User login
In tattoo removal, the impact of laser treatments in single office visits is limited because of the laser’s effects on the skin. Now, a new study suggests that a
“As a result,” the authors of the study wrote, “a lower total number of office visits will likely be required for complete tattoo removal leading to improved convenience and efficiency as well as increased satisfaction for both patients and clinicians.” The study, led by cosmetic surgeon Michael S. Kaminer, MD, of SkinCare Physicians in Chestnut Hill, Mass., appeared in Lasers in Surgery and Medicine.
In the study, he and his coauthors pointed out that tattoos are most frequently removed with short-pulse high-fluence lasers, such as a 1064-nm Nd:YAG Q‐switched (QS) laser. However, “the QS laser has a limited ability to affect the tattoo ink pigment particles in each treatment session due to shielding of the pigment particles caused by both the agglomeration of the pigment particles and laser‐induced epidermal and dermal vacuoles known as ‘whitening.’ ” Therefore, “use of the QS laser often requires 10 or more single‐pass office sessions to achieve acceptable fading results.”
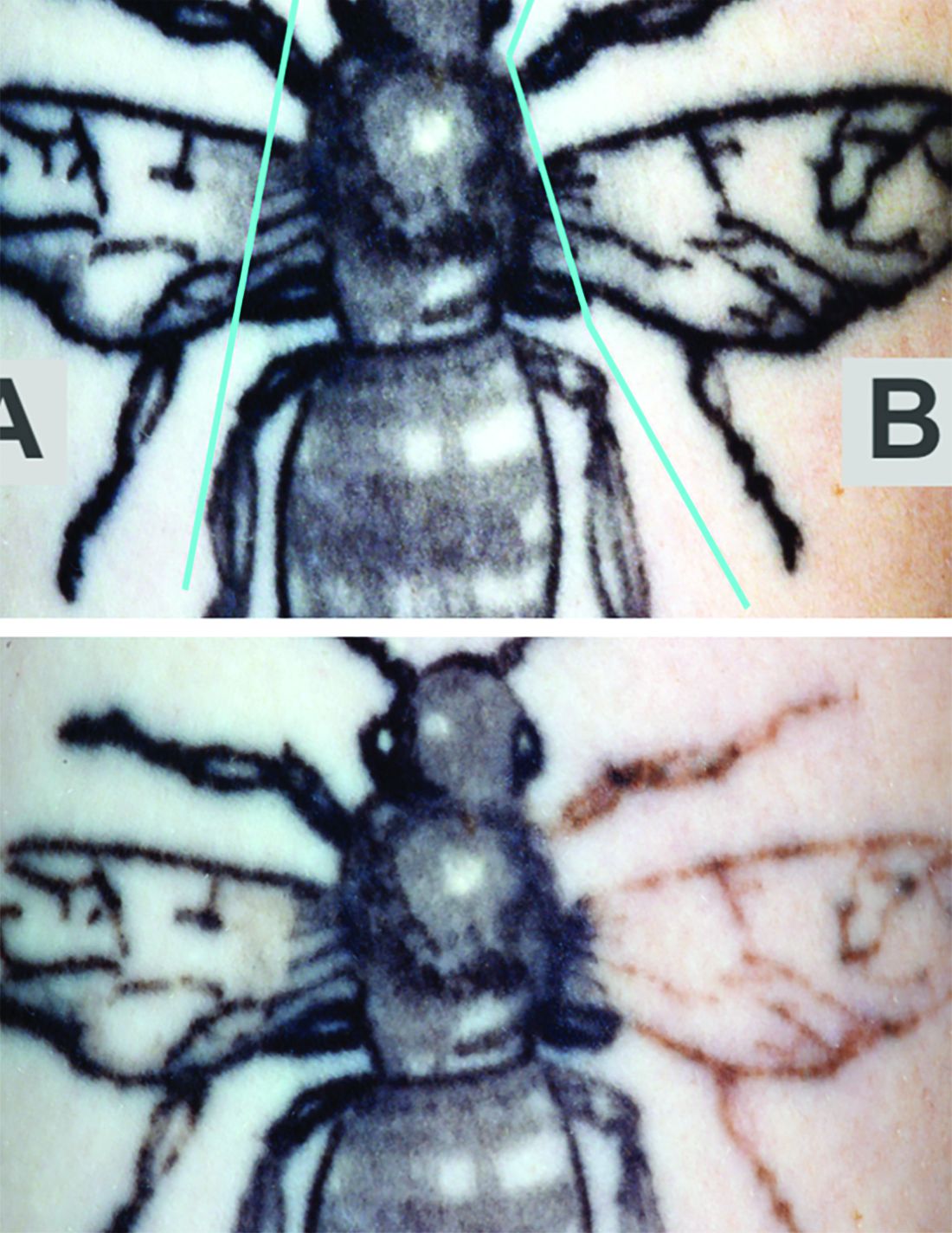
The study evaluated whether the use of a rapid acoustic pulse (RAP) device could reduce the whitening effect by clearing vacuoles and make it possible to increase the number of potential laser passes. In the single-center, prospective trial, they treated 32 black-ink tattoos in 21 patients, dividing the tattoos into zones and treating them differently: One zone received at least three consecutive laser passes alternating with a minute of treatment with the RAP device, one received single-pass laser treatment, and one received no treatment.
Reviewers assessed the tattoos for fading at 12 weeks. Average percent fading was higher in the laser/RAP group, compared with the laser-only group (44% and 25%, respectively, P less than .01). The percentages of tattoos with more than 50% fading (38% vs. 9%, P less than .01) and more than 75% fading (22% vs. 3%, P less than .05) were also higher in the laser/RAP group, compared with the laser-only group.
“Further clinical studies will be performed to investigate the broader applicability of the RAP device as an accessory device to reduce the number of laser tattoo removal sessions for other tattoo ink colors in a broader range of skin types,” the researchers commented, noting that the study included patients with Fitzpatrick skin types I-III.
The study was funded by Soliton, which provided the equipment. One of the six authors is an employee of the company The other authors reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Kaminer MS et al. Lasers Surg Med. 2019 Sep 19. doi: 10.1002/lsm.23163.
In tattoo removal, the impact of laser treatments in single office visits is limited because of the laser’s effects on the skin. Now, a new study suggests that a
“As a result,” the authors of the study wrote, “a lower total number of office visits will likely be required for complete tattoo removal leading to improved convenience and efficiency as well as increased satisfaction for both patients and clinicians.” The study, led by cosmetic surgeon Michael S. Kaminer, MD, of SkinCare Physicians in Chestnut Hill, Mass., appeared in Lasers in Surgery and Medicine.
In the study, he and his coauthors pointed out that tattoos are most frequently removed with short-pulse high-fluence lasers, such as a 1064-nm Nd:YAG Q‐switched (QS) laser. However, “the QS laser has a limited ability to affect the tattoo ink pigment particles in each treatment session due to shielding of the pigment particles caused by both the agglomeration of the pigment particles and laser‐induced epidermal and dermal vacuoles known as ‘whitening.’ ” Therefore, “use of the QS laser often requires 10 or more single‐pass office sessions to achieve acceptable fading results.”
The study evaluated whether the use of a rapid acoustic pulse (RAP) device could reduce the whitening effect by clearing vacuoles and make it possible to increase the number of potential laser passes. In the single-center, prospective trial, they treated 32 black-ink tattoos in 21 patients, dividing the tattoos into zones and treating them differently: One zone received at least three consecutive laser passes alternating with a minute of treatment with the RAP device, one received single-pass laser treatment, and one received no treatment.
Reviewers assessed the tattoos for fading at 12 weeks. Average percent fading was higher in the laser/RAP group, compared with the laser-only group (44% and 25%, respectively, P less than .01). The percentages of tattoos with more than 50% fading (38% vs. 9%, P less than .01) and more than 75% fading (22% vs. 3%, P less than .05) were also higher in the laser/RAP group, compared with the laser-only group.

“Further clinical studies will be performed to investigate the broader applicability of the RAP device as an accessory device to reduce the number of laser tattoo removal sessions for other tattoo ink colors in a broader range of skin types,” the researchers commented, noting that the study included patients with Fitzpatrick skin types I-III.
The study was funded by Soliton, which provided the equipment. One of the six authors is an employee of the company The other authors reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Kaminer MS et al. Lasers Surg Med. 2019 Sep 19. doi: 10.1002/lsm.23163.
In tattoo removal, the impact of laser treatments in single office visits is limited because of the laser’s effects on the skin. Now, a new study suggests that a
“As a result,” the authors of the study wrote, “a lower total number of office visits will likely be required for complete tattoo removal leading to improved convenience and efficiency as well as increased satisfaction for both patients and clinicians.” The study, led by cosmetic surgeon Michael S. Kaminer, MD, of SkinCare Physicians in Chestnut Hill, Mass., appeared in Lasers in Surgery and Medicine.
In the study, he and his coauthors pointed out that tattoos are most frequently removed with short-pulse high-fluence lasers, such as a 1064-nm Nd:YAG Q‐switched (QS) laser. However, “the QS laser has a limited ability to affect the tattoo ink pigment particles in each treatment session due to shielding of the pigment particles caused by both the agglomeration of the pigment particles and laser‐induced epidermal and dermal vacuoles known as ‘whitening.’ ” Therefore, “use of the QS laser often requires 10 or more single‐pass office sessions to achieve acceptable fading results.”
The study evaluated whether the use of a rapid acoustic pulse (RAP) device could reduce the whitening effect by clearing vacuoles and make it possible to increase the number of potential laser passes. In the single-center, prospective trial, they treated 32 black-ink tattoos in 21 patients, dividing the tattoos into zones and treating them differently: One zone received at least three consecutive laser passes alternating with a minute of treatment with the RAP device, one received single-pass laser treatment, and one received no treatment.
Reviewers assessed the tattoos for fading at 12 weeks. Average percent fading was higher in the laser/RAP group, compared with the laser-only group (44% and 25%, respectively, P less than .01). The percentages of tattoos with more than 50% fading (38% vs. 9%, P less than .01) and more than 75% fading (22% vs. 3%, P less than .05) were also higher in the laser/RAP group, compared with the laser-only group.

“Further clinical studies will be performed to investigate the broader applicability of the RAP device as an accessory device to reduce the number of laser tattoo removal sessions for other tattoo ink colors in a broader range of skin types,” the researchers commented, noting that the study included patients with Fitzpatrick skin types I-III.
The study was funded by Soliton, which provided the equipment. One of the six authors is an employee of the company The other authors reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Kaminer MS et al. Lasers Surg Med. 2019 Sep 19. doi: 10.1002/lsm.23163.
FROM LASERS IN SURGERY AND MEDICINE

