User login
Wegener's Granulomatosis
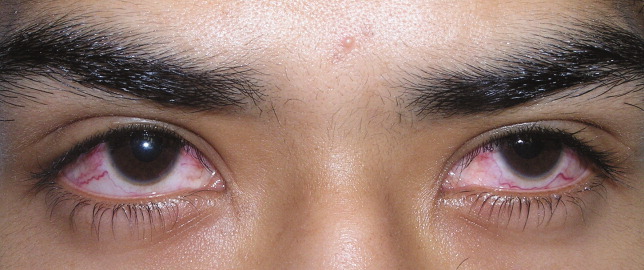
A previously healthy 21‐year‐old man presented with 6 weeks of low‐grade fever, sore throat, red eyes, and hematuria. Physical examination revealed episcleral injection consistent with episcleritis (Figure 1), oral ulcers (Figure 2, black arrows), diffuse fine crackles on chest auscultation and testicular tenderness. Laboratory workup was significant for leukocytosis (14,000 cell/mL), hematuria with red blood cell (RBC) casts and serum creatinine level of 2.1 mg/dL, which subsequently rose rapidly to 4.1 mg/dL. Test for cytoplasmic‐stainingantineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (C‐ANCA) was positive. Antiproteinase 3 (PR3) antibodies were also positive. Chest x‐ray showed bilateral pulmonary opacities and sinus computed tomography (CT) scan showed mucosal thickening of the sinuses consistent with sinusitis (Figure 3). Renal biopsy revealed segmental necrotizing glomerulonephritis that was pauci‐immune on immunofluorescence staining. The patient was diagnosed with Wegener's granulomatosis with rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. He was treated with intravenous corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide, and trimethoprim‐sulfamethoxazole. The patient's symptoms and acute renal failure resolved with this medical regimen.
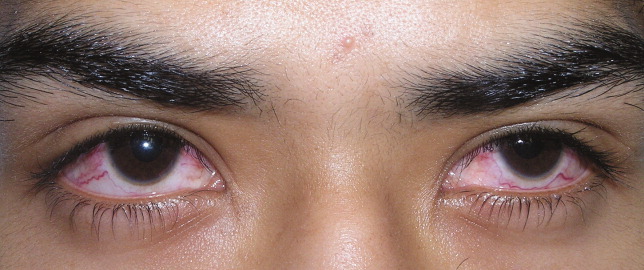
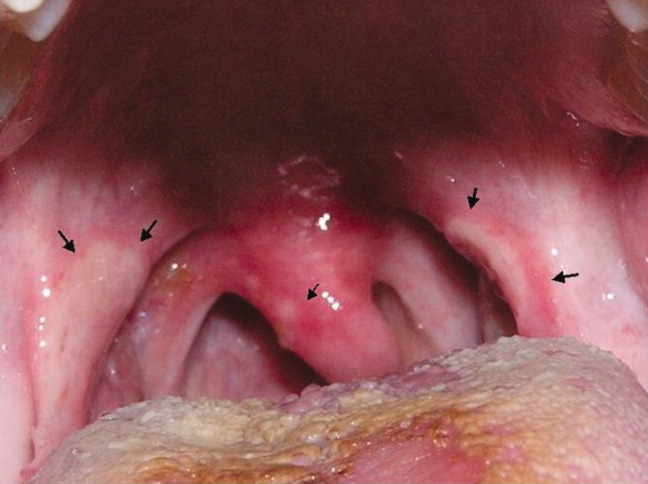
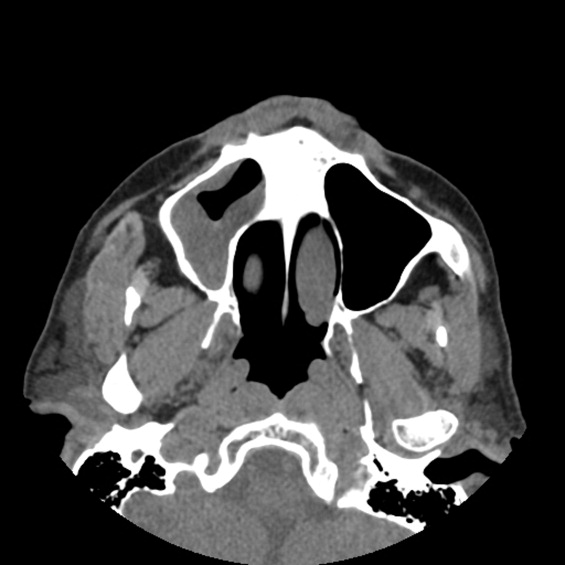
A previously healthy 21‐year‐old man presented with 6 weeks of low‐grade fever, sore throat, red eyes, and hematuria. Physical examination revealed episcleral injection consistent with episcleritis (Figure 1), oral ulcers (Figure 2, black arrows), diffuse fine crackles on chest auscultation and testicular tenderness. Laboratory workup was significant for leukocytosis (14,000 cell/mL), hematuria with red blood cell (RBC) casts and serum creatinine level of 2.1 mg/dL, which subsequently rose rapidly to 4.1 mg/dL. Test for cytoplasmic‐stainingantineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (C‐ANCA) was positive. Antiproteinase 3 (PR3) antibodies were also positive. Chest x‐ray showed bilateral pulmonary opacities and sinus computed tomography (CT) scan showed mucosal thickening of the sinuses consistent with sinusitis (Figure 3). Renal biopsy revealed segmental necrotizing glomerulonephritis that was pauci‐immune on immunofluorescence staining. The patient was diagnosed with Wegener's granulomatosis with rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. He was treated with intravenous corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide, and trimethoprim‐sulfamethoxazole. The patient's symptoms and acute renal failure resolved with this medical regimen.



A previously healthy 21‐year‐old man presented with 6 weeks of low‐grade fever, sore throat, red eyes, and hematuria. Physical examination revealed episcleral injection consistent with episcleritis (Figure 1), oral ulcers (Figure 2, black arrows), diffuse fine crackles on chest auscultation and testicular tenderness. Laboratory workup was significant for leukocytosis (14,000 cell/mL), hematuria with red blood cell (RBC) casts and serum creatinine level of 2.1 mg/dL, which subsequently rose rapidly to 4.1 mg/dL. Test for cytoplasmic‐stainingantineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (C‐ANCA) was positive. Antiproteinase 3 (PR3) antibodies were also positive. Chest x‐ray showed bilateral pulmonary opacities and sinus computed tomography (CT) scan showed mucosal thickening of the sinuses consistent with sinusitis (Figure 3). Renal biopsy revealed segmental necrotizing glomerulonephritis that was pauci‐immune on immunofluorescence staining. The patient was diagnosed with Wegener's granulomatosis with rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. He was treated with intravenous corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide, and trimethoprim‐sulfamethoxazole. The patient's symptoms and acute renal failure resolved with this medical regimen.