User login
Given the patient's symptomatology, laboratory studies, and the histopathology and immunophenotyping of the polypoid lesions in the transverse colon, this patient is diagnosed with advanced mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). The gastroenterologist shares the findings with the patient, and over the next several days, a multidisciplinary team forms to guide the patient through potential next steps and treatment options.
MCL is a type of B-cell neoplasm that, with advancements in the understanding of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in the past 30 years, has been defined as its own clinicopathologic entity by the Revised European-American Lymphoma and World Health Organization classifications. Up to 10% of all non-Hodgkin lymphomas are MCL. Clinical presentation includes advanced disease with B symptoms (eg, night sweats, fever, weight loss), generalized lymphadenopathy, abdominal distention associated with hepatosplenomegaly, and fatigue. One of the most frequent areas for extra-nodal MCL presentation is the gastrointestinal tract. Men are more likely to present with MCL than are women by a ratio of 3:1. Median age at presentation is 67 years.
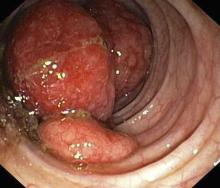
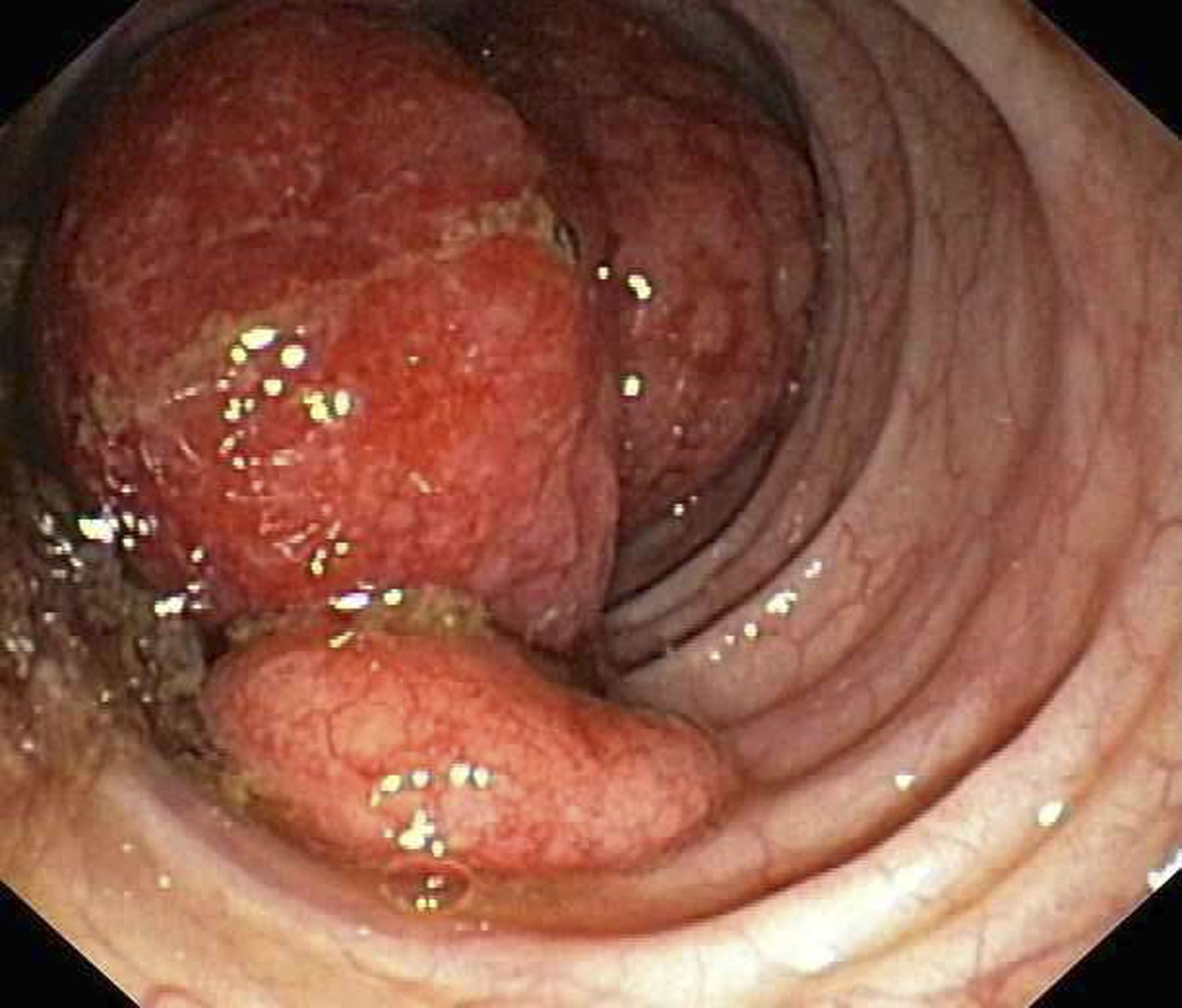
Diagnosing MCL is a multipronged approach. Physical examination may reveal lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly. Lymph node biopsy and aspiration with immunophenotyping in MCL reveals monoclonal B cells expressing surface immunoglobulin (Ig), IgM, or IgD, which are characteristically CD5+ and pan B-cell antigen–positive (eg, CD19, CD20, CD22) but lack expression of CD10 and CD23 and overexpress cyclin D1. Bone marrow aspirate/biopsy are used more for staging than for diagnosis. Blood studies, including anemia and cytopenias secondary to bone marrow infiltration (with up to 40% of cases showing lymphocytosis > 4000/μL), abnormal liver function tests, and a negative Coombs test, also help diagnose MCL. Gastrointestinal involvement of MCL typically presents as lymphoid polyposis on colonoscopy imaging and can appear in the colon, ileum, stomach, and duodenum.
Pathogenesis of MCL involves disordered lymphoproliferation in a subset of naive pregerminal center cells in primary follicles or in the mantle region of secondary follicles. Most cases are linked with translocation of chromosome 14 and 11, which induces overexpression of protein cyclin D1. Viral infection (Epstein-Barr virus, HIV, human T-lymphotropic virus type 1, human herpes virus 6), environmental factors, and primary and secondary immunodeficiency are also associated with the development of NHL.
Patient education should include detailed information about clinical trials, available treatment options and associated adverse events, as well as psychosocial and nutrition counseling.
Chemoimmunotherapy is standard initial treatment for MCL, but relapse is expected. Chemotherapy-free regimens with biologic targets, when used in second-line treatment, have increasingly become an important first-line treatment given their efficacy in the relapsed/refractory setting. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy is also a second-line treatment option. In patients with MCL and a TP53 mutation, clinical trial participation is encouraged because of poor prognosis.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Given the patient's symptomatology, laboratory studies, and the histopathology and immunophenotyping of the polypoid lesions in the transverse colon, this patient is diagnosed with advanced mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). The gastroenterologist shares the findings with the patient, and over the next several days, a multidisciplinary team forms to guide the patient through potential next steps and treatment options.
MCL is a type of B-cell neoplasm that, with advancements in the understanding of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in the past 30 years, has been defined as its own clinicopathologic entity by the Revised European-American Lymphoma and World Health Organization classifications. Up to 10% of all non-Hodgkin lymphomas are MCL. Clinical presentation includes advanced disease with B symptoms (eg, night sweats, fever, weight loss), generalized lymphadenopathy, abdominal distention associated with hepatosplenomegaly, and fatigue. One of the most frequent areas for extra-nodal MCL presentation is the gastrointestinal tract. Men are more likely to present with MCL than are women by a ratio of 3:1. Median age at presentation is 67 years.
Diagnosing MCL is a multipronged approach. Physical examination may reveal lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly. Lymph node biopsy and aspiration with immunophenotyping in MCL reveals monoclonal B cells expressing surface immunoglobulin (Ig), IgM, or IgD, which are characteristically CD5+ and pan B-cell antigen–positive (eg, CD19, CD20, CD22) but lack expression of CD10 and CD23 and overexpress cyclin D1. Bone marrow aspirate/biopsy are used more for staging than for diagnosis. Blood studies, including anemia and cytopenias secondary to bone marrow infiltration (with up to 40% of cases showing lymphocytosis > 4000/μL), abnormal liver function tests, and a negative Coombs test, also help diagnose MCL. Gastrointestinal involvement of MCL typically presents as lymphoid polyposis on colonoscopy imaging and can appear in the colon, ileum, stomach, and duodenum.
Pathogenesis of MCL involves disordered lymphoproliferation in a subset of naive pregerminal center cells in primary follicles or in the mantle region of secondary follicles. Most cases are linked with translocation of chromosome 14 and 11, which induces overexpression of protein cyclin D1. Viral infection (Epstein-Barr virus, HIV, human T-lymphotropic virus type 1, human herpes virus 6), environmental factors, and primary and secondary immunodeficiency are also associated with the development of NHL.
Patient education should include detailed information about clinical trials, available treatment options and associated adverse events, as well as psychosocial and nutrition counseling.
Chemoimmunotherapy is standard initial treatment for MCL, but relapse is expected. Chemotherapy-free regimens with biologic targets, when used in second-line treatment, have increasingly become an important first-line treatment given their efficacy in the relapsed/refractory setting. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy is also a second-line treatment option. In patients with MCL and a TP53 mutation, clinical trial participation is encouraged because of poor prognosis.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Given the patient's symptomatology, laboratory studies, and the histopathology and immunophenotyping of the polypoid lesions in the transverse colon, this patient is diagnosed with advanced mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). The gastroenterologist shares the findings with the patient, and over the next several days, a multidisciplinary team forms to guide the patient through potential next steps and treatment options.
MCL is a type of B-cell neoplasm that, with advancements in the understanding of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in the past 30 years, has been defined as its own clinicopathologic entity by the Revised European-American Lymphoma and World Health Organization classifications. Up to 10% of all non-Hodgkin lymphomas are MCL. Clinical presentation includes advanced disease with B symptoms (eg, night sweats, fever, weight loss), generalized lymphadenopathy, abdominal distention associated with hepatosplenomegaly, and fatigue. One of the most frequent areas for extra-nodal MCL presentation is the gastrointestinal tract. Men are more likely to present with MCL than are women by a ratio of 3:1. Median age at presentation is 67 years.
Diagnosing MCL is a multipronged approach. Physical examination may reveal lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly. Lymph node biopsy and aspiration with immunophenotyping in MCL reveals monoclonal B cells expressing surface immunoglobulin (Ig), IgM, or IgD, which are characteristically CD5+ and pan B-cell antigen–positive (eg, CD19, CD20, CD22) but lack expression of CD10 and CD23 and overexpress cyclin D1. Bone marrow aspirate/biopsy are used more for staging than for diagnosis. Blood studies, including anemia and cytopenias secondary to bone marrow infiltration (with up to 40% of cases showing lymphocytosis > 4000/μL), abnormal liver function tests, and a negative Coombs test, also help diagnose MCL. Gastrointestinal involvement of MCL typically presents as lymphoid polyposis on colonoscopy imaging and can appear in the colon, ileum, stomach, and duodenum.
Pathogenesis of MCL involves disordered lymphoproliferation in a subset of naive pregerminal center cells in primary follicles or in the mantle region of secondary follicles. Most cases are linked with translocation of chromosome 14 and 11, which induces overexpression of protein cyclin D1. Viral infection (Epstein-Barr virus, HIV, human T-lymphotropic virus type 1, human herpes virus 6), environmental factors, and primary and secondary immunodeficiency are also associated with the development of NHL.
Patient education should include detailed information about clinical trials, available treatment options and associated adverse events, as well as psychosocial and nutrition counseling.
Chemoimmunotherapy is standard initial treatment for MCL, but relapse is expected. Chemotherapy-free regimens with biologic targets, when used in second-line treatment, have increasingly become an important first-line treatment given their efficacy in the relapsed/refractory setting. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy is also a second-line treatment option. In patients with MCL and a TP53 mutation, clinical trial participation is encouraged because of poor prognosis.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 60-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with weight loss, constipation, and abdominal distention and pain as well as fatigue and night sweats that have lasted for several months. The physician orders a complete blood count with differential and an ultrasound of the abdomen. Lab studies reveal anemia and cytopenias; ultrasound reveals hepatosplenomegaly and abdominal lymphadenopathy. The physician refers the patient to gastroenterology; he undergoes a colonoscopy. Multiple polypoid lesions are found throughout the transverse colon. Immunophenotyping shows CD5 and CD20 expression but a lack of CD23 and CD10 expression; cyclin D1 is overexpressed. Additional blood studies show lymphocytosis > 4000/μL, elevated lactate dehydrogenase levels, abnormal liver function tests, and a negative result on Coombs test.