User login
Woman with throbbing unilateral headache
Migraine is a complex disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of headache, most often unilateral and in some cases associated with photophobia or phonophobia — a constellation known as aura — that usually arises before the head pain but may also occur during or afterward. Migraine is most common in women, and prevalence peaks between the ages of 25 and 55. In 2016, headache was the fifth most common reason for an ED visit and the third most common reason for an ED visit among female patients age 15-64.
Diagnosis of migraine is made on the basis of patient history. Examples of red flags in the differential would be the presence of neurologic symptoms, stiff neck, or fever, or history of head injury or major trauma. Migraine should also be distinguished from other common headaches. Tension-type headaches usually cause mild or moderate bilateral pain, with a deep, steady ache rather than the typical throbbing quality of migraine headache. In cluster headache, the patient experiences attacks of severe or very severe, strictly unilateral pain (orbital, supraorbital, or temporal pain), but the cadence of these headaches differs from that of migraines; these attacks last 15-180 minutes and occur from once every other day to eight times a day. Patients with basilar migraine, common among female patients, usually present with symptoms of vertebrobasilar insufficiency.
The American Headache Society defines migraine as when a patient reports at least five attacks. These episodes must last 4-72 hours and have at least two of these four characteristics: unilateral location, pulsating quality, moderate or severe pain intensity, and aggravation by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity. In addition, during attacks, the patient must experience either nausea and/or vomiting or photophobia and phonophobia. Signs and symptoms cannot be accounted for by another diagnosis.
Treatment of migraines is often associated with a trial-and-error period. For mild to moderate migraines, these agents may be considered: NSAIDs, nonopioid analgesics, acetaminophen, or caffeinated analgesic combinations. For moderate or severe attacks, or even mild to moderate attacks that do not respond well to therapy, migraine-specific agents are recommended: triptans, dihydroergotamine (DHE), small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists (gepants), and selective serotonin (5-HT1F) receptor agonists (ditans). Menstrual migraines are treated via the same approaches as nonmenstrual migraines.
Many patients, like the one described here, experience severe nausea or vomiting with their migraine attacks. For these cases, nonoral agents may be considered (these agents are also an option for patients whose headaches do not respond well to traditional oral medication). Patients should be advised to limit medication use to an average of two headache days per week, and those who feel it necessary to exceed this limit should be offered a preventive treatment.
Angeliki Vgontzas, MD, Instructor, Department of Neurology, Harvard Medical School; Associate Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Brigham and Women's Hospital/Brigham and Women's Faulkner Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts.
Angeliki Vgontzas, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Migraine is a complex disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of headache, most often unilateral and in some cases associated with photophobia or phonophobia — a constellation known as aura — that usually arises before the head pain but may also occur during or afterward. Migraine is most common in women, and prevalence peaks between the ages of 25 and 55. In 2016, headache was the fifth most common reason for an ED visit and the third most common reason for an ED visit among female patients age 15-64.
Diagnosis of migraine is made on the basis of patient history. Examples of red flags in the differential would be the presence of neurologic symptoms, stiff neck, or fever, or history of head injury or major trauma. Migraine should also be distinguished from other common headaches. Tension-type headaches usually cause mild or moderate bilateral pain, with a deep, steady ache rather than the typical throbbing quality of migraine headache. In cluster headache, the patient experiences attacks of severe or very severe, strictly unilateral pain (orbital, supraorbital, or temporal pain), but the cadence of these headaches differs from that of migraines; these attacks last 15-180 minutes and occur from once every other day to eight times a day. Patients with basilar migraine, common among female patients, usually present with symptoms of vertebrobasilar insufficiency.
The American Headache Society defines migraine as when a patient reports at least five attacks. These episodes must last 4-72 hours and have at least two of these four characteristics: unilateral location, pulsating quality, moderate or severe pain intensity, and aggravation by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity. In addition, during attacks, the patient must experience either nausea and/or vomiting or photophobia and phonophobia. Signs and symptoms cannot be accounted for by another diagnosis.
Treatment of migraines is often associated with a trial-and-error period. For mild to moderate migraines, these agents may be considered: NSAIDs, nonopioid analgesics, acetaminophen, or caffeinated analgesic combinations. For moderate or severe attacks, or even mild to moderate attacks that do not respond well to therapy, migraine-specific agents are recommended: triptans, dihydroergotamine (DHE), small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists (gepants), and selective serotonin (5-HT1F) receptor agonists (ditans). Menstrual migraines are treated via the same approaches as nonmenstrual migraines.
Many patients, like the one described here, experience severe nausea or vomiting with their migraine attacks. For these cases, nonoral agents may be considered (these agents are also an option for patients whose headaches do not respond well to traditional oral medication). Patients should be advised to limit medication use to an average of two headache days per week, and those who feel it necessary to exceed this limit should be offered a preventive treatment.
Angeliki Vgontzas, MD, Instructor, Department of Neurology, Harvard Medical School; Associate Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Brigham and Women's Hospital/Brigham and Women's Faulkner Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts.
Angeliki Vgontzas, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Migraine is a complex disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of headache, most often unilateral and in some cases associated with photophobia or phonophobia — a constellation known as aura — that usually arises before the head pain but may also occur during or afterward. Migraine is most common in women, and prevalence peaks between the ages of 25 and 55. In 2016, headache was the fifth most common reason for an ED visit and the third most common reason for an ED visit among female patients age 15-64.
Diagnosis of migraine is made on the basis of patient history. Examples of red flags in the differential would be the presence of neurologic symptoms, stiff neck, or fever, or history of head injury or major trauma. Migraine should also be distinguished from other common headaches. Tension-type headaches usually cause mild or moderate bilateral pain, with a deep, steady ache rather than the typical throbbing quality of migraine headache. In cluster headache, the patient experiences attacks of severe or very severe, strictly unilateral pain (orbital, supraorbital, or temporal pain), but the cadence of these headaches differs from that of migraines; these attacks last 15-180 minutes and occur from once every other day to eight times a day. Patients with basilar migraine, common among female patients, usually present with symptoms of vertebrobasilar insufficiency.
The American Headache Society defines migraine as when a patient reports at least five attacks. These episodes must last 4-72 hours and have at least two of these four characteristics: unilateral location, pulsating quality, moderate or severe pain intensity, and aggravation by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity. In addition, during attacks, the patient must experience either nausea and/or vomiting or photophobia and phonophobia. Signs and symptoms cannot be accounted for by another diagnosis.
Treatment of migraines is often associated with a trial-and-error period. For mild to moderate migraines, these agents may be considered: NSAIDs, nonopioid analgesics, acetaminophen, or caffeinated analgesic combinations. For moderate or severe attacks, or even mild to moderate attacks that do not respond well to therapy, migraine-specific agents are recommended: triptans, dihydroergotamine (DHE), small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists (gepants), and selective serotonin (5-HT1F) receptor agonists (ditans). Menstrual migraines are treated via the same approaches as nonmenstrual migraines.
Many patients, like the one described here, experience severe nausea or vomiting with their migraine attacks. For these cases, nonoral agents may be considered (these agents are also an option for patients whose headaches do not respond well to traditional oral medication). Patients should be advised to limit medication use to an average of two headache days per week, and those who feel it necessary to exceed this limit should be offered a preventive treatment.
Angeliki Vgontzas, MD, Instructor, Department of Neurology, Harvard Medical School; Associate Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Brigham and Women's Hospital/Brigham and Women's Faulkner Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts.
Angeliki Vgontzas, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
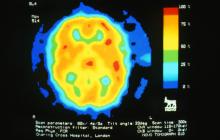
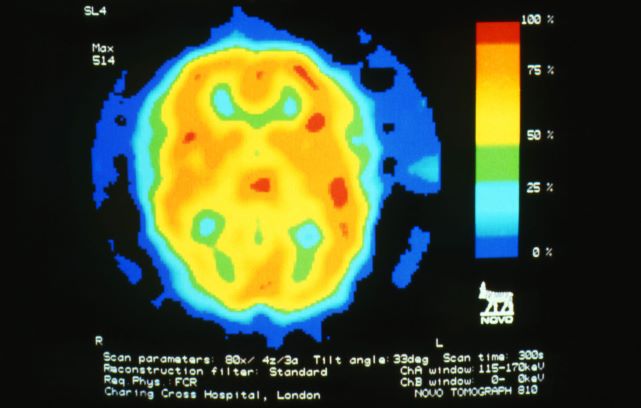
A 28-year-old woman presents with a throbbing unilateral headache (left side) and is very nauseated. She describes a white light in her line of vision. Her headaches are recurring, pulsating, and usually last for about 2 days without relief from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). She has been experiencing these episodes almost every month for the past 8 months and initially attributed them to her menstrual cycle, as she has always experienced moderate to severe headaches during this time. The patient is enrolled in a research trial in which single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging revealed low activity with reduced blood flow. The patient is nonfebrile.
Migraine Presentation and Diagnosis
Severe pain in the frontotemporal area
Migraine is a neurologic disease characterized by episodes of throbbing, often unilateral, headache. These attacks are associated with visual or other sensory symptoms (classic aura) related to the central nervous system, nausea, and vomiting, and are often set off or exacerbated by physical activity. The age-adjusted prevalence is estimated at 15.9% across all adults, but migraine is much more common in women, with a prevalence of 21% in women and 10.7% in men.
On the basis of the patient's history, clinical suspicion for chronic migraine should be high. Hemiplegic migraine usually presents with temporary unilateral hemiparesis, sometimes with speech disturbance. Attacks of chronic paroxysmal hemicrania are also unilateral but are characterized by their highly intense but short duration. Clinical suspicion for a space-occupying lesion should be raised in cases where patients with a history of headache present with new symptoms or abnormal signs.
The diagnosis of chronic migraine is a clinical one. The American Headache Society defines chronic migraine as at least five attacks of migraine-like or tension type–like headache that must fulfill specific criteria. If the migraine occurs with aura, it must occur 8 days or more per month for more than 3 months and be relieved by a triptan or ergot derivative. If the migraine occurs without aura, the same criteria apply, but it is important that the aforementioned signs and symptoms cannot be accounted for by another diagnosis.
For moderate or severe attacks, migraine-specific agents are recommended: triptans, dihydroergotamine (DHE), small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists (gepants), and selective serotonin (5-HT1F) receptor agonists (ditans). However, it is accepted that migraine treatment must be individualized, and that a trial-and-error period should be expected. Recent data suggest that about 30% of migraine patients who are prescribed a triptan have an insufficient response to this approach. Some research has shown that such patients have a better response after being switched to a second drug in the triptan class, while other studies have shown no difference. The patient in the current case might also be a candidate for preventive treatment, which should generally be considered when, in spite of acute treatment, migraine interferes with the patient's day-to-day routine or when attacks become frequent. The four CGRP monoclonal antibodies approved in the United States are eptinezumab, erenumab, fremanezumab, and galcanezumab.
Angeliki Vgontzas, MD, Instructor, Department of Neurology, Harvard Medical School; Associate Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Brigham and Women's Hospital/Brigham and Women's Faulkner Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts.
Angeliki Vgontzas, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Migraine is a neurologic disease characterized by episodes of throbbing, often unilateral, headache. These attacks are associated with visual or other sensory symptoms (classic aura) related to the central nervous system, nausea, and vomiting, and are often set off or exacerbated by physical activity. The age-adjusted prevalence is estimated at 15.9% across all adults, but migraine is much more common in women, with a prevalence of 21% in women and 10.7% in men.
On the basis of the patient's history, clinical suspicion for chronic migraine should be high. Hemiplegic migraine usually presents with temporary unilateral hemiparesis, sometimes with speech disturbance. Attacks of chronic paroxysmal hemicrania are also unilateral but are characterized by their highly intense but short duration. Clinical suspicion for a space-occupying lesion should be raised in cases where patients with a history of headache present with new symptoms or abnormal signs.
The diagnosis of chronic migraine is a clinical one. The American Headache Society defines chronic migraine as at least five attacks of migraine-like or tension type–like headache that must fulfill specific criteria. If the migraine occurs with aura, it must occur 8 days or more per month for more than 3 months and be relieved by a triptan or ergot derivative. If the migraine occurs without aura, the same criteria apply, but it is important that the aforementioned signs and symptoms cannot be accounted for by another diagnosis.
For moderate or severe attacks, migraine-specific agents are recommended: triptans, dihydroergotamine (DHE), small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists (gepants), and selective serotonin (5-HT1F) receptor agonists (ditans). However, it is accepted that migraine treatment must be individualized, and that a trial-and-error period should be expected. Recent data suggest that about 30% of migraine patients who are prescribed a triptan have an insufficient response to this approach. Some research has shown that such patients have a better response after being switched to a second drug in the triptan class, while other studies have shown no difference. The patient in the current case might also be a candidate for preventive treatment, which should generally be considered when, in spite of acute treatment, migraine interferes with the patient's day-to-day routine or when attacks become frequent. The four CGRP monoclonal antibodies approved in the United States are eptinezumab, erenumab, fremanezumab, and galcanezumab.
Angeliki Vgontzas, MD, Instructor, Department of Neurology, Harvard Medical School; Associate Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Brigham and Women's Hospital/Brigham and Women's Faulkner Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts.
Angeliki Vgontzas, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Migraine is a neurologic disease characterized by episodes of throbbing, often unilateral, headache. These attacks are associated with visual or other sensory symptoms (classic aura) related to the central nervous system, nausea, and vomiting, and are often set off or exacerbated by physical activity. The age-adjusted prevalence is estimated at 15.9% across all adults, but migraine is much more common in women, with a prevalence of 21% in women and 10.7% in men.
On the basis of the patient's history, clinical suspicion for chronic migraine should be high. Hemiplegic migraine usually presents with temporary unilateral hemiparesis, sometimes with speech disturbance. Attacks of chronic paroxysmal hemicrania are also unilateral but are characterized by their highly intense but short duration. Clinical suspicion for a space-occupying lesion should be raised in cases where patients with a history of headache present with new symptoms or abnormal signs.
The diagnosis of chronic migraine is a clinical one. The American Headache Society defines chronic migraine as at least five attacks of migraine-like or tension type–like headache that must fulfill specific criteria. If the migraine occurs with aura, it must occur 8 days or more per month for more than 3 months and be relieved by a triptan or ergot derivative. If the migraine occurs without aura, the same criteria apply, but it is important that the aforementioned signs and symptoms cannot be accounted for by another diagnosis.
For moderate or severe attacks, migraine-specific agents are recommended: triptans, dihydroergotamine (DHE), small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists (gepants), and selective serotonin (5-HT1F) receptor agonists (ditans). However, it is accepted that migraine treatment must be individualized, and that a trial-and-error period should be expected. Recent data suggest that about 30% of migraine patients who are prescribed a triptan have an insufficient response to this approach. Some research has shown that such patients have a better response after being switched to a second drug in the triptan class, while other studies have shown no difference. The patient in the current case might also be a candidate for preventive treatment, which should generally be considered when, in spite of acute treatment, migraine interferes with the patient's day-to-day routine or when attacks become frequent. The four CGRP monoclonal antibodies approved in the United States are eptinezumab, erenumab, fremanezumab, and galcanezumab.
Angeliki Vgontzas, MD, Instructor, Department of Neurology, Harvard Medical School; Associate Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Brigham and Women's Hospital/Brigham and Women's Faulkner Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts.
Angeliki Vgontzas, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
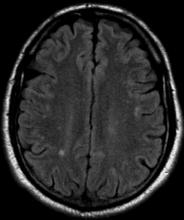
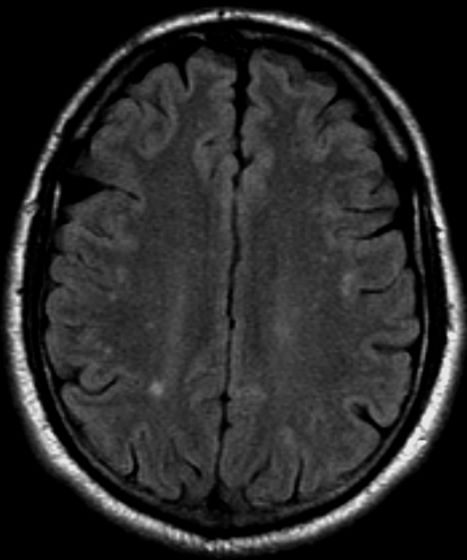
A 36-year-old man presents with severe pain in the frontotemporal area. He reports a history of severe headaches, sometimes with nausea. In the past year, these symptoms have begun to "knock him out" for nearly 2 weeks out of a month. The patient historically has been able to curtail his symptoms with a triptan. Physical examination is remarkable for Adie tonic pupil. A 1.5 T MRI of the brain is performed. Axial FLAIR sequence reveals scattered white matter lesions consistent with foci of demyelination.