User login
Implementing shared decision making in labor and delivery: TeamBirth is a model for person-centered birthing care
CASE The TeamBirth experience: Making a difference
“At a community hospital in Washington where we had implemented TeamBirth (a labor and delivery shared decision making model), a patient, her partner, a labor and delivery nurse, and myself (an ObGyn) were making a plan for the patient’s induction of labor admission. I asked the patient, a 29-year-old (G2P1001), how we could improve her care in relation to her first birth. Her answer was simple: I want to be treated with respect. Her partner went on to describe their past experience in which the provider was inappropriately texting while in between the patient’s knees during delivery. Our team had the opportunity to undo some of the trauma from her first birth. That’s what I like about TeamBirth. It gives every patient the opportunity, regardless of their background, to define safety and participate in their care experience.”
–Angela Chien, MD, Obstetrician and Quality Improvement leader, Washington
Unfortunately, disrespect and mistreatment are far from an anomaly in the obstetrics setting. In a systematic review of respectful maternity care, the World Health Organization delineated 7 dimensions of maternal mistreatment: physical abuse, sexual abuse, verbal abuse, stigma and discrimination, failure to meet professional standards of care, poor rapport between women and providers, and poor conditions and constraints presented by the health system.1 In 2019, the Giving Voice to Mothers study showed that 17% of birthing people in the United States reported experiencing 1 or more types of maternal mistreatment.2 Rates of mistreatment were disproportionately greater in populations of color, hospital-based births, and among those with social, economic, or health challenges.2 It is well known that Black and African American and American Indian and Alaska Native populations experience the rare events of severe maternal morbidity and mortality more frequently than their White counterparts; the disproportionate burden of mistreatment is lesser known and far more common.
Overlooking the longitudinal harm of a negative birth experience has cascading impact. While an empowering perinatal experience can foster preventive screening and management of chronic disease, a poor experience conversely can seed mistrust at an individual, generational, and community level.
The patient quality enterprise is beginning to shift attention toward maternal experience with the development of PREMs (patient-reported experience measures), PROMs (patient-reported outcome measures), and novel validated scales that assess autonomy and trust.3 Development of a maternal Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (CAHPS) survey on childbirth is forthcoming.4 Of course, continuing to prioritize physical safety through initiatives on blood pressure monitoring and severe maternal morbidity and mortality remains paramount. Yet emotional and psychological safety also must be recognized as essential pillars of patient safety. Transgressions related to autonomy and dignity, as well as racism, sexism, classicism, and ableism, should be treated as “adverse and never events.”5
How the TeamBirth model works
Shared decision making (SDM) is cited in medical pedagogy as the solution to respectfullyrecognizing social context, integrating subjective experience, and honoring patient autonomy.6 The onus has always been on individual clinicians to exercise SDM. A new practice model, TeamBirth, embeds SDM into the culture and workflow. It offers a behavioral framework to mitigate implicit bias and operationalizes SDM tools, such that every patient is an empowered participant in their care.
TeamBirth was created through Ariadne Labs’ Delivery Decisions Initiative, a research and social impact program that designs, tests, and scales transformative, systems-level solutions that promote quality, equity, and dignity in childbirth. By the end of 2023, TeamBirth will be implemented in more than 100 hospitals across the United States, cumulatively touching over 200,000 lives. (For more information on the TeamBirth model, view the “Why TeamBirth” video at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EoVrSaGk7gc.)
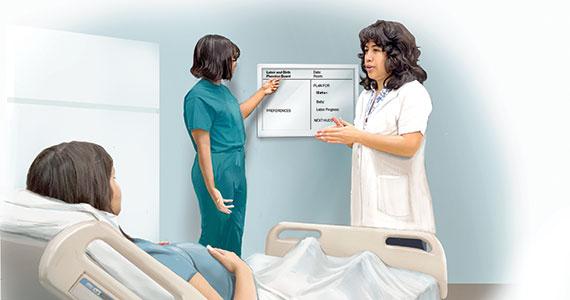
The tenets of TeamBirth are enacted through a patient-facing, shared whiteboard or dry-erase planning board in the labor room (FIGURE 1). Research has demonstrated how dry-erase boards in clinical settings can support safety and dignity in care, especially to improve patient-provider communication, teamwork, and patient satisfaction.7,8 The planning board is initially filled out by a clinical team member and is updated during team “huddles” throughout labor.

Huddles are care plan discussions with the full care team (the patient, nurse, doula and/or other support person(s), delivering provider, and interpreter or social worker as needed). At a minimum, huddles occur on admission, with changes to the clinical course and care plan, and at the request of any team member. Huddles can transpire through in-person, virtual, or phone communication.9 The concept builds on interdisciplinary and patient-centered rounding and establishes a communication system that is suited to the dynamic environment and amplified patient autonomy unique to labor and delivery. Dr. Bob Barbieri, a steadfast leader and champion of TeamBirth implementation at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston (and the Editor in Chief of OBG M
Continue to: Patient response to TeamBirth is positive...
Patient response to TeamBirth is positive
Patients and providers alike have endorsed TeamBirth. In initial pilot testing across 4 sites, 99% of all patients surveyed “definitely” or “somewhat” had the role they wanted in making decisions about their labor.9
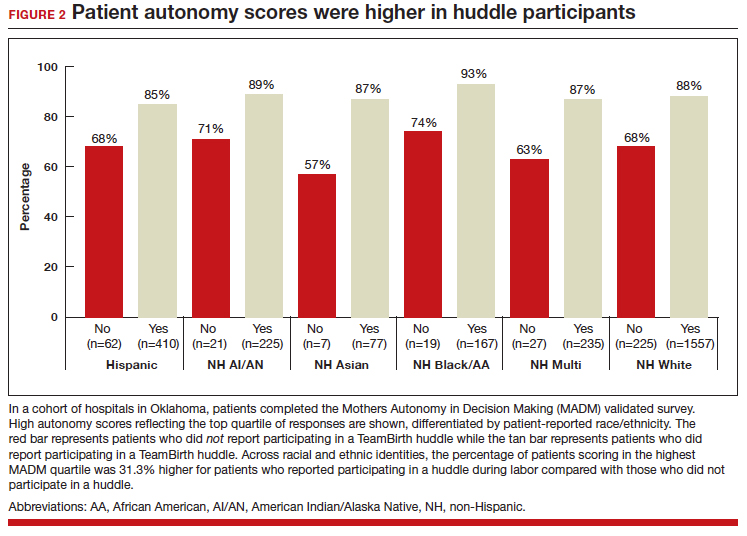
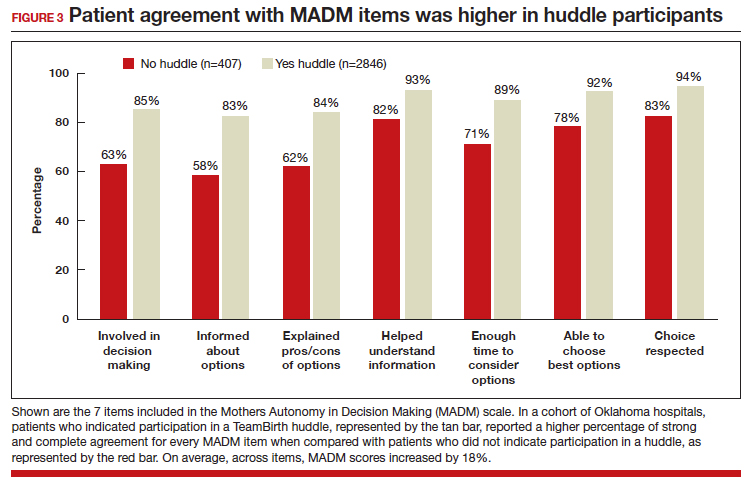
In partnership with the Oklahoma Perinatal Quality Improvement Collaborative (OPQIC), the impact of TeamBirth was assessed in a statewide patient cohort (n = 3,121) using the validated Mothers Autonomy in Decision Making (MADM) scale created by the Birth Place Lab at the University of British Columbia. The percentage of patients who scored in the highest MADM quartile was 31.3% higher for patients who indicated participation in a huddle during labor compared with those who did not participate in a huddle. This trend held across all racial and ethnic groups: For example, 93% of non-Hispanic Black/African American patients who had a TeamBirth huddle reported high autonomy, a nearly 20 percentage point increase from those without a huddle (FIGURE 2). Similarly, a higher percentage of agreement was observed across all 7 items in the MADM scale for patients who reported a TeamBirth huddle (FIGURE 3). TeamBirth’s effect has been observed across surveys and multiple validated metrics.
Data collection related to TeamBirth continues to be ongoing, with reported values retrieved on July 14, 2023. Rigorous review of patient-reported outcomes is forthcoming, and assessing impact on clinical outcomes, such as NTSV (nulliparous, term, singleton vertex) cesarean delivery rates and severe maternal morbidity, is on the horizon.
Qualitative survey responses reinforce how patients value TeamBirth and appreciate huddles and whiteboards.
Continue to: Patient testimonials...
Patient testimonials
The following testimonials were obtained from a TeamBirth survey that patients in participating Massachusetts hospitals completed in the postpartum unit prior to discharge.
According to one patient, “TeamBirth is great, feels like all obstacles are covered by multiple people with many talents, expertise. Feels like mom is part of the process, much different than my delivery 2 years ago when I felt like things were decided for me/I was ‘told’ what we were doing and questioned if I felt uneasy about it…. We felt safe and like all things were covered no matter what may happen.”
Another patient, also at a Massachusetts hospital, offered these comments about TeamBirth: “The entire staff was very genuine and my experience the best it could be. They deserve updated whiteboards in every room. I found them to be very useful.”
The clinician perspective
To be certain, clinician workflow must be a consideration for any practice change. The feasibility, acceptability, and safety of the TeamBirth model to clinicians was validated through a study at 4 community hospitals across the United States in which TeamBirth had been implemented in the 8 months prior.9
The clinician response rate was an impressive 78%. Ninety percent of clinicians, including physicians, midwives, and nurses, indicated that they would “definitely” (68%) or “probably” (22%) recommend TeamBirth for use in other labor and delivery units. None of the clinicians surveyed (n = 375) reported that TeamBirth negatively impacted care delivery.9
Obstetricians also provided qualitative commentary, noting that, while at times huddling infringed on efficiency, it also enhanced staff fulfillment. An obstetrician at a Massachusetts hospital observed, “Overall I think [TeamBirth is] helpful in slowing us down a little bit to really make sure that we’re providing the human part of the care, like the communication, and not just the medical care. And I think most providers value the human part and the communication. You know, we all think most providers value good communication with the patients, but when you’re in the middle of running around doing a bunch of stuff, you don’t always remember to prioritize it. And I think that at the end of the day…when you know you’ve communicated well with your patients, you end up feeling better about what you’re doing.”
As with most cross-sectional survey studies, selection bias remains an important caveat; patients and providers may decide to complete or not complete voluntary surveys based on particularly positive or negative experiences.
Metrics aside, obstetricians have an ethical duty to provide dignified and safe care, both physically and psychologically. Collectively, as a specialty, we share the responsibility to mitigate maternal mistreatment. As individuals, we can prevent perpetuation of birth trauma and foster healing and empowerment, one patient at a time, by employing tenets of TeamBirth.
To connect with Delivery Decisions Initiative, visit our website: https://www.ariadnelabs.org/deliverydecisions-initiative/ or contact: deliverydecisions@ ariadnelabs.org
Steps for implementing the TeamBirth model
To incorporate TeamBirth into your practice:
- Make patients the “team captain” and center them as the primary decision maker.
- Elicit patient preferences and subjective experiences to develop a collaborative plan on admission and when changes occur in clinical status.
- Round with and utilize the expertise of the full care team—nurse and midwife or obstetrician, as well as support person(s) and/or doula, learners, interpreter, and social worker as applicable.
- Ensure that the patient knows the names and roles of the care team members and provide updates at shift change.
- If your birthing rooms have a whiteboard, use it to keep the patient and team informed of the plan.
- Delineate status updates by maternal condition, fetal condition, and labor progress.
- Provide explicit permission for patients to call for a team huddle at any time and encourage support from their support people and/or doula. ●
This project is supported by:
- The Oklahoma Department of Health as part of the State Maternal Health Innovation Program Grant, Maternal and Child Health Bureau, Health Resources and Services Administration, Department of Health and Human Services.
- The Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) as part of an award to the Oklahoma State Department of Health. The contents are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the official views of, nor an endorsement, by HRSA, HHS, or the U.S. Government. For more information, please visit HRSA.gov.
- The Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) under grant T76MC00001 and entitled Training Grant in Maternal and Child Health.
- Point32 Health’s Clinical Innovation Fund.
Data included in this article was collected and analyzed in partnership with the Oklahoma Perinatal Quality Improvement Collaborative, Department of OB/GYN, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City.
- Bohren MA, Vogel JP, Hunter EC, et al. The mistreatment of women during childbirth in health facilities globally: a mixedmethods systematic review. PLoS Med. 2015;12:e100184. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001847
- Vedam S, Stoll K, Taiwo TK, et al. The Giving Voice to Mothers study: inequity and mistreatment during pregnancy and childbirth in the United States. Reprod Health. 2019;16. doi:10.1186/s12978-019-0729-2
- Kemmerer A, Alteras T. Evolving the maternal health quality measurement enterprise to support the communitybased maternity model. Maternal Health Hub. April 25, 2023. Accessed September 13, 2023. https:/www .maternalhealthhub.org
- Potential CAHPS survey to assess patients’ prenatal and childbirth care experiences. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. March 2023. Accessed September 13, 2023. https://www.ahrq.gov/news/cahps-comments-sought.html
- Lyndon A, Davis DA, Sharma AE, et al. Emotional safety is patient safety. BMJ Qual Saf. 2023;32:369-372. doi:10.1136 /bmjqs-2022-015573
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 819. Informed consent and shared decision making in obstetrics and gynecology. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;137:e34-e41. Accessed September 13, 2023. https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance /committee-opinion/articles/2021/02/informed -consent-and-shared-decision-making-in-obstetrics-and -gynecology
- Goyal AA, Tur K, Mann J, et al. Do bedside visual tools improve patient and caregiver satisfaction? A systematic review of the literature. J Hosp Med. 2017;12:930-936. doi:10.12788 /jhm.2871
- Sehgal NL, Green A, Vidyarthi AR, et al. Patient whiteboards as a communication tool in the hospital setting: a survey of practices and recommendations. J Hosp Med. 2010;5:234-239. doi:10.1002/jhm.638
- Weiseth A, Plough A, Aggarwal R, et al. Improving communication and teamwork during labor: a feasibility, acceptability, and safety study. Birth. 2022:49:637-647. doi:10.1111/birt.12630
CASE The TeamBirth experience: Making a difference
“At a community hospital in Washington where we had implemented TeamBirth (a labor and delivery shared decision making model), a patient, her partner, a labor and delivery nurse, and myself (an ObGyn) were making a plan for the patient’s induction of labor admission. I asked the patient, a 29-year-old (G2P1001), how we could improve her care in relation to her first birth. Her answer was simple: I want to be treated with respect. Her partner went on to describe their past experience in which the provider was inappropriately texting while in between the patient’s knees during delivery. Our team had the opportunity to undo some of the trauma from her first birth. That’s what I like about TeamBirth. It gives every patient the opportunity, regardless of their background, to define safety and participate in their care experience.”
–Angela Chien, MD, Obstetrician and Quality Improvement leader, Washington
Unfortunately, disrespect and mistreatment are far from an anomaly in the obstetrics setting. In a systematic review of respectful maternity care, the World Health Organization delineated 7 dimensions of maternal mistreatment: physical abuse, sexual abuse, verbal abuse, stigma and discrimination, failure to meet professional standards of care, poor rapport between women and providers, and poor conditions and constraints presented by the health system.1 In 2019, the Giving Voice to Mothers study showed that 17% of birthing people in the United States reported experiencing 1 or more types of maternal mistreatment.2 Rates of mistreatment were disproportionately greater in populations of color, hospital-based births, and among those with social, economic, or health challenges.2 It is well known that Black and African American and American Indian and Alaska Native populations experience the rare events of severe maternal morbidity and mortality more frequently than their White counterparts; the disproportionate burden of mistreatment is lesser known and far more common.
Overlooking the longitudinal harm of a negative birth experience has cascading impact. While an empowering perinatal experience can foster preventive screening and management of chronic disease, a poor experience conversely can seed mistrust at an individual, generational, and community level.
The patient quality enterprise is beginning to shift attention toward maternal experience with the development of PREMs (patient-reported experience measures), PROMs (patient-reported outcome measures), and novel validated scales that assess autonomy and trust.3 Development of a maternal Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (CAHPS) survey on childbirth is forthcoming.4 Of course, continuing to prioritize physical safety through initiatives on blood pressure monitoring and severe maternal morbidity and mortality remains paramount. Yet emotional and psychological safety also must be recognized as essential pillars of patient safety. Transgressions related to autonomy and dignity, as well as racism, sexism, classicism, and ableism, should be treated as “adverse and never events.”5
How the TeamBirth model works
Shared decision making (SDM) is cited in medical pedagogy as the solution to respectfullyrecognizing social context, integrating subjective experience, and honoring patient autonomy.6 The onus has always been on individual clinicians to exercise SDM. A new practice model, TeamBirth, embeds SDM into the culture and workflow. It offers a behavioral framework to mitigate implicit bias and operationalizes SDM tools, such that every patient is an empowered participant in their care.
TeamBirth was created through Ariadne Labs’ Delivery Decisions Initiative, a research and social impact program that designs, tests, and scales transformative, systems-level solutions that promote quality, equity, and dignity in childbirth. By the end of 2023, TeamBirth will be implemented in more than 100 hospitals across the United States, cumulatively touching over 200,000 lives. (For more information on the TeamBirth model, view the “Why TeamBirth” video at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EoVrSaGk7gc.)
The tenets of TeamBirth are enacted through a patient-facing, shared whiteboard or dry-erase planning board in the labor room (FIGURE 1). Research has demonstrated how dry-erase boards in clinical settings can support safety and dignity in care, especially to improve patient-provider communication, teamwork, and patient satisfaction.7,8 The planning board is initially filled out by a clinical team member and is updated during team “huddles” throughout labor.

Huddles are care plan discussions with the full care team (the patient, nurse, doula and/or other support person(s), delivering provider, and interpreter or social worker as needed). At a minimum, huddles occur on admission, with changes to the clinical course and care plan, and at the request of any team member. Huddles can transpire through in-person, virtual, or phone communication.9 The concept builds on interdisciplinary and patient-centered rounding and establishes a communication system that is suited to the dynamic environment and amplified patient autonomy unique to labor and delivery. Dr. Bob Barbieri, a steadfast leader and champion of TeamBirth implementation at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston (and the Editor in Chief of OBG M
Continue to: Patient response to TeamBirth is positive...
Patient response to TeamBirth is positive
Patients and providers alike have endorsed TeamBirth. In initial pilot testing across 4 sites, 99% of all patients surveyed “definitely” or “somewhat” had the role they wanted in making decisions about their labor.9
In partnership with the Oklahoma Perinatal Quality Improvement Collaborative (OPQIC), the impact of TeamBirth was assessed in a statewide patient cohort (n = 3,121) using the validated Mothers Autonomy in Decision Making (MADM) scale created by the Birth Place Lab at the University of British Columbia. The percentage of patients who scored in the highest MADM quartile was 31.3% higher for patients who indicated participation in a huddle during labor compared with those who did not participate in a huddle. This trend held across all racial and ethnic groups: For example, 93% of non-Hispanic Black/African American patients who had a TeamBirth huddle reported high autonomy, a nearly 20 percentage point increase from those without a huddle (FIGURE 2). Similarly, a higher percentage of agreement was observed across all 7 items in the MADM scale for patients who reported a TeamBirth huddle (FIGURE 3). TeamBirth’s effect has been observed across surveys and multiple validated metrics.


Data collection related to TeamBirth continues to be ongoing, with reported values retrieved on July 14, 2023. Rigorous review of patient-reported outcomes is forthcoming, and assessing impact on clinical outcomes, such as NTSV (nulliparous, term, singleton vertex) cesarean delivery rates and severe maternal morbidity, is on the horizon.
Qualitative survey responses reinforce how patients value TeamBirth and appreciate huddles and whiteboards.
Continue to: Patient testimonials...
Patient testimonials
The following testimonials were obtained from a TeamBirth survey that patients in participating Massachusetts hospitals completed in the postpartum unit prior to discharge.
According to one patient, “TeamBirth is great, feels like all obstacles are covered by multiple people with many talents, expertise. Feels like mom is part of the process, much different than my delivery 2 years ago when I felt like things were decided for me/I was ‘told’ what we were doing and questioned if I felt uneasy about it…. We felt safe and like all things were covered no matter what may happen.”
Another patient, also at a Massachusetts hospital, offered these comments about TeamBirth: “The entire staff was very genuine and my experience the best it could be. They deserve updated whiteboards in every room. I found them to be very useful.”
The clinician perspective
To be certain, clinician workflow must be a consideration for any practice change. The feasibility, acceptability, and safety of the TeamBirth model to clinicians was validated through a study at 4 community hospitals across the United States in which TeamBirth had been implemented in the 8 months prior.9
The clinician response rate was an impressive 78%. Ninety percent of clinicians, including physicians, midwives, and nurses, indicated that they would “definitely” (68%) or “probably” (22%) recommend TeamBirth for use in other labor and delivery units. None of the clinicians surveyed (n = 375) reported that TeamBirth negatively impacted care delivery.9
Obstetricians also provided qualitative commentary, noting that, while at times huddling infringed on efficiency, it also enhanced staff fulfillment. An obstetrician at a Massachusetts hospital observed, “Overall I think [TeamBirth is] helpful in slowing us down a little bit to really make sure that we’re providing the human part of the care, like the communication, and not just the medical care. And I think most providers value the human part and the communication. You know, we all think most providers value good communication with the patients, but when you’re in the middle of running around doing a bunch of stuff, you don’t always remember to prioritize it. And I think that at the end of the day…when you know you’ve communicated well with your patients, you end up feeling better about what you’re doing.”
As with most cross-sectional survey studies, selection bias remains an important caveat; patients and providers may decide to complete or not complete voluntary surveys based on particularly positive or negative experiences.
Metrics aside, obstetricians have an ethical duty to provide dignified and safe care, both physically and psychologically. Collectively, as a specialty, we share the responsibility to mitigate maternal mistreatment. As individuals, we can prevent perpetuation of birth trauma and foster healing and empowerment, one patient at a time, by employing tenets of TeamBirth.
To connect with Delivery Decisions Initiative, visit our website: https://www.ariadnelabs.org/deliverydecisions-initiative/ or contact: deliverydecisions@ ariadnelabs.org
Steps for implementing the TeamBirth model
To incorporate TeamBirth into your practice:
- Make patients the “team captain” and center them as the primary decision maker.
- Elicit patient preferences and subjective experiences to develop a collaborative plan on admission and when changes occur in clinical status.
- Round with and utilize the expertise of the full care team—nurse and midwife or obstetrician, as well as support person(s) and/or doula, learners, interpreter, and social worker as applicable.
- Ensure that the patient knows the names and roles of the care team members and provide updates at shift change.
- If your birthing rooms have a whiteboard, use it to keep the patient and team informed of the plan.
- Delineate status updates by maternal condition, fetal condition, and labor progress.
- Provide explicit permission for patients to call for a team huddle at any time and encourage support from their support people and/or doula. ●
This project is supported by:
- The Oklahoma Department of Health as part of the State Maternal Health Innovation Program Grant, Maternal and Child Health Bureau, Health Resources and Services Administration, Department of Health and Human Services.
- The Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) as part of an award to the Oklahoma State Department of Health. The contents are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the official views of, nor an endorsement, by HRSA, HHS, or the U.S. Government. For more information, please visit HRSA.gov.
- The Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) under grant T76MC00001 and entitled Training Grant in Maternal and Child Health.
- Point32 Health’s Clinical Innovation Fund.
Data included in this article was collected and analyzed in partnership with the Oklahoma Perinatal Quality Improvement Collaborative, Department of OB/GYN, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City.
CASE The TeamBirth experience: Making a difference
“At a community hospital in Washington where we had implemented TeamBirth (a labor and delivery shared decision making model), a patient, her partner, a labor and delivery nurse, and myself (an ObGyn) were making a plan for the patient’s induction of labor admission. I asked the patient, a 29-year-old (G2P1001), how we could improve her care in relation to her first birth. Her answer was simple: I want to be treated with respect. Her partner went on to describe their past experience in which the provider was inappropriately texting while in between the patient’s knees during delivery. Our team had the opportunity to undo some of the trauma from her first birth. That’s what I like about TeamBirth. It gives every patient the opportunity, regardless of their background, to define safety and participate in their care experience.”
–Angela Chien, MD, Obstetrician and Quality Improvement leader, Washington
Unfortunately, disrespect and mistreatment are far from an anomaly in the obstetrics setting. In a systematic review of respectful maternity care, the World Health Organization delineated 7 dimensions of maternal mistreatment: physical abuse, sexual abuse, verbal abuse, stigma and discrimination, failure to meet professional standards of care, poor rapport between women and providers, and poor conditions and constraints presented by the health system.1 In 2019, the Giving Voice to Mothers study showed that 17% of birthing people in the United States reported experiencing 1 or more types of maternal mistreatment.2 Rates of mistreatment were disproportionately greater in populations of color, hospital-based births, and among those with social, economic, or health challenges.2 It is well known that Black and African American and American Indian and Alaska Native populations experience the rare events of severe maternal morbidity and mortality more frequently than their White counterparts; the disproportionate burden of mistreatment is lesser known and far more common.
Overlooking the longitudinal harm of a negative birth experience has cascading impact. While an empowering perinatal experience can foster preventive screening and management of chronic disease, a poor experience conversely can seed mistrust at an individual, generational, and community level.
The patient quality enterprise is beginning to shift attention toward maternal experience with the development of PREMs (patient-reported experience measures), PROMs (patient-reported outcome measures), and novel validated scales that assess autonomy and trust.3 Development of a maternal Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (CAHPS) survey on childbirth is forthcoming.4 Of course, continuing to prioritize physical safety through initiatives on blood pressure monitoring and severe maternal morbidity and mortality remains paramount. Yet emotional and psychological safety also must be recognized as essential pillars of patient safety. Transgressions related to autonomy and dignity, as well as racism, sexism, classicism, and ableism, should be treated as “adverse and never events.”5
How the TeamBirth model works
Shared decision making (SDM) is cited in medical pedagogy as the solution to respectfullyrecognizing social context, integrating subjective experience, and honoring patient autonomy.6 The onus has always been on individual clinicians to exercise SDM. A new practice model, TeamBirth, embeds SDM into the culture and workflow. It offers a behavioral framework to mitigate implicit bias and operationalizes SDM tools, such that every patient is an empowered participant in their care.
TeamBirth was created through Ariadne Labs’ Delivery Decisions Initiative, a research and social impact program that designs, tests, and scales transformative, systems-level solutions that promote quality, equity, and dignity in childbirth. By the end of 2023, TeamBirth will be implemented in more than 100 hospitals across the United States, cumulatively touching over 200,000 lives. (For more information on the TeamBirth model, view the “Why TeamBirth” video at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EoVrSaGk7gc.)
The tenets of TeamBirth are enacted through a patient-facing, shared whiteboard or dry-erase planning board in the labor room (FIGURE 1). Research has demonstrated how dry-erase boards in clinical settings can support safety and dignity in care, especially to improve patient-provider communication, teamwork, and patient satisfaction.7,8 The planning board is initially filled out by a clinical team member and is updated during team “huddles” throughout labor.

Huddles are care plan discussions with the full care team (the patient, nurse, doula and/or other support person(s), delivering provider, and interpreter or social worker as needed). At a minimum, huddles occur on admission, with changes to the clinical course and care plan, and at the request of any team member. Huddles can transpire through in-person, virtual, or phone communication.9 The concept builds on interdisciplinary and patient-centered rounding and establishes a communication system that is suited to the dynamic environment and amplified patient autonomy unique to labor and delivery. Dr. Bob Barbieri, a steadfast leader and champion of TeamBirth implementation at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston (and the Editor in Chief of OBG M
Continue to: Patient response to TeamBirth is positive...
Patient response to TeamBirth is positive
Patients and providers alike have endorsed TeamBirth. In initial pilot testing across 4 sites, 99% of all patients surveyed “definitely” or “somewhat” had the role they wanted in making decisions about their labor.9
In partnership with the Oklahoma Perinatal Quality Improvement Collaborative (OPQIC), the impact of TeamBirth was assessed in a statewide patient cohort (n = 3,121) using the validated Mothers Autonomy in Decision Making (MADM) scale created by the Birth Place Lab at the University of British Columbia. The percentage of patients who scored in the highest MADM quartile was 31.3% higher for patients who indicated participation in a huddle during labor compared with those who did not participate in a huddle. This trend held across all racial and ethnic groups: For example, 93% of non-Hispanic Black/African American patients who had a TeamBirth huddle reported high autonomy, a nearly 20 percentage point increase from those without a huddle (FIGURE 2). Similarly, a higher percentage of agreement was observed across all 7 items in the MADM scale for patients who reported a TeamBirth huddle (FIGURE 3). TeamBirth’s effect has been observed across surveys and multiple validated metrics.


Data collection related to TeamBirth continues to be ongoing, with reported values retrieved on July 14, 2023. Rigorous review of patient-reported outcomes is forthcoming, and assessing impact on clinical outcomes, such as NTSV (nulliparous, term, singleton vertex) cesarean delivery rates and severe maternal morbidity, is on the horizon.
Qualitative survey responses reinforce how patients value TeamBirth and appreciate huddles and whiteboards.
Continue to: Patient testimonials...
Patient testimonials
The following testimonials were obtained from a TeamBirth survey that patients in participating Massachusetts hospitals completed in the postpartum unit prior to discharge.
According to one patient, “TeamBirth is great, feels like all obstacles are covered by multiple people with many talents, expertise. Feels like mom is part of the process, much different than my delivery 2 years ago when I felt like things were decided for me/I was ‘told’ what we were doing and questioned if I felt uneasy about it…. We felt safe and like all things were covered no matter what may happen.”
Another patient, also at a Massachusetts hospital, offered these comments about TeamBirth: “The entire staff was very genuine and my experience the best it could be. They deserve updated whiteboards in every room. I found them to be very useful.”
The clinician perspective
To be certain, clinician workflow must be a consideration for any practice change. The feasibility, acceptability, and safety of the TeamBirth model to clinicians was validated through a study at 4 community hospitals across the United States in which TeamBirth had been implemented in the 8 months prior.9
The clinician response rate was an impressive 78%. Ninety percent of clinicians, including physicians, midwives, and nurses, indicated that they would “definitely” (68%) or “probably” (22%) recommend TeamBirth for use in other labor and delivery units. None of the clinicians surveyed (n = 375) reported that TeamBirth negatively impacted care delivery.9
Obstetricians also provided qualitative commentary, noting that, while at times huddling infringed on efficiency, it also enhanced staff fulfillment. An obstetrician at a Massachusetts hospital observed, “Overall I think [TeamBirth is] helpful in slowing us down a little bit to really make sure that we’re providing the human part of the care, like the communication, and not just the medical care. And I think most providers value the human part and the communication. You know, we all think most providers value good communication with the patients, but when you’re in the middle of running around doing a bunch of stuff, you don’t always remember to prioritize it. And I think that at the end of the day…when you know you’ve communicated well with your patients, you end up feeling better about what you’re doing.”
As with most cross-sectional survey studies, selection bias remains an important caveat; patients and providers may decide to complete or not complete voluntary surveys based on particularly positive or negative experiences.
Metrics aside, obstetricians have an ethical duty to provide dignified and safe care, both physically and psychologically. Collectively, as a specialty, we share the responsibility to mitigate maternal mistreatment. As individuals, we can prevent perpetuation of birth trauma and foster healing and empowerment, one patient at a time, by employing tenets of TeamBirth.
To connect with Delivery Decisions Initiative, visit our website: https://www.ariadnelabs.org/deliverydecisions-initiative/ or contact: deliverydecisions@ ariadnelabs.org
Steps for implementing the TeamBirth model
To incorporate TeamBirth into your practice:
- Make patients the “team captain” and center them as the primary decision maker.
- Elicit patient preferences and subjective experiences to develop a collaborative plan on admission and when changes occur in clinical status.
- Round with and utilize the expertise of the full care team—nurse and midwife or obstetrician, as well as support person(s) and/or doula, learners, interpreter, and social worker as applicable.
- Ensure that the patient knows the names and roles of the care team members and provide updates at shift change.
- If your birthing rooms have a whiteboard, use it to keep the patient and team informed of the plan.
- Delineate status updates by maternal condition, fetal condition, and labor progress.
- Provide explicit permission for patients to call for a team huddle at any time and encourage support from their support people and/or doula. ●
This project is supported by:
- The Oklahoma Department of Health as part of the State Maternal Health Innovation Program Grant, Maternal and Child Health Bureau, Health Resources and Services Administration, Department of Health and Human Services.
- The Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) as part of an award to the Oklahoma State Department of Health. The contents are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the official views of, nor an endorsement, by HRSA, HHS, or the U.S. Government. For more information, please visit HRSA.gov.
- The Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) under grant T76MC00001 and entitled Training Grant in Maternal and Child Health.
- Point32 Health’s Clinical Innovation Fund.
Data included in this article was collected and analyzed in partnership with the Oklahoma Perinatal Quality Improvement Collaborative, Department of OB/GYN, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City.
- Bohren MA, Vogel JP, Hunter EC, et al. The mistreatment of women during childbirth in health facilities globally: a mixedmethods systematic review. PLoS Med. 2015;12:e100184. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001847
- Vedam S, Stoll K, Taiwo TK, et al. The Giving Voice to Mothers study: inequity and mistreatment during pregnancy and childbirth in the United States. Reprod Health. 2019;16. doi:10.1186/s12978-019-0729-2
- Kemmerer A, Alteras T. Evolving the maternal health quality measurement enterprise to support the communitybased maternity model. Maternal Health Hub. April 25, 2023. Accessed September 13, 2023. https:/www .maternalhealthhub.org
- Potential CAHPS survey to assess patients’ prenatal and childbirth care experiences. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. March 2023. Accessed September 13, 2023. https://www.ahrq.gov/news/cahps-comments-sought.html
- Lyndon A, Davis DA, Sharma AE, et al. Emotional safety is patient safety. BMJ Qual Saf. 2023;32:369-372. doi:10.1136 /bmjqs-2022-015573
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 819. Informed consent and shared decision making in obstetrics and gynecology. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;137:e34-e41. Accessed September 13, 2023. https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance /committee-opinion/articles/2021/02/informed -consent-and-shared-decision-making-in-obstetrics-and -gynecology
- Goyal AA, Tur K, Mann J, et al. Do bedside visual tools improve patient and caregiver satisfaction? A systematic review of the literature. J Hosp Med. 2017;12:930-936. doi:10.12788 /jhm.2871
- Sehgal NL, Green A, Vidyarthi AR, et al. Patient whiteboards as a communication tool in the hospital setting: a survey of practices and recommendations. J Hosp Med. 2010;5:234-239. doi:10.1002/jhm.638
- Weiseth A, Plough A, Aggarwal R, et al. Improving communication and teamwork during labor: a feasibility, acceptability, and safety study. Birth. 2022:49:637-647. doi:10.1111/birt.12630
- Bohren MA, Vogel JP, Hunter EC, et al. The mistreatment of women during childbirth in health facilities globally: a mixedmethods systematic review. PLoS Med. 2015;12:e100184. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001847
- Vedam S, Stoll K, Taiwo TK, et al. The Giving Voice to Mothers study: inequity and mistreatment during pregnancy and childbirth in the United States. Reprod Health. 2019;16. doi:10.1186/s12978-019-0729-2
- Kemmerer A, Alteras T. Evolving the maternal health quality measurement enterprise to support the communitybased maternity model. Maternal Health Hub. April 25, 2023. Accessed September 13, 2023. https:/www .maternalhealthhub.org
- Potential CAHPS survey to assess patients’ prenatal and childbirth care experiences. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. March 2023. Accessed September 13, 2023. https://www.ahrq.gov/news/cahps-comments-sought.html
- Lyndon A, Davis DA, Sharma AE, et al. Emotional safety is patient safety. BMJ Qual Saf. 2023;32:369-372. doi:10.1136 /bmjqs-2022-015573
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 819. Informed consent and shared decision making in obstetrics and gynecology. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;137:e34-e41. Accessed September 13, 2023. https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance /committee-opinion/articles/2021/02/informed -consent-and-shared-decision-making-in-obstetrics-and -gynecology
- Goyal AA, Tur K, Mann J, et al. Do bedside visual tools improve patient and caregiver satisfaction? A systematic review of the literature. J Hosp Med. 2017;12:930-936. doi:10.12788 /jhm.2871
- Sehgal NL, Green A, Vidyarthi AR, et al. Patient whiteboards as a communication tool in the hospital setting: a survey of practices and recommendations. J Hosp Med. 2010;5:234-239. doi:10.1002/jhm.638
- Weiseth A, Plough A, Aggarwal R, et al. Improving communication and teamwork during labor: a feasibility, acceptability, and safety study. Birth. 2022:49:637-647. doi:10.1111/birt.12630