User login
Closing the GAP in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
5 things you should know about IPF. American Lung Association. April 12, 2023. Accessed June 21, 2024. https://www.lung.org/blog/idiopathic-pulmonary-fibrosis-things-to-know
Raghu G, Chen SY, Yeh WS, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in US Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years and older: incidence, prevalence, and survival, 2001-11. Lancet Respir Med. 2014;2(7):566-572. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70101-8
Morrow T. Improving outcomes and managing costs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Manag Care. 2019;25(11 suppl):S204-S209. PMID: 31419090
Man RK, Gogikar A, Nanda A, et al. A comparison of the effectiveness of nintedanib and pirfenidone in treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a systematic review. Cureus. 2024;16(2):e54268. doi:10.7759/cureus.54268
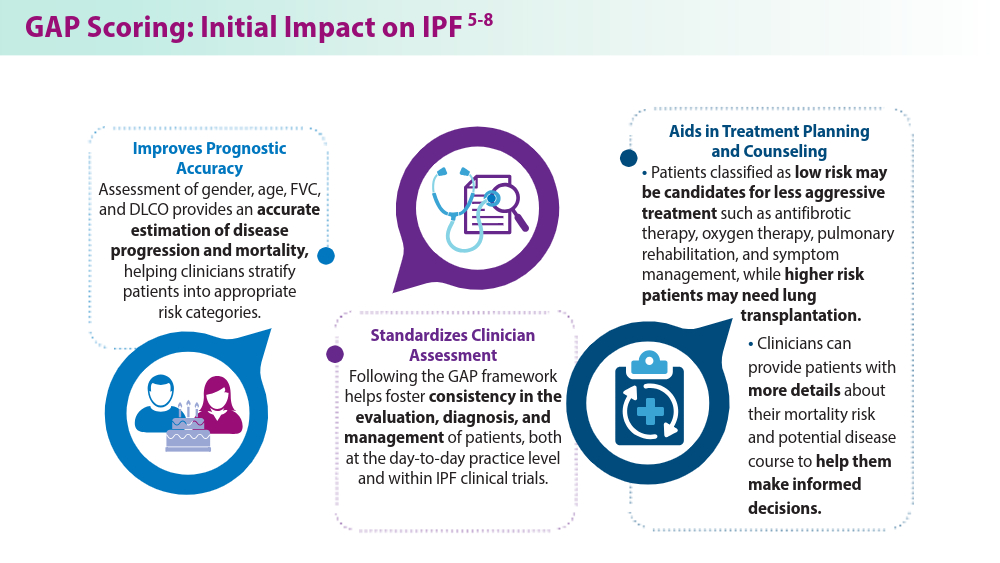
Ley B, Ryerson CJ, Vittinghoff E, et al. A multidimensional index and staging system for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ann Intern Med. 2012;156(10):684-691. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-156-10-201205150-00004
Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, et al. Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198(5):e44-e68. doi:10.1164/rccm.201807-1255ST
Collard HR, Ryerson CJ, Corte TJ, et al. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An International Working Group report. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;194(3):265-275. doi:10.1164/rccm.201604-0801CI
Abuserewa ST, Duff R, Becker G. Treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Cureus. 2021;13(5):e15360. doi:10.7759/cureus.15360
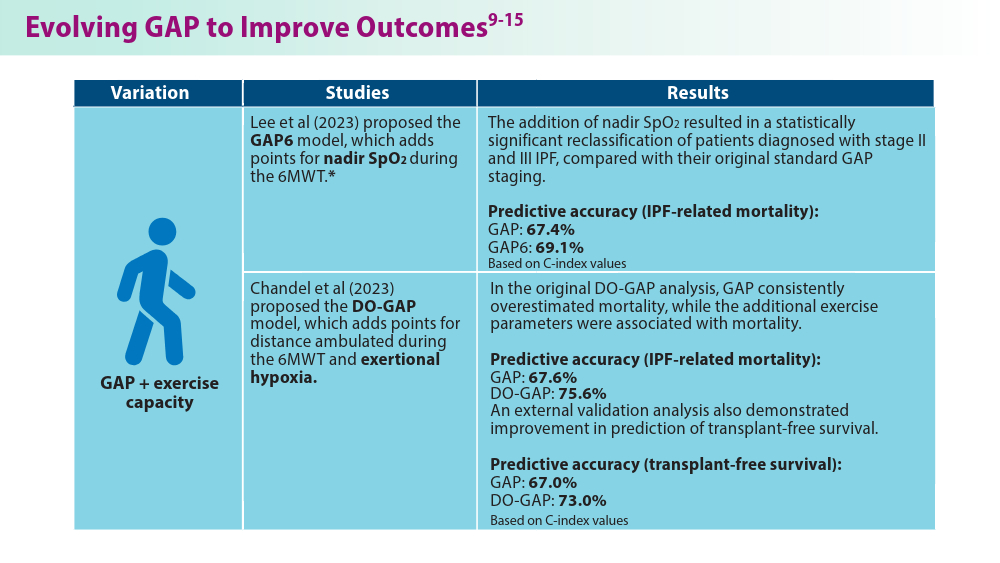
Lee JH, Jang JH, Jang HJ, et al. New prognostic scoring system for mortality in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by modifying the gender, age, and physiology model with desaturation during the six-minute walk test. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1052129. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1052129
Chandel A, Pastre J, Valery S, King CS, Nathan SD. Derivation and validation of a simple multidimensional index incorporating exercise capacity parameters for survival prediction in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax. 2023;78(4):368-375. doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2021-218440
Chandel A, King CS, Ignacio RV, et al. External validation and longitudinal application of the DO-GAP index to individualise survival prediction in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. ERJ Open Res. 2023;9(3):00124-2023. doi:10.1183/23120541.00124-2023
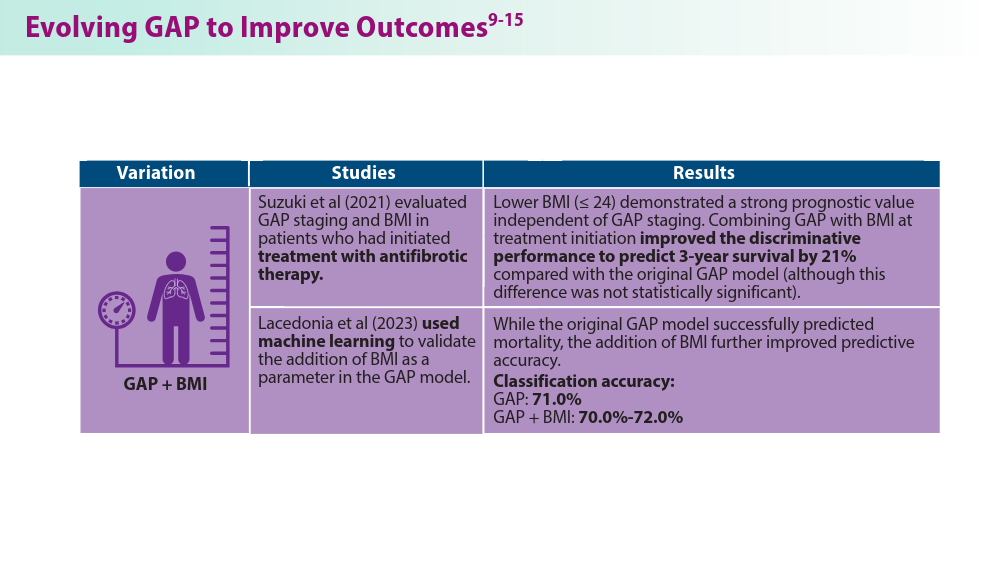
Suzuki Y, Mori K, Aono Y, et al. Combined assessment of the GAP index and body mass index at antifibrotic therapy initiation for prognosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):18579. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-98161-y
Lacedonia D, De Pace CC, Rea G, et al. Machine learning and BMI improve the prognostic value of GAP index in treated IPF patients. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023;10(2):251. doi:10.3390/bioengineering10020251
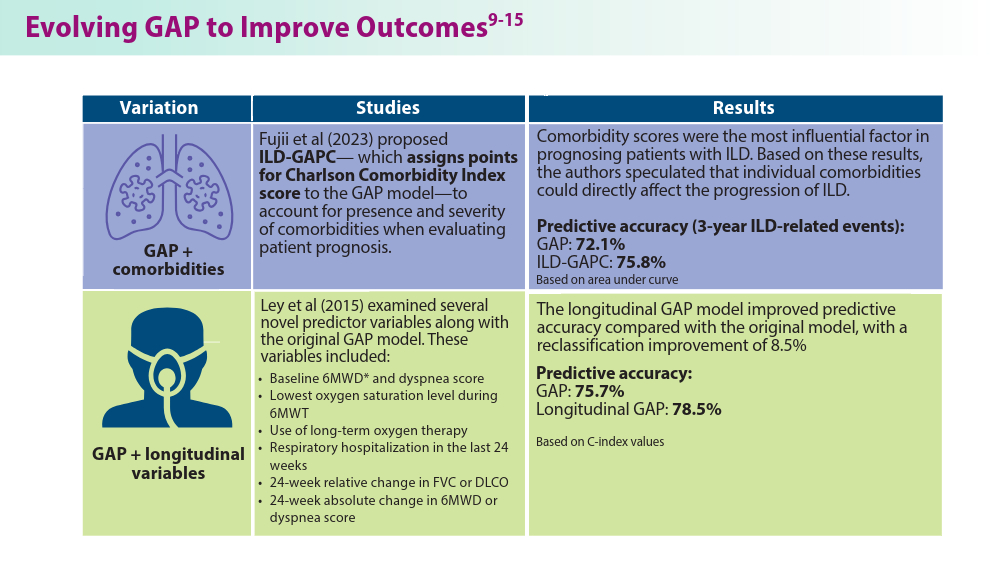
Fujii H, Hara Y, Saigusa Y, et al. ILD-GAP combined with the Charlson Comorbidity Index score (ILD-GAPC) as a prognostic prediction model in patients with interstitial lung disease. Can Respir J. 2023;2023:5088207. doi:10.1155/2023/5088207
Ley B, Bradford WZ, Weycker D, Vittinghoff E, du Bois RM, Collard HR. Unified baseline and longitudinal mortality prediction in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2015;45(5):1374-1381. doi:10.1183/09031936.00146314
Kreuter M, Lee JS, Tzouvelekis A, et al. Monocyte count as a prognostic biomarker in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;204(1):74-81. doi:10.1164/rccm.202003-0669OC
Kreuter M, Lee JS, Tzouvelekis A, et al. A modified blood cell GAP (cGAP) to prognosticate outcomes in IPF. Poster presented at: European Respiratory Society International Congress; September 4-6, 2022. https://medically.gene.com/global/en/unrestricted/respiratory/ERS-2022/ers-2022-poster-kreuter-a-modified-blood-cell-gap.html
Nishikiori H, Chiba H, Lee SH, et al. A modified GAP model for East-Asian populations with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Investig. 2020;58(5):395-402. doi:10.1016/j.resinv.2020.04.001
5 things you should know about IPF. American Lung Association. April 12, 2023. Accessed June 21, 2024. https://www.lung.org/blog/idiopathic-pulmonary-fibrosis-things-to-know
Raghu G, Chen SY, Yeh WS, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in US Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years and older: incidence, prevalence, and survival, 2001-11. Lancet Respir Med. 2014;2(7):566-572. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70101-8
Morrow T. Improving outcomes and managing costs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Manag Care. 2019;25(11 suppl):S204-S209. PMID: 31419090
Man RK, Gogikar A, Nanda A, et al. A comparison of the effectiveness of nintedanib and pirfenidone in treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a systematic review. Cureus. 2024;16(2):e54268. doi:10.7759/cureus.54268
Ley B, Ryerson CJ, Vittinghoff E, et al. A multidimensional index and staging system for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ann Intern Med. 2012;156(10):684-691. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-156-10-201205150-00004
Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, et al. Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198(5):e44-e68. doi:10.1164/rccm.201807-1255ST
Collard HR, Ryerson CJ, Corte TJ, et al. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An International Working Group report. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;194(3):265-275. doi:10.1164/rccm.201604-0801CI
Abuserewa ST, Duff R, Becker G. Treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Cureus. 2021;13(5):e15360. doi:10.7759/cureus.15360
Lee JH, Jang JH, Jang HJ, et al. New prognostic scoring system for mortality in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by modifying the gender, age, and physiology model with desaturation during the six-minute walk test. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1052129. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1052129
Chandel A, Pastre J, Valery S, King CS, Nathan SD. Derivation and validation of a simple multidimensional index incorporating exercise capacity parameters for survival prediction in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax. 2023;78(4):368-375. doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2021-218440
Chandel A, King CS, Ignacio RV, et al. External validation and longitudinal application of the DO-GAP index to individualise survival prediction in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. ERJ Open Res. 2023;9(3):00124-2023. doi:10.1183/23120541.00124-2023
Suzuki Y, Mori K, Aono Y, et al. Combined assessment of the GAP index and body mass index at antifibrotic therapy initiation for prognosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):18579. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-98161-y
Lacedonia D, De Pace CC, Rea G, et al. Machine learning and BMI improve the prognostic value of GAP index in treated IPF patients. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023;10(2):251. doi:10.3390/bioengineering10020251
Fujii H, Hara Y, Saigusa Y, et al. ILD-GAP combined with the Charlson Comorbidity Index score (ILD-GAPC) as a prognostic prediction model in patients with interstitial lung disease. Can Respir J. 2023;2023:5088207. doi:10.1155/2023/5088207
Ley B, Bradford WZ, Weycker D, Vittinghoff E, du Bois RM, Collard HR. Unified baseline and longitudinal mortality prediction in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2015;45(5):1374-1381. doi:10.1183/09031936.00146314
Kreuter M, Lee JS, Tzouvelekis A, et al. Monocyte count as a prognostic biomarker in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;204(1):74-81. doi:10.1164/rccm.202003-0669OC
Kreuter M, Lee JS, Tzouvelekis A, et al. A modified blood cell GAP (cGAP) to prognosticate outcomes in IPF. Poster presented at: European Respiratory Society International Congress; September 4-6, 2022. https://medically.gene.com/global/en/unrestricted/respiratory/ERS-2022/ers-2022-poster-kreuter-a-modified-blood-cell-gap.html
Nishikiori H, Chiba H, Lee SH, et al. A modified GAP model for East-Asian populations with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Investig. 2020;58(5):395-402. doi:10.1016/j.resinv.2020.04.001
5 things you should know about IPF. American Lung Association. April 12, 2023. Accessed June 21, 2024. https://www.lung.org/blog/idiopathic-pulmonary-fibrosis-things-to-know
Raghu G, Chen SY, Yeh WS, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in US Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years and older: incidence, prevalence, and survival, 2001-11. Lancet Respir Med. 2014;2(7):566-572. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70101-8
Morrow T. Improving outcomes and managing costs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Manag Care. 2019;25(11 suppl):S204-S209. PMID: 31419090
Man RK, Gogikar A, Nanda A, et al. A comparison of the effectiveness of nintedanib and pirfenidone in treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a systematic review. Cureus. 2024;16(2):e54268. doi:10.7759/cureus.54268
Ley B, Ryerson CJ, Vittinghoff E, et al. A multidimensional index and staging system for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ann Intern Med. 2012;156(10):684-691. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-156-10-201205150-00004
Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, et al. Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198(5):e44-e68. doi:10.1164/rccm.201807-1255ST
Collard HR, Ryerson CJ, Corte TJ, et al. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An International Working Group report. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;194(3):265-275. doi:10.1164/rccm.201604-0801CI
Abuserewa ST, Duff R, Becker G. Treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Cureus. 2021;13(5):e15360. doi:10.7759/cureus.15360
Lee JH, Jang JH, Jang HJ, et al. New prognostic scoring system for mortality in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by modifying the gender, age, and physiology model with desaturation during the six-minute walk test. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1052129. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1052129
Chandel A, Pastre J, Valery S, King CS, Nathan SD. Derivation and validation of a simple multidimensional index incorporating exercise capacity parameters for survival prediction in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax. 2023;78(4):368-375. doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2021-218440
Chandel A, King CS, Ignacio RV, et al. External validation and longitudinal application of the DO-GAP index to individualise survival prediction in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. ERJ Open Res. 2023;9(3):00124-2023. doi:10.1183/23120541.00124-2023
Suzuki Y, Mori K, Aono Y, et al. Combined assessment of the GAP index and body mass index at antifibrotic therapy initiation for prognosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):18579. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-98161-y
Lacedonia D, De Pace CC, Rea G, et al. Machine learning and BMI improve the prognostic value of GAP index in treated IPF patients. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023;10(2):251. doi:10.3390/bioengineering10020251
Fujii H, Hara Y, Saigusa Y, et al. ILD-GAP combined with the Charlson Comorbidity Index score (ILD-GAPC) as a prognostic prediction model in patients with interstitial lung disease. Can Respir J. 2023;2023:5088207. doi:10.1155/2023/5088207
Ley B, Bradford WZ, Weycker D, Vittinghoff E, du Bois RM, Collard HR. Unified baseline and longitudinal mortality prediction in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2015;45(5):1374-1381. doi:10.1183/09031936.00146314
Kreuter M, Lee JS, Tzouvelekis A, et al. Monocyte count as a prognostic biomarker in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;204(1):74-81. doi:10.1164/rccm.202003-0669OC
Kreuter M, Lee JS, Tzouvelekis A, et al. A modified blood cell GAP (cGAP) to prognosticate outcomes in IPF. Poster presented at: European Respiratory Society International Congress; September 4-6, 2022. https://medically.gene.com/global/en/unrestricted/respiratory/ERS-2022/ers-2022-poster-kreuter-a-modified-blood-cell-gap.html
Nishikiori H, Chiba H, Lee SH, et al. A modified GAP model for East-Asian populations with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Investig. 2020;58(5):395-402. doi:10.1016/j.resinv.2020.04.001
Highlights of the 2024 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule proposed rule
The suggested Medicare Physician Fee Schedule for calendar year (CY) 2024 was announced by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) in July 2023. Physicians who specialize in pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine will be impacted by a number of policy and payment changes. Additionally, keep in mind that this is the proposed rule. Following are some of the key points for our readers:
1. The conversion factor that CMS is suggesting for 2024 is $32.75, which represents a $1.14 (–3.34%) reduction. The current conversion factor is $33.89. This is specifically meant to lower total Medicare spending.
2. It is forecast that pulmonary specialists will experience an estimated 1.09% reduction in Medicare reimbursements if the proposed changes are approved. Medicare reimbursements for critical care specialists will be reduced by 2.51%, and sleep medicine specialists will be seeing a 0.75% increase.
3. Interestingly, CMS is proposing a Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) code G2211 that will have a distinct add-on payment starting on January 1, 2024. With the help of this add-on code, the resource costs of evaluation and management visits for primary care and long-term treatment of difficult patients will be more accurately recognized. In general, it will be used as an additional payment for outpatient office visits in recognition of the potential expenditures that doctors may face when treating a patient’s single, significant, or complex chronic condition over time. Payment for this add-on code would have a redistributive impact on all other CY 2024 payments, which are still lower than what was previously predicted for this policy in CY 2021 under the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule, which was not implemented at the request of various surgical specialties.
4. As you all are aware, split (or shared) E/M visits in hospitals and other institutional settings are those that are provided in part by doctors and in part by other practitioners of the same specialty but billed under a single provider. Thankfully CMS is recommending delaying the application of the “substantive portion” definition of more than 50% of the total period to at least December 31, 2024. Instead, they are going to keep the present definition of the “substantive portion” for CY 2024, which permits use of either more than half of the visit’s total time or one of the three major components (history, exam, or MDM) to determine who bills the visit. Please remember that Critical Care services (99291/99292) may also be shared or split; however, in this case, billing is based only on time.
5. According to CMS’s current regulatory stance, teaching physicians have to be physically present to charge for services involving residents at the end of the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency. Congress, on the other hand, stepped in and passed legislation to expand Medicare coverage of a number of telehealth services. In accordance with the expanded telehealth policies adopted by Congress, CMS is recommending that teaching physicians be permitted to employ audio/video real-time communications technology when the resident physician provides telehealth services to Medicare beneficiaries for CY 2024.
The CMS’s document is fairly comprehensive, so please visit this link for more information
The suggested Medicare Physician Fee Schedule for calendar year (CY) 2024 was announced by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) in July 2023. Physicians who specialize in pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine will be impacted by a number of policy and payment changes. Additionally, keep in mind that this is the proposed rule. Following are some of the key points for our readers:
1. The conversion factor that CMS is suggesting for 2024 is $32.75, which represents a $1.14 (–3.34%) reduction. The current conversion factor is $33.89. This is specifically meant to lower total Medicare spending.
2. It is forecast that pulmonary specialists will experience an estimated 1.09% reduction in Medicare reimbursements if the proposed changes are approved. Medicare reimbursements for critical care specialists will be reduced by 2.51%, and sleep medicine specialists will be seeing a 0.75% increase.
3. Interestingly, CMS is proposing a Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) code G2211 that will have a distinct add-on payment starting on January 1, 2024. With the help of this add-on code, the resource costs of evaluation and management visits for primary care and long-term treatment of difficult patients will be more accurately recognized. In general, it will be used as an additional payment for outpatient office visits in recognition of the potential expenditures that doctors may face when treating a patient’s single, significant, or complex chronic condition over time. Payment for this add-on code would have a redistributive impact on all other CY 2024 payments, which are still lower than what was previously predicted for this policy in CY 2021 under the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule, which was not implemented at the request of various surgical specialties.
4. As you all are aware, split (or shared) E/M visits in hospitals and other institutional settings are those that are provided in part by doctors and in part by other practitioners of the same specialty but billed under a single provider. Thankfully CMS is recommending delaying the application of the “substantive portion” definition of more than 50% of the total period to at least December 31, 2024. Instead, they are going to keep the present definition of the “substantive portion” for CY 2024, which permits use of either more than half of the visit’s total time or one of the three major components (history, exam, or MDM) to determine who bills the visit. Please remember that Critical Care services (99291/99292) may also be shared or split; however, in this case, billing is based only on time.
5. According to CMS’s current regulatory stance, teaching physicians have to be physically present to charge for services involving residents at the end of the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency. Congress, on the other hand, stepped in and passed legislation to expand Medicare coverage of a number of telehealth services. In accordance with the expanded telehealth policies adopted by Congress, CMS is recommending that teaching physicians be permitted to employ audio/video real-time communications technology when the resident physician provides telehealth services to Medicare beneficiaries for CY 2024.
The CMS’s document is fairly comprehensive, so please visit this link for more information
The suggested Medicare Physician Fee Schedule for calendar year (CY) 2024 was announced by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) in July 2023. Physicians who specialize in pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine will be impacted by a number of policy and payment changes. Additionally, keep in mind that this is the proposed rule. Following are some of the key points for our readers:
1. The conversion factor that CMS is suggesting for 2024 is $32.75, which represents a $1.14 (–3.34%) reduction. The current conversion factor is $33.89. This is specifically meant to lower total Medicare spending.
2. It is forecast that pulmonary specialists will experience an estimated 1.09% reduction in Medicare reimbursements if the proposed changes are approved. Medicare reimbursements for critical care specialists will be reduced by 2.51%, and sleep medicine specialists will be seeing a 0.75% increase.
3. Interestingly, CMS is proposing a Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) code G2211 that will have a distinct add-on payment starting on January 1, 2024. With the help of this add-on code, the resource costs of evaluation and management visits for primary care and long-term treatment of difficult patients will be more accurately recognized. In general, it will be used as an additional payment for outpatient office visits in recognition of the potential expenditures that doctors may face when treating a patient’s single, significant, or complex chronic condition over time. Payment for this add-on code would have a redistributive impact on all other CY 2024 payments, which are still lower than what was previously predicted for this policy in CY 2021 under the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule, which was not implemented at the request of various surgical specialties.
4. As you all are aware, split (or shared) E/M visits in hospitals and other institutional settings are those that are provided in part by doctors and in part by other practitioners of the same specialty but billed under a single provider. Thankfully CMS is recommending delaying the application of the “substantive portion” definition of more than 50% of the total period to at least December 31, 2024. Instead, they are going to keep the present definition of the “substantive portion” for CY 2024, which permits use of either more than half of the visit’s total time or one of the three major components (history, exam, or MDM) to determine who bills the visit. Please remember that Critical Care services (99291/99292) may also be shared or split; however, in this case, billing is based only on time.
5. According to CMS’s current regulatory stance, teaching physicians have to be physically present to charge for services involving residents at the end of the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency. Congress, on the other hand, stepped in and passed legislation to expand Medicare coverage of a number of telehealth services. In accordance with the expanded telehealth policies adopted by Congress, CMS is recommending that teaching physicians be permitted to employ audio/video real-time communications technology when the resident physician provides telehealth services to Medicare beneficiaries for CY 2024.
The CMS’s document is fairly comprehensive, so please visit this link for more information
2022 billing and coding updates
Telehealth and Teaching Physician Services and ICD-10 codes updates
In my previous article in June, 2022, we plowed through the billing and coding updates regarding critical care services, and, I hope that it helped our readers get more acquainted with the nuances of billing and coding in the ICU. In this piece, I would like to briefly elucidate three other areas of practice, which will be relevant to all physicians across various specialties.
Telehealth services
(PHE). Initially, the plan was to remove these from the list of covered services by the latter end of the COVID-19 PHE, which, created some uncertainty, or by December 31, 2021. Fortunately, CMS finalized that they will extend it through the end of the calendar year (CY) 2023. So, now all the telehealth services will remain on the CMS list until December 31, 2023. The general principle behind this ruling is to allow for more time for CMS and stakeholders to gather data and to submit support for requesting these services to be permanently added to the Medicare telehealth services list.
Not only has CMS extended the deadline for telehealth services but also they have gone far and beyond to extend some of the codes for cardiac and intensive cardiac rehabilitation until December 31, 2023, as well.
There has been a lot of debate regarding the geographic restrictions when it comes to telehealth visits for diagnosis, evaluation, or treatment of a mental health disorder. As per the latest Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2021 (Section 123), the home of the patient is a permissible site. But, the caveat is that there must be an in-person service with the practitioner/physician within 6 months prior to the initial telehealth visit. Additionally, there has to be a set frequency for subsequent in-person visits. And, usually the subsequent visits will need to be provided at least every 12 months. These requirements are not set in stone and can be changed on a case-by-case basis provided there is appropriate documentation in the chart.
Lastly, it is important to understand and use the appropriate telecommunication systems for the telehealth visits and the modifiers that are associated with them. By definition, it has to be audio and video equipment that allows two-way, real-time interactive communication between the patient and the provider when used for telehealth services for the diagnosis, evaluation, or treatment of mental health disorders. But, CMS is in the process of amending it to include audio-only communications technology. At this time, the use of audio-only interactive telecommunications system is limited to practitioners who have the capability to provide two-way audio/video communications but, where the patient is not capable, or does not consent to, the use of two-way audio/video technology. Modifier FQ should be attached to all the mental health services that were furnished using audio-only communications. And, mental health services can include services for treatment of substance use disorders (SUD). Please do not confuse modifier FQ with modifier 93 as FQ is only for behavioral health services. And, remember that the totality of the communication of information exchanged between the provider and the patient during the course of the synchronous telemedicine service (rendered via telephone or other real-time interactive audio only telecommunication system) must be of an amount and nature that is sufficient to meet the key components and/or requirements of the same service when rendered via a face-to-face interaction.
Teaching physician services
As a general rule, a teaching physician can bill for the resident services only if they are present for the critical (key) portion of the service. But, there is one exception called the “primary care exception” under which in certain teaching hospital primary care centers, the teaching physician can bill for certain services as furnished independently by the resident without the teaching physician being physically present, but with the teaching physician’s review.
The current model to bill for office/outpatient E/M visit level is either based on either total time spent (personally) or medical-decision-making (MDM). When time is used to select the visit level only the time spent by the teaching physician in qualifying activities can be included for the purposes of the visit level selection. And, this includes the time the teaching physician was present with the resident performing those qualifying activities. Also, under the primary care exception, time cannot be used to select the visit level. This is to guard against the possibility of inappropriate coding that reflects residents’ inefficiencies rather than a measure of the total medically necessary time required to furnish the E/M services.
ICD-10 updates
Usually, the ICD-10 codes are updated annually and take effect every October 1. Some of the most relevant updates are as follows:
1. U09.9 Post COVID-19 condition, unspecified: This should be used to document sequelae of COVID-19 or “long COVID” conditions, after the acute illness has resolved. But, remember to code the conditions related to COVID-19 first and do not use this code with an active or current COVID-19 infection.
2. U07.0 Vaping-related disorder: This should be used for all vaping-related illnesses. However, additional codes for other diagnoses such as acute respiratory failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome, or pneumonitis can also be used with this code. Other respiratory signs and symptoms such as cough and shortness of breath should not be coded separately.
3. Cough is one of the most common reasons for referral to a pulmonologist. The CDC has expanded these codes so please remember to code the most specific diagnosis as deemed appropriate.
R05.1 Acute cough
R05.2 Subacute cough
R05.3 Chronic cough
R05.4 Cough, syncope
R05.8 Other specified cough
R05.9 Cough, unspecified
We will be back with some more exciting and intriguing billing and coding updates in our next article and hope to see everyone at CHEST 2022 in Nashville., TN.
Telehealth and Teaching Physician Services and ICD-10 codes updates
Telehealth and Teaching Physician Services and ICD-10 codes updates
In my previous article in June, 2022, we plowed through the billing and coding updates regarding critical care services, and, I hope that it helped our readers get more acquainted with the nuances of billing and coding in the ICU. In this piece, I would like to briefly elucidate three other areas of practice, which will be relevant to all physicians across various specialties.
Telehealth services
(PHE). Initially, the plan was to remove these from the list of covered services by the latter end of the COVID-19 PHE, which, created some uncertainty, or by December 31, 2021. Fortunately, CMS finalized that they will extend it through the end of the calendar year (CY) 2023. So, now all the telehealth services will remain on the CMS list until December 31, 2023. The general principle behind this ruling is to allow for more time for CMS and stakeholders to gather data and to submit support for requesting these services to be permanently added to the Medicare telehealth services list.
Not only has CMS extended the deadline for telehealth services but also they have gone far and beyond to extend some of the codes for cardiac and intensive cardiac rehabilitation until December 31, 2023, as well.
There has been a lot of debate regarding the geographic restrictions when it comes to telehealth visits for diagnosis, evaluation, or treatment of a mental health disorder. As per the latest Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2021 (Section 123), the home of the patient is a permissible site. But, the caveat is that there must be an in-person service with the practitioner/physician within 6 months prior to the initial telehealth visit. Additionally, there has to be a set frequency for subsequent in-person visits. And, usually the subsequent visits will need to be provided at least every 12 months. These requirements are not set in stone and can be changed on a case-by-case basis provided there is appropriate documentation in the chart.
Lastly, it is important to understand and use the appropriate telecommunication systems for the telehealth visits and the modifiers that are associated with them. By definition, it has to be audio and video equipment that allows two-way, real-time interactive communication between the patient and the provider when used for telehealth services for the diagnosis, evaluation, or treatment of mental health disorders. But, CMS is in the process of amending it to include audio-only communications technology. At this time, the use of audio-only interactive telecommunications system is limited to practitioners who have the capability to provide two-way audio/video communications but, where the patient is not capable, or does not consent to, the use of two-way audio/video technology. Modifier FQ should be attached to all the mental health services that were furnished using audio-only communications. And, mental health services can include services for treatment of substance use disorders (SUD). Please do not confuse modifier FQ with modifier 93 as FQ is only for behavioral health services. And, remember that the totality of the communication of information exchanged between the provider and the patient during the course of the synchronous telemedicine service (rendered via telephone or other real-time interactive audio only telecommunication system) must be of an amount and nature that is sufficient to meet the key components and/or requirements of the same service when rendered via a face-to-face interaction.
Teaching physician services
As a general rule, a teaching physician can bill for the resident services only if they are present for the critical (key) portion of the service. But, there is one exception called the “primary care exception” under which in certain teaching hospital primary care centers, the teaching physician can bill for certain services as furnished independently by the resident without the teaching physician being physically present, but with the teaching physician’s review.
The current model to bill for office/outpatient E/M visit level is either based on either total time spent (personally) or medical-decision-making (MDM). When time is used to select the visit level only the time spent by the teaching physician in qualifying activities can be included for the purposes of the visit level selection. And, this includes the time the teaching physician was present with the resident performing those qualifying activities. Also, under the primary care exception, time cannot be used to select the visit level. This is to guard against the possibility of inappropriate coding that reflects residents’ inefficiencies rather than a measure of the total medically necessary time required to furnish the E/M services.
ICD-10 updates
Usually, the ICD-10 codes are updated annually and take effect every October 1. Some of the most relevant updates are as follows:
1. U09.9 Post COVID-19 condition, unspecified: This should be used to document sequelae of COVID-19 or “long COVID” conditions, after the acute illness has resolved. But, remember to code the conditions related to COVID-19 first and do not use this code with an active or current COVID-19 infection.
2. U07.0 Vaping-related disorder: This should be used for all vaping-related illnesses. However, additional codes for other diagnoses such as acute respiratory failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome, or pneumonitis can also be used with this code. Other respiratory signs and symptoms such as cough and shortness of breath should not be coded separately.
3. Cough is one of the most common reasons for referral to a pulmonologist. The CDC has expanded these codes so please remember to code the most specific diagnosis as deemed appropriate.
R05.1 Acute cough
R05.2 Subacute cough
R05.3 Chronic cough
R05.4 Cough, syncope
R05.8 Other specified cough
R05.9 Cough, unspecified
We will be back with some more exciting and intriguing billing and coding updates in our next article and hope to see everyone at CHEST 2022 in Nashville., TN.
In my previous article in June, 2022, we plowed through the billing and coding updates regarding critical care services, and, I hope that it helped our readers get more acquainted with the nuances of billing and coding in the ICU. In this piece, I would like to briefly elucidate three other areas of practice, which will be relevant to all physicians across various specialties.
Telehealth services
(PHE). Initially, the plan was to remove these from the list of covered services by the latter end of the COVID-19 PHE, which, created some uncertainty, or by December 31, 2021. Fortunately, CMS finalized that they will extend it through the end of the calendar year (CY) 2023. So, now all the telehealth services will remain on the CMS list until December 31, 2023. The general principle behind this ruling is to allow for more time for CMS and stakeholders to gather data and to submit support for requesting these services to be permanently added to the Medicare telehealth services list.
Not only has CMS extended the deadline for telehealth services but also they have gone far and beyond to extend some of the codes for cardiac and intensive cardiac rehabilitation until December 31, 2023, as well.
There has been a lot of debate regarding the geographic restrictions when it comes to telehealth visits for diagnosis, evaluation, or treatment of a mental health disorder. As per the latest Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2021 (Section 123), the home of the patient is a permissible site. But, the caveat is that there must be an in-person service with the practitioner/physician within 6 months prior to the initial telehealth visit. Additionally, there has to be a set frequency for subsequent in-person visits. And, usually the subsequent visits will need to be provided at least every 12 months. These requirements are not set in stone and can be changed on a case-by-case basis provided there is appropriate documentation in the chart.
Lastly, it is important to understand and use the appropriate telecommunication systems for the telehealth visits and the modifiers that are associated with them. By definition, it has to be audio and video equipment that allows two-way, real-time interactive communication between the patient and the provider when used for telehealth services for the diagnosis, evaluation, or treatment of mental health disorders. But, CMS is in the process of amending it to include audio-only communications technology. At this time, the use of audio-only interactive telecommunications system is limited to practitioners who have the capability to provide two-way audio/video communications but, where the patient is not capable, or does not consent to, the use of two-way audio/video technology. Modifier FQ should be attached to all the mental health services that were furnished using audio-only communications. And, mental health services can include services for treatment of substance use disorders (SUD). Please do not confuse modifier FQ with modifier 93 as FQ is only for behavioral health services. And, remember that the totality of the communication of information exchanged between the provider and the patient during the course of the synchronous telemedicine service (rendered via telephone or other real-time interactive audio only telecommunication system) must be of an amount and nature that is sufficient to meet the key components and/or requirements of the same service when rendered via a face-to-face interaction.
Teaching physician services
As a general rule, a teaching physician can bill for the resident services only if they are present for the critical (key) portion of the service. But, there is one exception called the “primary care exception” under which in certain teaching hospital primary care centers, the teaching physician can bill for certain services as furnished independently by the resident without the teaching physician being physically present, but with the teaching physician’s review.
The current model to bill for office/outpatient E/M visit level is either based on either total time spent (personally) or medical-decision-making (MDM). When time is used to select the visit level only the time spent by the teaching physician in qualifying activities can be included for the purposes of the visit level selection. And, this includes the time the teaching physician was present with the resident performing those qualifying activities. Also, under the primary care exception, time cannot be used to select the visit level. This is to guard against the possibility of inappropriate coding that reflects residents’ inefficiencies rather than a measure of the total medically necessary time required to furnish the E/M services.
ICD-10 updates
Usually, the ICD-10 codes are updated annually and take effect every October 1. Some of the most relevant updates are as follows:
1. U09.9 Post COVID-19 condition, unspecified: This should be used to document sequelae of COVID-19 or “long COVID” conditions, after the acute illness has resolved. But, remember to code the conditions related to COVID-19 first and do not use this code with an active or current COVID-19 infection.
2. U07.0 Vaping-related disorder: This should be used for all vaping-related illnesses. However, additional codes for other diagnoses such as acute respiratory failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome, or pneumonitis can also be used with this code. Other respiratory signs and symptoms such as cough and shortness of breath should not be coded separately.
3. Cough is one of the most common reasons for referral to a pulmonologist. The CDC has expanded these codes so please remember to code the most specific diagnosis as deemed appropriate.
R05.1 Acute cough
R05.2 Subacute cough
R05.3 Chronic cough
R05.4 Cough, syncope
R05.8 Other specified cough
R05.9 Cough, unspecified
We will be back with some more exciting and intriguing billing and coding updates in our next article and hope to see everyone at CHEST 2022 in Nashville., TN.
2022 Billing and coding updates: Critical care services
The principal idea behind this article is to summarize comprehensively yet concisely the 2022 CMS updates regarding the critical care services. I would encourage and urge all the members to read this section attentively to stay abreast with all the recent developments.
As a general reminder the two critical care services billing codes for the evaluation and management of the critically ill injured patients are:
99291: First 30-74 minutes
99292: Each additional 30 minutes
And, the five major changes for 2022 as proposed by the CMS for critical care services are:
1. It is allowed for the physicians and APPs in the same specialty to bill concurrent critical care services.
Previously, same specialty practitioners were required to bill and were paid as “one” when multiple practitioners provided services on the same date. Now, they can bill for critical care services as subsequent care or as aggregate time, and they are highlighted below with examples:
Subsequent care
Initial visit by a provider for 65 minutes (bill as 99291 as the first claim)
Subsequent visit at a later time on the same day for 60 minutes (bill as 99292 x2 as the second claim)
Aggregate time
Time of multiple practitioners in the same specialty can be added to meet 99291 or 99292. If Practitioner A spends 15 minutes of critical care, then 99291 cannot be billed; but, if Practitioner B spends 30 minutes of critical care, they can bill 99291 with a total time of 45 minutes as one claim
The prerequisites are that the visits are medically necessary, and each visit meets the definition of critical care.
2. Modifier FS needs to be used for split sharing of critical care services.
Previously, critical care services could not be split shared, but it can be done in 2022. The practitioner who provides the significant portion of the visit needs to bill. A significant or substantive portion is considered to be more than half the cumulative total time of both providers.
Example: The APP spends 20 minutes in critical care services and the physician spends 30 minutes. Total time spent is 50 minutes, and the physician may bill 99291.
It is crucial to note that each provider needs to document a note for the medically necessary critical care that they personally performed and the time they spent. Additionally, upon review of the medical records, the two providers should be easily identifiable, and the medical record must be signed and dated by the provider who performed the substantive portion and billed.
Lastly, do not forget to submit the modifier FS.
3. Modifier 25 needs to be used to get paid for an ED visit or other E/M service on the same day as critical care.
Previously, hospital ED services were not paid on the same date as critical care by the same provider. But, in 2022, the practitioners may bill for ED visit at the hospital and also for other E/M services on the same day when there is supporting documentation. The practitioners will need to document that the E/M service was provided prior to the time when the patient did not require critical care, that the service was medically necessary, and that the service was separate and distinct with no duplication.
Of note, do not forget to submit the modifier 25.
4. Critical care visits will be separately billable from global surgery when unrelated with the use of modifier FT.
Previously pre- and postoperative critical care was included in the surgical package of many procedures with a global period of 10-90 days, and critical care visits would be paid only if the service was unrelated to the procedure. The concept remains the same in 2022 but, now, new modifier FT will need to be used to report critical care services unrelated to the procedure. Also, the service provided will need to meet the definition of critical care, which is usually above and beyond the procedure performed and should be unrelated to the specific injury or general surgical procedure performed.
5. There will be certain critical care medical record documentation requirements.
It is paramount that each practitioner must document the exact total critical care time and not a range or approximation of time. Additionally, it is equally as important for the documentation to indicate that the services provided were medically reasonable and necessary. In the setting of split/shared billing, the role of each practitioner should be clearly identifiable (the condition for which each practitioner treated the patient, how the care was concurrent either subsequent or aggregate, and the total time of each practitioner).
Hopefully, this review will provide a good perception for our members in regards to major updates for 2022, help them navigate the regulatory rules, and avoid any unnecessary setbacks. In the upcoming months, we will try to cover some more topics on practice management and administration, such as Medicare Physician Fee Schedule Rule, Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment Rule, and coding/billing for teaching physicians, telehealth, and pulmonary rehabilitation services.
The principal idea behind this article is to summarize comprehensively yet concisely the 2022 CMS updates regarding the critical care services. I would encourage and urge all the members to read this section attentively to stay abreast with all the recent developments.
As a general reminder the two critical care services billing codes for the evaluation and management of the critically ill injured patients are:
99291: First 30-74 minutes
99292: Each additional 30 minutes
And, the five major changes for 2022 as proposed by the CMS for critical care services are:
1. It is allowed for the physicians and APPs in the same specialty to bill concurrent critical care services.
Previously, same specialty practitioners were required to bill and were paid as “one” when multiple practitioners provided services on the same date. Now, they can bill for critical care services as subsequent care or as aggregate time, and they are highlighted below with examples:
Subsequent care
Initial visit by a provider for 65 minutes (bill as 99291 as the first claim)
Subsequent visit at a later time on the same day for 60 minutes (bill as 99292 x2 as the second claim)
Aggregate time
Time of multiple practitioners in the same specialty can be added to meet 99291 or 99292. If Practitioner A spends 15 minutes of critical care, then 99291 cannot be billed; but, if Practitioner B spends 30 minutes of critical care, they can bill 99291 with a total time of 45 minutes as one claim
The prerequisites are that the visits are medically necessary, and each visit meets the definition of critical care.
2. Modifier FS needs to be used for split sharing of critical care services.
Previously, critical care services could not be split shared, but it can be done in 2022. The practitioner who provides the significant portion of the visit needs to bill. A significant or substantive portion is considered to be more than half the cumulative total time of both providers.
Example: The APP spends 20 minutes in critical care services and the physician spends 30 minutes. Total time spent is 50 minutes, and the physician may bill 99291.
It is crucial to note that each provider needs to document a note for the medically necessary critical care that they personally performed and the time they spent. Additionally, upon review of the medical records, the two providers should be easily identifiable, and the medical record must be signed and dated by the provider who performed the substantive portion and billed.
Lastly, do not forget to submit the modifier FS.
3. Modifier 25 needs to be used to get paid for an ED visit or other E/M service on the same day as critical care.
Previously, hospital ED services were not paid on the same date as critical care by the same provider. But, in 2022, the practitioners may bill for ED visit at the hospital and also for other E/M services on the same day when there is supporting documentation. The practitioners will need to document that the E/M service was provided prior to the time when the patient did not require critical care, that the service was medically necessary, and that the service was separate and distinct with no duplication.
Of note, do not forget to submit the modifier 25.
4. Critical care visits will be separately billable from global surgery when unrelated with the use of modifier FT.
Previously pre- and postoperative critical care was included in the surgical package of many procedures with a global period of 10-90 days, and critical care visits would be paid only if the service was unrelated to the procedure. The concept remains the same in 2022 but, now, new modifier FT will need to be used to report critical care services unrelated to the procedure. Also, the service provided will need to meet the definition of critical care, which is usually above and beyond the procedure performed and should be unrelated to the specific injury or general surgical procedure performed.
5. There will be certain critical care medical record documentation requirements.
It is paramount that each practitioner must document the exact total critical care time and not a range or approximation of time. Additionally, it is equally as important for the documentation to indicate that the services provided were medically reasonable and necessary. In the setting of split/shared billing, the role of each practitioner should be clearly identifiable (the condition for which each practitioner treated the patient, how the care was concurrent either subsequent or aggregate, and the total time of each practitioner).
Hopefully, this review will provide a good perception for our members in regards to major updates for 2022, help them navigate the regulatory rules, and avoid any unnecessary setbacks. In the upcoming months, we will try to cover some more topics on practice management and administration, such as Medicare Physician Fee Schedule Rule, Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment Rule, and coding/billing for teaching physicians, telehealth, and pulmonary rehabilitation services.
The principal idea behind this article is to summarize comprehensively yet concisely the 2022 CMS updates regarding the critical care services. I would encourage and urge all the members to read this section attentively to stay abreast with all the recent developments.
As a general reminder the two critical care services billing codes for the evaluation and management of the critically ill injured patients are:
99291: First 30-74 minutes
99292: Each additional 30 minutes
And, the five major changes for 2022 as proposed by the CMS for critical care services are:
1. It is allowed for the physicians and APPs in the same specialty to bill concurrent critical care services.
Previously, same specialty practitioners were required to bill and were paid as “one” when multiple practitioners provided services on the same date. Now, they can bill for critical care services as subsequent care or as aggregate time, and they are highlighted below with examples:
Subsequent care
Initial visit by a provider for 65 minutes (bill as 99291 as the first claim)
Subsequent visit at a later time on the same day for 60 minutes (bill as 99292 x2 as the second claim)
Aggregate time
Time of multiple practitioners in the same specialty can be added to meet 99291 or 99292. If Practitioner A spends 15 minutes of critical care, then 99291 cannot be billed; but, if Practitioner B spends 30 minutes of critical care, they can bill 99291 with a total time of 45 minutes as one claim
The prerequisites are that the visits are medically necessary, and each visit meets the definition of critical care.
2. Modifier FS needs to be used for split sharing of critical care services.
Previously, critical care services could not be split shared, but it can be done in 2022. The practitioner who provides the significant portion of the visit needs to bill. A significant or substantive portion is considered to be more than half the cumulative total time of both providers.
Example: The APP spends 20 minutes in critical care services and the physician spends 30 minutes. Total time spent is 50 minutes, and the physician may bill 99291.
It is crucial to note that each provider needs to document a note for the medically necessary critical care that they personally performed and the time they spent. Additionally, upon review of the medical records, the two providers should be easily identifiable, and the medical record must be signed and dated by the provider who performed the substantive portion and billed.
Lastly, do not forget to submit the modifier FS.
3. Modifier 25 needs to be used to get paid for an ED visit or other E/M service on the same day as critical care.
Previously, hospital ED services were not paid on the same date as critical care by the same provider. But, in 2022, the practitioners may bill for ED visit at the hospital and also for other E/M services on the same day when there is supporting documentation. The practitioners will need to document that the E/M service was provided prior to the time when the patient did not require critical care, that the service was medically necessary, and that the service was separate and distinct with no duplication.
Of note, do not forget to submit the modifier 25.
4. Critical care visits will be separately billable from global surgery when unrelated with the use of modifier FT.
Previously pre- and postoperative critical care was included in the surgical package of many procedures with a global period of 10-90 days, and critical care visits would be paid only if the service was unrelated to the procedure. The concept remains the same in 2022 but, now, new modifier FT will need to be used to report critical care services unrelated to the procedure. Also, the service provided will need to meet the definition of critical care, which is usually above and beyond the procedure performed and should be unrelated to the specific injury or general surgical procedure performed.
5. There will be certain critical care medical record documentation requirements.
It is paramount that each practitioner must document the exact total critical care time and not a range or approximation of time. Additionally, it is equally as important for the documentation to indicate that the services provided were medically reasonable and necessary. In the setting of split/shared billing, the role of each practitioner should be clearly identifiable (the condition for which each practitioner treated the patient, how the care was concurrent either subsequent or aggregate, and the total time of each practitioner).
Hopefully, this review will provide a good perception for our members in regards to major updates for 2022, help them navigate the regulatory rules, and avoid any unnecessary setbacks. In the upcoming months, we will try to cover some more topics on practice management and administration, such as Medicare Physician Fee Schedule Rule, Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment Rule, and coding/billing for teaching physicians, telehealth, and pulmonary rehabilitation services.