User login
Negotiating the VUCA World Through Tiered Huddles
Negotiating the VUCA World Through Tiered Huddles
To see what is in front of one’s nose needs a constant struggle.
George Orwell (1946)1
In 2019, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) initiated a process to become a high reliability organization (HRO).2 The COVID-19 pandemic has been described in medical literature as a volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA) event, underscoring the necessity of resilient communication strategies.3 Challenges posed by 2024 Hurricanes Helene and Milton further highlighted the need for resilient communication strategies within HRO implementation.
Central to the HRO journey within the VHA has been the development of tiered huddles, an evolution of the safety huddle concept.4 Emerging organically as an effective communication mechanism across multiple facilities between 2019 and 2020, tiered huddles were, in part, spurred by the onset of COVID-19. Tiered huddles represent a proactive approach to identifying and addressing organizational threats in their early stages, thereby preventing their escalation to a VUCA-laden crisis.5 When conditions evolve beyond the horizon of tractability, where challenges are easily identified and resolved, tiered huddles serve as a resilient mechanism to restore dynamic equilibrium within the organization.6,7
This article describes how tiered huddles were integrated within Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) 4 and explores why these huddles are essential, particularly in the context of VUCA events. What began as a local-level tactic has now gained widespread acceptance and continues to evolve across the VHA with full support from the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary for Health.8
The VHA is divided into 18 VISNs. Nine VA Medical Centers (VAMCs) and 46 outpatient clinics across Pennsylvania, Delaware, and parts of Ohio, New York, and New Jersey make up VISN 4. Disseminating vital information across VISN 4, in addition to the 17 other VISNs—including 170 VAMCs and 1193 clinics—presents a formidable challenge. As the largest integrated system in the US, the VHA is realigning its workforce to address organizational inefficiencies. An enterprise of this scale, shaped by recurrent organizational change, faces ongoing challenges in sustaining clear communication across all levels. These transitions create uncertainty for staff as roles and resources shift, underscoring the need for dependable vertical and horizontal information flow. Tiered huddles offer a steady means to support coordinated communication and strengthen the system’s ability to adapt.9
ERIE VA MEDICAL CENTER HRO JOURNEY
In 2019, John Gennaro, the Erie VAMC executive director, attended a presentation that showcased the Cleveland Clinic’s tiered huddle process, with an opportunity to observe its 5-tiered system.10 Erie VAMC already had a 3-tiered huddle system, but the Cleveland Clinic’s more robust model inspired Gennaro to propose a VISN 4 pilot program. Tiered huddles were perceived as innovative, yet not fully embraced within the VHA; nonetheless, VISN 4, much like several other VISNs, moved forward and established a VISN-level (Tier 4) huddle.8 It is important to note that there was a notional fifth-tier capability as VISN and program office leaders already participated in daily VHA-wide meetings under the auspices of the Hospital Operations Center (HOC).
Expanding the Tiered Huddle Process
The Erie VAMC huddle process begins with the unit level Managers and Frontline Staff (Tier 1), then moves to Service Chiefs and Managers (Tier 2). Tier 3 involves facility executive leadership team and service chiefs, clinical directors and top VAMC administrators (these configurations may vary depending on context). The sequencing and flow of information is bidirectional across levels, reflecting the importance of closed-loop communication to ensure staff at all levels understand that issues raised are followed up on and/or closed out (Figure 1).2
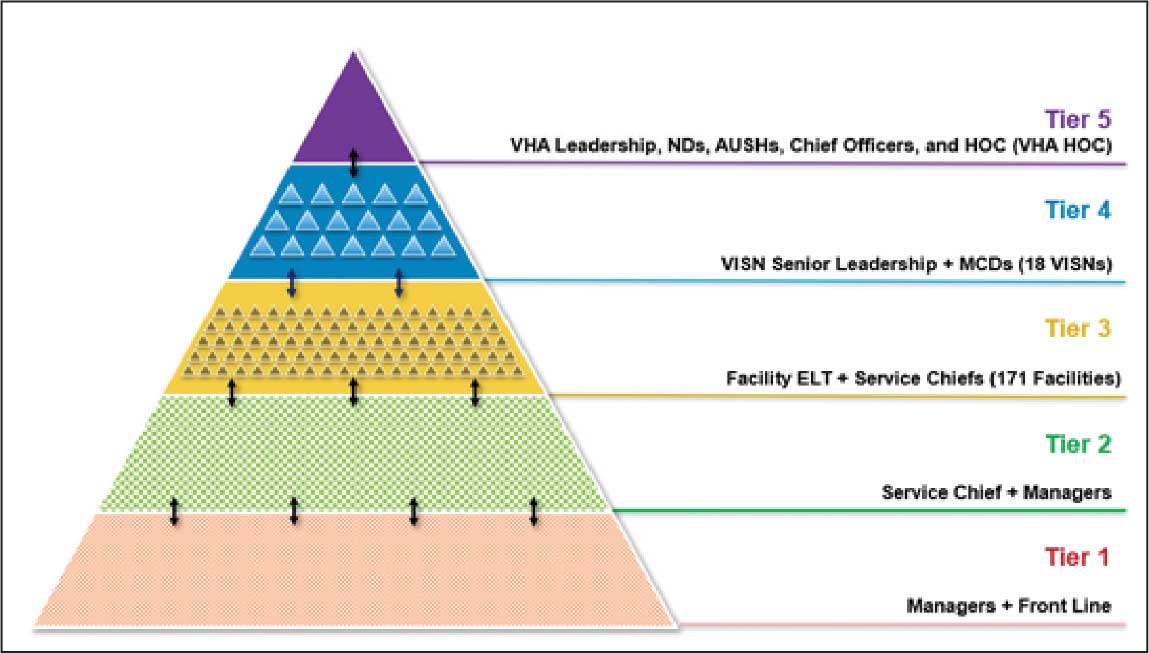
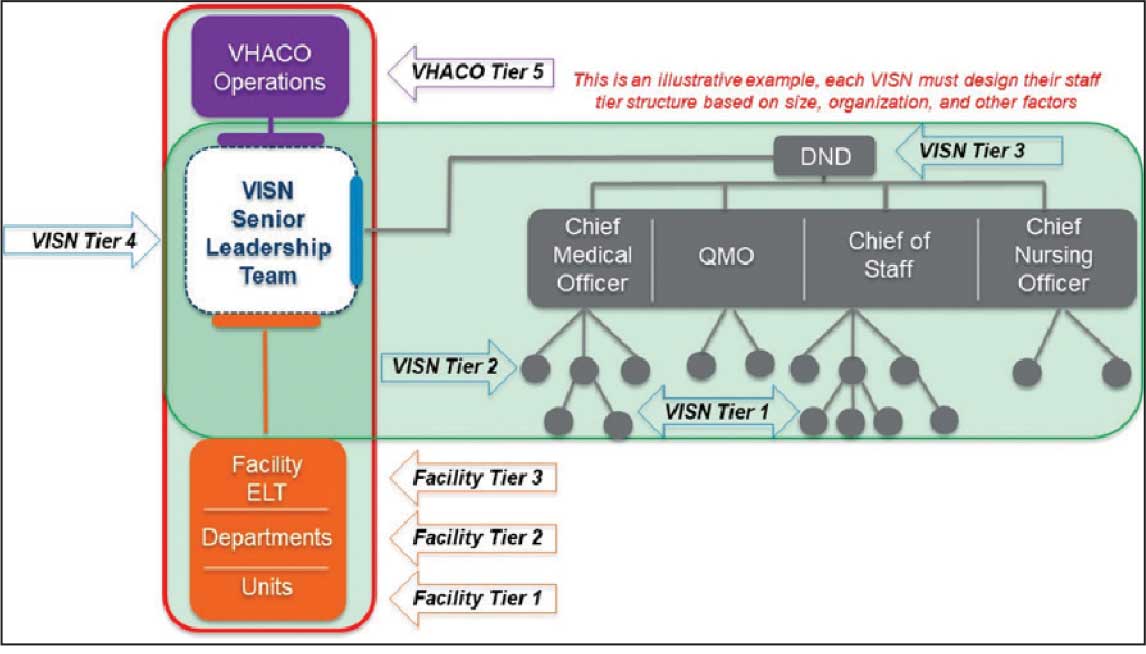
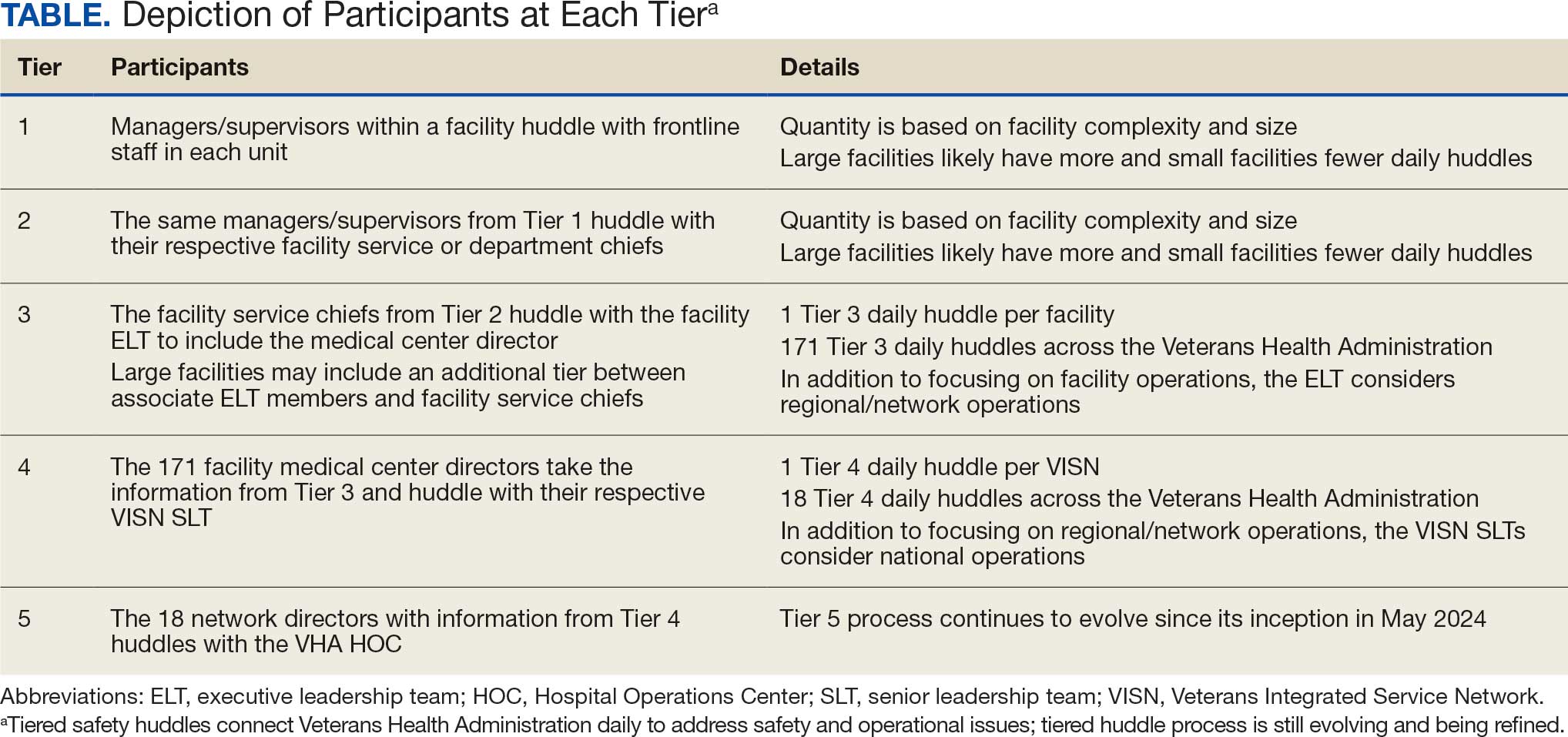
Tier 4 composition may vary among VISNs depending on size and unique mission requirements.8,11 The VISN 4 Tier 4 huddle includes the VISN director, 9 VAMC directors, and key network administrators and clinical experts. The Tier 5 huddle includes 18 VISN 4 directors with the VHA HOC (Figure 2). The tiered huddle process emphasizes team-based culture and psychological safety.12-15 Staff at all levels are encouraged to identify and transparently resolve issues, fostering a proactive and problem-solving environment across the organization. A more nuanced and detailed process across tier levels is depicted in the Table.
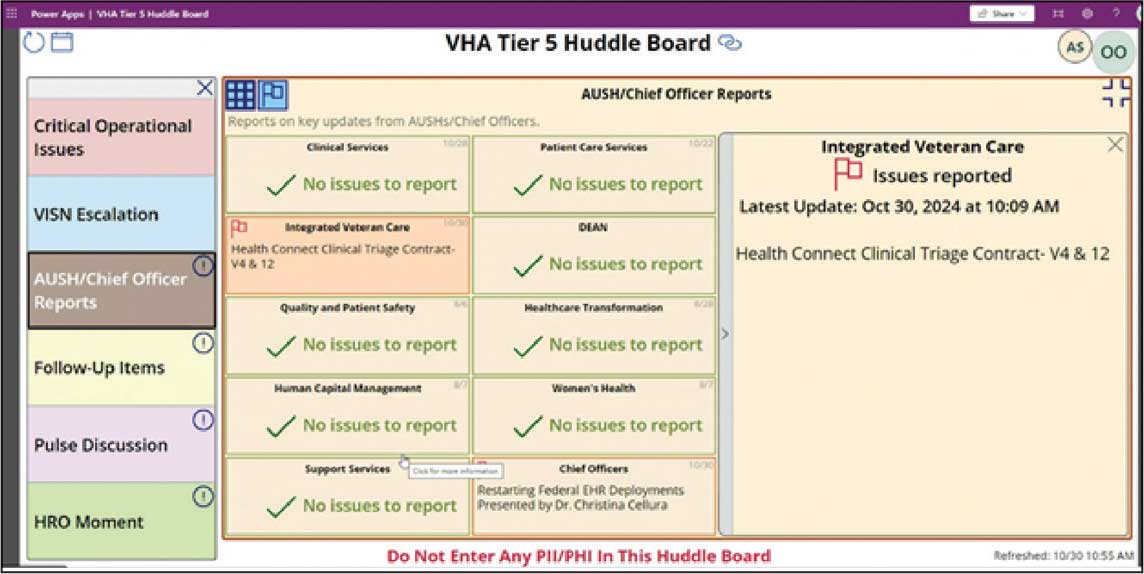
The vetting and distillation of information can present challenges as vital information ascends and spreads across organization levels. Visual management systems (VMS), whether a whiteboard or a digital platform, are key to facilitate decision-making related to what needs to be prioritized and disseminated at each tier level.2,8 At Tier 5, the HOC uses a digital VMS to provide a structured, user-friendly format for categorizing issues and topics and enhances clarity and accessibility (Figure 3). The Tier 5 VMS also facilitates tracking and reciprocal information exchange, helping to close the loop on emerging issues by monitoring their progression and resolution up and across tiers.2,8 The Tier 5 huddle process and technology supporting continue to evolve offering increasing sophistication in organizational situational awareness and responsiveness.
VUCA: A Lens for Health Care Challenges
First introduced by social scientists at the US Army War College in 1995, VUCA describes complex and unpredictable conditions often encountered in military operations.16,17 Prompted by the COVID-19 pandemic, the acronym VUCA gained recognition in health care, as leaders acknowledged the challenge of navigating rapidly changing environments. van Stralen, Byrum and Inozu, recognized authorities in high reliability, cited VUCA as the rationale for implementing HRO principles and practices. They argued that “HRO solves the problem of operations and performance in a volatile, uncertain, complex, ambiguous environment.” 18 To fully appreciate the VUCA environment and its relevance to health care, it is essential to unpack the 4 components of the acronym: volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous.
Volatile refers to the speed and unpredictability of change. Health care systems are interactively complex and tightly coupled, meaning that changes in 1 part of the system can rapidly impact others.6,18,19 This high degree of interdependence amplifies volatility, especially when unexpected events occur. The rapid spread of COVID- 19 and the evolving nature of its transmission challenged health care systems’ ability to respond swiftly and effectively. Volatility also may emerge in acute medical situations, such as the rapid deterioration of a patient’s condition.
Uncertain captures the lack of predictability inherent in complex systems. In health care, uncertainty arises when there is insufficient information or when an excess of data make it difficult to discern meaningful patterns. COVID-19 and recent natural disasters have introduced profound uncertainty, as the disease’s behavior, transmission, and impact were initially unknown. Health care practitioners struggled to make decisions in real time, lacking clear guidance or precedent.3,20 While health care planning and established protocols are grounded in predictability, the COVID-19 pandemic revealed that as complexity increases, predictability diminishes. Moreover, complexity can complicate protocol selection, as situations may arise in which multiple protocols conflict or compete. The cognitive challenge of operating in this environment is analogous to what military strategists call the fog of war, where situational awareness is low and decision-makers must navigate without clarity.21 Tiered huddles, a core practice in HROs, mitigate uncertainty by fostering real-time communication and shared situational awareness among teams.20
Complex refers to the intricate interplay of multiple, interconnected factors within a system.22 In health care, this complexity is heightened by the sociotechnical nature of the field—where human, technology, and organizational elements all converge.19 Systems designed to prevent failures, such as redundancies and safety protocols, can themselves contribute to increased complexity. HRO practices such as tiered huddles are implemented to mitigate the risk of catastrophic failure by fostering collaborative sensemaking, enhanced situational awareness, and rapid problem-solving.5,20,23
Ambiguous refers to situations in which multiple interpretations, causes, or outcomes are possible. It explains how, despite following protocols, failure can still occur, or how individuals may reach different conclusions from the same data. Ambiguity does not offer binary solutions; instead, it presents a murky, multifaceted reality that requires thoughtful interpretation and adaptive responses. In these moments, leaders must act decisively, even in the absence of complete information, making trade-offs that balance immediate needs with long-term consequences.
MANAGING VUCA ENVIRONMENTS WITH TIERED HUDDLES
The tiered huddle process provides several key benefits that enable real-time issue resolution. These include the rapid dissemination of vital information, enhanced agility and resilience, and improved sensemaking within a VUCA environment. Additionally, tiered huddles prevent organizational drift by fostering heightened situational awareness. The tiered huddle process also supports leadership development, as unit-level leaders gain valuable insights into strategic decision-making through active participation. Each component is outlined in the following section.
Spread: The Challenge of Communicating
“The hallmark of a great organization is how quickly bad news travels upward,” argued Jay Forrester, the father of system dynamics.24 Unfortunately, steep power gradients and siloed organizational structures inhibit the flow of unfavorable information from frontline staff to senior leadership. This suppression is not necessarily intentional but is often a byproduct of organizational culture. Tiered huddles address the weakness of top-down communication models by promoting a reciprocal, bidirectional information exchange, with an emphasis on closed-loop communication. Open communication can foster a culture of trust and transparency, allowing leaders to make more informed decisions and respond quickly to emerging risks.
Enhancing Agility and Resilience
Tiered huddles contribute to a mindful infrastructure, an important aspect of maintaining organizational awareness and agility.21,25 A mindful infrastructure enables an organization to detect early warning signs of potential disruptions and respond to them before they escalate. In this sense, tiered huddles serve as a signal-sensing mechanism, providing the agility needed to adapt to changing circumstances and prevent patient harm. Tiered huddles facilitate self-organization, a concept from chaos theory known as autopoiesis. 26 This self-organizing capability allows teams to develop novel solutions in response to unforeseen challenges, exemplifying the adaptability and resilience needed in a VUCA environment. The diverse backgrounds of tiered huddle participants—both cognitively and culturally—enable a broader range of perspectives, which is critical for making sound decisions in complex and uncertain situations. “HROs cultivate diversity not just because it helps them notice more in complex environments, but also because it helps them adapt to the complexities they do spot,” argues Weick et al.27 This diversity of thought and experience enhances the organization’s ability to respond to complexity, much like firefighters continually adapt to the VUCA conditions they face.
Sensemaking and Sensitivity to Operations
Leaders at all levels must be attuned to what is happening both within and outside their organization. This continual sensing of the environment—looking for weak signals, threats, and opportunities—is important for HROs. This signal detection capability allows organizations to address problems in their nascent emerging state within a tractable horizon to successfully manage fluctuations. The horizon of tractability reflects a zone where weak signals and evolving issues can be identified, addressed, and resolved early before they evolve and cascade outside of safe operations. 7 Tiered huddles facilitate this process by creating a platform for team members to engage in respectful, collaborative dialogue. The diversity inherent in tiered huddles also supports sensemaking, a process of interpreting and understanding complex situations.27 In a VUCA environment, this multiperspective approach helps filter out noise and identify the most important signals. Tiered huddles can help overcome the phenomenon of dysfunctional momentum associated with cognitive lockup, fixation error, and tunnel vision, in which individuals or teams fixate on a particular solution, thus missing important alternative views.21,28 By fostering a common operating picture of the fluctuating environment, tiered huddles can enable more accurate decision-making and improve organizational resilience.
Avoiding Organizational Drift
One of the most significant contributions of tiered huddles is the ability to detect early signs of organizational drift, or subtle deviations from standard practices that can accumulate over time and lead to serious failures. By continuously monitoring for precursor conditions and weak signals, tiered huddles allow organizations to intervene early and prevent drift from becoming catastrophic.29,30 This vigilance is essential in health care, where complacency can lead to patient harm. Tiered huddles foster a culture of mindfulness and accountability, ensuring that staff stay engaged and alert to potential risks. This proactive approach is a safeguard against human error and the gradual erosion of safety standards.
Leadership Development
Tiered huddles serve as a powerful tool for leadership development. Effective leaders must be able to anticipate potential risks and foresee system failures. Involving future leaders in tiered huddles can facilitate the transfer of these critical skills. When emerging leaders at lower tiers participate in ascending-tier huddles, they gain a unique opportunity to engage in a structured, collaborative setting. This environment provides a safe space to develop and practice strategic skills, enhancing their ability to think proactively and manage complexity. By integrating future leaders into tiered huddles, organizations offer essential, hands-on experience in real-time decision making. This experiential learning is invaluable for preparing leaders to navigate the demands of a VUCA environment.
CONCLUSIONS
Since implementing the tiered huddle process, the Erie VAMC and VISN 4 have emerged as early adopters of VUCA, thus contributing to the expansion of this innovative communication approach across the VHA. Tiered huddles strengthen organizational resilience and agility, facilitate critical information flow to manage risk, and support the cultivation of future leaders. The Erie VAMC director and the VISN 4 network director regard the expansion of tiered huddles, including Tiers 4 and 5, as an adaptable model for the VHA. While tiered huddles have not yet been mandated across the VHA, a pilot at the Tier 5 HOC level was initiated on May 20, 2024. In a complex world in which VUCA events will continue to be inevitable, implementation of robust tiered huddles within complex health care systems provides the opportunity for improved responses and delivery of care.
- Orwell S, Angus I, eds. In Front of Your Nose, 1945-1950. Godine; 2000. Orwell G. The Collected Essays, Journalism, and Letters of George Orwell; vol 4.
- Murray JS, Baghdadi A, Dannenberg W, Crews P, Walsh ND. The role of high reliability organization foundational practices in building a culture of safety. Fed Pract. 2024;41:214-221. doi:10.12788/fp.0486
- Goldenhar LM, Brady PW, Sutcliffe KM, Muething SE. Huddling for high reliability and situation awareness. BMJ Qual Saf. 2013;22:899-906. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2012-001467
- Pandit M. Critical factors for successful management of VUCA times. BMJ Lead. 2021;5:121-123. doi:10.1136/leader-2020-000305
- Mihaljevic T. Tiered daily huddles: the power of teamwork in managing large healthcare organisations. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29:1050-1052. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-010575
- van Stralen D, Mercer TA. High-reliability organizing (HRO) in the COVID-19 liminal zone: characteristics of workers and local leaders. Neonatology Today. 2021;16:90-101. http://www.neonatologytoday.net /newsletters/nt-apr21.pdf
- Nemeth C, Wears R, Woods D, Hollnagel E, Cook R. Minding the gaps: creating resilience in health care. In: Henriksen K, Battles JB, Keyes MA, Grady ML, eds. Advances in Patient Safety: New Directions and Alternative Approaches. Vol 3: Performance and Tools. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2008.
- Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Montoya A, Cox GR, Murray JS. Creating a process for the implementation of tiered huddles in a Veterans Affairs medical center. Mil Med. 2023;188:901-906. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac073
- Starbuck WH, Farjoun M, eds. Organization at the Limit: Lessons From the Columbia Disaster. 1st ed. Wiley-Blackwell; 2005.
- Mihaljevic T. Tiered daily huddles: the power of teamwork in managing large healthcare organisations. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29:1050-1052. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-010575
- Donnelly LF, Cherian SS, Chua KB, et al. The Daily Readiness Huddle: a process to rapidly identify issues and foster improvement through problem-solving accountability. Pediatr Radiol. 2017;47:22-30. doi:10.1007/s00247-016-3712-x
- Clark TR. The 4 Stages of Psychological Safety: Defining the Path to Inclusion and Innovation. Berrett-Koehler Publishers, Inc.; 2020.
- Edmondson AC. The Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and Growth. John Wiley & Sons; 2018.
- Edmondson AC. The Right Kind of Wrong: The Science of Failing Well. Simon Element/Simon Acumen; 2023.
- Murray JS, Kelly S, Hanover C. Promoting psychological safety in healthcare organizations. Mil Med. 2022;187:808 -810. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac041
- Barber HF. Developing strategic leadership: the US Army War College experience. J Manag Dev. 1992;11:4-12. doi:10.1108/02621719210018208
- US Army Heritage & Education Center. Who first originated the term VUCA (volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity)? Accessed November 5, 2025. https://usawc .libanswers.com/ahec/faq/84869
- van Stralen D, Byrum SL, Inozu B. High Reliability for a Highly Unreliable World: Preparing for Code Blue Through Daily Operations in Healthcare. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform; 2018.
- Perrow C. Normal Accidents: Living With High-Risk Technologies. Princeton University Press; 2000.
- Sculli G, Essen K. Soaring to Success: The Path to Developing High-Reliability Clinical Teams. HCPro; 2021. Accessed November 5, 2025. https://hcmarketplace.com /media/wysiwyg/CRM3_browse.pdf
- Barton MA, Sutcliffe KM, Vogus TJ, DeWitt T. Performing under uncertainty: contextualized engagement in wildland firefighting. J Contingencies Crisis Manag. 2015;23:74-83. doi:10.1111/1468-5973.12076
- Sutcliffe KM. Mindful organizing. In: Ramanujam R, Roberts KH, eds. Organizing for Reliability: A Guide for Research and Practice. Stanford University Press; 2018:61-89.
- Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Dealino-Perez C, Xiang J, Montoya A Jr, Murray JS. A high-reliability organization mindset. Am J Med Qual. 2022;37:504-510. doi:10.1097/jmq.0000000000000086
- Senge PM. The Fifth Discipline Fieldbook: Strategies and Tools for Building a Learning Organization. Crown Currency; 1994.
- Ramanujam R, Roberts KH, eds. Organizing for Reliability: A Guide for Research and Practice. Stanford University Press; 2018.
- Coveney PV. Self-organization and complexity: a new age for theory, computation and experiment. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2003;361:1057-1079. doi:10.1098/rsta.2003.1191
- Weick KE, Sutcliffe KM. Managing the Unexpected: Sustained Performance in a Complex World. 3rd ed. Wiley; 2015.
- Barton M, Sutcliffe K. Overcoming dysfunctional momentum: organizational safety as a social achievement. Hum Relations. 2009;62:1327-1356. doi:10.1177/0018726709334491
- Dekker S. Drift Into Failure: From Hunting Broken Components to Understanding Complex Systems. Routledge; 2011.
- Price MR, Williams TC. When doing wrong feels so right: normalization of deviance. J Patient Saf. 2018;14:1-2. doi:10.1097/pts.0000000000000157
To see what is in front of one’s nose needs a constant struggle.
George Orwell (1946)1
In 2019, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) initiated a process to become a high reliability organization (HRO).2 The COVID-19 pandemic has been described in medical literature as a volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA) event, underscoring the necessity of resilient communication strategies.3 Challenges posed by 2024 Hurricanes Helene and Milton further highlighted the need for resilient communication strategies within HRO implementation.
Central to the HRO journey within the VHA has been the development of tiered huddles, an evolution of the safety huddle concept.4 Emerging organically as an effective communication mechanism across multiple facilities between 2019 and 2020, tiered huddles were, in part, spurred by the onset of COVID-19. Tiered huddles represent a proactive approach to identifying and addressing organizational threats in their early stages, thereby preventing their escalation to a VUCA-laden crisis.5 When conditions evolve beyond the horizon of tractability, where challenges are easily identified and resolved, tiered huddles serve as a resilient mechanism to restore dynamic equilibrium within the organization.6,7
This article describes how tiered huddles were integrated within Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) 4 and explores why these huddles are essential, particularly in the context of VUCA events. What began as a local-level tactic has now gained widespread acceptance and continues to evolve across the VHA with full support from the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary for Health.8
The VHA is divided into 18 VISNs. Nine VA Medical Centers (VAMCs) and 46 outpatient clinics across Pennsylvania, Delaware, and parts of Ohio, New York, and New Jersey make up VISN 4. Disseminating vital information across VISN 4, in addition to the 17 other VISNs—including 170 VAMCs and 1193 clinics—presents a formidable challenge. As the largest integrated system in the US, the VHA is realigning its workforce to address organizational inefficiencies. An enterprise of this scale, shaped by recurrent organizational change, faces ongoing challenges in sustaining clear communication across all levels. These transitions create uncertainty for staff as roles and resources shift, underscoring the need for dependable vertical and horizontal information flow. Tiered huddles offer a steady means to support coordinated communication and strengthen the system’s ability to adapt.9
ERIE VA MEDICAL CENTER HRO JOURNEY
In 2019, John Gennaro, the Erie VAMC executive director, attended a presentation that showcased the Cleveland Clinic’s tiered huddle process, with an opportunity to observe its 5-tiered system.10 Erie VAMC already had a 3-tiered huddle system, but the Cleveland Clinic’s more robust model inspired Gennaro to propose a VISN 4 pilot program. Tiered huddles were perceived as innovative, yet not fully embraced within the VHA; nonetheless, VISN 4, much like several other VISNs, moved forward and established a VISN-level (Tier 4) huddle.8 It is important to note that there was a notional fifth-tier capability as VISN and program office leaders already participated in daily VHA-wide meetings under the auspices of the Hospital Operations Center (HOC).
Expanding the Tiered Huddle Process
The Erie VAMC huddle process begins with the unit level Managers and Frontline Staff (Tier 1), then moves to Service Chiefs and Managers (Tier 2). Tier 3 involves facility executive leadership team and service chiefs, clinical directors and top VAMC administrators (these configurations may vary depending on context). The sequencing and flow of information is bidirectional across levels, reflecting the importance of closed-loop communication to ensure staff at all levels understand that issues raised are followed up on and/or closed out (Figure 1).2

Tier 4 composition may vary among VISNs depending on size and unique mission requirements.8,11 The VISN 4 Tier 4 huddle includes the VISN director, 9 VAMC directors, and key network administrators and clinical experts. The Tier 5 huddle includes 18 VISN 4 directors with the VHA HOC (Figure 2). The tiered huddle process emphasizes team-based culture and psychological safety.12-15 Staff at all levels are encouraged to identify and transparently resolve issues, fostering a proactive and problem-solving environment across the organization. A more nuanced and detailed process across tier levels is depicted in the Table.


The vetting and distillation of information can present challenges as vital information ascends and spreads across organization levels. Visual management systems (VMS), whether a whiteboard or a digital platform, are key to facilitate decision-making related to what needs to be prioritized and disseminated at each tier level.2,8 At Tier 5, the HOC uses a digital VMS to provide a structured, user-friendly format for categorizing issues and topics and enhances clarity and accessibility (Figure 3). The Tier 5 VMS also facilitates tracking and reciprocal information exchange, helping to close the loop on emerging issues by monitoring their progression and resolution up and across tiers.2,8 The Tier 5 huddle process and technology supporting continue to evolve offering increasing sophistication in organizational situational awareness and responsiveness.

VUCA: A Lens for Health Care Challenges
First introduced by social scientists at the US Army War College in 1995, VUCA describes complex and unpredictable conditions often encountered in military operations.16,17 Prompted by the COVID-19 pandemic, the acronym VUCA gained recognition in health care, as leaders acknowledged the challenge of navigating rapidly changing environments. van Stralen, Byrum and Inozu, recognized authorities in high reliability, cited VUCA as the rationale for implementing HRO principles and practices. They argued that “HRO solves the problem of operations and performance in a volatile, uncertain, complex, ambiguous environment.” 18 To fully appreciate the VUCA environment and its relevance to health care, it is essential to unpack the 4 components of the acronym: volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous.
Volatile refers to the speed and unpredictability of change. Health care systems are interactively complex and tightly coupled, meaning that changes in 1 part of the system can rapidly impact others.6,18,19 This high degree of interdependence amplifies volatility, especially when unexpected events occur. The rapid spread of COVID- 19 and the evolving nature of its transmission challenged health care systems’ ability to respond swiftly and effectively. Volatility also may emerge in acute medical situations, such as the rapid deterioration of a patient’s condition.
Uncertain captures the lack of predictability inherent in complex systems. In health care, uncertainty arises when there is insufficient information or when an excess of data make it difficult to discern meaningful patterns. COVID-19 and recent natural disasters have introduced profound uncertainty, as the disease’s behavior, transmission, and impact were initially unknown. Health care practitioners struggled to make decisions in real time, lacking clear guidance or precedent.3,20 While health care planning and established protocols are grounded in predictability, the COVID-19 pandemic revealed that as complexity increases, predictability diminishes. Moreover, complexity can complicate protocol selection, as situations may arise in which multiple protocols conflict or compete. The cognitive challenge of operating in this environment is analogous to what military strategists call the fog of war, where situational awareness is low and decision-makers must navigate without clarity.21 Tiered huddles, a core practice in HROs, mitigate uncertainty by fostering real-time communication and shared situational awareness among teams.20
Complex refers to the intricate interplay of multiple, interconnected factors within a system.22 In health care, this complexity is heightened by the sociotechnical nature of the field—where human, technology, and organizational elements all converge.19 Systems designed to prevent failures, such as redundancies and safety protocols, can themselves contribute to increased complexity. HRO practices such as tiered huddles are implemented to mitigate the risk of catastrophic failure by fostering collaborative sensemaking, enhanced situational awareness, and rapid problem-solving.5,20,23
Ambiguous refers to situations in which multiple interpretations, causes, or outcomes are possible. It explains how, despite following protocols, failure can still occur, or how individuals may reach different conclusions from the same data. Ambiguity does not offer binary solutions; instead, it presents a murky, multifaceted reality that requires thoughtful interpretation and adaptive responses. In these moments, leaders must act decisively, even in the absence of complete information, making trade-offs that balance immediate needs with long-term consequences.
MANAGING VUCA ENVIRONMENTS WITH TIERED HUDDLES
The tiered huddle process provides several key benefits that enable real-time issue resolution. These include the rapid dissemination of vital information, enhanced agility and resilience, and improved sensemaking within a VUCA environment. Additionally, tiered huddles prevent organizational drift by fostering heightened situational awareness. The tiered huddle process also supports leadership development, as unit-level leaders gain valuable insights into strategic decision-making through active participation. Each component is outlined in the following section.
Spread: The Challenge of Communicating
“The hallmark of a great organization is how quickly bad news travels upward,” argued Jay Forrester, the father of system dynamics.24 Unfortunately, steep power gradients and siloed organizational structures inhibit the flow of unfavorable information from frontline staff to senior leadership. This suppression is not necessarily intentional but is often a byproduct of organizational culture. Tiered huddles address the weakness of top-down communication models by promoting a reciprocal, bidirectional information exchange, with an emphasis on closed-loop communication. Open communication can foster a culture of trust and transparency, allowing leaders to make more informed decisions and respond quickly to emerging risks.
Enhancing Agility and Resilience
Tiered huddles contribute to a mindful infrastructure, an important aspect of maintaining organizational awareness and agility.21,25 A mindful infrastructure enables an organization to detect early warning signs of potential disruptions and respond to them before they escalate. In this sense, tiered huddles serve as a signal-sensing mechanism, providing the agility needed to adapt to changing circumstances and prevent patient harm. Tiered huddles facilitate self-organization, a concept from chaos theory known as autopoiesis. 26 This self-organizing capability allows teams to develop novel solutions in response to unforeseen challenges, exemplifying the adaptability and resilience needed in a VUCA environment. The diverse backgrounds of tiered huddle participants—both cognitively and culturally—enable a broader range of perspectives, which is critical for making sound decisions in complex and uncertain situations. “HROs cultivate diversity not just because it helps them notice more in complex environments, but also because it helps them adapt to the complexities they do spot,” argues Weick et al.27 This diversity of thought and experience enhances the organization’s ability to respond to complexity, much like firefighters continually adapt to the VUCA conditions they face.
Sensemaking and Sensitivity to Operations
Leaders at all levels must be attuned to what is happening both within and outside their organization. This continual sensing of the environment—looking for weak signals, threats, and opportunities—is important for HROs. This signal detection capability allows organizations to address problems in their nascent emerging state within a tractable horizon to successfully manage fluctuations. The horizon of tractability reflects a zone where weak signals and evolving issues can be identified, addressed, and resolved early before they evolve and cascade outside of safe operations. 7 Tiered huddles facilitate this process by creating a platform for team members to engage in respectful, collaborative dialogue. The diversity inherent in tiered huddles also supports sensemaking, a process of interpreting and understanding complex situations.27 In a VUCA environment, this multiperspective approach helps filter out noise and identify the most important signals. Tiered huddles can help overcome the phenomenon of dysfunctional momentum associated with cognitive lockup, fixation error, and tunnel vision, in which individuals or teams fixate on a particular solution, thus missing important alternative views.21,28 By fostering a common operating picture of the fluctuating environment, tiered huddles can enable more accurate decision-making and improve organizational resilience.
Avoiding Organizational Drift
One of the most significant contributions of tiered huddles is the ability to detect early signs of organizational drift, or subtle deviations from standard practices that can accumulate over time and lead to serious failures. By continuously monitoring for precursor conditions and weak signals, tiered huddles allow organizations to intervene early and prevent drift from becoming catastrophic.29,30 This vigilance is essential in health care, where complacency can lead to patient harm. Tiered huddles foster a culture of mindfulness and accountability, ensuring that staff stay engaged and alert to potential risks. This proactive approach is a safeguard against human error and the gradual erosion of safety standards.
Leadership Development
Tiered huddles serve as a powerful tool for leadership development. Effective leaders must be able to anticipate potential risks and foresee system failures. Involving future leaders in tiered huddles can facilitate the transfer of these critical skills. When emerging leaders at lower tiers participate in ascending-tier huddles, they gain a unique opportunity to engage in a structured, collaborative setting. This environment provides a safe space to develop and practice strategic skills, enhancing their ability to think proactively and manage complexity. By integrating future leaders into tiered huddles, organizations offer essential, hands-on experience in real-time decision making. This experiential learning is invaluable for preparing leaders to navigate the demands of a VUCA environment.
CONCLUSIONS
Since implementing the tiered huddle process, the Erie VAMC and VISN 4 have emerged as early adopters of VUCA, thus contributing to the expansion of this innovative communication approach across the VHA. Tiered huddles strengthen organizational resilience and agility, facilitate critical information flow to manage risk, and support the cultivation of future leaders. The Erie VAMC director and the VISN 4 network director regard the expansion of tiered huddles, including Tiers 4 and 5, as an adaptable model for the VHA. While tiered huddles have not yet been mandated across the VHA, a pilot at the Tier 5 HOC level was initiated on May 20, 2024. In a complex world in which VUCA events will continue to be inevitable, implementation of robust tiered huddles within complex health care systems provides the opportunity for improved responses and delivery of care.
To see what is in front of one’s nose needs a constant struggle.
George Orwell (1946)1
In 2019, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) initiated a process to become a high reliability organization (HRO).2 The COVID-19 pandemic has been described in medical literature as a volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA) event, underscoring the necessity of resilient communication strategies.3 Challenges posed by 2024 Hurricanes Helene and Milton further highlighted the need for resilient communication strategies within HRO implementation.
Central to the HRO journey within the VHA has been the development of tiered huddles, an evolution of the safety huddle concept.4 Emerging organically as an effective communication mechanism across multiple facilities between 2019 and 2020, tiered huddles were, in part, spurred by the onset of COVID-19. Tiered huddles represent a proactive approach to identifying and addressing organizational threats in their early stages, thereby preventing their escalation to a VUCA-laden crisis.5 When conditions evolve beyond the horizon of tractability, where challenges are easily identified and resolved, tiered huddles serve as a resilient mechanism to restore dynamic equilibrium within the organization.6,7
This article describes how tiered huddles were integrated within Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) 4 and explores why these huddles are essential, particularly in the context of VUCA events. What began as a local-level tactic has now gained widespread acceptance and continues to evolve across the VHA with full support from the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary for Health.8
The VHA is divided into 18 VISNs. Nine VA Medical Centers (VAMCs) and 46 outpatient clinics across Pennsylvania, Delaware, and parts of Ohio, New York, and New Jersey make up VISN 4. Disseminating vital information across VISN 4, in addition to the 17 other VISNs—including 170 VAMCs and 1193 clinics—presents a formidable challenge. As the largest integrated system in the US, the VHA is realigning its workforce to address organizational inefficiencies. An enterprise of this scale, shaped by recurrent organizational change, faces ongoing challenges in sustaining clear communication across all levels. These transitions create uncertainty for staff as roles and resources shift, underscoring the need for dependable vertical and horizontal information flow. Tiered huddles offer a steady means to support coordinated communication and strengthen the system’s ability to adapt.9
ERIE VA MEDICAL CENTER HRO JOURNEY
In 2019, John Gennaro, the Erie VAMC executive director, attended a presentation that showcased the Cleveland Clinic’s tiered huddle process, with an opportunity to observe its 5-tiered system.10 Erie VAMC already had a 3-tiered huddle system, but the Cleveland Clinic’s more robust model inspired Gennaro to propose a VISN 4 pilot program. Tiered huddles were perceived as innovative, yet not fully embraced within the VHA; nonetheless, VISN 4, much like several other VISNs, moved forward and established a VISN-level (Tier 4) huddle.8 It is important to note that there was a notional fifth-tier capability as VISN and program office leaders already participated in daily VHA-wide meetings under the auspices of the Hospital Operations Center (HOC).
Expanding the Tiered Huddle Process
The Erie VAMC huddle process begins with the unit level Managers and Frontline Staff (Tier 1), then moves to Service Chiefs and Managers (Tier 2). Tier 3 involves facility executive leadership team and service chiefs, clinical directors and top VAMC administrators (these configurations may vary depending on context). The sequencing and flow of information is bidirectional across levels, reflecting the importance of closed-loop communication to ensure staff at all levels understand that issues raised are followed up on and/or closed out (Figure 1).2

Tier 4 composition may vary among VISNs depending on size and unique mission requirements.8,11 The VISN 4 Tier 4 huddle includes the VISN director, 9 VAMC directors, and key network administrators and clinical experts. The Tier 5 huddle includes 18 VISN 4 directors with the VHA HOC (Figure 2). The tiered huddle process emphasizes team-based culture and psychological safety.12-15 Staff at all levels are encouraged to identify and transparently resolve issues, fostering a proactive and problem-solving environment across the organization. A more nuanced and detailed process across tier levels is depicted in the Table.


The vetting and distillation of information can present challenges as vital information ascends and spreads across organization levels. Visual management systems (VMS), whether a whiteboard or a digital platform, are key to facilitate decision-making related to what needs to be prioritized and disseminated at each tier level.2,8 At Tier 5, the HOC uses a digital VMS to provide a structured, user-friendly format for categorizing issues and topics and enhances clarity and accessibility (Figure 3). The Tier 5 VMS also facilitates tracking and reciprocal information exchange, helping to close the loop on emerging issues by monitoring their progression and resolution up and across tiers.2,8 The Tier 5 huddle process and technology supporting continue to evolve offering increasing sophistication in organizational situational awareness and responsiveness.

VUCA: A Lens for Health Care Challenges
First introduced by social scientists at the US Army War College in 1995, VUCA describes complex and unpredictable conditions often encountered in military operations.16,17 Prompted by the COVID-19 pandemic, the acronym VUCA gained recognition in health care, as leaders acknowledged the challenge of navigating rapidly changing environments. van Stralen, Byrum and Inozu, recognized authorities in high reliability, cited VUCA as the rationale for implementing HRO principles and practices. They argued that “HRO solves the problem of operations and performance in a volatile, uncertain, complex, ambiguous environment.” 18 To fully appreciate the VUCA environment and its relevance to health care, it is essential to unpack the 4 components of the acronym: volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous.
Volatile refers to the speed and unpredictability of change. Health care systems are interactively complex and tightly coupled, meaning that changes in 1 part of the system can rapidly impact others.6,18,19 This high degree of interdependence amplifies volatility, especially when unexpected events occur. The rapid spread of COVID- 19 and the evolving nature of its transmission challenged health care systems’ ability to respond swiftly and effectively. Volatility also may emerge in acute medical situations, such as the rapid deterioration of a patient’s condition.
Uncertain captures the lack of predictability inherent in complex systems. In health care, uncertainty arises when there is insufficient information or when an excess of data make it difficult to discern meaningful patterns. COVID-19 and recent natural disasters have introduced profound uncertainty, as the disease’s behavior, transmission, and impact were initially unknown. Health care practitioners struggled to make decisions in real time, lacking clear guidance or precedent.3,20 While health care planning and established protocols are grounded in predictability, the COVID-19 pandemic revealed that as complexity increases, predictability diminishes. Moreover, complexity can complicate protocol selection, as situations may arise in which multiple protocols conflict or compete. The cognitive challenge of operating in this environment is analogous to what military strategists call the fog of war, where situational awareness is low and decision-makers must navigate without clarity.21 Tiered huddles, a core practice in HROs, mitigate uncertainty by fostering real-time communication and shared situational awareness among teams.20
Complex refers to the intricate interplay of multiple, interconnected factors within a system.22 In health care, this complexity is heightened by the sociotechnical nature of the field—where human, technology, and organizational elements all converge.19 Systems designed to prevent failures, such as redundancies and safety protocols, can themselves contribute to increased complexity. HRO practices such as tiered huddles are implemented to mitigate the risk of catastrophic failure by fostering collaborative sensemaking, enhanced situational awareness, and rapid problem-solving.5,20,23
Ambiguous refers to situations in which multiple interpretations, causes, or outcomes are possible. It explains how, despite following protocols, failure can still occur, or how individuals may reach different conclusions from the same data. Ambiguity does not offer binary solutions; instead, it presents a murky, multifaceted reality that requires thoughtful interpretation and adaptive responses. In these moments, leaders must act decisively, even in the absence of complete information, making trade-offs that balance immediate needs with long-term consequences.
MANAGING VUCA ENVIRONMENTS WITH TIERED HUDDLES
The tiered huddle process provides several key benefits that enable real-time issue resolution. These include the rapid dissemination of vital information, enhanced agility and resilience, and improved sensemaking within a VUCA environment. Additionally, tiered huddles prevent organizational drift by fostering heightened situational awareness. The tiered huddle process also supports leadership development, as unit-level leaders gain valuable insights into strategic decision-making through active participation. Each component is outlined in the following section.
Spread: The Challenge of Communicating
“The hallmark of a great organization is how quickly bad news travels upward,” argued Jay Forrester, the father of system dynamics.24 Unfortunately, steep power gradients and siloed organizational structures inhibit the flow of unfavorable information from frontline staff to senior leadership. This suppression is not necessarily intentional but is often a byproduct of organizational culture. Tiered huddles address the weakness of top-down communication models by promoting a reciprocal, bidirectional information exchange, with an emphasis on closed-loop communication. Open communication can foster a culture of trust and transparency, allowing leaders to make more informed decisions and respond quickly to emerging risks.
Enhancing Agility and Resilience
Tiered huddles contribute to a mindful infrastructure, an important aspect of maintaining organizational awareness and agility.21,25 A mindful infrastructure enables an organization to detect early warning signs of potential disruptions and respond to them before they escalate. In this sense, tiered huddles serve as a signal-sensing mechanism, providing the agility needed to adapt to changing circumstances and prevent patient harm. Tiered huddles facilitate self-organization, a concept from chaos theory known as autopoiesis. 26 This self-organizing capability allows teams to develop novel solutions in response to unforeseen challenges, exemplifying the adaptability and resilience needed in a VUCA environment. The diverse backgrounds of tiered huddle participants—both cognitively and culturally—enable a broader range of perspectives, which is critical for making sound decisions in complex and uncertain situations. “HROs cultivate diversity not just because it helps them notice more in complex environments, but also because it helps them adapt to the complexities they do spot,” argues Weick et al.27 This diversity of thought and experience enhances the organization’s ability to respond to complexity, much like firefighters continually adapt to the VUCA conditions they face.
Sensemaking and Sensitivity to Operations
Leaders at all levels must be attuned to what is happening both within and outside their organization. This continual sensing of the environment—looking for weak signals, threats, and opportunities—is important for HROs. This signal detection capability allows organizations to address problems in their nascent emerging state within a tractable horizon to successfully manage fluctuations. The horizon of tractability reflects a zone where weak signals and evolving issues can be identified, addressed, and resolved early before they evolve and cascade outside of safe operations. 7 Tiered huddles facilitate this process by creating a platform for team members to engage in respectful, collaborative dialogue. The diversity inherent in tiered huddles also supports sensemaking, a process of interpreting and understanding complex situations.27 In a VUCA environment, this multiperspective approach helps filter out noise and identify the most important signals. Tiered huddles can help overcome the phenomenon of dysfunctional momentum associated with cognitive lockup, fixation error, and tunnel vision, in which individuals or teams fixate on a particular solution, thus missing important alternative views.21,28 By fostering a common operating picture of the fluctuating environment, tiered huddles can enable more accurate decision-making and improve organizational resilience.
Avoiding Organizational Drift
One of the most significant contributions of tiered huddles is the ability to detect early signs of organizational drift, or subtle deviations from standard practices that can accumulate over time and lead to serious failures. By continuously monitoring for precursor conditions and weak signals, tiered huddles allow organizations to intervene early and prevent drift from becoming catastrophic.29,30 This vigilance is essential in health care, where complacency can lead to patient harm. Tiered huddles foster a culture of mindfulness and accountability, ensuring that staff stay engaged and alert to potential risks. This proactive approach is a safeguard against human error and the gradual erosion of safety standards.
Leadership Development
Tiered huddles serve as a powerful tool for leadership development. Effective leaders must be able to anticipate potential risks and foresee system failures. Involving future leaders in tiered huddles can facilitate the transfer of these critical skills. When emerging leaders at lower tiers participate in ascending-tier huddles, they gain a unique opportunity to engage in a structured, collaborative setting. This environment provides a safe space to develop and practice strategic skills, enhancing their ability to think proactively and manage complexity. By integrating future leaders into tiered huddles, organizations offer essential, hands-on experience in real-time decision making. This experiential learning is invaluable for preparing leaders to navigate the demands of a VUCA environment.
CONCLUSIONS
Since implementing the tiered huddle process, the Erie VAMC and VISN 4 have emerged as early adopters of VUCA, thus contributing to the expansion of this innovative communication approach across the VHA. Tiered huddles strengthen organizational resilience and agility, facilitate critical information flow to manage risk, and support the cultivation of future leaders. The Erie VAMC director and the VISN 4 network director regard the expansion of tiered huddles, including Tiers 4 and 5, as an adaptable model for the VHA. While tiered huddles have not yet been mandated across the VHA, a pilot at the Tier 5 HOC level was initiated on May 20, 2024. In a complex world in which VUCA events will continue to be inevitable, implementation of robust tiered huddles within complex health care systems provides the opportunity for improved responses and delivery of care.
- Orwell S, Angus I, eds. In Front of Your Nose, 1945-1950. Godine; 2000. Orwell G. The Collected Essays, Journalism, and Letters of George Orwell; vol 4.
- Murray JS, Baghdadi A, Dannenberg W, Crews P, Walsh ND. The role of high reliability organization foundational practices in building a culture of safety. Fed Pract. 2024;41:214-221. doi:10.12788/fp.0486
- Goldenhar LM, Brady PW, Sutcliffe KM, Muething SE. Huddling for high reliability and situation awareness. BMJ Qual Saf. 2013;22:899-906. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2012-001467
- Pandit M. Critical factors for successful management of VUCA times. BMJ Lead. 2021;5:121-123. doi:10.1136/leader-2020-000305
- Mihaljevic T. Tiered daily huddles: the power of teamwork in managing large healthcare organisations. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29:1050-1052. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-010575
- van Stralen D, Mercer TA. High-reliability organizing (HRO) in the COVID-19 liminal zone: characteristics of workers and local leaders. Neonatology Today. 2021;16:90-101. http://www.neonatologytoday.net /newsletters/nt-apr21.pdf
- Nemeth C, Wears R, Woods D, Hollnagel E, Cook R. Minding the gaps: creating resilience in health care. In: Henriksen K, Battles JB, Keyes MA, Grady ML, eds. Advances in Patient Safety: New Directions and Alternative Approaches. Vol 3: Performance and Tools. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2008.
- Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Montoya A, Cox GR, Murray JS. Creating a process for the implementation of tiered huddles in a Veterans Affairs medical center. Mil Med. 2023;188:901-906. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac073
- Starbuck WH, Farjoun M, eds. Organization at the Limit: Lessons From the Columbia Disaster. 1st ed. Wiley-Blackwell; 2005.
- Mihaljevic T. Tiered daily huddles: the power of teamwork in managing large healthcare organisations. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29:1050-1052. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-010575
- Donnelly LF, Cherian SS, Chua KB, et al. The Daily Readiness Huddle: a process to rapidly identify issues and foster improvement through problem-solving accountability. Pediatr Radiol. 2017;47:22-30. doi:10.1007/s00247-016-3712-x
- Clark TR. The 4 Stages of Psychological Safety: Defining the Path to Inclusion and Innovation. Berrett-Koehler Publishers, Inc.; 2020.
- Edmondson AC. The Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and Growth. John Wiley & Sons; 2018.
- Edmondson AC. The Right Kind of Wrong: The Science of Failing Well. Simon Element/Simon Acumen; 2023.
- Murray JS, Kelly S, Hanover C. Promoting psychological safety in healthcare organizations. Mil Med. 2022;187:808 -810. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac041
- Barber HF. Developing strategic leadership: the US Army War College experience. J Manag Dev. 1992;11:4-12. doi:10.1108/02621719210018208
- US Army Heritage & Education Center. Who first originated the term VUCA (volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity)? Accessed November 5, 2025. https://usawc .libanswers.com/ahec/faq/84869
- van Stralen D, Byrum SL, Inozu B. High Reliability for a Highly Unreliable World: Preparing for Code Blue Through Daily Operations in Healthcare. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform; 2018.
- Perrow C. Normal Accidents: Living With High-Risk Technologies. Princeton University Press; 2000.
- Sculli G, Essen K. Soaring to Success: The Path to Developing High-Reliability Clinical Teams. HCPro; 2021. Accessed November 5, 2025. https://hcmarketplace.com /media/wysiwyg/CRM3_browse.pdf
- Barton MA, Sutcliffe KM, Vogus TJ, DeWitt T. Performing under uncertainty: contextualized engagement in wildland firefighting. J Contingencies Crisis Manag. 2015;23:74-83. doi:10.1111/1468-5973.12076
- Sutcliffe KM. Mindful organizing. In: Ramanujam R, Roberts KH, eds. Organizing for Reliability: A Guide for Research and Practice. Stanford University Press; 2018:61-89.
- Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Dealino-Perez C, Xiang J, Montoya A Jr, Murray JS. A high-reliability organization mindset. Am J Med Qual. 2022;37:504-510. doi:10.1097/jmq.0000000000000086
- Senge PM. The Fifth Discipline Fieldbook: Strategies and Tools for Building a Learning Organization. Crown Currency; 1994.
- Ramanujam R, Roberts KH, eds. Organizing for Reliability: A Guide for Research and Practice. Stanford University Press; 2018.
- Coveney PV. Self-organization and complexity: a new age for theory, computation and experiment. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2003;361:1057-1079. doi:10.1098/rsta.2003.1191
- Weick KE, Sutcliffe KM. Managing the Unexpected: Sustained Performance in a Complex World. 3rd ed. Wiley; 2015.
- Barton M, Sutcliffe K. Overcoming dysfunctional momentum: organizational safety as a social achievement. Hum Relations. 2009;62:1327-1356. doi:10.1177/0018726709334491
- Dekker S. Drift Into Failure: From Hunting Broken Components to Understanding Complex Systems. Routledge; 2011.
- Price MR, Williams TC. When doing wrong feels so right: normalization of deviance. J Patient Saf. 2018;14:1-2. doi:10.1097/pts.0000000000000157
- Orwell S, Angus I, eds. In Front of Your Nose, 1945-1950. Godine; 2000. Orwell G. The Collected Essays, Journalism, and Letters of George Orwell; vol 4.
- Murray JS, Baghdadi A, Dannenberg W, Crews P, Walsh ND. The role of high reliability organization foundational practices in building a culture of safety. Fed Pract. 2024;41:214-221. doi:10.12788/fp.0486
- Goldenhar LM, Brady PW, Sutcliffe KM, Muething SE. Huddling for high reliability and situation awareness. BMJ Qual Saf. 2013;22:899-906. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2012-001467
- Pandit M. Critical factors for successful management of VUCA times. BMJ Lead. 2021;5:121-123. doi:10.1136/leader-2020-000305
- Mihaljevic T. Tiered daily huddles: the power of teamwork in managing large healthcare organisations. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29:1050-1052. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-010575
- van Stralen D, Mercer TA. High-reliability organizing (HRO) in the COVID-19 liminal zone: characteristics of workers and local leaders. Neonatology Today. 2021;16:90-101. http://www.neonatologytoday.net /newsletters/nt-apr21.pdf
- Nemeth C, Wears R, Woods D, Hollnagel E, Cook R. Minding the gaps: creating resilience in health care. In: Henriksen K, Battles JB, Keyes MA, Grady ML, eds. Advances in Patient Safety: New Directions and Alternative Approaches. Vol 3: Performance and Tools. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2008.
- Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Montoya A, Cox GR, Murray JS. Creating a process for the implementation of tiered huddles in a Veterans Affairs medical center. Mil Med. 2023;188:901-906. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac073
- Starbuck WH, Farjoun M, eds. Organization at the Limit: Lessons From the Columbia Disaster. 1st ed. Wiley-Blackwell; 2005.
- Mihaljevic T. Tiered daily huddles: the power of teamwork in managing large healthcare organisations. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29:1050-1052. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-010575
- Donnelly LF, Cherian SS, Chua KB, et al. The Daily Readiness Huddle: a process to rapidly identify issues and foster improvement through problem-solving accountability. Pediatr Radiol. 2017;47:22-30. doi:10.1007/s00247-016-3712-x
- Clark TR. The 4 Stages of Psychological Safety: Defining the Path to Inclusion and Innovation. Berrett-Koehler Publishers, Inc.; 2020.
- Edmondson AC. The Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and Growth. John Wiley & Sons; 2018.
- Edmondson AC. The Right Kind of Wrong: The Science of Failing Well. Simon Element/Simon Acumen; 2023.
- Murray JS, Kelly S, Hanover C. Promoting psychological safety in healthcare organizations. Mil Med. 2022;187:808 -810. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac041
- Barber HF. Developing strategic leadership: the US Army War College experience. J Manag Dev. 1992;11:4-12. doi:10.1108/02621719210018208
- US Army Heritage & Education Center. Who first originated the term VUCA (volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity)? Accessed November 5, 2025. https://usawc .libanswers.com/ahec/faq/84869
- van Stralen D, Byrum SL, Inozu B. High Reliability for a Highly Unreliable World: Preparing for Code Blue Through Daily Operations in Healthcare. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform; 2018.
- Perrow C. Normal Accidents: Living With High-Risk Technologies. Princeton University Press; 2000.
- Sculli G, Essen K. Soaring to Success: The Path to Developing High-Reliability Clinical Teams. HCPro; 2021. Accessed November 5, 2025. https://hcmarketplace.com /media/wysiwyg/CRM3_browse.pdf
- Barton MA, Sutcliffe KM, Vogus TJ, DeWitt T. Performing under uncertainty: contextualized engagement in wildland firefighting. J Contingencies Crisis Manag. 2015;23:74-83. doi:10.1111/1468-5973.12076
- Sutcliffe KM. Mindful organizing. In: Ramanujam R, Roberts KH, eds. Organizing for Reliability: A Guide for Research and Practice. Stanford University Press; 2018:61-89.
- Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Dealino-Perez C, Xiang J, Montoya A Jr, Murray JS. A high-reliability organization mindset. Am J Med Qual. 2022;37:504-510. doi:10.1097/jmq.0000000000000086
- Senge PM. The Fifth Discipline Fieldbook: Strategies and Tools for Building a Learning Organization. Crown Currency; 1994.
- Ramanujam R, Roberts KH, eds. Organizing for Reliability: A Guide for Research and Practice. Stanford University Press; 2018.
- Coveney PV. Self-organization and complexity: a new age for theory, computation and experiment. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2003;361:1057-1079. doi:10.1098/rsta.2003.1191
- Weick KE, Sutcliffe KM. Managing the Unexpected: Sustained Performance in a Complex World. 3rd ed. Wiley; 2015.
- Barton M, Sutcliffe K. Overcoming dysfunctional momentum: organizational safety as a social achievement. Hum Relations. 2009;62:1327-1356. doi:10.1177/0018726709334491
- Dekker S. Drift Into Failure: From Hunting Broken Components to Understanding Complex Systems. Routledge; 2011.
- Price MR, Williams TC. When doing wrong feels so right: normalization of deviance. J Patient Saf. 2018;14:1-2. doi:10.1097/pts.0000000000000157
Negotiating the VUCA World Through Tiered Huddles
Negotiating the VUCA World Through Tiered Huddles
