User login
Caught in the Hotbox
A 19-year-old woman presented to the emergency department (ED) with a 14-day history of progressive fevers, night sweats, abdominal pain, nonbloody and nonbilious vomiting, diarrhea, cough, and myalgia. The fever occurred daily with no noted temporal pattern, and she had no significant weight loss. The abdominal pain was diffuse and exacerbated by eating. She experienced multiple sporadic episodes of vomiting and diarrhea daily. She denied any rash or arthralgia.
She had no known medical history and took no medications. Family history was negative for autoinflammatory and autoimmune conditions. She had emigrated from Kenya to the United States 28 days ago. Her immunization status was unknown.
This patient has prolonged fevers and evidence of multisystem involvement. The most likely etiologic categories are infectious, inflammatory, rheumatologic, and neoplastic. For febrile patients who have recently emigrated to or travelled outside of the United States, it is important to consider common infections, as well as those endemic to the nation of exposure, which in this case includes malaria, typhoid fever, tuberculosis, cholera, acute viral hepatitis, chikungunya fever, dengue fever, yellow fever, and rickettsial disease. All of these, other than tuberculosis, commonly present with fever, vomiting, diarrhea, and myalgia. She may also have bacterial pneumonia or influenza given her fever and cough, although the chronicity and persistence of symptoms would be atypical. Acute infectious gastroenteritis is a common cause of fever, vomiting, and diarrhea. Most cases resolve in 7 to 10 days, so the duration raises suspicion for a nonviral etiology or an immunocompromised state.
Inflammatory causes could include the first presentation of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), particularly if the patient develops weight loss or eye, skin, or joint manifestations. The lack of rash or arthralgia makes rheumatologic conditions less likely. Prolonged fevers and night sweats could indicate malignancy such as intra-abdominal lymphoma, although infectious etiologies should be ruled out first.
Previously, on day 9 of symptoms, the patient presented to an ED at another institution. Laboratory evaluation at that time demonstrated an elevated aspartate aminotransferase (AST) level of 229 IU/L (reference, 0-40 IU/L) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level of 60 IU/L (reference, 0-32 IU/L) with normal alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin levels, proteinuria to 3+ (normal, negative/trace), ketonuria to 2+ (normal, negative), and hematuria to 2+ (normal, negative). Complete blood count and electrolytes were normal. Computed tomography (CT) scans of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis with intravenous contrast were normal and without evidence of organomegaly.
AST and ALT elevations often indicate hepatocellular damage, although the normal bilirubin levels suggest normal hepatic function. Because CT may miss extrahepatic biliary pathology, a right upper quadrant ultrasound should be obtained to better evaluate patency of the biliary system and hepatic echotexture. Coagulation studies and viral hepatitis serology should be obtained. The disproportionate elevation of AST versus ALT can suggest alcohol use or nonhepatic etiologies such as myositis. Acute viral hepatitis is less likely given there is only mild to moderate elevation in aminotransferase levels. However, the remaining infectious etiologies can have this level of elevation and should still be considered.
Enteritis and IBD are still considerations despite the normal CT results. Transient asymptomatic hematuria or proteinuria can be seen in multiple conditions, particularly proteinuria with febrile illnesses. Urine microscopy to evaluate for casts could indicate a glomerular origin of the hematuria. First morning urine protein-to-creatinine ratio would help quantify the degree of proteinuria. Serum creatinine level should be measured to determine whether there is any renal dysfunction.
While early imaging can be falsely negative, the unremarkable chest CT makes pneumonia and active pulmonary tuberculosis less likely.
Vital signs during this presentation were: temperature, 39.7 °C; heart rate, 126 beats per minute; blood pressure, 109/64 mm Hg; respiratory rate, 20 breaths per minute; and oxygen saturation, 98% on room air. She was ill-appearing, with diffuse abdominal tenderness without peritoneal signs. Other than her tachycardia, findings from her cardiopulmonary, neurologic, and skin exams were normal.
Laboratory testing revealed a white blood cell count of 4,300/µL (reference range, 4,500-13,000/µL), a hemoglobin level of 10.9 g/dL (reference range, 11.7-15.7 g/dL) with a mean corpuscular volume of 77 fL (reference range, 80-96 fL) and reticulocyte percentage of 0.5% (reference range, 0.5%-1.5%), and a platelet count of 59,000/µL (reference range, 135,000-466,000/µL). Her prothrombin time was 13.5 seconds (reference range, 9.6-11.6 seconds) with an international normalized ratio of 1.3 (reference range, 0.8-1.1), erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 46 mm/h (reference range, 0-20 mm/h), C-reactive protein level of 7.49 mg/dL (reference range, <0.3 mg/dL), and AST level of 194 units/L (reference range, 9-35 units/L). ALT, total and direct bilirubin, lipase, electrolytes, and creatinine levels were normal. An abdominal x-ray showed scattered air-fluid levels in a nonobstructed pattern.
Her mildly elevated prothrombin time and international normalized ratio suggest a coagulopathy involving either her extrinsic or common coagulation pathway, with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) being most likely given her new thrombocytopenia and anemia. Hemolytic uremic syndrome and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura should be considered but would not cause coagulopathy. A peripheral smear to evaluate for schistocytes associated with microangiopathic hemolysis and serum fibrinogen to distinguish between DIC (low) and thrombocytopenic purpura or hemolytic uremic syndrome (normal or elevated) should be obtained. A thick and thin smear for malaria should also be performed.
Her new pancytopenia suggests bone marrow suppression or infiltration with or without a concomitant consumptive process such as sepsis with resulting DIC. Given her clinical picture, marrow infiltrative processes might include tuberculosis or malignancy, and marrow suppression may be caused by HIV or other viral infection. If she is found to have HIV, disseminated fungal or mycobacterial infections would become more likely. She now has an isolated elevated AST level, which could be secondary to hemolysis rather than hepatocyte damage. Findings from her abdominal exam are nonfocal; this is consistent with her x-ray findings, which reflect possible enteritis or colitis.
The most likely diagnosis currently is an infectious enteritis with resulting hematologic and hepatic abnormalities. Given her recent emigration from Kenya, typhoid fever and cholera are both possible, although cholera typically does not present with prolonged fever or severe abdominal pain. The severity and duration of her illness, and the abnormalities of her laboratory findings, warrant empiric therapy with ceftriaxone to treat possible severe Salmonella enterica infection while awaiting blood and stool cultures.
The patient was admitted to the hospital and her symptoms continued. Results of serum HIV 1 and 2 polymerase chain reactions, herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 polymerase chain reactions, three malaria smears, human T-lymphotropic virus serologies, Toxoplasma serology, Bartonella serology, a stool culture, and multiple large volume blood cultures were negative. Serologic testing for hepatitis A, B, and C, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and dengue virus were negative for acute infection. Results of an interferon-gamma release assay were indeterminate; results of purified protein derivative (PPD) and Candida antigen control testing were both negative. Ceruloplasmin and α1-antitrypsin levels were normal. An abdominal ultrasound showed central intrahepatic biliary duct dilatation, splenomegaly, and sluggish portal venous flow.
While central intrahepatic biliary ductal dilation could be caused by an obstructive lesion, none were seen on CT or ultrasound. Her normal alkaline phosphatase and bilirbuin levels also suggest functional patency of the biliary system. The thrombocytopenia, splenomegaly, and sluggish portal venous flow suggest possible portal hypertension, though no cirrhotic changes were noted on the ultrasound or abdominal CT. Her negative PPD and Candida antigen control results may suggest underlying immune dysregulation or suppression, though anergy could be secondary to sepsis.
Given her negative initial infectious evaluation, other etiologies such as atypical infections, rheumatologic disorders, and malignancies warrant consideration. She has no murmur; however, subacute bacterial endocarditis with a fastidious organism is possible, which could be investigated with a transthoracic echocardiogram. Other tests to consider include blood cultures for fungi and atypical mycobacterial species, and serology for Coxiella burnetii, chikungunya virus, and yellow fever. Rheumatologic conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), or adult Still’s disease should be considered. Complement levels and an antinuclear antibody panel, including those for dsDNA and Smith antigen, should be performed to evaluate for systemic lupus erythematosus. Serum ferritin, fibrinogen, and triglyceride levels should be measured to evaluate for HLH. Hematologic malignancy is also a consideration, particularly given her pancytopenia. Multicentric Castleman disease can cause prolonged fevers, pancytopenia, and elevated inflammatory markers, but is less likely without lymphadenopathy. A peripheral blood smear should be sent, and a bone marrow biopsy may be needed.
Empiric ciprofloxacin was initiated; however, the patient continued to have fevers up to 39.9 °C, abdominal pain, and myalgia. Ferritin level was over 3,000 ng/mL (reference range, 8-255 ng/mL), and a soluble interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor level was 1,188 units/mL (reference range, 45-1,105 units/mL). Triglycerides were normal.
The elevated ferritin and soluble IL-2 levels raise concern for HLH. Hyperferritinemia is relatively nonspecific because extremely elevated ferritin can be seen with other conditions, such as renal failure, hepatocellular injury, infection, rheumatologic conditions, and hematologic malignancy. Soluble IL-2 receptor elevation is more specific for HLH than ferritin or triglycerides, but alone does not make the diagnosis because it can be elevated in other rheumatologic disorders and malignancy. The HLH-2004 criteria are commonly used and require either molecular diagnostic testing or meeting at least five out of eight clinical and lab criteria to make the diagnosis. Our patient currently meets three criteria (fever, splenomegaly, and elevated ferritin). Elevated soluble IL-2 is part of the HLH-2004 criteria, but her level of elevation does not meet the required threshold (≥2,400 units/mL). Her cytopenias have also not quite met the HLH-2004 thresholds (two of the following three: hemoglobin <9 g/dL, platelets <100,000/µL, and/or absolute neutrophil count <1,000/µL). Elevated aminotransferase levels and DIC are not part of the HLH-2004 criteria but are often seen with HLH.
Evaluation for an underlying infectious, rheumatologic, or malignant trigger should continue as previously discussed. If this patient does have HLH, it is most likely secondary to an infection, autoimmune disease, or malignancy rather than genetic HLH. HLH has a high mortality rate, but before beginning treatment with immunosuppressive agents, a peripheral smear and a bone marrow biopsy should be performed to evaluate for hematologic malignancy or signs of hemophagocytosis.
Empiric ciprofloxacin covers most bacterial etiologies of diarrhea, including those previously mentioned such as cholera and most strains of S enterica. Her symptoms and laboratory findings (including cytopenias, elevated aminotransferases, and coagulopathy) could suggest enteric fever due to S enterica serovar Typhi, which is endemic in Kenya. Results of blood and stool cultures, though negative, are relatively insensitive for this organism, particularly this far into the illness course. A bone marrow biopsy may also help with diagnosis of occult typhoid fever because marrow culture can be more sensitive than blood or stool culture.
A bone marrow aspiration revealed hemophagocytic histiocytes, no malignant cells, and negative bacterial (including anaerobic), fungal, and acid-fast bacilli cultures. Considering the high mortality rate of untreated HLH/macrophage activation syndrome (MAS), empiric glucocorticoid administration was considered. However, this was withheld due to concern for ongoing undetected infection given her persistent fever and systemic symptoms.
There should still be high suspicion for HLH. Further evaluation for other laboratory manifestations of HLH such as fibrinogen and natural killer cell activity should be considered, as well as repeating her complete blood count to see if her cytopenias have progressed. Her marrow shows no evidence of hematologic malignancy, so other triggers of possible HLH should be sought out by continuing the workup. Consulting specialists from rheumatology and infectious disease may help clarify possible underlying diagnoses and the best management plan. If she continues to have organ damage or clinically worsens, it may be prudent to empirically broaden her antibiotic coverage and begin antifungal agents while starting glucocorticoid therapy for suspected HLH.
A stool molecular screen from admission was returned positive for S enterica serovar Typhi. Ciprofloxacin was discontinued and ceftriaxone was started out of concern for antibiotic resistance. On hospital day 14, the patient’s brother presented to the ED with fever. His blood and stool cultures were positive for S enterica serovar Typhi with intermediate sensitivity to ciprofloxacin and sensitivity to ceftriaxone. With continued treatment with ceftriaxone, the patient improved significantly. Following discharge, she remained afebrile and asymptomatic. During outpatient follow up, a repeat PPD was positive and she was diagnosed with and treated for latent tuberculosis.
COMMENTARY
The evaluation of a patient who has recently emigrated from a foreign nation requires a broad differential diagnosis and a keen awareness of the clinical conditions present in the patient’s country of origin. This often involves knowledge of diseases infrequently encountered in daily practice, as well as awareness of the nuances of rare presentations and possible complications. When the presentation is not classic for a relevant infectious disease and clinical conditions from other diagnostic classes are considered, the evaluation and management of the patient is particularly challenging.
Typhoid fever is a severe systemic illness caused by the organism S enterica serovar Typhi. The organism is ingested, penetrates the small intestinal epithelium, enters the lymphoid tissue, and disseminates via the lymphatic and hematogenous routes. Onset of symptoms typically occurs 5 to 21 days after ingestion of contaminated food or water. Clinical features include fever, chills, relative bradycardia (pulse-temperature dissociation), abdominal pain, rose spots (salmon-colored macules) on the trunk and abdomen, and hepatosplenomegaly. Diarrhea is not a typical symptom of patients with typhoid fever, which can lead to a delayed or missed diagnosis. Life-threatening complications can be seen, including gastrointestinal bleeding, intestinal perforation, and meningitis.1 Typhoid fever is most prevalent in impoverished areas with poor access to sanitation. Regions with the highest incidence include south-central Asia, southeast Asia, and southern Africa.2-4 Approximately 200 to 300 cases are reported in the United States each year.5
Classically, the diagnosis is made by means of clinical symptoms and a positive culture from a sterile site. A recent study of 529 patients found that 61% had positive blood cultures and 96% had positive bone marrow cultures.6 Our patient’s diagnosis was significantly delayed by multiple negative cultures and failure to improve on first-line antibiotics, which initially suggested that the S enterica serovar Typhi stool molecular screen likely represented carriage caused by colonization. Chronic S enterica serovar Typhi carriage is defined as excretion of the organism in stool or urine 1 year or longer after acute infection. Rates of carriage range from 1% to 6%, and up to 25% of carriers have no history of typhoid fever.1,7,8 Carriage is more common in females and in those with biliary tract abnormalities.9,10
Once a presumptive diagnosis is made, antibiotic choice remains a challenge. Resistance to fluoroquinolones, the preferred drug for multidrug-resistant typhoid fever, is growing but remains rare, at approximately 5%.11,12 Ceftriaxone and azithromycin have been used successfully in areas with high resistance.13 Given the patient’s slow response to therapy even after transitioning from ciprofloxacin to ceftriaxone, her brother’s presentation and obtaining the antibiotic sensitivities for his organism were critical to confirming that our diagnosis and management decisions were correct.
One strongly considered diagnosis was HLH/MAS. MAS is an aggressive syndrome of excessive inflammation and tissue destruction caused by inappropriate immune system activation. It belongs to a group of histiocytic disorders collectively known as HLH. Aside from primary (genetic) forms, secondary forms exist that can be triggered by malignancy, infection, or rheumatologic disorders. In infection-associated HLH/MAS, viral infections are a common trigger, with Epstein-Barr virus being the most common. Association with bacterial infections, including tuberculosis and typhoid fever, has also been reported.14 Prompt therapy, often with immunosuppressive agents such as glucocorticoids, is essential for survival because there is a reported mortality rate of up to 50% when untreated.15 When infection-induced HLH/MAS occurs, treatment of the underlying infection is critical.14,15 The greatest barrier to a favorable outcome from HLH/MAS is often a delay in diagnosis because the rarity of this disease, the variable clinical presentation, and the lack of specificity of the clinical and laboratory findings make a conclusive diagnosis challenging.
In the presented case, diagnostic uncertainty challenged the decision to administer systemic glucocorticoids. Glucocorticoids conferred a risk of harm for multiple diagnoses that remained on the differential, including malignancy and infection. Her diagnostic evaluation made malignancy less likely, but because testing was unable to rule out tuberculosis as either the underlying cause or coinfection, the team opted to defer initiating glucocorticoids and instead closely monitor for a worsening inflammatory response. Following appropriate treatment of her systemic infection, her PPD was repeated and became positive. The negative PPD and Candida control obtained during her hospitalization were, therefore, likely caused by anergy in the setting of overwhelming systemic illness. Initiation of glucocorticoids prematurely in this case could have led to further harm because immunosuppression may have led to reactivation of latent tuberculosis or exacerbation of illness from an alternative but then undiagnosed infection.
The patient’s ultimate unifying diagnosis was typhoid fever; however, there are mixed expert opinions as to whether the systemic immune activation was significant enough to merit the diagnosis of infection-induced secondary HLH/MAS. Despite the high morbidity and mortality that can accompany HLH/MAS, it has been reported that a significant proportion of cases of secondary HLH/MAS can be managed effectively with treatment of the underlying etiology; this may have been the case for our patient.14,15 The clinicians in this case were caught between diagnoses, unable to safely reach either one—much like a baseball player stranded between bases. Fortunately for this patient, the diagnosis ultimately emerged after a careful and thorough workup, assisted by the more straightforward diagnosis of her brother with the same disease.
KEY TEACHING POINTS
- Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi has a high false-negative rate in blood and stool cultures; therefore, clinical suspicion should remain high in the setting of a high pre-test probability.
- Fluoroquinolones are traditionally first-line therapy for typhoid fever, but the use of ceftriaxone and azithromycin is increasing because of rising fluoroquinolone resistance.
- Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis/macrophage activation syndrome is characterized by excessive inflammation and tissue destruction caused by inappropriate immune system activation. This syndrome can be fatal without appropriate immunosuppressive therapy; however, glucocorticoid administration must be pursued with caution when infection and malignancy are on the differential diagnosis.
1. Parry CM, Hien TT, Dougan G, et al. Typhoid fever. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(22):1770-1782. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmra020201
2. Crump JA, Luby SP, Mintz ED. The global burden of typhoid fever. Bull World Health Organ. 2004;82(5):346-353.
3. Buckle GC, Walker CL, Black RE. Typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever: systematic review to estimate global morbidity and mortality for 2010. J Glob Health. 2012;2(1):010401. https://doi.org/10.7189/jogh.02.010401
4. Mogasale V, Maskery B, Ochiai RL, et al. Burden of typhoid fever in low-income and middle-income countries: a systematic, literature-based update with risk-factor adjustment. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2(10):e570-e580. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2214-109x(14)70301-8
5. Lynch MF, Blanton EM, Bulens S, et al. Typhoid fever in the United States, 1999-2006. JAMA. 2009;302(8):859-865. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.1229
6. Mogasale V, Ramani E, Mogasale VV, Park J. What proportion of Salmonella typhi cases are detected by blood culture? a systematic literature review. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2016;15(1):32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12941-016-0147-z
7. Merselis JG Jr, Kaye D, Connolly CS, Hook EW. Quantitative bacteriology of the Typhoid carrier state. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1964;13:425-429. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.1964.13.425
8. Lanata CF, Levine MM, Ristori C, et al. Vi serology in detection of chronic Salmonella typhi carriers in an endemic area. Lancet. 1983;2(8347):441-443. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90401-4
9. Lai CW, Chan RC, Cheng AF, Sung JY, Leung JW. Common bile duct stones: a cause of chronic salmonellosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992;87(9):1198-1199.
10. Hofmann E, Chianale J, Rollán A, Pereira J, Ferrecio C, Sotomayor V. Blood group antigen secretion and gallstone disease in the Salmonella typhi chronic carrier state. J Infect Dis. 1993;167(4):993-994. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/167.4.993
11. Steel AD, Hay Burgess DC, Diaz Z, Carey ME, Zaidi AKM. Challenges and opportunities for typhoid fever control: a call for coordinated action. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62 (Suppl 1):S4-S8. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/civ976
12. Hendriksen RS, Leekitcharoenphon P, Lukjancenko O, et al. Genomic signature of multidrug resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi isolates related to a massive outbreak in Zambia between 2010 and 2012. J Clin Microbiol. 2015;53(1):262-272. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.02026-14
13. Crump JA, Sjölund-Karlsson M, Gordon MA, Parry CM. Epidemiology, clinical presentation, laboratory diagnosis, antimicrobial resistance, and antimicrobial management of Salmonella infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015;28(4):901-936. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.00002-15
14. Rouphael NG, Talati NJ, Vaughan C, Cunningham K, Moreira R, Gould C. Infections associated with haemophagocytic syndrome. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7(12):814-822. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1473-3099(07)70290-6
15. Fisman DN. Hemophagocytic syndromes and infection. Emerg Infect Dis. 2000;6(6):601-608. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid0606.000608
A 19-year-old woman presented to the emergency department (ED) with a 14-day history of progressive fevers, night sweats, abdominal pain, nonbloody and nonbilious vomiting, diarrhea, cough, and myalgia. The fever occurred daily with no noted temporal pattern, and she had no significant weight loss. The abdominal pain was diffuse and exacerbated by eating. She experienced multiple sporadic episodes of vomiting and diarrhea daily. She denied any rash or arthralgia.
She had no known medical history and took no medications. Family history was negative for autoinflammatory and autoimmune conditions. She had emigrated from Kenya to the United States 28 days ago. Her immunization status was unknown.
This patient has prolonged fevers and evidence of multisystem involvement. The most likely etiologic categories are infectious, inflammatory, rheumatologic, and neoplastic. For febrile patients who have recently emigrated to or travelled outside of the United States, it is important to consider common infections, as well as those endemic to the nation of exposure, which in this case includes malaria, typhoid fever, tuberculosis, cholera, acute viral hepatitis, chikungunya fever, dengue fever, yellow fever, and rickettsial disease. All of these, other than tuberculosis, commonly present with fever, vomiting, diarrhea, and myalgia. She may also have bacterial pneumonia or influenza given her fever and cough, although the chronicity and persistence of symptoms would be atypical. Acute infectious gastroenteritis is a common cause of fever, vomiting, and diarrhea. Most cases resolve in 7 to 10 days, so the duration raises suspicion for a nonviral etiology or an immunocompromised state.
Inflammatory causes could include the first presentation of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), particularly if the patient develops weight loss or eye, skin, or joint manifestations. The lack of rash or arthralgia makes rheumatologic conditions less likely. Prolonged fevers and night sweats could indicate malignancy such as intra-abdominal lymphoma, although infectious etiologies should be ruled out first.
Previously, on day 9 of symptoms, the patient presented to an ED at another institution. Laboratory evaluation at that time demonstrated an elevated aspartate aminotransferase (AST) level of 229 IU/L (reference, 0-40 IU/L) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level of 60 IU/L (reference, 0-32 IU/L) with normal alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin levels, proteinuria to 3+ (normal, negative/trace), ketonuria to 2+ (normal, negative), and hematuria to 2+ (normal, negative). Complete blood count and electrolytes were normal. Computed tomography (CT) scans of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis with intravenous contrast were normal and without evidence of organomegaly.
AST and ALT elevations often indicate hepatocellular damage, although the normal bilirubin levels suggest normal hepatic function. Because CT may miss extrahepatic biliary pathology, a right upper quadrant ultrasound should be obtained to better evaluate patency of the biliary system and hepatic echotexture. Coagulation studies and viral hepatitis serology should be obtained. The disproportionate elevation of AST versus ALT can suggest alcohol use or nonhepatic etiologies such as myositis. Acute viral hepatitis is less likely given there is only mild to moderate elevation in aminotransferase levels. However, the remaining infectious etiologies can have this level of elevation and should still be considered.
Enteritis and IBD are still considerations despite the normal CT results. Transient asymptomatic hematuria or proteinuria can be seen in multiple conditions, particularly proteinuria with febrile illnesses. Urine microscopy to evaluate for casts could indicate a glomerular origin of the hematuria. First morning urine protein-to-creatinine ratio would help quantify the degree of proteinuria. Serum creatinine level should be measured to determine whether there is any renal dysfunction.
While early imaging can be falsely negative, the unremarkable chest CT makes pneumonia and active pulmonary tuberculosis less likely.
Vital signs during this presentation were: temperature, 39.7 °C; heart rate, 126 beats per minute; blood pressure, 109/64 mm Hg; respiratory rate, 20 breaths per minute; and oxygen saturation, 98% on room air. She was ill-appearing, with diffuse abdominal tenderness without peritoneal signs. Other than her tachycardia, findings from her cardiopulmonary, neurologic, and skin exams were normal.
Laboratory testing revealed a white blood cell count of 4,300/µL (reference range, 4,500-13,000/µL), a hemoglobin level of 10.9 g/dL (reference range, 11.7-15.7 g/dL) with a mean corpuscular volume of 77 fL (reference range, 80-96 fL) and reticulocyte percentage of 0.5% (reference range, 0.5%-1.5%), and a platelet count of 59,000/µL (reference range, 135,000-466,000/µL). Her prothrombin time was 13.5 seconds (reference range, 9.6-11.6 seconds) with an international normalized ratio of 1.3 (reference range, 0.8-1.1), erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 46 mm/h (reference range, 0-20 mm/h), C-reactive protein level of 7.49 mg/dL (reference range, <0.3 mg/dL), and AST level of 194 units/L (reference range, 9-35 units/L). ALT, total and direct bilirubin, lipase, electrolytes, and creatinine levels were normal. An abdominal x-ray showed scattered air-fluid levels in a nonobstructed pattern.
Her mildly elevated prothrombin time and international normalized ratio suggest a coagulopathy involving either her extrinsic or common coagulation pathway, with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) being most likely given her new thrombocytopenia and anemia. Hemolytic uremic syndrome and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura should be considered but would not cause coagulopathy. A peripheral smear to evaluate for schistocytes associated with microangiopathic hemolysis and serum fibrinogen to distinguish between DIC (low) and thrombocytopenic purpura or hemolytic uremic syndrome (normal or elevated) should be obtained. A thick and thin smear for malaria should also be performed.
Her new pancytopenia suggests bone marrow suppression or infiltration with or without a concomitant consumptive process such as sepsis with resulting DIC. Given her clinical picture, marrow infiltrative processes might include tuberculosis or malignancy, and marrow suppression may be caused by HIV or other viral infection. If she is found to have HIV, disseminated fungal or mycobacterial infections would become more likely. She now has an isolated elevated AST level, which could be secondary to hemolysis rather than hepatocyte damage. Findings from her abdominal exam are nonfocal; this is consistent with her x-ray findings, which reflect possible enteritis or colitis.
The most likely diagnosis currently is an infectious enteritis with resulting hematologic and hepatic abnormalities. Given her recent emigration from Kenya, typhoid fever and cholera are both possible, although cholera typically does not present with prolonged fever or severe abdominal pain. The severity and duration of her illness, and the abnormalities of her laboratory findings, warrant empiric therapy with ceftriaxone to treat possible severe Salmonella enterica infection while awaiting blood and stool cultures.
The patient was admitted to the hospital and her symptoms continued. Results of serum HIV 1 and 2 polymerase chain reactions, herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 polymerase chain reactions, three malaria smears, human T-lymphotropic virus serologies, Toxoplasma serology, Bartonella serology, a stool culture, and multiple large volume blood cultures were negative. Serologic testing for hepatitis A, B, and C, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and dengue virus were negative for acute infection. Results of an interferon-gamma release assay were indeterminate; results of purified protein derivative (PPD) and Candida antigen control testing were both negative. Ceruloplasmin and α1-antitrypsin levels were normal. An abdominal ultrasound showed central intrahepatic biliary duct dilatation, splenomegaly, and sluggish portal venous flow.
While central intrahepatic biliary ductal dilation could be caused by an obstructive lesion, none were seen on CT or ultrasound. Her normal alkaline phosphatase and bilirbuin levels also suggest functional patency of the biliary system. The thrombocytopenia, splenomegaly, and sluggish portal venous flow suggest possible portal hypertension, though no cirrhotic changes were noted on the ultrasound or abdominal CT. Her negative PPD and Candida antigen control results may suggest underlying immune dysregulation or suppression, though anergy could be secondary to sepsis.
Given her negative initial infectious evaluation, other etiologies such as atypical infections, rheumatologic disorders, and malignancies warrant consideration. She has no murmur; however, subacute bacterial endocarditis with a fastidious organism is possible, which could be investigated with a transthoracic echocardiogram. Other tests to consider include blood cultures for fungi and atypical mycobacterial species, and serology for Coxiella burnetii, chikungunya virus, and yellow fever. Rheumatologic conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), or adult Still’s disease should be considered. Complement levels and an antinuclear antibody panel, including those for dsDNA and Smith antigen, should be performed to evaluate for systemic lupus erythematosus. Serum ferritin, fibrinogen, and triglyceride levels should be measured to evaluate for HLH. Hematologic malignancy is also a consideration, particularly given her pancytopenia. Multicentric Castleman disease can cause prolonged fevers, pancytopenia, and elevated inflammatory markers, but is less likely without lymphadenopathy. A peripheral blood smear should be sent, and a bone marrow biopsy may be needed.
Empiric ciprofloxacin was initiated; however, the patient continued to have fevers up to 39.9 °C, abdominal pain, and myalgia. Ferritin level was over 3,000 ng/mL (reference range, 8-255 ng/mL), and a soluble interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor level was 1,188 units/mL (reference range, 45-1,105 units/mL). Triglycerides were normal.
The elevated ferritin and soluble IL-2 levels raise concern for HLH. Hyperferritinemia is relatively nonspecific because extremely elevated ferritin can be seen with other conditions, such as renal failure, hepatocellular injury, infection, rheumatologic conditions, and hematologic malignancy. Soluble IL-2 receptor elevation is more specific for HLH than ferritin or triglycerides, but alone does not make the diagnosis because it can be elevated in other rheumatologic disorders and malignancy. The HLH-2004 criteria are commonly used and require either molecular diagnostic testing or meeting at least five out of eight clinical and lab criteria to make the diagnosis. Our patient currently meets three criteria (fever, splenomegaly, and elevated ferritin). Elevated soluble IL-2 is part of the HLH-2004 criteria, but her level of elevation does not meet the required threshold (≥2,400 units/mL). Her cytopenias have also not quite met the HLH-2004 thresholds (two of the following three: hemoglobin <9 g/dL, platelets <100,000/µL, and/or absolute neutrophil count <1,000/µL). Elevated aminotransferase levels and DIC are not part of the HLH-2004 criteria but are often seen with HLH.
Evaluation for an underlying infectious, rheumatologic, or malignant trigger should continue as previously discussed. If this patient does have HLH, it is most likely secondary to an infection, autoimmune disease, or malignancy rather than genetic HLH. HLH has a high mortality rate, but before beginning treatment with immunosuppressive agents, a peripheral smear and a bone marrow biopsy should be performed to evaluate for hematologic malignancy or signs of hemophagocytosis.
Empiric ciprofloxacin covers most bacterial etiologies of diarrhea, including those previously mentioned such as cholera and most strains of S enterica. Her symptoms and laboratory findings (including cytopenias, elevated aminotransferases, and coagulopathy) could suggest enteric fever due to S enterica serovar Typhi, which is endemic in Kenya. Results of blood and stool cultures, though negative, are relatively insensitive for this organism, particularly this far into the illness course. A bone marrow biopsy may also help with diagnosis of occult typhoid fever because marrow culture can be more sensitive than blood or stool culture.
A bone marrow aspiration revealed hemophagocytic histiocytes, no malignant cells, and negative bacterial (including anaerobic), fungal, and acid-fast bacilli cultures. Considering the high mortality rate of untreated HLH/macrophage activation syndrome (MAS), empiric glucocorticoid administration was considered. However, this was withheld due to concern for ongoing undetected infection given her persistent fever and systemic symptoms.
There should still be high suspicion for HLH. Further evaluation for other laboratory manifestations of HLH such as fibrinogen and natural killer cell activity should be considered, as well as repeating her complete blood count to see if her cytopenias have progressed. Her marrow shows no evidence of hematologic malignancy, so other triggers of possible HLH should be sought out by continuing the workup. Consulting specialists from rheumatology and infectious disease may help clarify possible underlying diagnoses and the best management plan. If she continues to have organ damage or clinically worsens, it may be prudent to empirically broaden her antibiotic coverage and begin antifungal agents while starting glucocorticoid therapy for suspected HLH.
A stool molecular screen from admission was returned positive for S enterica serovar Typhi. Ciprofloxacin was discontinued and ceftriaxone was started out of concern for antibiotic resistance. On hospital day 14, the patient’s brother presented to the ED with fever. His blood and stool cultures were positive for S enterica serovar Typhi with intermediate sensitivity to ciprofloxacin and sensitivity to ceftriaxone. With continued treatment with ceftriaxone, the patient improved significantly. Following discharge, she remained afebrile and asymptomatic. During outpatient follow up, a repeat PPD was positive and she was diagnosed with and treated for latent tuberculosis.
COMMENTARY
The evaluation of a patient who has recently emigrated from a foreign nation requires a broad differential diagnosis and a keen awareness of the clinical conditions present in the patient’s country of origin. This often involves knowledge of diseases infrequently encountered in daily practice, as well as awareness of the nuances of rare presentations and possible complications. When the presentation is not classic for a relevant infectious disease and clinical conditions from other diagnostic classes are considered, the evaluation and management of the patient is particularly challenging.
Typhoid fever is a severe systemic illness caused by the organism S enterica serovar Typhi. The organism is ingested, penetrates the small intestinal epithelium, enters the lymphoid tissue, and disseminates via the lymphatic and hematogenous routes. Onset of symptoms typically occurs 5 to 21 days after ingestion of contaminated food or water. Clinical features include fever, chills, relative bradycardia (pulse-temperature dissociation), abdominal pain, rose spots (salmon-colored macules) on the trunk and abdomen, and hepatosplenomegaly. Diarrhea is not a typical symptom of patients with typhoid fever, which can lead to a delayed or missed diagnosis. Life-threatening complications can be seen, including gastrointestinal bleeding, intestinal perforation, and meningitis.1 Typhoid fever is most prevalent in impoverished areas with poor access to sanitation. Regions with the highest incidence include south-central Asia, southeast Asia, and southern Africa.2-4 Approximately 200 to 300 cases are reported in the United States each year.5
Classically, the diagnosis is made by means of clinical symptoms and a positive culture from a sterile site. A recent study of 529 patients found that 61% had positive blood cultures and 96% had positive bone marrow cultures.6 Our patient’s diagnosis was significantly delayed by multiple negative cultures and failure to improve on first-line antibiotics, which initially suggested that the S enterica serovar Typhi stool molecular screen likely represented carriage caused by colonization. Chronic S enterica serovar Typhi carriage is defined as excretion of the organism in stool or urine 1 year or longer after acute infection. Rates of carriage range from 1% to 6%, and up to 25% of carriers have no history of typhoid fever.1,7,8 Carriage is more common in females and in those with biliary tract abnormalities.9,10
Once a presumptive diagnosis is made, antibiotic choice remains a challenge. Resistance to fluoroquinolones, the preferred drug for multidrug-resistant typhoid fever, is growing but remains rare, at approximately 5%.11,12 Ceftriaxone and azithromycin have been used successfully in areas with high resistance.13 Given the patient’s slow response to therapy even after transitioning from ciprofloxacin to ceftriaxone, her brother’s presentation and obtaining the antibiotic sensitivities for his organism were critical to confirming that our diagnosis and management decisions were correct.
One strongly considered diagnosis was HLH/MAS. MAS is an aggressive syndrome of excessive inflammation and tissue destruction caused by inappropriate immune system activation. It belongs to a group of histiocytic disorders collectively known as HLH. Aside from primary (genetic) forms, secondary forms exist that can be triggered by malignancy, infection, or rheumatologic disorders. In infection-associated HLH/MAS, viral infections are a common trigger, with Epstein-Barr virus being the most common. Association with bacterial infections, including tuberculosis and typhoid fever, has also been reported.14 Prompt therapy, often with immunosuppressive agents such as glucocorticoids, is essential for survival because there is a reported mortality rate of up to 50% when untreated.15 When infection-induced HLH/MAS occurs, treatment of the underlying infection is critical.14,15 The greatest barrier to a favorable outcome from HLH/MAS is often a delay in diagnosis because the rarity of this disease, the variable clinical presentation, and the lack of specificity of the clinical and laboratory findings make a conclusive diagnosis challenging.
In the presented case, diagnostic uncertainty challenged the decision to administer systemic glucocorticoids. Glucocorticoids conferred a risk of harm for multiple diagnoses that remained on the differential, including malignancy and infection. Her diagnostic evaluation made malignancy less likely, but because testing was unable to rule out tuberculosis as either the underlying cause or coinfection, the team opted to defer initiating glucocorticoids and instead closely monitor for a worsening inflammatory response. Following appropriate treatment of her systemic infection, her PPD was repeated and became positive. The negative PPD and Candida control obtained during her hospitalization were, therefore, likely caused by anergy in the setting of overwhelming systemic illness. Initiation of glucocorticoids prematurely in this case could have led to further harm because immunosuppression may have led to reactivation of latent tuberculosis or exacerbation of illness from an alternative but then undiagnosed infection.
The patient’s ultimate unifying diagnosis was typhoid fever; however, there are mixed expert opinions as to whether the systemic immune activation was significant enough to merit the diagnosis of infection-induced secondary HLH/MAS. Despite the high morbidity and mortality that can accompany HLH/MAS, it has been reported that a significant proportion of cases of secondary HLH/MAS can be managed effectively with treatment of the underlying etiology; this may have been the case for our patient.14,15 The clinicians in this case were caught between diagnoses, unable to safely reach either one—much like a baseball player stranded between bases. Fortunately for this patient, the diagnosis ultimately emerged after a careful and thorough workup, assisted by the more straightforward diagnosis of her brother with the same disease.
KEY TEACHING POINTS
- Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi has a high false-negative rate in blood and stool cultures; therefore, clinical suspicion should remain high in the setting of a high pre-test probability.
- Fluoroquinolones are traditionally first-line therapy for typhoid fever, but the use of ceftriaxone and azithromycin is increasing because of rising fluoroquinolone resistance.
- Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis/macrophage activation syndrome is characterized by excessive inflammation and tissue destruction caused by inappropriate immune system activation. This syndrome can be fatal without appropriate immunosuppressive therapy; however, glucocorticoid administration must be pursued with caution when infection and malignancy are on the differential diagnosis.
A 19-year-old woman presented to the emergency department (ED) with a 14-day history of progressive fevers, night sweats, abdominal pain, nonbloody and nonbilious vomiting, diarrhea, cough, and myalgia. The fever occurred daily with no noted temporal pattern, and she had no significant weight loss. The abdominal pain was diffuse and exacerbated by eating. She experienced multiple sporadic episodes of vomiting and diarrhea daily. She denied any rash or arthralgia.
She had no known medical history and took no medications. Family history was negative for autoinflammatory and autoimmune conditions. She had emigrated from Kenya to the United States 28 days ago. Her immunization status was unknown.
This patient has prolonged fevers and evidence of multisystem involvement. The most likely etiologic categories are infectious, inflammatory, rheumatologic, and neoplastic. For febrile patients who have recently emigrated to or travelled outside of the United States, it is important to consider common infections, as well as those endemic to the nation of exposure, which in this case includes malaria, typhoid fever, tuberculosis, cholera, acute viral hepatitis, chikungunya fever, dengue fever, yellow fever, and rickettsial disease. All of these, other than tuberculosis, commonly present with fever, vomiting, diarrhea, and myalgia. She may also have bacterial pneumonia or influenza given her fever and cough, although the chronicity and persistence of symptoms would be atypical. Acute infectious gastroenteritis is a common cause of fever, vomiting, and diarrhea. Most cases resolve in 7 to 10 days, so the duration raises suspicion for a nonviral etiology or an immunocompromised state.
Inflammatory causes could include the first presentation of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), particularly if the patient develops weight loss or eye, skin, or joint manifestations. The lack of rash or arthralgia makes rheumatologic conditions less likely. Prolonged fevers and night sweats could indicate malignancy such as intra-abdominal lymphoma, although infectious etiologies should be ruled out first.
Previously, on day 9 of symptoms, the patient presented to an ED at another institution. Laboratory evaluation at that time demonstrated an elevated aspartate aminotransferase (AST) level of 229 IU/L (reference, 0-40 IU/L) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level of 60 IU/L (reference, 0-32 IU/L) with normal alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin levels, proteinuria to 3+ (normal, negative/trace), ketonuria to 2+ (normal, negative), and hematuria to 2+ (normal, negative). Complete blood count and electrolytes were normal. Computed tomography (CT) scans of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis with intravenous contrast were normal and without evidence of organomegaly.
AST and ALT elevations often indicate hepatocellular damage, although the normal bilirubin levels suggest normal hepatic function. Because CT may miss extrahepatic biliary pathology, a right upper quadrant ultrasound should be obtained to better evaluate patency of the biliary system and hepatic echotexture. Coagulation studies and viral hepatitis serology should be obtained. The disproportionate elevation of AST versus ALT can suggest alcohol use or nonhepatic etiologies such as myositis. Acute viral hepatitis is less likely given there is only mild to moderate elevation in aminotransferase levels. However, the remaining infectious etiologies can have this level of elevation and should still be considered.
Enteritis and IBD are still considerations despite the normal CT results. Transient asymptomatic hematuria or proteinuria can be seen in multiple conditions, particularly proteinuria with febrile illnesses. Urine microscopy to evaluate for casts could indicate a glomerular origin of the hematuria. First morning urine protein-to-creatinine ratio would help quantify the degree of proteinuria. Serum creatinine level should be measured to determine whether there is any renal dysfunction.
While early imaging can be falsely negative, the unremarkable chest CT makes pneumonia and active pulmonary tuberculosis less likely.
Vital signs during this presentation were: temperature, 39.7 °C; heart rate, 126 beats per minute; blood pressure, 109/64 mm Hg; respiratory rate, 20 breaths per minute; and oxygen saturation, 98% on room air. She was ill-appearing, with diffuse abdominal tenderness without peritoneal signs. Other than her tachycardia, findings from her cardiopulmonary, neurologic, and skin exams were normal.
Laboratory testing revealed a white blood cell count of 4,300/µL (reference range, 4,500-13,000/µL), a hemoglobin level of 10.9 g/dL (reference range, 11.7-15.7 g/dL) with a mean corpuscular volume of 77 fL (reference range, 80-96 fL) and reticulocyte percentage of 0.5% (reference range, 0.5%-1.5%), and a platelet count of 59,000/µL (reference range, 135,000-466,000/µL). Her prothrombin time was 13.5 seconds (reference range, 9.6-11.6 seconds) with an international normalized ratio of 1.3 (reference range, 0.8-1.1), erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 46 mm/h (reference range, 0-20 mm/h), C-reactive protein level of 7.49 mg/dL (reference range, <0.3 mg/dL), and AST level of 194 units/L (reference range, 9-35 units/L). ALT, total and direct bilirubin, lipase, electrolytes, and creatinine levels were normal. An abdominal x-ray showed scattered air-fluid levels in a nonobstructed pattern.
Her mildly elevated prothrombin time and international normalized ratio suggest a coagulopathy involving either her extrinsic or common coagulation pathway, with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) being most likely given her new thrombocytopenia and anemia. Hemolytic uremic syndrome and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura should be considered but would not cause coagulopathy. A peripheral smear to evaluate for schistocytes associated with microangiopathic hemolysis and serum fibrinogen to distinguish between DIC (low) and thrombocytopenic purpura or hemolytic uremic syndrome (normal or elevated) should be obtained. A thick and thin smear for malaria should also be performed.
Her new pancytopenia suggests bone marrow suppression or infiltration with or without a concomitant consumptive process such as sepsis with resulting DIC. Given her clinical picture, marrow infiltrative processes might include tuberculosis or malignancy, and marrow suppression may be caused by HIV or other viral infection. If she is found to have HIV, disseminated fungal or mycobacterial infections would become more likely. She now has an isolated elevated AST level, which could be secondary to hemolysis rather than hepatocyte damage. Findings from her abdominal exam are nonfocal; this is consistent with her x-ray findings, which reflect possible enteritis or colitis.
The most likely diagnosis currently is an infectious enteritis with resulting hematologic and hepatic abnormalities. Given her recent emigration from Kenya, typhoid fever and cholera are both possible, although cholera typically does not present with prolonged fever or severe abdominal pain. The severity and duration of her illness, and the abnormalities of her laboratory findings, warrant empiric therapy with ceftriaxone to treat possible severe Salmonella enterica infection while awaiting blood and stool cultures.
The patient was admitted to the hospital and her symptoms continued. Results of serum HIV 1 and 2 polymerase chain reactions, herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 polymerase chain reactions, three malaria smears, human T-lymphotropic virus serologies, Toxoplasma serology, Bartonella serology, a stool culture, and multiple large volume blood cultures were negative. Serologic testing for hepatitis A, B, and C, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and dengue virus were negative for acute infection. Results of an interferon-gamma release assay were indeterminate; results of purified protein derivative (PPD) and Candida antigen control testing were both negative. Ceruloplasmin and α1-antitrypsin levels were normal. An abdominal ultrasound showed central intrahepatic biliary duct dilatation, splenomegaly, and sluggish portal venous flow.
While central intrahepatic biliary ductal dilation could be caused by an obstructive lesion, none were seen on CT or ultrasound. Her normal alkaline phosphatase and bilirbuin levels also suggest functional patency of the biliary system. The thrombocytopenia, splenomegaly, and sluggish portal venous flow suggest possible portal hypertension, though no cirrhotic changes were noted on the ultrasound or abdominal CT. Her negative PPD and Candida antigen control results may suggest underlying immune dysregulation or suppression, though anergy could be secondary to sepsis.
Given her negative initial infectious evaluation, other etiologies such as atypical infections, rheumatologic disorders, and malignancies warrant consideration. She has no murmur; however, subacute bacterial endocarditis with a fastidious organism is possible, which could be investigated with a transthoracic echocardiogram. Other tests to consider include blood cultures for fungi and atypical mycobacterial species, and serology for Coxiella burnetii, chikungunya virus, and yellow fever. Rheumatologic conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), or adult Still’s disease should be considered. Complement levels and an antinuclear antibody panel, including those for dsDNA and Smith antigen, should be performed to evaluate for systemic lupus erythematosus. Serum ferritin, fibrinogen, and triglyceride levels should be measured to evaluate for HLH. Hematologic malignancy is also a consideration, particularly given her pancytopenia. Multicentric Castleman disease can cause prolonged fevers, pancytopenia, and elevated inflammatory markers, but is less likely without lymphadenopathy. A peripheral blood smear should be sent, and a bone marrow biopsy may be needed.
Empiric ciprofloxacin was initiated; however, the patient continued to have fevers up to 39.9 °C, abdominal pain, and myalgia. Ferritin level was over 3,000 ng/mL (reference range, 8-255 ng/mL), and a soluble interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor level was 1,188 units/mL (reference range, 45-1,105 units/mL). Triglycerides were normal.
The elevated ferritin and soluble IL-2 levels raise concern for HLH. Hyperferritinemia is relatively nonspecific because extremely elevated ferritin can be seen with other conditions, such as renal failure, hepatocellular injury, infection, rheumatologic conditions, and hematologic malignancy. Soluble IL-2 receptor elevation is more specific for HLH than ferritin or triglycerides, but alone does not make the diagnosis because it can be elevated in other rheumatologic disorders and malignancy. The HLH-2004 criteria are commonly used and require either molecular diagnostic testing or meeting at least five out of eight clinical and lab criteria to make the diagnosis. Our patient currently meets three criteria (fever, splenomegaly, and elevated ferritin). Elevated soluble IL-2 is part of the HLH-2004 criteria, but her level of elevation does not meet the required threshold (≥2,400 units/mL). Her cytopenias have also not quite met the HLH-2004 thresholds (two of the following three: hemoglobin <9 g/dL, platelets <100,000/µL, and/or absolute neutrophil count <1,000/µL). Elevated aminotransferase levels and DIC are not part of the HLH-2004 criteria but are often seen with HLH.
Evaluation for an underlying infectious, rheumatologic, or malignant trigger should continue as previously discussed. If this patient does have HLH, it is most likely secondary to an infection, autoimmune disease, or malignancy rather than genetic HLH. HLH has a high mortality rate, but before beginning treatment with immunosuppressive agents, a peripheral smear and a bone marrow biopsy should be performed to evaluate for hematologic malignancy or signs of hemophagocytosis.
Empiric ciprofloxacin covers most bacterial etiologies of diarrhea, including those previously mentioned such as cholera and most strains of S enterica. Her symptoms and laboratory findings (including cytopenias, elevated aminotransferases, and coagulopathy) could suggest enteric fever due to S enterica serovar Typhi, which is endemic in Kenya. Results of blood and stool cultures, though negative, are relatively insensitive for this organism, particularly this far into the illness course. A bone marrow biopsy may also help with diagnosis of occult typhoid fever because marrow culture can be more sensitive than blood or stool culture.
A bone marrow aspiration revealed hemophagocytic histiocytes, no malignant cells, and negative bacterial (including anaerobic), fungal, and acid-fast bacilli cultures. Considering the high mortality rate of untreated HLH/macrophage activation syndrome (MAS), empiric glucocorticoid administration was considered. However, this was withheld due to concern for ongoing undetected infection given her persistent fever and systemic symptoms.
There should still be high suspicion for HLH. Further evaluation for other laboratory manifestations of HLH such as fibrinogen and natural killer cell activity should be considered, as well as repeating her complete blood count to see if her cytopenias have progressed. Her marrow shows no evidence of hematologic malignancy, so other triggers of possible HLH should be sought out by continuing the workup. Consulting specialists from rheumatology and infectious disease may help clarify possible underlying diagnoses and the best management plan. If she continues to have organ damage or clinically worsens, it may be prudent to empirically broaden her antibiotic coverage and begin antifungal agents while starting glucocorticoid therapy for suspected HLH.
A stool molecular screen from admission was returned positive for S enterica serovar Typhi. Ciprofloxacin was discontinued and ceftriaxone was started out of concern for antibiotic resistance. On hospital day 14, the patient’s brother presented to the ED with fever. His blood and stool cultures were positive for S enterica serovar Typhi with intermediate sensitivity to ciprofloxacin and sensitivity to ceftriaxone. With continued treatment with ceftriaxone, the patient improved significantly. Following discharge, she remained afebrile and asymptomatic. During outpatient follow up, a repeat PPD was positive and she was diagnosed with and treated for latent tuberculosis.
COMMENTARY
The evaluation of a patient who has recently emigrated from a foreign nation requires a broad differential diagnosis and a keen awareness of the clinical conditions present in the patient’s country of origin. This often involves knowledge of diseases infrequently encountered in daily practice, as well as awareness of the nuances of rare presentations and possible complications. When the presentation is not classic for a relevant infectious disease and clinical conditions from other diagnostic classes are considered, the evaluation and management of the patient is particularly challenging.
Typhoid fever is a severe systemic illness caused by the organism S enterica serovar Typhi. The organism is ingested, penetrates the small intestinal epithelium, enters the lymphoid tissue, and disseminates via the lymphatic and hematogenous routes. Onset of symptoms typically occurs 5 to 21 days after ingestion of contaminated food or water. Clinical features include fever, chills, relative bradycardia (pulse-temperature dissociation), abdominal pain, rose spots (salmon-colored macules) on the trunk and abdomen, and hepatosplenomegaly. Diarrhea is not a typical symptom of patients with typhoid fever, which can lead to a delayed or missed diagnosis. Life-threatening complications can be seen, including gastrointestinal bleeding, intestinal perforation, and meningitis.1 Typhoid fever is most prevalent in impoverished areas with poor access to sanitation. Regions with the highest incidence include south-central Asia, southeast Asia, and southern Africa.2-4 Approximately 200 to 300 cases are reported in the United States each year.5
Classically, the diagnosis is made by means of clinical symptoms and a positive culture from a sterile site. A recent study of 529 patients found that 61% had positive blood cultures and 96% had positive bone marrow cultures.6 Our patient’s diagnosis was significantly delayed by multiple negative cultures and failure to improve on first-line antibiotics, which initially suggested that the S enterica serovar Typhi stool molecular screen likely represented carriage caused by colonization. Chronic S enterica serovar Typhi carriage is defined as excretion of the organism in stool or urine 1 year or longer after acute infection. Rates of carriage range from 1% to 6%, and up to 25% of carriers have no history of typhoid fever.1,7,8 Carriage is more common in females and in those with biliary tract abnormalities.9,10
Once a presumptive diagnosis is made, antibiotic choice remains a challenge. Resistance to fluoroquinolones, the preferred drug for multidrug-resistant typhoid fever, is growing but remains rare, at approximately 5%.11,12 Ceftriaxone and azithromycin have been used successfully in areas with high resistance.13 Given the patient’s slow response to therapy even after transitioning from ciprofloxacin to ceftriaxone, her brother’s presentation and obtaining the antibiotic sensitivities for his organism were critical to confirming that our diagnosis and management decisions were correct.
One strongly considered diagnosis was HLH/MAS. MAS is an aggressive syndrome of excessive inflammation and tissue destruction caused by inappropriate immune system activation. It belongs to a group of histiocytic disorders collectively known as HLH. Aside from primary (genetic) forms, secondary forms exist that can be triggered by malignancy, infection, or rheumatologic disorders. In infection-associated HLH/MAS, viral infections are a common trigger, with Epstein-Barr virus being the most common. Association with bacterial infections, including tuberculosis and typhoid fever, has also been reported.14 Prompt therapy, often with immunosuppressive agents such as glucocorticoids, is essential for survival because there is a reported mortality rate of up to 50% when untreated.15 When infection-induced HLH/MAS occurs, treatment of the underlying infection is critical.14,15 The greatest barrier to a favorable outcome from HLH/MAS is often a delay in diagnosis because the rarity of this disease, the variable clinical presentation, and the lack of specificity of the clinical and laboratory findings make a conclusive diagnosis challenging.
In the presented case, diagnostic uncertainty challenged the decision to administer systemic glucocorticoids. Glucocorticoids conferred a risk of harm for multiple diagnoses that remained on the differential, including malignancy and infection. Her diagnostic evaluation made malignancy less likely, but because testing was unable to rule out tuberculosis as either the underlying cause or coinfection, the team opted to defer initiating glucocorticoids and instead closely monitor for a worsening inflammatory response. Following appropriate treatment of her systemic infection, her PPD was repeated and became positive. The negative PPD and Candida control obtained during her hospitalization were, therefore, likely caused by anergy in the setting of overwhelming systemic illness. Initiation of glucocorticoids prematurely in this case could have led to further harm because immunosuppression may have led to reactivation of latent tuberculosis or exacerbation of illness from an alternative but then undiagnosed infection.
The patient’s ultimate unifying diagnosis was typhoid fever; however, there are mixed expert opinions as to whether the systemic immune activation was significant enough to merit the diagnosis of infection-induced secondary HLH/MAS. Despite the high morbidity and mortality that can accompany HLH/MAS, it has been reported that a significant proportion of cases of secondary HLH/MAS can be managed effectively with treatment of the underlying etiology; this may have been the case for our patient.14,15 The clinicians in this case were caught between diagnoses, unable to safely reach either one—much like a baseball player stranded between bases. Fortunately for this patient, the diagnosis ultimately emerged after a careful and thorough workup, assisted by the more straightforward diagnosis of her brother with the same disease.
KEY TEACHING POINTS
- Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi has a high false-negative rate in blood and stool cultures; therefore, clinical suspicion should remain high in the setting of a high pre-test probability.
- Fluoroquinolones are traditionally first-line therapy for typhoid fever, but the use of ceftriaxone and azithromycin is increasing because of rising fluoroquinolone resistance.
- Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis/macrophage activation syndrome is characterized by excessive inflammation and tissue destruction caused by inappropriate immune system activation. This syndrome can be fatal without appropriate immunosuppressive therapy; however, glucocorticoid administration must be pursued with caution when infection and malignancy are on the differential diagnosis.
1. Parry CM, Hien TT, Dougan G, et al. Typhoid fever. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(22):1770-1782. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmra020201
2. Crump JA, Luby SP, Mintz ED. The global burden of typhoid fever. Bull World Health Organ. 2004;82(5):346-353.
3. Buckle GC, Walker CL, Black RE. Typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever: systematic review to estimate global morbidity and mortality for 2010. J Glob Health. 2012;2(1):010401. https://doi.org/10.7189/jogh.02.010401
4. Mogasale V, Maskery B, Ochiai RL, et al. Burden of typhoid fever in low-income and middle-income countries: a systematic, literature-based update with risk-factor adjustment. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2(10):e570-e580. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2214-109x(14)70301-8
5. Lynch MF, Blanton EM, Bulens S, et al. Typhoid fever in the United States, 1999-2006. JAMA. 2009;302(8):859-865. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.1229
6. Mogasale V, Ramani E, Mogasale VV, Park J. What proportion of Salmonella typhi cases are detected by blood culture? a systematic literature review. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2016;15(1):32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12941-016-0147-z
7. Merselis JG Jr, Kaye D, Connolly CS, Hook EW. Quantitative bacteriology of the Typhoid carrier state. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1964;13:425-429. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.1964.13.425
8. Lanata CF, Levine MM, Ristori C, et al. Vi serology in detection of chronic Salmonella typhi carriers in an endemic area. Lancet. 1983;2(8347):441-443. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90401-4
9. Lai CW, Chan RC, Cheng AF, Sung JY, Leung JW. Common bile duct stones: a cause of chronic salmonellosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992;87(9):1198-1199.
10. Hofmann E, Chianale J, Rollán A, Pereira J, Ferrecio C, Sotomayor V. Blood group antigen secretion and gallstone disease in the Salmonella typhi chronic carrier state. J Infect Dis. 1993;167(4):993-994. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/167.4.993
11. Steel AD, Hay Burgess DC, Diaz Z, Carey ME, Zaidi AKM. Challenges and opportunities for typhoid fever control: a call for coordinated action. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62 (Suppl 1):S4-S8. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/civ976
12. Hendriksen RS, Leekitcharoenphon P, Lukjancenko O, et al. Genomic signature of multidrug resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi isolates related to a massive outbreak in Zambia between 2010 and 2012. J Clin Microbiol. 2015;53(1):262-272. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.02026-14
13. Crump JA, Sjölund-Karlsson M, Gordon MA, Parry CM. Epidemiology, clinical presentation, laboratory diagnosis, antimicrobial resistance, and antimicrobial management of Salmonella infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015;28(4):901-936. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.00002-15
14. Rouphael NG, Talati NJ, Vaughan C, Cunningham K, Moreira R, Gould C. Infections associated with haemophagocytic syndrome. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7(12):814-822. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1473-3099(07)70290-6
15. Fisman DN. Hemophagocytic syndromes and infection. Emerg Infect Dis. 2000;6(6):601-608. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid0606.000608
1. Parry CM, Hien TT, Dougan G, et al. Typhoid fever. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(22):1770-1782. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmra020201
2. Crump JA, Luby SP, Mintz ED. The global burden of typhoid fever. Bull World Health Organ. 2004;82(5):346-353.
3. Buckle GC, Walker CL, Black RE. Typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever: systematic review to estimate global morbidity and mortality for 2010. J Glob Health. 2012;2(1):010401. https://doi.org/10.7189/jogh.02.010401
4. Mogasale V, Maskery B, Ochiai RL, et al. Burden of typhoid fever in low-income and middle-income countries: a systematic, literature-based update with risk-factor adjustment. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2(10):e570-e580. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2214-109x(14)70301-8
5. Lynch MF, Blanton EM, Bulens S, et al. Typhoid fever in the United States, 1999-2006. JAMA. 2009;302(8):859-865. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.1229
6. Mogasale V, Ramani E, Mogasale VV, Park J. What proportion of Salmonella typhi cases are detected by blood culture? a systematic literature review. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2016;15(1):32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12941-016-0147-z
7. Merselis JG Jr, Kaye D, Connolly CS, Hook EW. Quantitative bacteriology of the Typhoid carrier state. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1964;13:425-429. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.1964.13.425
8. Lanata CF, Levine MM, Ristori C, et al. Vi serology in detection of chronic Salmonella typhi carriers in an endemic area. Lancet. 1983;2(8347):441-443. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90401-4
9. Lai CW, Chan RC, Cheng AF, Sung JY, Leung JW. Common bile duct stones: a cause of chronic salmonellosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992;87(9):1198-1199.
10. Hofmann E, Chianale J, Rollán A, Pereira J, Ferrecio C, Sotomayor V. Blood group antigen secretion and gallstone disease in the Salmonella typhi chronic carrier state. J Infect Dis. 1993;167(4):993-994. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/167.4.993
11. Steel AD, Hay Burgess DC, Diaz Z, Carey ME, Zaidi AKM. Challenges and opportunities for typhoid fever control: a call for coordinated action. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62 (Suppl 1):S4-S8. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/civ976
12. Hendriksen RS, Leekitcharoenphon P, Lukjancenko O, et al. Genomic signature of multidrug resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi isolates related to a massive outbreak in Zambia between 2010 and 2012. J Clin Microbiol. 2015;53(1):262-272. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.02026-14
13. Crump JA, Sjölund-Karlsson M, Gordon MA, Parry CM. Epidemiology, clinical presentation, laboratory diagnosis, antimicrobial resistance, and antimicrobial management of Salmonella infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015;28(4):901-936. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.00002-15
14. Rouphael NG, Talati NJ, Vaughan C, Cunningham K, Moreira R, Gould C. Infections associated with haemophagocytic syndrome. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7(12):814-822. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1473-3099(07)70290-6
15. Fisman DN. Hemophagocytic syndromes and infection. Emerg Infect Dis. 2000;6(6):601-608. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid0606.000608
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine
A Smoky Dilemma
A 23-year-old woman presented to the emergency department complaining of “feeling terrible” for the past week. She described subjective fevers, chills, nonproductive cough, myalgias, and nausea. Her symptoms worsened on the day of presentation, with drenching night sweats, worsening myalgias, and generalized fatigue. She was unable to tolerate oral intake due to persistent nausea and had one episode of emesis.
While the initial constellation of symptoms suggests a viral syndrome, its progression over a week raises concern for something more ominous. Of her relatively nonspecific symptoms, prominent myalgias accompanied by a febrile illness may be most helpful. Fever, myalgias, and nonproductive cough are typical of seasonal influenza, although the presence of nausea and vomiting is atypical in adults. (Though this patient presented for care prior to the coronavirus disease 2019 [COVID-19] pandemic, depending on the timing of this presentation, COVID-19 should be considered.) Acute viral myositis can complicate many viral illnesses, such as influenza, coxsackie, and Epstein-Barr virus infections. Other infectious causes of myositis include systemic bacterial infections, spirochete diseases, and other viral infections, including dengue fever. Myalgias can also be a prominent feature of noninfectious systemic inflammatory conditions, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, polymyositis, and systemic vasculitis. Night sweats, while concerning, can be present in myriad conditions, and are not usually a discriminating symptom.
Her past medical history included depression, nephrolithiasis, frequent urinary tract infections, bladder spasms, and recurrent genital herpes simplex virus infection. Her medications included bupropion, microgestin, mirabegron, and valacyclovir. Her father had emphysema.
The patient was employed as a physical therapy assistant in a geriatric care center. Two weeks prior to presentation, she traveled from her home in North Carolina to visit a friend in Atlanta, Georgia. Shortly after the patient returned home, her friend in Atlanta became ill and was treated empirically for Legionella infection because of a recent outbreak in the area. One week prior to presentation, the patient and her boyfriend went on a day hike in the Smoky Mountains in North Carolina, but the patient did not recall any insect or tick bites. Her boyfriend had not been ill.
This history elucidates several potentially relevant medication and environmental exposures. Although bupropion can cause myalgias, neither it nor the other medications she is taking are likely to cause her constellation of symptoms. Her travel history to Atlanta suggests possible, though unconfirmed, exposure to Legionella pneumophila. Notably, she would have had to be exposed to the same source as her friend, since transmission of Legionella occurs via contaminated water and soil, not by human-to-human contact. Legionella infection typically causes a pneumonic process as described here, but her prominent myalgias would not be typical.
Her hike in the Smoky Mountains could have exposed her to several vector-borne diseases. Mosquito-borne dengue in North Carolina is extremely rare, but West Nile virus and eastern equine virus are found within that region. West Nile virus could cause a similar illness, although the cough and lack of neurologic symptoms would be unusual. Eastern equine virus can also cause similar symptoms but is quite rare.
Tick-borne illnesses that should be considered for this region include Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF), ehrlichiosis, and babesiosis. These tend to present with nonspecific symptoms, but myalgias and fever are consistent features. Lyme disease this close to tick exposure usually presents with the characteristic erythema migrans rash, present in 80% of cases, with or without an influenza-like illness. Approximately 80% of patients do not recall a tick bite, even though a tick must be attached for 36 to 48 hours to transmit the spirochete. RMSF often presents with fever and myalgias, with arthralgias and headache, which are lacking in this case. The common, characteristic rash of blanching erythematous macules that convert to petechiae, starting at the ankles and wrists and spreading to the trunk, is often absent at presentation, showing up at days 3 to 5 in most patients.
Ehrlichiosis presents with an influenza-like illness, but up to half of patients also have nausea and cough. It can also present with a macular and petechial rash in a minority of patients. Lastly, babesiosis presents with an influenza-like illness and less often with cough or nausea. At this juncture, RMSF and ehrlichiosis are possibilities given the hiking history and symptoms, although the absence of a rash points more to ehrlichiosis.
The patient did not smoke cigarettes but had used a JUUL© vaporizer daily for the prior 2 years. Her last use was 1 week prior to admission. She used tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) pods purchased online in the vaporizer on a few occasions 1month prior but had not used THC since that time. She denied alcohol or other drug use.
Until recently, this important detail about vaping use would have been passed over without much consideration. Though reports of acute lung injury from vaping were published as early as 2017, it first came to national attention in August 2019 when the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention posted a Health Advisory about severe lung injury associated with e-cigarette use. Of note, this advisory and subsequent published case series outline that e-cigarette, or vaping, use-associated lung injury (EVALI) may present with more than just respiratory symptoms. Most patients have respiratory symptoms such as shortness of breath, cough, or pleurisy, but many have gastrointestinal symptoms which may include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.1 Constitutional symptoms, including fever, chills, or weight loss, may also predominate.2 In some cases, the gastrointestinal symptoms precede the pulmonary symptoms. This patient’s symptoms warrant consideration of EVALI starting with a chest x-ray (CXR), which is usually abnormal in this disease.2
Physical examination revealed that the patient was alert, diaphoretic, and in mild respiratory distress. Temperature was 103.6 °F, blood pressure 129/75 mm Hg, pulse 130 beats per minute, respiratory rate 20 per minute, and oxygen saturation 97% while breathing ambient air. Cardiac examination revealed tachycardia without murmurs, rubs, or gallops. Lung exam revealed scattered rhonchi over the left posterior lower chest without egophony or dullness to percussion. Findings from abdominal, skin, neurologic, lymph node, and musculoskeletal exams were unremarkable.
Her fever, tachycardia, and respiratory distress point to a pulmonary process such as pneumonia or EVALI, even though she does not have definitive physical exam evidence of pneumonia. She presents with systemic inflammatory response syndrome without significant hypoxia and with borderline tachypnea, which could be related to sepsis or lactic acidosis from a systemic infection other than pneumonia. Her symptom complex could also be compatible with severe influenza infection. The absence of rash makes RMSF less likely.
Results of a complete blood count demonstrated a white blood cell count of 12,600/µL with 87% neutrophils. Results of a metabolic panel were normal, and a urine pregnancy test was negative. The electrocardiogram revealed sinus tachycardia without other abnormalities. A CXR showed no evidence of acute cardiopulmonary abnormalities.
Her lab studies lack thrombocytopenia, which is often found in ehrlichiosis and RMSF. Leukopenia is also absent, which can be seen in Lyme disease and ehrlichiosis. The mild leukocytosis could be consistent with pneumonia, influenza, and EVALI and is not discriminating. The normal CXR goes against pneumonia or EVALI; however, 9% of patients with EVALI in one case series had a normal CXR, while computed tomography (CT) of the chest demonstrated bilateral ground-glass opacities.3 Chest CT is indicated in this case given the poor correlation of the CXR findings and this patient’s pronounced respiratory symptoms.
CT of the chest with contrast did not show a pulmonary embolism but revealed diffuse ground-glass opacities, predominantly in the dependent lower lobes (Figure 1).
Acute conditions with diffuse ground-glass opacities include mycoplasma, Pneumocystis jiroveci and viral pneumonias, pulmonary hemorrhage and edema, acute interstitial pneumonia, eosinophilic lung diseases, and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Diffuse ground-glass opacities are also seen in almost all patients with EVALI. Though less likely, RMSF, babesiosis, and ehrlichiosis are not ruled out by these chest CT findings, since these disease entities can sometimes cause pulmonary manifestations, including pneumonia, pulmonary edema, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).4
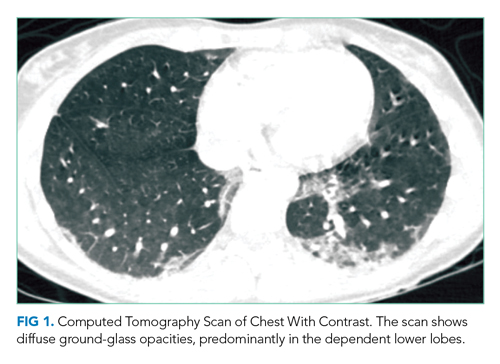
In addition to Legionella and pneumococcal urinary antigen tests, respiratory viral panel, and blood cultures, it would be judicious to obtain HIV, C-reactive protein, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) testing; these last two tests are often markedly elevated in EVALI. The utility of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) in suspected EVALI cases is not clearly defined, but should be considered in this case to ensure that infectious etiologies are not missed.2 Because of her potential environmental exposures, serologic testing for RMSF and ehrlichiosis should be sent.
Given the overlap in signs and symptoms of EVALI with various, potentially life-threatening infections, she should be empirically treated with antibiotics to cover for community-acquired pneumonia. Adding or even substituting doxycycline for a macrolide antibiotic in this regimen should be considered given that it would treat both RMSF and ehrlichiosis pending further test results. Delay in treating RMSF is associated with worse outcomes. If she is presenting during influenza season, she should also be treated with a neuraminidase inhibitor while awaiting influenza test results. Though the pathophysiology of EVALI is not entirely known, it appears to be inflammatory in nature. Most presumed cases have responded to corticosteroids, with improvement in oxygenation.2 Therefore, treatment with corticosteroids may be warranted to improve oxygenation while ruling out infectious processes.
The patient was admitted to the general medicine wards and started on ceftriaxone and azithromycin for empiric treatment of community-acquired pneumonia. On hospital day 2, a respiratory viral panel returned negative. Procalcitonin, HIV, and blood cultures all returned negative. An ESR was elevated at 86 mm/h. The patient continued to have daily fevers and developed erythematous, blanching macules on the neck, chest, back, and arms, which were noted to occur during febrile periods. Ceftriaxone and azithromycin were discontinued, and doxycycline was started. By hospital day 4, the patient’s oxygen saturation worsened to 86% on ambient air. She continued to have fevers and her cough worsened, with occasional blood-streaked sputum. The patient was transferred to the intensive care unit for closer monitoring.
On hospital day 5, she required intubation for worsening hypoxia. Bronchoscopy was performed, which revealed small mucosal crypts along the left mainstem bronchus. A small amount of bleeding after transbronchial biopsy of the left lower lobe was noted, which resolved with occlusion using the bronchoscope. BAL was performed, which revealed red, cloudy aspirate with 1,100 white blood cells (85% neutrophils) and 22,400 red blood cells. No bacteria were identified.
The patient has developed hypoxic respiratory failure despite appropriate antibiotics and negative cultures, increasing the likelihood of a noninfectious etiology. Her rash is not typical for RMSF, which usually starts as a macular or petechial rash at the ankles and wrists, and spreads centrally to the trunk. Rash is not typically associated with EVALI, and in this case, may represent miliaria caused by her fever.
The mucosal crypts seen on bronchoscopy are nonspecific, likely indicating inflammation from vaping. The BAL otherwise suggests diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH), although sequential BAL aliquots are needed to confirm this diagnosis. DAH is usually caused by pulmonary capillaritis from vasculitis, Goodpasture disease, rheumatic diseases, or diffuse alveolar damage from toxins, infections, rheumatic diseases, or interstitial or organizing pneumonias. Diffuse alveolar damage is the pathologic finding of ARDS, which can be seen in severe cases of many of the conditions discussed, including EVALI, ehrlichiosis, babesiosis, sepsis, and community-acquired pneumonia.4
The BAL is most consistent with EVALI, which often shows elevated neutrophils. DAH due to vaping has also been reported.5 In patients with EVALI, varied pathologic findings of acute lung injury have been reported, including diffuse alveolar damage.6 At this point, laboratory evaluation for rheumatologic diseases and vasculitis should be obtained, and lung biopsy results reviewed. Given her clinical deterioration, treatment with intravenous corticosteroids for presumed EVALI is warranted.
Urine Legionella and Streptococcal pneumoniae antigen tests were negative. The patient was started on methylprednisolone 40 mg intravenously every 8 hours. Further testing included antinuclear antibodies, which was positive at 1:320, with a dense, fine speckled pattern. Perinuclear antineutrophilic cytoplasmic autoantibody, cytoplasmic antineutrophilic cytoplasmic autoantibody, myeloperoxidase, proteinase 3, double-stranded DNA, and glomerular basement membrane IgG were all negative. Transbronchial lung biopsy revealed severe acute lung injury consistent with diffuse alveolar damage. The pulmonary interstitium was mildly expanded by edema, with a moderate number of eosinophilic hyaline membranes. There were no eosinophils or evidence of hemorrhage, granulomas, or giant cells. These changes, within this clinical context, were diagnostic for EVALI.
The patient was intubated for 4 days and completed a course of empiric antibiotics as well as a 10-day course of prednisone. She was discharged on hospital day 17 on 2 L continuous oxygen via nasal cannula. Two days after discharge, she developed worsening dyspnea and chest pain and was readmitted with worsening ground-glass opacities, left upper lobe and right- sided pneumothoraces, and subcutaneous emphysema (Figure 2). She was treated with continuous oxygen to maintain oxygen saturation at 100% and eventually discharged home 3 days later on 3 L continuous oxygen. She attended pulmonary rehabilitation and was weaned off oxygen 2 months later, with marked improvement in aeration of both lungs (Figure 3). She continued to abstain from tobacco and THC products.
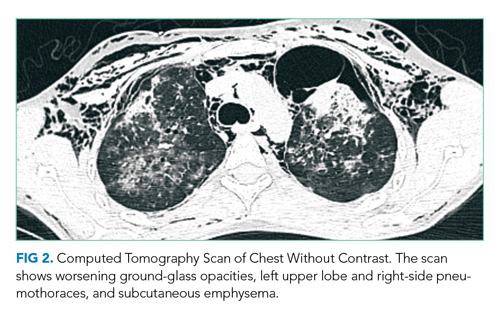
DISCUSSION
The first electronic cigarette (e-cigarette) device was developed in 2003 by a Chinese pharmacist and introduced to the American market in 2007.7 E-cigarettes produce an inhalable aerosol by heating a liquid containing a variety of chemicals, nicotine, and flavors, with or without other additives. Originally promoted as a safer nontobacco and cessation device by producers, e-cigarette sales grew at an annual rate of 115% between 2009 and 2012.8 E-cigarettes can also be used to deliver THC, the psychoactive component of cannabis.
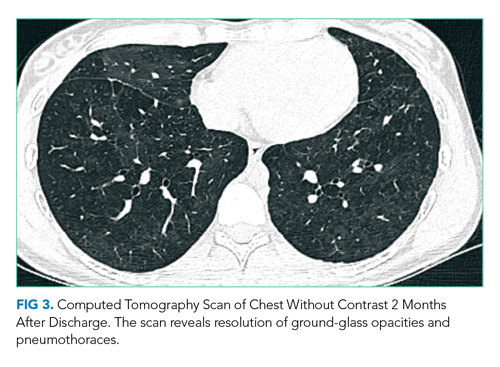
Since the advent of e-cigarettes, their safety has been a topic of concern. In August 2019, the CDC announced 215 possible cases of severe pulmonary disease associated with the use of e-cigarette products that were reported by 25 state health departments.1 By February 2020, EVALI had affected more than 2,800 patients hospitalized across the United States.9
The presenting symptoms of EVALI are varied and nonspecific. The largest EVALI case series, published by Layden et al in 2020, included 98 patients who had a median duration of 6 days of symptoms prior to presentation.3 Respiratory symptoms occurred in 97% of patients, including shortness of breath, any chest pain, pleuritic chest pain, cough, and hemoptysis.3 Presentations also included a variety of gastrointestinal (77%) and constitutional (100%) symptoms, which most commonly included nausea, vomiting, and fever.3 Additional case series have supported a specific pattern of presentation, most commonly including pleuritic chest pain, nonproductive cough, or shortness of breath occurring days to weeks prior to presentation. Associated fatigue, fever, and tachycardia may be present, as well as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal pain, and in some cases, these have preceded respiratory symptoms.3,10,11
The vital signs and physical examination, laboratory, and imaging results associated with EVALI are also fairly nonspecific. The most common reason for hospitalization in EVALI is hypoxia, which can progress to acute respiratory failure requiring supplemental oxygen or, as in this case, mechanical ventilation. The most common laboratory finding is leukocytosis greater than 11,000/µL, with more than 80% neutrophils and an ESR greater than 30 mm/hr. In the Layden et al case series, 83% of patients had an abnormal CXR. All patients who underwent CT scan of the chest had bilateral ground-glass opacities, often with subpleural sparing.3 A minority of patients were found to have a pneumothorax, generally a late finding.3,12 Accordingly, the CDC now defines confirmed EVALI as use of e-cigarettes during the 90 days before symptom onset with the presence of pulmonary infiltrates (opacities on CXR or ground-glass opacities on chest CT), negative results on testing for all clinically indicated respiratory infections including respiratory viral panel and influenza PCR, and no alternative plausible diagnoses.13
The presumed etiology of EVALI is chemical exposure because no consistent infectious etiology has been identified.6 No consistent e-cigarette product, substance, or additive has been identified in all cases, nor has one product been directly linked to EVALI. However, the CDC recently announced that vitamin E acetate in vaping products appears to be associated with EVALI.9 In December 2019, Blount et al identified vitamin E acetate in BAL fluid samples from 48 of 51 EVALI patients.14 Additionally, while no other toxins were identified, 94% of samples contained THC or its metabolites or patients had reported vaping THC within 90 days preceding illness.14
The most effective treatment strategy for EVALI is still unknown. It is recommended to treat with empiric antibiotics for at least 48 hours (and antivirals during influenza season) if the history is unclear or if the patient is intubated or has severe hypoxemia.2 If antibiotic and/or antiviral therapies do not lead to clinical improvement, corticosteroids should be added, as they lead to improved oxygenation in many patients.2 Kalininskiy et al recommend initial administration of methylprednisolone 40 mg every 8 hours, with transition to oral prednisone to complete a 2-week course.2 Given rates of rehospitalization (2.7%) and death (2%) in EVALI, the CDC advises that patients should be clinically stable for 24 to 48 hours prior to discharge; that follow-up visits should be arranged within 48 hours of discharge; and that cases of EVALI should be reported to the state and local health departments.15 As seen in the case presented here, with time and continued abstinence from e-cigarette use, the pulmonary effects of EVALI can improve, but long-term outcomes remain unclear. Clinicians must now consider EVALI in patients presenting with respiratory, constitutional, and gastrointestinal complaints when a history of e-cigarette use is present.
KEY TEACHING POINTS
- EVALI presents most commonly with a combination of respiratory, gastrointestinal, and constitutional symptoms. including shortness of breath, cough, nausea, vomiting, and fever.
- When considering EVALI, evaluate and treat for potential infectious causes of disease first.
- Corticosteroids are the mainstay of therapy in EVALI, leading to improvement in oxygenation in many patients.
- Most of the reported cases of EVALI have occurred in patients who have vaped THC-containing products.
1. Schier JG, Meiman JG, Layden J, et al. Severe pulmonary disease associated with electronic-cigarette-product use – Interim guidance. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019; 68(36):787-790. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6836e2
2. Kalininskiy A, Bach CT, Nacca NE, et al. E-cigarette, or vaping, product use associated lung injury (EVALI): case series and diagnostic approach. Lancet Respir Med. 2019;7(12):1017-1026. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-2600(19)30415-1
3. Layden JE, Ghinai I, Pray I, et al. Pulmonary illness related to e-cigarette use in Illiniois and Wisconsin – final report. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(10):903-916. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1911614
4. Faul JL, Doyle RL, Kao PN, Ruoss SJ. Tick-borne pulmonary disease: update on diagnosis and management. Chest. 1999;116(1):222-230. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.116.1.222
5. Agustin M, Yamamoto M, Cabrera F, Eusebio R. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage induced by vaping. Case Rep Pulmonol. 2018;2018:9724530. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9724530
6. Butt YM, Smith ML, Tazelaar HD, et al. Pathology of vaping-associated lung injury. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(18):1780-1781. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmc1913069
7. Office of the Surgeon General. E-Cigarette Use Among Youth and Young Adults. Chapter 1. Public Health Service, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services; 2016. Accessed January 22, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/data_statistics/sgr/e-cigarettes/index.htm
8. Grana R, Benowitz N, Glantz SA. Background Paper on E-cigarettes (Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems). UCSF: Center for Tobacco Control Research and Education; 2013. https://escholarship.org/uc/item/13p2b72n
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreak of lung injury associated with e-cigarette use, or vaping. December 12, 2019. Updated February 25, 2020. Accessed January 22, 2020 and July 16, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/basic_information/e-cigarettes/severe-lung-disease.html
10. Davidson K, Brancato A, Heetkerks P, et al. Outbreak of e-cigarette-associated acute lipoid pneumonia—North Carolina, July-August 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68(36);784-786. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6836e1
11. Maddock SD, Cirulis MM, Callahan SJ, et al. Pulmonary lipid-laden macrophages and vaping. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(15):1488-1489. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmc1912038
12. Henry TS, Kanne JP, Klingerman SJ. Imaging of vaping-associated lung disease. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(15):1486-1487. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmc1911995
13. Smoking and Tobacco Use: For State, Local, Territorial, and Tribal Health Departments. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed Jan 24, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/basic_information/e-cigarettes/severe-lung-disease/health-departments/index.html
14. Blount BC, Karwowski MP, Shields PG, et al. Vitamin E acetate in bronchoalveolar-lavage fluid associated with EVALI. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(8):697-705. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1916433
15. Evans ME, Twentyman E, Click ES, et al. Update: Interim guidance for health care professionals evaluating and caring for patients with suspected e-cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury and for reducing the risk for rehospitalization and death following hospital discharge — United States, December 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;68(5152):1189-1194. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm685152e2
A 23-year-old woman presented to the emergency department complaining of “feeling terrible” for the past week. She described subjective fevers, chills, nonproductive cough, myalgias, and nausea. Her symptoms worsened on the day of presentation, with drenching night sweats, worsening myalgias, and generalized fatigue. She was unable to tolerate oral intake due to persistent nausea and had one episode of emesis.
While the initial constellation of symptoms suggests a viral syndrome, its progression over a week raises concern for something more ominous. Of her relatively nonspecific symptoms, prominent myalgias accompanied by a febrile illness may be most helpful. Fever, myalgias, and nonproductive cough are typical of seasonal influenza, although the presence of nausea and vomiting is atypical in adults. (Though this patient presented for care prior to the coronavirus disease 2019 [COVID-19] pandemic, depending on the timing of this presentation, COVID-19 should be considered.) Acute viral myositis can complicate many viral illnesses, such as influenza, coxsackie, and Epstein-Barr virus infections. Other infectious causes of myositis include systemic bacterial infections, spirochete diseases, and other viral infections, including dengue fever. Myalgias can also be a prominent feature of noninfectious systemic inflammatory conditions, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, polymyositis, and systemic vasculitis. Night sweats, while concerning, can be present in myriad conditions, and are not usually a discriminating symptom.
Her past medical history included depression, nephrolithiasis, frequent urinary tract infections, bladder spasms, and recurrent genital herpes simplex virus infection. Her medications included bupropion, microgestin, mirabegron, and valacyclovir. Her father had emphysema.
The patient was employed as a physical therapy assistant in a geriatric care center. Two weeks prior to presentation, she traveled from her home in North Carolina to visit a friend in Atlanta, Georgia. Shortly after the patient returned home, her friend in Atlanta became ill and was treated empirically for Legionella infection because of a recent outbreak in the area. One week prior to presentation, the patient and her boyfriend went on a day hike in the Smoky Mountains in North Carolina, but the patient did not recall any insect or tick bites. Her boyfriend had not been ill.
This history elucidates several potentially relevant medication and environmental exposures. Although bupropion can cause myalgias, neither it nor the other medications she is taking are likely to cause her constellation of symptoms. Her travel history to Atlanta suggests possible, though unconfirmed, exposure to Legionella pneumophila. Notably, she would have had to be exposed to the same source as her friend, since transmission of Legionella occurs via contaminated water and soil, not by human-to-human contact. Legionella infection typically causes a pneumonic process as described here, but her prominent myalgias would not be typical.
Her hike in the Smoky Mountains could have exposed her to several vector-borne diseases. Mosquito-borne dengue in North Carolina is extremely rare, but West Nile virus and eastern equine virus are found within that region. West Nile virus could cause a similar illness, although the cough and lack of neurologic symptoms would be unusual. Eastern equine virus can also cause similar symptoms but is quite rare.
Tick-borne illnesses that should be considered for this region include Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF), ehrlichiosis, and babesiosis. These tend to present with nonspecific symptoms, but myalgias and fever are consistent features. Lyme disease this close to tick exposure usually presents with the characteristic erythema migrans rash, present in 80% of cases, with or without an influenza-like illness. Approximately 80% of patients do not recall a tick bite, even though a tick must be attached for 36 to 48 hours to transmit the spirochete. RMSF often presents with fever and myalgias, with arthralgias and headache, which are lacking in this case. The common, characteristic rash of blanching erythematous macules that convert to petechiae, starting at the ankles and wrists and spreading to the trunk, is often absent at presentation, showing up at days 3 to 5 in most patients.
Ehrlichiosis presents with an influenza-like illness, but up to half of patients also have nausea and cough. It can also present with a macular and petechial rash in a minority of patients. Lastly, babesiosis presents with an influenza-like illness and less often with cough or nausea. At this juncture, RMSF and ehrlichiosis are possibilities given the hiking history and symptoms, although the absence of a rash points more to ehrlichiosis.
The patient did not smoke cigarettes but had used a JUUL© vaporizer daily for the prior 2 years. Her last use was 1 week prior to admission. She used tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) pods purchased online in the vaporizer on a few occasions 1month prior but had not used THC since that time. She denied alcohol or other drug use.
Until recently, this important detail about vaping use would have been passed over without much consideration. Though reports of acute lung injury from vaping were published as early as 2017, it first came to national attention in August 2019 when the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention posted a Health Advisory about severe lung injury associated with e-cigarette use. Of note, this advisory and subsequent published case series outline that e-cigarette, or vaping, use-associated lung injury (EVALI) may present with more than just respiratory symptoms. Most patients have respiratory symptoms such as shortness of breath, cough, or pleurisy, but many have gastrointestinal symptoms which may include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.1 Constitutional symptoms, including fever, chills, or weight loss, may also predominate.2 In some cases, the gastrointestinal symptoms precede the pulmonary symptoms. This patient’s symptoms warrant consideration of EVALI starting with a chest x-ray (CXR), which is usually abnormal in this disease.2
Physical examination revealed that the patient was alert, diaphoretic, and in mild respiratory distress. Temperature was 103.6 °F, blood pressure 129/75 mm Hg, pulse 130 beats per minute, respiratory rate 20 per minute, and oxygen saturation 97% while breathing ambient air. Cardiac examination revealed tachycardia without murmurs, rubs, or gallops. Lung exam revealed scattered rhonchi over the left posterior lower chest without egophony or dullness to percussion. Findings from abdominal, skin, neurologic, lymph node, and musculoskeletal exams were unremarkable.
Her fever, tachycardia, and respiratory distress point to a pulmonary process such as pneumonia or EVALI, even though she does not have definitive physical exam evidence of pneumonia. She presents with systemic inflammatory response syndrome without significant hypoxia and with borderline tachypnea, which could be related to sepsis or lactic acidosis from a systemic infection other than pneumonia. Her symptom complex could also be compatible with severe influenza infection. The absence of rash makes RMSF less likely.
Results of a complete blood count demonstrated a white blood cell count of 12,600/µL with 87% neutrophils. Results of a metabolic panel were normal, and a urine pregnancy test was negative. The electrocardiogram revealed sinus tachycardia without other abnormalities. A CXR showed no evidence of acute cardiopulmonary abnormalities.
Her lab studies lack thrombocytopenia, which is often found in ehrlichiosis and RMSF. Leukopenia is also absent, which can be seen in Lyme disease and ehrlichiosis. The mild leukocytosis could be consistent with pneumonia, influenza, and EVALI and is not discriminating. The normal CXR goes against pneumonia or EVALI; however, 9% of patients with EVALI in one case series had a normal CXR, while computed tomography (CT) of the chest demonstrated bilateral ground-glass opacities.3 Chest CT is indicated in this case given the poor correlation of the CXR findings and this patient’s pronounced respiratory symptoms.
CT of the chest with contrast did not show a pulmonary embolism but revealed diffuse ground-glass opacities, predominantly in the dependent lower lobes (Figure 1).
Acute conditions with diffuse ground-glass opacities include mycoplasma, Pneumocystis jiroveci and viral pneumonias, pulmonary hemorrhage and edema, acute interstitial pneumonia, eosinophilic lung diseases, and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Diffuse ground-glass opacities are also seen in almost all patients with EVALI. Though less likely, RMSF, babesiosis, and ehrlichiosis are not ruled out by these chest CT findings, since these disease entities can sometimes cause pulmonary manifestations, including pneumonia, pulmonary edema, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).4

In addition to Legionella and pneumococcal urinary antigen tests, respiratory viral panel, and blood cultures, it would be judicious to obtain HIV, C-reactive protein, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) testing; these last two tests are often markedly elevated in EVALI. The utility of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) in suspected EVALI cases is not clearly defined, but should be considered in this case to ensure that infectious etiologies are not missed.2 Because of her potential environmental exposures, serologic testing for RMSF and ehrlichiosis should be sent.
Given the overlap in signs and symptoms of EVALI with various, potentially life-threatening infections, she should be empirically treated with antibiotics to cover for community-acquired pneumonia. Adding or even substituting doxycycline for a macrolide antibiotic in this regimen should be considered given that it would treat both RMSF and ehrlichiosis pending further test results. Delay in treating RMSF is associated with worse outcomes. If she is presenting during influenza season, she should also be treated with a neuraminidase inhibitor while awaiting influenza test results. Though the pathophysiology of EVALI is not entirely known, it appears to be inflammatory in nature. Most presumed cases have responded to corticosteroids, with improvement in oxygenation.2 Therefore, treatment with corticosteroids may be warranted to improve oxygenation while ruling out infectious processes.
The patient was admitted to the general medicine wards and started on ceftriaxone and azithromycin for empiric treatment of community-acquired pneumonia. On hospital day 2, a respiratory viral panel returned negative. Procalcitonin, HIV, and blood cultures all returned negative. An ESR was elevated at 86 mm/h. The patient continued to have daily fevers and developed erythematous, blanching macules on the neck, chest, back, and arms, which were noted to occur during febrile periods. Ceftriaxone and azithromycin were discontinued, and doxycycline was started. By hospital day 4, the patient’s oxygen saturation worsened to 86% on ambient air. She continued to have fevers and her cough worsened, with occasional blood-streaked sputum. The patient was transferred to the intensive care unit for closer monitoring.
On hospital day 5, she required intubation for worsening hypoxia. Bronchoscopy was performed, which revealed small mucosal crypts along the left mainstem bronchus. A small amount of bleeding after transbronchial biopsy of the left lower lobe was noted, which resolved with occlusion using the bronchoscope. BAL was performed, which revealed red, cloudy aspirate with 1,100 white blood cells (85% neutrophils) and 22,400 red blood cells. No bacteria were identified.
The patient has developed hypoxic respiratory failure despite appropriate antibiotics and negative cultures, increasing the likelihood of a noninfectious etiology. Her rash is not typical for RMSF, which usually starts as a macular or petechial rash at the ankles and wrists, and spreads centrally to the trunk. Rash is not typically associated with EVALI, and in this case, may represent miliaria caused by her fever.
The mucosal crypts seen on bronchoscopy are nonspecific, likely indicating inflammation from vaping. The BAL otherwise suggests diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH), although sequential BAL aliquots are needed to confirm this diagnosis. DAH is usually caused by pulmonary capillaritis from vasculitis, Goodpasture disease, rheumatic diseases, or diffuse alveolar damage from toxins, infections, rheumatic diseases, or interstitial or organizing pneumonias. Diffuse alveolar damage is the pathologic finding of ARDS, which can be seen in severe cases of many of the conditions discussed, including EVALI, ehrlichiosis, babesiosis, sepsis, and community-acquired pneumonia.4
The BAL is most consistent with EVALI, which often shows elevated neutrophils. DAH due to vaping has also been reported.5 In patients with EVALI, varied pathologic findings of acute lung injury have been reported, including diffuse alveolar damage.6 At this point, laboratory evaluation for rheumatologic diseases and vasculitis should be obtained, and lung biopsy results reviewed. Given her clinical deterioration, treatment with intravenous corticosteroids for presumed EVALI is warranted.
Urine Legionella and Streptococcal pneumoniae antigen tests were negative. The patient was started on methylprednisolone 40 mg intravenously every 8 hours. Further testing included antinuclear antibodies, which was positive at 1:320, with a dense, fine speckled pattern. Perinuclear antineutrophilic cytoplasmic autoantibody, cytoplasmic antineutrophilic cytoplasmic autoantibody, myeloperoxidase, proteinase 3, double-stranded DNA, and glomerular basement membrane IgG were all negative. Transbronchial lung biopsy revealed severe acute lung injury consistent with diffuse alveolar damage. The pulmonary interstitium was mildly expanded by edema, with a moderate number of eosinophilic hyaline membranes. There were no eosinophils or evidence of hemorrhage, granulomas, or giant cells. These changes, within this clinical context, were diagnostic for EVALI.
The patient was intubated for 4 days and completed a course of empiric antibiotics as well as a 10-day course of prednisone. She was discharged on hospital day 17 on 2 L continuous oxygen via nasal cannula. Two days after discharge, she developed worsening dyspnea and chest pain and was readmitted with worsening ground-glass opacities, left upper lobe and right- sided pneumothoraces, and subcutaneous emphysema (Figure 2). She was treated with continuous oxygen to maintain oxygen saturation at 100% and eventually discharged home 3 days later on 3 L continuous oxygen. She attended pulmonary rehabilitation and was weaned off oxygen 2 months later, with marked improvement in aeration of both lungs (Figure 3). She continued to abstain from tobacco and THC products.

DISCUSSION
The first electronic cigarette (e-cigarette) device was developed in 2003 by a Chinese pharmacist and introduced to the American market in 2007.7 E-cigarettes produce an inhalable aerosol by heating a liquid containing a variety of chemicals, nicotine, and flavors, with or without other additives. Originally promoted as a safer nontobacco and cessation device by producers, e-cigarette sales grew at an annual rate of 115% between 2009 and 2012.8 E-cigarettes can also be used to deliver THC, the psychoactive component of cannabis.

Since the advent of e-cigarettes, their safety has been a topic of concern. In August 2019, the CDC announced 215 possible cases of severe pulmonary disease associated with the use of e-cigarette products that were reported by 25 state health departments.1 By February 2020, EVALI had affected more than 2,800 patients hospitalized across the United States.9
The presenting symptoms of EVALI are varied and nonspecific. The largest EVALI case series, published by Layden et al in 2020, included 98 patients who had a median duration of 6 days of symptoms prior to presentation.3 Respiratory symptoms occurred in 97% of patients, including shortness of breath, any chest pain, pleuritic chest pain, cough, and hemoptysis.3 Presentations also included a variety of gastrointestinal (77%) and constitutional (100%) symptoms, which most commonly included nausea, vomiting, and fever.3 Additional case series have supported a specific pattern of presentation, most commonly including pleuritic chest pain, nonproductive cough, or shortness of breath occurring days to weeks prior to presentation. Associated fatigue, fever, and tachycardia may be present, as well as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal pain, and in some cases, these have preceded respiratory symptoms.3,10,11
The vital signs and physical examination, laboratory, and imaging results associated with EVALI are also fairly nonspecific. The most common reason for hospitalization in EVALI is hypoxia, which can progress to acute respiratory failure requiring supplemental oxygen or, as in this case, mechanical ventilation. The most common laboratory finding is leukocytosis greater than 11,000/µL, with more than 80% neutrophils and an ESR greater than 30 mm/hr. In the Layden et al case series, 83% of patients had an abnormal CXR. All patients who underwent CT scan of the chest had bilateral ground-glass opacities, often with subpleural sparing.3 A minority of patients were found to have a pneumothorax, generally a late finding.3,12 Accordingly, the CDC now defines confirmed EVALI as use of e-cigarettes during the 90 days before symptom onset with the presence of pulmonary infiltrates (opacities on CXR or ground-glass opacities on chest CT), negative results on testing for all clinically indicated respiratory infections including respiratory viral panel and influenza PCR, and no alternative plausible diagnoses.13
The presumed etiology of EVALI is chemical exposure because no consistent infectious etiology has been identified.6 No consistent e-cigarette product, substance, or additive has been identified in all cases, nor has one product been directly linked to EVALI. However, the CDC recently announced that vitamin E acetate in vaping products appears to be associated with EVALI.9 In December 2019, Blount et al identified vitamin E acetate in BAL fluid samples from 48 of 51 EVALI patients.14 Additionally, while no other toxins were identified, 94% of samples contained THC or its metabolites or patients had reported vaping THC within 90 days preceding illness.14
The most effective treatment strategy for EVALI is still unknown. It is recommended to treat with empiric antibiotics for at least 48 hours (and antivirals during influenza season) if the history is unclear or if the patient is intubated or has severe hypoxemia.2 If antibiotic and/or antiviral therapies do not lead to clinical improvement, corticosteroids should be added, as they lead to improved oxygenation in many patients.2 Kalininskiy et al recommend initial administration of methylprednisolone 40 mg every 8 hours, with transition to oral prednisone to complete a 2-week course.2 Given rates of rehospitalization (2.7%) and death (2%) in EVALI, the CDC advises that patients should be clinically stable for 24 to 48 hours prior to discharge; that follow-up visits should be arranged within 48 hours of discharge; and that cases of EVALI should be reported to the state and local health departments.15 As seen in the case presented here, with time and continued abstinence from e-cigarette use, the pulmonary effects of EVALI can improve, but long-term outcomes remain unclear. Clinicians must now consider EVALI in patients presenting with respiratory, constitutional, and gastrointestinal complaints when a history of e-cigarette use is present.
KEY TEACHING POINTS
- EVALI presents most commonly with a combination of respiratory, gastrointestinal, and constitutional symptoms. including shortness of breath, cough, nausea, vomiting, and fever.
- When considering EVALI, evaluate and treat for potential infectious causes of disease first.
- Corticosteroids are the mainstay of therapy in EVALI, leading to improvement in oxygenation in many patients.
- Most of the reported cases of EVALI have occurred in patients who have vaped THC-containing products.
A 23-year-old woman presented to the emergency department complaining of “feeling terrible” for the past week. She described subjective fevers, chills, nonproductive cough, myalgias, and nausea. Her symptoms worsened on the day of presentation, with drenching night sweats, worsening myalgias, and generalized fatigue. She was unable to tolerate oral intake due to persistent nausea and had one episode of emesis.
While the initial constellation of symptoms suggests a viral syndrome, its progression over a week raises concern for something more ominous. Of her relatively nonspecific symptoms, prominent myalgias accompanied by a febrile illness may be most helpful. Fever, myalgias, and nonproductive cough are typical of seasonal influenza, although the presence of nausea and vomiting is atypical in adults. (Though this patient presented for care prior to the coronavirus disease 2019 [COVID-19] pandemic, depending on the timing of this presentation, COVID-19 should be considered.) Acute viral myositis can complicate many viral illnesses, such as influenza, coxsackie, and Epstein-Barr virus infections. Other infectious causes of myositis include systemic bacterial infections, spirochete diseases, and other viral infections, including dengue fever. Myalgias can also be a prominent feature of noninfectious systemic inflammatory conditions, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, polymyositis, and systemic vasculitis. Night sweats, while concerning, can be present in myriad conditions, and are not usually a discriminating symptom.
Her past medical history included depression, nephrolithiasis, frequent urinary tract infections, bladder spasms, and recurrent genital herpes simplex virus infection. Her medications included bupropion, microgestin, mirabegron, and valacyclovir. Her father had emphysema.
The patient was employed as a physical therapy assistant in a geriatric care center. Two weeks prior to presentation, she traveled from her home in North Carolina to visit a friend in Atlanta, Georgia. Shortly after the patient returned home, her friend in Atlanta became ill and was treated empirically for Legionella infection because of a recent outbreak in the area. One week prior to presentation, the patient and her boyfriend went on a day hike in the Smoky Mountains in North Carolina, but the patient did not recall any insect or tick bites. Her boyfriend had not been ill.
This history elucidates several potentially relevant medication and environmental exposures. Although bupropion can cause myalgias, neither it nor the other medications she is taking are likely to cause her constellation of symptoms. Her travel history to Atlanta suggests possible, though unconfirmed, exposure to Legionella pneumophila. Notably, she would have had to be exposed to the same source as her friend, since transmission of Legionella occurs via contaminated water and soil, not by human-to-human contact. Legionella infection typically causes a pneumonic process as described here, but her prominent myalgias would not be typical.
Her hike in the Smoky Mountains could have exposed her to several vector-borne diseases. Mosquito-borne dengue in North Carolina is extremely rare, but West Nile virus and eastern equine virus are found within that region. West Nile virus could cause a similar illness, although the cough and lack of neurologic symptoms would be unusual. Eastern equine virus can also cause similar symptoms but is quite rare.
Tick-borne illnesses that should be considered for this region include Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF), ehrlichiosis, and babesiosis. These tend to present with nonspecific symptoms, but myalgias and fever are consistent features. Lyme disease this close to tick exposure usually presents with the characteristic erythema migrans rash, present in 80% of cases, with or without an influenza-like illness. Approximately 80% of patients do not recall a tick bite, even though a tick must be attached for 36 to 48 hours to transmit the spirochete. RMSF often presents with fever and myalgias, with arthralgias and headache, which are lacking in this case. The common, characteristic rash of blanching erythematous macules that convert to petechiae, starting at the ankles and wrists and spreading to the trunk, is often absent at presentation, showing up at days 3 to 5 in most patients.
Ehrlichiosis presents with an influenza-like illness, but up to half of patients also have nausea and cough. It can also present with a macular and petechial rash in a minority of patients. Lastly, babesiosis presents with an influenza-like illness and less often with cough or nausea. At this juncture, RMSF and ehrlichiosis are possibilities given the hiking history and symptoms, although the absence of a rash points more to ehrlichiosis.
The patient did not smoke cigarettes but had used a JUUL© vaporizer daily for the prior 2 years. Her last use was 1 week prior to admission. She used tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) pods purchased online in the vaporizer on a few occasions 1month prior but had not used THC since that time. She denied alcohol or other drug use.
Until recently, this important detail about vaping use would have been passed over without much consideration. Though reports of acute lung injury from vaping were published as early as 2017, it first came to national attention in August 2019 when the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention posted a Health Advisory about severe lung injury associated with e-cigarette use. Of note, this advisory and subsequent published case series outline that e-cigarette, or vaping, use-associated lung injury (EVALI) may present with more than just respiratory symptoms. Most patients have respiratory symptoms such as shortness of breath, cough, or pleurisy, but many have gastrointestinal symptoms which may include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.1 Constitutional symptoms, including fever, chills, or weight loss, may also predominate.2 In some cases, the gastrointestinal symptoms precede the pulmonary symptoms. This patient’s symptoms warrant consideration of EVALI starting with a chest x-ray (CXR), which is usually abnormal in this disease.2
Physical examination revealed that the patient was alert, diaphoretic, and in mild respiratory distress. Temperature was 103.6 °F, blood pressure 129/75 mm Hg, pulse 130 beats per minute, respiratory rate 20 per minute, and oxygen saturation 97% while breathing ambient air. Cardiac examination revealed tachycardia without murmurs, rubs, or gallops. Lung exam revealed scattered rhonchi over the left posterior lower chest without egophony or dullness to percussion. Findings from abdominal, skin, neurologic, lymph node, and musculoskeletal exams were unremarkable.
Her fever, tachycardia, and respiratory distress point to a pulmonary process such as pneumonia or EVALI, even though she does not have definitive physical exam evidence of pneumonia. She presents with systemic inflammatory response syndrome without significant hypoxia and with borderline tachypnea, which could be related to sepsis or lactic acidosis from a systemic infection other than pneumonia. Her symptom complex could also be compatible with severe influenza infection. The absence of rash makes RMSF less likely.
Results of a complete blood count demonstrated a white blood cell count of 12,600/µL with 87% neutrophils. Results of a metabolic panel were normal, and a urine pregnancy test was negative. The electrocardiogram revealed sinus tachycardia without other abnormalities. A CXR showed no evidence of acute cardiopulmonary abnormalities.
Her lab studies lack thrombocytopenia, which is often found in ehrlichiosis and RMSF. Leukopenia is also absent, which can be seen in Lyme disease and ehrlichiosis. The mild leukocytosis could be consistent with pneumonia, influenza, and EVALI and is not discriminating. The normal CXR goes against pneumonia or EVALI; however, 9% of patients with EVALI in one case series had a normal CXR, while computed tomography (CT) of the chest demonstrated bilateral ground-glass opacities.3 Chest CT is indicated in this case given the poor correlation of the CXR findings and this patient’s pronounced respiratory symptoms.
CT of the chest with contrast did not show a pulmonary embolism but revealed diffuse ground-glass opacities, predominantly in the dependent lower lobes (Figure 1).
Acute conditions with diffuse ground-glass opacities include mycoplasma, Pneumocystis jiroveci and viral pneumonias, pulmonary hemorrhage and edema, acute interstitial pneumonia, eosinophilic lung diseases, and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Diffuse ground-glass opacities are also seen in almost all patients with EVALI. Though less likely, RMSF, babesiosis, and ehrlichiosis are not ruled out by these chest CT findings, since these disease entities can sometimes cause pulmonary manifestations, including pneumonia, pulmonary edema, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).4

In addition to Legionella and pneumococcal urinary antigen tests, respiratory viral panel, and blood cultures, it would be judicious to obtain HIV, C-reactive protein, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) testing; these last two tests are often markedly elevated in EVALI. The utility of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) in suspected EVALI cases is not clearly defined, but should be considered in this case to ensure that infectious etiologies are not missed.2 Because of her potential environmental exposures, serologic testing for RMSF and ehrlichiosis should be sent.
Given the overlap in signs and symptoms of EVALI with various, potentially life-threatening infections, she should be empirically treated with antibiotics to cover for community-acquired pneumonia. Adding or even substituting doxycycline for a macrolide antibiotic in this regimen should be considered given that it would treat both RMSF and ehrlichiosis pending further test results. Delay in treating RMSF is associated with worse outcomes. If she is presenting during influenza season, she should also be treated with a neuraminidase inhibitor while awaiting influenza test results. Though the pathophysiology of EVALI is not entirely known, it appears to be inflammatory in nature. Most presumed cases have responded to corticosteroids, with improvement in oxygenation.2 Therefore, treatment with corticosteroids may be warranted to improve oxygenation while ruling out infectious processes.
The patient was admitted to the general medicine wards and started on ceftriaxone and azithromycin for empiric treatment of community-acquired pneumonia. On hospital day 2, a respiratory viral panel returned negative. Procalcitonin, HIV, and blood cultures all returned negative. An ESR was elevated at 86 mm/h. The patient continued to have daily fevers and developed erythematous, blanching macules on the neck, chest, back, and arms, which were noted to occur during febrile periods. Ceftriaxone and azithromycin were discontinued, and doxycycline was started. By hospital day 4, the patient’s oxygen saturation worsened to 86% on ambient air. She continued to have fevers and her cough worsened, with occasional blood-streaked sputum. The patient was transferred to the intensive care unit for closer monitoring.
On hospital day 5, she required intubation for worsening hypoxia. Bronchoscopy was performed, which revealed small mucosal crypts along the left mainstem bronchus. A small amount of bleeding after transbronchial biopsy of the left lower lobe was noted, which resolved with occlusion using the bronchoscope. BAL was performed, which revealed red, cloudy aspirate with 1,100 white blood cells (85% neutrophils) and 22,400 red blood cells. No bacteria were identified.
The patient has developed hypoxic respiratory failure despite appropriate antibiotics and negative cultures, increasing the likelihood of a noninfectious etiology. Her rash is not typical for RMSF, which usually starts as a macular or petechial rash at the ankles and wrists, and spreads centrally to the trunk. Rash is not typically associated with EVALI, and in this case, may represent miliaria caused by her fever.
The mucosal crypts seen on bronchoscopy are nonspecific, likely indicating inflammation from vaping. The BAL otherwise suggests diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH), although sequential BAL aliquots are needed to confirm this diagnosis. DAH is usually caused by pulmonary capillaritis from vasculitis, Goodpasture disease, rheumatic diseases, or diffuse alveolar damage from toxins, infections, rheumatic diseases, or interstitial or organizing pneumonias. Diffuse alveolar damage is the pathologic finding of ARDS, which can be seen in severe cases of many of the conditions discussed, including EVALI, ehrlichiosis, babesiosis, sepsis, and community-acquired pneumonia.4
The BAL is most consistent with EVALI, which often shows elevated neutrophils. DAH due to vaping has also been reported.5 In patients with EVALI, varied pathologic findings of acute lung injury have been reported, including diffuse alveolar damage.6 At this point, laboratory evaluation for rheumatologic diseases and vasculitis should be obtained, and lung biopsy results reviewed. Given her clinical deterioration, treatment with intravenous corticosteroids for presumed EVALI is warranted.
Urine Legionella and Streptococcal pneumoniae antigen tests were negative. The patient was started on methylprednisolone 40 mg intravenously every 8 hours. Further testing included antinuclear antibodies, which was positive at 1:320, with a dense, fine speckled pattern. Perinuclear antineutrophilic cytoplasmic autoantibody, cytoplasmic antineutrophilic cytoplasmic autoantibody, myeloperoxidase, proteinase 3, double-stranded DNA, and glomerular basement membrane IgG were all negative. Transbronchial lung biopsy revealed severe acute lung injury consistent with diffuse alveolar damage. The pulmonary interstitium was mildly expanded by edema, with a moderate number of eosinophilic hyaline membranes. There were no eosinophils or evidence of hemorrhage, granulomas, or giant cells. These changes, within this clinical context, were diagnostic for EVALI.
The patient was intubated for 4 days and completed a course of empiric antibiotics as well as a 10-day course of prednisone. She was discharged on hospital day 17 on 2 L continuous oxygen via nasal cannula. Two days after discharge, she developed worsening dyspnea and chest pain and was readmitted with worsening ground-glass opacities, left upper lobe and right- sided pneumothoraces, and subcutaneous emphysema (Figure 2). She was treated with continuous oxygen to maintain oxygen saturation at 100% and eventually discharged home 3 days later on 3 L continuous oxygen. She attended pulmonary rehabilitation and was weaned off oxygen 2 months later, with marked improvement in aeration of both lungs (Figure 3). She continued to abstain from tobacco and THC products.

DISCUSSION
The first electronic cigarette (e-cigarette) device was developed in 2003 by a Chinese pharmacist and introduced to the American market in 2007.7 E-cigarettes produce an inhalable aerosol by heating a liquid containing a variety of chemicals, nicotine, and flavors, with or without other additives. Originally promoted as a safer nontobacco and cessation device by producers, e-cigarette sales grew at an annual rate of 115% between 2009 and 2012.8 E-cigarettes can also be used to deliver THC, the psychoactive component of cannabis.

Since the advent of e-cigarettes, their safety has been a topic of concern. In August 2019, the CDC announced 215 possible cases of severe pulmonary disease associated with the use of e-cigarette products that were reported by 25 state health departments.1 By February 2020, EVALI had affected more than 2,800 patients hospitalized across the United States.9
The presenting symptoms of EVALI are varied and nonspecific. The largest EVALI case series, published by Layden et al in 2020, included 98 patients who had a median duration of 6 days of symptoms prior to presentation.3 Respiratory symptoms occurred in 97% of patients, including shortness of breath, any chest pain, pleuritic chest pain, cough, and hemoptysis.3 Presentations also included a variety of gastrointestinal (77%) and constitutional (100%) symptoms, which most commonly included nausea, vomiting, and fever.3 Additional case series have supported a specific pattern of presentation, most commonly including pleuritic chest pain, nonproductive cough, or shortness of breath occurring days to weeks prior to presentation. Associated fatigue, fever, and tachycardia may be present, as well as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal pain, and in some cases, these have preceded respiratory symptoms.3,10,11
The vital signs and physical examination, laboratory, and imaging results associated with EVALI are also fairly nonspecific. The most common reason for hospitalization in EVALI is hypoxia, which can progress to acute respiratory failure requiring supplemental oxygen or, as in this case, mechanical ventilation. The most common laboratory finding is leukocytosis greater than 11,000/µL, with more than 80% neutrophils and an ESR greater than 30 mm/hr. In the Layden et al case series, 83% of patients had an abnormal CXR. All patients who underwent CT scan of the chest had bilateral ground-glass opacities, often with subpleural sparing.3 A minority of patients were found to have a pneumothorax, generally a late finding.3,12 Accordingly, the CDC now defines confirmed EVALI as use of e-cigarettes during the 90 days before symptom onset with the presence of pulmonary infiltrates (opacities on CXR or ground-glass opacities on chest CT), negative results on testing for all clinically indicated respiratory infections including respiratory viral panel and influenza PCR, and no alternative plausible diagnoses.13
The presumed etiology of EVALI is chemical exposure because no consistent infectious etiology has been identified.6 No consistent e-cigarette product, substance, or additive has been identified in all cases, nor has one product been directly linked to EVALI. However, the CDC recently announced that vitamin E acetate in vaping products appears to be associated with EVALI.9 In December 2019, Blount et al identified vitamin E acetate in BAL fluid samples from 48 of 51 EVALI patients.14 Additionally, while no other toxins were identified, 94% of samples contained THC or its metabolites or patients had reported vaping THC within 90 days preceding illness.14
The most effective treatment strategy for EVALI is still unknown. It is recommended to treat with empiric antibiotics for at least 48 hours (and antivirals during influenza season) if the history is unclear or if the patient is intubated or has severe hypoxemia.2 If antibiotic and/or antiviral therapies do not lead to clinical improvement, corticosteroids should be added, as they lead to improved oxygenation in many patients.2 Kalininskiy et al recommend initial administration of methylprednisolone 40 mg every 8 hours, with transition to oral prednisone to complete a 2-week course.2 Given rates of rehospitalization (2.7%) and death (2%) in EVALI, the CDC advises that patients should be clinically stable for 24 to 48 hours prior to discharge; that follow-up visits should be arranged within 48 hours of discharge; and that cases of EVALI should be reported to the state and local health departments.15 As seen in the case presented here, with time and continued abstinence from e-cigarette use, the pulmonary effects of EVALI can improve, but long-term outcomes remain unclear. Clinicians must now consider EVALI in patients presenting with respiratory, constitutional, and gastrointestinal complaints when a history of e-cigarette use is present.
KEY TEACHING POINTS
- EVALI presents most commonly with a combination of respiratory, gastrointestinal, and constitutional symptoms. including shortness of breath, cough, nausea, vomiting, and fever.
- When considering EVALI, evaluate and treat for potential infectious causes of disease first.
- Corticosteroids are the mainstay of therapy in EVALI, leading to improvement in oxygenation in many patients.
- Most of the reported cases of EVALI have occurred in patients who have vaped THC-containing products.
1. Schier JG, Meiman JG, Layden J, et al. Severe pulmonary disease associated with electronic-cigarette-product use – Interim guidance. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019; 68(36):787-790. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6836e2
2. Kalininskiy A, Bach CT, Nacca NE, et al. E-cigarette, or vaping, product use associated lung injury (EVALI): case series and diagnostic approach. Lancet Respir Med. 2019;7(12):1017-1026. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-2600(19)30415-1
3. Layden JE, Ghinai I, Pray I, et al. Pulmonary illness related to e-cigarette use in Illiniois and Wisconsin – final report. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(10):903-916. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1911614
4. Faul JL, Doyle RL, Kao PN, Ruoss SJ. Tick-borne pulmonary disease: update on diagnosis and management. Chest. 1999;116(1):222-230. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.116.1.222
5. Agustin M, Yamamoto M, Cabrera F, Eusebio R. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage induced by vaping. Case Rep Pulmonol. 2018;2018:9724530. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9724530
6. Butt YM, Smith ML, Tazelaar HD, et al. Pathology of vaping-associated lung injury. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(18):1780-1781. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmc1913069
7. Office of the Surgeon General. E-Cigarette Use Among Youth and Young Adults. Chapter 1. Public Health Service, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services; 2016. Accessed January 22, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/data_statistics/sgr/e-cigarettes/index.htm
8. Grana R, Benowitz N, Glantz SA. Background Paper on E-cigarettes (Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems). UCSF: Center for Tobacco Control Research and Education; 2013. https://escholarship.org/uc/item/13p2b72n
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreak of lung injury associated with e-cigarette use, or vaping. December 12, 2019. Updated February 25, 2020. Accessed January 22, 2020 and July 16, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/basic_information/e-cigarettes/severe-lung-disease.html
10. Davidson K, Brancato A, Heetkerks P, et al. Outbreak of e-cigarette-associated acute lipoid pneumonia—North Carolina, July-August 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68(36);784-786. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6836e1
11. Maddock SD, Cirulis MM, Callahan SJ, et al. Pulmonary lipid-laden macrophages and vaping. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(15):1488-1489. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmc1912038
12. Henry TS, Kanne JP, Klingerman SJ. Imaging of vaping-associated lung disease. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(15):1486-1487. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmc1911995
13. Smoking and Tobacco Use: For State, Local, Territorial, and Tribal Health Departments. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed Jan 24, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/basic_information/e-cigarettes/severe-lung-disease/health-departments/index.html
14. Blount BC, Karwowski MP, Shields PG, et al. Vitamin E acetate in bronchoalveolar-lavage fluid associated with EVALI. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(8):697-705. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1916433
15. Evans ME, Twentyman E, Click ES, et al. Update: Interim guidance for health care professionals evaluating and caring for patients with suspected e-cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury and for reducing the risk for rehospitalization and death following hospital discharge — United States, December 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;68(5152):1189-1194. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm685152e2
1. Schier JG, Meiman JG, Layden J, et al. Severe pulmonary disease associated with electronic-cigarette-product use – Interim guidance. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019; 68(36):787-790. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6836e2
2. Kalininskiy A, Bach CT, Nacca NE, et al. E-cigarette, or vaping, product use associated lung injury (EVALI): case series and diagnostic approach. Lancet Respir Med. 2019;7(12):1017-1026. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-2600(19)30415-1
3. Layden JE, Ghinai I, Pray I, et al. Pulmonary illness related to e-cigarette use in Illiniois and Wisconsin – final report. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(10):903-916. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1911614
4. Faul JL, Doyle RL, Kao PN, Ruoss SJ. Tick-borne pulmonary disease: update on diagnosis and management. Chest. 1999;116(1):222-230. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.116.1.222
5. Agustin M, Yamamoto M, Cabrera F, Eusebio R. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage induced by vaping. Case Rep Pulmonol. 2018;2018:9724530. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9724530
6. Butt YM, Smith ML, Tazelaar HD, et al. Pathology of vaping-associated lung injury. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(18):1780-1781. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmc1913069
7. Office of the Surgeon General. E-Cigarette Use Among Youth and Young Adults. Chapter 1. Public Health Service, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services; 2016. Accessed January 22, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/data_statistics/sgr/e-cigarettes/index.htm
8. Grana R, Benowitz N, Glantz SA. Background Paper on E-cigarettes (Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems). UCSF: Center for Tobacco Control Research and Education; 2013. https://escholarship.org/uc/item/13p2b72n
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreak of lung injury associated with e-cigarette use, or vaping. December 12, 2019. Updated February 25, 2020. Accessed January 22, 2020 and July 16, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/basic_information/e-cigarettes/severe-lung-disease.html
10. Davidson K, Brancato A, Heetkerks P, et al. Outbreak of e-cigarette-associated acute lipoid pneumonia—North Carolina, July-August 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68(36);784-786. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6836e1
11. Maddock SD, Cirulis MM, Callahan SJ, et al. Pulmonary lipid-laden macrophages and vaping. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(15):1488-1489. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmc1912038
12. Henry TS, Kanne JP, Klingerman SJ. Imaging of vaping-associated lung disease. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(15):1486-1487. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmc1911995
13. Smoking and Tobacco Use: For State, Local, Territorial, and Tribal Health Departments. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed Jan 24, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/basic_information/e-cigarettes/severe-lung-disease/health-departments/index.html
14. Blount BC, Karwowski MP, Shields PG, et al. Vitamin E acetate in bronchoalveolar-lavage fluid associated with EVALI. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(8):697-705. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1916433
15. Evans ME, Twentyman E, Click ES, et al. Update: Interim guidance for health care professionals evaluating and caring for patients with suspected e-cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury and for reducing the risk for rehospitalization and death following hospital discharge — United States, December 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;68(5152):1189-1194. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm685152e2
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine