User login
Recent unintended weight loss
PCOS is most often defined according to the Rotterdam criteria, which stipulate that at least two of the following be present: irregular ovulation, biochemical/clinical hyperandrogenism, and polycystic ovaries (seen in the MRI scan above). Insulin resistance is part of the pathogenesis of PCOS, and insulin resistance is associated with T2D in PCOS.
In fact, PCOS is an independent risk factor for T2D, even after adjustment for BMI and obesity. Even normal-weight women with PCOS have an increased risk for T2D. More than half of women with PCOS develop T2D by age 40.
Even though family history and obesity are major contributors in the development of diabetes in patients with PCOS, diabetes can still occur in lean patients with PCOS who have no family history, mainly secondary to insulin resistance.
The Endocrine Society recommends that all individuals with PCOS undergo an oral glucose tolerance test every 3-5 years, with more frequent screening for those who develop symptoms of T2D, significant weight gain, or central adiposity. In guidelines published in 2015 by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, the American College of Endocrinology, and the Androgen Excess and PCOS Society, an annual oral glucose tolerance test is recommended for patients with PCOS and impaired glucose tolerance, whereas those with a family history of T2D or a BMI above 30 should be screened every 1-2 years.
Management of T2D with PCOS is similar to that of T2D without PCOS. Accordingly, metformin and lifestyle changes are the treatments of choice; any antidiabetic agent may be added in patients who do not achieve glycemic targets despite treatment with metformin.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships
PCOS is most often defined according to the Rotterdam criteria, which stipulate that at least two of the following be present: irregular ovulation, biochemical/clinical hyperandrogenism, and polycystic ovaries (seen in the MRI scan above). Insulin resistance is part of the pathogenesis of PCOS, and insulin resistance is associated with T2D in PCOS.
In fact, PCOS is an independent risk factor for T2D, even after adjustment for BMI and obesity. Even normal-weight women with PCOS have an increased risk for T2D. More than half of women with PCOS develop T2D by age 40.
Even though family history and obesity are major contributors in the development of diabetes in patients with PCOS, diabetes can still occur in lean patients with PCOS who have no family history, mainly secondary to insulin resistance.
The Endocrine Society recommends that all individuals with PCOS undergo an oral glucose tolerance test every 3-5 years, with more frequent screening for those who develop symptoms of T2D, significant weight gain, or central adiposity. In guidelines published in 2015 by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, the American College of Endocrinology, and the Androgen Excess and PCOS Society, an annual oral glucose tolerance test is recommended for patients with PCOS and impaired glucose tolerance, whereas those with a family history of T2D or a BMI above 30 should be screened every 1-2 years.
Management of T2D with PCOS is similar to that of T2D without PCOS. Accordingly, metformin and lifestyle changes are the treatments of choice; any antidiabetic agent may be added in patients who do not achieve glycemic targets despite treatment with metformin.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships
PCOS is most often defined according to the Rotterdam criteria, which stipulate that at least two of the following be present: irregular ovulation, biochemical/clinical hyperandrogenism, and polycystic ovaries (seen in the MRI scan above). Insulin resistance is part of the pathogenesis of PCOS, and insulin resistance is associated with T2D in PCOS.
In fact, PCOS is an independent risk factor for T2D, even after adjustment for BMI and obesity. Even normal-weight women with PCOS have an increased risk for T2D. More than half of women with PCOS develop T2D by age 40.
Even though family history and obesity are major contributors in the development of diabetes in patients with PCOS, diabetes can still occur in lean patients with PCOS who have no family history, mainly secondary to insulin resistance.
The Endocrine Society recommends that all individuals with PCOS undergo an oral glucose tolerance test every 3-5 years, with more frequent screening for those who develop symptoms of T2D, significant weight gain, or central adiposity. In guidelines published in 2015 by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, the American College of Endocrinology, and the Androgen Excess and PCOS Society, an annual oral glucose tolerance test is recommended for patients with PCOS and impaired glucose tolerance, whereas those with a family history of T2D or a BMI above 30 should be screened every 1-2 years.
Management of T2D with PCOS is similar to that of T2D without PCOS. Accordingly, metformin and lifestyle changes are the treatments of choice; any antidiabetic agent may be added in patients who do not achieve glycemic targets despite treatment with metformin.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships
A 36-year-old woman presents with recent unintended weight loss of 12 lb in 2 months. Currently, she weighs 153 lb (BMI 24.7). She complains of increased thirst, increased urination, lack of energy, and fatigue.
Metabolic workup reveals that A1c is 7.1%, fasting blood glucose level is 131 mg/dL, oral glucose tolerance test level is 210 mg/dL, and random blood glucose level is 215 mg/dL, all of which are diagnostic for type 2 diabetes (T2D). She has no family history of diabetes.
A lipid panel shows a low-density lipoprotein cholesterol of 140 mg/dL, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol 38 mg/dL, and triglycerides 210 mg/dL. Blood pressure is 150/95 mm Hg.
The patient had been diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) at age 33, during a workup for infertility. At the time of her PCOS diagnosis, she weighed 190 lb (BMI, 30.7). She gave birth to an 8-lb son 14 months ago.
Type 2 Diabetes Comorbidities
Recent onset of polyuria and polydipsia
The patient's clinical presentation and laboratory findings are consistent with a diagnosis of T2D.
The prevalence of T2D is increasing dramatically in children and adolescents. Like adult-onset T2D, obesity, family history, and sedentary lifestyle are major predisposing risk factors for T2D in children and adolescents. Significantly, the onset of diabetes at a younger age is associated with longer disease exposure and increased risk for chronic complications. Moreover, T2D in adolescents manifests as a severe progressive phenotype that often presents with complications, poor treatment response, and rapid progression of microvascular and macrovascular complications. Studies have shown that the risk for complications is greater in youth-onset T2D than it is in type 1 diabetes (T1D) and adult-onset T2D.
T2D has a variable presentation in children and adolescents. Approximately one third of patients are diagnosed without having typical diabetes signs or symptoms. In most cases, these patients are in their mid-adolescence are obese and were screened because of one or more positive risk factors or because glycosuria was detected on a random urine test. These patients typically have one or more of the typical characteristics of metabolic syndrome, such as hypertension and dyslipidemia.
Polyuria and polydipsia are seen in approximately 67% of youth with T2D at presentation. Recent weight loss may be present, but it is usually less severe in patients with T2D compared with T1D. Additionally, frequent fungal skin infections or severe vulvovaginitis because of Candida in adolescent girls can be the presenting complaint.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is present in less than 1 in 10 adolescents diagnosed with T2D. Most of these patients belong to ethnic minority groups, report polyuria, polydipsia, fatigue, and lethargy, and require hospital admission, rehydration, and insulin replacement therapy. Patients with symptoms such as vomiting can decline rapidly and need urgent evaluation and management.
Certain adolescent patients with obesity who present with diabetic ketoacidosis and are diagnosed with T2D at presentation can also have T1D and will require lifelong insulin treatment. Therefore, following a diagnosis of diabetes in an adolescent, it is critical to differentiate T2D from type 1 diabetes, as well as from other more rare diabetes types, to ensure proper long-term management. Given the substantial overlap between T2D and T1D symptoms, a combination of history clues, clinical characteristics, and laboratory studies must be used to reliably make the distinction. Important clues in the patient's history include:
• Age. Patients with T2D typically present after the onset of puberty, at a mean age of 13.5 years. Conversely, nearly one half of patients with T1D present before 10 years of age, regardless of race or ethnicity.
• Family history. Up to 90% of patients with T2D have an affected first- or second-degree relative; the corresponding percentage for patients with T1D is less than 10%.
• Ethnicity. T2D disproportionately affects youth of ethnic and racial minorities. Compared with White individuals, youth belonging to minority groups such as Native American, African American, Hispanic, and Pacific Islander have a much higher risk of developing T2D.
• Body weight. Most adolescents with T2D have obesity (BMI ≥ 95 percentile for age and sex), whereas those with T1D are usually of normal weight and may report a recent history of weight loss.
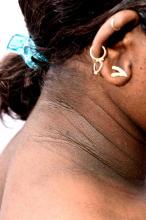
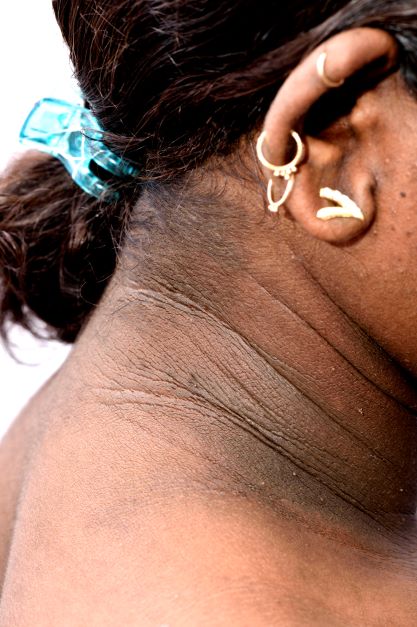
• Clinical findings. Adolescents with T2D usually present with features of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome, such as acanthosis nigricans, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and polycystic ovary syndrome, whereas these findings are rare in youth with T1D. One study showed that up to 90% of youth diagnosed with T2D had acanthosis nigricans, in contrast to only 12% of those diagnosed with T1D.
Additionally, when the diagnosis of T2D is being considered in children and adolescents, a panel of pancreatic autoantibodies should be tested to exclude the possibility of autoimmune T1D. Because T2D is not immunologically mediated, the identification of one or more pancreatic (islet) cell antibodies in a diabetic adolescent with obesity supports the diagnosis of autoimmune diabetes. Antibodies that are usually measured include islet cell antibodies (against cytoplasmic proteins in the beta cell), anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase, and tyrosine phosphatase insulinoma-associated antigen 2, as well as anti-insulin antibodies if insulin replacement therapy has not been used for more than 2 weeks. In addition, a beta cell–specific autoantibody to zinc transporter 8 is frequently detected in children with T1D and can aid in the differential diagnosis. However, up to one third of children with T2D can have at least one detectable beta-cell autoantibody; therefore, total absence of diabetes autoimmune markers is not required for the diagnosis of T2D in children and adolescents.
When a diagnosis of T2D has been established, treatment should consist of lifestyle management, diabetes self-management education, and pharmacologic therapy. According to the 2022 American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care, the management of diabetes in children and adolescents cannot simply be drawn from the typical care provided to adults with diabetes. The epidemiology, pathophysiology, developmental considerations, and response to therapy in pediatric populations often vary from adult diabetes, and differences exist in recommended care for children and adolescents with T1D, T2D, and other forms of pediatric diabetes.
Because the diabetes type is often uncertain in the first few weeks of treatment, initial therapy should address the hyperglycemia and associated metabolic derangements regardless of the ultimate diabetes type; therapy should then be adjusted once metabolic compensation has been established and subsequent information, such as islet autoantibody results, becomes available.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships
The patient's clinical presentation and laboratory findings are consistent with a diagnosis of T2D.
The prevalence of T2D is increasing dramatically in children and adolescents. Like adult-onset T2D, obesity, family history, and sedentary lifestyle are major predisposing risk factors for T2D in children and adolescents. Significantly, the onset of diabetes at a younger age is associated with longer disease exposure and increased risk for chronic complications. Moreover, T2D in adolescents manifests as a severe progressive phenotype that often presents with complications, poor treatment response, and rapid progression of microvascular and macrovascular complications. Studies have shown that the risk for complications is greater in youth-onset T2D than it is in type 1 diabetes (T1D) and adult-onset T2D.
T2D has a variable presentation in children and adolescents. Approximately one third of patients are diagnosed without having typical diabetes signs or symptoms. In most cases, these patients are in their mid-adolescence are obese and were screened because of one or more positive risk factors or because glycosuria was detected on a random urine test. These patients typically have one or more of the typical characteristics of metabolic syndrome, such as hypertension and dyslipidemia.
Polyuria and polydipsia are seen in approximately 67% of youth with T2D at presentation. Recent weight loss may be present, but it is usually less severe in patients with T2D compared with T1D. Additionally, frequent fungal skin infections or severe vulvovaginitis because of Candida in adolescent girls can be the presenting complaint.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is present in less than 1 in 10 adolescents diagnosed with T2D. Most of these patients belong to ethnic minority groups, report polyuria, polydipsia, fatigue, and lethargy, and require hospital admission, rehydration, and insulin replacement therapy. Patients with symptoms such as vomiting can decline rapidly and need urgent evaluation and management.
Certain adolescent patients with obesity who present with diabetic ketoacidosis and are diagnosed with T2D at presentation can also have T1D and will require lifelong insulin treatment. Therefore, following a diagnosis of diabetes in an adolescent, it is critical to differentiate T2D from type 1 diabetes, as well as from other more rare diabetes types, to ensure proper long-term management. Given the substantial overlap between T2D and T1D symptoms, a combination of history clues, clinical characteristics, and laboratory studies must be used to reliably make the distinction. Important clues in the patient's history include:
• Age. Patients with T2D typically present after the onset of puberty, at a mean age of 13.5 years. Conversely, nearly one half of patients with T1D present before 10 years of age, regardless of race or ethnicity.
• Family history. Up to 90% of patients with T2D have an affected first- or second-degree relative; the corresponding percentage for patients with T1D is less than 10%.
• Ethnicity. T2D disproportionately affects youth of ethnic and racial minorities. Compared with White individuals, youth belonging to minority groups such as Native American, African American, Hispanic, and Pacific Islander have a much higher risk of developing T2D.
• Body weight. Most adolescents with T2D have obesity (BMI ≥ 95 percentile for age and sex), whereas those with T1D are usually of normal weight and may report a recent history of weight loss.
• Clinical findings. Adolescents with T2D usually present with features of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome, such as acanthosis nigricans, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and polycystic ovary syndrome, whereas these findings are rare in youth with T1D. One study showed that up to 90% of youth diagnosed with T2D had acanthosis nigricans, in contrast to only 12% of those diagnosed with T1D.
Additionally, when the diagnosis of T2D is being considered in children and adolescents, a panel of pancreatic autoantibodies should be tested to exclude the possibility of autoimmune T1D. Because T2D is not immunologically mediated, the identification of one or more pancreatic (islet) cell antibodies in a diabetic adolescent with obesity supports the diagnosis of autoimmune diabetes. Antibodies that are usually measured include islet cell antibodies (against cytoplasmic proteins in the beta cell), anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase, and tyrosine phosphatase insulinoma-associated antigen 2, as well as anti-insulin antibodies if insulin replacement therapy has not been used for more than 2 weeks. In addition, a beta cell–specific autoantibody to zinc transporter 8 is frequently detected in children with T1D and can aid in the differential diagnosis. However, up to one third of children with T2D can have at least one detectable beta-cell autoantibody; therefore, total absence of diabetes autoimmune markers is not required for the diagnosis of T2D in children and adolescents.
When a diagnosis of T2D has been established, treatment should consist of lifestyle management, diabetes self-management education, and pharmacologic therapy. According to the 2022 American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care, the management of diabetes in children and adolescents cannot simply be drawn from the typical care provided to adults with diabetes. The epidemiology, pathophysiology, developmental considerations, and response to therapy in pediatric populations often vary from adult diabetes, and differences exist in recommended care for children and adolescents with T1D, T2D, and other forms of pediatric diabetes.
Because the diabetes type is often uncertain in the first few weeks of treatment, initial therapy should address the hyperglycemia and associated metabolic derangements regardless of the ultimate diabetes type; therapy should then be adjusted once metabolic compensation has been established and subsequent information, such as islet autoantibody results, becomes available.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships
The patient's clinical presentation and laboratory findings are consistent with a diagnosis of T2D.
The prevalence of T2D is increasing dramatically in children and adolescents. Like adult-onset T2D, obesity, family history, and sedentary lifestyle are major predisposing risk factors for T2D in children and adolescents. Significantly, the onset of diabetes at a younger age is associated with longer disease exposure and increased risk for chronic complications. Moreover, T2D in adolescents manifests as a severe progressive phenotype that often presents with complications, poor treatment response, and rapid progression of microvascular and macrovascular complications. Studies have shown that the risk for complications is greater in youth-onset T2D than it is in type 1 diabetes (T1D) and adult-onset T2D.
T2D has a variable presentation in children and adolescents. Approximately one third of patients are diagnosed without having typical diabetes signs or symptoms. In most cases, these patients are in their mid-adolescence are obese and were screened because of one or more positive risk factors or because glycosuria was detected on a random urine test. These patients typically have one or more of the typical characteristics of metabolic syndrome, such as hypertension and dyslipidemia.
Polyuria and polydipsia are seen in approximately 67% of youth with T2D at presentation. Recent weight loss may be present, but it is usually less severe in patients with T2D compared with T1D. Additionally, frequent fungal skin infections or severe vulvovaginitis because of Candida in adolescent girls can be the presenting complaint.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is present in less than 1 in 10 adolescents diagnosed with T2D. Most of these patients belong to ethnic minority groups, report polyuria, polydipsia, fatigue, and lethargy, and require hospital admission, rehydration, and insulin replacement therapy. Patients with symptoms such as vomiting can decline rapidly and need urgent evaluation and management.
Certain adolescent patients with obesity who present with diabetic ketoacidosis and are diagnosed with T2D at presentation can also have T1D and will require lifelong insulin treatment. Therefore, following a diagnosis of diabetes in an adolescent, it is critical to differentiate T2D from type 1 diabetes, as well as from other more rare diabetes types, to ensure proper long-term management. Given the substantial overlap between T2D and T1D symptoms, a combination of history clues, clinical characteristics, and laboratory studies must be used to reliably make the distinction. Important clues in the patient's history include:
• Age. Patients with T2D typically present after the onset of puberty, at a mean age of 13.5 years. Conversely, nearly one half of patients with T1D present before 10 years of age, regardless of race or ethnicity.
• Family history. Up to 90% of patients with T2D have an affected first- or second-degree relative; the corresponding percentage for patients with T1D is less than 10%.
• Ethnicity. T2D disproportionately affects youth of ethnic and racial minorities. Compared with White individuals, youth belonging to minority groups such as Native American, African American, Hispanic, and Pacific Islander have a much higher risk of developing T2D.
• Body weight. Most adolescents with T2D have obesity (BMI ≥ 95 percentile for age and sex), whereas those with T1D are usually of normal weight and may report a recent history of weight loss.
• Clinical findings. Adolescents with T2D usually present with features of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome, such as acanthosis nigricans, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and polycystic ovary syndrome, whereas these findings are rare in youth with T1D. One study showed that up to 90% of youth diagnosed with T2D had acanthosis nigricans, in contrast to only 12% of those diagnosed with T1D.
Additionally, when the diagnosis of T2D is being considered in children and adolescents, a panel of pancreatic autoantibodies should be tested to exclude the possibility of autoimmune T1D. Because T2D is not immunologically mediated, the identification of one or more pancreatic (islet) cell antibodies in a diabetic adolescent with obesity supports the diagnosis of autoimmune diabetes. Antibodies that are usually measured include islet cell antibodies (against cytoplasmic proteins in the beta cell), anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase, and tyrosine phosphatase insulinoma-associated antigen 2, as well as anti-insulin antibodies if insulin replacement therapy has not been used for more than 2 weeks. In addition, a beta cell–specific autoantibody to zinc transporter 8 is frequently detected in children with T1D and can aid in the differential diagnosis. However, up to one third of children with T2D can have at least one detectable beta-cell autoantibody; therefore, total absence of diabetes autoimmune markers is not required for the diagnosis of T2D in children and adolescents.
When a diagnosis of T2D has been established, treatment should consist of lifestyle management, diabetes self-management education, and pharmacologic therapy. According to the 2022 American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care, the management of diabetes in children and adolescents cannot simply be drawn from the typical care provided to adults with diabetes. The epidemiology, pathophysiology, developmental considerations, and response to therapy in pediatric populations often vary from adult diabetes, and differences exist in recommended care for children and adolescents with T1D, T2D, and other forms of pediatric diabetes.
Because the diabetes type is often uncertain in the first few weeks of treatment, initial therapy should address the hyperglycemia and associated metabolic derangements regardless of the ultimate diabetes type; therapy should then be adjusted once metabolic compensation has been established and subsequent information, such as islet autoantibody results, becomes available.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships
A 14-year-old Black girl presents with complaints of increasing fatigue and recent onset of polyuria and polydipsia. According to the patient's chart, she has lost approximately 5 lb since her last examination 8 months ago. Physical examination revealed a blood pressure of 120/80 mm Hg, pulse of 79, and temperature of 100.4°F (38°C). Her weight is 165 lb (75 kg, 96th percentile), height is 62 in (157.5 cm, 32nd percentile), and BMI is 30.2 (97th percentile). Acanthosis nigricans is present. The patient is at Tanner stage 3 of sexual development. There is a positive first-degree family history of type 2 diabetes (T2D), hypertension, and obesity, as well as premature cardiac death in an uncle. Laboratory findings include an A1c value of 7.4%, HDL-C 220 mg/dL, LDL-C 144 mg/dL, and serum creatinine 1.1 mg/dL.
Type 2 Diabetes Workup
Shortness of breath and abdominal pain
On the basis of the patient's history and clinical presentation, the likely diagnosis is ketosis-prone diabetes (KPD) type 2. KPD is widely thought of as an atypical diabetes syndrome, though some groups consider it to be a common clinical presentation in newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) rather than a subtype of disease. The condition is more prevalent in males and among Black and Hispanic populations.
Definitive diagnosis of the type of diabetes can present a clinical challenge during acute presentation. Although the majority of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) episodes occur in patients previously diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, an estimated 34% occur in patients with T2D. For patients who are obese or have a family history of diabetes, there should be a high index of suspicion for new-onset DKA in type 2 diabetes.
Patients with KPD typically present in a state of ketoacidosis with a brief but acute history of hyperglycemic symptoms. Hyperglycemia, elevated anion gap acidosis, and ketonemia form the expected constellation of DKA symptoms. A key consideration in the differential diagnosis is hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS). Patients with HHS are much more likely to have altered mental status than are patients with DKA. Metabolic acidosis and ketonemia are absent or mild, and anion gap is either normal or slightly elevated. In HHS, extreme elevations of glucose are seen, with a lack of significant ketoacidosis. Glucose levels tend to be higher in HHS than in DKA; they are almost always > 600 mg/dL, and levels > 1000 mg/dL are not uncommon. In DKA, glucose levels are still markedly high — generally 500-800 mg/dL but rarely exceeding 900 mg/dL. Patients with DKA also usually present with an A1c > 10% and a blood pH < 7.30.
Treatment for KPD is initially acute, beginning with aggressive intravenous fluid and insulin therapy A. Once this state resolves, insulin requirements typically decrease for patients with T2D, and they are able to maintain adequate glycemic control with an oral therapy regimen.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
On the basis of the patient's history and clinical presentation, the likely diagnosis is ketosis-prone diabetes (KPD) type 2. KPD is widely thought of as an atypical diabetes syndrome, though some groups consider it to be a common clinical presentation in newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) rather than a subtype of disease. The condition is more prevalent in males and among Black and Hispanic populations.
Definitive diagnosis of the type of diabetes can present a clinical challenge during acute presentation. Although the majority of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) episodes occur in patients previously diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, an estimated 34% occur in patients with T2D. For patients who are obese or have a family history of diabetes, there should be a high index of suspicion for new-onset DKA in type 2 diabetes.
Patients with KPD typically present in a state of ketoacidosis with a brief but acute history of hyperglycemic symptoms. Hyperglycemia, elevated anion gap acidosis, and ketonemia form the expected constellation of DKA symptoms. A key consideration in the differential diagnosis is hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS). Patients with HHS are much more likely to have altered mental status than are patients with DKA. Metabolic acidosis and ketonemia are absent or mild, and anion gap is either normal or slightly elevated. In HHS, extreme elevations of glucose are seen, with a lack of significant ketoacidosis. Glucose levels tend to be higher in HHS than in DKA; they are almost always > 600 mg/dL, and levels > 1000 mg/dL are not uncommon. In DKA, glucose levels are still markedly high — generally 500-800 mg/dL but rarely exceeding 900 mg/dL. Patients with DKA also usually present with an A1c > 10% and a blood pH < 7.30.
Treatment for KPD is initially acute, beginning with aggressive intravenous fluid and insulin therapy A. Once this state resolves, insulin requirements typically decrease for patients with T2D, and they are able to maintain adequate glycemic control with an oral therapy regimen.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
On the basis of the patient's history and clinical presentation, the likely diagnosis is ketosis-prone diabetes (KPD) type 2. KPD is widely thought of as an atypical diabetes syndrome, though some groups consider it to be a common clinical presentation in newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) rather than a subtype of disease. The condition is more prevalent in males and among Black and Hispanic populations.
Definitive diagnosis of the type of diabetes can present a clinical challenge during acute presentation. Although the majority of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) episodes occur in patients previously diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, an estimated 34% occur in patients with T2D. For patients who are obese or have a family history of diabetes, there should be a high index of suspicion for new-onset DKA in type 2 diabetes.
Patients with KPD typically present in a state of ketoacidosis with a brief but acute history of hyperglycemic symptoms. Hyperglycemia, elevated anion gap acidosis, and ketonemia form the expected constellation of DKA symptoms. A key consideration in the differential diagnosis is hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS). Patients with HHS are much more likely to have altered mental status than are patients with DKA. Metabolic acidosis and ketonemia are absent or mild, and anion gap is either normal or slightly elevated. In HHS, extreme elevations of glucose are seen, with a lack of significant ketoacidosis. Glucose levels tend to be higher in HHS than in DKA; they are almost always > 600 mg/dL, and levels > 1000 mg/dL are not uncommon. In DKA, glucose levels are still markedly high — generally 500-800 mg/dL but rarely exceeding 900 mg/dL. Patients with DKA also usually present with an A1c > 10% and a blood pH < 7.30.
Treatment for KPD is initially acute, beginning with aggressive intravenous fluid and insulin therapy A. Once this state resolves, insulin requirements typically decrease for patients with T2D, and they are able to maintain adequate glycemic control with an oral therapy regimen.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
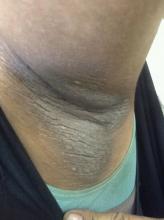
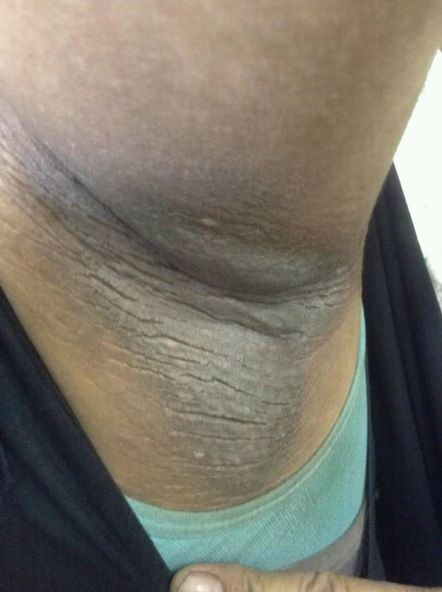
A 21-year-old man presents with shortness of breath and abdominal pain. He has a BMI of 34.6 and explains that he has had asthma for several years, using an inhaler when needed. He reports a few weeks of polydipsia and polyuria. The patient notes that his father has kidney disease. He believes other close relatives are managing chronic metabolic conditions but does not know any further detail regarding their diagnoses. On laboratory testing, blood pH is 6.30 and bicarbonate level is 11.1 mmol/L. A1c is 12.0%. Acanthosis nigricans are noted on the neck and in the axilla bilaterally.
Type 2 Diabetes Presentation
Patient with tachycardia
On the basis of the patient's personal and family history together with his presentation, the likely diagnosis is latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA). LADA is characterized by beta-cell loss and insulin resistance. This slowly evolving form of autoimmune diabetes comprises 2%-12% of all patients with adult-onset diabetes. Patients with LADA present with evidence of autoimmunity and varying C-peptide levels, which decrease more slowly in this subgroup than in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D). They also have immunogenic markers associated with T1D, primarily anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) antibodies.
Patients with LADA are often misdiagnosed as having T2D. The clinical picture of LADA overlaps with that of T2D, with patients being insulin resistant and often overweight. In addition, presenting symptoms of LADA — excessive thirst, blurred vision, and high blood glucose — are also seen in T2D. Although LADA is technically classified as T1D, some groups posit that the condition exists on a spectrum between T1D and T2D. Compared with patients with T2D, those with LADA are generally younger at diagnosis (often in their 30s), have lower BMI, and report a personal or family history of autoimmune diseases, such as the patient in this quiz. Throughout the disease course, individuals with LADA show a reduced frequency of metabolic syndrome compared with those with T2D.
Key to diagnosis is the absence of insulin requirement for at least 6 months. Anti-GAD antibodies are the most sensitive marker for LADA; other autoantibodies that occur less frequently include ICA, IA-2A, ZnT8A, and tetraspanin 7 autoantibodies. With a paucity of large-scale clinical trials in LADA, current treatment strategies are not based on consensus guidelines, though an expert panel has published management recommendations. Category 1 patients (defined as a C-peptide level < 0.3 nmol/L) are treated with intensive insulin therapy. The recommendation for category 2 patients (defined as C-peptide values ≥ 0.3 and ≤ 0.7 nmol/L) is a modified American Diabetes Association/European Association for the Study of Diabetes algorithm for T2D. However, patients with category 2 LADA may need to initiate insulin therapy earlier to combat beta-cell failure (ostensibly because LADA is an autoimmune disease beta-cell function declines much faster than in T2D). For category 3 patients (defined as C-peptide values > 0.7 nmol/L), treatment decisions are made in response to changing C-peptide levels.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
On the basis of the patient's personal and family history together with his presentation, the likely diagnosis is latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA). LADA is characterized by beta-cell loss and insulin resistance. This slowly evolving form of autoimmune diabetes comprises 2%-12% of all patients with adult-onset diabetes. Patients with LADA present with evidence of autoimmunity and varying C-peptide levels, which decrease more slowly in this subgroup than in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D). They also have immunogenic markers associated with T1D, primarily anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) antibodies.
Patients with LADA are often misdiagnosed as having T2D. The clinical picture of LADA overlaps with that of T2D, with patients being insulin resistant and often overweight. In addition, presenting symptoms of LADA — excessive thirst, blurred vision, and high blood glucose — are also seen in T2D. Although LADA is technically classified as T1D, some groups posit that the condition exists on a spectrum between T1D and T2D. Compared with patients with T2D, those with LADA are generally younger at diagnosis (often in their 30s), have lower BMI, and report a personal or family history of autoimmune diseases, such as the patient in this quiz. Throughout the disease course, individuals with LADA show a reduced frequency of metabolic syndrome compared with those with T2D.
Key to diagnosis is the absence of insulin requirement for at least 6 months. Anti-GAD antibodies are the most sensitive marker for LADA; other autoantibodies that occur less frequently include ICA, IA-2A, ZnT8A, and tetraspanin 7 autoantibodies. With a paucity of large-scale clinical trials in LADA, current treatment strategies are not based on consensus guidelines, though an expert panel has published management recommendations. Category 1 patients (defined as a C-peptide level < 0.3 nmol/L) are treated with intensive insulin therapy. The recommendation for category 2 patients (defined as C-peptide values ≥ 0.3 and ≤ 0.7 nmol/L) is a modified American Diabetes Association/European Association for the Study of Diabetes algorithm for T2D. However, patients with category 2 LADA may need to initiate insulin therapy earlier to combat beta-cell failure (ostensibly because LADA is an autoimmune disease beta-cell function declines much faster than in T2D). For category 3 patients (defined as C-peptide values > 0.7 nmol/L), treatment decisions are made in response to changing C-peptide levels.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
On the basis of the patient's personal and family history together with his presentation, the likely diagnosis is latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA). LADA is characterized by beta-cell loss and insulin resistance. This slowly evolving form of autoimmune diabetes comprises 2%-12% of all patients with adult-onset diabetes. Patients with LADA present with evidence of autoimmunity and varying C-peptide levels, which decrease more slowly in this subgroup than in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D). They also have immunogenic markers associated with T1D, primarily anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) antibodies.
Patients with LADA are often misdiagnosed as having T2D. The clinical picture of LADA overlaps with that of T2D, with patients being insulin resistant and often overweight. In addition, presenting symptoms of LADA — excessive thirst, blurred vision, and high blood glucose — are also seen in T2D. Although LADA is technically classified as T1D, some groups posit that the condition exists on a spectrum between T1D and T2D. Compared with patients with T2D, those with LADA are generally younger at diagnosis (often in their 30s), have lower BMI, and report a personal or family history of autoimmune diseases, such as the patient in this quiz. Throughout the disease course, individuals with LADA show a reduced frequency of metabolic syndrome compared with those with T2D.
Key to diagnosis is the absence of insulin requirement for at least 6 months. Anti-GAD antibodies are the most sensitive marker for LADA; other autoantibodies that occur less frequently include ICA, IA-2A, ZnT8A, and tetraspanin 7 autoantibodies. With a paucity of large-scale clinical trials in LADA, current treatment strategies are not based on consensus guidelines, though an expert panel has published management recommendations. Category 1 patients (defined as a C-peptide level < 0.3 nmol/L) are treated with intensive insulin therapy. The recommendation for category 2 patients (defined as C-peptide values ≥ 0.3 and ≤ 0.7 nmol/L) is a modified American Diabetes Association/European Association for the Study of Diabetes algorithm for T2D. However, patients with category 2 LADA may need to initiate insulin therapy earlier to combat beta-cell failure (ostensibly because LADA is an autoimmune disease beta-cell function declines much faster than in T2D). For category 3 patients (defined as C-peptide values > 0.7 nmol/L), treatment decisions are made in response to changing C-peptide levels.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
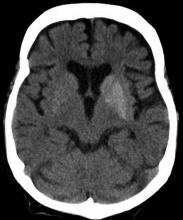
A 33-year-old man presents with blurred vision and tachycardia. Physical examination is remarkable for a BMI of 27 kg/m2. The patient explains that he feels he has lost weight. However, he attributes this change to a new exercise regimen he undertook when he was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes (T2D) about 8 months ago. The patient also notes polydipsia over a series of weeks. He reports that his first cousin may have lupus, though her diagnosis is still uncertain. Axial noncontrast CT demonstrates hyperattenuation that is more pronounced on the left side and involves the lentiform and caudate nuclei bilaterally.