User login
Over 3 Years, Atopic Dermatitis Well-Controlled with Lebrikizumab
AMSTERDAM — among those followed up for an additional 2 years, according to the latest data from an extension study.
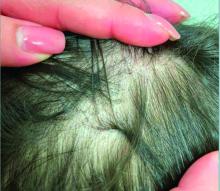
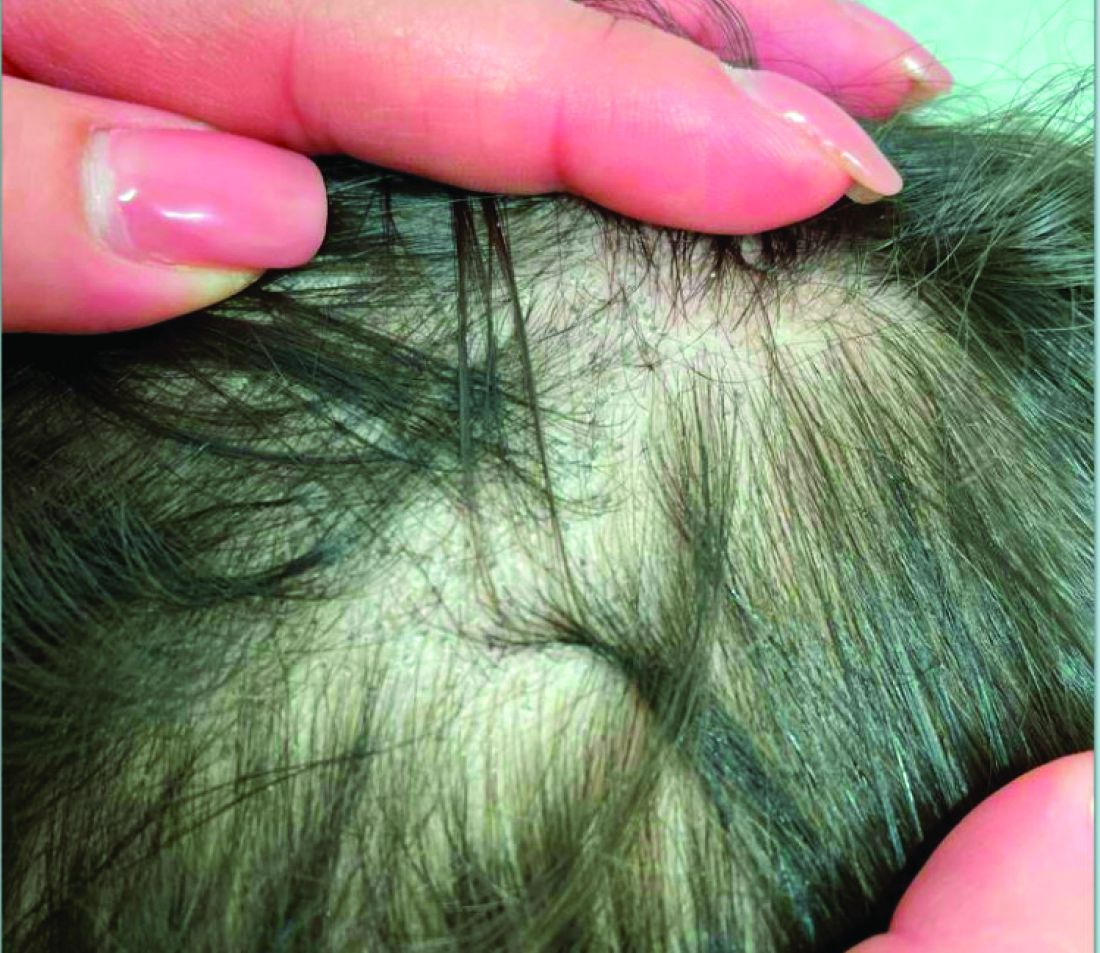
At the end of the maintenance phase of the pivotal trials at 12 months, 84% of the patients enrolled into the extension had clear or almost clear skin, as per the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA). This overall figure as well as the proportion with even better responses have persisted unchanged, reported Diamant Thaçi, MD, PhD, professor and head of the Comprehensive Center for Inflammatory Medicine, University of Lübeck in Germany.
Responses at 3 Years Maintained
“This is really quite remarkable,” Dr. Thaçi said. “Roughly all the patients maintained their response.” These results became even more remarkable when patients were assessed for their use of adjunctive therapy to control flares.
“Over the whole follow-up, 90% had no need for topical corticosteroids or any other rescue therapy,” Dr. Thaçi reported, providing data from the ADjoin lebrikizumab extension study during a late-breaking news session at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
The patients in ADjoin were enrolled from the pivotal phase 3 ADvocate 1 and 2 trials completed almost 2 years ago and published together in March 2023. Lebrikizumab was approved in the United States in September 2024 for moderate to severe AD in patients aged ≥ 12 years, following previous approvals in Europe in 2023 and in Japan in January 2024.
In these two identical trials with a total of 564 patients, the primary endpoint was an IGA of 0 or 1, signifying clear or almost clear skin. At nearly 40%, the proportion of patients reaching this outcome at 16 weeks was about threefold greater (P < .001) on lebrikizumab than on placebo. The benefit was similar on secondary endpoints, such as 75% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI75) score.
At the end of the double-blind, placebo-controlled 16-week phase of the ADvocate 1 and 2 trials, which enrolled adults and adolescents aged ≥ 12 years, responders were enrolled into a maintenance phase in which they were rerandomized to 250 mg lebrikizumab every 2 weeks (Q2W) or every 4 weeks (Q4W). The latter is the approved maintenance dose.
At the end of the maintenance phase, which lasted another 32 weeks (total exposure of 52 weeks for those initially randomized to lebrikizumab), patients were invited into the ADjoin extension. The only exclusions from the extension were serious adverse events related to lebrikizumab and noncompliance.
Response Curves Appear as Straight Lines
Over the next 2 years of ADjoin, response curves appeared as straight lines not only for the overall response but when patients were stratified for different levels of response at the extension study entry. Specifically, 81.5% and 83.3% had an IGA score of 0 or 1 in the Q2W and Q4W arms at completion of the ADvocate 16-week double-blind phase. At 3 years, the rates were 84.0% and 82.9%, respectively.
For the subgroup who entered ADjoin with an EASI75 or an EASI90 response, the persistence of this level of response over 2 years was similar, although there was some gain observed among those who entered the trial with an EASI75 response.
“Not only did these patients maintain their response, but the response on average slowly improved, so that there were more patients with an EASI90 response at the 3-year timepoint,” Dr. Thaçi said.
Of the 181 patients in the ADjoin extension, 82 patients were maintained on Q2W dosing and 99 were maintained on Q4W lebrikizumab. Their mean age was about 35 years, more than half were women, and nearly 40% had severe AD at the time they enrolled in the ADvocate trials. There was essentially no difference in response rates among those in the Q2W and Q4W arms over time in ADjoin.
Side Effect Profile Essentially Unchanged
The side effect and tolerability profiles, which were favorable in the original 16-week placebo-controlled study, have remained unchanged over the subsequent maintenance phase and through the additional 2 years of the ADjoin extension.
“There continued to be reports of conjunctivitis, which is very specific for anti–IL-13 therapies,” Dr. Thaçi said. However, he said that the incidence did not increase over time, and because it was easy to treat, “most patients do not discontinue lebrikizumab for this reason.” Moreover, he said the impression was that “the number of patients experiencing adverse effects has been decreasing over time.”
Calling these long-term results “very exciting,” Dr. Thaçi called lebrikizumab “a very valuable option for long-term AD care.”
Asked for his perspective on the results, Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, Director of Clinical Research, Department of Dermatology, George Washington University, Washington, DC, said that it is important to study long-term efficacy, and these results are positive. Without direct comparisons to other biologics available for AD, nothing can be implied about the relative efficacy of monoclonal antibodies approved for AD.
“These data are important both from an efficacy and safety perspective” for those advising patients who need chronic AD treatment, said Dr. Silverberg, who was the principal investigator of the ADvocate trials.
Earlier this year, 5-year follow-up data were published for dupilumab. Of 326 patients who remained on therapy this long, 220 (67%) maintained an IGA of 0 or 1 at the end of the study. There were no unexpected adverse events, which were generally stable or declined throughout the study.
Dr. Thaçi has financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Galderma, Leo Pharma, L’Oreal, Janssen-Cilag, New Bridge, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, UCB, and Vichy. Dr. Silverberg reported financial relationships with more than 40 pharmaceutical companies including those that make drugs for AD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM — among those followed up for an additional 2 years, according to the latest data from an extension study.
At the end of the maintenance phase of the pivotal trials at 12 months, 84% of the patients enrolled into the extension had clear or almost clear skin, as per the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA). This overall figure as well as the proportion with even better responses have persisted unchanged, reported Diamant Thaçi, MD, PhD, professor and head of the Comprehensive Center for Inflammatory Medicine, University of Lübeck in Germany.
Responses at 3 Years Maintained
“This is really quite remarkable,” Dr. Thaçi said. “Roughly all the patients maintained their response.” These results became even more remarkable when patients were assessed for their use of adjunctive therapy to control flares.
“Over the whole follow-up, 90% had no need for topical corticosteroids or any other rescue therapy,” Dr. Thaçi reported, providing data from the ADjoin lebrikizumab extension study during a late-breaking news session at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
The patients in ADjoin were enrolled from the pivotal phase 3 ADvocate 1 and 2 trials completed almost 2 years ago and published together in March 2023. Lebrikizumab was approved in the United States in September 2024 for moderate to severe AD in patients aged ≥ 12 years, following previous approvals in Europe in 2023 and in Japan in January 2024.
In these two identical trials with a total of 564 patients, the primary endpoint was an IGA of 0 or 1, signifying clear or almost clear skin. At nearly 40%, the proportion of patients reaching this outcome at 16 weeks was about threefold greater (P < .001) on lebrikizumab than on placebo. The benefit was similar on secondary endpoints, such as 75% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI75) score.
At the end of the double-blind, placebo-controlled 16-week phase of the ADvocate 1 and 2 trials, which enrolled adults and adolescents aged ≥ 12 years, responders were enrolled into a maintenance phase in which they were rerandomized to 250 mg lebrikizumab every 2 weeks (Q2W) or every 4 weeks (Q4W). The latter is the approved maintenance dose.
At the end of the maintenance phase, which lasted another 32 weeks (total exposure of 52 weeks for those initially randomized to lebrikizumab), patients were invited into the ADjoin extension. The only exclusions from the extension were serious adverse events related to lebrikizumab and noncompliance.
Response Curves Appear as Straight Lines
Over the next 2 years of ADjoin, response curves appeared as straight lines not only for the overall response but when patients were stratified for different levels of response at the extension study entry. Specifically, 81.5% and 83.3% had an IGA score of 0 or 1 in the Q2W and Q4W arms at completion of the ADvocate 16-week double-blind phase. At 3 years, the rates were 84.0% and 82.9%, respectively.
For the subgroup who entered ADjoin with an EASI75 or an EASI90 response, the persistence of this level of response over 2 years was similar, although there was some gain observed among those who entered the trial with an EASI75 response.
“Not only did these patients maintain their response, but the response on average slowly improved, so that there were more patients with an EASI90 response at the 3-year timepoint,” Dr. Thaçi said.
Of the 181 patients in the ADjoin extension, 82 patients were maintained on Q2W dosing and 99 were maintained on Q4W lebrikizumab. Their mean age was about 35 years, more than half were women, and nearly 40% had severe AD at the time they enrolled in the ADvocate trials. There was essentially no difference in response rates among those in the Q2W and Q4W arms over time in ADjoin.
Side Effect Profile Essentially Unchanged
The side effect and tolerability profiles, which were favorable in the original 16-week placebo-controlled study, have remained unchanged over the subsequent maintenance phase and through the additional 2 years of the ADjoin extension.
“There continued to be reports of conjunctivitis, which is very specific for anti–IL-13 therapies,” Dr. Thaçi said. However, he said that the incidence did not increase over time, and because it was easy to treat, “most patients do not discontinue lebrikizumab for this reason.” Moreover, he said the impression was that “the number of patients experiencing adverse effects has been decreasing over time.”
Calling these long-term results “very exciting,” Dr. Thaçi called lebrikizumab “a very valuable option for long-term AD care.”
Asked for his perspective on the results, Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, Director of Clinical Research, Department of Dermatology, George Washington University, Washington, DC, said that it is important to study long-term efficacy, and these results are positive. Without direct comparisons to other biologics available for AD, nothing can be implied about the relative efficacy of monoclonal antibodies approved for AD.
“These data are important both from an efficacy and safety perspective” for those advising patients who need chronic AD treatment, said Dr. Silverberg, who was the principal investigator of the ADvocate trials.
Earlier this year, 5-year follow-up data were published for dupilumab. Of 326 patients who remained on therapy this long, 220 (67%) maintained an IGA of 0 or 1 at the end of the study. There were no unexpected adverse events, which were generally stable or declined throughout the study.
Dr. Thaçi has financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Galderma, Leo Pharma, L’Oreal, Janssen-Cilag, New Bridge, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, UCB, and Vichy. Dr. Silverberg reported financial relationships with more than 40 pharmaceutical companies including those that make drugs for AD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM — among those followed up for an additional 2 years, according to the latest data from an extension study.
At the end of the maintenance phase of the pivotal trials at 12 months, 84% of the patients enrolled into the extension had clear or almost clear skin, as per the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA). This overall figure as well as the proportion with even better responses have persisted unchanged, reported Diamant Thaçi, MD, PhD, professor and head of the Comprehensive Center for Inflammatory Medicine, University of Lübeck in Germany.
Responses at 3 Years Maintained
“This is really quite remarkable,” Dr. Thaçi said. “Roughly all the patients maintained their response.” These results became even more remarkable when patients were assessed for their use of adjunctive therapy to control flares.
“Over the whole follow-up, 90% had no need for topical corticosteroids or any other rescue therapy,” Dr. Thaçi reported, providing data from the ADjoin lebrikizumab extension study during a late-breaking news session at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
The patients in ADjoin were enrolled from the pivotal phase 3 ADvocate 1 and 2 trials completed almost 2 years ago and published together in March 2023. Lebrikizumab was approved in the United States in September 2024 for moderate to severe AD in patients aged ≥ 12 years, following previous approvals in Europe in 2023 and in Japan in January 2024.
In these two identical trials with a total of 564 patients, the primary endpoint was an IGA of 0 or 1, signifying clear or almost clear skin. At nearly 40%, the proportion of patients reaching this outcome at 16 weeks was about threefold greater (P < .001) on lebrikizumab than on placebo. The benefit was similar on secondary endpoints, such as 75% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI75) score.
At the end of the double-blind, placebo-controlled 16-week phase of the ADvocate 1 and 2 trials, which enrolled adults and adolescents aged ≥ 12 years, responders were enrolled into a maintenance phase in which they were rerandomized to 250 mg lebrikizumab every 2 weeks (Q2W) or every 4 weeks (Q4W). The latter is the approved maintenance dose.
At the end of the maintenance phase, which lasted another 32 weeks (total exposure of 52 weeks for those initially randomized to lebrikizumab), patients were invited into the ADjoin extension. The only exclusions from the extension were serious adverse events related to lebrikizumab and noncompliance.
Response Curves Appear as Straight Lines
Over the next 2 years of ADjoin, response curves appeared as straight lines not only for the overall response but when patients were stratified for different levels of response at the extension study entry. Specifically, 81.5% and 83.3% had an IGA score of 0 or 1 in the Q2W and Q4W arms at completion of the ADvocate 16-week double-blind phase. At 3 years, the rates were 84.0% and 82.9%, respectively.
For the subgroup who entered ADjoin with an EASI75 or an EASI90 response, the persistence of this level of response over 2 years was similar, although there was some gain observed among those who entered the trial with an EASI75 response.
“Not only did these patients maintain their response, but the response on average slowly improved, so that there were more patients with an EASI90 response at the 3-year timepoint,” Dr. Thaçi said.
Of the 181 patients in the ADjoin extension, 82 patients were maintained on Q2W dosing and 99 were maintained on Q4W lebrikizumab. Their mean age was about 35 years, more than half were women, and nearly 40% had severe AD at the time they enrolled in the ADvocate trials. There was essentially no difference in response rates among those in the Q2W and Q4W arms over time in ADjoin.
Side Effect Profile Essentially Unchanged
The side effect and tolerability profiles, which were favorable in the original 16-week placebo-controlled study, have remained unchanged over the subsequent maintenance phase and through the additional 2 years of the ADjoin extension.
“There continued to be reports of conjunctivitis, which is very specific for anti–IL-13 therapies,” Dr. Thaçi said. However, he said that the incidence did not increase over time, and because it was easy to treat, “most patients do not discontinue lebrikizumab for this reason.” Moreover, he said the impression was that “the number of patients experiencing adverse effects has been decreasing over time.”
Calling these long-term results “very exciting,” Dr. Thaçi called lebrikizumab “a very valuable option for long-term AD care.”
Asked for his perspective on the results, Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, Director of Clinical Research, Department of Dermatology, George Washington University, Washington, DC, said that it is important to study long-term efficacy, and these results are positive. Without direct comparisons to other biologics available for AD, nothing can be implied about the relative efficacy of monoclonal antibodies approved for AD.
“These data are important both from an efficacy and safety perspective” for those advising patients who need chronic AD treatment, said Dr. Silverberg, who was the principal investigator of the ADvocate trials.
Earlier this year, 5-year follow-up data were published for dupilumab. Of 326 patients who remained on therapy this long, 220 (67%) maintained an IGA of 0 or 1 at the end of the study. There were no unexpected adverse events, which were generally stable or declined throughout the study.
Dr. Thaçi has financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Galderma, Leo Pharma, L’Oreal, Janssen-Cilag, New Bridge, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, UCB, and Vichy. Dr. Silverberg reported financial relationships with more than 40 pharmaceutical companies including those that make drugs for AD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EADV 2024
State of Confusion: Should All Children Get Lipid Labs for High Cholesterol?
Clinicians receive conflicting advice on whether to order blood tests to screen for lipids in children. A new study could add to the confusion. Researchers found that a combination of physical proxy measures such as hypertension and body mass index (BMI) predicted the risk for future cardiovascular events as well as the physical model plus lipid labs, questioning the value of those blood tests.
Some medical organizations advise screening only for high-risk children because more research is needed to define the harms and benefits of universal screening. Diet and behavioral changes are sufficient for most children, and universal screening could lead to false positives and unnecessary further testing, they said.
Groups that favor lipid tests for all children say these measurements detect familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) that would not otherwise be diagnosed, leading to treatment with drugs like statins and a greater chance of preventing cardiovascular disease (CVD) in adulthood.
Researchers from the new study said their findings do not address screenings for FH, which affects 1 in 250 US children and puts them at a risk for atherosclerotic CVD.
Recommending Blood Tests in Age Groups
One of the seminal guidelines on screening lipids in children came from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), which in 2011 recommended children undergo dyslipidemia screening between the ages of 9 and 11 years and again between 17 and 21 years. Children should receive a screening starting at age 2 years if they have a family history of CVD or dyslipidemia or have diabetes, an elevated BMI, or hypertension. The American Academy of Pediatrics shortly followed suit, issuing similar recommendations.
Screening for the two subsets of ages was an expansion from the original 1992 guidelines from the National Cholesterol Education Program, which recommended screening only for children with either a family history of early CVD or elevated total cholesterol levels.
A 2011 panel for the NHLBI said the older approach identified significantly fewer children with abnormal levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) than the addition of two age groups for screening, adding that many children do not have a complete family history. The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association later supported NHLBI’s stance in their joint guidelines on the management of cholesterol.
Mark Corkins, MD, chair of the AAP’s Committee on Nutrition, told Medscape Medical News that if children are screened only because they have obesity or a family history of FH, some with elevated lipid levels will be missed. For instance, studies indicate caregiver recall of FH often is inaccurate, and the genetic disorder that causes the condition is not related to obesity.
“The screening is to find familial hypercholesterolemia, to try to find the ones that need therapy,” that would not be caught by the risk-based screening earlier on in childhood, Corkins said.
Only Screen Children With Risk Factors
But other groups do not agree. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) found insufficient evidence to recommend for or against screening for lipid disorders in asymptomatic children and teens.
The group also said it found inadequate evidence that lipid-lowering interventions in the general pediatric population lead to reductions in cardiovascular events or all-cause mortality once they reached adulthood. USPSTF also raised questions about the safety of lipid-lowering drugs in children.
“The current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening for lipid disorders in children and adolescents 20 years or younger,” the panel wrote.
The American Academy of Family Physicians supports USPSTF’s recommendations.
Low Rate of Screening
While the uncertainty over screening in children continues, the practice has been adopted by a minority of clinicians.
A study published in JAMA Network Open in July found 9% of 700,000 9- to 11-year-olds had a documented result from a lipid screening. Among more than 1.3 million 17- to 21-year-olds, 13% had received a screening.
As BMI went up, so did screening rates. A little over 9% children and teens with a healthy weight were screened compared with 14.7% of those with moderate obesity and 21.9% of those with severe obesity.
Among those screened, 32.3% of 9- to 11-year-olds and 30.2% of 17- to 21-year-olds had abnormal lipid levels, defined as having one elevated measure out of five, including total cholesterol of 200 mg/dL or higher or LDL-C levels of 130 mg/dL or higher.
Justin Zachariah, MD, MPH, an associate professor of pediatrics-cardiology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, spoke about physicians screening children based only on factors like obesity during a presentation at the recent annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics. He cited research showing roughly one in four children with abnormal lipids had a normal weight.
If a clinician is reserving a lipid screening for a child who is overweight or has obesity, “you’re missing nearly half the problem,” Zachariah said during his presentation.
One reason for the low rate of universal screening may be inattention to FH by clinicians, according to Samuel S. Gidding, MD, a professor in the Department of Genomic Health at Geisinger College of Health Sciences in Bridgewater Corners, Vermont.
For instance, a clinician has only a set amount of time during a well-child visit and other issues may take precedence, “so it doesn’t make sense to broach preventive screening for something that could happen 30 or 40 years from now, vs this [other] very immediate problem,” he said.
Clinicians “are triggered to act on the LDL level, but don’t think about FH as a possible diagnosis,” Gidding told Medscape Medical News.
Another barrier is that in some settings, caregivers must take children and teens to another facility on a different day to fulfill an order for a lipid test.
“It’s reluctance of doctors to order it, knowing patients won’t go through with it,” Gidding said.
Gidding is a consultant for Esperion Therapeutics. Other sources in this story reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinicians receive conflicting advice on whether to order blood tests to screen for lipids in children. A new study could add to the confusion. Researchers found that a combination of physical proxy measures such as hypertension and body mass index (BMI) predicted the risk for future cardiovascular events as well as the physical model plus lipid labs, questioning the value of those blood tests.
Some medical organizations advise screening only for high-risk children because more research is needed to define the harms and benefits of universal screening. Diet and behavioral changes are sufficient for most children, and universal screening could lead to false positives and unnecessary further testing, they said.
Groups that favor lipid tests for all children say these measurements detect familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) that would not otherwise be diagnosed, leading to treatment with drugs like statins and a greater chance of preventing cardiovascular disease (CVD) in adulthood.
Researchers from the new study said their findings do not address screenings for FH, which affects 1 in 250 US children and puts them at a risk for atherosclerotic CVD.
Recommending Blood Tests in Age Groups
One of the seminal guidelines on screening lipids in children came from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), which in 2011 recommended children undergo dyslipidemia screening between the ages of 9 and 11 years and again between 17 and 21 years. Children should receive a screening starting at age 2 years if they have a family history of CVD or dyslipidemia or have diabetes, an elevated BMI, or hypertension. The American Academy of Pediatrics shortly followed suit, issuing similar recommendations.
Screening for the two subsets of ages was an expansion from the original 1992 guidelines from the National Cholesterol Education Program, which recommended screening only for children with either a family history of early CVD or elevated total cholesterol levels.
A 2011 panel for the NHLBI said the older approach identified significantly fewer children with abnormal levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) than the addition of two age groups for screening, adding that many children do not have a complete family history. The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association later supported NHLBI’s stance in their joint guidelines on the management of cholesterol.
Mark Corkins, MD, chair of the AAP’s Committee on Nutrition, told Medscape Medical News that if children are screened only because they have obesity or a family history of FH, some with elevated lipid levels will be missed. For instance, studies indicate caregiver recall of FH often is inaccurate, and the genetic disorder that causes the condition is not related to obesity.
“The screening is to find familial hypercholesterolemia, to try to find the ones that need therapy,” that would not be caught by the risk-based screening earlier on in childhood, Corkins said.
Only Screen Children With Risk Factors
But other groups do not agree. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) found insufficient evidence to recommend for or against screening for lipid disorders in asymptomatic children and teens.
The group also said it found inadequate evidence that lipid-lowering interventions in the general pediatric population lead to reductions in cardiovascular events or all-cause mortality once they reached adulthood. USPSTF also raised questions about the safety of lipid-lowering drugs in children.
“The current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening for lipid disorders in children and adolescents 20 years or younger,” the panel wrote.
The American Academy of Family Physicians supports USPSTF’s recommendations.
Low Rate of Screening
While the uncertainty over screening in children continues, the practice has been adopted by a minority of clinicians.
A study published in JAMA Network Open in July found 9% of 700,000 9- to 11-year-olds had a documented result from a lipid screening. Among more than 1.3 million 17- to 21-year-olds, 13% had received a screening.
As BMI went up, so did screening rates. A little over 9% children and teens with a healthy weight were screened compared with 14.7% of those with moderate obesity and 21.9% of those with severe obesity.
Among those screened, 32.3% of 9- to 11-year-olds and 30.2% of 17- to 21-year-olds had abnormal lipid levels, defined as having one elevated measure out of five, including total cholesterol of 200 mg/dL or higher or LDL-C levels of 130 mg/dL or higher.
Justin Zachariah, MD, MPH, an associate professor of pediatrics-cardiology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, spoke about physicians screening children based only on factors like obesity during a presentation at the recent annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics. He cited research showing roughly one in four children with abnormal lipids had a normal weight.
If a clinician is reserving a lipid screening for a child who is overweight or has obesity, “you’re missing nearly half the problem,” Zachariah said during his presentation.
One reason for the low rate of universal screening may be inattention to FH by clinicians, according to Samuel S. Gidding, MD, a professor in the Department of Genomic Health at Geisinger College of Health Sciences in Bridgewater Corners, Vermont.
For instance, a clinician has only a set amount of time during a well-child visit and other issues may take precedence, “so it doesn’t make sense to broach preventive screening for something that could happen 30 or 40 years from now, vs this [other] very immediate problem,” he said.
Clinicians “are triggered to act on the LDL level, but don’t think about FH as a possible diagnosis,” Gidding told Medscape Medical News.
Another barrier is that in some settings, caregivers must take children and teens to another facility on a different day to fulfill an order for a lipid test.
“It’s reluctance of doctors to order it, knowing patients won’t go through with it,” Gidding said.
Gidding is a consultant for Esperion Therapeutics. Other sources in this story reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinicians receive conflicting advice on whether to order blood tests to screen for lipids in children. A new study could add to the confusion. Researchers found that a combination of physical proxy measures such as hypertension and body mass index (BMI) predicted the risk for future cardiovascular events as well as the physical model plus lipid labs, questioning the value of those blood tests.
Some medical organizations advise screening only for high-risk children because more research is needed to define the harms and benefits of universal screening. Diet and behavioral changes are sufficient for most children, and universal screening could lead to false positives and unnecessary further testing, they said.
Groups that favor lipid tests for all children say these measurements detect familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) that would not otherwise be diagnosed, leading to treatment with drugs like statins and a greater chance of preventing cardiovascular disease (CVD) in adulthood.
Researchers from the new study said their findings do not address screenings for FH, which affects 1 in 250 US children and puts them at a risk for atherosclerotic CVD.
Recommending Blood Tests in Age Groups
One of the seminal guidelines on screening lipids in children came from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), which in 2011 recommended children undergo dyslipidemia screening between the ages of 9 and 11 years and again between 17 and 21 years. Children should receive a screening starting at age 2 years if they have a family history of CVD or dyslipidemia or have diabetes, an elevated BMI, or hypertension. The American Academy of Pediatrics shortly followed suit, issuing similar recommendations.
Screening for the two subsets of ages was an expansion from the original 1992 guidelines from the National Cholesterol Education Program, which recommended screening only for children with either a family history of early CVD or elevated total cholesterol levels.
A 2011 panel for the NHLBI said the older approach identified significantly fewer children with abnormal levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) than the addition of two age groups for screening, adding that many children do not have a complete family history. The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association later supported NHLBI’s stance in their joint guidelines on the management of cholesterol.
Mark Corkins, MD, chair of the AAP’s Committee on Nutrition, told Medscape Medical News that if children are screened only because they have obesity or a family history of FH, some with elevated lipid levels will be missed. For instance, studies indicate caregiver recall of FH often is inaccurate, and the genetic disorder that causes the condition is not related to obesity.
“The screening is to find familial hypercholesterolemia, to try to find the ones that need therapy,” that would not be caught by the risk-based screening earlier on in childhood, Corkins said.
Only Screen Children With Risk Factors
But other groups do not agree. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) found insufficient evidence to recommend for or against screening for lipid disorders in asymptomatic children and teens.
The group also said it found inadequate evidence that lipid-lowering interventions in the general pediatric population lead to reductions in cardiovascular events or all-cause mortality once they reached adulthood. USPSTF also raised questions about the safety of lipid-lowering drugs in children.
“The current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening for lipid disorders in children and adolescents 20 years or younger,” the panel wrote.
The American Academy of Family Physicians supports USPSTF’s recommendations.
Low Rate of Screening
While the uncertainty over screening in children continues, the practice has been adopted by a minority of clinicians.
A study published in JAMA Network Open in July found 9% of 700,000 9- to 11-year-olds had a documented result from a lipid screening. Among more than 1.3 million 17- to 21-year-olds, 13% had received a screening.
As BMI went up, so did screening rates. A little over 9% children and teens with a healthy weight were screened compared with 14.7% of those with moderate obesity and 21.9% of those with severe obesity.
Among those screened, 32.3% of 9- to 11-year-olds and 30.2% of 17- to 21-year-olds had abnormal lipid levels, defined as having one elevated measure out of five, including total cholesterol of 200 mg/dL or higher or LDL-C levels of 130 mg/dL or higher.
Justin Zachariah, MD, MPH, an associate professor of pediatrics-cardiology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, spoke about physicians screening children based only on factors like obesity during a presentation at the recent annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics. He cited research showing roughly one in four children with abnormal lipids had a normal weight.
If a clinician is reserving a lipid screening for a child who is overweight or has obesity, “you’re missing nearly half the problem,” Zachariah said during his presentation.
One reason for the low rate of universal screening may be inattention to FH by clinicians, according to Samuel S. Gidding, MD, a professor in the Department of Genomic Health at Geisinger College of Health Sciences in Bridgewater Corners, Vermont.
For instance, a clinician has only a set amount of time during a well-child visit and other issues may take precedence, “so it doesn’t make sense to broach preventive screening for something that could happen 30 or 40 years from now, vs this [other] very immediate problem,” he said.
Clinicians “are triggered to act on the LDL level, but don’t think about FH as a possible diagnosis,” Gidding told Medscape Medical News.
Another barrier is that in some settings, caregivers must take children and teens to another facility on a different day to fulfill an order for a lipid test.
“It’s reluctance of doctors to order it, knowing patients won’t go through with it,” Gidding said.
Gidding is a consultant for Esperion Therapeutics. Other sources in this story reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Type 2 Diabetes More Prevalent Than Type 1 Among Adolescents in Some Areas
“This is an emerging epidemic,” said Orit Pinhas-Hamiel, MD, director of the Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes Unit at Sheba Medical Center in Ramat Gan, Israel, at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, noting that these young patients, most with obesity, exhibit a significantly higher incidence of complications than adults with type 2 diabetes or young people with type 1 diabetes.
In 2017-2018, the incidence of type 2 diabetes among patients aged 15-19 years (19.7 per 100,000) surpassed that of type 1 diabetes (14.6 per 100,000), according to data from the United States.
“This is the first time that the incidence of type 2 diabetes has exceeded that of type 1 among youth,” said Pinhas-Hamiel. A review of 2021 published a few months ago highlighted this surge, with countries like China, India, the United States, Brazil, and Mexico leading the way.
SEARCH and TODAY
The SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study, which was launched in 2000, is a multicenter observational study in the United States aimed at estimating the prevalence, incidence, and complications of types 1 and 2 diabetes among young patients. The Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents and Youth (TODAY) study is an interventional study focusing on adolescents with type 2 diabetes to evaluate the effectiveness of various treatment options.
“Diabesity” — the dual global epidemic of obesity and type 2 diabetes — has visible consequences from the moment of diagnosis, including hypertension. In the TODAY study, 11.6% adolescents had hypertension at diagnosis. A study conducted in Hong Kong involving 391 children younger than 18 years revealed that 22.5% had hypertension. In SEARCH, 27% young patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes for 1.5 years had hypertension.
In addition, the SEARCH study found that 27% young individuals had low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, while 25% had high triglyceride levels, at 1.5 years after diagnosis.
Overall, the cumulative incidence of long-term diabetic complications was assessed in 500 adolescents participating in TODAY (mean age, 26.4 ± 2.8 years; mean time since diagnosis, 13.3 ± 1.8 years). The initial prevalence was 19.2%, while the cumulative incidence rose to 67.5% after 15 years of follow-up.
For dyslipidemia, the initial prevalence was 20.8%, with a cumulative incidence of 51.6%. The incidence of diabetic nephropathy was 54.8% and neuropathies was 32.4%. The prevalence of retinopathy was 13.7% for the period 2010-2011 and 51% for 2017-2018.
At least one complication was observed in 60.1% participants and at least two in 28.4%. As expected, risk factors for developing complications included belonging to a racial or ethnic minority, hyperglycemia, hypertension, and dyslipidemia.
“Among those who developed type 2 diabetes in adolescence, the risk for complications, including microvascular complications, has continuously increased and affected most participants in young adulthood,” said Pinhas-Hamiel.
At the same time, the rate of treatment with lipid-lowering and antihypertensive medications remains low among young people with type 2 diabetes. The management of dyslipidemia is suboptimal, with only 5% young patients with diabetes and dyslipidemia receiving appropriate medications. Furthermore, treatment adherence is lacking. In the TODAY cohort, for example, only one third of participants with high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol were on lipid-lowering medications, and only half of the young patients with hypertension were taking antihypertensives.
Focus on Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetic kidney disease is the leading microvascular complication of type 2 diabetes in adolescents. It is associated with rapid progression and poor prognosis. The natural history begins with hyperfiltration: A consequence of obesity and impaired glucose tolerance. Structural renal changes can be detected as early as 1.5 years after diagnosis.
The second stage is characterized by a reduction in the glomerular filtration rate. At this stage, “the structural changes in the kidney are typical but often present,” said Pinhas-Hamiel, making this period critical for reducing risk factors.
In TODAY, the cumulative incidence of diabetic nephropathy was 54.8%. The prevalence at inclusion was 8%. In SEARCH, after 8 years, the prevalence of diabetic kidney disease was 19.9% among adolescents with type 2 diabetes vs 5.8% among those with type 1 diabetes. A pre-analysis revealed that the overall prevalence of macroalbuminuria among 730 children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes was 3.8%. The ages at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes ranged from 6.5 to 21 years, and the duration of the disease varied from diagnosis to 15 years after.
Diabetic retinopathy was present in 50% participants in the TODAY study at age 25 years (ie, after 12 years of disease). In SEARCH, 56% young patients had diabetic retinopathy after 12.5 years of diabetes. In addition, in the same study, the prevalence of peripheral neuropathy, assessed after 8 years, was 22% among adolescents with type 2 diabetes vs 7% among those with type 1 diabetes.
Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy
A decrease in heart rate variability was observed in 47% young patients with type 2 diabetes after an average disease duration of only 1.7 years. In SEARCH, the prevalence of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy, assessed after 8 years of disease, was 17% in adolescents with type 2 diabetes versus 12% in those with type 1 diabetes.
Overall, 7.1% participants had three complications: nephropathy, retinopathy, and neuropathy. The cumulative incidence of microvascular complications was 80%.
Moreover, A1c levels deteriorated progressively throughout the follow-up period. Approximately 45% participants had an A1c of at least 10%, and 20% were between 8% and 10%. Body mass index consistently remained between 35 and 37.5.
Young patients with type 2 diabetes exhibit endothelial dysfunction, increased carotid intima-media thickness, elevated arterial stiffness, left ventricular hypertrophy, diastolic dysfunction, and reduced maximal exercise capacity. All these factors predict cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
In TODAY, 17 serious cardiovascular events were recorded, including four myocardial infarctions, six cases of congestive heart failure, three coronary events, and four strokes.
In an analysis of the TODAY and SEARCH studies, although the average duration of diabetes was similar, complications were more frequent among young patients with type 2 diabetes than among those with type 1 diabetes. Microvascular complications were 2.5 times more frequent, and macrovascular complications were four times more frequent.
In SEARCH, excessive mortality was observed among young adults for each type of diabetes. Differences in risk were associated with diabetes type, age, race/ethnicity, and sex. Mortality ratios were 1.5 and 2.3 for types 1 and 2 diabetes, respectively.
Women had higher mortality rates than men. Diabetes was the underlying cause of death in 9.1% cases, which was comparable to cardiovascular diseases or cancer (10.9%). According to a life expectancy model, young patients with type 2 diabetes lose about 15 years of life.
Eating Disorders and Depression
Beyond these complications, other issues are often present among adolescents with type 2 diabetes. Approximately 50% have eating disorders (compared with 21% among those with type 1 diabetes), 19.3% report depressive symptoms, and 18.9% have expressed thoughts of self-harm. In addition, 19.6% have polycystic ovary syndrome. Z-scores for bone mineral density at the femoral neck and lumbar spine were significantly lower in adolescents with type 2 diabetes than in healthy peers. The presence of metabolic dysfunction–associated fatty liver disease is also more pronounced.
“The recent approvals of new pharmacological interventions for weight loss and improved glycemic control in adolescents offer hope. We hope that, over the next decade, the prevalence of complications among these young patients with type 2 diabetes will decline. In the meantime, a proactive approach is essential to prevent complications related to type 2 diabetes in these youth,” Pinhas-Hamiel concluded.
For more information, see ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2022: Type 2 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents.
Pinhas-Hamiel reported no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
“This is an emerging epidemic,” said Orit Pinhas-Hamiel, MD, director of the Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes Unit at Sheba Medical Center in Ramat Gan, Israel, at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, noting that these young patients, most with obesity, exhibit a significantly higher incidence of complications than adults with type 2 diabetes or young people with type 1 diabetes.
In 2017-2018, the incidence of type 2 diabetes among patients aged 15-19 years (19.7 per 100,000) surpassed that of type 1 diabetes (14.6 per 100,000), according to data from the United States.
“This is the first time that the incidence of type 2 diabetes has exceeded that of type 1 among youth,” said Pinhas-Hamiel. A review of 2021 published a few months ago highlighted this surge, with countries like China, India, the United States, Brazil, and Mexico leading the way.
SEARCH and TODAY
The SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study, which was launched in 2000, is a multicenter observational study in the United States aimed at estimating the prevalence, incidence, and complications of types 1 and 2 diabetes among young patients. The Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents and Youth (TODAY) study is an interventional study focusing on adolescents with type 2 diabetes to evaluate the effectiveness of various treatment options.
“Diabesity” — the dual global epidemic of obesity and type 2 diabetes — has visible consequences from the moment of diagnosis, including hypertension. In the TODAY study, 11.6% adolescents had hypertension at diagnosis. A study conducted in Hong Kong involving 391 children younger than 18 years revealed that 22.5% had hypertension. In SEARCH, 27% young patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes for 1.5 years had hypertension.
In addition, the SEARCH study found that 27% young individuals had low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, while 25% had high triglyceride levels, at 1.5 years after diagnosis.
Overall, the cumulative incidence of long-term diabetic complications was assessed in 500 adolescents participating in TODAY (mean age, 26.4 ± 2.8 years; mean time since diagnosis, 13.3 ± 1.8 years). The initial prevalence was 19.2%, while the cumulative incidence rose to 67.5% after 15 years of follow-up.
For dyslipidemia, the initial prevalence was 20.8%, with a cumulative incidence of 51.6%. The incidence of diabetic nephropathy was 54.8% and neuropathies was 32.4%. The prevalence of retinopathy was 13.7% for the period 2010-2011 and 51% for 2017-2018.
At least one complication was observed in 60.1% participants and at least two in 28.4%. As expected, risk factors for developing complications included belonging to a racial or ethnic minority, hyperglycemia, hypertension, and dyslipidemia.
“Among those who developed type 2 diabetes in adolescence, the risk for complications, including microvascular complications, has continuously increased and affected most participants in young adulthood,” said Pinhas-Hamiel.
At the same time, the rate of treatment with lipid-lowering and antihypertensive medications remains low among young people with type 2 diabetes. The management of dyslipidemia is suboptimal, with only 5% young patients with diabetes and dyslipidemia receiving appropriate medications. Furthermore, treatment adherence is lacking. In the TODAY cohort, for example, only one third of participants with high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol were on lipid-lowering medications, and only half of the young patients with hypertension were taking antihypertensives.
Focus on Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetic kidney disease is the leading microvascular complication of type 2 diabetes in adolescents. It is associated with rapid progression and poor prognosis. The natural history begins with hyperfiltration: A consequence of obesity and impaired glucose tolerance. Structural renal changes can be detected as early as 1.5 years after diagnosis.
The second stage is characterized by a reduction in the glomerular filtration rate. At this stage, “the structural changes in the kidney are typical but often present,” said Pinhas-Hamiel, making this period critical for reducing risk factors.
In TODAY, the cumulative incidence of diabetic nephropathy was 54.8%. The prevalence at inclusion was 8%. In SEARCH, after 8 years, the prevalence of diabetic kidney disease was 19.9% among adolescents with type 2 diabetes vs 5.8% among those with type 1 diabetes. A pre-analysis revealed that the overall prevalence of macroalbuminuria among 730 children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes was 3.8%. The ages at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes ranged from 6.5 to 21 years, and the duration of the disease varied from diagnosis to 15 years after.
Diabetic retinopathy was present in 50% participants in the TODAY study at age 25 years (ie, after 12 years of disease). In SEARCH, 56% young patients had diabetic retinopathy after 12.5 years of diabetes. In addition, in the same study, the prevalence of peripheral neuropathy, assessed after 8 years, was 22% among adolescents with type 2 diabetes vs 7% among those with type 1 diabetes.
Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy
A decrease in heart rate variability was observed in 47% young patients with type 2 diabetes after an average disease duration of only 1.7 years. In SEARCH, the prevalence of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy, assessed after 8 years of disease, was 17% in adolescents with type 2 diabetes versus 12% in those with type 1 diabetes.
Overall, 7.1% participants had three complications: nephropathy, retinopathy, and neuropathy. The cumulative incidence of microvascular complications was 80%.
Moreover, A1c levels deteriorated progressively throughout the follow-up period. Approximately 45% participants had an A1c of at least 10%, and 20% were between 8% and 10%. Body mass index consistently remained between 35 and 37.5.
Young patients with type 2 diabetes exhibit endothelial dysfunction, increased carotid intima-media thickness, elevated arterial stiffness, left ventricular hypertrophy, diastolic dysfunction, and reduced maximal exercise capacity. All these factors predict cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
In TODAY, 17 serious cardiovascular events were recorded, including four myocardial infarctions, six cases of congestive heart failure, three coronary events, and four strokes.
In an analysis of the TODAY and SEARCH studies, although the average duration of diabetes was similar, complications were more frequent among young patients with type 2 diabetes than among those with type 1 diabetes. Microvascular complications were 2.5 times more frequent, and macrovascular complications were four times more frequent.
In SEARCH, excessive mortality was observed among young adults for each type of diabetes. Differences in risk were associated with diabetes type, age, race/ethnicity, and sex. Mortality ratios were 1.5 and 2.3 for types 1 and 2 diabetes, respectively.
Women had higher mortality rates than men. Diabetes was the underlying cause of death in 9.1% cases, which was comparable to cardiovascular diseases or cancer (10.9%). According to a life expectancy model, young patients with type 2 diabetes lose about 15 years of life.
Eating Disorders and Depression
Beyond these complications, other issues are often present among adolescents with type 2 diabetes. Approximately 50% have eating disorders (compared with 21% among those with type 1 diabetes), 19.3% report depressive symptoms, and 18.9% have expressed thoughts of self-harm. In addition, 19.6% have polycystic ovary syndrome. Z-scores for bone mineral density at the femoral neck and lumbar spine were significantly lower in adolescents with type 2 diabetes than in healthy peers. The presence of metabolic dysfunction–associated fatty liver disease is also more pronounced.
“The recent approvals of new pharmacological interventions for weight loss and improved glycemic control in adolescents offer hope. We hope that, over the next decade, the prevalence of complications among these young patients with type 2 diabetes will decline. In the meantime, a proactive approach is essential to prevent complications related to type 2 diabetes in these youth,” Pinhas-Hamiel concluded.
For more information, see ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2022: Type 2 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents.
Pinhas-Hamiel reported no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
“This is an emerging epidemic,” said Orit Pinhas-Hamiel, MD, director of the Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes Unit at Sheba Medical Center in Ramat Gan, Israel, at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, noting that these young patients, most with obesity, exhibit a significantly higher incidence of complications than adults with type 2 diabetes or young people with type 1 diabetes.
In 2017-2018, the incidence of type 2 diabetes among patients aged 15-19 years (19.7 per 100,000) surpassed that of type 1 diabetes (14.6 per 100,000), according to data from the United States.
“This is the first time that the incidence of type 2 diabetes has exceeded that of type 1 among youth,” said Pinhas-Hamiel. A review of 2021 published a few months ago highlighted this surge, with countries like China, India, the United States, Brazil, and Mexico leading the way.
SEARCH and TODAY
The SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study, which was launched in 2000, is a multicenter observational study in the United States aimed at estimating the prevalence, incidence, and complications of types 1 and 2 diabetes among young patients. The Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents and Youth (TODAY) study is an interventional study focusing on adolescents with type 2 diabetes to evaluate the effectiveness of various treatment options.
“Diabesity” — the dual global epidemic of obesity and type 2 diabetes — has visible consequences from the moment of diagnosis, including hypertension. In the TODAY study, 11.6% adolescents had hypertension at diagnosis. A study conducted in Hong Kong involving 391 children younger than 18 years revealed that 22.5% had hypertension. In SEARCH, 27% young patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes for 1.5 years had hypertension.
In addition, the SEARCH study found that 27% young individuals had low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, while 25% had high triglyceride levels, at 1.5 years after diagnosis.
Overall, the cumulative incidence of long-term diabetic complications was assessed in 500 adolescents participating in TODAY (mean age, 26.4 ± 2.8 years; mean time since diagnosis, 13.3 ± 1.8 years). The initial prevalence was 19.2%, while the cumulative incidence rose to 67.5% after 15 years of follow-up.
For dyslipidemia, the initial prevalence was 20.8%, with a cumulative incidence of 51.6%. The incidence of diabetic nephropathy was 54.8% and neuropathies was 32.4%. The prevalence of retinopathy was 13.7% for the period 2010-2011 and 51% for 2017-2018.
At least one complication was observed in 60.1% participants and at least two in 28.4%. As expected, risk factors for developing complications included belonging to a racial or ethnic minority, hyperglycemia, hypertension, and dyslipidemia.
“Among those who developed type 2 diabetes in adolescence, the risk for complications, including microvascular complications, has continuously increased and affected most participants in young adulthood,” said Pinhas-Hamiel.
At the same time, the rate of treatment with lipid-lowering and antihypertensive medications remains low among young people with type 2 diabetes. The management of dyslipidemia is suboptimal, with only 5% young patients with diabetes and dyslipidemia receiving appropriate medications. Furthermore, treatment adherence is lacking. In the TODAY cohort, for example, only one third of participants with high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol were on lipid-lowering medications, and only half of the young patients with hypertension were taking antihypertensives.
Focus on Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetic kidney disease is the leading microvascular complication of type 2 diabetes in adolescents. It is associated with rapid progression and poor prognosis. The natural history begins with hyperfiltration: A consequence of obesity and impaired glucose tolerance. Structural renal changes can be detected as early as 1.5 years after diagnosis.
The second stage is characterized by a reduction in the glomerular filtration rate. At this stage, “the structural changes in the kidney are typical but often present,” said Pinhas-Hamiel, making this period critical for reducing risk factors.
In TODAY, the cumulative incidence of diabetic nephropathy was 54.8%. The prevalence at inclusion was 8%. In SEARCH, after 8 years, the prevalence of diabetic kidney disease was 19.9% among adolescents with type 2 diabetes vs 5.8% among those with type 1 diabetes. A pre-analysis revealed that the overall prevalence of macroalbuminuria among 730 children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes was 3.8%. The ages at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes ranged from 6.5 to 21 years, and the duration of the disease varied from diagnosis to 15 years after.
Diabetic retinopathy was present in 50% participants in the TODAY study at age 25 years (ie, after 12 years of disease). In SEARCH, 56% young patients had diabetic retinopathy after 12.5 years of diabetes. In addition, in the same study, the prevalence of peripheral neuropathy, assessed after 8 years, was 22% among adolescents with type 2 diabetes vs 7% among those with type 1 diabetes.
Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy
A decrease in heart rate variability was observed in 47% young patients with type 2 diabetes after an average disease duration of only 1.7 years. In SEARCH, the prevalence of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy, assessed after 8 years of disease, was 17% in adolescents with type 2 diabetes versus 12% in those with type 1 diabetes.
Overall, 7.1% participants had three complications: nephropathy, retinopathy, and neuropathy. The cumulative incidence of microvascular complications was 80%.
Moreover, A1c levels deteriorated progressively throughout the follow-up period. Approximately 45% participants had an A1c of at least 10%, and 20% were between 8% and 10%. Body mass index consistently remained between 35 and 37.5.
Young patients with type 2 diabetes exhibit endothelial dysfunction, increased carotid intima-media thickness, elevated arterial stiffness, left ventricular hypertrophy, diastolic dysfunction, and reduced maximal exercise capacity. All these factors predict cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
In TODAY, 17 serious cardiovascular events were recorded, including four myocardial infarctions, six cases of congestive heart failure, three coronary events, and four strokes.
In an analysis of the TODAY and SEARCH studies, although the average duration of diabetes was similar, complications were more frequent among young patients with type 2 diabetes than among those with type 1 diabetes. Microvascular complications were 2.5 times more frequent, and macrovascular complications were four times more frequent.
In SEARCH, excessive mortality was observed among young adults for each type of diabetes. Differences in risk were associated with diabetes type, age, race/ethnicity, and sex. Mortality ratios were 1.5 and 2.3 for types 1 and 2 diabetes, respectively.
Women had higher mortality rates than men. Diabetes was the underlying cause of death in 9.1% cases, which was comparable to cardiovascular diseases or cancer (10.9%). According to a life expectancy model, young patients with type 2 diabetes lose about 15 years of life.
Eating Disorders and Depression
Beyond these complications, other issues are often present among adolescents with type 2 diabetes. Approximately 50% have eating disorders (compared with 21% among those with type 1 diabetes), 19.3% report depressive symptoms, and 18.9% have expressed thoughts of self-harm. In addition, 19.6% have polycystic ovary syndrome. Z-scores for bone mineral density at the femoral neck and lumbar spine were significantly lower in adolescents with type 2 diabetes than in healthy peers. The presence of metabolic dysfunction–associated fatty liver disease is also more pronounced.
“The recent approvals of new pharmacological interventions for weight loss and improved glycemic control in adolescents offer hope. We hope that, over the next decade, the prevalence of complications among these young patients with type 2 diabetes will decline. In the meantime, a proactive approach is essential to prevent complications related to type 2 diabetes in these youth,” Pinhas-Hamiel concluded.
For more information, see ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2022: Type 2 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents.
Pinhas-Hamiel reported no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
From EASD 2024
Overuse of Digital Devices in the Exam Room: A Teaching Opportunity
A 3-year-old presents to my clinic for evaluation of a possible autism spectrum disorder/difference. He has a history of severe emotional dysregulation, as well as reduced social skills and multiple sensory sensitivities. When I enter the exam room he is watching videos on his mom’s phone, and has some difficulty transitioning to play with toys when I encourage him to do so. He is eventually able to cooperate with my testing, though a bit reluctantly, and scores within the low average range for both language and pre-academic skills. His neurologic exam is within normal limits. He utilizes reasonably well-modulated eye contact paired with some typical use of gestures, and his affect is moderately directed and reactive. He displays typical intonation and prosody of speech, though engages in less spontaneous, imaginative, and reciprocal play than would be expected for his age. His mother reports decreased pretend play at home, minimal interest in toys, and difficulty playing cooperatively with other children.
Upon further history, it becomes apparent that the child spends a majority of his time on electronic devices, and has done so since early toddlerhood. Further dialogue suggests that the family became isolated during the COVID-19 pandemic, and has not yet re-engaged with the community in a meaningful way. The child has had rare opportunity for social interactions with other children, and minimal access to outdoor play. His most severe meltdowns generally involve transitions away from screens, and his overwhelmed parents often resort to use of additional screens to calm him once he is dysregulated.
At the end of the visit, through shared decision making, we agree that enrolling the child in a high-quality public preschool will help parents make a concerted effort towards a significant reduction in the hours per day in which the child utilizes electronic devices, while also providing him more exposure to peers. We plan for the child to return in 6 months for a re-evaluation around social-emotional skills, given his current limited exposure to peers and limited “unplugged” play-time.
Overutilization of Electronic Devices
As clinicians, we can all see how pervasive the use of electronic devices has become in the lives of the families we care for, as well as in our own lives, and how challenging some aspects of modern parenting have become. The developmental impact of early and excessive use of screens in young children is well documented,1 but as clinicians it can be tricky to help empower parents to find ways to limit screen time. When parents use screens to comfort and amuse their children during a clinic visit, this situation may serve as an excellent opportunity for a meaningful and respectful conversation around skill deficits which can result from overutilization of electronic devices in young children.
One scenario I often encounter during my patient evaluations as a developmental and behavioral pediatrician is children begging their parents for use of their phone throughout their visits with me. Not infrequently, a child is already on a screen when I enter the exam room, even when there has been a minimal wait time, which often leads to some resistance on behalf of the child as I explain to the family that a significant portion of the visit involves my interactions with the child, testing the child, and observing their child at play. I always provide ample amounts of age-appropriate art supplies, puzzles, fidgets, building toys, and imaginative play items to children during their 30 to 90 minute evaluations, but these are often not appealing to children when they have been very recently engaged with an electronic device. At times I also need to ask caretakers themselves to please disengage from their own electronic devices during the visit so that I can involve them in a detailed discussion about their child.
One challenge with the practice of allowing children access to entertainment on their parent’s smartphones in particular, lies in the fact that these devices are almost always present, meaning there is no natural boundary to inhibit access, in contrast to a television set or stationary computer parked in the family living room. Not dissimilar to candy visible in a parent’s purse, a cell phone becomes a constant temptation for children accustomed to utilizing them at home and public venues, and the incessant begging can wear down already stressed parents.
Children can become conditioned to utilize the distraction of screens to avoid feelings of discomfort or stress, and so can be very persistent and emotional when asking for the use of screens in public settings. Out in the community, I very frequently see young children and toddlers quietly staring at their phones and tablets while at restaurants and stores. While I have empathy for exhausted parents desperate for a moment of quiet, if this type of screen use is the rule rather than the exception for a child, there is risk for missed opportunities for the development of self-regulation skills.
Additionally, I have seen very young children present to my clinic with poor posture and neck pain secondary to chronic smartphone use, and young children who are getting minimal exercise or outdoor time due to excessive screen use, leading to concerns around fine and gross motor skills as well.
While allowing a child to stay occupied with or be soothed by a highly interesting digital experience can create a more calm environment for all, if habitual, this use can come at a cost regarding opportunities for the growth of executive functioning skills, general coping skills, general situational awareness, and experiential learning. Reliance on screens to decrease uncomfortable experiences decreases the opportunity for building distress tolerance, patience, and coping skills.
Of course there are times of extreme distress where a lollipop or bit of screen time might be reasonable to help keep a child safe or further avoid emotional trauma, but in general, other methods of soothing can very often be utilized, and in the long run would serve to increase the child’s general adaptive functioning.
A Teachable Moment
When clinicians encounter screens being used by parents to entertain their kids in clinic, it provides a valuable teaching moment around the risks of using screens to keep kids regulated and occupied during life’s less interesting or more anxiety provoking experiences. Having a meaningful conversation about the use of electronic devices with caregivers by clinicians in the exam room can be a delicate dance between providing supportive education while avoiding judgmental tones or verbiage. Normalizing and sympathizing with the difficulty of managing challenging behaviors from children in public spaces can help parents feel less desperate to keep their child quiet at all costs, and thus allow for greater development of coping skills.
Some parents may benefit from learning simple ideas for keeping a child regulated and occupied during times of waiting such as silly songs and dances, verbal games like “I spy,” and clapping routines. For a child with additional sensory or developmental needs, a referral to an occupational therapist to work on emotional regulation by way of specific sensory tools can be helpful. Parent-Child Interaction Therapy for kids ages 2 to 7 can also help build some relational activities and skills that can be utilized during trying situations to help keep a child settled and occupied.
If a child has qualified for Developmental Disability Services (DDS), medical providers can also write “prescriptions’ for sensory calming items which are often covered financially by DDS, such as chewies, weighted vests, stuffed animals, and fidgets. Encouraging parents to schedule allowed screen time at home in a very predictable and controlled manner is one method to help limit excessive use, as well as it’s utilization as an emotional regulation tool.
For public outings with children with special needs, and in particular in situations where meltdowns are likely to occur, some families find it helpful to dress their children in clothing or accessories that increase community awareness about their child’s condition (such as an autism awareness t-shirt). This effort can also help deflect unhelpful attention or advice from the public. Some parents choose to carry small cards explaining the child’s developmental differences, which can then be easily handed to unsupportive strangers in community settings during trying moments.
Clinicians can work to utilize even quick visits with families as an opportunity to review the American Academy of Pediatrics screen time recommendations with families, and also direct them to the Family Media Plan creation resources. Parenting in the modern era presents many challenges regarding choices around the use of electronic devices with children, and using the exam room experience as a teaching opportunity may be a helpful way to decrease utilization of screens as emotional regulation tools for children, while also providing general education around healthy use of screens.
Dr. Roth is a developmental and behavioral pediatrician in Eugene, Oregon.
Reference
1. Takahashi I et al. Screen Time at Age 1 Year and Communication and Problem-Solving Developmental Delays at 2 and 4 years. JAMA Pediatr. 2023 Oct 1;177(10):1039-1046. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.3057.
A 3-year-old presents to my clinic for evaluation of a possible autism spectrum disorder/difference. He has a history of severe emotional dysregulation, as well as reduced social skills and multiple sensory sensitivities. When I enter the exam room he is watching videos on his mom’s phone, and has some difficulty transitioning to play with toys when I encourage him to do so. He is eventually able to cooperate with my testing, though a bit reluctantly, and scores within the low average range for both language and pre-academic skills. His neurologic exam is within normal limits. He utilizes reasonably well-modulated eye contact paired with some typical use of gestures, and his affect is moderately directed and reactive. He displays typical intonation and prosody of speech, though engages in less spontaneous, imaginative, and reciprocal play than would be expected for his age. His mother reports decreased pretend play at home, minimal interest in toys, and difficulty playing cooperatively with other children.
Upon further history, it becomes apparent that the child spends a majority of his time on electronic devices, and has done so since early toddlerhood. Further dialogue suggests that the family became isolated during the COVID-19 pandemic, and has not yet re-engaged with the community in a meaningful way. The child has had rare opportunity for social interactions with other children, and minimal access to outdoor play. His most severe meltdowns generally involve transitions away from screens, and his overwhelmed parents often resort to use of additional screens to calm him once he is dysregulated.
At the end of the visit, through shared decision making, we agree that enrolling the child in a high-quality public preschool will help parents make a concerted effort towards a significant reduction in the hours per day in which the child utilizes electronic devices, while also providing him more exposure to peers. We plan for the child to return in 6 months for a re-evaluation around social-emotional skills, given his current limited exposure to peers and limited “unplugged” play-time.
Overutilization of Electronic Devices
As clinicians, we can all see how pervasive the use of electronic devices has become in the lives of the families we care for, as well as in our own lives, and how challenging some aspects of modern parenting have become. The developmental impact of early and excessive use of screens in young children is well documented,1 but as clinicians it can be tricky to help empower parents to find ways to limit screen time. When parents use screens to comfort and amuse their children during a clinic visit, this situation may serve as an excellent opportunity for a meaningful and respectful conversation around skill deficits which can result from overutilization of electronic devices in young children.
One scenario I often encounter during my patient evaluations as a developmental and behavioral pediatrician is children begging their parents for use of their phone throughout their visits with me. Not infrequently, a child is already on a screen when I enter the exam room, even when there has been a minimal wait time, which often leads to some resistance on behalf of the child as I explain to the family that a significant portion of the visit involves my interactions with the child, testing the child, and observing their child at play. I always provide ample amounts of age-appropriate art supplies, puzzles, fidgets, building toys, and imaginative play items to children during their 30 to 90 minute evaluations, but these are often not appealing to children when they have been very recently engaged with an electronic device. At times I also need to ask caretakers themselves to please disengage from their own electronic devices during the visit so that I can involve them in a detailed discussion about their child.
One challenge with the practice of allowing children access to entertainment on their parent’s smartphones in particular, lies in the fact that these devices are almost always present, meaning there is no natural boundary to inhibit access, in contrast to a television set or stationary computer parked in the family living room. Not dissimilar to candy visible in a parent’s purse, a cell phone becomes a constant temptation for children accustomed to utilizing them at home and public venues, and the incessant begging can wear down already stressed parents.
Children can become conditioned to utilize the distraction of screens to avoid feelings of discomfort or stress, and so can be very persistent and emotional when asking for the use of screens in public settings. Out in the community, I very frequently see young children and toddlers quietly staring at their phones and tablets while at restaurants and stores. While I have empathy for exhausted parents desperate for a moment of quiet, if this type of screen use is the rule rather than the exception for a child, there is risk for missed opportunities for the development of self-regulation skills.
Additionally, I have seen very young children present to my clinic with poor posture and neck pain secondary to chronic smartphone use, and young children who are getting minimal exercise or outdoor time due to excessive screen use, leading to concerns around fine and gross motor skills as well.
While allowing a child to stay occupied with or be soothed by a highly interesting digital experience can create a more calm environment for all, if habitual, this use can come at a cost regarding opportunities for the growth of executive functioning skills, general coping skills, general situational awareness, and experiential learning. Reliance on screens to decrease uncomfortable experiences decreases the opportunity for building distress tolerance, patience, and coping skills.
Of course there are times of extreme distress where a lollipop or bit of screen time might be reasonable to help keep a child safe or further avoid emotional trauma, but in general, other methods of soothing can very often be utilized, and in the long run would serve to increase the child’s general adaptive functioning.
A Teachable Moment
When clinicians encounter screens being used by parents to entertain their kids in clinic, it provides a valuable teaching moment around the risks of using screens to keep kids regulated and occupied during life’s less interesting or more anxiety provoking experiences. Having a meaningful conversation about the use of electronic devices with caregivers by clinicians in the exam room can be a delicate dance between providing supportive education while avoiding judgmental tones or verbiage. Normalizing and sympathizing with the difficulty of managing challenging behaviors from children in public spaces can help parents feel less desperate to keep their child quiet at all costs, and thus allow for greater development of coping skills.
Some parents may benefit from learning simple ideas for keeping a child regulated and occupied during times of waiting such as silly songs and dances, verbal games like “I spy,” and clapping routines. For a child with additional sensory or developmental needs, a referral to an occupational therapist to work on emotional regulation by way of specific sensory tools can be helpful. Parent-Child Interaction Therapy for kids ages 2 to 7 can also help build some relational activities and skills that can be utilized during trying situations to help keep a child settled and occupied.
If a child has qualified for Developmental Disability Services (DDS), medical providers can also write “prescriptions’ for sensory calming items which are often covered financially by DDS, such as chewies, weighted vests, stuffed animals, and fidgets. Encouraging parents to schedule allowed screen time at home in a very predictable and controlled manner is one method to help limit excessive use, as well as it’s utilization as an emotional regulation tool.
For public outings with children with special needs, and in particular in situations where meltdowns are likely to occur, some families find it helpful to dress their children in clothing or accessories that increase community awareness about their child’s condition (such as an autism awareness t-shirt). This effort can also help deflect unhelpful attention or advice from the public. Some parents choose to carry small cards explaining the child’s developmental differences, which can then be easily handed to unsupportive strangers in community settings during trying moments.
Clinicians can work to utilize even quick visits with families as an opportunity to review the American Academy of Pediatrics screen time recommendations with families, and also direct them to the Family Media Plan creation resources. Parenting in the modern era presents many challenges regarding choices around the use of electronic devices with children, and using the exam room experience as a teaching opportunity may be a helpful way to decrease utilization of screens as emotional regulation tools for children, while also providing general education around healthy use of screens.
Dr. Roth is a developmental and behavioral pediatrician in Eugene, Oregon.
Reference
1. Takahashi I et al. Screen Time at Age 1 Year and Communication and Problem-Solving Developmental Delays at 2 and 4 years. JAMA Pediatr. 2023 Oct 1;177(10):1039-1046. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.3057.
A 3-year-old presents to my clinic for evaluation of a possible autism spectrum disorder/difference. He has a history of severe emotional dysregulation, as well as reduced social skills and multiple sensory sensitivities. When I enter the exam room he is watching videos on his mom’s phone, and has some difficulty transitioning to play with toys when I encourage him to do so. He is eventually able to cooperate with my testing, though a bit reluctantly, and scores within the low average range for both language and pre-academic skills. His neurologic exam is within normal limits. He utilizes reasonably well-modulated eye contact paired with some typical use of gestures, and his affect is moderately directed and reactive. He displays typical intonation and prosody of speech, though engages in less spontaneous, imaginative, and reciprocal play than would be expected for his age. His mother reports decreased pretend play at home, minimal interest in toys, and difficulty playing cooperatively with other children.
Upon further history, it becomes apparent that the child spends a majority of his time on electronic devices, and has done so since early toddlerhood. Further dialogue suggests that the family became isolated during the COVID-19 pandemic, and has not yet re-engaged with the community in a meaningful way. The child has had rare opportunity for social interactions with other children, and minimal access to outdoor play. His most severe meltdowns generally involve transitions away from screens, and his overwhelmed parents often resort to use of additional screens to calm him once he is dysregulated.
At the end of the visit, through shared decision making, we agree that enrolling the child in a high-quality public preschool will help parents make a concerted effort towards a significant reduction in the hours per day in which the child utilizes electronic devices, while also providing him more exposure to peers. We plan for the child to return in 6 months for a re-evaluation around social-emotional skills, given his current limited exposure to peers and limited “unplugged” play-time.
Overutilization of Electronic Devices
As clinicians, we can all see how pervasive the use of electronic devices has become in the lives of the families we care for, as well as in our own lives, and how challenging some aspects of modern parenting have become. The developmental impact of early and excessive use of screens in young children is well documented,1 but as clinicians it can be tricky to help empower parents to find ways to limit screen time. When parents use screens to comfort and amuse their children during a clinic visit, this situation may serve as an excellent opportunity for a meaningful and respectful conversation around skill deficits which can result from overutilization of electronic devices in young children.
One scenario I often encounter during my patient evaluations as a developmental and behavioral pediatrician is children begging their parents for use of their phone throughout their visits with me. Not infrequently, a child is already on a screen when I enter the exam room, even when there has been a minimal wait time, which often leads to some resistance on behalf of the child as I explain to the family that a significant portion of the visit involves my interactions with the child, testing the child, and observing their child at play. I always provide ample amounts of age-appropriate art supplies, puzzles, fidgets, building toys, and imaginative play items to children during their 30 to 90 minute evaluations, but these are often not appealing to children when they have been very recently engaged with an electronic device. At times I also need to ask caretakers themselves to please disengage from their own electronic devices during the visit so that I can involve them in a detailed discussion about their child.
One challenge with the practice of allowing children access to entertainment on their parent’s smartphones in particular, lies in the fact that these devices are almost always present, meaning there is no natural boundary to inhibit access, in contrast to a television set or stationary computer parked in the family living room. Not dissimilar to candy visible in a parent’s purse, a cell phone becomes a constant temptation for children accustomed to utilizing them at home and public venues, and the incessant begging can wear down already stressed parents.
Children can become conditioned to utilize the distraction of screens to avoid feelings of discomfort or stress, and so can be very persistent and emotional when asking for the use of screens in public settings. Out in the community, I very frequently see young children and toddlers quietly staring at their phones and tablets while at restaurants and stores. While I have empathy for exhausted parents desperate for a moment of quiet, if this type of screen use is the rule rather than the exception for a child, there is risk for missed opportunities for the development of self-regulation skills.
Additionally, I have seen very young children present to my clinic with poor posture and neck pain secondary to chronic smartphone use, and young children who are getting minimal exercise or outdoor time due to excessive screen use, leading to concerns around fine and gross motor skills as well.
While allowing a child to stay occupied with or be soothed by a highly interesting digital experience can create a more calm environment for all, if habitual, this use can come at a cost regarding opportunities for the growth of executive functioning skills, general coping skills, general situational awareness, and experiential learning. Reliance on screens to decrease uncomfortable experiences decreases the opportunity for building distress tolerance, patience, and coping skills.
Of course there are times of extreme distress where a lollipop or bit of screen time might be reasonable to help keep a child safe or further avoid emotional trauma, but in general, other methods of soothing can very often be utilized, and in the long run would serve to increase the child’s general adaptive functioning.
A Teachable Moment
When clinicians encounter screens being used by parents to entertain their kids in clinic, it provides a valuable teaching moment around the risks of using screens to keep kids regulated and occupied during life’s less interesting or more anxiety provoking experiences. Having a meaningful conversation about the use of electronic devices with caregivers by clinicians in the exam room can be a delicate dance between providing supportive education while avoiding judgmental tones or verbiage. Normalizing and sympathizing with the difficulty of managing challenging behaviors from children in public spaces can help parents feel less desperate to keep their child quiet at all costs, and thus allow for greater development of coping skills.
Some parents may benefit from learning simple ideas for keeping a child regulated and occupied during times of waiting such as silly songs and dances, verbal games like “I spy,” and clapping routines. For a child with additional sensory or developmental needs, a referral to an occupational therapist to work on emotional regulation by way of specific sensory tools can be helpful. Parent-Child Interaction Therapy for kids ages 2 to 7 can also help build some relational activities and skills that can be utilized during trying situations to help keep a child settled and occupied.
If a child has qualified for Developmental Disability Services (DDS), medical providers can also write “prescriptions’ for sensory calming items which are often covered financially by DDS, such as chewies, weighted vests, stuffed animals, and fidgets. Encouraging parents to schedule allowed screen time at home in a very predictable and controlled manner is one method to help limit excessive use, as well as it’s utilization as an emotional regulation tool.
For public outings with children with special needs, and in particular in situations where meltdowns are likely to occur, some families find it helpful to dress their children in clothing or accessories that increase community awareness about their child’s condition (such as an autism awareness t-shirt). This effort can also help deflect unhelpful attention or advice from the public. Some parents choose to carry small cards explaining the child’s developmental differences, which can then be easily handed to unsupportive strangers in community settings during trying moments.
Clinicians can work to utilize even quick visits with families as an opportunity to review the American Academy of Pediatrics screen time recommendations with families, and also direct them to the Family Media Plan creation resources. Parenting in the modern era presents many challenges regarding choices around the use of electronic devices with children, and using the exam room experience as a teaching opportunity may be a helpful way to decrease utilization of screens as emotional regulation tools for children, while also providing general education around healthy use of screens.
Dr. Roth is a developmental and behavioral pediatrician in Eugene, Oregon.
Reference
1. Takahashi I et al. Screen Time at Age 1 Year and Communication and Problem-Solving Developmental Delays at 2 and 4 years. JAMA Pediatr. 2023 Oct 1;177(10):1039-1046. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.3057.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Reduce Suicidal Behavior in Adolescents With Obesity
, a large international retrospective study found.
A study published in JAMA Pediatrics suggested that GLP-1 RAs such as semaglutide, liraglutide, and tirzepatide, which are widely used to treat type 2 diabetes (T2D), have a favorable psychiatric safety profile and open up potential avenues for prospective studies of psychiatric outcomes in adolescents with obesity.
Investigators Liya Kerem, MD, MSc, and Joshua Stokar, MD, of Hadassah University Medical Center in Jerusalem, Israel, reported that the reduced risk in GLP-1 RA recipients was maintained up to 3 years follow-up compared with propensity score–matched controls treated with behavioral interventions alone.
“These findings support the notion that childhood obesity does not result from lack of willpower and shed light on underlying mechanisms that can be targeted by pharmacotherapy.” Kerem and Stokar wrote.
Other research has suggested these agents have neurobiologic effects unrelated to weight loss that positively affect mood and mental health.
Study Details
The analysis included data from December 2019 to June 2024, drawn from 120 international healthcare organizations, mainly in the United States. A total of 4052 racially and ethnically diverse adolescents with obesity (aged 12-18 years [mean age, about 15.5 years]) being treated with an anti-obesity intervention were identified for the GLP-1 RA cohort and 50,112 for the control cohort. The arms were balanced for baseline demographic characteristics, psychiatric medications and comorbidities, and diagnoses associated with socioeconomic status and healthcare access.
Propensity score matching (PSM) resulted in 3456 participants in each of two balanced cohorts.
Before PSM, intervention patients were older (mean age, 15.5 vs 14.7 years), were more likely to be female (59% vs 49%), and had a higher body mass index (41.9 vs 33.8). They also had a higher prevalence of diabetes (40% vs 4%) and treatment with antidiabetic medications.
GLP-1 RA recipients also had a history of psychiatric diagnoses (17% vs 9% for mood disorders) and psychiatric medications (18% vs 7% for antidepressants). Previous use of non–GLP-1 RA anti-obesity medications was uncommon in the cohort overall, although more common in the GLP-1 RA cohort (2.5% vs 0.2% for phentermine).
Prescription of GLP-1 RA was associated with a 33% reduced risk for suicidal ideation or attempts over 12 months of follow-up: 1.45% vs 2.26% (hazard ratio [HR], 0.67; 95% CI, 0.47-0.95; P = .02). It was also associated with a higher rate of gastrointestinal symptoms: 6.9% vs 5.4% (HR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.12-1.78; P = .003). There was no difference in rates of upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs), although some research suggests these agents reduce URTIs.
Mechanisms
The etiology of childhood obesity is complex and multifactorial, the authors wrote, and genetic predisposition to adiposity, an obesogenic environment, and a sedentary lifestyle synergistically contribute to its development. Variants in genes active in the hypothalamic appetite-regulation neurocircuitry appear to be associated with the development of childhood and adolescent obesity.
The authors noted that adolescence carries an increased risk for psychiatric disorders and suicidal ideation. “The amelioration of obesity could indirectly improve these psychiatric comorbidities,” they wrote. In addition, preclinical studies suggested that GLP-1 RA may improve depression-related neuropathology, including neuroinflammation and neurotransmitter imbalance, and may promote neurogenesis.
A recent meta-analysis found that adults with T2D treated with GLP-1 RA showed significant reduction in depression scale scores compared with those treated with non-GLP-1 RA antidiabetic medications.
Commenting on the study but not involved in it, psychiatrist Robert H. Dicker, MD, associate director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Northwell Zucker Hillside Hospital in Glen Oaks, New York, cautioned that these are preliminary data limited by a retrospective review, not a prospective double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
“The mechanism is unknown — is it a direct effect on weight loss with an improvement of quality of life, more positive feedback by the community, enhanced ability to exercise, and a decrease in depressive symptoms?” he asked.
Dicker suggested an alternative hypothesis: Does the GLP-1 RA have a direct effect on neurotransmitters and inflammation and, thus, an impact on mood, emotional regulation, impulse control, and suicide?
“To further answer these questions, prospective studies must be conducted. It is far too early to conclude that these medications are effective in treating mood disorders in our youth,” Dicker said. “But it is promising that these treatments do not appear to increase suicidal ideas and behavior.”
Adding another outsider’s perspective on the study, Suzanne E. Cuda, MD, FOMA, FAAP, a pediatrician who treats childhood obesity in San Antonio, said that while there was no risk for increased psychiatric disease and a suggestion that GLP-1 RAs may reduce suicidal ideation or attempts, “I don’t think this translates to a treatment for depression in adolescents. Nor does this study indicate there could be a decrease in depression due specifically to the use of GLP1Rs. If the results in this study are replicated, however, it would be reassuring to know that adolescents would not be at risk for an increase in suicidal ideation or attempts.”
This study had no external funding. Kerem reported receiving personal fees from Novo Nordisk for lectures on childhood obesity outside of the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Dicker and Cuda had no competing interests relevant to their comments.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, a large international retrospective study found.
A study published in JAMA Pediatrics suggested that GLP-1 RAs such as semaglutide, liraglutide, and tirzepatide, which are widely used to treat type 2 diabetes (T2D), have a favorable psychiatric safety profile and open up potential avenues for prospective studies of psychiatric outcomes in adolescents with obesity.
Investigators Liya Kerem, MD, MSc, and Joshua Stokar, MD, of Hadassah University Medical Center in Jerusalem, Israel, reported that the reduced risk in GLP-1 RA recipients was maintained up to 3 years follow-up compared with propensity score–matched controls treated with behavioral interventions alone.
“These findings support the notion that childhood obesity does not result from lack of willpower and shed light on underlying mechanisms that can be targeted by pharmacotherapy.” Kerem and Stokar wrote.
Other research has suggested these agents have neurobiologic effects unrelated to weight loss that positively affect mood and mental health.
Study Details
The analysis included data from December 2019 to June 2024, drawn from 120 international healthcare organizations, mainly in the United States. A total of 4052 racially and ethnically diverse adolescents with obesity (aged 12-18 years [mean age, about 15.5 years]) being treated with an anti-obesity intervention were identified for the GLP-1 RA cohort and 50,112 for the control cohort. The arms were balanced for baseline demographic characteristics, psychiatric medications and comorbidities, and diagnoses associated with socioeconomic status and healthcare access.
Propensity score matching (PSM) resulted in 3456 participants in each of two balanced cohorts.
Before PSM, intervention patients were older (mean age, 15.5 vs 14.7 years), were more likely to be female (59% vs 49%), and had a higher body mass index (41.9 vs 33.8). They also had a higher prevalence of diabetes (40% vs 4%) and treatment with antidiabetic medications.
GLP-1 RA recipients also had a history of psychiatric diagnoses (17% vs 9% for mood disorders) and psychiatric medications (18% vs 7% for antidepressants). Previous use of non–GLP-1 RA anti-obesity medications was uncommon in the cohort overall, although more common in the GLP-1 RA cohort (2.5% vs 0.2% for phentermine).
Prescription of GLP-1 RA was associated with a 33% reduced risk for suicidal ideation or attempts over 12 months of follow-up: 1.45% vs 2.26% (hazard ratio [HR], 0.67; 95% CI, 0.47-0.95; P = .02). It was also associated with a higher rate of gastrointestinal symptoms: 6.9% vs 5.4% (HR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.12-1.78; P = .003). There was no difference in rates of upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs), although some research suggests these agents reduce URTIs.
Mechanisms
The etiology of childhood obesity is complex and multifactorial, the authors wrote, and genetic predisposition to adiposity, an obesogenic environment, and a sedentary lifestyle synergistically contribute to its development. Variants in genes active in the hypothalamic appetite-regulation neurocircuitry appear to be associated with the development of childhood and adolescent obesity.
The authors noted that adolescence carries an increased risk for psychiatric disorders and suicidal ideation. “The amelioration of obesity could indirectly improve these psychiatric comorbidities,” they wrote. In addition, preclinical studies suggested that GLP-1 RA may improve depression-related neuropathology, including neuroinflammation and neurotransmitter imbalance, and may promote neurogenesis.
A recent meta-analysis found that adults with T2D treated with GLP-1 RA showed significant reduction in depression scale scores compared with those treated with non-GLP-1 RA antidiabetic medications.
Commenting on the study but not involved in it, psychiatrist Robert H. Dicker, MD, associate director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Northwell Zucker Hillside Hospital in Glen Oaks, New York, cautioned that these are preliminary data limited by a retrospective review, not a prospective double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
“The mechanism is unknown — is it a direct effect on weight loss with an improvement of quality of life, more positive feedback by the community, enhanced ability to exercise, and a decrease in depressive symptoms?” he asked.
Dicker suggested an alternative hypothesis: Does the GLP-1 RA have a direct effect on neurotransmitters and inflammation and, thus, an impact on mood, emotional regulation, impulse control, and suicide?
“To further answer these questions, prospective studies must be conducted. It is far too early to conclude that these medications are effective in treating mood disorders in our youth,” Dicker said. “But it is promising that these treatments do not appear to increase suicidal ideas and behavior.”
Adding another outsider’s perspective on the study, Suzanne E. Cuda, MD, FOMA, FAAP, a pediatrician who treats childhood obesity in San Antonio, said that while there was no risk for increased psychiatric disease and a suggestion that GLP-1 RAs may reduce suicidal ideation or attempts, “I don’t think this translates to a treatment for depression in adolescents. Nor does this study indicate there could be a decrease in depression due specifically to the use of GLP1Rs. If the results in this study are replicated, however, it would be reassuring to know that adolescents would not be at risk for an increase in suicidal ideation or attempts.”
This study had no external funding. Kerem reported receiving personal fees from Novo Nordisk for lectures on childhood obesity outside of the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Dicker and Cuda had no competing interests relevant to their comments.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, a large international retrospective study found.
A study published in JAMA Pediatrics suggested that GLP-1 RAs such as semaglutide, liraglutide, and tirzepatide, which are widely used to treat type 2 diabetes (T2D), have a favorable psychiatric safety profile and open up potential avenues for prospective studies of psychiatric outcomes in adolescents with obesity.
Investigators Liya Kerem, MD, MSc, and Joshua Stokar, MD, of Hadassah University Medical Center in Jerusalem, Israel, reported that the reduced risk in GLP-1 RA recipients was maintained up to 3 years follow-up compared with propensity score–matched controls treated with behavioral interventions alone.
“These findings support the notion that childhood obesity does not result from lack of willpower and shed light on underlying mechanisms that can be targeted by pharmacotherapy.” Kerem and Stokar wrote.
Other research has suggested these agents have neurobiologic effects unrelated to weight loss that positively affect mood and mental health.
Study Details
The analysis included data from December 2019 to June 2024, drawn from 120 international healthcare organizations, mainly in the United States. A total of 4052 racially and ethnically diverse adolescents with obesity (aged 12-18 years [mean age, about 15.5 years]) being treated with an anti-obesity intervention were identified for the GLP-1 RA cohort and 50,112 for the control cohort. The arms were balanced for baseline demographic characteristics, psychiatric medications and comorbidities, and diagnoses associated with socioeconomic status and healthcare access.
Propensity score matching (PSM) resulted in 3456 participants in each of two balanced cohorts.
Before PSM, intervention patients were older (mean age, 15.5 vs 14.7 years), were more likely to be female (59% vs 49%), and had a higher body mass index (41.9 vs 33.8). They also had a higher prevalence of diabetes (40% vs 4%) and treatment with antidiabetic medications.
GLP-1 RA recipients also had a history of psychiatric diagnoses (17% vs 9% for mood disorders) and psychiatric medications (18% vs 7% for antidepressants). Previous use of non–GLP-1 RA anti-obesity medications was uncommon in the cohort overall, although more common in the GLP-1 RA cohort (2.5% vs 0.2% for phentermine).
Prescription of GLP-1 RA was associated with a 33% reduced risk for suicidal ideation or attempts over 12 months of follow-up: 1.45% vs 2.26% (hazard ratio [HR], 0.67; 95% CI, 0.47-0.95; P = .02). It was also associated with a higher rate of gastrointestinal symptoms: 6.9% vs 5.4% (HR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.12-1.78; P = .003). There was no difference in rates of upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs), although some research suggests these agents reduce URTIs.
Mechanisms
The etiology of childhood obesity is complex and multifactorial, the authors wrote, and genetic predisposition to adiposity, an obesogenic environment, and a sedentary lifestyle synergistically contribute to its development. Variants in genes active in the hypothalamic appetite-regulation neurocircuitry appear to be associated with the development of childhood and adolescent obesity.
The authors noted that adolescence carries an increased risk for psychiatric disorders and suicidal ideation. “The amelioration of obesity could indirectly improve these psychiatric comorbidities,” they wrote. In addition, preclinical studies suggested that GLP-1 RA may improve depression-related neuropathology, including neuroinflammation and neurotransmitter imbalance, and may promote neurogenesis.
A recent meta-analysis found that adults with T2D treated with GLP-1 RA showed significant reduction in depression scale scores compared with those treated with non-GLP-1 RA antidiabetic medications.
Commenting on the study but not involved in it, psychiatrist Robert H. Dicker, MD, associate director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Northwell Zucker Hillside Hospital in Glen Oaks, New York, cautioned that these are preliminary data limited by a retrospective review, not a prospective double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
“The mechanism is unknown — is it a direct effect on weight loss with an improvement of quality of life, more positive feedback by the community, enhanced ability to exercise, and a decrease in depressive symptoms?” he asked.
Dicker suggested an alternative hypothesis: Does the GLP-1 RA have a direct effect on neurotransmitters and inflammation and, thus, an impact on mood, emotional regulation, impulse control, and suicide?
“To further answer these questions, prospective studies must be conducted. It is far too early to conclude that these medications are effective in treating mood disorders in our youth,” Dicker said. “But it is promising that these treatments do not appear to increase suicidal ideas and behavior.”
Adding another outsider’s perspective on the study, Suzanne E. Cuda, MD, FOMA, FAAP, a pediatrician who treats childhood obesity in San Antonio, said that while there was no risk for increased psychiatric disease and a suggestion that GLP-1 RAs may reduce suicidal ideation or attempts, “I don’t think this translates to a treatment for depression in adolescents. Nor does this study indicate there could be a decrease in depression due specifically to the use of GLP1Rs. If the results in this study are replicated, however, it would be reassuring to know that adolescents would not be at risk for an increase in suicidal ideation or attempts.”
This study had no external funding. Kerem reported receiving personal fees from Novo Nordisk for lectures on childhood obesity outside of the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Dicker and Cuda had no competing interests relevant to their comments.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
From JAMA Pediatrics
PCPs Play a Key Role in Managing and Preventing the Atopic March in Children
Primary care physicians (PCPs) play a key role in treating young patients as they progress through the “atopic march” from atopic dermatitis through food allergy, asthma, and allergic rhinitis. They can also help prevent the process from starting.
“The PCP is usually the first clinician a family with concerns about atopic conditions sees, unless they first visit urgent care or an emergency department after an allergic reaction to food. Either way, families rely on their PCP for ongoing guidance,” said Terri F. Brown-Whitehorn, MD, attending physician in the Division of Allergy and Immunology at the Center for Pediatric Eosinophilic Disorders and the Integrative Health Program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“The most important thing PCPs can do is know that the atopic march exists, how it progresses over time, and what signs and symptoms to look for,” she told this news organization.
The Atopic March
The atopic march describes the progression of allergic diseases in a child over time, with atopic dermatitis and food allergy in infancy tending to be followed by allergic rhinitis and asthma into later childhood and adulthood.
Although the pathophysiology of the inflammation that precedes atopic dermatitis is unclear, two main hypotheses have been proposed. The first suggests a primary immune dysfunction leads to immunoglobulin E (IgE) sensitization, allergic inflammation, and a secondary disturbance of the epithelial barrier; the second starts with a primary defect in the epithelial barrier that leads to secondary immunologic dysregulation and results in inflammation.
Genetics, infection, hygiene, extreme climate, food allergens, probiotics, aeroallergens, and tobacco smoke are thought to play roles in atopic dermatitis. An estimated 10%-12% of children and 1% of adults in the United States have been reported to have the condition, and the prevalence appears to be increasing. An estimated 85% of cases occur during the first year of life and 95% before the age of 5 years.
“Atopy often, though not always, runs in families, so PCPs should inquire about the history of atopic dermatitis, IgE-mediated food allergies, allergic rhinitis, and asthma in the patient’s siblings, parents, and grandparents,” Brown-Whitehorn said.
Key Educators
PCPs treat the full gamut of atopic conditions and are key educators on ways families can help mitigate their children’s atopic march or stop it before it begins, said Gerald Bell Lee, MD, an allergist and immunologist at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta and an associate professor in the Division of Allergy and Immunology at Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta.
“Most parents who bring their infants with eczema to the PCP assume their child ate something that caused their rash. But the relationship between atopic dermatitis, a type of eczema, and food allergy is more complicated,” he added.
Lee said PCPs should explain to their patients what atopic dermatitis is, how it starts and progresses, and how families can help prevent the condition by, for example, introducing allergenic foods to infants at around 4-6 months of age.
Atopic Dermatitis
PCPs should inform parents and other caregivers to wash their hands before moisturizing their child, take care not to contaminate the moisturizer, and bathe their child only when the child is dirty.
“Soap removes protective natural skin oils and increases moisture loss, and exposure to soap and bathing is a main contributor to eczema,” said Lee. “Dry skin loses its protective barrier, allowing outside agents to penetrate and be identified by the immune system.”
“According to one hypothesis, parents may eat food, not wash their hands afterwards, then moisturize their baby. This unhygienic practice spreads food proteins from the adult’s meal, and possibly from contaminants present in the moisturizer, all over the baby’s body,” he added.
Lee said he and his colleagues discourage overbathing babies to minimize the risk for skin injury that begins the atopic march: “New parents are inundated with infant skincare messaging and products. But we need to weigh societal pressures against practicality and ask, ‘Is the child’s skin actually dirty?’ ”
Atopic dermatitis tends to appear on the extensor surfaces, face, and scalp in infants and around arm and leg creases in toddlers and older children. Severe forms of the condition can be more widely distributed on the body, said Aarti P. Pandya, MD, medical director of the Food Allergy Center at Children’s Mercy Kansas City and clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, Missouri.
Avoid Triggers, Minimize Flares
Triggers of eczema are varied and common. To help minimize flares, PCPs can encourage caregivers to avoid products with fragrances or dyes, minimize the use of soaps, and completely rinse laundry detergent from clothing and household items. “Advise them to keep fingernails short and control dander, pollen, mold, household chemicals, and tobacco smoke, as well as the child’s stress and anxiety, which can also be a trigger,” Lee said.
“Skin infections from organisms such as staph, herpes, or coxsackie can also exacerbate symptoms,” Brown-Whitehorn added. “PCPs can educate caregivers to avoid all known triggers and give them an ‘action plan’ to carry out when skin flares.”
Food Allergies
Parents may be unaware food allergens can travel far beyond the plate, Lee said. Researchers vacuuming household bedding, carpets, furniture, and other surfaces have detected unnoticeably tiny quantities of allergenic food proteins in ordinary house dust. Touching this dust appears to provide the main exposure to those allergens.
“According to the dual exposure to allergen hypothesis, an infant’s tolerance to antigens occurs through high-dose exposure by mouth, and allergic sensitization occurs through low-dose exposure through the skin,” he said. “As young as four to six months of age, even before eating solid food, a child develops eczema, has a leaky skin barrier, comes in contact with food, and develops a food allergy.”
IgE-mediated food allergies can begin at any age. “Symptoms occur when a food is ingested and the patient develops symptoms including but not limited to urticaria, angioedema, pruritus, flushing, vomiting, diarrhea, coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, presyncope, or syncope,” Pandya noted.
In the case of eosinophilic esophagitis, which may also be part of the atopic march, infants and toddlers often have challenging-to-treat symptoms of reflux, while school-age children have reflux and abdominal pain, and adolescents and adults may experience difficulty swallowing and impactions of food or pills, Brown-Whitehorn said.
To differentiate between food allergy and contact dermatitis, Lee suggested providers ask, “ ’Is the rash hives? If yes, is the rash generalized or in a limited area?’ Then consider the statistical probabilities. Skin problems after milk, egg, wheat, soy, peanut, tree nut, fish, shellfish, or sesame are likely due to IgE-mediated food allergy, but after ketchup or strawberry are probably from skin contact.”
Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma
“For asthma, ask about frequency of night cough and symptoms with exercise, laughing, or crying. For allergic rhinitis, look for runny nose, itchy eyes, or sneezing,” Brown-Whitehorn said.
Testing and Monitoring
Assessing the extent of eczema with the Eczema Area and Severity Index or the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis index takes time but may be necessary to obtain insurance coverage for treatments such as biologics.
Avoid ordering IgE food panels, which can result in false positives that can lead to loss of tolerance and nutritional deficiencies; psychological harm from bullying, anxiety, and decreased quality of life; and higher food and healthcare costs, Pandya said.
Treatments
Caregivers may be wary about treatments, and all the three experts this news organization spoke with stressed the importance of educating caregivers about how treatments work and what to expect from them.
“Early and aggressive atopic dermatitis treatment could prevent sensitization to food or aeroallergens, which could help prevent additional atopic diseases, including those on the atopic march,” Pandya said. “Topical steroids are considered first line at any age. Topical phosphodiesterase inhibitors are approved at 3 months of age and above. Topical calcineurin inhibitors are approved at 2 years of age and above. Wet wrap therapy and bleach baths can be effective. Other options include biologic therapy, allergen immunotherapy, and UV therapy.”
“Epinephrine auto-injectors can counteract food reactions. For allergic rhinitis, non-sedating antihistamines, steroidal nasal sprays, and nasal antihistamines help. Asthma treatments include various inhaled medications,” Brown-Whitehorn added.
When to Refer to Specialists
Involving an allergist, dermatologist, pulmonologist, or ear nose throat specialist to the patient’s care team is advisable in more challenging cases.
If a child is younger than 3 months and has moderate to severe atopic dermatitis, an underlying immune defect may be to blame, so an allergy and immunology assessment is warranted, Brown-Whitehorn said. “An allergist can help any child who has recurrent coughing or wheezing avoid the emergency room or hospitalization.”
“In pediatrics, we always try to find the medication, regimen, and avoidance strategies that use the least treatment to provide the best care for each patient,” Brown-Whitehorn added. “Children eat, play, learn, and sleep, and every stage of the atopic march affects each of these activities. As clinicians, we need to be sure that we are helping children make the best of all these activities.”
Brown-Whitehorn reported financial relationships with DBV Technologies and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Lee reported financial relationships with Novartis. Pandya reported financial relationships with DBV Technologies, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary care physicians (PCPs) play a key role in treating young patients as they progress through the “atopic march” from atopic dermatitis through food allergy, asthma, and allergic rhinitis. They can also help prevent the process from starting.
“The PCP is usually the first clinician a family with concerns about atopic conditions sees, unless they first visit urgent care or an emergency department after an allergic reaction to food. Either way, families rely on their PCP for ongoing guidance,” said Terri F. Brown-Whitehorn, MD, attending physician in the Division of Allergy and Immunology at the Center for Pediatric Eosinophilic Disorders and the Integrative Health Program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“The most important thing PCPs can do is know that the atopic march exists, how it progresses over time, and what signs and symptoms to look for,” she told this news organization.
The Atopic March
The atopic march describes the progression of allergic diseases in a child over time, with atopic dermatitis and food allergy in infancy tending to be followed by allergic rhinitis and asthma into later childhood and adulthood.
Although the pathophysiology of the inflammation that precedes atopic dermatitis is unclear, two main hypotheses have been proposed. The first suggests a primary immune dysfunction leads to immunoglobulin E (IgE) sensitization, allergic inflammation, and a secondary disturbance of the epithelial barrier; the second starts with a primary defect in the epithelial barrier that leads to secondary immunologic dysregulation and results in inflammation.
Genetics, infection, hygiene, extreme climate, food allergens, probiotics, aeroallergens, and tobacco smoke are thought to play roles in atopic dermatitis. An estimated 10%-12% of children and 1% of adults in the United States have been reported to have the condition, and the prevalence appears to be increasing. An estimated 85% of cases occur during the first year of life and 95% before the age of 5 years.
“Atopy often, though not always, runs in families, so PCPs should inquire about the history of atopic dermatitis, IgE-mediated food allergies, allergic rhinitis, and asthma in the patient’s siblings, parents, and grandparents,” Brown-Whitehorn said.
Key Educators
PCPs treat the full gamut of atopic conditions and are key educators on ways families can help mitigate their children’s atopic march or stop it before it begins, said Gerald Bell Lee, MD, an allergist and immunologist at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta and an associate professor in the Division of Allergy and Immunology at Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta.
“Most parents who bring their infants with eczema to the PCP assume their child ate something that caused their rash. But the relationship between atopic dermatitis, a type of eczema, and food allergy is more complicated,” he added.
Lee said PCPs should explain to their patients what atopic dermatitis is, how it starts and progresses, and how families can help prevent the condition by, for example, introducing allergenic foods to infants at around 4-6 months of age.
Atopic Dermatitis
PCPs should inform parents and other caregivers to wash their hands before moisturizing their child, take care not to contaminate the moisturizer, and bathe their child only when the child is dirty.
“Soap removes protective natural skin oils and increases moisture loss, and exposure to soap and bathing is a main contributor to eczema,” said Lee. “Dry skin loses its protective barrier, allowing outside agents to penetrate and be identified by the immune system.”
“According to one hypothesis, parents may eat food, not wash their hands afterwards, then moisturize their baby. This unhygienic practice spreads food proteins from the adult’s meal, and possibly from contaminants present in the moisturizer, all over the baby’s body,” he added.
Lee said he and his colleagues discourage overbathing babies to minimize the risk for skin injury that begins the atopic march: “New parents are inundated with infant skincare messaging and products. But we need to weigh societal pressures against practicality and ask, ‘Is the child’s skin actually dirty?’ ”
Atopic dermatitis tends to appear on the extensor surfaces, face, and scalp in infants and around arm and leg creases in toddlers and older children. Severe forms of the condition can be more widely distributed on the body, said Aarti P. Pandya, MD, medical director of the Food Allergy Center at Children’s Mercy Kansas City and clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, Missouri.
Avoid Triggers, Minimize Flares
Triggers of eczema are varied and common. To help minimize flares, PCPs can encourage caregivers to avoid products with fragrances or dyes, minimize the use of soaps, and completely rinse laundry detergent from clothing and household items. “Advise them to keep fingernails short and control dander, pollen, mold, household chemicals, and tobacco smoke, as well as the child’s stress and anxiety, which can also be a trigger,” Lee said.
“Skin infections from organisms such as staph, herpes, or coxsackie can also exacerbate symptoms,” Brown-Whitehorn added. “PCPs can educate caregivers to avoid all known triggers and give them an ‘action plan’ to carry out when skin flares.”
Food Allergies
Parents may be unaware food allergens can travel far beyond the plate, Lee said. Researchers vacuuming household bedding, carpets, furniture, and other surfaces have detected unnoticeably tiny quantities of allergenic food proteins in ordinary house dust. Touching this dust appears to provide the main exposure to those allergens.
“According to the dual exposure to allergen hypothesis, an infant’s tolerance to antigens occurs through high-dose exposure by mouth, and allergic sensitization occurs through low-dose exposure through the skin,” he said. “As young as four to six months of age, even before eating solid food, a child develops eczema, has a leaky skin barrier, comes in contact with food, and develops a food allergy.”
IgE-mediated food allergies can begin at any age. “Symptoms occur when a food is ingested and the patient develops symptoms including but not limited to urticaria, angioedema, pruritus, flushing, vomiting, diarrhea, coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, presyncope, or syncope,” Pandya noted.
In the case of eosinophilic esophagitis, which may also be part of the atopic march, infants and toddlers often have challenging-to-treat symptoms of reflux, while school-age children have reflux and abdominal pain, and adolescents and adults may experience difficulty swallowing and impactions of food or pills, Brown-Whitehorn said.
To differentiate between food allergy and contact dermatitis, Lee suggested providers ask, “ ’Is the rash hives? If yes, is the rash generalized or in a limited area?’ Then consider the statistical probabilities. Skin problems after milk, egg, wheat, soy, peanut, tree nut, fish, shellfish, or sesame are likely due to IgE-mediated food allergy, but after ketchup or strawberry are probably from skin contact.”
Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma
“For asthma, ask about frequency of night cough and symptoms with exercise, laughing, or crying. For allergic rhinitis, look for runny nose, itchy eyes, or sneezing,” Brown-Whitehorn said.
Testing and Monitoring
Assessing the extent of eczema with the Eczema Area and Severity Index or the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis index takes time but may be necessary to obtain insurance coverage for treatments such as biologics.
Avoid ordering IgE food panels, which can result in false positives that can lead to loss of tolerance and nutritional deficiencies; psychological harm from bullying, anxiety, and decreased quality of life; and higher food and healthcare costs, Pandya said.
Treatments
Caregivers may be wary about treatments, and all the three experts this news organization spoke with stressed the importance of educating caregivers about how treatments work and what to expect from them.
“Early and aggressive atopic dermatitis treatment could prevent sensitization to food or aeroallergens, which could help prevent additional atopic diseases, including those on the atopic march,” Pandya said. “Topical steroids are considered first line at any age. Topical phosphodiesterase inhibitors are approved at 3 months of age and above. Topical calcineurin inhibitors are approved at 2 years of age and above. Wet wrap therapy and bleach baths can be effective. Other options include biologic therapy, allergen immunotherapy, and UV therapy.”
“Epinephrine auto-injectors can counteract food reactions. For allergic rhinitis, non-sedating antihistamines, steroidal nasal sprays, and nasal antihistamines help. Asthma treatments include various inhaled medications,” Brown-Whitehorn added.
When to Refer to Specialists
Involving an allergist, dermatologist, pulmonologist, or ear nose throat specialist to the patient’s care team is advisable in more challenging cases.
If a child is younger than 3 months and has moderate to severe atopic dermatitis, an underlying immune defect may be to blame, so an allergy and immunology assessment is warranted, Brown-Whitehorn said. “An allergist can help any child who has recurrent coughing or wheezing avoid the emergency room or hospitalization.”
“In pediatrics, we always try to find the medication, regimen, and avoidance strategies that use the least treatment to provide the best care for each patient,” Brown-Whitehorn added. “Children eat, play, learn, and sleep, and every stage of the atopic march affects each of these activities. As clinicians, we need to be sure that we are helping children make the best of all these activities.”
Brown-Whitehorn reported financial relationships with DBV Technologies and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Lee reported financial relationships with Novartis. Pandya reported financial relationships with DBV Technologies, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary care physicians (PCPs) play a key role in treating young patients as they progress through the “atopic march” from atopic dermatitis through food allergy, asthma, and allergic rhinitis. They can also help prevent the process from starting.
“The PCP is usually the first clinician a family with concerns about atopic conditions sees, unless they first visit urgent care or an emergency department after an allergic reaction to food. Either way, families rely on their PCP for ongoing guidance,” said Terri F. Brown-Whitehorn, MD, attending physician in the Division of Allergy and Immunology at the Center for Pediatric Eosinophilic Disorders and the Integrative Health Program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“The most important thing PCPs can do is know that the atopic march exists, how it progresses over time, and what signs and symptoms to look for,” she told this news organization.
The Atopic March
The atopic march describes the progression of allergic diseases in a child over time, with atopic dermatitis and food allergy in infancy tending to be followed by allergic rhinitis and asthma into later childhood and adulthood.
Although the pathophysiology of the inflammation that precedes atopic dermatitis is unclear, two main hypotheses have been proposed. The first suggests a primary immune dysfunction leads to immunoglobulin E (IgE) sensitization, allergic inflammation, and a secondary disturbance of the epithelial barrier; the second starts with a primary defect in the epithelial barrier that leads to secondary immunologic dysregulation and results in inflammation.
Genetics, infection, hygiene, extreme climate, food allergens, probiotics, aeroallergens, and tobacco smoke are thought to play roles in atopic dermatitis. An estimated 10%-12% of children and 1% of adults in the United States have been reported to have the condition, and the prevalence appears to be increasing. An estimated 85% of cases occur during the first year of life and 95% before the age of 5 years.
“Atopy often, though not always, runs in families, so PCPs should inquire about the history of atopic dermatitis, IgE-mediated food allergies, allergic rhinitis, and asthma in the patient’s siblings, parents, and grandparents,” Brown-Whitehorn said.
Key Educators
PCPs treat the full gamut of atopic conditions and are key educators on ways families can help mitigate their children’s atopic march or stop it before it begins, said Gerald Bell Lee, MD, an allergist and immunologist at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta and an associate professor in the Division of Allergy and Immunology at Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta.
“Most parents who bring their infants with eczema to the PCP assume their child ate something that caused their rash. But the relationship between atopic dermatitis, a type of eczema, and food allergy is more complicated,” he added.
Lee said PCPs should explain to their patients what atopic dermatitis is, how it starts and progresses, and how families can help prevent the condition by, for example, introducing allergenic foods to infants at around 4-6 months of age.
Atopic Dermatitis
PCPs should inform parents and other caregivers to wash their hands before moisturizing their child, take care not to contaminate the moisturizer, and bathe their child only when the child is dirty.
“Soap removes protective natural skin oils and increases moisture loss, and exposure to soap and bathing is a main contributor to eczema,” said Lee. “Dry skin loses its protective barrier, allowing outside agents to penetrate and be identified by the immune system.”
“According to one hypothesis, parents may eat food, not wash their hands afterwards, then moisturize their baby. This unhygienic practice spreads food proteins from the adult’s meal, and possibly from contaminants present in the moisturizer, all over the baby’s body,” he added.
Lee said he and his colleagues discourage overbathing babies to minimize the risk for skin injury that begins the atopic march: “New parents are inundated with infant skincare messaging and products. But we need to weigh societal pressures against practicality and ask, ‘Is the child’s skin actually dirty?’ ”
Atopic dermatitis tends to appear on the extensor surfaces, face, and scalp in infants and around arm and leg creases in toddlers and older children. Severe forms of the condition can be more widely distributed on the body, said Aarti P. Pandya, MD, medical director of the Food Allergy Center at Children’s Mercy Kansas City and clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, Missouri.
Avoid Triggers, Minimize Flares
Triggers of eczema are varied and common. To help minimize flares, PCPs can encourage caregivers to avoid products with fragrances or dyes, minimize the use of soaps, and completely rinse laundry detergent from clothing and household items. “Advise them to keep fingernails short and control dander, pollen, mold, household chemicals, and tobacco smoke, as well as the child’s stress and anxiety, which can also be a trigger,” Lee said.
“Skin infections from organisms such as staph, herpes, or coxsackie can also exacerbate symptoms,” Brown-Whitehorn added. “PCPs can educate caregivers to avoid all known triggers and give them an ‘action plan’ to carry out when skin flares.”
Food Allergies
Parents may be unaware food allergens can travel far beyond the plate, Lee said. Researchers vacuuming household bedding, carpets, furniture, and other surfaces have detected unnoticeably tiny quantities of allergenic food proteins in ordinary house dust. Touching this dust appears to provide the main exposure to those allergens.
“According to the dual exposure to allergen hypothesis, an infant’s tolerance to antigens occurs through high-dose exposure by mouth, and allergic sensitization occurs through low-dose exposure through the skin,” he said. “As young as four to six months of age, even before eating solid food, a child develops eczema, has a leaky skin barrier, comes in contact with food, and develops a food allergy.”
IgE-mediated food allergies can begin at any age. “Symptoms occur when a food is ingested and the patient develops symptoms including but not limited to urticaria, angioedema, pruritus, flushing, vomiting, diarrhea, coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, presyncope, or syncope,” Pandya noted.
In the case of eosinophilic esophagitis, which may also be part of the atopic march, infants and toddlers often have challenging-to-treat symptoms of reflux, while school-age children have reflux and abdominal pain, and adolescents and adults may experience difficulty swallowing and impactions of food or pills, Brown-Whitehorn said.
To differentiate between food allergy and contact dermatitis, Lee suggested providers ask, “ ’Is the rash hives? If yes, is the rash generalized or in a limited area?’ Then consider the statistical probabilities. Skin problems after milk, egg, wheat, soy, peanut, tree nut, fish, shellfish, or sesame are likely due to IgE-mediated food allergy, but after ketchup or strawberry are probably from skin contact.”
Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma
“For asthma, ask about frequency of night cough and symptoms with exercise, laughing, or crying. For allergic rhinitis, look for runny nose, itchy eyes, or sneezing,” Brown-Whitehorn said.
Testing and Monitoring
Assessing the extent of eczema with the Eczema Area and Severity Index or the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis index takes time but may be necessary to obtain insurance coverage for treatments such as biologics.
Avoid ordering IgE food panels, which can result in false positives that can lead to loss of tolerance and nutritional deficiencies; psychological harm from bullying, anxiety, and decreased quality of life; and higher food and healthcare costs, Pandya said.
Treatments
Caregivers may be wary about treatments, and all the three experts this news organization spoke with stressed the importance of educating caregivers about how treatments work and what to expect from them.
“Early and aggressive atopic dermatitis treatment could prevent sensitization to food or aeroallergens, which could help prevent additional atopic diseases, including those on the atopic march,” Pandya said. “Topical steroids are considered first line at any age. Topical phosphodiesterase inhibitors are approved at 3 months of age and above. Topical calcineurin inhibitors are approved at 2 years of age and above. Wet wrap therapy and bleach baths can be effective. Other options include biologic therapy, allergen immunotherapy, and UV therapy.”
“Epinephrine auto-injectors can counteract food reactions. For allergic rhinitis, non-sedating antihistamines, steroidal nasal sprays, and nasal antihistamines help. Asthma treatments include various inhaled medications,” Brown-Whitehorn added.
When to Refer to Specialists
Involving an allergist, dermatologist, pulmonologist, or ear nose throat specialist to the patient’s care team is advisable in more challenging cases.
If a child is younger than 3 months and has moderate to severe atopic dermatitis, an underlying immune defect may be to blame, so an allergy and immunology assessment is warranted, Brown-Whitehorn said. “An allergist can help any child who has recurrent coughing or wheezing avoid the emergency room or hospitalization.”
“In pediatrics, we always try to find the medication, regimen, and avoidance strategies that use the least treatment to provide the best care for each patient,” Brown-Whitehorn added. “Children eat, play, learn, and sleep, and every stage of the atopic march affects each of these activities. As clinicians, we need to be sure that we are helping children make the best of all these activities.”
Brown-Whitehorn reported financial relationships with DBV Technologies and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Lee reported financial relationships with Novartis. Pandya reported financial relationships with DBV Technologies, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Live Rotavirus Vaccine Safe for Newborns of Biologic-Treated Moms With IBD
No adverse events or impairment of the immune system emerged in babies at 7 days, 1 month, and 9 months post vaccination, in findings from a small Canadian study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
The study found normal extended immune function testing in infants despite third-trimester maternal biologic therapy and regardless of circulating drug levels. The data provide reassurance about live rotavirus vaccination in this population and may also offer insights into the safety of other live vaccines in biologic-exposed individuals, wrote investigators led by gastroenterologist Cynthia H. Seow, MD, a professor in the Cumming School of Medicine at the University of Calgary in Alberta, Canada.
“Despite the well-established safety and effectiveness of non–live vaccination in individuals with IBD, including those on immunomodulators and biologic therapy, vaccine uptake in pregnant women with IBD and their infants remains suboptimal,” Seow said in an interview. This largely arises from maternal and physician concerns regarding transplacental transfer of IBD therapies and their impact on the safety of vaccination.
“These concerns were heightened after reports emerged of five fatal outcomes following the administration of the live Bacille Calmette-Guérin [BCG] vaccine in biologic-exposed infants. However, it had already been reported that inadvertent administration of the live oral rotavirus vaccine, a very different vaccine in terms of target and mechanism of action, in biologic-exposed individuals had not been associated with significant adverse effects,” she said.
They undertook their analysis with the hypothesis that vaccination would carry low risk, although the live oral vaccine is not currently recommended in biologic-exposed infants. “Yet rotavirus is a leading cause of severe, dehydrating diarrhea in children under the age of 5 years globally, and vaccination has led to significant reductions in hospitalizations and mortality,” Seow added.
Provision of the vaccine to anti–tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–exposed infants has been incorporated into the Canadian Public Health and Immunization guidelines, as the majority of the biologic-exposed infants were exposed to anti-TNF agents. “And with collection of further data, we expect that this will be extended to other biologic agent exposure. These data are important to pregnant women with IBD as they help to normalize their care. Pregnancy is difficult enough without having to remember exceptions to care,” Seow said.
“Before some of the studies came out, broad guidelines recommended that live vaccines should not be used in biologic-exposed infants, but this had been thought to be overly zealous and too conservative, and the risk was thought to be low,” said Elizabeth Spencer, MD, an assistant professor of pediatrics in the Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, in an interview. Spencer was not involved in the Canadian study.
“At our center, we had some moms on biologics during pregnancy who forgot and had their babies vaccinated for rotavirus, and the babies were all fine,” she said.
The safety of this vaccine has been confirmed by several small studies and recently the PIANO Helmsley Global Consensus on Pregnancy and Inflammatory Bowel Disease, which was presented at Digestive Disease Week 2024. The consensus encompasses preconception counseling and the safety of IBD medications during pregnancy and lactation.
“Another concern, however, was that giving a live GI bug like rotavirus to babies might overstimulate their immune systems and provoke IBD,” Spencer added. “While a number of population-based studies in the US and Europe showed that was not the case, at least in the general population, there was a suggestion that, down the road, vaccination might be mildly protective against IBD in some cases.”
She added the caveat that these studies were not done in mothers and their babies with IBD, who might be inherently at greater risk for IBD. “So, a question for future research would be, ‘Is immune stimulation of the gut in IBD moms and their babies a good or a bad thing for their gut?’ ”
Spencer conceded that “the data present a bit of a blurry picture, but I think it’s always better just to vaccinate according to the regular schedule. The current data say there is no added risk, but it would be nice to look specifically at risk in moms with IBD and their children.”
The Study
The prospective cohort study is a substudy of a larger 2023 one that included biologic use in a range of maternal illnesses, not just IBD.
For the current study, Seow and colleagues identified 57 infants born to 52 mothers with IBD attending a pregnancy clinic at the University of Calgary in the period 2019-2023. Almost 81% of the mothers had Crohn’s disease, and the median duration of IBD was 10 years. The median gestational age at delivery was 39 weeks, and almost 60% of deliveries were vaginal. The infants had been exposed in utero to infliximab (n = 21), adalimumab (n = 19), vedolizumab (n = 10), and ustekinumab (n = 7) in the third trimester.
The 57 biologic-exposed infants underwent standardized clinical assessments, drug concentration, and immune function testing. The live oral rotavirus vaccine series was provided to 50 infants, with the first dose at a median of 13 weeks of age. Immunologic assessments validated for age were normal in all infants despite median infliximab concentrations of 6.1 μg/mL (range, 0.4-28.8 μg/mL), adalimumab concentrations of 1.7 μg/mL (range, 0.7-7.9 μg/mL), ustekinumab concentrations of 0.6 μg/mL (range, 0-1.1), and undetectable for vedolizumab at 10.7 weeks of age.
As anticipated, infant immune function was normal regardless of circulating drug levels.
The overall message, said Seow, is “healthy mum equals healthy baby. Be more concerned regarding active inflammation than active medications. In almost all circumstances, treat to target in pregnancy as you would in the nonpregnant state.” She added, however, that further studies are needed to determine the safety and optimal timing of other live vaccines, such as the BCG, in the presence of biologic therapy.
This study was funded by the Alberta Children’s Hospital Research Institute. Seow reported advisory/speaker’s fees for Janssen, AbbVie, Takeda, Pfizer, Fresenius Kabi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pharmascience, and Lilly, as well as funding from Alberta Children’s Hospital Research Institute, Crohn’s and Colitis Canada, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and Calgary Health Trust, and data safety monitoring from New South Wales Government Health, Australia. Multiple coauthors disclosed similar consulting or speaker relationships with private industry. Spencer had no competing interests with regard to her comments.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No adverse events or impairment of the immune system emerged in babies at 7 days, 1 month, and 9 months post vaccination, in findings from a small Canadian study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
The study found normal extended immune function testing in infants despite third-trimester maternal biologic therapy and regardless of circulating drug levels. The data provide reassurance about live rotavirus vaccination in this population and may also offer insights into the safety of other live vaccines in biologic-exposed individuals, wrote investigators led by gastroenterologist Cynthia H. Seow, MD, a professor in the Cumming School of Medicine at the University of Calgary in Alberta, Canada.
“Despite the well-established safety and effectiveness of non–live vaccination in individuals with IBD, including those on immunomodulators and biologic therapy, vaccine uptake in pregnant women with IBD and their infants remains suboptimal,” Seow said in an interview. This largely arises from maternal and physician concerns regarding transplacental transfer of IBD therapies and their impact on the safety of vaccination.
“These concerns were heightened after reports emerged of five fatal outcomes following the administration of the live Bacille Calmette-Guérin [BCG] vaccine in biologic-exposed infants. However, it had already been reported that inadvertent administration of the live oral rotavirus vaccine, a very different vaccine in terms of target and mechanism of action, in biologic-exposed individuals had not been associated with significant adverse effects,” she said.
They undertook their analysis with the hypothesis that vaccination would carry low risk, although the live oral vaccine is not currently recommended in biologic-exposed infants. “Yet rotavirus is a leading cause of severe, dehydrating diarrhea in children under the age of 5 years globally, and vaccination has led to significant reductions in hospitalizations and mortality,” Seow added.
Provision of the vaccine to anti–tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–exposed infants has been incorporated into the Canadian Public Health and Immunization guidelines, as the majority of the biologic-exposed infants were exposed to anti-TNF agents. “And with collection of further data, we expect that this will be extended to other biologic agent exposure. These data are important to pregnant women with IBD as they help to normalize their care. Pregnancy is difficult enough without having to remember exceptions to care,” Seow said.
“Before some of the studies came out, broad guidelines recommended that live vaccines should not be used in biologic-exposed infants, but this had been thought to be overly zealous and too conservative, and the risk was thought to be low,” said Elizabeth Spencer, MD, an assistant professor of pediatrics in the Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, in an interview. Spencer was not involved in the Canadian study.
“At our center, we had some moms on biologics during pregnancy who forgot and had their babies vaccinated for rotavirus, and the babies were all fine,” she said.
The safety of this vaccine has been confirmed by several small studies and recently the PIANO Helmsley Global Consensus on Pregnancy and Inflammatory Bowel Disease, which was presented at Digestive Disease Week 2024. The consensus encompasses preconception counseling and the safety of IBD medications during pregnancy and lactation.
“Another concern, however, was that giving a live GI bug like rotavirus to babies might overstimulate their immune systems and provoke IBD,” Spencer added. “While a number of population-based studies in the US and Europe showed that was not the case, at least in the general population, there was a suggestion that, down the road, vaccination might be mildly protective against IBD in some cases.”
She added the caveat that these studies were not done in mothers and their babies with IBD, who might be inherently at greater risk for IBD. “So, a question for future research would be, ‘Is immune stimulation of the gut in IBD moms and their babies a good or a bad thing for their gut?’ ”
Spencer conceded that “the data present a bit of a blurry picture, but I think it’s always better just to vaccinate according to the regular schedule. The current data say there is no added risk, but it would be nice to look specifically at risk in moms with IBD and their children.”
The Study
The prospective cohort study is a substudy of a larger 2023 one that included biologic use in a range of maternal illnesses, not just IBD.
For the current study, Seow and colleagues identified 57 infants born to 52 mothers with IBD attending a pregnancy clinic at the University of Calgary in the period 2019-2023. Almost 81% of the mothers had Crohn’s disease, and the median duration of IBD was 10 years. The median gestational age at delivery was 39 weeks, and almost 60% of deliveries were vaginal. The infants had been exposed in utero to infliximab (n = 21), adalimumab (n = 19), vedolizumab (n = 10), and ustekinumab (n = 7) in the third trimester.
The 57 biologic-exposed infants underwent standardized clinical assessments, drug concentration, and immune function testing. The live oral rotavirus vaccine series was provided to 50 infants, with the first dose at a median of 13 weeks of age. Immunologic assessments validated for age were normal in all infants despite median infliximab concentrations of 6.1 μg/mL (range, 0.4-28.8 μg/mL), adalimumab concentrations of 1.7 μg/mL (range, 0.7-7.9 μg/mL), ustekinumab concentrations of 0.6 μg/mL (range, 0-1.1), and undetectable for vedolizumab at 10.7 weeks of age.
As anticipated, infant immune function was normal regardless of circulating drug levels.
The overall message, said Seow, is “healthy mum equals healthy baby. Be more concerned regarding active inflammation than active medications. In almost all circumstances, treat to target in pregnancy as you would in the nonpregnant state.” She added, however, that further studies are needed to determine the safety and optimal timing of other live vaccines, such as the BCG, in the presence of biologic therapy.
This study was funded by the Alberta Children’s Hospital Research Institute. Seow reported advisory/speaker’s fees for Janssen, AbbVie, Takeda, Pfizer, Fresenius Kabi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pharmascience, and Lilly, as well as funding from Alberta Children’s Hospital Research Institute, Crohn’s and Colitis Canada, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and Calgary Health Trust, and data safety monitoring from New South Wales Government Health, Australia. Multiple coauthors disclosed similar consulting or speaker relationships with private industry. Spencer had no competing interests with regard to her comments.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No adverse events or impairment of the immune system emerged in babies at 7 days, 1 month, and 9 months post vaccination, in findings from a small Canadian study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
The study found normal extended immune function testing in infants despite third-trimester maternal biologic therapy and regardless of circulating drug levels. The data provide reassurance about live rotavirus vaccination in this population and may also offer insights into the safety of other live vaccines in biologic-exposed individuals, wrote investigators led by gastroenterologist Cynthia H. Seow, MD, a professor in the Cumming School of Medicine at the University of Calgary in Alberta, Canada.
“Despite the well-established safety and effectiveness of non–live vaccination in individuals with IBD, including those on immunomodulators and biologic therapy, vaccine uptake in pregnant women with IBD and their infants remains suboptimal,” Seow said in an interview. This largely arises from maternal and physician concerns regarding transplacental transfer of IBD therapies and their impact on the safety of vaccination.
“These concerns were heightened after reports emerged of five fatal outcomes following the administration of the live Bacille Calmette-Guérin [BCG] vaccine in biologic-exposed infants. However, it had already been reported that inadvertent administration of the live oral rotavirus vaccine, a very different vaccine in terms of target and mechanism of action, in biologic-exposed individuals had not been associated with significant adverse effects,” she said.
They undertook their analysis with the hypothesis that vaccination would carry low risk, although the live oral vaccine is not currently recommended in biologic-exposed infants. “Yet rotavirus is a leading cause of severe, dehydrating diarrhea in children under the age of 5 years globally, and vaccination has led to significant reductions in hospitalizations and mortality,” Seow added.
Provision of the vaccine to anti–tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–exposed infants has been incorporated into the Canadian Public Health and Immunization guidelines, as the majority of the biologic-exposed infants were exposed to anti-TNF agents. “And with collection of further data, we expect that this will be extended to other biologic agent exposure. These data are important to pregnant women with IBD as they help to normalize their care. Pregnancy is difficult enough without having to remember exceptions to care,” Seow said.
“Before some of the studies came out, broad guidelines recommended that live vaccines should not be used in biologic-exposed infants, but this had been thought to be overly zealous and too conservative, and the risk was thought to be low,” said Elizabeth Spencer, MD, an assistant professor of pediatrics in the Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, in an interview. Spencer was not involved in the Canadian study.
“At our center, we had some moms on biologics during pregnancy who forgot and had their babies vaccinated for rotavirus, and the babies were all fine,” she said.
The safety of this vaccine has been confirmed by several small studies and recently the PIANO Helmsley Global Consensus on Pregnancy and Inflammatory Bowel Disease, which was presented at Digestive Disease Week 2024. The consensus encompasses preconception counseling and the safety of IBD medications during pregnancy and lactation.
“Another concern, however, was that giving a live GI bug like rotavirus to babies might overstimulate their immune systems and provoke IBD,” Spencer added. “While a number of population-based studies in the US and Europe showed that was not the case, at least in the general population, there was a suggestion that, down the road, vaccination might be mildly protective against IBD in some cases.”
She added the caveat that these studies were not done in mothers and their babies with IBD, who might be inherently at greater risk for IBD. “So, a question for future research would be, ‘Is immune stimulation of the gut in IBD moms and their babies a good or a bad thing for their gut?’ ”
Spencer conceded that “the data present a bit of a blurry picture, but I think it’s always better just to vaccinate according to the regular schedule. The current data say there is no added risk, but it would be nice to look specifically at risk in moms with IBD and their children.”
The Study
The prospective cohort study is a substudy of a larger 2023 one that included biologic use in a range of maternal illnesses, not just IBD.
For the current study, Seow and colleagues identified 57 infants born to 52 mothers with IBD attending a pregnancy clinic at the University of Calgary in the period 2019-2023. Almost 81% of the mothers had Crohn’s disease, and the median duration of IBD was 10 years. The median gestational age at delivery was 39 weeks, and almost 60% of deliveries were vaginal. The infants had been exposed in utero to infliximab (n = 21), adalimumab (n = 19), vedolizumab (n = 10), and ustekinumab (n = 7) in the third trimester.
The 57 biologic-exposed infants underwent standardized clinical assessments, drug concentration, and immune function testing. The live oral rotavirus vaccine series was provided to 50 infants, with the first dose at a median of 13 weeks of age. Immunologic assessments validated for age were normal in all infants despite median infliximab concentrations of 6.1 μg/mL (range, 0.4-28.8 μg/mL), adalimumab concentrations of 1.7 μg/mL (range, 0.7-7.9 μg/mL), ustekinumab concentrations of 0.6 μg/mL (range, 0-1.1), and undetectable for vedolizumab at 10.7 weeks of age.
As anticipated, infant immune function was normal regardless of circulating drug levels.
The overall message, said Seow, is “healthy mum equals healthy baby. Be more concerned regarding active inflammation than active medications. In almost all circumstances, treat to target in pregnancy as you would in the nonpregnant state.” She added, however, that further studies are needed to determine the safety and optimal timing of other live vaccines, such as the BCG, in the presence of biologic therapy.
This study was funded by the Alberta Children’s Hospital Research Institute. Seow reported advisory/speaker’s fees for Janssen, AbbVie, Takeda, Pfizer, Fresenius Kabi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pharmascience, and Lilly, as well as funding from Alberta Children’s Hospital Research Institute, Crohn’s and Colitis Canada, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and Calgary Health Trust, and data safety monitoring from New South Wales Government Health, Australia. Multiple coauthors disclosed similar consulting or speaker relationships with private industry. Spencer had no competing interests with regard to her comments.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Maternal Serum Folate Levels During Pregnancy Linked to Congenital Heart Disease Risk
TOPLINE:
Maternal serum folate levels during early to midpregnancy show a U-shaped association with congenital heart disease (CHD) risk in offspring. Both low and high folate levels are linked to an increased risk, with vitamin B12 deficiency and elevated homocysteine levels further exacerbating this risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case-control study with 129 participants with CHD and 516 matched control participants from Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital in China between 2015 and 2018.
- Maternal serum levels of folate, vitamin B12, and homocysteine were measured at around 16 weeks of gestation using a chemiluminescence microparticle immunoassay.
- CHD was confirmed using echocardiography, and the participants were matched by maternal age at a ratio of 1:4.
- Covariates included periconceptional folic acid supplementation, maternal education, occupation, parity, abortion history, pregnancy complications, and genetic polymorphisms related to folate metabolism.
- Conditional logistic regression was used to assess the associations, with adjustments for various covariates and sensitivity analyses excluding participants with missing genetic data.
TAKEAWAY:
- A U-shaped association was found between maternal serum folate levels and CHD risk in offspring, with both low and high levels linked to increased risk (P < .001).
- Low maternal folate levels were associated with an adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of 3.09 (95% CI, 1.88-5.08) for CHD risk, whereas high levels had an aOR of 1.81 (95% CI, 1.07-3.06).
- Using World Health Organization criteria, folate deficiency (< 5.9 ng/mL) had an aOR of 18.97 (95% CI, 3.87-93.11) and elevated levels (> 20 ng/mL) had an aOR of 5.71 (95% CI, 2.72-11.98) for CHD risk.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency and elevated homocysteine levels further increased the risk associated with both low and high maternal folate levels.
IN PRACTICE:
“Insufficient folate and vitamin B12 can lead to increased homocysteine levels, which is harmful to the cardiovascular system. Thus, homocysteine might act as a central mediator in the relationships between deficiencies in folate and vitamin B12 and the risk of CHD. Additionally, the role of folate extends beyond homocysteine mediation, contributing independently to placental implantation and vascular remodeling, irrespective of vitamin B12 and homocysteine levels,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yanji Qu, PhD, and Jie Li, PhD, Global Health Research Center, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s limitations included the measurement of maternal serum folate levels at a single time point, which may not reflect preconception and early postconception periods. The study’s findings may not be generalizable to other populations as participants were recruited from a single cardiac referral center in Southern China. Additionally, the lack of dietary intake data limited the ability to account for related biases. The sample size, while relatively large for CHD research, may lack sufficient power for stratified analyses.
DISCLOSURES:
One coauthor reported receiving personal fees from Guangdong Cardiovascular Institute outside the submitted work. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Maternal serum folate levels during early to midpregnancy show a U-shaped association with congenital heart disease (CHD) risk in offspring. Both low and high folate levels are linked to an increased risk, with vitamin B12 deficiency and elevated homocysteine levels further exacerbating this risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case-control study with 129 participants with CHD and 516 matched control participants from Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital in China between 2015 and 2018.
- Maternal serum levels of folate, vitamin B12, and homocysteine were measured at around 16 weeks of gestation using a chemiluminescence microparticle immunoassay.
- CHD was confirmed using echocardiography, and the participants were matched by maternal age at a ratio of 1:4.
- Covariates included periconceptional folic acid supplementation, maternal education, occupation, parity, abortion history, pregnancy complications, and genetic polymorphisms related to folate metabolism.
- Conditional logistic regression was used to assess the associations, with adjustments for various covariates and sensitivity analyses excluding participants with missing genetic data.
TAKEAWAY:
- A U-shaped association was found between maternal serum folate levels and CHD risk in offspring, with both low and high levels linked to increased risk (P < .001).
- Low maternal folate levels were associated with an adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of 3.09 (95% CI, 1.88-5.08) for CHD risk, whereas high levels had an aOR of 1.81 (95% CI, 1.07-3.06).
- Using World Health Organization criteria, folate deficiency (< 5.9 ng/mL) had an aOR of 18.97 (95% CI, 3.87-93.11) and elevated levels (> 20 ng/mL) had an aOR of 5.71 (95% CI, 2.72-11.98) for CHD risk.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency and elevated homocysteine levels further increased the risk associated with both low and high maternal folate levels.
IN PRACTICE:
“Insufficient folate and vitamin B12 can lead to increased homocysteine levels, which is harmful to the cardiovascular system. Thus, homocysteine might act as a central mediator in the relationships between deficiencies in folate and vitamin B12 and the risk of CHD. Additionally, the role of folate extends beyond homocysteine mediation, contributing independently to placental implantation and vascular remodeling, irrespective of vitamin B12 and homocysteine levels,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yanji Qu, PhD, and Jie Li, PhD, Global Health Research Center, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s limitations included the measurement of maternal serum folate levels at a single time point, which may not reflect preconception and early postconception periods. The study’s findings may not be generalizable to other populations as participants were recruited from a single cardiac referral center in Southern China. Additionally, the lack of dietary intake data limited the ability to account for related biases. The sample size, while relatively large for CHD research, may lack sufficient power for stratified analyses.
DISCLOSURES:
One coauthor reported receiving personal fees from Guangdong Cardiovascular Institute outside the submitted work. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Maternal serum folate levels during early to midpregnancy show a U-shaped association with congenital heart disease (CHD) risk in offspring. Both low and high folate levels are linked to an increased risk, with vitamin B12 deficiency and elevated homocysteine levels further exacerbating this risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case-control study with 129 participants with CHD and 516 matched control participants from Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital in China between 2015 and 2018.
- Maternal serum levels of folate, vitamin B12, and homocysteine were measured at around 16 weeks of gestation using a chemiluminescence microparticle immunoassay.
- CHD was confirmed using echocardiography, and the participants were matched by maternal age at a ratio of 1:4.
- Covariates included periconceptional folic acid supplementation, maternal education, occupation, parity, abortion history, pregnancy complications, and genetic polymorphisms related to folate metabolism.
- Conditional logistic regression was used to assess the associations, with adjustments for various covariates and sensitivity analyses excluding participants with missing genetic data.
TAKEAWAY:
- A U-shaped association was found between maternal serum folate levels and CHD risk in offspring, with both low and high levels linked to increased risk (P < .001).
- Low maternal folate levels were associated with an adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of 3.09 (95% CI, 1.88-5.08) for CHD risk, whereas high levels had an aOR of 1.81 (95% CI, 1.07-3.06).
- Using World Health Organization criteria, folate deficiency (< 5.9 ng/mL) had an aOR of 18.97 (95% CI, 3.87-93.11) and elevated levels (> 20 ng/mL) had an aOR of 5.71 (95% CI, 2.72-11.98) for CHD risk.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency and elevated homocysteine levels further increased the risk associated with both low and high maternal folate levels.
IN PRACTICE:
“Insufficient folate and vitamin B12 can lead to increased homocysteine levels, which is harmful to the cardiovascular system. Thus, homocysteine might act as a central mediator in the relationships between deficiencies in folate and vitamin B12 and the risk of CHD. Additionally, the role of folate extends beyond homocysteine mediation, contributing independently to placental implantation and vascular remodeling, irrespective of vitamin B12 and homocysteine levels,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yanji Qu, PhD, and Jie Li, PhD, Global Health Research Center, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s limitations included the measurement of maternal serum folate levels at a single time point, which may not reflect preconception and early postconception periods. The study’s findings may not be generalizable to other populations as participants were recruited from a single cardiac referral center in Southern China. Additionally, the lack of dietary intake data limited the ability to account for related biases. The sample size, while relatively large for CHD research, may lack sufficient power for stratified analyses.
DISCLOSURES:
One coauthor reported receiving personal fees from Guangdong Cardiovascular Institute outside the submitted work. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Room for Improvement in Screening for Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Syphilis. It is often called the “great imitator.” It is speculated that this infection led to King George III of England going mad and likely contributing to his death. In the modern era, the discovery of penicillin in 1928 was instrumental in treating this once-deadly infection. Over the ensuing decades, rates of syphilis continued to decline. However, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, from 2018-2022 reported cases of syphilis in the United States have increased by 79% and continue to increase each year. Men who have sex with men (MSM) accounted for 41.4% of infections nationwide during this time period. This extraordinary rise highlights the need for better screening in our patients.
I currently live and practice in Texas, so I will use it as a case example. In 2013, Texas reported 1,471 cases of primary or secondary syphilis. By 2022, this number had risen to 4,655, a 216% increase. CDC data shows that Texas cases among men increased from 1,917 in 2019 to 3,324 in 2022, with MSM accounting for 1,341 (40%) of those infections. Adolescents and young adults aged 15-24 accounted for the second-highest number of new infections. Interestingly, rates of syphilis in men began to rise in Texas starting in 2013, the first full year that Truvada (emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) was available for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). While no definitive study has proven that the availability of PrEP caused an increase in condomless sexual intercourse, the number of high school students in Texas who did not use a condom at their last intercourse increased from 47.1% in 2013 to 50% in 2021.
The data above highlights the need to increase screening, especially in primary care and emergency room settings. According to the 2021 Youth Risk Behavior Survey, 94.8% of high school students surveyed that they were not tested for STIs in the 12 months prior to the survey. This compares with 91.4% in the 2019 survey. When STI testing is done, many adolescents often choose to forgo blood testing for HIV and syphilis and decide only to do urine NAATs testing for Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis. Therefore, those physicians and other healthcare providers who take care of adolescents and young adults must work to improve screening for ALL STIs. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics Bright Futures Periodicity Guidelines, pediatricians should screen for HIV in all patients at least once starting at age 15 and then thereafter based on risk assessment. Adding syphilis screening at the same time as the above HIV screening is an easy way to improve testing and treatment for this potentially deadly condition. If access to phlebotomy is not available, there are rapid HIV and syphilis tests that can be done in physicians’ offices. To perform these risk assessments, pediatricians must spend time alone with their adolescent and young patients at nearly every visit to discuss behaviors. Pediatricians should also be aware to consider syphilis on their differential for patients with unexplained rashes, sores in the mouth, or flu-like symptoms if that young person is sexually active.
Compounding the issue of increasing cases of syphilis is a national shortage of intramuscular penicillin G benzathine, the preferred treatment, which began in April 2023 only recently began to improve as of August 2024. Oral doxycycline can be used as a backup for some patients. Still, IM penicillin G is the only recommended treatment available for pregnant patients or those with advanced disease. The increasing number of cases, as well as the medication shortages, remind all of us that
Dr. M. Brett Cooper, is an assistant professor of pediatrics at University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, and an adolescent medicine specialist at Children’s Medical Center Dallas.
Syphilis. It is often called the “great imitator.” It is speculated that this infection led to King George III of England going mad and likely contributing to his death. In the modern era, the discovery of penicillin in 1928 was instrumental in treating this once-deadly infection. Over the ensuing decades, rates of syphilis continued to decline. However, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, from 2018-2022 reported cases of syphilis in the United States have increased by 79% and continue to increase each year. Men who have sex with men (MSM) accounted for 41.4% of infections nationwide during this time period. This extraordinary rise highlights the need for better screening in our patients.
I currently live and practice in Texas, so I will use it as a case example. In 2013, Texas reported 1,471 cases of primary or secondary syphilis. By 2022, this number had risen to 4,655, a 216% increase. CDC data shows that Texas cases among men increased from 1,917 in 2019 to 3,324 in 2022, with MSM accounting for 1,341 (40%) of those infections. Adolescents and young adults aged 15-24 accounted for the second-highest number of new infections. Interestingly, rates of syphilis in men began to rise in Texas starting in 2013, the first full year that Truvada (emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) was available for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). While no definitive study has proven that the availability of PrEP caused an increase in condomless sexual intercourse, the number of high school students in Texas who did not use a condom at their last intercourse increased from 47.1% in 2013 to 50% in 2021.
The data above highlights the need to increase screening, especially in primary care and emergency room settings. According to the 2021 Youth Risk Behavior Survey, 94.8% of high school students surveyed that they were not tested for STIs in the 12 months prior to the survey. This compares with 91.4% in the 2019 survey. When STI testing is done, many adolescents often choose to forgo blood testing for HIV and syphilis and decide only to do urine NAATs testing for Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis. Therefore, those physicians and other healthcare providers who take care of adolescents and young adults must work to improve screening for ALL STIs. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics Bright Futures Periodicity Guidelines, pediatricians should screen for HIV in all patients at least once starting at age 15 and then thereafter based on risk assessment. Adding syphilis screening at the same time as the above HIV screening is an easy way to improve testing and treatment for this potentially deadly condition. If access to phlebotomy is not available, there are rapid HIV and syphilis tests that can be done in physicians’ offices. To perform these risk assessments, pediatricians must spend time alone with their adolescent and young patients at nearly every visit to discuss behaviors. Pediatricians should also be aware to consider syphilis on their differential for patients with unexplained rashes, sores in the mouth, or flu-like symptoms if that young person is sexually active.
Compounding the issue of increasing cases of syphilis is a national shortage of intramuscular penicillin G benzathine, the preferred treatment, which began in April 2023 only recently began to improve as of August 2024. Oral doxycycline can be used as a backup for some patients. Still, IM penicillin G is the only recommended treatment available for pregnant patients or those with advanced disease. The increasing number of cases, as well as the medication shortages, remind all of us that
Dr. M. Brett Cooper, is an assistant professor of pediatrics at University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, and an adolescent medicine specialist at Children’s Medical Center Dallas.
Syphilis. It is often called the “great imitator.” It is speculated that this infection led to King George III of England going mad and likely contributing to his death. In the modern era, the discovery of penicillin in 1928 was instrumental in treating this once-deadly infection. Over the ensuing decades, rates of syphilis continued to decline. However, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, from 2018-2022 reported cases of syphilis in the United States have increased by 79% and continue to increase each year. Men who have sex with men (MSM) accounted for 41.4% of infections nationwide during this time period. This extraordinary rise highlights the need for better screening in our patients.
I currently live and practice in Texas, so I will use it as a case example. In 2013, Texas reported 1,471 cases of primary or secondary syphilis. By 2022, this number had risen to 4,655, a 216% increase. CDC data shows that Texas cases among men increased from 1,917 in 2019 to 3,324 in 2022, with MSM accounting for 1,341 (40%) of those infections. Adolescents and young adults aged 15-24 accounted for the second-highest number of new infections. Interestingly, rates of syphilis in men began to rise in Texas starting in 2013, the first full year that Truvada (emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) was available for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). While no definitive study has proven that the availability of PrEP caused an increase in condomless sexual intercourse, the number of high school students in Texas who did not use a condom at their last intercourse increased from 47.1% in 2013 to 50% in 2021.
The data above highlights the need to increase screening, especially in primary care and emergency room settings. According to the 2021 Youth Risk Behavior Survey, 94.8% of high school students surveyed that they were not tested for STIs in the 12 months prior to the survey. This compares with 91.4% in the 2019 survey. When STI testing is done, many adolescents often choose to forgo blood testing for HIV and syphilis and decide only to do urine NAATs testing for Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis. Therefore, those physicians and other healthcare providers who take care of adolescents and young adults must work to improve screening for ALL STIs. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics Bright Futures Periodicity Guidelines, pediatricians should screen for HIV in all patients at least once starting at age 15 and then thereafter based on risk assessment. Adding syphilis screening at the same time as the above HIV screening is an easy way to improve testing and treatment for this potentially deadly condition. If access to phlebotomy is not available, there are rapid HIV and syphilis tests that can be done in physicians’ offices. To perform these risk assessments, pediatricians must spend time alone with their adolescent and young patients at nearly every visit to discuss behaviors. Pediatricians should also be aware to consider syphilis on their differential for patients with unexplained rashes, sores in the mouth, or flu-like symptoms if that young person is sexually active.
Compounding the issue of increasing cases of syphilis is a national shortage of intramuscular penicillin G benzathine, the preferred treatment, which began in April 2023 only recently began to improve as of August 2024. Oral doxycycline can be used as a backup for some patients. Still, IM penicillin G is the only recommended treatment available for pregnant patients or those with advanced disease. The increasing number of cases, as well as the medication shortages, remind all of us that
Dr. M. Brett Cooper, is an assistant professor of pediatrics at University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, and an adolescent medicine specialist at Children’s Medical Center Dallas.
A 7-Year-Old Boy Presents With Dark Spots on His Scalp and Areas of Poor Hair Growth
Given the trichoscopic findings, scrapings from the scaly areas were taken and revealed hyphae, confirming the diagnosis of tinea capitis. A fungal culture identified Trichophyton tonsurans as the causative organism.
Tinea capitis is the most common dermatophyte infection in children. Risk factors include participation in close-contact sports like wrestling or jiu-jitsu, attendance at daycare for younger children, African American hair care practices, pet ownership (particularly cats and rodents), and living in overcrowded conditions.
Diagnosis of tinea capitis requires a thorough clinical history to identify potential risk factors. On physical examination, patchy hair loss with associated scaling should raise suspicion for tinea capitis. Inflammatory signs, such as pustules and swelling, may suggest the presence of a kerion, further supporting the diagnosis. Although some practitioners use Wood’s lamp to help with diagnosis, its utility is limited. It detects fluorescence in Microsporum species (exothrix infections) but not in Trichophyton species (endothrix infections).
Trichoscopy can be a valuable tool when inflammation is minimal, and only hair loss and scaling are observed. Trichoscopic findings suggestive of tinea capitis include comma hairs, corkscrew hairs (as seen in this patient), Morse code-like hairs, zigzag hairs, bent hairs, block hairs, and i-hairs. Other common, though not characteristic, findings include broken hairs, black dots, perifollicular scaling, and diffuse scaling.
KOH (potassium hydroxide) analysis is another useful method for detecting fungal elements, though it does not identify the specific fungus and may not be available in all clinical settings. Mycologic culture remains the gold standard for diagnosing tinea capitis, though results can take 3-4 weeks. Newer diagnostic techniques, such as PCR analysis and MALDI-TOF/MS, offer more rapid identification of the causative organism.
The differential diagnosis includes:
- Seborrheic dermatitis, which presents with greasy, yellowish scales and itching, with trichoscopy showing twisted, coiled hairs and yellowish scaling.
- Psoriasis, which can mimic tinea capitis but presents with well-demarcated red plaques and silvery-white scales. Trichoscopy shows red dots and uniform scaling.
- Alopecia areata, which causes patchy hair loss without inflammation or scaling, with trichoscopic findings of exclamation mark hairs, black dots, and yellow dots.
- Trichotillomania, a hair-pulling disorder, which results in irregular patches of hair loss. Trichoscopy shows broken hairs of varying lengths, V-sign hairs, and flame-shaped residues at follicular openings.
Treatment of tinea capitis requires systemic antifungals and topical agents to prevent fungal spore spread. Several treatment guidelines are available from different institutions. Griseofulvin (FDA-approved for patients > 2 years of age) has been widely used, particularly for Microsporum canis infections. However, due to limited availability in many countries, terbinafine (FDA-approved for patients > 4 years of age) is now commonly used as first-line therapy, especially for Trichophyton species. Treatment typically lasts 4-6 weeks, and post-treatment cultures may be recommended to confirm mycologic cure.
Concerns about drug resistance have emerged, particularly for terbinafine-resistant dermatophytes linked to mutations in the squalene epoxidase enzyme. Resistance may be driven by limited antifungal availability and poor adherence to prolonged treatment regimens. While fluconazole and itraconazole are used off-label, growing evidence supports their effectiveness, although one large trial showed suboptimal cure rates with fluconazole.
Though systemic antifungals are generally safe, hepatotoxicity remains a concern, especially in patients with hepatic conditions or other comorbidities. Lab monitoring is advised for patients on prolonged or multiple therapies, or for those with coexisting conditions. The decision to conduct lab monitoring should be discussed with parents, balancing the very low risk of hepatotoxicity in healthy children against their comfort level.
An alternative to systemic therapy is photodynamic therapy (PDT), which has been reported as successful in treating tinea capitis infections, particularly in cases of T. mentagrophytes and M. canis. However, large-scale trials are needed to confirm PDT’s efficacy and safety.
In conclusion, children presenting with hair loss, scaling, and associated dark spots on the scalp should be evaluated for fungal infection. While trichoscopy can aid in diagnosis, fungal culture remains the gold standard for confirmation.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Rudnicka L et al. Hair shafts in trichoscopy: clues for diagnosis of hair and scalp diseases. Dermatol Clin. 2013 Oct;31(4):695-708, x. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2013.06.007.
Gupta AK et al. An update on tinea capitis in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2024 Aug 7. doi: 10.1111/pde.15708.
Anna Waskiel-Burnat et al. Trichoscopy of tinea capitis: A systematic review. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020 Feb;10(1):43-52. doi: 10.1007/s13555-019-00350-1.
Given the trichoscopic findings, scrapings from the scaly areas were taken and revealed hyphae, confirming the diagnosis of tinea capitis. A fungal culture identified Trichophyton tonsurans as the causative organism.
Tinea capitis is the most common dermatophyte infection in children. Risk factors include participation in close-contact sports like wrestling or jiu-jitsu, attendance at daycare for younger children, African American hair care practices, pet ownership (particularly cats and rodents), and living in overcrowded conditions.
Diagnosis of tinea capitis requires a thorough clinical history to identify potential risk factors. On physical examination, patchy hair loss with associated scaling should raise suspicion for tinea capitis. Inflammatory signs, such as pustules and swelling, may suggest the presence of a kerion, further supporting the diagnosis. Although some practitioners use Wood’s lamp to help with diagnosis, its utility is limited. It detects fluorescence in Microsporum species (exothrix infections) but not in Trichophyton species (endothrix infections).
Trichoscopy can be a valuable tool when inflammation is minimal, and only hair loss and scaling are observed. Trichoscopic findings suggestive of tinea capitis include comma hairs, corkscrew hairs (as seen in this patient), Morse code-like hairs, zigzag hairs, bent hairs, block hairs, and i-hairs. Other common, though not characteristic, findings include broken hairs, black dots, perifollicular scaling, and diffuse scaling.
KOH (potassium hydroxide) analysis is another useful method for detecting fungal elements, though it does not identify the specific fungus and may not be available in all clinical settings. Mycologic culture remains the gold standard for diagnosing tinea capitis, though results can take 3-4 weeks. Newer diagnostic techniques, such as PCR analysis and MALDI-TOF/MS, offer more rapid identification of the causative organism.
The differential diagnosis includes:
- Seborrheic dermatitis, which presents with greasy, yellowish scales and itching, with trichoscopy showing twisted, coiled hairs and yellowish scaling.
- Psoriasis, which can mimic tinea capitis but presents with well-demarcated red plaques and silvery-white scales. Trichoscopy shows red dots and uniform scaling.
- Alopecia areata, which causes patchy hair loss without inflammation or scaling, with trichoscopic findings of exclamation mark hairs, black dots, and yellow dots.
- Trichotillomania, a hair-pulling disorder, which results in irregular patches of hair loss. Trichoscopy shows broken hairs of varying lengths, V-sign hairs, and flame-shaped residues at follicular openings.
Treatment of tinea capitis requires systemic antifungals and topical agents to prevent fungal spore spread. Several treatment guidelines are available from different institutions. Griseofulvin (FDA-approved for patients > 2 years of age) has been widely used, particularly for Microsporum canis infections. However, due to limited availability in many countries, terbinafine (FDA-approved for patients > 4 years of age) is now commonly used as first-line therapy, especially for Trichophyton species. Treatment typically lasts 4-6 weeks, and post-treatment cultures may be recommended to confirm mycologic cure.
Concerns about drug resistance have emerged, particularly for terbinafine-resistant dermatophytes linked to mutations in the squalene epoxidase enzyme. Resistance may be driven by limited antifungal availability and poor adherence to prolonged treatment regimens. While fluconazole and itraconazole are used off-label, growing evidence supports their effectiveness, although one large trial showed suboptimal cure rates with fluconazole.
Though systemic antifungals are generally safe, hepatotoxicity remains a concern, especially in patients with hepatic conditions or other comorbidities. Lab monitoring is advised for patients on prolonged or multiple therapies, or for those with coexisting conditions. The decision to conduct lab monitoring should be discussed with parents, balancing the very low risk of hepatotoxicity in healthy children against their comfort level.
An alternative to systemic therapy is photodynamic therapy (PDT), which has been reported as successful in treating tinea capitis infections, particularly in cases of T. mentagrophytes and M. canis. However, large-scale trials are needed to confirm PDT’s efficacy and safety.
In conclusion, children presenting with hair loss, scaling, and associated dark spots on the scalp should be evaluated for fungal infection. While trichoscopy can aid in diagnosis, fungal culture remains the gold standard for confirmation.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Rudnicka L et al. Hair shafts in trichoscopy: clues for diagnosis of hair and scalp diseases. Dermatol Clin. 2013 Oct;31(4):695-708, x. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2013.06.007.
Gupta AK et al. An update on tinea capitis in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2024 Aug 7. doi: 10.1111/pde.15708.
Anna Waskiel-Burnat et al. Trichoscopy of tinea capitis: A systematic review. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020 Feb;10(1):43-52. doi: 10.1007/s13555-019-00350-1.
Given the trichoscopic findings, scrapings from the scaly areas were taken and revealed hyphae, confirming the diagnosis of tinea capitis. A fungal culture identified Trichophyton tonsurans as the causative organism.
Tinea capitis is the most common dermatophyte infection in children. Risk factors include participation in close-contact sports like wrestling or jiu-jitsu, attendance at daycare for younger children, African American hair care practices, pet ownership (particularly cats and rodents), and living in overcrowded conditions.
Diagnosis of tinea capitis requires a thorough clinical history to identify potential risk factors. On physical examination, patchy hair loss with associated scaling should raise suspicion for tinea capitis. Inflammatory signs, such as pustules and swelling, may suggest the presence of a kerion, further supporting the diagnosis. Although some practitioners use Wood’s lamp to help with diagnosis, its utility is limited. It detects fluorescence in Microsporum species (exothrix infections) but not in Trichophyton species (endothrix infections).
Trichoscopy can be a valuable tool when inflammation is minimal, and only hair loss and scaling are observed. Trichoscopic findings suggestive of tinea capitis include comma hairs, corkscrew hairs (as seen in this patient), Morse code-like hairs, zigzag hairs, bent hairs, block hairs, and i-hairs. Other common, though not characteristic, findings include broken hairs, black dots, perifollicular scaling, and diffuse scaling.
KOH (potassium hydroxide) analysis is another useful method for detecting fungal elements, though it does not identify the specific fungus and may not be available in all clinical settings. Mycologic culture remains the gold standard for diagnosing tinea capitis, though results can take 3-4 weeks. Newer diagnostic techniques, such as PCR analysis and MALDI-TOF/MS, offer more rapid identification of the causative organism.
The differential diagnosis includes:
- Seborrheic dermatitis, which presents with greasy, yellowish scales and itching, with trichoscopy showing twisted, coiled hairs and yellowish scaling.
- Psoriasis, which can mimic tinea capitis but presents with well-demarcated red plaques and silvery-white scales. Trichoscopy shows red dots and uniform scaling.
- Alopecia areata, which causes patchy hair loss without inflammation or scaling, with trichoscopic findings of exclamation mark hairs, black dots, and yellow dots.
- Trichotillomania, a hair-pulling disorder, which results in irregular patches of hair loss. Trichoscopy shows broken hairs of varying lengths, V-sign hairs, and flame-shaped residues at follicular openings.
Treatment of tinea capitis requires systemic antifungals and topical agents to prevent fungal spore spread. Several treatment guidelines are available from different institutions. Griseofulvin (FDA-approved for patients > 2 years of age) has been widely used, particularly for Microsporum canis infections. However, due to limited availability in many countries, terbinafine (FDA-approved for patients > 4 years of age) is now commonly used as first-line therapy, especially for Trichophyton species. Treatment typically lasts 4-6 weeks, and post-treatment cultures may be recommended to confirm mycologic cure.
Concerns about drug resistance have emerged, particularly for terbinafine-resistant dermatophytes linked to mutations in the squalene epoxidase enzyme. Resistance may be driven by limited antifungal availability and poor adherence to prolonged treatment regimens. While fluconazole and itraconazole are used off-label, growing evidence supports their effectiveness, although one large trial showed suboptimal cure rates with fluconazole.
Though systemic antifungals are generally safe, hepatotoxicity remains a concern, especially in patients with hepatic conditions or other comorbidities. Lab monitoring is advised for patients on prolonged or multiple therapies, or for those with coexisting conditions. The decision to conduct lab monitoring should be discussed with parents, balancing the very low risk of hepatotoxicity in healthy children against their comfort level.
An alternative to systemic therapy is photodynamic therapy (PDT), which has been reported as successful in treating tinea capitis infections, particularly in cases of T. mentagrophytes and M. canis. However, large-scale trials are needed to confirm PDT’s efficacy and safety.
In conclusion, children presenting with hair loss, scaling, and associated dark spots on the scalp should be evaluated for fungal infection. While trichoscopy can aid in diagnosis, fungal culture remains the gold standard for confirmation.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Rudnicka L et al. Hair shafts in trichoscopy: clues for diagnosis of hair and scalp diseases. Dermatol Clin. 2013 Oct;31(4):695-708, x. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2013.06.007.
Gupta AK et al. An update on tinea capitis in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2024 Aug 7. doi: 10.1111/pde.15708.
Anna Waskiel-Burnat et al. Trichoscopy of tinea capitis: A systematic review. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020 Feb;10(1):43-52. doi: 10.1007/s13555-019-00350-1.