years, identified several domains affecting the adoption of healthcare technology, two of which were resistance to new technology and having family or friends that could help with.
Wehry said many older adults “don’t resist this technology because they’re unable to figure out how to use it. Instead, they see the technology as too impersonal.”
One study found many older adults fear technologies may end up replacing face-to-face contact.
“I’m beginning to encourage primary care providers to take a step back and refocus on the doctor-patient relationship. When communication is limited to the technological approach, it can erode trust in that relationship,” Wehry said.
The American Medical Association recommends clinicians “provide a method other than electronic communication for patients who are without technological proficiency or access.”
Some busy clinicians might be concerned phone calls will be too time-consuming, Wehry said. Patients should be informed of hours of phone availability, how much time is allotted to calls, and how many days or hours a response may take. Clinicians might also use tools that allow patients to use their cell phone to text their practice with medical questions.
Cavanaugh ended up finding technological help from a professional organizer whom she hired to help rearrange her closets.
“She’s knowledgeable and patient, and she’s helping me with the portal,” she said. “If I hadn’t serendipitously found the organizer, I’d still be struggling and unable to access proper medical care.”
Wehry and Patel disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Beth Cavanaugh, 79, was starting a new medication when she ran into a modern hurdle: Her doctor’s office required all follow–up questions, even those about side effects of the drug, to go through the patient portal.
Cavanaugh said she did not know how to set up or use the system.
“I tried to explain that, but the receptionist said that was the only way to contact the doctor. I felt lost,” said Cavanaugh, a retired psychotherapist near Albany, New York.
Cavanaugh is far from alone. Many older people balk at the idea of communicating with their physicians over the internet. They may have limited digital skills, have physical challenges, or simply prefer human connection.
As medicine leans harder on electronic portals and telehealth, these patients are finding themselves shut out of their own care. Experts warn this approach deepens inequities in access to care and can worsen health outcomes.
Clinicians should “offer options for various types of communication, such as phone calls or texts, because whenever an older adult — or anyone, for that matter — is given a choice, they feel more empowered and more committed to their care,” said Susan Wehry, MD, associate clinical professor at the University of New England College of Osteopathic Medicine in Biddeford, Maine.
Tech Support
Use of medical communication tools varies among older adults. One study in JAMA Network Open found nearly two thirds of those older than 65 years who filled out surveys via phone or internet had used a patient portal, while a little under half used telehealth, and only 44% used a medical health application.
Older patients tend to fall into two camps, said Neela Patel, MD, MPH, CMD, chief of the Division of Geriatrics and Supportive Care at the UT Health San Antonio.
Her patients “are at two extremes of the spectrum — some technologically savvy and others with limited digital literacy or limited or no access to the Internet,” Patel, who is also the vice chair of the Health Systems Innovations and Technology Committee of the American Geriatric Society, said.
Patel’s practice has dedicated staff to help patients master certain technologies. For example, a pharmacist teaches patients how to use a glucometer and a blood pressure cuff. Other staff teach them how to use smartphone apps that track blood pressure or glucose.
She usually sees patients in person before offering telehealth as an option, ensuring the person has “enough digital literacy to utilize them and that the patient can see and hear the visit.”
If technological limitations impede a telehealth appointment, clinicians can help patients navigate their computer screen. Patel recounted the story of an older woman who was unable to come to the clinic in person, so had a telehealth visit instead.
“She had trouble hearing me, so I asked her to share her screen with me. I walked her through how to do that. Then I showed her where the ‘volume’ button was located. It turns out her volume was at zero,” Patel said. “Once that was adjusted, we were able to proceed with the appointment.”
Educating older adults on how to use health technology does not have to fall upon clinicians and their staff, according to Wehry. She routinely refers her patients to community resources to help them develop digital skills.
Local libraries and community centers often offer digital education. Some retirement communities and assisted living facilities also have tech support personnel or classes available to residents.
Wehry refers some of her patients to the National Digital Equity Center which teaches older adults how to hold a telehealth visit.
Roughly 90% of Patel’s patients are signed up for the patient portal, but they may not be operating the technology, she said. She advises these patients to ask their children or caregivers for help as appropriate.
Teaching patients to use the communication technology early on can also be helpful in other ways. If patients who have been technologically proficient start having difficulty, “it’s a clue there may be cognitive changes, and we follow up on those,” Patel said.
Additional resources to help older adults develop digital competence include Cyber Seniors, Older Adults Technology Services, AARP, AARP Find Digital Courses, Area Agencies on Aging, and Senior Navigator.
Human Touch
Some older adults may simply want a more traditional means of communicating with their clinician. A review of 29 papers, encompassing over 6200 adults older than 60 years, identified several domains affecting the adoption of healthcare technology, two of which were resistance to new technology and having family or friends that could help with.
Wehry said many older adults “don’t resist this technology because they’re unable to figure out how to use it. Instead, they see the technology as too impersonal.”
One study found many older adults fear technologies may end up replacing face-to-face contact.
“I’m beginning to encourage primary care providers to take a step back and refocus on the doctor-patient relationship. When communication is limited to the technological approach, it can erode trust in that relationship,” Wehry said.
The American Medical Association recommends clinicians “provide a method other than electronic communication for patients who are without technological proficiency or access.”
Some busy clinicians might be concerned phone calls will be too time-consuming, Wehry said. Patients should be informed of hours of phone availability, how much time is allotted to calls, and how many days or hours a response may take. Clinicians might also use tools that allow patients to use their cell phone to text their practice with medical questions.
Cavanaugh ended up finding technological help from a professional organizer whom she hired to help rearrange her closets.
“She’s knowledgeable and patient, and she’s helping me with the portal,” she said. “If I hadn’t serendipitously found the organizer, I’d still be struggling and unable to access proper medical care.”
Wehry and Patel disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Beth Cavanaugh, 79, was starting a new medication when she ran into a modern hurdle: Her doctor’s office required all follow–up questions, even those about side effects of the drug, to go through the patient portal.
Cavanaugh said she did not know how to set up or use the system.
“I tried to explain that, but the receptionist said that was the only way to contact the doctor. I felt lost,” said Cavanaugh, a retired psychotherapist near Albany, New York.
Cavanaugh is far from alone. Many older people balk at the idea of communicating with their physicians over the internet. They may have limited digital skills, have physical challenges, or simply prefer human connection.
As medicine leans harder on electronic portals and telehealth, these patients are finding themselves shut out of their own care. Experts warn this approach deepens inequities in access to care and can worsen health outcomes.
Clinicians should “offer options for various types of communication, such as phone calls or texts, because whenever an older adult — or anyone, for that matter — is given a choice, they feel more empowered and more committed to their care,” said Susan Wehry, MD, associate clinical professor at the University of New England College of Osteopathic Medicine in Biddeford, Maine.
Tech Support
Use of medical communication tools varies among older adults. One study in JAMA Network Open found nearly two thirds of those older than 65 years who filled out surveys via phone or internet had used a patient portal, while a little under half used telehealth, and only 44% used a medical health application.
Older patients tend to fall into two camps, said Neela Patel, MD, MPH, CMD, chief of the Division of Geriatrics and Supportive Care at the UT Health San Antonio.
Her patients “are at two extremes of the spectrum — some technologically savvy and others with limited digital literacy or limited or no access to the Internet,” Patel, who is also the vice chair of the Health Systems Innovations and Technology Committee of the American Geriatric Society, said.
Patel’s practice has dedicated staff to help patients master certain technologies. For example, a pharmacist teaches patients how to use a glucometer and a blood pressure cuff. Other staff teach them how to use smartphone apps that track blood pressure or glucose.
She usually sees patients in person before offering telehealth as an option, ensuring the person has “enough digital literacy to utilize them and that the patient can see and hear the visit.”
If technological limitations impede a telehealth appointment, clinicians can help patients navigate their computer screen. Patel recounted the story of an older woman who was unable to come to the clinic in person, so had a telehealth visit instead.
“She had trouble hearing me, so I asked her to share her screen with me. I walked her through how to do that. Then I showed her where the ‘volume’ button was located. It turns out her volume was at zero,” Patel said. “Once that was adjusted, we were able to proceed with the appointment.”
Educating older adults on how to use health technology does not have to fall upon clinicians and their staff, according to Wehry. She routinely refers her patients to community resources to help them develop digital skills.
Local libraries and community centers often offer digital education. Some retirement communities and assisted living facilities also have tech support personnel or classes available to residents.
Wehry refers some of her patients to the National Digital Equity Center which teaches older adults how to hold a telehealth visit.
Roughly 90% of Patel’s patients are signed up for the patient portal, but they may not be operating the technology, she said. She advises these patients to ask their children or caregivers for help as appropriate.
Teaching patients to use the communication technology early on can also be helpful in other ways. If patients who have been technologically proficient start having difficulty, “it’s a clue there may be cognitive changes, and we follow up on those,” Patel said.
Additional resources to help older adults develop digital competence include Cyber Seniors, Older Adults Technology Services, AARP, AARP Find Digital Courses, Area Agencies on Aging, and Senior Navigator.
Human Touch
Some older adults may simply want a more traditional means of communicating with their clinician. A review of 29 papers, encompassing over 6200 adults older than 60 years, identified several domains affecting the adoption of healthcare technology, two of which were resistance to new technology and having family or friends that could help with.
Wehry said many older adults “don’t resist this technology because they’re unable to figure out how to use it. Instead, they see the technology as too impersonal.”
One study found many older adults fear technologies may end up replacing face-to-face contact.
“I’m beginning to encourage primary care providers to take a step back and refocus on the doctor-patient relationship. When communication is limited to the technological approach, it can erode trust in that relationship,” Wehry said.
The American Medical Association recommends clinicians “provide a method other than electronic communication for patients who are without technological proficiency or access.”
Some busy clinicians might be concerned phone calls will be too time-consuming, Wehry said. Patients should be informed of hours of phone availability, how much time is allotted to calls, and how many days or hours a response may take. Clinicians might also use tools that allow patients to use their cell phone to text their practice with medical questions.
Cavanaugh ended up finding technological help from a professional organizer whom she hired to help rearrange her closets.
“She’s knowledgeable and patient, and she’s helping me with the portal,” she said. “If I hadn’t serendipitously found the organizer, I’d still be struggling and unable to access proper medical care.”
Wehry and Patel disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Reticulated Hyperpigmentation on the Knee and Thigh
Reticulated Hyperpigmentation on the Knee and Thigh
The patient was diagnosed with erythema ab igne based on characteristic skin findings on physical examination along with a convincing history of chronic localized heat exposure. Erythema ab igne manifests as a persistent reticulated, erythematous, or hyperpigmented rash at sites of chronic heat exposure.1 Commonplace items that emit heat such as electric heaters, car heaters, heating pads, hot water bottles, and, in our case, laptops also emit infrared radiation, which can lead to changes in the skin with long-term exposure.2 Because exposure to these sources often is limited to one area of the body, erythema ab igne usually manifests locally, as exemplified in this case. Chronic heat exposure and infrared radiation from these sources are thought to induce hyperthermia below the threshold for a thermal burn, and the cutaneous findings correspond with the dermal venous plexus.3
Diagnosis of erythema ab igne primarily is made clinically based on characteristic skin findings and exposure history. Relevant history may include occupations with prolonged heat exposure, such as baking, silversmithing, or foundry work. Heat exposure also may result from cultural practices such as cupping with moxibustion.4 Additionally, repeated use of heating pads or hot water bottles for pain relief by patients diagnosed with chronic pain or an underlying illness may contribute to development of erythema ab igne.1,4
Biopsy was not needed for diagnosis of this patient, but if the presentation is equivocal and history of potential exposures is unclear, a biopsy may be taken. A hematoxylin and eosin stain would reveal dilation of small vascular channels in the superficial dermis, contributing to the classic reticulated appearance. Biopsy findings also would reveal either an interface dermatitis or pigment incontinence containing melanin-laden macrophages correlating to either the erythema or hyperpigmentation, respectively.4
The prognosis for erythema ab igne is excellent, especially if diagnosed early. Treatment involves removal of the inciting heat source.1 The discoloration may resolve within a few months to years or may persist. If the hyperpigmentation is persistent, patients may consider laser treatments or lightening agents such as topical hydroquinone or topical tretinoin.4 However, if undiagnosed, patients may be at risk for development of a cutaneous malignancy, such as squamous cell carcinoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, poorly differentiated carcinoma, or cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma.2,4 Malignant transformation has been reported to occur decades after the initial skin eruption, although the risk is rare5; however, due to this risk, patients with erythema ab igne should be followed regularly and screened for new lesions in the affected areas.
- Tan S, Bertucci V. Erythema ab igne: an old condition new again. CMAJ. 2000;162:77-78.
- Miller K, Hunt R, Chu J, et al. Erythema ab igne. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:28.
- Kesty K, Feldman SR. Erythema ab igne: evolving technology, evolving presentation. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:13030.
- Harview CL, Krenitsky A. Erythema ab igne: a clinical review. Cutis. 2023;111:E33-E38. doi:10.12788/cutis.0771
- Wipf AJ, Brown MR. Malignant transformation of erythema ab igne. JAAD Case Rep. 2022;26:85-87. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2022.06.018
The patient was diagnosed with erythema ab igne based on characteristic skin findings on physical examination along with a convincing history of chronic localized heat exposure. Erythema ab igne manifests as a persistent reticulated, erythematous, or hyperpigmented rash at sites of chronic heat exposure.1 Commonplace items that emit heat such as electric heaters, car heaters, heating pads, hot water bottles, and, in our case, laptops also emit infrared radiation, which can lead to changes in the skin with long-term exposure.2 Because exposure to these sources often is limited to one area of the body, erythema ab igne usually manifests locally, as exemplified in this case. Chronic heat exposure and infrared radiation from these sources are thought to induce hyperthermia below the threshold for a thermal burn, and the cutaneous findings correspond with the dermal venous plexus.3
Diagnosis of erythema ab igne primarily is made clinically based on characteristic skin findings and exposure history. Relevant history may include occupations with prolonged heat exposure, such as baking, silversmithing, or foundry work. Heat exposure also may result from cultural practices such as cupping with moxibustion.4 Additionally, repeated use of heating pads or hot water bottles for pain relief by patients diagnosed with chronic pain or an underlying illness may contribute to development of erythema ab igne.1,4
Biopsy was not needed for diagnosis of this patient, but if the presentation is equivocal and history of potential exposures is unclear, a biopsy may be taken. A hematoxylin and eosin stain would reveal dilation of small vascular channels in the superficial dermis, contributing to the classic reticulated appearance. Biopsy findings also would reveal either an interface dermatitis or pigment incontinence containing melanin-laden macrophages correlating to either the erythema or hyperpigmentation, respectively.4
The prognosis for erythema ab igne is excellent, especially if diagnosed early. Treatment involves removal of the inciting heat source.1 The discoloration may resolve within a few months to years or may persist. If the hyperpigmentation is persistent, patients may consider laser treatments or lightening agents such as topical hydroquinone or topical tretinoin.4 However, if undiagnosed, patients may be at risk for development of a cutaneous malignancy, such as squamous cell carcinoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, poorly differentiated carcinoma, or cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma.2,4 Malignant transformation has been reported to occur decades after the initial skin eruption, although the risk is rare5; however, due to this risk, patients with erythema ab igne should be followed regularly and screened for new lesions in the affected areas.
The patient was diagnosed with erythema ab igne based on characteristic skin findings on physical examination along with a convincing history of chronic localized heat exposure. Erythema ab igne manifests as a persistent reticulated, erythematous, or hyperpigmented rash at sites of chronic heat exposure.1 Commonplace items that emit heat such as electric heaters, car heaters, heating pads, hot water bottles, and, in our case, laptops also emit infrared radiation, which can lead to changes in the skin with long-term exposure.2 Because exposure to these sources often is limited to one area of the body, erythema ab igne usually manifests locally, as exemplified in this case. Chronic heat exposure and infrared radiation from these sources are thought to induce hyperthermia below the threshold for a thermal burn, and the cutaneous findings correspond with the dermal venous plexus.3
Diagnosis of erythema ab igne primarily is made clinically based on characteristic skin findings and exposure history. Relevant history may include occupations with prolonged heat exposure, such as baking, silversmithing, or foundry work. Heat exposure also may result from cultural practices such as cupping with moxibustion.4 Additionally, repeated use of heating pads or hot water bottles for pain relief by patients diagnosed with chronic pain or an underlying illness may contribute to development of erythema ab igne.1,4
Biopsy was not needed for diagnosis of this patient, but if the presentation is equivocal and history of potential exposures is unclear, a biopsy may be taken. A hematoxylin and eosin stain would reveal dilation of small vascular channels in the superficial dermis, contributing to the classic reticulated appearance. Biopsy findings also would reveal either an interface dermatitis or pigment incontinence containing melanin-laden macrophages correlating to either the erythema or hyperpigmentation, respectively.4
The prognosis for erythema ab igne is excellent, especially if diagnosed early. Treatment involves removal of the inciting heat source.1 The discoloration may resolve within a few months to years or may persist. If the hyperpigmentation is persistent, patients may consider laser treatments or lightening agents such as topical hydroquinone or topical tretinoin.4 However, if undiagnosed, patients may be at risk for development of a cutaneous malignancy, such as squamous cell carcinoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, poorly differentiated carcinoma, or cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma.2,4 Malignant transformation has been reported to occur decades after the initial skin eruption, although the risk is rare5; however, due to this risk, patients with erythema ab igne should be followed regularly and screened for new lesions in the affected areas.
- Tan S, Bertucci V. Erythema ab igne: an old condition new again. CMAJ. 2000;162:77-78.
- Miller K, Hunt R, Chu J, et al. Erythema ab igne. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:28.
- Kesty K, Feldman SR. Erythema ab igne: evolving technology, evolving presentation. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:13030.
- Harview CL, Krenitsky A. Erythema ab igne: a clinical review. Cutis. 2023;111:E33-E38. doi:10.12788/cutis.0771
- Wipf AJ, Brown MR. Malignant transformation of erythema ab igne. JAAD Case Rep. 2022;26:85-87. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2022.06.018
- Tan S, Bertucci V. Erythema ab igne: an old condition new again. CMAJ. 2000;162:77-78.
- Miller K, Hunt R, Chu J, et al. Erythema ab igne. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:28.
- Kesty K, Feldman SR. Erythema ab igne: evolving technology, evolving presentation. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:13030.
- Harview CL, Krenitsky A. Erythema ab igne: a clinical review. Cutis. 2023;111:E33-E38. doi:10.12788/cutis.0771
- Wipf AJ, Brown MR. Malignant transformation of erythema ab igne. JAAD Case Rep. 2022;26:85-87. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2022.06.018
Reticulated Hyperpigmentation on the Knee and Thigh
Reticulated Hyperpigmentation on the Knee and Thigh
A 25-year-old woman with an unremarkable medical history presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of a persistent rash on the right knee and distal thigh of several months’ duration. The patient noted that the rash had been asymptomatic, and she denied any history of trauma to the area. She reported that she worked as a teacher and had repeatedly stayed up late using her laptop for months. Rather than use a desk, she often would work sitting with her laptop in her lap.