User login
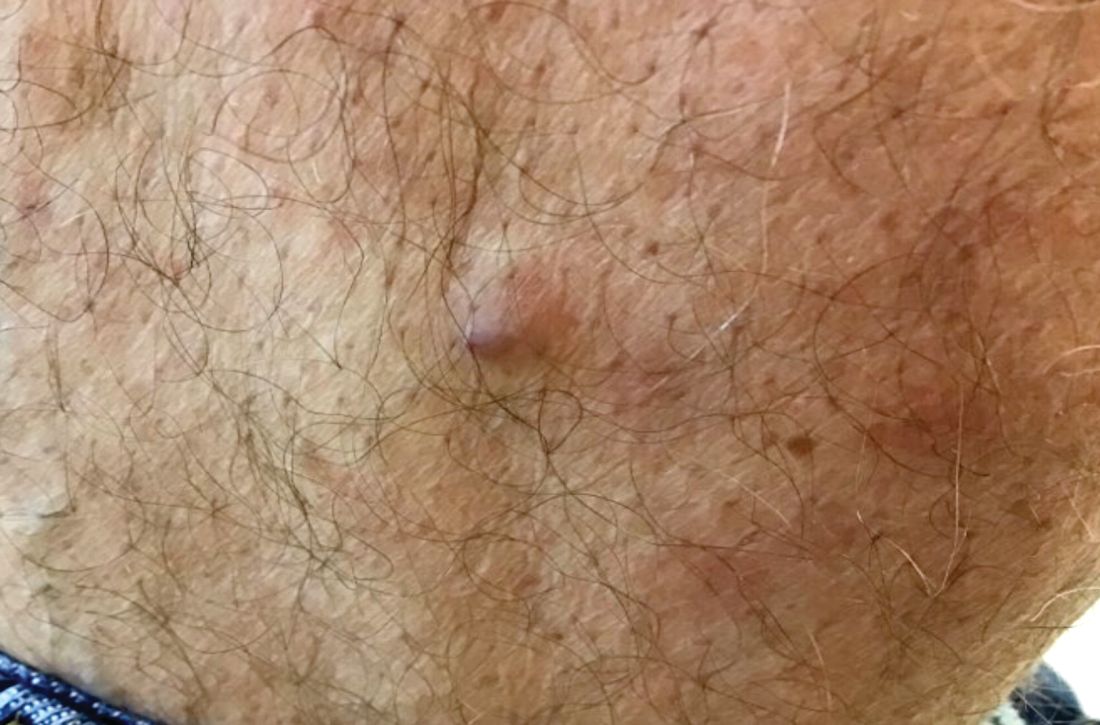
Benign tumors consisting of glomus cells may be subdivided into two types: glomus tumors and glomuvenous malformations or glomangiomas. Glomus cells are modified smooth muscle cells that normally line the Sucquet-Hoyer canal, an arteriovenous fistula that is involved in temperature regulation in the digits.
. In women, lesions more frequently occur on the fingers (especially nail beds). Glomus tumors are firm subcutaneous nodules, often skin colored or bluish in color. Subungual tumors tend to appear bluish under the nail plate. Lesions are extremely tender or painful, with worse pain upon palpation. Occasionally, nontender lesions can be seen.
In children, multiple nontender lesions are called glomangiomas or glomuvenous malformations. They may be sporadic or can be inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion due to a mutation in glomulin on chromosome 1p21-p22. Multiple lesions may be scattered or grouped, often in a segmental distribution. Congenital lesions tend to be large, blue-purple in color with a cobblestone appearance. They are more superficial than venous malformations.
Histologically, a proliferation of blood vessels surrounded by glomus cells is seen. Glomus cells appear as monotonous cells with a dense, round nucleus and abundant pink cytoplasm. Glomus cells can also be appreciated single-filing through pale stroma, resembling strings of black pearls. Glomus cells stain positive for smooth muscle actin and vimentin.
The painful tumor differential diagnosis has been described in the literature by the mnemonic “LEND AN EGG:” leiomyoma, eccrine spiradenoma, neuroma, dermatofibroma, angiolipoma, neurilemmoma, endometrioma, glomus tumor, and granular cell tumor.
The malignant counterpart is glomangiosarcoma, which is a rare tumor. These lesions are often large and deeply located on the extremities. Histologically, sarcomatous areas are mixed with areas of benign glomus tumor.
Surgical excision is the treatment of choice for solitary glomus tumors to provide pain relief. Subungual tumors are more challenging due to their small size, but may be excised as well. Glomuvenous malformations may require different treatment modalities, such as surgery and laser, due to their larger size.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at www.mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Benign tumors consisting of glomus cells may be subdivided into two types: glomus tumors and glomuvenous malformations or glomangiomas. Glomus cells are modified smooth muscle cells that normally line the Sucquet-Hoyer canal, an arteriovenous fistula that is involved in temperature regulation in the digits.
. In women, lesions more frequently occur on the fingers (especially nail beds). Glomus tumors are firm subcutaneous nodules, often skin colored or bluish in color. Subungual tumors tend to appear bluish under the nail plate. Lesions are extremely tender or painful, with worse pain upon palpation. Occasionally, nontender lesions can be seen.
In children, multiple nontender lesions are called glomangiomas or glomuvenous malformations. They may be sporadic or can be inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion due to a mutation in glomulin on chromosome 1p21-p22. Multiple lesions may be scattered or grouped, often in a segmental distribution. Congenital lesions tend to be large, blue-purple in color with a cobblestone appearance. They are more superficial than venous malformations.
Histologically, a proliferation of blood vessels surrounded by glomus cells is seen. Glomus cells appear as monotonous cells with a dense, round nucleus and abundant pink cytoplasm. Glomus cells can also be appreciated single-filing through pale stroma, resembling strings of black pearls. Glomus cells stain positive for smooth muscle actin and vimentin.
The painful tumor differential diagnosis has been described in the literature by the mnemonic “LEND AN EGG:” leiomyoma, eccrine spiradenoma, neuroma, dermatofibroma, angiolipoma, neurilemmoma, endometrioma, glomus tumor, and granular cell tumor.
The malignant counterpart is glomangiosarcoma, which is a rare tumor. These lesions are often large and deeply located on the extremities. Histologically, sarcomatous areas are mixed with areas of benign glomus tumor.
Surgical excision is the treatment of choice for solitary glomus tumors to provide pain relief. Subungual tumors are more challenging due to their small size, but may be excised as well. Glomuvenous malformations may require different treatment modalities, such as surgery and laser, due to their larger size.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at www.mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Benign tumors consisting of glomus cells may be subdivided into two types: glomus tumors and glomuvenous malformations or glomangiomas. Glomus cells are modified smooth muscle cells that normally line the Sucquet-Hoyer canal, an arteriovenous fistula that is involved in temperature regulation in the digits.
. In women, lesions more frequently occur on the fingers (especially nail beds). Glomus tumors are firm subcutaneous nodules, often skin colored or bluish in color. Subungual tumors tend to appear bluish under the nail plate. Lesions are extremely tender or painful, with worse pain upon palpation. Occasionally, nontender lesions can be seen.
In children, multiple nontender lesions are called glomangiomas or glomuvenous malformations. They may be sporadic or can be inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion due to a mutation in glomulin on chromosome 1p21-p22. Multiple lesions may be scattered or grouped, often in a segmental distribution. Congenital lesions tend to be large, blue-purple in color with a cobblestone appearance. They are more superficial than venous malformations.
Histologically, a proliferation of blood vessels surrounded by glomus cells is seen. Glomus cells appear as monotonous cells with a dense, round nucleus and abundant pink cytoplasm. Glomus cells can also be appreciated single-filing through pale stroma, resembling strings of black pearls. Glomus cells stain positive for smooth muscle actin and vimentin.
The painful tumor differential diagnosis has been described in the literature by the mnemonic “LEND AN EGG:” leiomyoma, eccrine spiradenoma, neuroma, dermatofibroma, angiolipoma, neurilemmoma, endometrioma, glomus tumor, and granular cell tumor.
The malignant counterpart is glomangiosarcoma, which is a rare tumor. These lesions are often large and deeply located on the extremities. Histologically, sarcomatous areas are mixed with areas of benign glomus tumor.
Surgical excision is the treatment of choice for solitary glomus tumors to provide pain relief. Subungual tumors are more challenging due to their small size, but may be excised as well. Glomuvenous malformations may require different treatment modalities, such as surgery and laser, due to their larger size.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at www.mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
A 60-year-old white male presented with a painful nodule on the right lateral thigh that had been present for years. It has slowly been increasing in size over time.